The Innate Immune System
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key concepts and definitions related to the innate immune system, cell types involved, genetic deficiencies, cytokine storms, and relevant treatments.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is the innate immune system?
The first line of defense against harmful or foreign substances.
What happens to the innate immune system as humans age?
It becomes less efficient and is subject to immunosenescence.
What type of cells are abundant in the innate immune system?
Non-specific cells such as phagocytes including neutrophils and macrophages.
Is the innate immune system present at birth?
Yes, but it is not as efficient.
Why is the innate immune system less efficient at birth?
Because there is a limited quantity of phagocytes.
How does the innate immune system change over time?
It becomes more efficient as humans grow.
When is the immune system at its peak function?
During the juvenile and young adult stage.
Why is the immune system highly effective in young adults?
Because the body contains many non-specific immune cells that quickly fight harmful or foreign bodies.
How does the immune system function in adults?
It still functions well but begins to weaken over time.
What contributes to the weakening of the immune system in adults?
Repeated exposure to infections and allergens like pollen.
Define immunosenescence.
The eventual deterioration of the immune system as the body ages.
Which cells are classified as phagocytes?
Neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, eosinophils.
What is the function of skin and mucosa in the innate immune system?
Acts as a barrier and chemical shield between the internal and external environment.
Chemical shield - epidermis is made up of keratinocytes → tightly linked → Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR) which triggers the produces cytokines → inflammation.
What triggers the production of cytokines in the innate immune system?
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR) in response to harmful stimuli.
What is the role of neutrophils?
first group of cells to respond
circulate blood
ingests pathogens
short life span most abundant phagocytes t
How do macrophages contribute to the immune response?
in all tissues that use phagocytosis
activates part of the immune system
recruits other immune cells
long-lived cells
alert immune system → inflammation
What do eosinophils attack?
njest the bacteria, but will attack foreign cells that can’t be ingested
Releases toxic enzymes → leaves holes
Less active than neutrophils and macrophages
What do basophils and mast cells contain that contributes to inflammation?
Contains granules filled with histamine
Encounters allergens (antigens that cause allergic reactions)
Histamine causes an increased blood flow to the damaged tissues —> swelling and inflammation
How do dendritic cells bridge the innate and adaptive immune systems?
By phagocytosing pathogens and presenting antigens to T cells.
What do natural killer (NK) cells do?
keeps viral infections and tumors in check
attach to the infected cell → releases chemical (cytotoxins) to kill instead of engulfing (phagocytosis)
What is classical natural killer cell deficiency?
The absence of NK cells in white blood cells, leading to no function.
What is functional natural killer cell deficiency?
Presence of dysfunctional NK cells in white blood cells.
What is a common age for NK cell deficiency to occur?
Around 13 years old but can be seen at any age
What causes CNKD1?
GATA2 haploinsufficiency.
What does the GATA2 gene do?
It produces transcription factors that help manage blood cell differentiation and regulate the development of NK (natural killer) cells.
How many copies of the GATA2 gene are people born with?
It occurs when one copy of GATA2 is mutated and the other is functioning.
What effect does GATA2 haploinsufficiency have on NK cells?
It leads to the loss of CD56^bright NK cells and dysfunction of CD56^dim NK cells.
What are CD56 bright cells?
subset of NK cells
less mature
in charge of producing cytokines
What are CD56 dim cells?
subset of NK cells
more mature
in charge of target cell killing
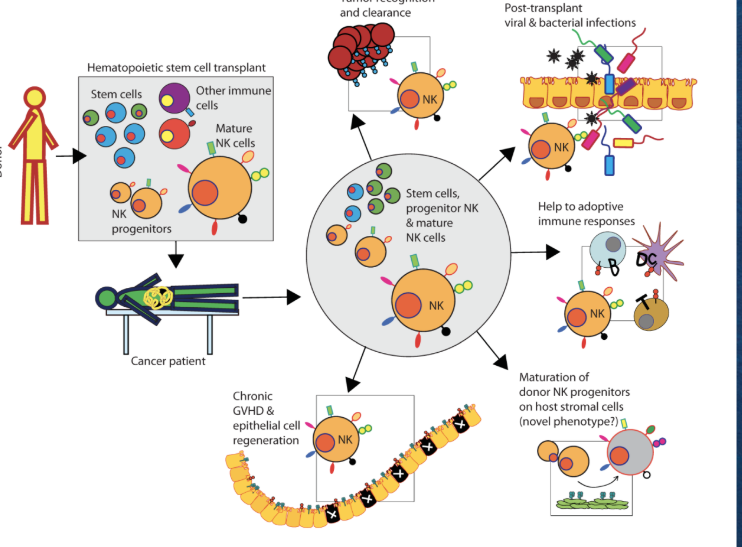
What is the treatment for Classical Natural Killer Cell Deficiency (CNKD1)?
