11.3 Inflation and Deflation
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is inflation
Inflation is the sustained rise in the general price level over time, leading to a decrease in purchasing power of money
What is deflation
Deflation is the opposite of inflation, where the average price level in the economy falls, and there is a negative inflation rate
What is disinflation
Disinflation is the falling rate of inflation, where the price level is still rising, but at a slower rate than before
What is demand-pull inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand grows unsustainably, putting pressure on resources and causing producers to increase prices
Draw demand-pull inflation
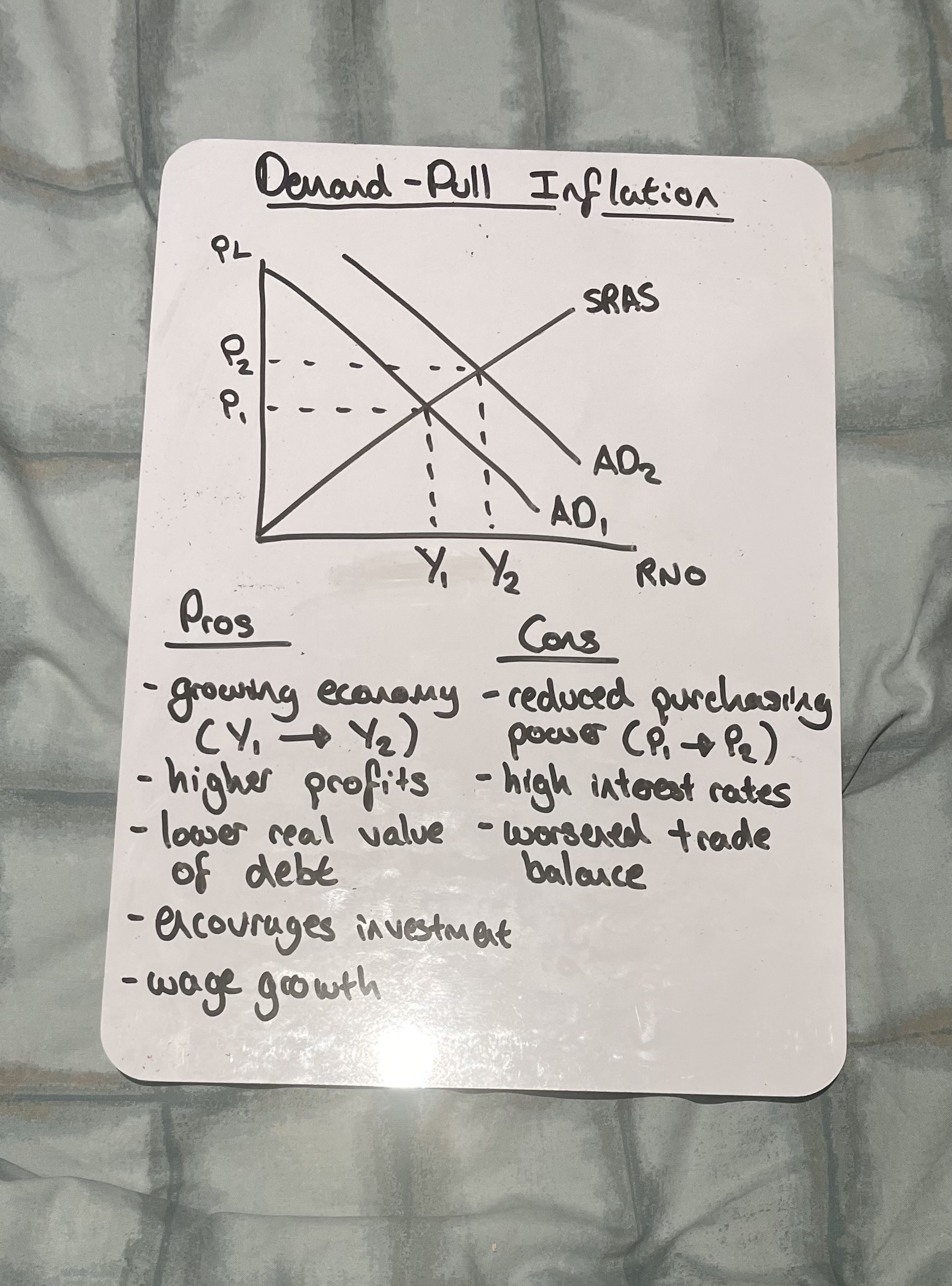
What are the key trigger for demand-pull inflation
Depreciation of the exchange rate
Fiscal stimulus (Lower taxes or more govt spending)
Lower interest rates
High growth in export markets
What is cost-push inflation
Cost-push inflation occurs when firms face rising costs of production, pushing up the general price level
Draw cost-push inflation

What are the key factors causing cost-push inflation
Rising commodity prices (e.g. oil)
Increased labour costs
Indirect taxes
Depreciation of the exchange rate
Effect of inflation on consumers
Consumers on low and fixed incomes are hardest hit by inflation due to the rising costs of necessities, which reduces their purchasing power
Effect of inflation on loans
Inflation reduces the real value of debt, making it easier for consumers with loans to repay them
Effect of inflation on firms
High inflation can make borrowing and investing less attractive
Workers may demand higher wages, increasing production costs
Firms may lose global competitiveness if inflation is higher than in other countries
Effect of inflation on the govt
The government may need to increase state pensions and welfare payments due to the rising cost of living
Effect of inflation on workers
Real incomes fall, reducing disposable income
Firms may make redundancies to cut costs
Economic effects of deflation
Economic decline and rising unemployment
Consumers with high debt face more difficulty repaying loans
Wages may fall, leading to lower disposable income and spending
What is Fisher’s equation of exchange
Fisher’s equation is: MV = PQ
M= money supply
V = velocity of circulation
P = price level
Q = quantity of real goods sold