All chapter terms
1/403
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
404 Terms
Environmental value system (EVS)
A worldview or paradigm that shapes the way an individual or group of people perceive and evaluate environmental issues. This will be influenced by the cultural, religious, economic and socio-political context.
Environmental movement
Originated in the 1960s when influential individuals, independent pressure groups, corporate businesses, governments, and intergovernmental bodies are taking action to consider and find solutions to global environmental and world development issues.
Bhopal disaster
On December 3rd, 1984, a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India released 40 tons of methyl isocyanate gas, killing 3000 people immediately and over 20 thousand more later. Worst industrial disaster.
Chernobyl
The worst nuclear disaster ever near Kiev, Ukraine in the year 1986. The nuclear power plant reactor exploded, causing a nuclear meltdown which caused a cloud of radioactive material to drift over Europe, causing radiation poisoning and cancer.
Fukushima Daiichi
In 2011, a nuclear power plant was damaged by a tsunami, causing radioactive material to leak into the water, causing 1 million people to evacuate.
Ecocentric worldview
An environmental philosophy that places ecology and nature as central to humanity,
Emphasizing a less materialistic approach to life.
Life-centered and respects the rights of nature due to a dependency on nature.
Followers are known as ecocentrists.
Deep ecologists
Term to describe extreme ecocentrists that follow the ecocentric worldview.
Puts more value on nature than humanity
Believes humans have no right to interfere with nature
Wants reduced human impact
Anthropocentric worldview
Environmental philosophy that believes humans must sustainably manage the global system.
Promotes the use of taxes, environmental regulation, and legislation
Human-centered
Believes nature exists to benefit humans
Followers are known as anthropocentrists
Technocentric worldview
Environmental philosophy which believes that technological developments will provide solutions to environmental problems.
Followers are known as technocentrists
Cornucopians
Term to describe extreme technocentrists that follow the technocentric worldview.
Believes world has infinite resources to benefit humanity
Technology can solve any problem
Growth provides all answers
Environmental managers
Term to describe another branch of technocentrists.
Believes Earth is garden and humans are caretakers (stewardship worldview)
Government needs to legislate to protect environment
Look after planet, then planet looks after us
Biocentric worldview
An environmental philosophy that is life-centered and believes all life has value.
Should prevent the extinction of species
Animal rights activists often follow this
Humans are not more important than any other species
System
A set of inter-related parts working together to make a complex whole
Can be big or small
Can be stable or unstable
Can be open, closed or isolated
Open system
A system that exchanges matter and energy with its surroundings
Movement of material through living organisms (predator-prey)
Movement of material in nonliving process (stream water)
Most ecosystems are open
Transfers
When energy or matter flows and changes location but does not change its state.
Transformations
Occur when energy or matter flows and changes its state.
Can either be a physical change or a chemical change
Light to heat
Matter to energy (fossil fuels)
Closed system
A system where energy is exchanged but not matter
Extreme uncommon
Earth is closed system (matter doesn’t escape but light energy transferred)
Isolated system
Neither matter nor energy is exchanged in that system
Benefits and disadvantages of models
Benefits
Easier to work with
Can predict outcomes
Helps see patterns
Weaknesses
Less accurate
Wrong model due to wrong assumption
Inaccurate predictions
First law of thermodynamics (Principle of conservation)
Energy in an isolated system can be transformed but cannot be created or destroyed.
Second law of thermodytnamics
The entropy of an isolated system not in equilibrium will increase over time.
More entropy means less order
Energy is always lost when transferred
Entropy
A measure of disorder of a system, referring to the spreading out of energy.
Efficiency
The useful energy or the work or output produced by a process divided by the amount of energy consumed being the input to the process
Efficiency = Work or energy produced / energy consumed
Feedback loop
When information that starts a reaction in turn may input more information which may start another reaction.
Positive feedback loop
A feedback loop where feedback causes a further increase or decrease in the output that changes the system
Moves the system towards a new equilibrium point.
Negative feedback loops
A stabilizing feedback loop occurs when the output of a process inhibits or reverses the operation of the same process in such a way to reduce change.
Static equilibrium
Type of equilibrium where there is no change over time
Pile of books does not move or change
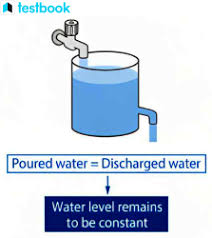
Steady-state equilibrium
A characteristic of open systems where there are continuous inputs and outputs of energy and matter, but the system as a whole remains in a more or less constant state.
Water tank stays at constant water level as rate of water goin in and out stays same.
Stable equilibrium
System tends to return to same equilibrium after a disturbance.
Unstable equilibrium
The system returns to a new equilibrium after a disturbance.
Ecosystem resilience
The tendency of an ecosystem to resist change
Factors that affect ecosystem resilience
More diverse and complex
Greater species diversity
Greater genetic diversity
Larger the ecosystem
Reproduction rate
Tipping point
When an ecosystem experiences a shift to a new state in which there are significant changes to its biodiversity and the services it provides (typically negative).
