Water cycle
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Inputs
How the water enters the system
Precipitation
Includes all of the ways that moisture comes out of the atmosphere, mainly rain but can also be snow, hail and sleet
Channel fall
Precipitation falling directly into the river
Stores
Water stored in the system
Interception storage
Rainwater that lands on vegetation and other structures before reaching the soil, creating a temporary but significant store of water in wooded areas
Vegetation storage
Water that has been taken up by plants
Surface storage
Water in puddles, ponds and lakes
Soil storage
Moisture in the pores of the soil (unsaturated)
Groundwater storage
Water stored in the ground, either in the saturated soil beneath the water table or in bedrock.
Aquifers
Porous rocks beneath the water table that store water
Channel storage
Water held in the river or stream
Flows
Water flowing from one place to another
Infiltration
Vertical movement of water from the surface into unsaturated soil
What affects rates of infiltration
Soil type, structure and saturation
Overland flow
Water flows over the surface
Causes of overland flow
Saturated soil that cannot soak up more rain or rain is falling faster than it can be infiltrated
Through fall
Water dripping from a leaf
Stemflow
Water running down a plant stem or tree trunk
Throughflow
Water moving slowly downhill through unsaturated soil
Percolation
Vertical movement from unsaturated soil to saturated soil (across the water table)
Groundwater flow
Water flowing very slowly downhill through saturated soil and permeable bedrock
Baseflow
Groundwater flow that flows into rivers
Channel flow
Water flowing in the river, known as discharge
Outputs
Water leaving the system
Evaporation
Water turning into water vapour
Transpiration
Evaporation from the stomata at found of the underside of a leaf, helps to regulate water storage in a plant
Evapotranspiration
The process of evaporation and transpiration together
River discharge / flow
Water flowing into the sea
Input
Matter or energy added to a system
Output
Matter or energy leaves a system
Transfer
Matter or energy moves from one store to another
Open system
Both energy and matter can enter and leave the system
Closed system
Energy can but matter cannot enter or leave a system
Equilibrium
Inputs and outputs of a system are balanced
Dynamic equilibrium
When there are minor changes to the inputs and outputs of a system buy they do little to nothing to change the overall balance of the system
Positive feedback
A change to an input that amplifies the output of a system
Negative feedback
Changes to an input that nullifies the output of a system
Biosphere
The subsystem where organisms are found
Cryosphere
The subsystem that is frozen - ice
Hydrosphere
The subsystem that contains all of the water
Atmosphere
The subsystem that makes up the layer of gas between the Earth’s surface and space
How to work out the water balance
The changes to the inputs and outputs
Soil moisture surplus
When there is an excess of water in the soil – inputs greatly exceed outputs.
Soil moisture utilisation
When soil moisture is being used up – due to increases in outputs of evapotranspiration
Soil moisture deficit
The point when all soil moisture has been used up
Soil moisture recharge
When soil moisture increases following utilisation in the summer.
Field capacity
The point at which the soil becomes fully saturated in autumn
Flood hydrograph
A graph that shows how a river reacts to rainfall
Discharge
The amount of water that passes a point in a river in one second
Bankfull
The point when a river will overflow
Rising Limb
Shows how quickly a river responds to a storm
Falling Limb
Shows how quickly a river recedes after a storm
Baseflow (rivers)
The amount of water that would be in the river without the water from the storm
Lag Time
Time between peak rainfall and peak discharge
Atmospheric water
12900km³ of water stored as ice, water and mainly vapour which absorbs, reflects and scatters incoming radiation
Oceanic water
1.32-1.37 billion km³ of water covering 72% of the Earth’s surface
Cryospheric water
The major store of water as a solid (ice)
Terrestrial water
The major store of water on Earth’s surface which has 4 main categories
Sea ice
Frozen seawater which, when thawed, doesn’t cause sea levels to rise
Ice sheet
Masses of glacial ice that are larger than 50000km²
Ice cap
Masses of glacial ice that are smaller than 50000km²
Alpine glacier
Thick masses of ice found in deep valleys that are fed by ice caps
Permafrost
Ground that is frozen for at least 2 years at depths of up to 15000 m
Surface water
Water stored on the surface, including rivers and lakes - a major terrestrial store
Groundwater
Water held underground in the soil or in pores in the rock
Soil water
Water that is naturally found in the soil
Urbanisation
Replacement of vegetation with impermaible concrete and tarmac
Impermiable
Does not allow water to soak in
Aquifer
Freshwater stored in rocks forming underground reservoirs
Deforestation
Cutting down trees leading to increased soil erosion and reduced soil water stores
ITCZ
The intertropical convergence zone is an area of low pressure found in equatorial regions
Irrigation
Artificial watering of crops
Water abstraction
Taking water from rivers and groundwater aquifers
Percentage of the Earth’s water in the ocean
97%
Percentage of Earth’s water that is freshwater
3%
Percentage of freshwater that is in the cryosphere
79%
Percentage of freshwater that is groundwater
20%
Percentage of surface water that is in lakes
52%
Percentage of surface water that is in soil
38%
Percentage of surface water that is in the atmosphere
8%
Percentage of surface water that is in biomass and rivers
2% - 1% each
Latent heat
The energy that is absorbed during evaporation and released during condensation
Dew point
The temperature when condensation of vapour occurs
Frontal rain
Rainfall formation where warm and cold air meet along a front, causing the warm air to rise, condensing.
