vasc 2 midterm
1/682
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
683 Terms
Change in frequency of sounds, light, or other waves caused by the motion of the source or the observer
What is the Doppler effect
Change in frequency of sound caused by the motion of rbc's
What is doppler in ultrasound
Difference between transmitted frequency and received frequency
What is the doppler shift
Receiver frequency - transmitted frequency
How do you calculate the doppler shift
Doppler shift equation, not the complicated one
How do the machine detect/calculate doppler shift
Rbc's moving toward transducer, antegrade flow
What is a positive doppler shift
Cells moving away from the transducer, retrograde flow
What is a negative doppler shift
Larger
If the cells are moving toward the transducer will the echo frequency be larger or smaller
Smaller
If the cell are moving away from the transducer will the echo frequency be large or smaller
Blood velocity and cosine of the doppler angle
What are the two most important factors that affect the doppler shift
F= (2Fo x v x Cos0) / C
What is the doppler equation
Hertz or kilohertz
What unit is the doppler shift usually in
True
T/F: the doppler shift is usually in the audible range
We can hear spectral doppler
What does it mean that the doppler shift is usually in the audible range
Blood velocity
What is the doppler shift directly proportional to
Higher shifts
Faster blood =
Angle
What is the doppler shift inversely related to
Higher shifts
Smaller angles =
Lower shifts
Larger angles =
No shift
Perpendicular (90 degrees) =
False
T/F: when there is no doppler shift it always means that there is no flow
No flow, poor doppler angle, poor setup
What can the absence of Doppler shift be caused by
Average doppler shifts
What does colour doppler detect within the colour box
Lower doppler shifts
What does darker colours mean on the colour map
Higher doppler shifts
