Abdomen anatomy and pathology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
abdominal pelvic cavity contains what cavities
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
the abdominal cavity is the _____,______ portion
large, superior
the pelvic cavity is the ____,_____ portion
smaller, inferior
where does the abdominal cavity extend
from the diaphragm to superior aspect of bony pelvis
the abdominal cavity consists of
stomach
small and large intestines
liver
gallbladder
spleen
pancreas
kidneys
the pelvic cavity lies within
margins of bony pelvis
the pelvic cavity contains
rectum and sigmoid regions of colon
urinary bladder
reproductive organs
Pelvic cavity boney positioning points
iliac crest
ASIS
pubic symphysis
what does the abdominal peritoneum enclose
the abdominopelvic cavity
the double walled membrane consists of:
parietal peritoneum
visceral peritoneum
the parietal peritoneum is the
outer portion
lines cavity
the visceral peritoneum is the
inner portion
surrounds organs
peritoneal cavity is
in-between; contains fluid
retroperitoneum is the
cavity behind the peritoneum
the retroperitoneum includes:
kidneys
pancreas
where does the right kidney lie compared to the left kidney
lower
how does the right flexure of the colon lie compared to the left flexure
lower
what is volvulus
twisting of bowel on itself
what are the technical factors for volvulus
typically subtractive
may have to decrease technique due to abundance of air
if known opaque obstruction, then increase technique
what is pneumoperitoneum
free air in the peritoneal cavity
what is the technical factors for pneumoperitoneum
subtractive
decrease technique due to additional air
what is ascites
accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity
what is the technical factor for ascites
additive
may have to increase technique
what is a bowel obstruction
partial or full blockage of large or small bowel that does not allow substances to pass through
what is the technical factor for a bowel obstruction
depending on blockage, may need to increase/decrease technical factors
what is pica
psychological disorder of intentional and craving consumption of non-nutritive substances over a period of time
what is the technical factor for pica
depending on blockage, may need to increase technical factors
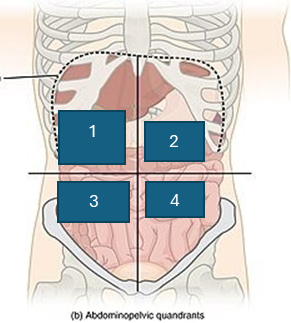
what is quadrant 1
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
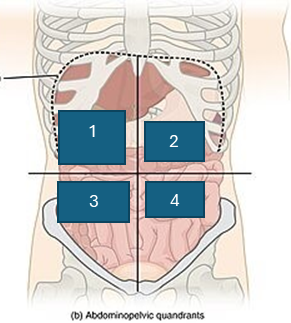
what is quadrant 2
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
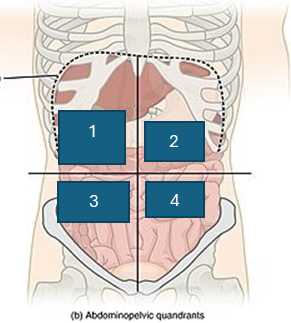
what is quadrant 3
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
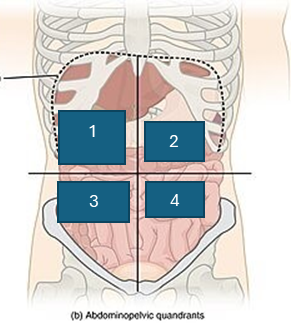
what is quadrant 4
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
