Special Senses Review - Vision/Eye
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the general pathway for light as it enters through each part of the eye?
Light, cornea, aqueous humor, pupil, lens, vitreous humor, retina, optic nerve.
What is the fovea centralis?
This is in the back of your retina that contains only cones and allows for the sharpest image.
What is the optic disc?
It’s the blindspot where the origin of the optic nerve is.
What is the job of the lens?
It refracts incoming light and flips the image upside down and backwards (brain interprets it to correct it).
What happens after light passes through the retina to turn it into a visual nerve impulse?
After reaching the retina, light will pass through the neutral layer to the R.P.E (Retinal Pigment Epithelium)
What happens when light passes through the R.P.E?
The RPE experiences a molecular change when light hits that which then initiates a nerve impulse.
FROM THERE, the nerve impulse will enter rods and cones. THEN, it will send nerve impulses to bipolar cells and then to ganglion cells which will send the signal to the occipital lobe of the brain.
What are bipolar cells?
These are cells in the retina that transmit signals from photoreceptors (rods and cones) to ganglion cells.
What are ganglion cells?
These are axons that merge into the optic nerve FROM BIPOLAR CELLS. They then carry visual information from the retina to the brain.
What are rods? (are they sensitive, distributed in the retina, what kind of light do they detect)
These are photoreceptors that are sensitive, distributed ALL OVER the retina, and pick up shades of light, not color!
What are cones? (are they sensitive, distributed in the retina, what kind of light do they detect)
They are concentrated in the CENTER of the retina, are not sensitive, and pick up colors (red green blue).
What is myopia?
This is a vision condition where close objects appear clearly, but distant ones do not, often caused by an elongation of the eyeball.
What is hyperopia?
This is when the eyeball is too short and the retina is located too far from the lens, causing distant objects to be clearer than close ones.
What are the internal structures of the eye?
Cornea
Lens
Ciliary Muscles
Optic Nerve
What is the function of the ciliary muscles?
These are the ligaments that bend and flatten the LENS. (They control the lens)
What is the function of the lens?
This is a semi-solid disc that bends/refracts light to hit the retina. (cataracts are hardened lens)
What are the internal fluids of the eye?
Aqueous Humor & Vitreous Humor
What are the internal layers of the eye?
Sclera, Choroid, and Retina.
What is the function of the aqueous humor?
It’s a “watery” fluid in front of the lens that nourishes the cornea.
What is the function of the vitreous humor?
It is jelly-like and is within the eye (in front of the retina) that bends and refracts light.
What is the function of the sclera?
It’s the “white” of the eye that contains fibrous connective tissue to protect and maintain the eye’s shape.
What is the function of the choroid? What does this include?
It’s a pigmented and vascular (blood vessels) membrane that helps to nourish the retina and absorb excess light.
This includes the iris and the pupil.
What are the two retina layers? Define them both!
Pigmented Retina - Has photoreceptors that convert light into nerve impulses.
Neutral Retina - It carries the nerve impulses to the optic nerve.
Where are tears made?
They are made in the lacrimal glands.
What do tears contain?
Mucus, antibodies, lysozymes,
What is the process of tears flowing?
They are first made in the lacrimal glands, then flow through the ducts of the canaliculi, to the lacrimal sac, nasolacrimal duct, and finally into your nose.
What is the conjunctiva?
This is the thin membrane that covers the eye and the lid which secretes mucus for lubrication (this is why we blink).
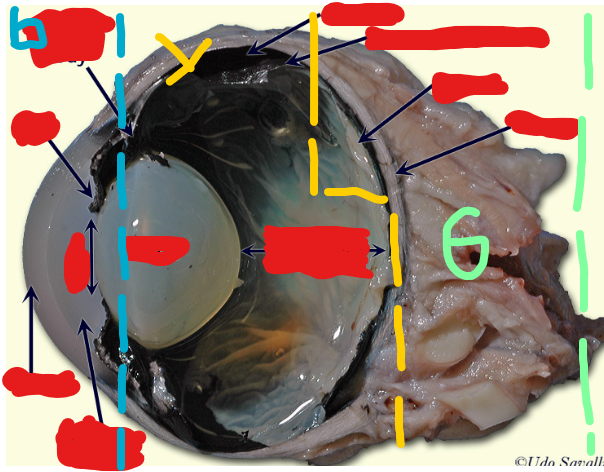
Label the following from TOP TO BOTTOM. Start with the BLUE section first (leftmost), then the yellow section do this left to right (middle), then the green section (rightmost).
Ciliary Body, Iris, Pupil, Cornea, Aqueous Humor. (Blue Section)
Lens (left), Vitreous Humor (right). (Yellow Section)
Choroid, Tapetum Lucidum, Retina, Sclera. (Green Section)
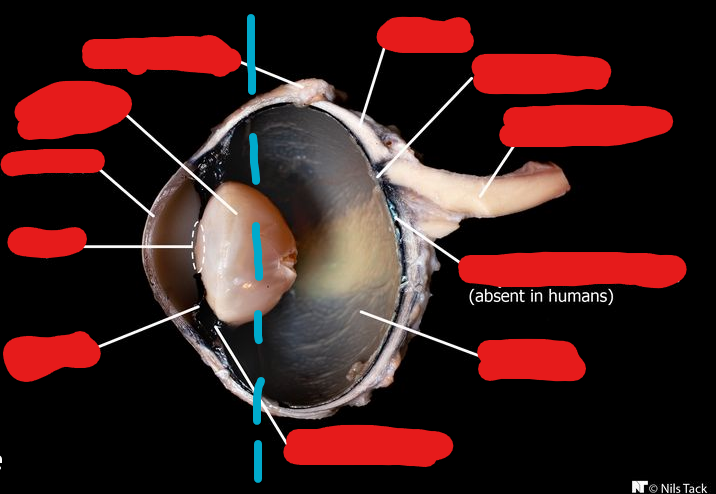
Label the following images from TOP TO BOTTOM. Start on the left side (left of the blue stripes), then do the right side.
Conjunctiva, Lens, Cornea, Pupil, Iris. (leftmost side)
Sclera, Optic Disc, Optic Nerve, Tapetum Lucidum (not visible in humans), Retina, Ciliary Body. (rightmost side)