Section 2.6: Particles: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons in Atoms
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Protons
In the center, in the nucleus and are the identity of an element.
Isotopes depend on
the number of neutrons (mass)
Electrons are responsible for
charge ( c ) and reactivity.
All atoms are composed of the same subatomic particles
Protons, neutrons and electrons.
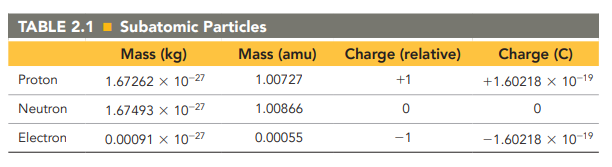
Protons and neutrons have nearly identical
masses: neutrons being slightly heavier than protons: 1.67493 × 10-27kg. Proton: 1.67262 × 10-27kg
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
a standard unit for measuring the mass of atoms and molecules, defined as exactly one-twelfth the mass of a single carbon-12 atom
The proton and electron both have
an electrical charge
The proton is assigned a charge of
positive one (+1)
the electron is assigned a charge of
negative one (-1)
the neutron has
no charge.
Matter is usually charge-neutral (no overall charge) because
protons and electrons are normally present in equal numbers.
When matter does acquire charge imbalances…
these imbalances usually equalize quickly, often in dramatic ways. EX: Lightning is an equalization of charge imbalances that develop during electrical storms.
The properties of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
see image
What makes the atoms of one element different from those of another?
The number of particles. The most important number to the identity of an atom is the number of protons in its nucleus.
The number of protons
defines the element. (is the identity of an element).
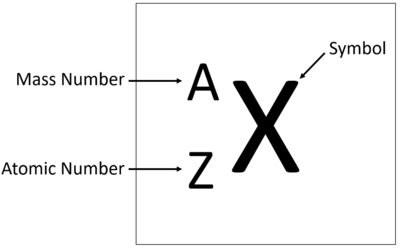
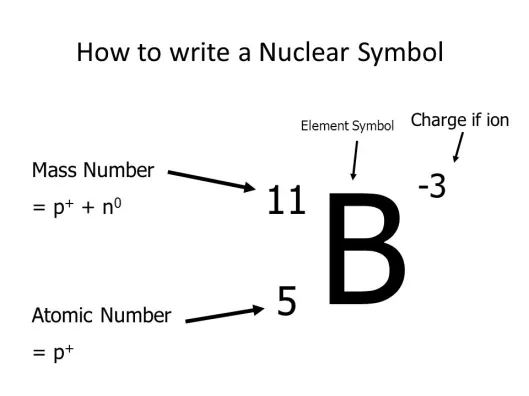
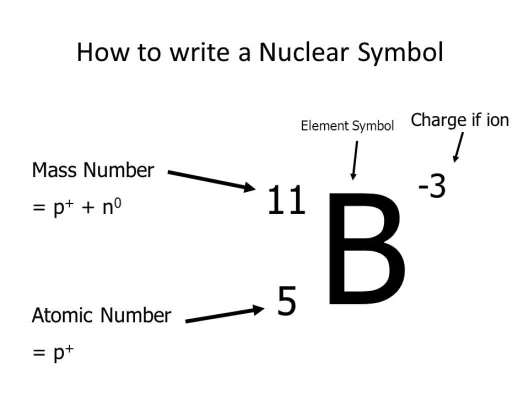
Atomic Number
(Z) the number of protons in an atoms nucleus. (see image)
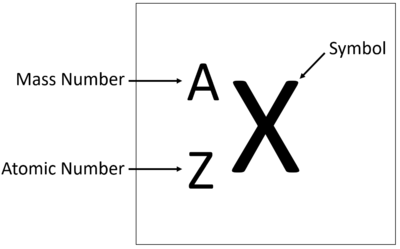
Chemical Symbol
(X) A one or two-letter abbreviation listed directly below its atomic number on the periodic table. EX: the chemical symbol for Carbon is C. (remember that chemical symbols only contain 1 capital letter). (see image)
The chemical symbol and the atomic number always
go together. EX: If the atomic number is 2, the chemical symbol must be He (helium). (remember that # of protons defines the element).
The elements in the periodic table are arranged so that
those with similar properties are in the same column.
All atoms of a given element have the same number of
protons. (However, they do not have the same number of neutrons.
All atoms of a given element do not have the same
mass. (This is because they have a different number of neutrons. Remember that neutrons play a big part in an atoms mass. So although two atoms of the same element can have the same number of protons, they can have a different number of neutrons, giving them all slightly different masses).
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons (basically atoms of the same element with different masses).
Natural Abundance
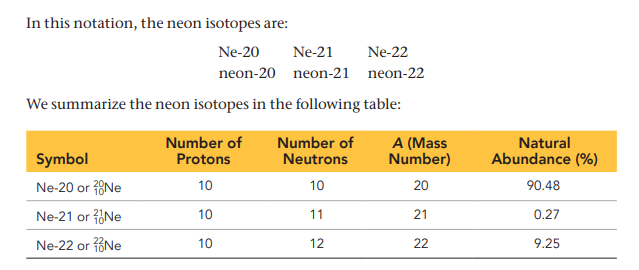
the percentage of a specific isotope of a chemical element found in nature, typically on Earth. Each element has its own characteristic natural abundance of isotopes. EX: In any natural sample of neon atoms, 90.48% of them are isotopes with 10 neutrons, 0.27% are the isotope with 11 neutrons, and 9.25% are the isotope with 12 neutrons.
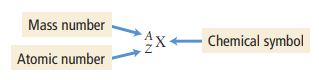
Mass Number
(A) the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atom. The symbol for mass number is A. So, #P + #N = A (see image)
Common Notation for Isotopes to be written
Its chemical symbol followed by a dash and the mass number of the isotope. (see image).
The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to
the number or protons in its nucleus. During chemical changes however, this is different. Atoms can lose or gain electrons during this process.
Ions
During chemical changes, atoms can gain (-1) or lose (+1) electrons and become charged particles called ions. (see image)
The charge of an ion is written…
in the upper right corner of the chemical symbol. (see image)
Cations
Positively Charged Ions (+)
Anions
Negatively charged Ions (-)
Ions behave differently than their corresponding atoms
EX: Neutral sodium atoms are extremely unstable and react violently with most things they contact. Sodium cations (Na+) however are inert, we eat them all the time! (table salt). In ordinary matter, cations and anions always occur together, so that matters charge is neutral overall.
cations (positive ions) and anions (negative ions) are fundamentally linked by strong electrostatic attraction
This forms ionic bonds in compounds like salt (NaCl), but they don't always form a simple 1:1 pair; they combine in ratios to achieve overall electrical neutrality, can be polyatomic, and might interact in complex ways in solutions, but the attraction between opposite charges is the driving force.
energy is stored
in the bond
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy or matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
in chemical reactions, breaking old bonds…
creates new ones.