Lecture 4: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Imaging of soft tissues discovered by…
Felix Block and Edward Mills Purcell in 1947
what can be used to give 3D image of soft tissue?
MRI scans
MRIs are used to give 3D image of soft tissue because…
tissues contain water
how does MRI work?
hydrogen nucleus has a proton with a pos charge, it spins like a top, in the MRI the protons spin align according to magnetic field
Radiofrequency (RF) pulse is used to… Energy released by the protons when RF is turned off is…
‘excite’ the proton, measured and turned into an image
Protons in different molecules resonate… and have different…
differently following a RF pulse, T1 and T2 relaxation time constants
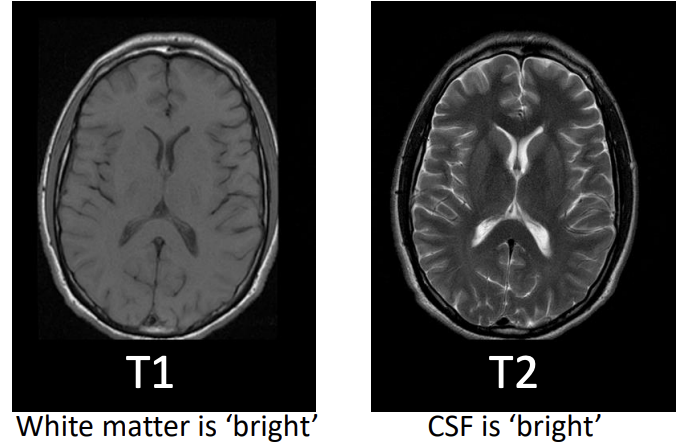
what does T1 and T2 relaxation time constants allow for?
the contrast between grey matter and white matter
T1 refers to…
longitudinal relaxation, realignment with magnetic field
T2 refers to…
resumption of proton spinning around it’s own axis
is T1 or T2 quicker?
T2 is quicker than T1
Dephasing leads to…
loss of horizontal magnetisation
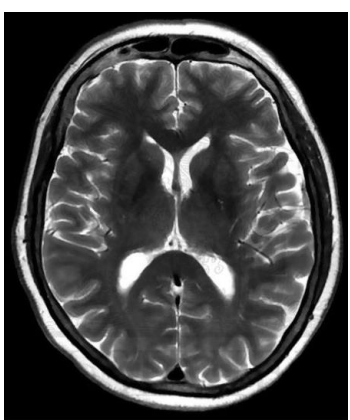
for T2-images, water compartments appear … and tissues with high fat content appear…
bright, dark
T2 (transverse relaxation time) is the…
time constant which determines the rate at which excited protons reach equilibrium or go out of phase with each other
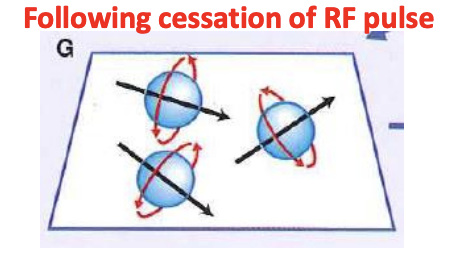
T2 relaxation time is a measure of the time taken for…
the loss of synchrony of spinning protons as they relax back to initial alignment
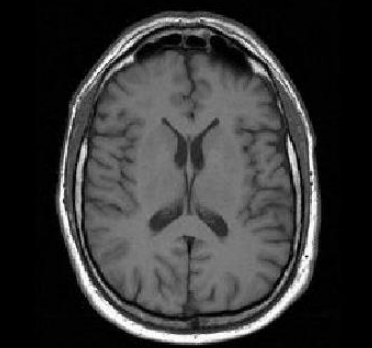
for T1-images, water compartments appear … and tissues with high fat content appear…
darker, brighter
what are T1 images good for?
anatomy
what are T2 images good for?
detecting pathology
what is T1 (longitudinal relaxation time)?