What does lighter colours mean on the colour map
True
T/F: for any vascular study, the baseline is typically centred
Colour map
What are the doppler shifts coded according to
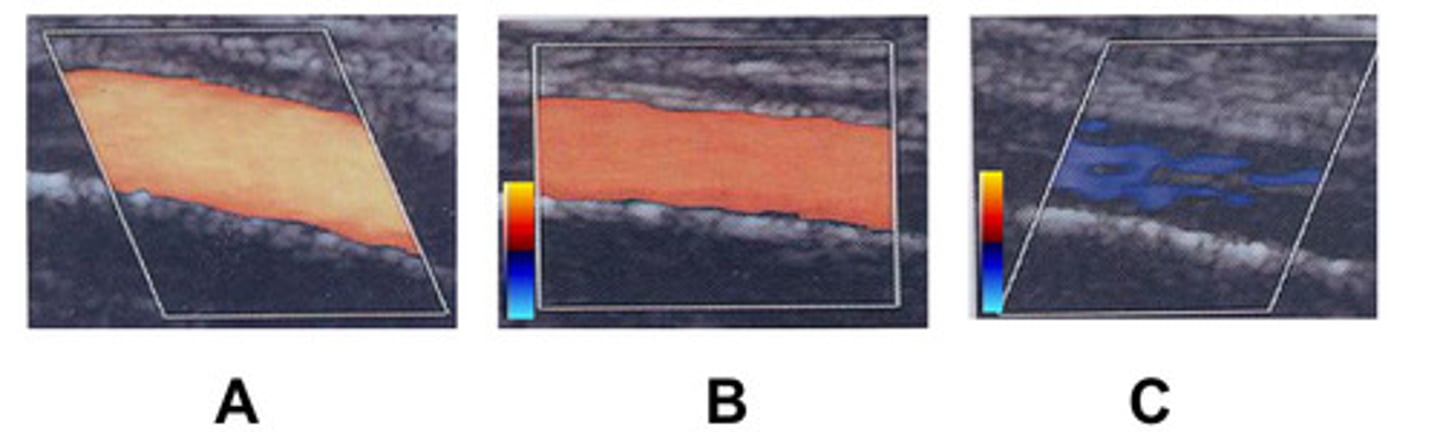
A
Which is the most ideal box steering
Amplifies the doppler shifted echoes
What does colour gain do
Overwrite soft tissues
What does over gain do
Displays poor colour filling
What does under gain do
Range of doppler doppler shifts that can be displayed
What does colour scale determine
PRF
What is the colour scale also known as
Doppler shifts exceed the NyQuist limit
When does aliasing occur
1/2 the PRF
What is the nyquist limit
False
T/F: you can see colour separation when the colour flow is aliasing
Removes low doppler shifts
What does the colour wall filter do
Increase
Do you increase or decrease the colour wall filter if you want to remove low doppler shift noise
Decrease
To you increase or decrease the colour wall filter if you want to display low doppler shifts
