Thermodynamic Processes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Nonquasi-static process
(i)
Quasi-static process
(ii)
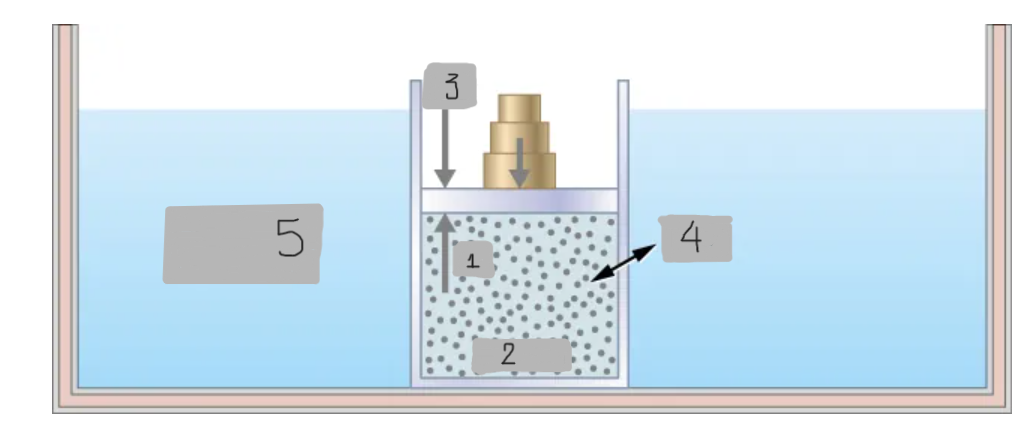
pin
(1)
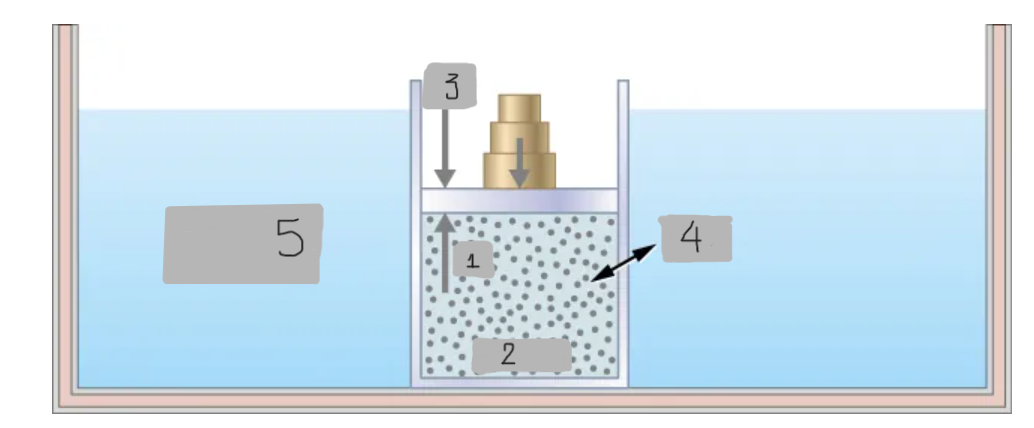
System
(2)
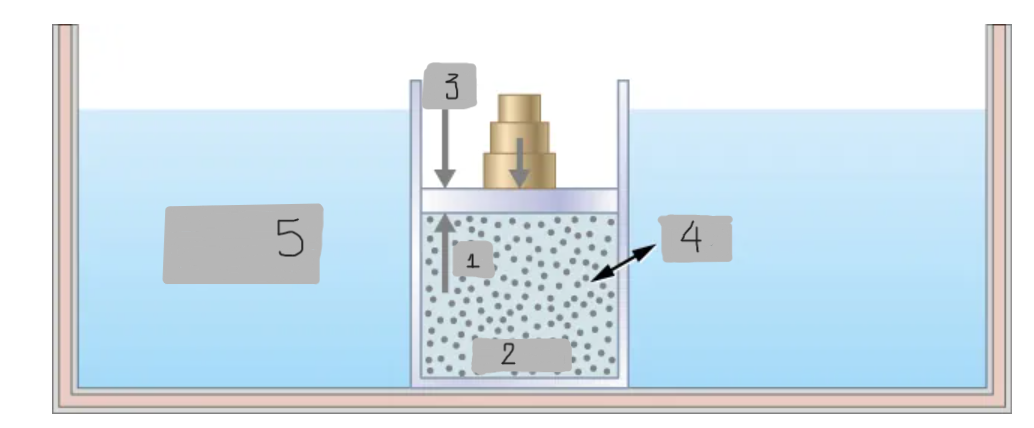
pout
(3)
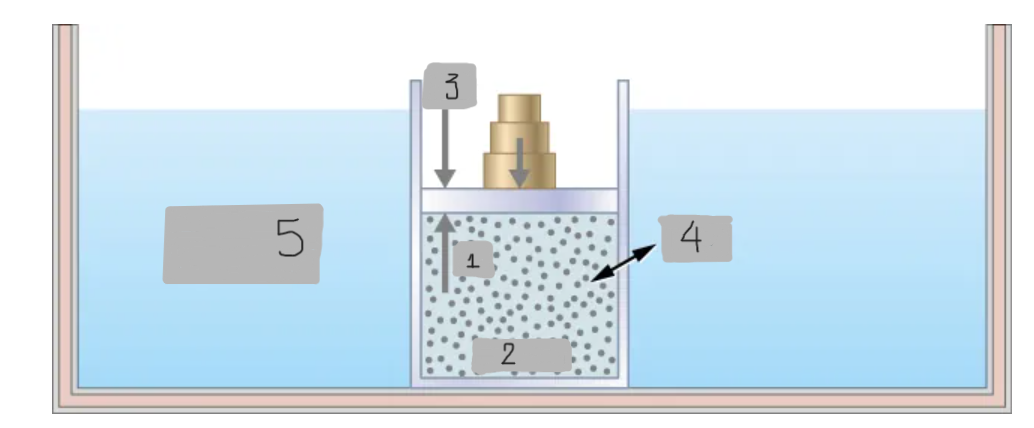
Heat
(4)
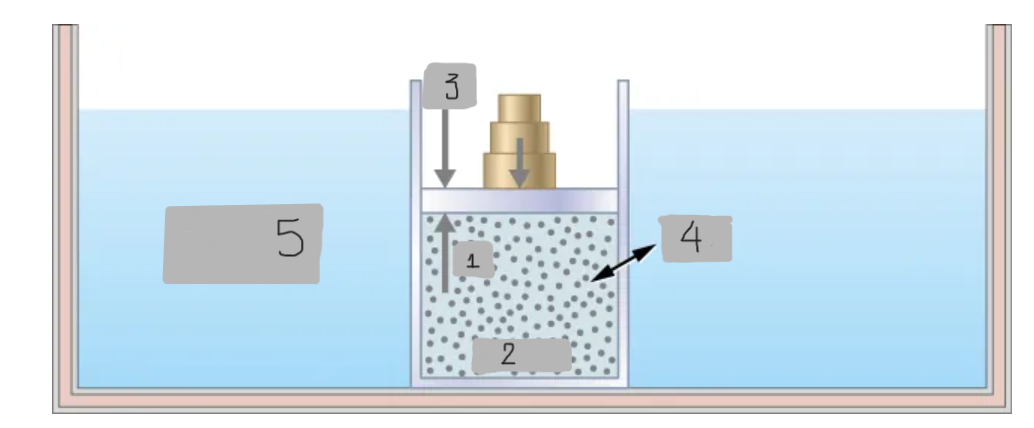
Constant T heat bath
(5)
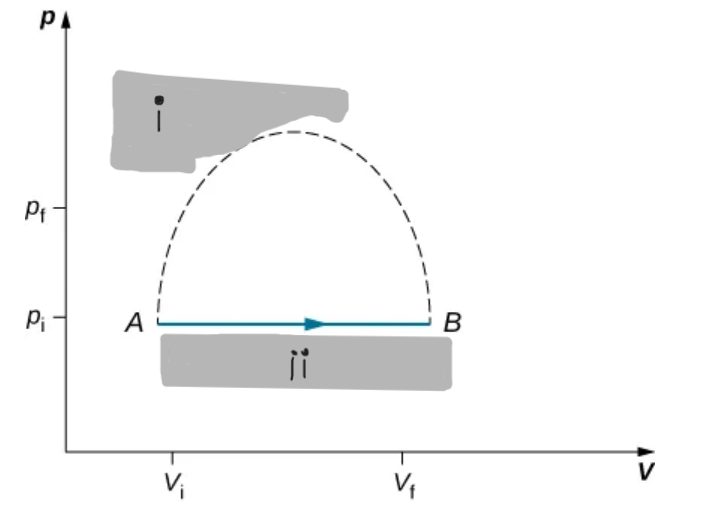
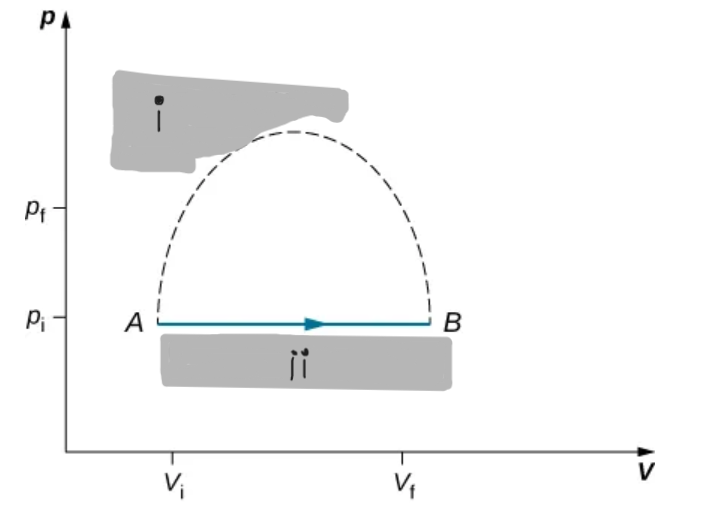
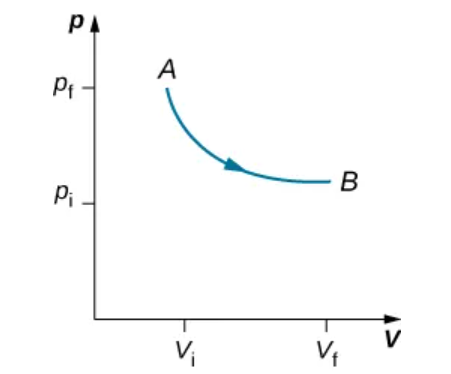
An isothermal expression from a state labeled A to another state labeled B on a pV diagram. The curve represents the relation between pressure and volume in a ideal gas at constant temperature.
Thermodynamic System
The part of the universe selected for study, whose properties (pressure, volume, temperature, etc.) are of interest
Surroundings
Everything outside the system that can exchange heat or work with it.
Thermodynamic Variables
Macroscopic quantities that describe a system’s state (e.g., p, V, T, n for an ideal gas).
State of a System
A unique condition defined by its thermodynamic variables (e.g., specific p, V, T)
Thermodynamic Process