the time constant which determines the rate at which excited protons return to equilibrium
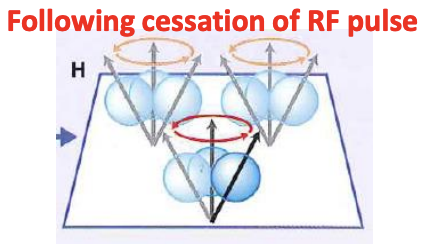
T1 relaxation time is a measure of time taken for…
spinning protons to realign with the external magnetic field
protons in water and tissue align with…
magnetic field, not their own axes
-A radio frequency pulse (RF) disrupts… and causes them to resonate
-creates a… that can be detected by a coil
-as protons return to their original alignment with the magnetic field, the changes can be detected by…
the alignment of protons, magnetic field and a small electric current, t1 and t2 relaxation time constants
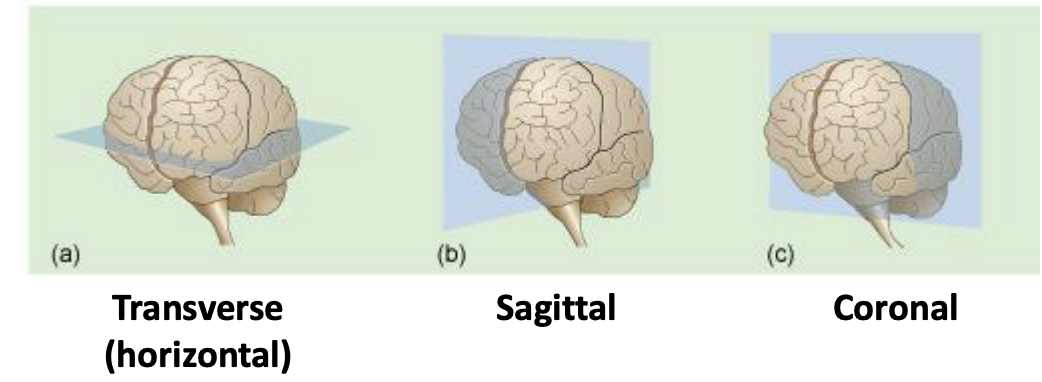
Passing electromagnetic energy (RF pulses etc) through the head at different angles allows…
the collection of images from a series of different planes or slices
Most MRI scanners are…
1-3 Tesla (10,000 or 30,000 Gauss)
T1-weighted imaging can also be performed while infusing…
Gadolinium (Gad), a non-toxic paramagnetic contrast enhancement agent
Gad enhanced images are especially useful in looking at…
blood vessels and diseased/inflamed tissue with leaky blood vessel
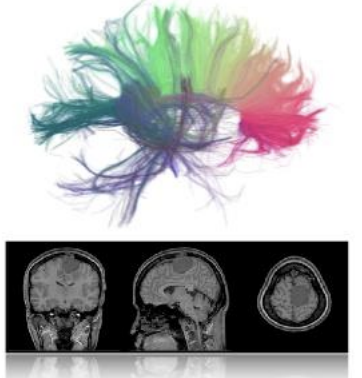
structural MRI studies…
brain anatomy,
functional MRI(fMRI) stuudies…
brain function
Deoxyhaemoglobin … whereas oxyhaemoglobin is not
paramagnetic (magnetic field induced in the presence of a magnetic field)
functional MRI use…
BOLD – blood oxygen level detection
Increase in oxygenated blood flow believed to…
reflect increased metabolic demand of synaptically active neurons
fMRI has been used to detect…
consciousness in comatose patients
The temporal resolution for fMRI BOLD imaging is…
relatively slow
what is Positron Emission Tomography (PET) useful for?
assessing molecular function and activity rather than structure
how does PET imaging work?
radioactive isotopes injected into the body, decay and emit positrons, positron collides with an electron, a photon is emitted and is detected by the PET scanner
PET Scan can be used to label…
β-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease