Bio 305: Reproduction
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Only system not participating in homeostasis
reproductive
Primary reproductive Organs
Gonads (testies, ovaries)
-Produce reproductive calls (gameostais = gametes (sperm +egg)
-secrete sex hormones
accessory reproductive organs
ducts, glands, and external genitalia
DNA: _____ chromosomes, ____ homologous pairs
46;23 (1 is sex chromosome)
Cells divide by _________, during most life of the life cycle
mitosis
Cell division for reproduction
meiosis
Reduction Division
Chromosomes reduced from 46 (diploid, 2n) to 23 (haploid, n)
Two successful divisions to form gametes
meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
crossing over
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring.
3 hormone chain of command controls reproduction
Hypothalamus - Anterior Pituitary - Gonads
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
Secreted by the anterior pituitary and stimulates the gonads to produce sperm and egg.
LH
Causes the production of corpus lutium to produce sex hormones
path of spermatozoa
Tubules - rete testis - epidiymis - efferent ductules - vas deferens
Semi vesicles
-fructose
-Prostaglandins
alkaline fluid
Produced in the prostate gland; Neutralizes acids produced by the prostate gland and vagina
Why do sperm and urine never mix
sphincter in the urea
bulbourethral glands
the two glands below the prostate that secrete a sticky fluid that becomes a component of semen, helps with lubricating
Single ejaculate is about ______- _____ ml
3-6 ; 200-400 million sperm
Spermiogenesis
generate haploid gametes capable of fertilizing eggs
Process to go from Spermatogonia to Primary spermatocyte
Mitosis
Primary spermatocytes to Secondary
Meiosis 1
Secondary spermatocytes to Spermatids
meiosis 2
Spermatids to spermatozoa
Differentiation
Sperm develop from the ______ _____
outside- in
Sertoli cells
support sperm development in tight junctions between each cell to create blood testis barrier
anatomy of sperm
head, midpiece, flagellum
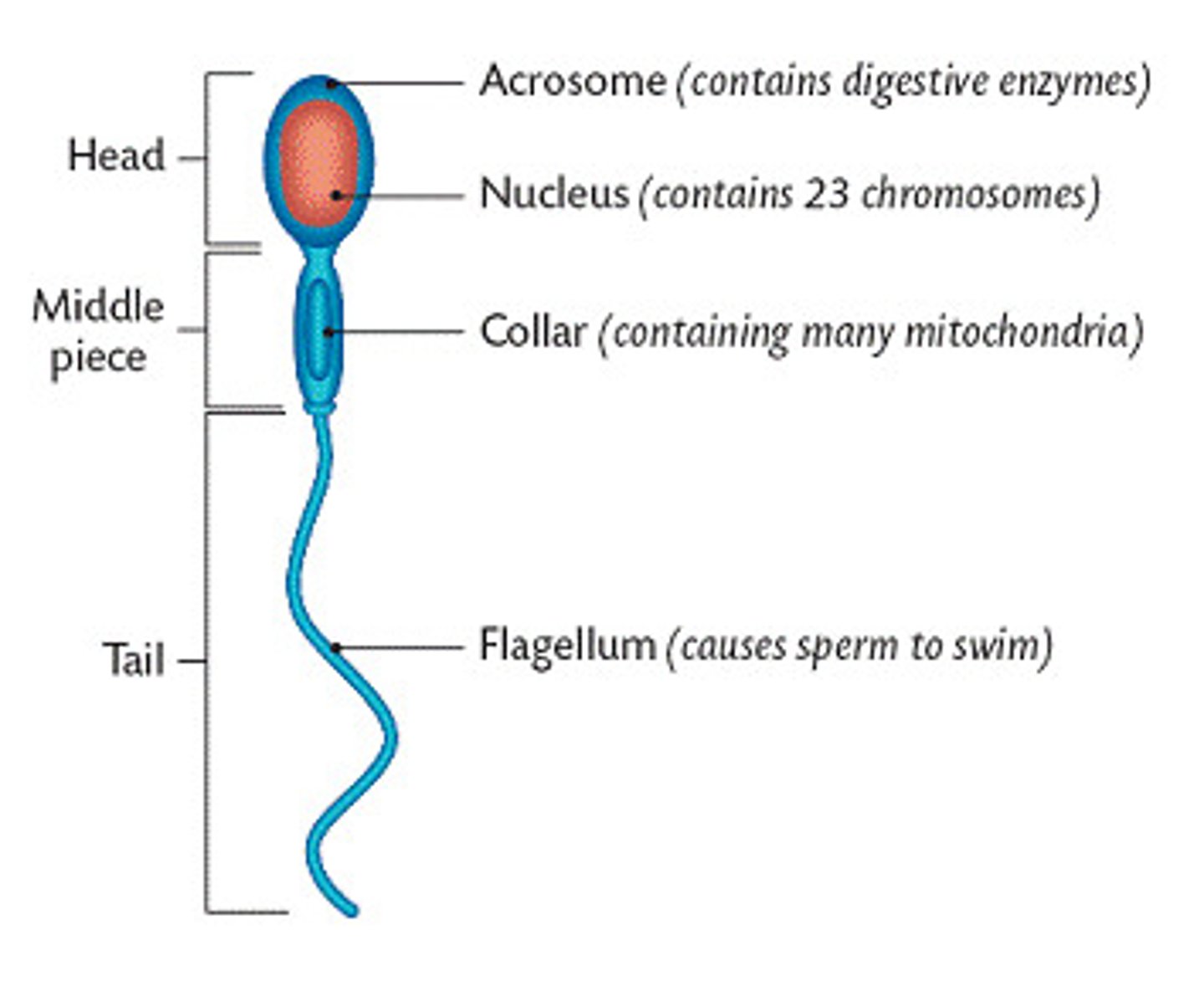
Flagellum aids in _____ of sperm
motility
acrosome of sperm
carries the enzymes that help digest the exterior coats of the egg. At the head of the sperm
GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus.
Leydig cells
produce testosterone
Hormone control in Males
GnRH - Anterior pituitary- Sertoli or Leydig cells - Inhibin + Testosterone + Stimulate spermatogenesis
What is responsible for maintaining sperm generation at a constant level
negative feedback
Effects of testasterone?
- required for initial and maintaining
-Decreases GnRH
Where does spermiogenesis occur?
seminiferous tubules
Which cells produce testosterone?
Leydig cells
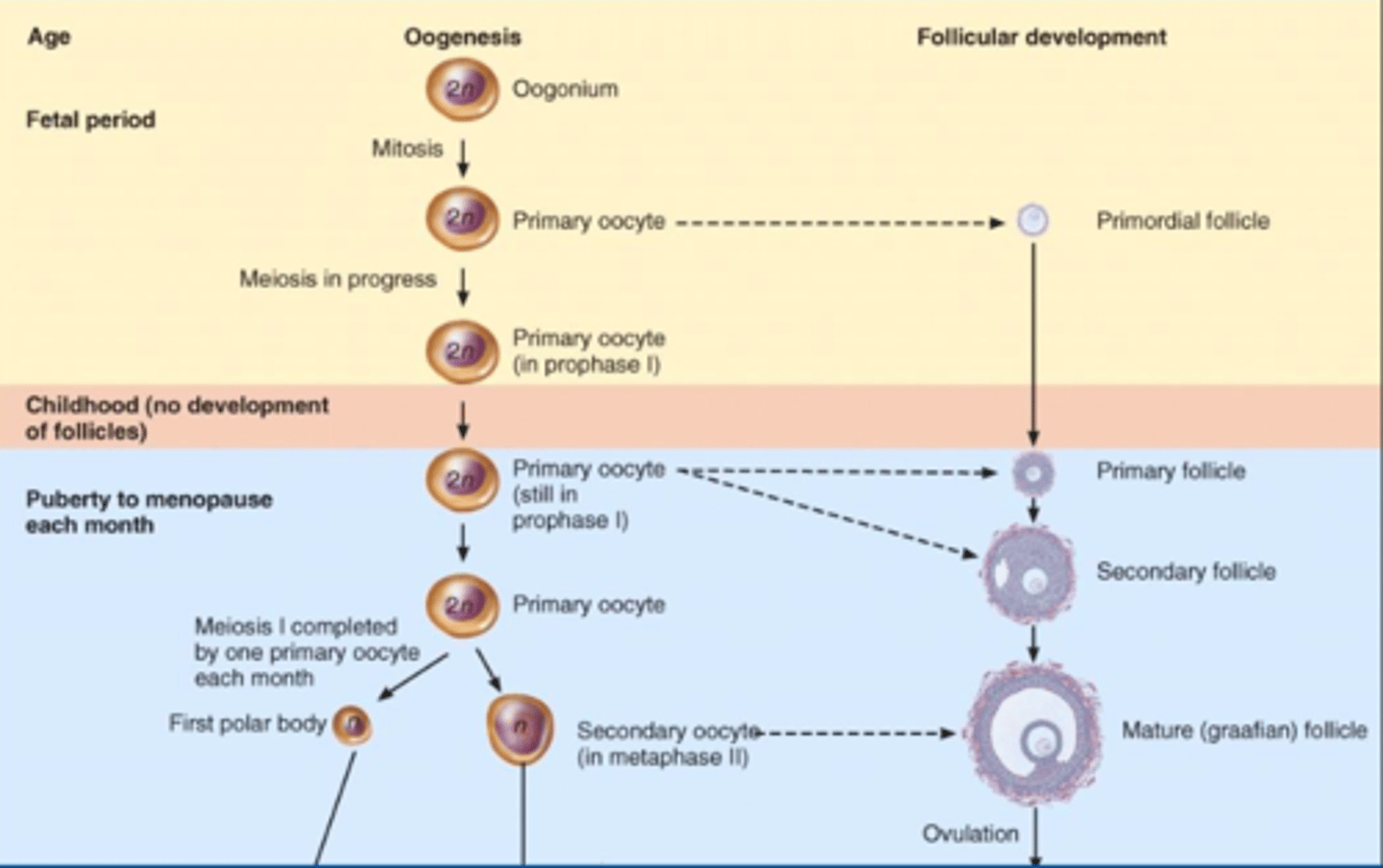
Oogenesis
secretion of sex hormones estrogen and progesterone
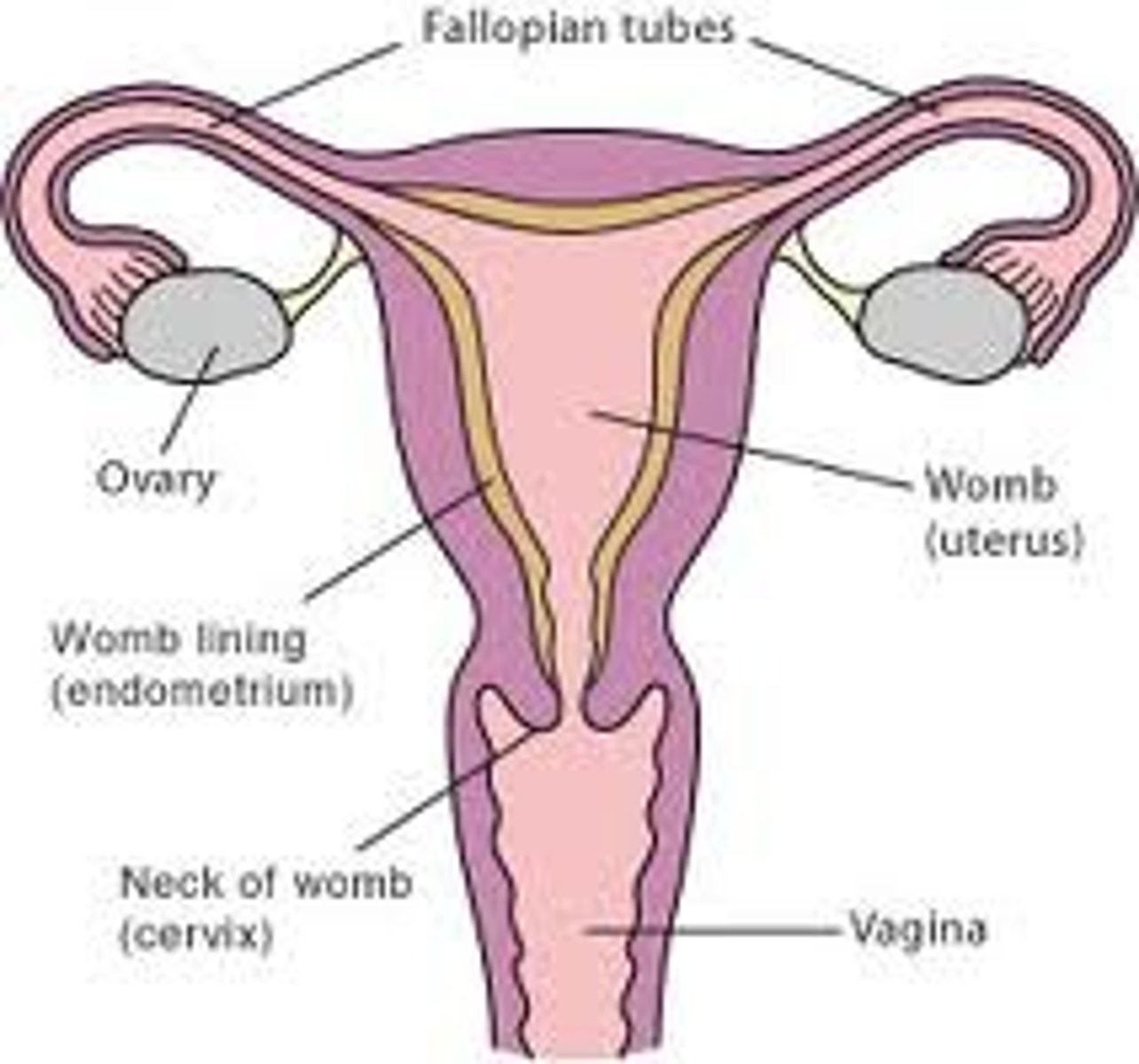
anatomy of female reproductive system
Eggs are contained in ______ within the ovary
follicles
Each month about 10-25 eggs __________ _ __________ but only ____ fully matures and ovulates
start to mature; 1
How many eggs are left after puberty
200-400,000
Approx ______ mature eggs are released in a female lifetime
400
Menapause
When menstration ceases. usually occurs between 45-52 years.
