photosynthesis ao1
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
why are plant leaves green?
photosynthetic pigments (e.g. chlorophyll) are found on the thylakoid membrane. Chlorophyll absorbs most wavelengths of light, but reflects green light
photosynthetic pigments
chlorophyll a
chlorophyll b
carotenes
xanthophylls
what is chromatography?
separation technique used to separate pigments in plant leaves
Rf values
show how far a pigment has travelled compared to the solvent front.
formular for Rf values
Rf = distance moved by pigment/ distance moved by solvent front
what is an absorption spectrum?
a graph showing how much light of different wavelengths is absorbed by a pigment
(chlorophyll absorb light strongly in blue and red regions, carotenes and xanthophylls absorb in the blue - green region)
what is an action spectrum?
a graph showing the rate of photosynthesis at different wavelengths of light (action spectrum is closely aligned with absorption spectrum of chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids - suggests main pigments involved in photosynthesis)
what is a photosystem?
an arrangement of photosynthetic pigments within the thylakoid membrane. There are 2 categories - primary pigments = 2 forms of chlorophyll a. form reaction centres
antennae pigments = chlorophyll a and b , carotenes and xanthophylls. Form an antennae complex
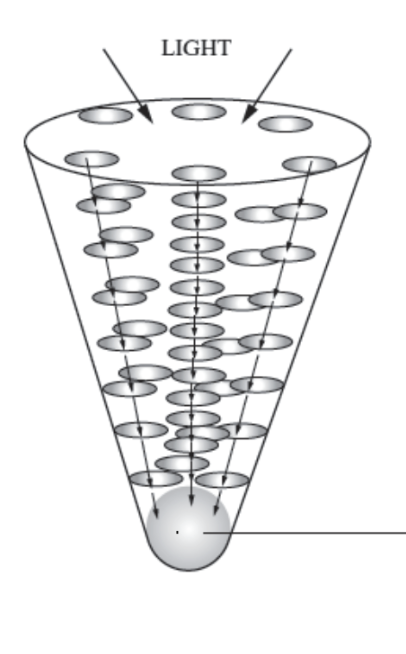
photosystem structure
antennae pigments arranged in a antenna complex
reaction centre contains a primary pigment (molecule of chlorophyll a)
light harvesting by photosystems
when light energy is absorbed by a photosystem, the antenna pigment molecules pass photons of light to the primary pigment in the reaction centre.
primary pigment = molecule of chlorophyll a which contains pair of electrons
light energy is used to excite pairs of electrons which are emited from the electron centre
what are the 2 types of photosystem
PSI - arranged around a molecule of chlorophyll a, absorbs light at a wavelngth of 700nm. Reaction centre = P700
PSII - arranged around a molecule of chlorophyll a, absorbs light at a wavelngth of 680nm. Reaction centre = P680
what are the 2 types of photosynthesis reactions?
light dependent
non-cyclic photophosphorylation
cyclic photophosphorylation
light independent
light dependent reactions
transduce solar energy to electrical energy and then chemical energy - end products are NADPH2 and ATP
light independent reactions
reduce carbon dioxide to make glucose. the ATP generated by the light dependent reactions provides the energy, and the NADPH2 provides the hydrogen
law of limiting factors
states that at any given moment, the rate of a physiological process will be limited by the factor which is in the shortest supply
name 3 limiting factors
temperature
light intensity
CO2 concentration (usually the natural limiting factor)
nitrogen supply as a limiting factor
needed to sythesise proteins, nucleic acids and chlorophyll. Usually transported as nitrates in the xylem and aas in the phloem. A lack of N results in stunted growth, chlorosis (yellowing leaves)
magnesium supply as a limiting factor
transported as Mg2+ in the xylem. Required for chlorophyll manufacture, and a deficiency leads to chlorosis, inability to photosynthesis and death. Mg is required for activation of ATPase