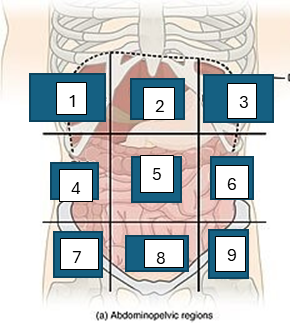
what is region 1
right hypochondriac region
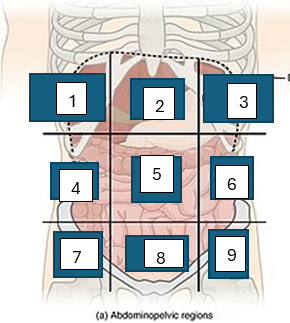
what is region 2
epigastric region
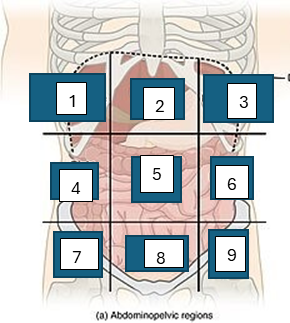
what is region 3
left hypogastric region
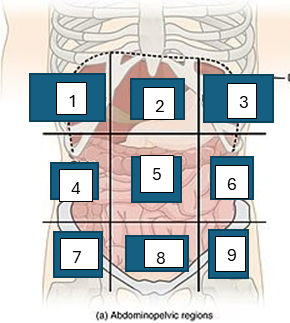
what is region 4
right lumbar region
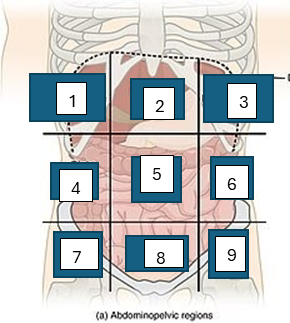
what is region 5
umbilical region
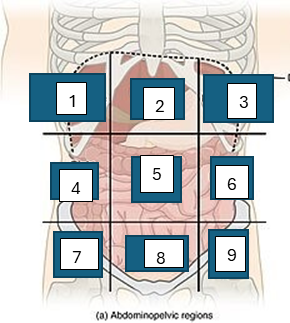
what is region 6
left lumbar region
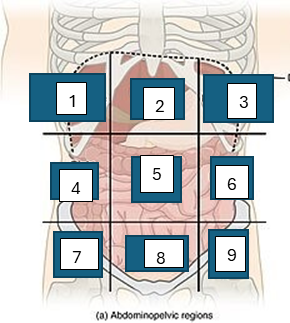
what is region 7
right iliac region
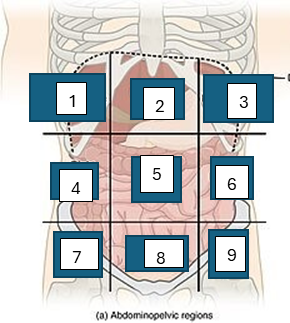
what is region 8
hypogastric region
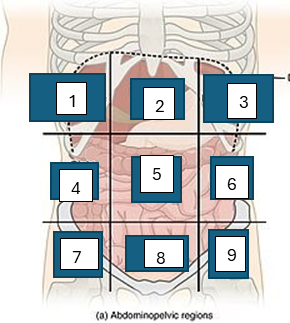
what is region 9
left iliac region
AP supine for GI concerns OR part of abdomen routine
entire bowel pattern must be visualized if performed as part of an obstruction series or if KUB for bowel related concern such as obstruction, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
AP supine for urinary tract
if kidneys, ureter and bladder are of primary concern that is all that needs to be included
criteria for AP supine
area from public symph to the upper abdomen
two images may be necessary
criteria for AP erect
Entire diaphragm without motion must be visualized (there should ne minimal amount of lung visualized)
verterbral column should be in the center of the image
ribs, pelvis, and hips should be equidistant to the edges of the image on both sides
AP ERECT needs to be annotated on the image
left lateral decubitus
diaphragm must be included without motion
the right side should demonstrate free air if present
abdominal wall, flank structures and the diaphragm should be visualized
DECUBITUS annotation on the image
RH note for a left lateral decubitus
only right side of the diaphragm is needed on left lateral decubitus view
criteria for transabdominal/ dorsal decubitus
highest point of abdomen must be visualized without motion (RH)
no rotation
superimposed ilia
superimposed lumbar vertegraw pedicles and open intervertebral foramina
TRANS. ABD annotated on the image
what is merrils’s criteria for a TRANS ABD
must have the whole diaphragm
Pediatric abdomen light field
top of symph
to right about the nipple line
if the patient is <5 ft how many inches from the jugular notch is symph found
21 inches
if the patient is 5-6 ft how many inches from the jugular notch is symph found
22 inches
if the patient is 6 ft how many inches from the jugular notch is symph found
24 inches
additional positioning aides
greater trochanter is at level of pubic symphysis
what breathing is used on all abdomen views
expiration
psoas muscles
long shape muscle of the lower back, upper lumbar region all the way down through the pelvis and into the top of the femur, where the kidneys are located