Involves positive feedback loops
Extinction is an example of a tipping point for a population
Sustainability
The use and management of resources that allow full natural replacement of the resources exploited and full recovery of the ecosystems affect by their extraction and use.
Sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Sustainability indicators
How people measure sustainability
GDP
Air quality
Environmental vulnerability
Water poverty
Tragedy of the commons
A concept where individuals exploit shared resources for personal gain, leading to depletion and harm to the common good.
Natural capital
Natural resources that can produce a sustainable natural income of goods or services
Forest
Environmental impact assessment
Report prepared before development project to change use of land.
Examines environmental impacts
used in large scale projects
Ecological footprint
Area of land and water required to sustainably provide all resources at the rate at which they are being consumed by a given population
Indicates unsustainability typically
Pollution
The addition of a substance or an agent to an environment by human activity at a rate greater than that at which it can be rendered harmless by the environment, and which has an appreciable effect on the organisms within it.
Primary pollutants
Pollutants that are active on emission
Ex: Carbon dioxide
Secondary pollutants
Pollutants that are formed by primary pollutants undergoing physical or chemical changes
Commonly triggered by water or sunlight
Ex: Sulphuric acid
Major sources of pollutants
Source | Pollutant | Effect |
|---|---|---|
Combustion of fossil fuels | Carbon dioxide, Sulphur dioxide, photochemical smog | Global warming, acid deposition, respiratory infections |
Industrial waste | Heavy metals, heat, lead, acid | Poisoning, disabilities |
Agricultural waste | Nitrates, organic waste, pesticides | Bioaccumulation, eutrophication, disease |
Point source pollution
Release of pollutants from a single, clearly identifiable site
Ex: Factory
Non point source pollution
Release of pollutants from numerous widely, dispersed origins
Impossible to tell where coming from
Ex: Air pollution from cars
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
Pesticides that are resistant to breaking down and remain active in the environment.
Extremely harmful to the environment
Ex: Polyvinyl chloride
Biodegradable pollutants
Pollutants that do not persist in the environment and break down quickly due to physical processes or decomposers
Ex: Soap, starch, glyphosate
Acute pollution
When a large amount of pollutant is released causing lots of harm
Chronic pollution
The long-term release of a pollutant in small amounts
Goes unnoticed typically
Widespread
Harmful over time
Ex: Air pollution
Pollution management strategy
Changing human activity
Regulating pollutant release
Cleaning and restoring damaged ecosystems
Species
A group of organisms sharing common characteristics that interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Population
A group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time which are capable of interbreeding.
Population density
Average number of individuals in a stated area
Habitat
The environment in which a species normally lives in.
Niche
The specific role or function of an organism or species within an ecosystem, including its habitat, behavior, and interactions with other organisms.
No 2 species can have the same niche or not enough resources
Abiotic factors
Non living, physical factors that influence the organisms and ecosystems
Ex: Temperature, sunlight, rock
Biotic factors
The living components of an ecosystem, their interactions or their waste that directly or indirectly affect another organism.
Ex: Animals, plants, bacteria
Fundamental niche
The full range of conditions and resources in which a species could survive or reproduce.
Realized niche
The actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interaction
Limiting factors
Factors which slow down the growth of apopulation as it reaches its carrying capacity.
Typically things like space or food
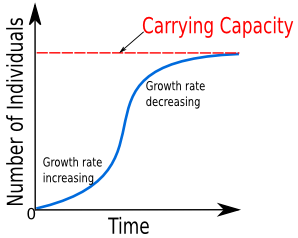
Carrying capacity
The maximum number of species that can be sustainably supported by a given area.
Population dynamics
The study of the factors that cause changes to population size
Competition, predation, herbivory, parasitism, mutualism, disease
Competition
The impact organisms have on each other due to the limited supply of a specific resource.
Intraspecific competition
Competition that occurs between members of the same species
Typically occurs with large population sizes in a limited area
Helps stabilize population sizes
Interspecific competition
Individuals of different species that are competing for the same resource.
Competitive exclusion
When one species entirely outcompetes another species for a specific resource.
Ex: Weeds in garden
Predation
Interaction where one organism hunts and consumes another for food, influencing population dynamics and shaping ecosystems.
Herbivory
An herbivore eating a green plant
Parasitism
A relationship between 2 species where one species lives in or on another (host) gaining food from it.
Mutualism
A relationship between 2 species where both species benefit.
Ex: Lichen with the fungus and algae
Commensalism
A relationship where one species benefits while the other doesn’t experience any good or bad impacts.
S-curves
A population pattern that starts with exponential growth and then plateaus due to carrying capacity.
Seen with bacteria
J-curves
A population pattern that sees rapid exponential growth at first and then a period of collapses (diebacks) and increases in population (overshoot) which go over and under the carrying capacity.