Penetration
Lower frequency has better ________________
Resolution
Higher frequency has better ___________________
Amplitude of blood flow
What does power doppler colour code
More sensitive to slow flow and less angle-dependent
What are the advantages of power doppler
Very motion sensitive and may not display directional information
What are the disadvantages of power doppler
Trickle flow and tortuous vessels
What is power doppler used to assess
Spectral doppler with range resolution, can determine at what depth we would like to sample
What is pulsed doppler
One crystal is used to fire and then listens for returning echoes
Explain what is happening to the crystals in pulsed doppler
Velocity
What is the y-axis
Time
What is the x-axis
Amplitude
What is the z-axis
False
T/F: the baseline should be centred for pulsed doppler
Spectral broadening
What does a large sample volume increase
Increase SPL (ring time)
Increasing the size of the sample volume will:
True
T/F: aliasing is never useful in pulsed doppler
Optimize baseline and increase the scale
What are the two option to fix aliasing
Align with the jet
How should you adjust the angle correct is there is an eccentric flow jet
Amplifies the doppler-shifted echoes and affects the brightness of spectral display and waveform
What does doppler gain do
Removes low doppler shifts
What does the doppler wall filter do
Sound waves that are emitted continuously from one crystal and the reflected sound is continuously received by a second crystal
What is continuous wave doppler
False
T/F: there is still a limit to the velocities that can be detected by continuous wave Doppler
True
T/F: there is no range resolution or 2D image with continuous wave doppler
Zone of sensitivity
Where does continuous wave doppler sample from
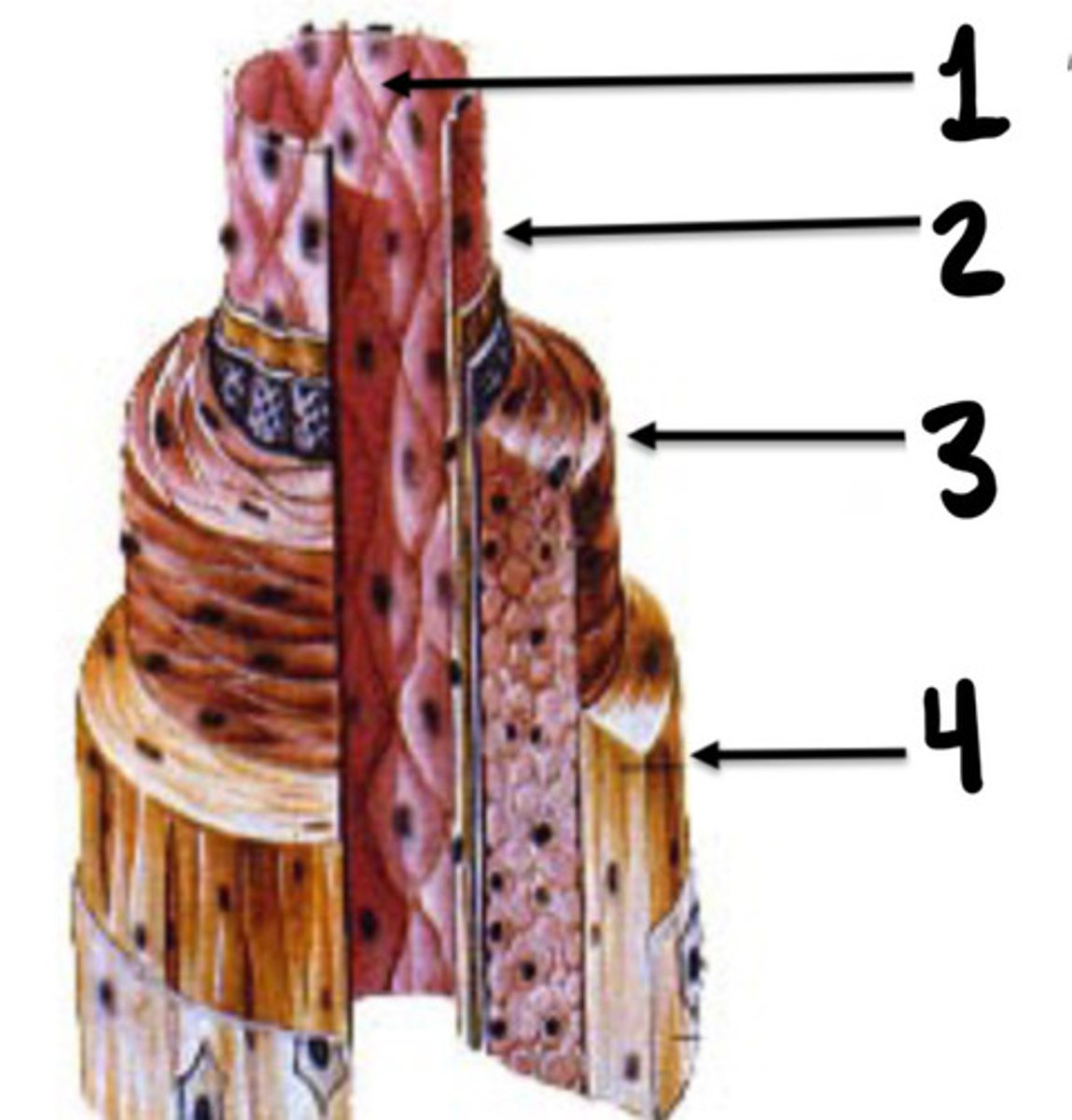
Tunica intima, media, and adventicia