Relief rain
Warm air meets mountains, forcing it to rise, cool and condense.
Conventional rain
Sun heats up the ground, causing a column of warm air to rise and the cools and condenses to make rain.
The Water Balance
The balance of inputs and outputs in the water cycle
Equation for the water balance
Precipitation = Total Runoff + Evpotranspiration ± Storage
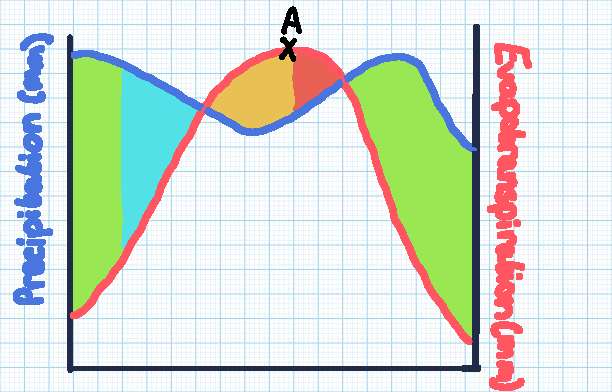
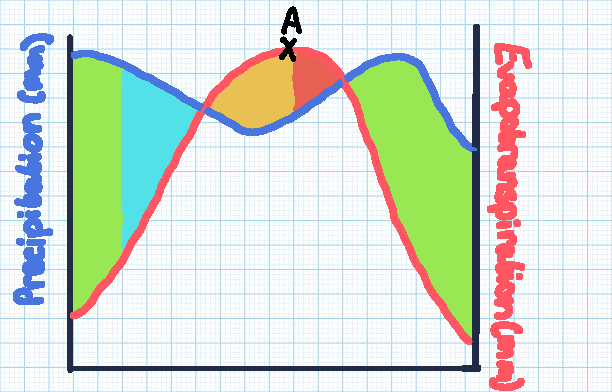
Green section
Soil moisture recharge
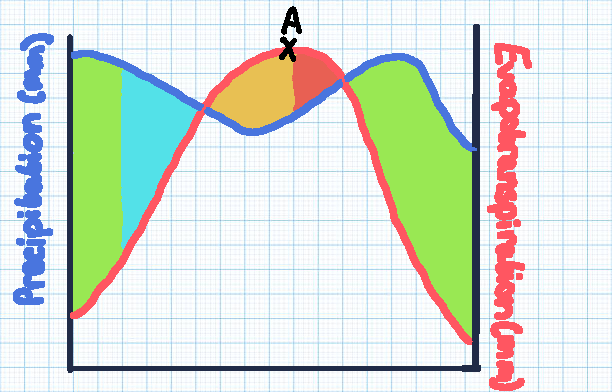
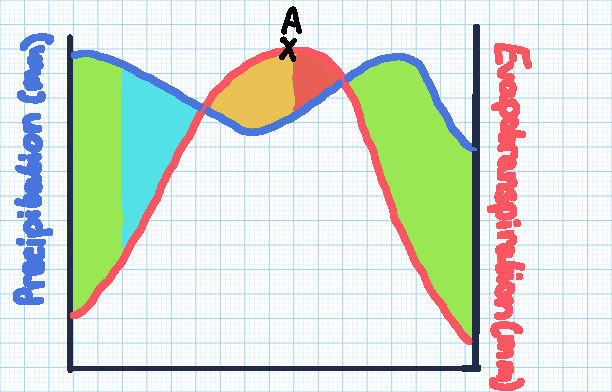
Blue section
Soil moisture surplus
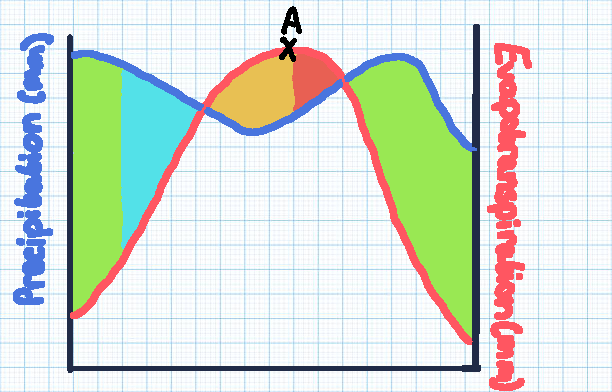
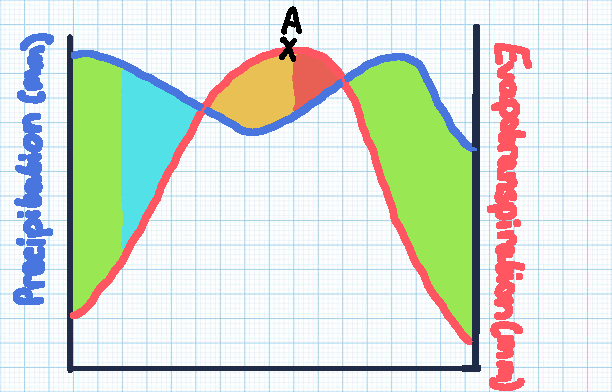
Orange section
Soil moisture utilisation
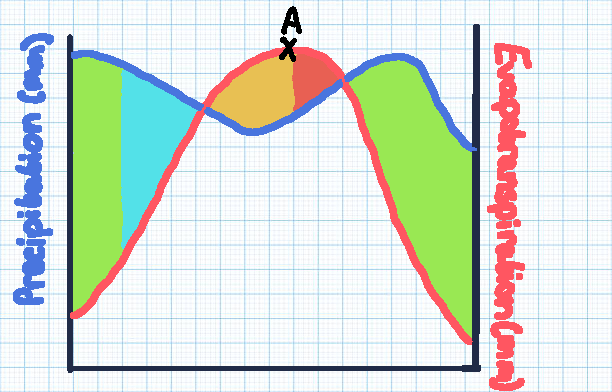
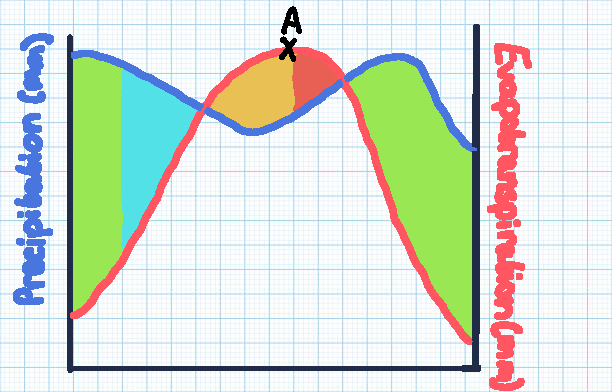
Red section
Soil moisture deficit
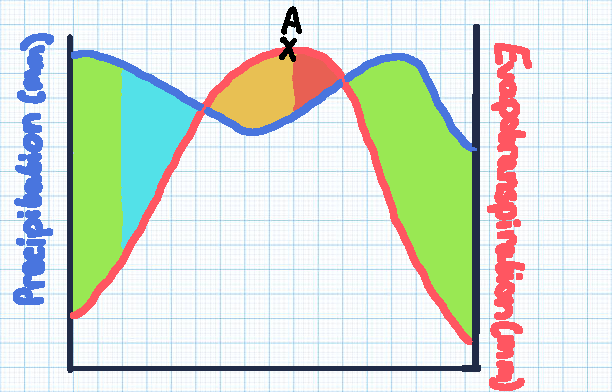
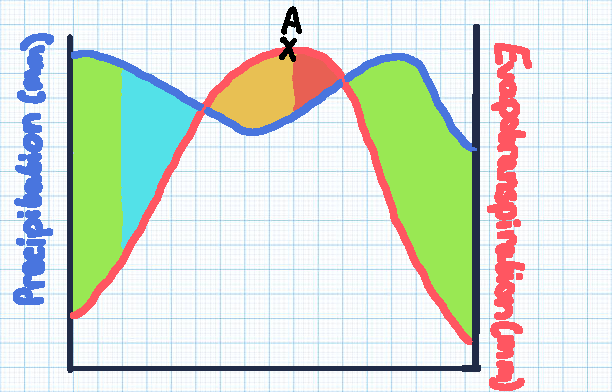
Point A
The point of maximum evaporation, with the highest risk of drought
Natural factors which cause change to the water cycle
Storms and precipitation, seasonal changes, movement in the ITCZ in equatorial zones and glacial / interglacial cycles
Human factors which cause change in the water cycle
Farming practices, land use changes and water abstraction
How storms and precipitation cause change to the water cycle
Larger input of water increases the size of stores - some flows may not be able to occur quick enough to withstand - increased surface runoff and a higher flood risk.
How seasonal changes cause change to the water cycle
Size of the flows and stores change with the seasons - flows decrease in winter - cryosphere increases - flows increase in summer due to an increase in seasonal vegetation.
How the ITCZ cause change to the water cycle
The band of low pressure moves with the seasons, causing heavy rainfall in summer months.
How glacial and interglacial cycles chase change to the water cycle
Glacial periods - 100000 years - cryosphere increases - more water is frozen - interglacial periods - hydrosphere and atmosphere increase - more ice thaws and evaporation rates increase.
How ploughing causes change to the water cycle
Breaks up the soil surface - higher infiltration rates