Seen with fish and mammals
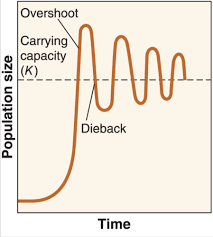
Community
A group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat
Ecosystem
A community and the physical environment it interacts with.
3 key ecological concepts
Photosynthesis, respiration and productivity
Respiration
The conversion of organic matter into carbon dioxide and water in all living organisms releasing energy.
Used in living processes
Aerobic respiration
Flashcard: Process that uses oxygen to break down glucose into energy, producing carbon dioxide, water, and ATP as byproducts.
Photosynthesis
The process by which green plants make their own food from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight.
Chemical formula: Carbon dioxide + water + light energy → glucose + oxygen
Creates biomass
Compensation point
The period where the net biomass being created by a plant is at equilibrium. Occurs near night typically due to low light.
Food chain
The flow of energy from one organism to the next.
Shows feeding relationships between species in ecosystem
Trophic level
The position that an organism occupies in a food chain, or a group of organisms in a community that occupy the same position in food chains.
Producers (autotrophs)
Green plants that make their food from carbon dioxide.
Bottom of the food chain typically
Consumers (heterotrophs)
Organisms that feed on autotrophs or other heterotrophs to obtain energy as they can’t produce it.
Hierarchy of feeding
Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers
Food webs
A complex network of int errelated food chains
Omnivore
Organisms that eat plants and animals
Ecological pyramid
Model of a pyramid food chain using numbers, biomass, and productivity at each level.
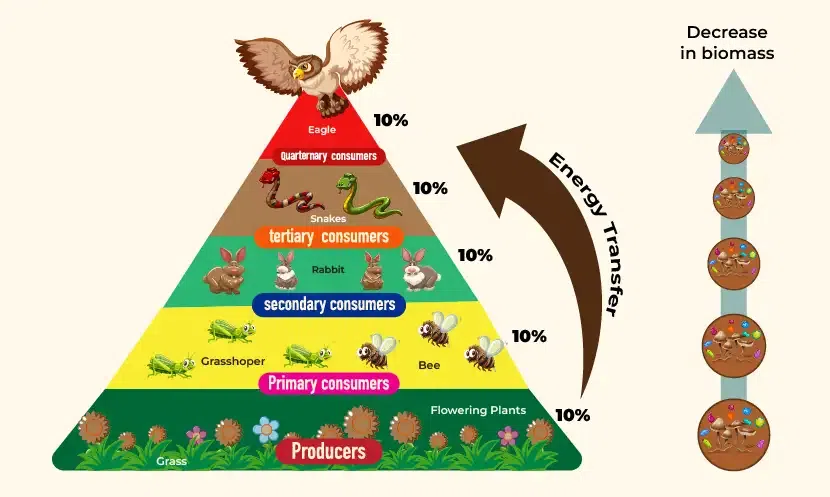
Pyramid of numbers
Pyramid that shows the number of organisms at each trophic level at one time (standing crop)
Pyramid of biomass
The total biomass of all organisms at each trophic level
Pyramid of productivity
The rate of flow of energy or biomass through each trophic level
The amount of energy or biomass being generated as food to the next trophic level
Pyramid for healthy ecosystem should always look like a nice pyramid shape
Bioaccumulation
The accumulation of chemicals inside an organism over time
Biomagnification
The increase in concentration of a substance, e.g a pesticide, in the tissues of organisms at successively higher levels in a food chain.
This occurs because organisms at higher trophic levels eat animals with small amounts of toxins and it build up over time
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)
Insecticide that was banned which significantly impacted animals on the top of the food chain due to bio accumulation
Ex: Peregrine falcon eggs thinning
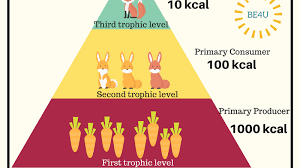
Trophic efficiency
Only 10% of the energy in 1 trophic level is transferred into the next trophic level.
Solar constant
The amount of solar energy reaching the top of the atmosphere of Earth being 1400 watts per second.
Productivity
The conversion of energy into biomass over a given period of time.
Rate of growth of biomass in plants and animals
measured in unit area per unit time
Primary
Dealing with plants
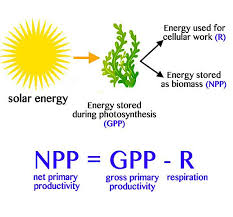
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
The total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by green plants.
Energy converted from light to chemical energy
Doesn’t consider anything loss
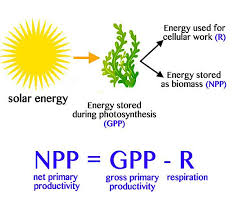
Net primary productivity (NPP)
Total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by green plants after allowing for losses to respiration
Increase in biomass of plant
Calculated with NPP = GPP-R
R = respiration