What are the 3 layers of vessels
Tunica intima
What is the innermost layer of vessels consisting of endothelial cells
Tunica media
What layer of vessels is made up of smooth muscle cells
Tunica adventitia
What layer of vessel is consisting of connective tissue, nerve fibres and small vessel capillaries
Tunica media
What layer of vessels is the thickest
Tunica adventitia
What lay of vessels does vasa vasorum originate in
Small vessel capillaries
What are vasa vasorum
Endothelial lining
What is 1
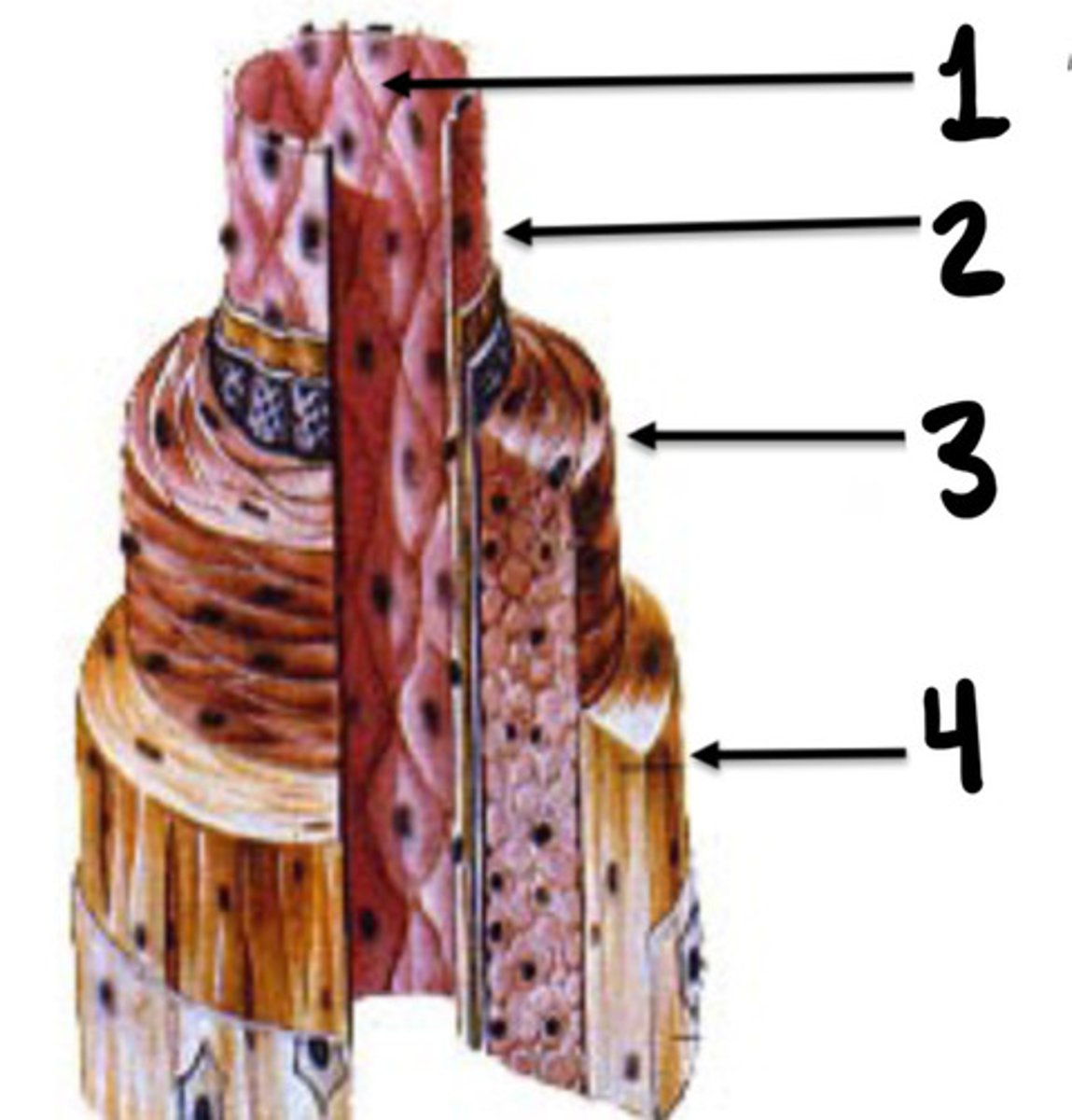
Intima
What is 2
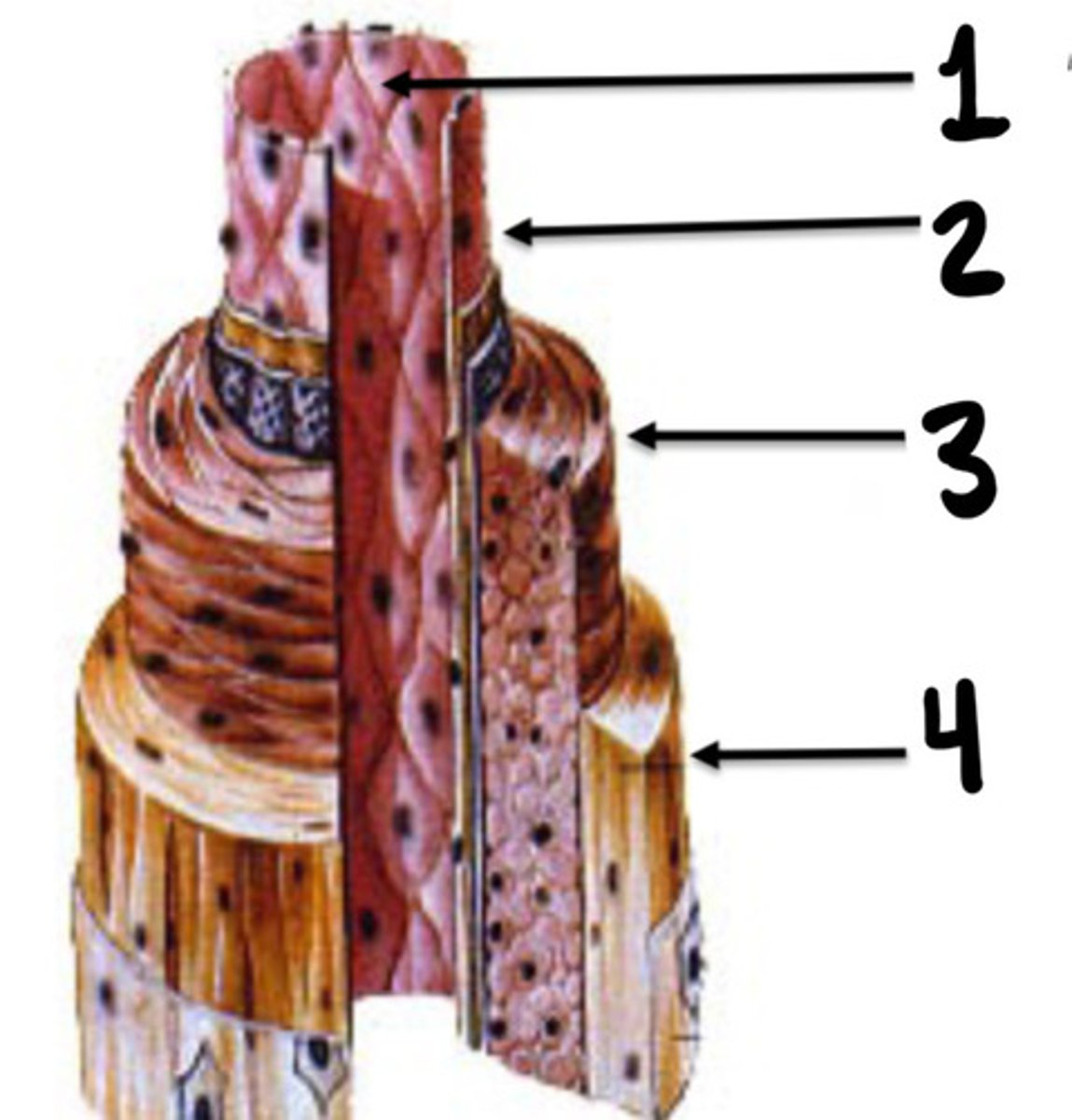
Media
What is 3
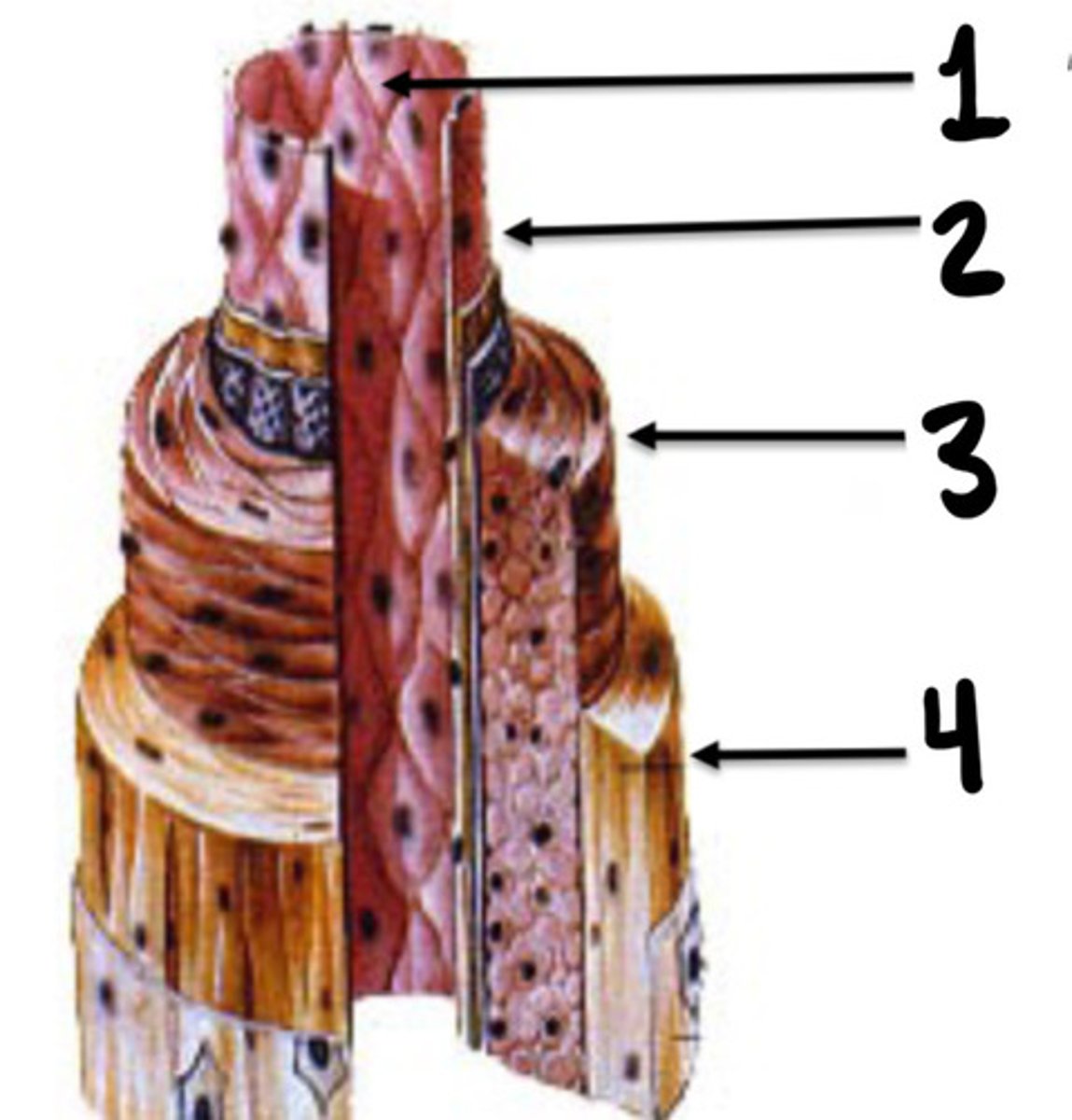
Adventicia
What is 4
Stopcocks
Arterioles are the ___________ of the vascular system
Resistance
The arterioles are the main providers of ___________ to blood flow within the vascular system
All arteries except the aorta and major branches
What does small and medium sized arteries include
True