Travel path of egg
ovary- ova duct-
Where is the egg fertilized
fallopian tube
myometrium of uterus
the thick wall of the uterus consisting of smooth muscle and connective tissue
endometrium of uterus
inner layer of the uterus, thickens as the month goes one; if egg is fertilized it will remain, if not it will shed
summary of oogenesis
Oogonia - Mitosis Differentiation - Primary oocytes - 1st Meiotic division - Secondary oocytes - 2nd Meiotic division - ovum
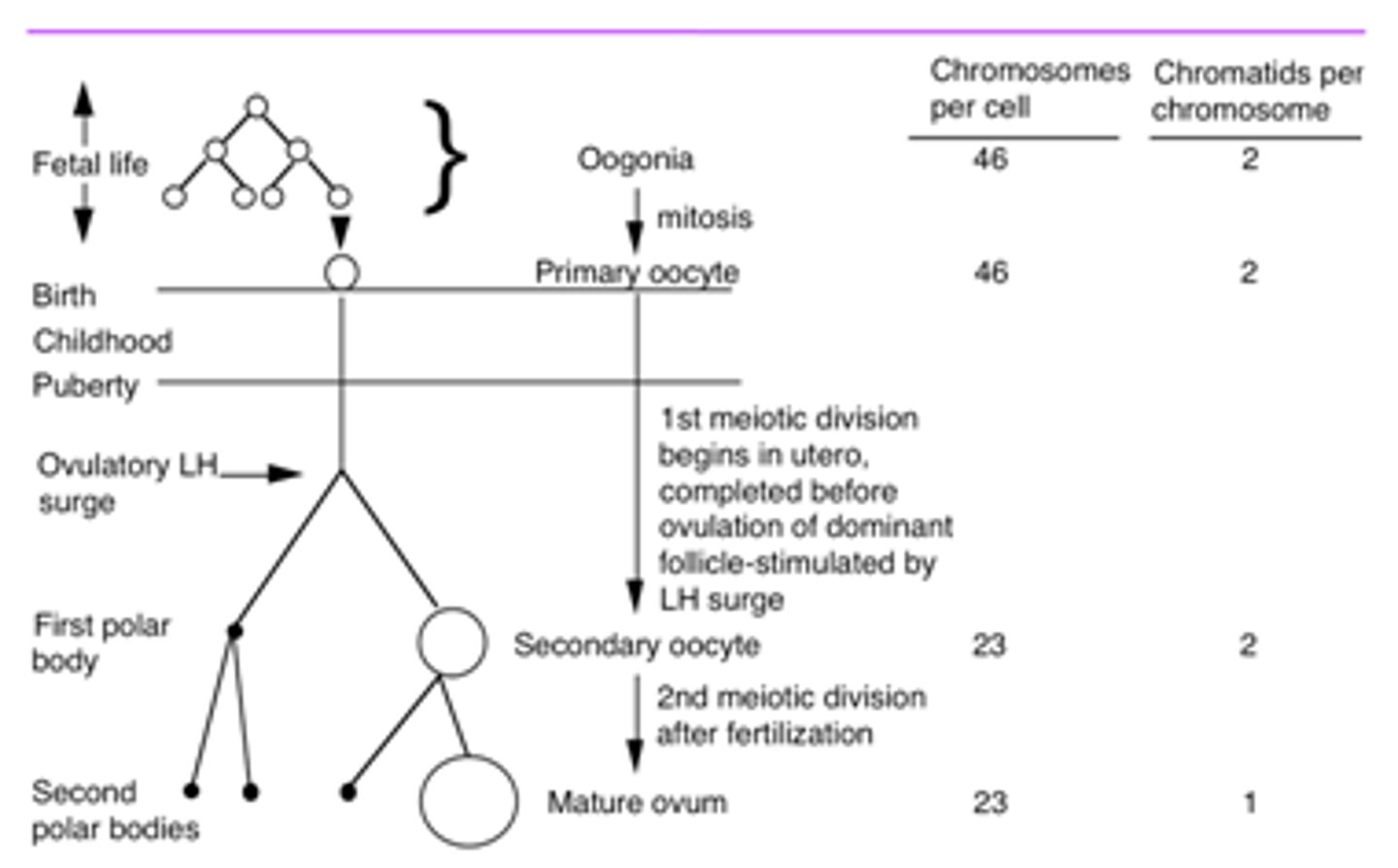
1st Meiotic Division in females :
Begins in utero, completed prior to ovulation
2nd meotic division
Happens after fertilization from sperm
theca cells
estrogen-producing cells in a maturing ovarian follicle
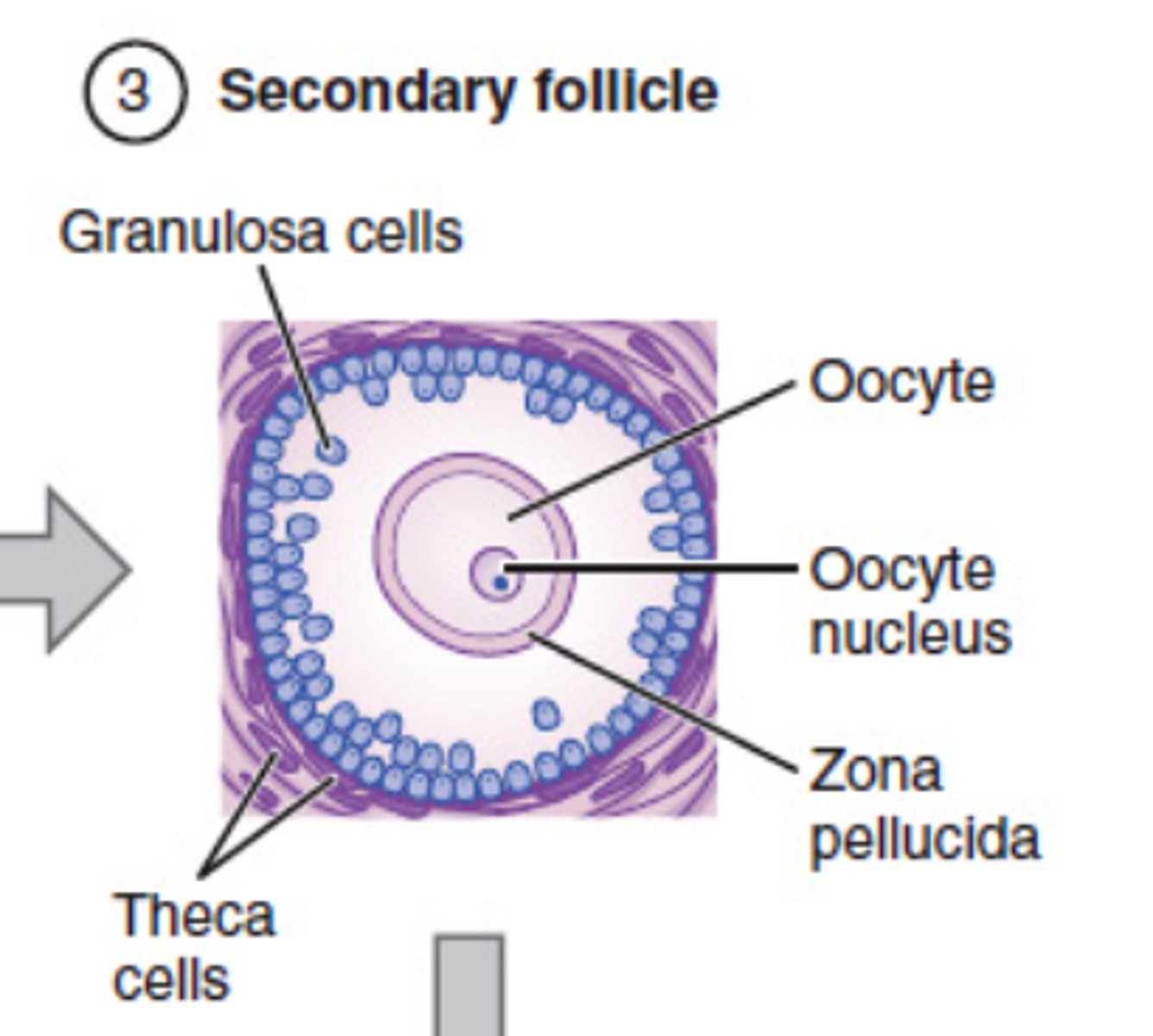
granulosa cells
the majority of the cells surrounding an oocyte in a follicle. Granulosa cells secrete estrogen during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle (before ovulation).