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant.
What enzyme is produced by the ADA gene?
Adenosine deaminase.
What is the function of adenosine deaminase?
It converts deoxyadenosine into deoxyinosine.
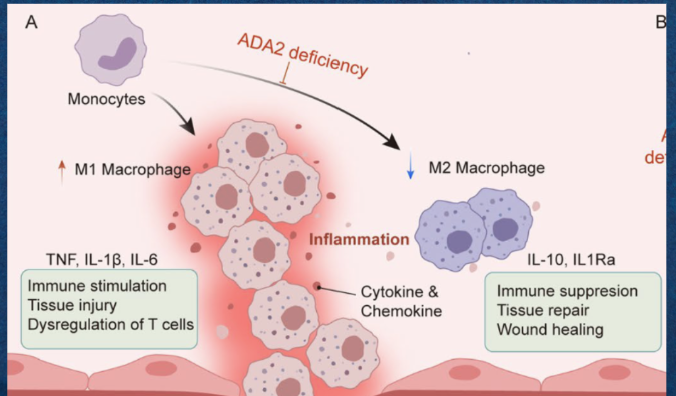
What happens when there is a mutation in the ADA gene?
It limits the production of adenosine deaminase, causing a buildup of deoxyadenosine in lymphocytes.
What is the result of deoxyadenosine buildup in lymphocytes?
An increase in M1 macrophages (proinflammatory responses) and elevated inflammation.
At what age is Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency typically diagnosed?
In infancy or early childhood.
What are some symptoms of adenosine deaminase deficiency?
Symptoms begin to show within the first six to twelve months of life
failure to thrive
developmental delays
serious infections
severe combined immunodeficiency
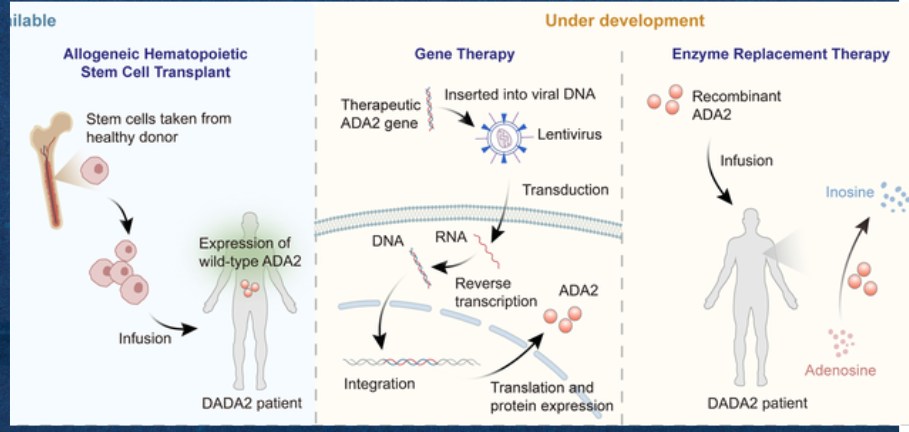
Treatment for ADA2
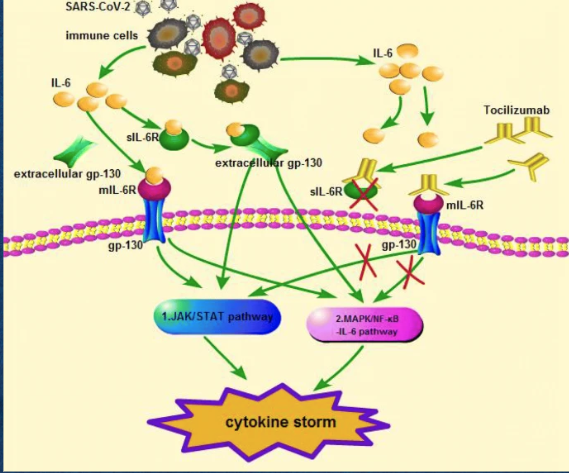
What therapy helps mitigate the cytokine storm associated with COVID-19?
Tocilizumab, an IL-6 receptor antagonist.
Binds to the membrane bound receptor for IL-6 and soluble receptor for IL-6
Prohibiting the activation of signaling pathways that cause a cytokine storm
What is a monoclonal antibody?