T/F: small and medium sized arteries are more elastic and fibrous than arterioles
Aorta and its largest branches
What does large elastic arteries include
Large amount of elastic fibres and less smooth muscle cells
Describe the composition of the walls of large arteries (aorta and its branches)
Size
What are arteries classified according to
Four
How many vessels supplies the brain
2 ICA's and 2 vertebral arteries
What 4 arteries supply the brain
Brachiocephalic, LT cca, and LT subclavian (arteries coming off the aortic arch)
What supplies the central nervous system
Brachiocephalic, LT CCA, LT subclavian
What are the 3 branches of the aortic arch
Slightly posterior from the arch to the right side of the neck
Describe the path of the Brachiocephalic artery
Innominate artery
What is another term for the Brachiocephalic artery
Rt CCA and rt subclavian artery
What does the innominate artery branch into
Upper border of the right sternoclavicular junction
Where does the Brachiocephalic artery branch into the RT CCA and RT Subclavian artery
Left sternoclavicular joint
What does the LT CCA pass underneath after ascending from the aortic arch
False
T/F: the common carotid arteries have a lot of branches coming off them as they travel toward the brain
Internal and external carotid arteries
what does the common carotid artery split into?
Upper border of the thyroid cartilage
Where does the cca divide into internal and external carotids
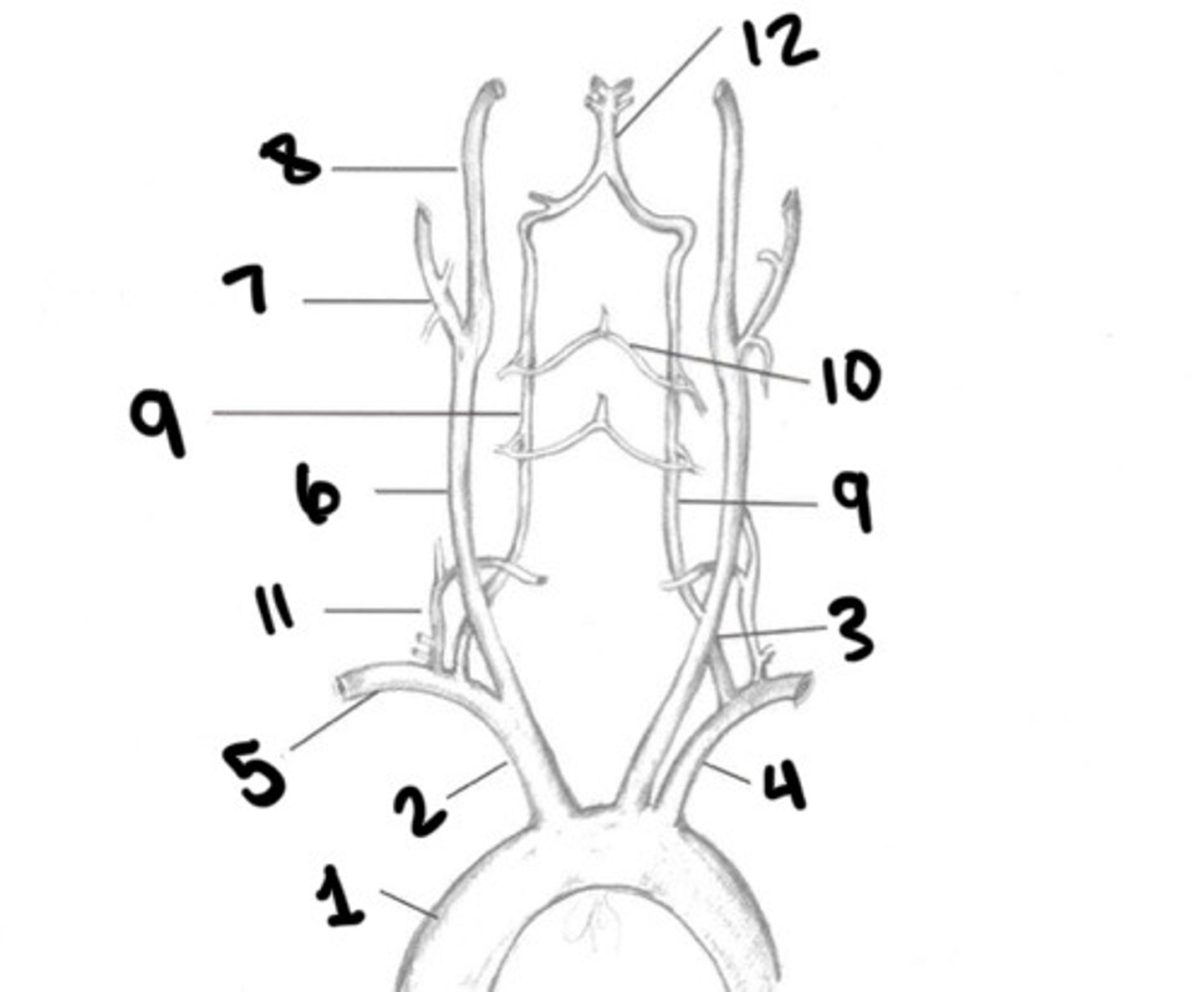
Aorta
What is 1
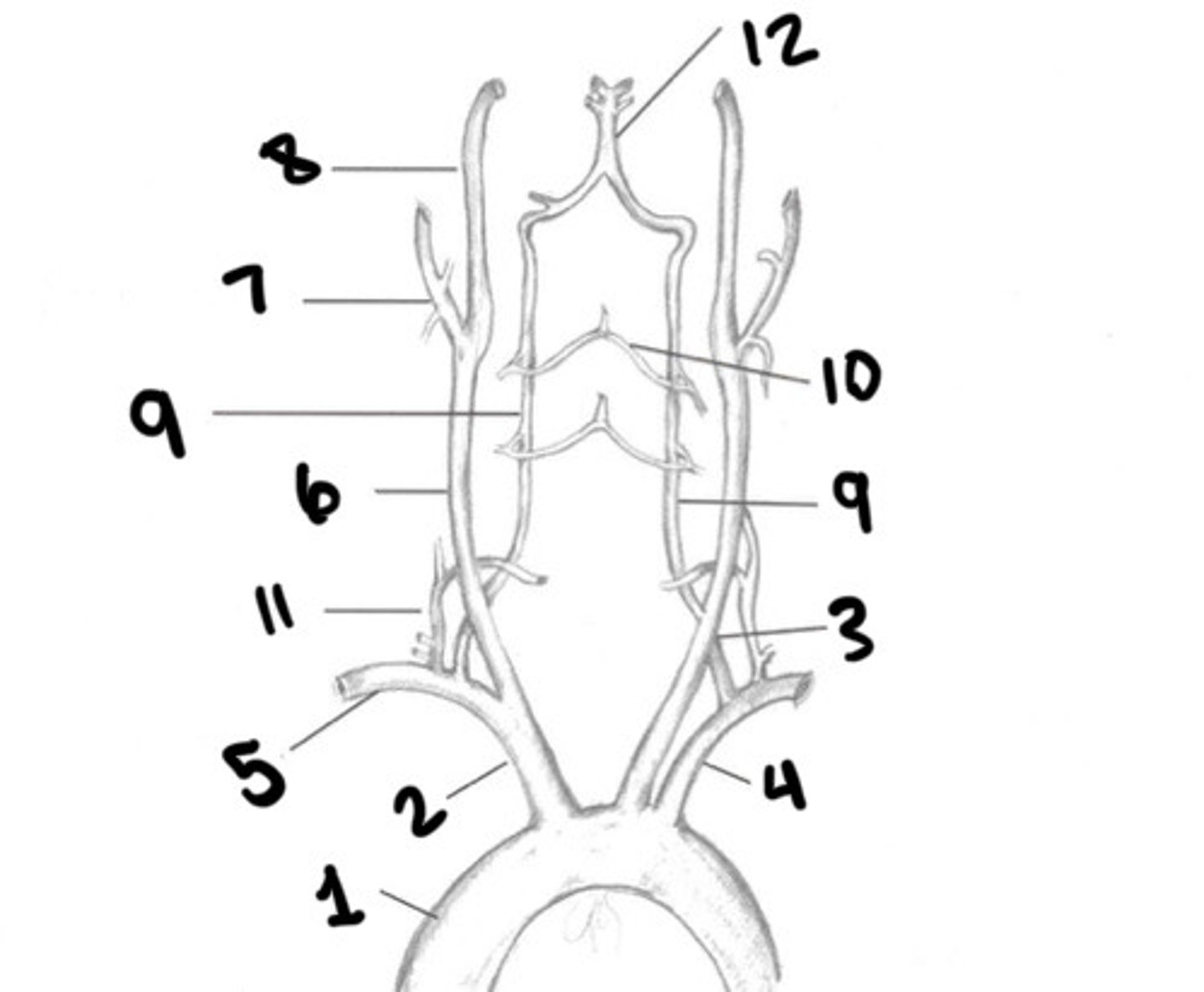
Innominate
What is 2
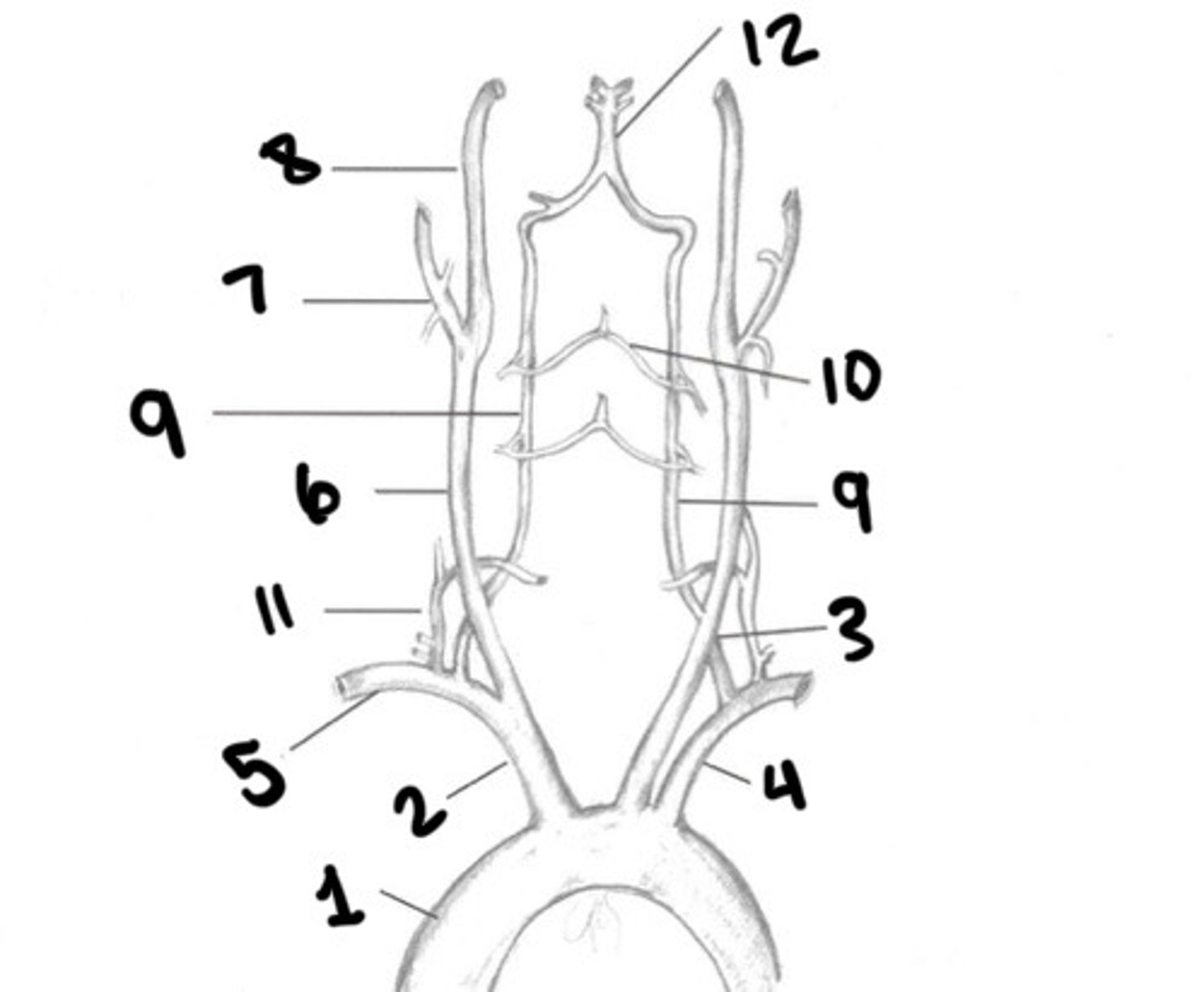
LT CCA
What is 3
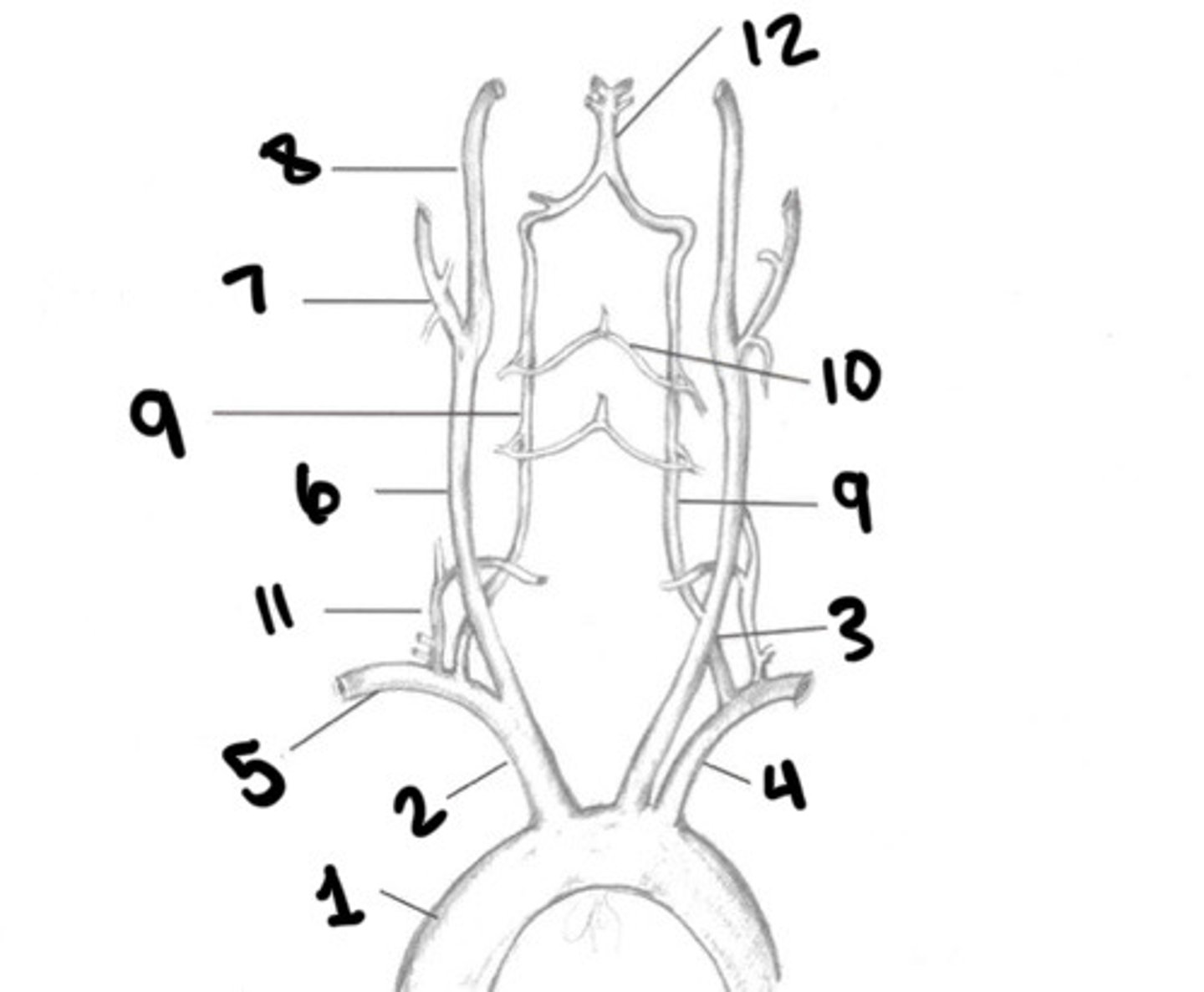
LT subclavian
What is 4
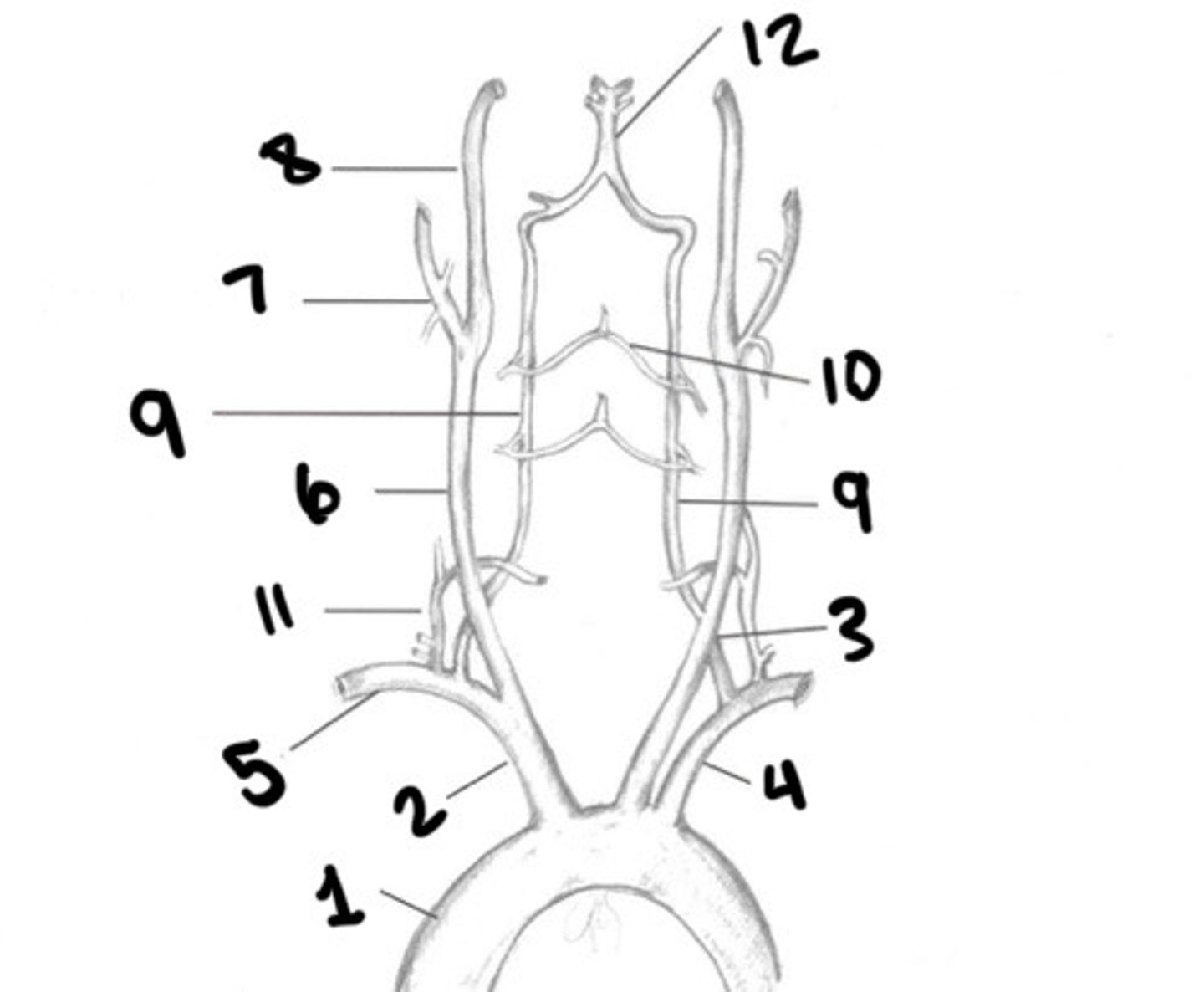
RT subclavian
What is 5
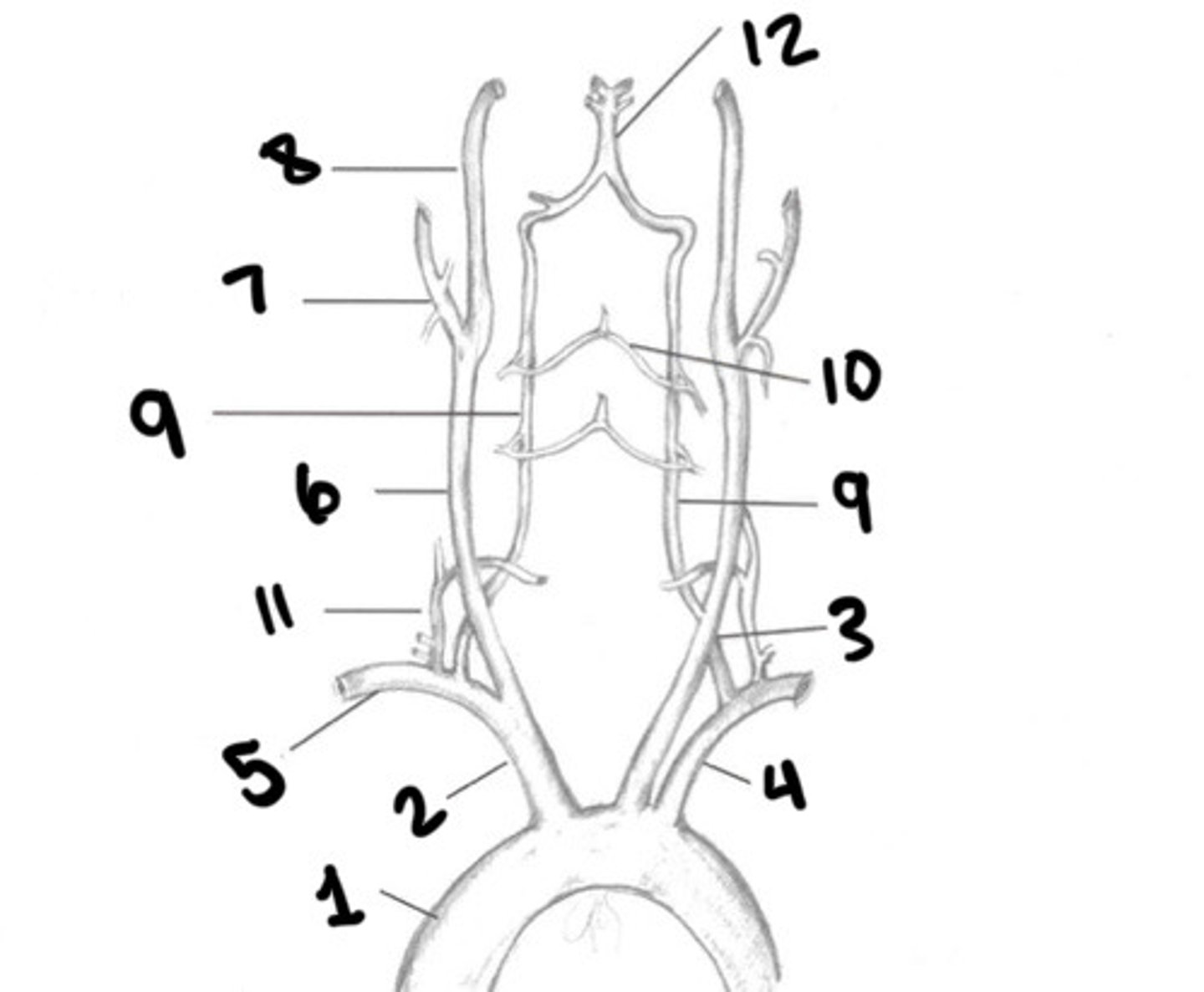
RT CCA
What is 6
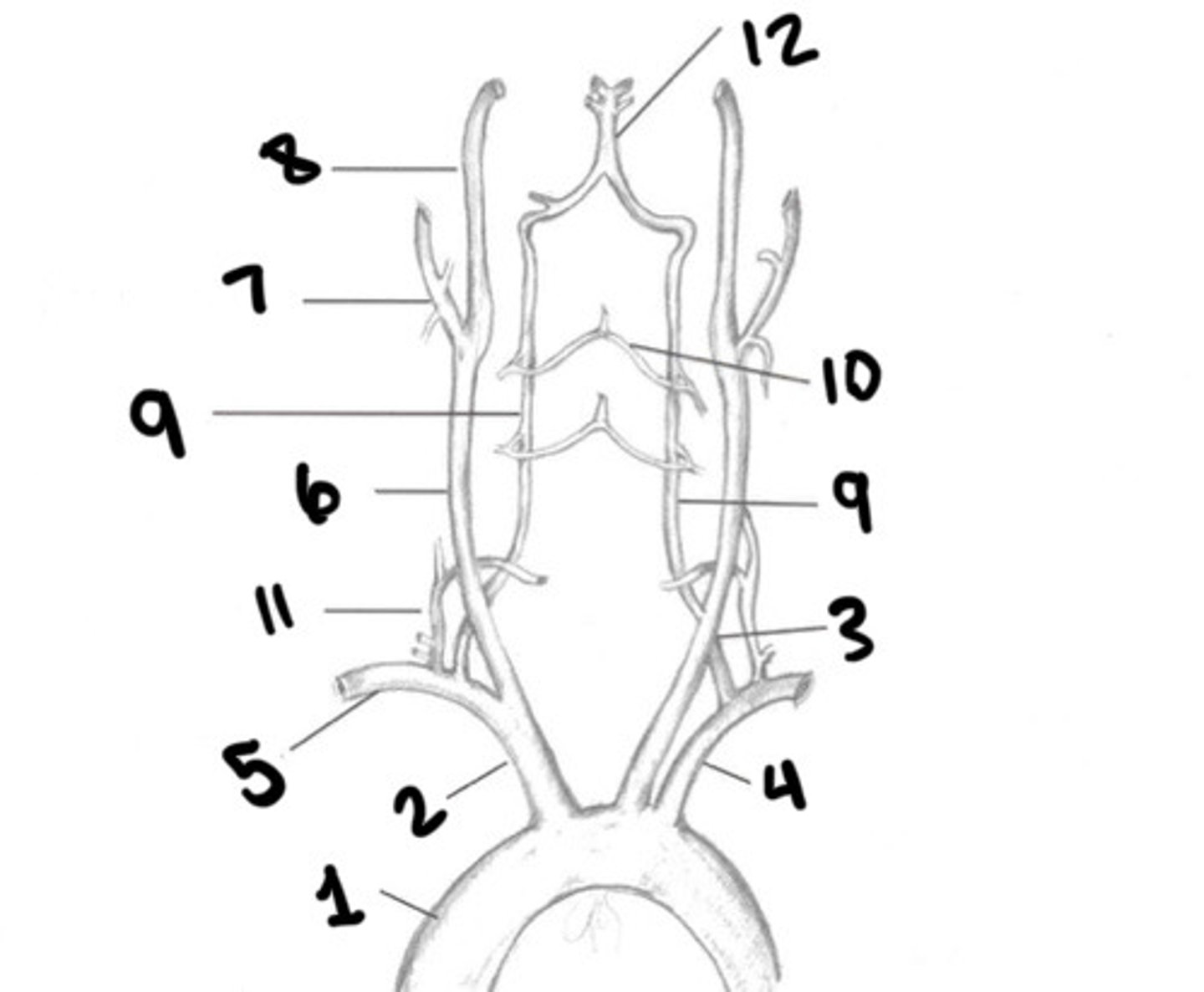
ECA
What is 7
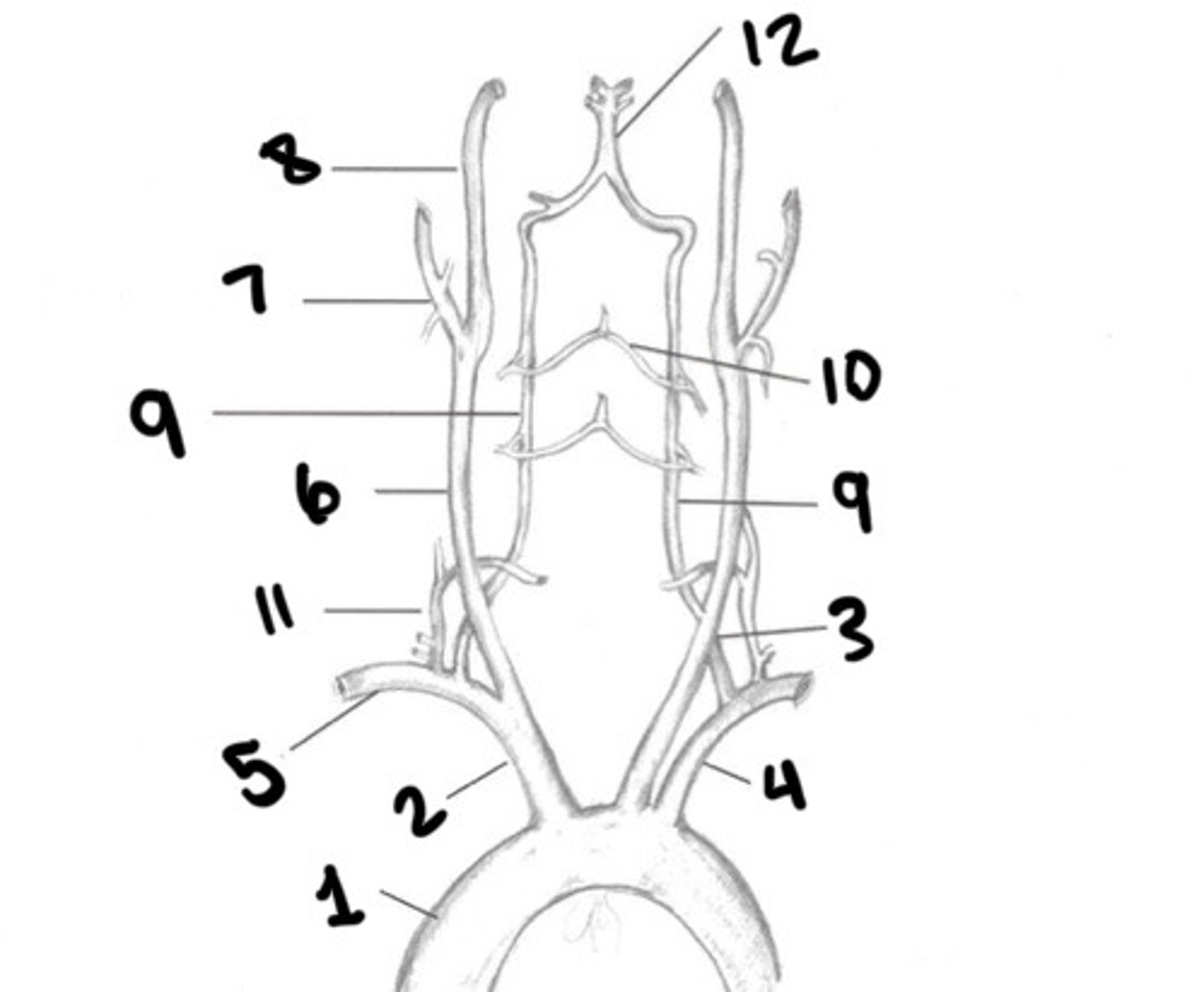
ICA
What is 8