Development of ovarian follicles
primordial follicle, primary follicle, secondary follicle, graafian follicle, ovulation
luteinization
the process by which granulosa and theca cells are transformed into luteal cells
follicular phase
- Uterine Bleeding (Day 1-7)
- Multiple follicles develop (Day 1-7)
-One follicles becomes dominant (7)
- Dominant follicle mature (estrogen is produced) (7-14)
-Inhibin is produced by granulose cells (7-14)
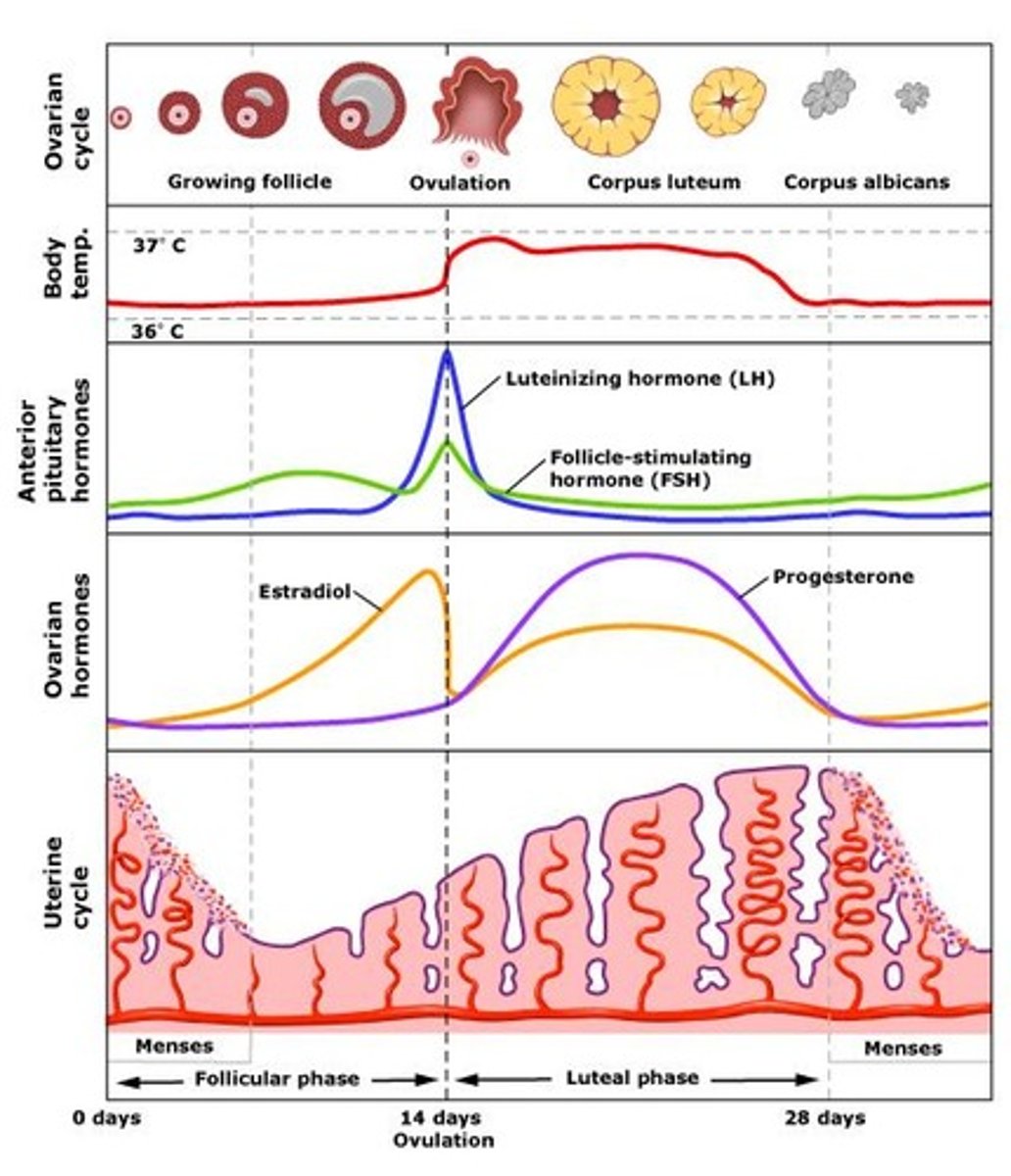
luteal phase
-End of Ovulation (14)
- Corpus luteum functions (Day 14-25)
-Corpus luteum degenerates (25-28)