A laboratory-made molecule designed to supplement antibodies in the immune system.
What causes the cytokine storm in COVID-19?
Extensive release of cytokines including IL-6.
What key immune cells and molecules are involved in the cytokine storm during SARS-CoV-2 infection?
Macrophages, natural killer cells, and cytokines like Interleukin-6 (IL-6).
What is the function of Interleukin-6 (IL-6)?
It promotes inflammation and aids the innate immune response.
How can IL-6 negatively affect the body during SARS-CoV-2 infection?
It can block or weaken immune responses that fight the virus and promote inflammation-related damage.
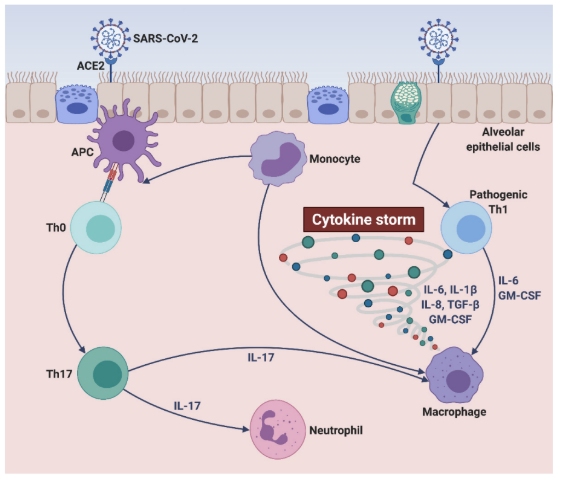
What is a cytokine storm?
A hyper-inflammatory response involving the excessive release of cytokines.
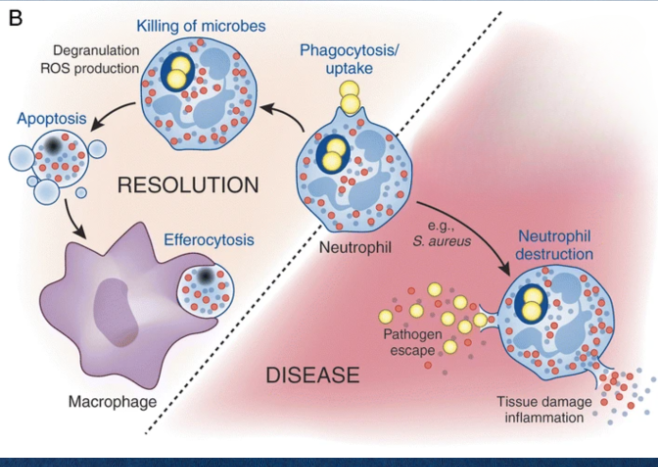
What is the relationship between Staphylococcus aureus and neutrophils?
Neutrophils attempt to kill the bacteria using reactive oxygen species.
What does Staph produce that hampers the immune response?
Catalase, an enzyme that neutralizes reactive oxygen species.
Which type of penicillin can combat Staphylococcus aureus infections?
Penicillinase-resistant penicillins.
stops bacterial cell wall synthesis by invading the peptidoglycans
Causing the bacteria to burst
What is a characteristic of neutrophil action against pathogens?
Degranulation and production of reactive oxygen species.
What are the effects of proinflammatory cytokines like TNF and IL-6?
Promote inflammation and immune stimulation.
What is the role of M2 macrophages?
Immune suppression and tissue repair.
How does age increase vulnerability to cytokine storms?
Older individuals and those with underlying conditions are at higher risk.
What is the significance of flow cytometry in diagnosing NK cell deficiencies?
It quantifies NK cells in blood.
What is the relationship between cytokine release and inflammation?
Cytokines promote and regulate inflammation.
What do cytotoxins do in the response to infected cells?
They kill the infected cells instead of engulfing them.
What does TNF inhibitor treatment target?
Proinflammatory cytokines involved in inflammatory responses.
What is GATA2's role in the immune system?
It produces transcription factors essential for NK cell development.
What should be done if secondary causes of NK cell deficiency are suspected?
Conduct further functional evaluations.
What immune response do macrophages assist with in infection?
They alert the immune system leading to inflammation.
What is one of the most dangerous aspects of a COVID-19 related cytokine storm?
It can weaken immune responses against the virus.
What is the primary function of B cells in the immune system?
They produce antibodies in response to antigens.
How does an increased number of M1 macrophages affect inflammation?
It leads to greater inflammation and tissue injury.
How does the immune system change from birth to geriatric age?
It peaks in young adults and weakens with age.