Any change that moves a system from one equilibrium state to another.
Quasi-static Process
An idealized, infinitely slow process during which the system remains in internal equilibrium at all times.
Non-quasi-static Process
A real, finite-speed change through states that are not in equilibrium; intermediate states are not well defined.
Only quasi-static cells processes have a well-defined paths on a pV diagram and allow use of W = ∫pdV.
Why quasi-static Matters?
Isothermal Process
A process that occurs at constant temperature; requires continuous thermal contact with a heat bath.
Isobaric Process
A thermodynamic process in which the pressure remains constant.
Isochoric (Isovolumetric) Process
A process in which the volume remains constant; thus, no work is done (W = 0)
Adiabatic Process
A process during which no heat enters or leaves the system (Q = 0); temperature changes due to work.
Adiabatic Expansion
Gas expands without heat input; internal energy decreases → temperature falls
Adiabatic Compression
Gas is compressed without heat loss; internal energy increases → temperature rises.
Cyclic Process
A process in which the system returns to its initial state; all state variables return to original values
ΔEint = 0
Mathematical representation of the internal energy in a cycle
First Law for a Cycle
Net heat absorbed equals net work done over the cycle.
Q = W
Mathematical representation of the First Law of Cycle
Reversible Process
A quasi-static process that can be reversed by infinitesimal changes in the surroundings; no dissipation
Irreversible Process
Any process involving finite changes, friction, turbulence, or dissipation; cannot retrace original states.
Path on a pV Diagram
Graphical representation of a quasi-static process, and volume change.
Isothermal Curve on pV Diagram
A hyperbola showing p ∝ 1/V for an ideal gas at constant T.
Because intermediate states aren’t equilibrium states, no unique pV curve can be drawn.
Why is the path undefined for non-quasi-static Process
Heat Bath
An idealized system with constant temperature, capable of absorbing or releasing heat without changing T.
The system must remain in continuous thermal equilibrium with the heat bath.
What is the requirement for isothermal quasi-static change?
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
The state in which macroscopic properties are uniform and unchanging throughout the system.