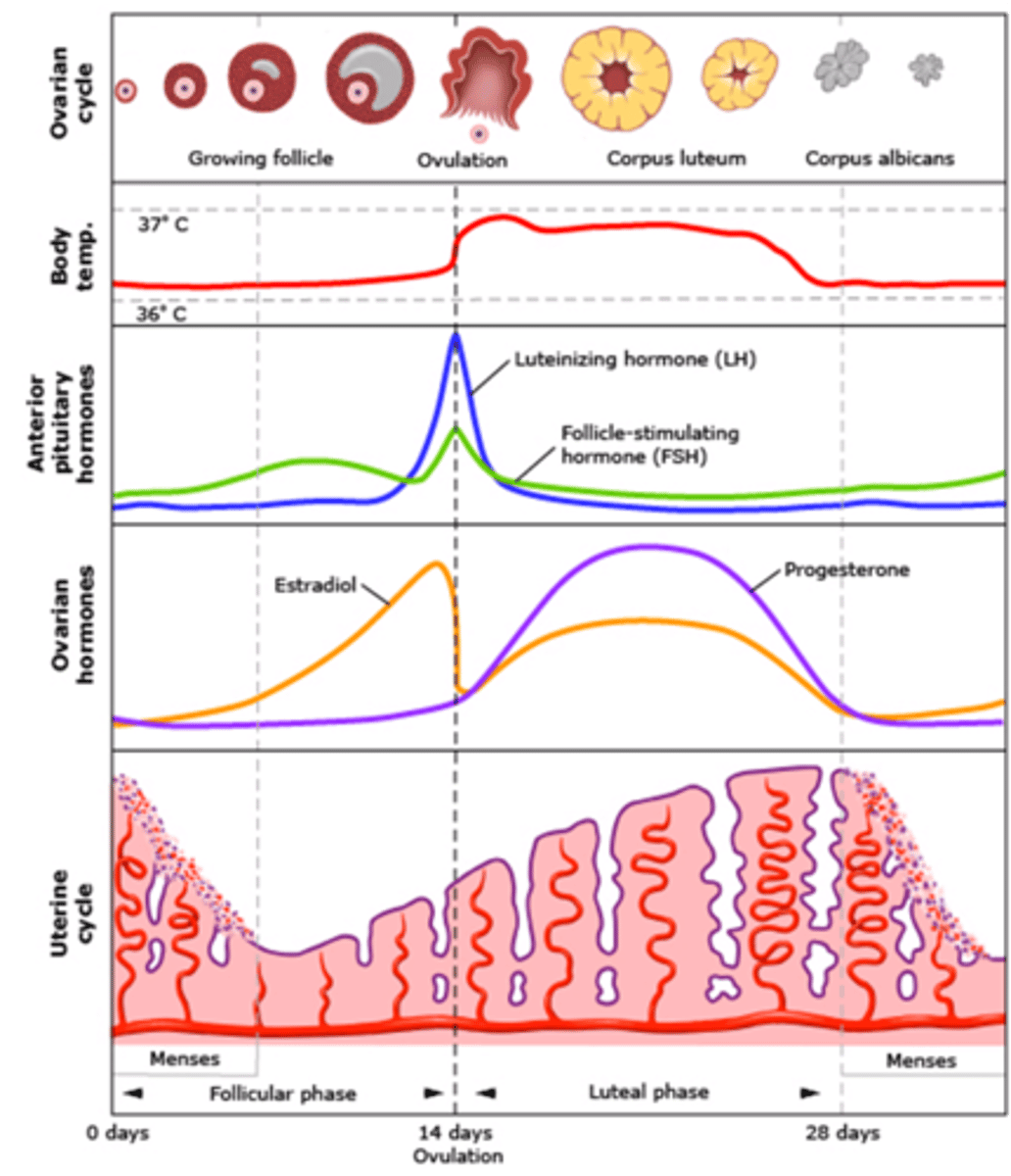
Ovulation is triggered by:
a surge in LH and marks the transition to the luteal phase
Small increases in LH and FSH lead to _________ _________ and an _________ in the synthesis and secretion of ovarian __________
follicular maturation; increase; estrogen
LH surge
triggers ovulation +luteinization of corpus lutetium from remaining cells in the ovary to produce progesterone
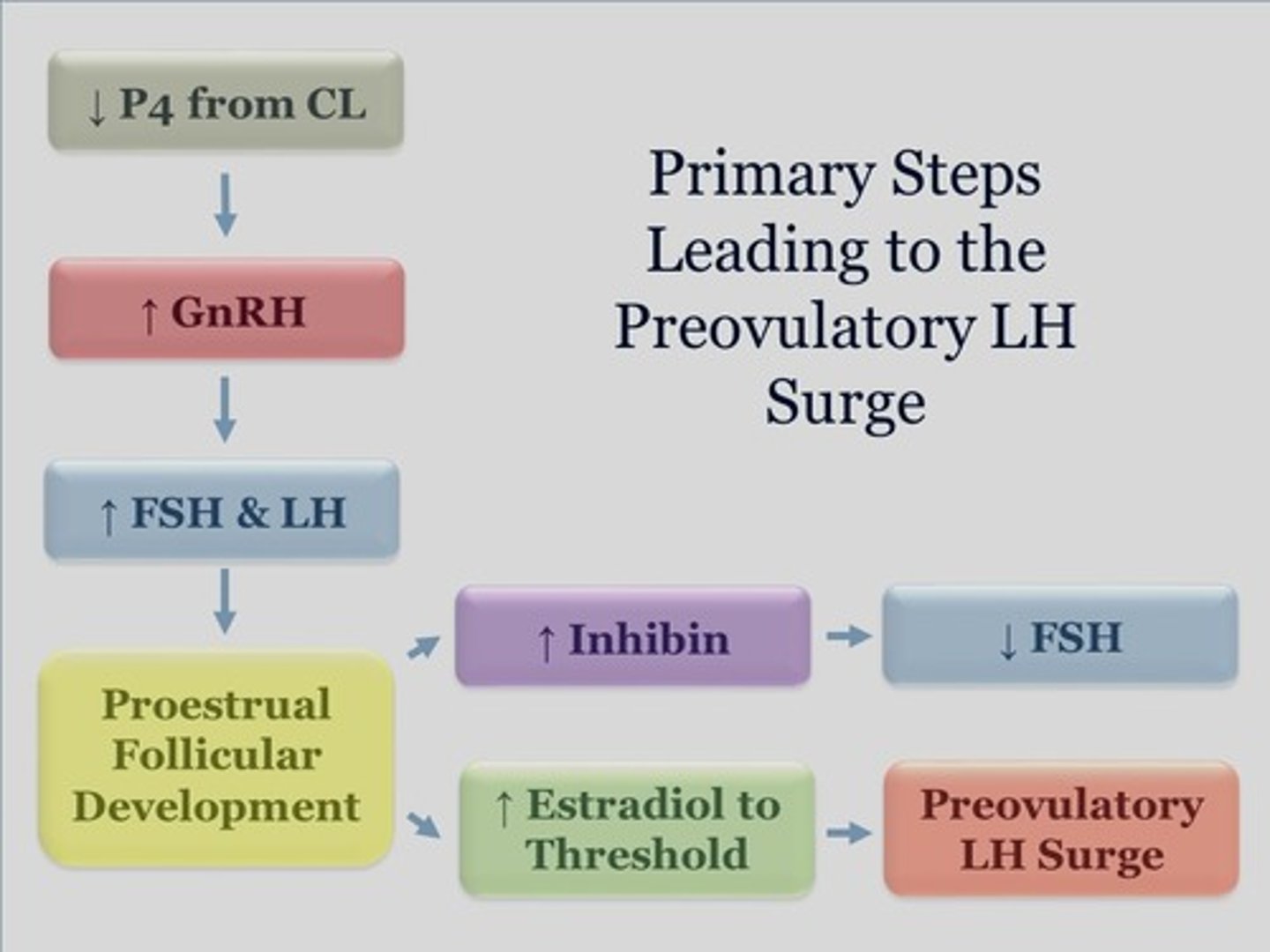
Fertilized eggs secrete ______ that keep corpus luteum alive
...
Aromatase
enzyme that converts testosterone to estradiol
What causes the androgens from the theca cells to become estrogen after being converted by the granulosa cells
LH-Theca-Diffusion-Granulosa-Estrogen
dysmenorrhea
pain caused by uterine cramps during a menstrual period
fertilized egg is called
zygote
optimal site for fertilization
Ampulla of the oviduct
Sperm is ___________ _________
Receptor dependent
It takes _________ to break down the egg to allow sperm in
many (ultimately they all help 1 sperm)
Cortical reaction
cortical cells break open and release toxins so no other sperm can survive
The only time a women makes HCG
Pregnancy