Exam 1 Anatomy
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
Anatomy
The branch of science concerned with the structure and organization of body parts and their relationships.
Physiology
The branch of science dealing with the function of body parts and the body's overall functioning.
Levels of structural organization
Hierarchy from chemical level to chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism; shows how parts fit together. (Atoms-molecules-cells-tissues-organs-organ system-organism)
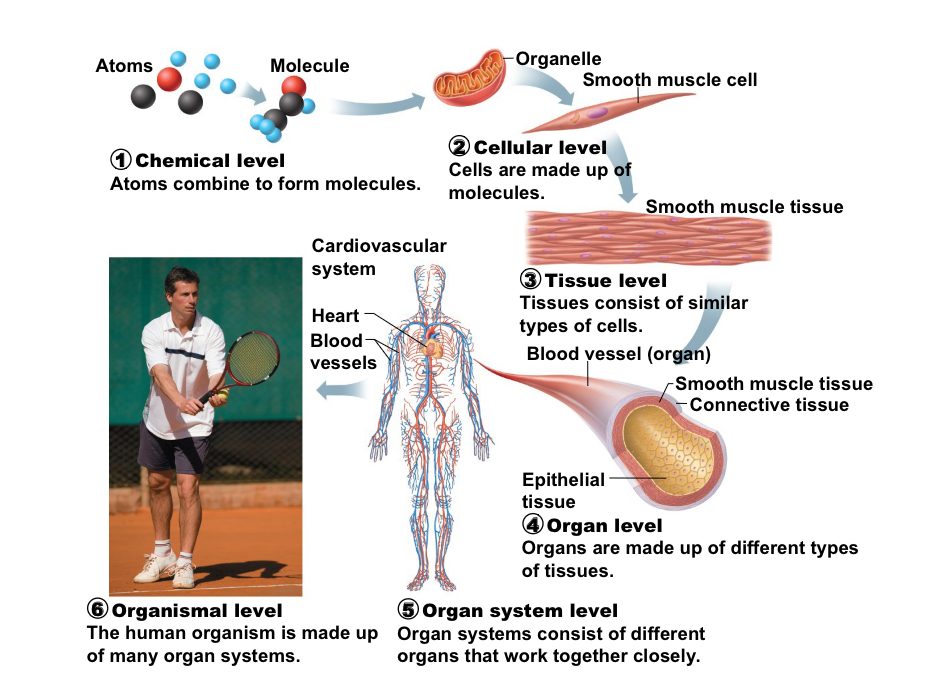
Principle of Complementarity
The function of a system is dependent upon the form of the structure that composes that system
What are the 11 body systems ? (MINESRRCDLU)
Muscular, Integumentary, Nervous, Endocrine, Skeletal, Respiratory, Reproductive, Cardiovascular, Digestive, Lymphatic, Urinary

Integumentary
hair,skin, nails; houses pain and pressure receptors
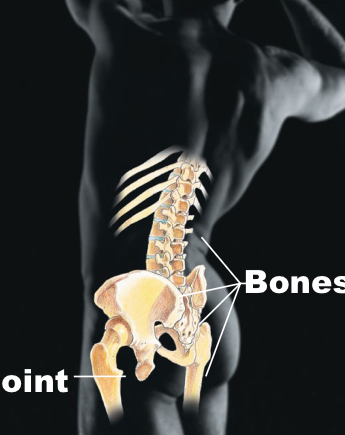
Skeletal
Bones, joints; framework and supports body organs
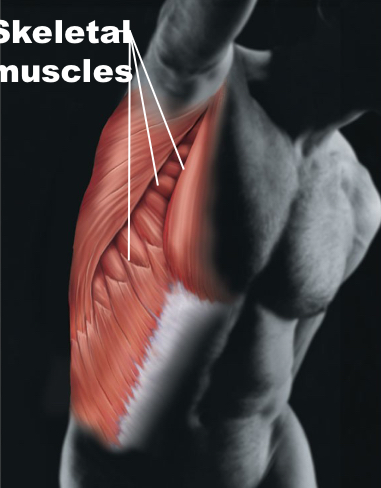
Muscular
Muscles; locomotion, maintains posture and produces heat
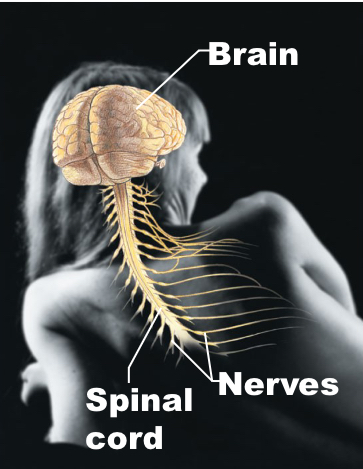
Nervous
Brain, spinal cord, nerves; body’s control system, activated muscles and glands
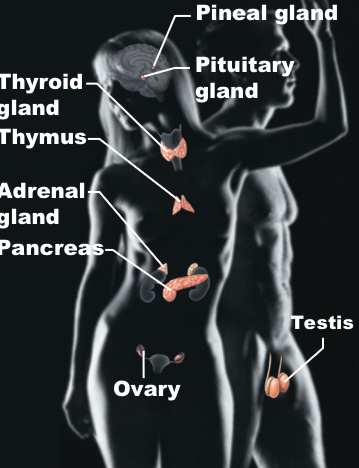
Endocrine
Pineal, pituitary,adrenal and thyroid glands, thymus, ovary, testes; secrete hormones for growth, reproduction, and metabolism
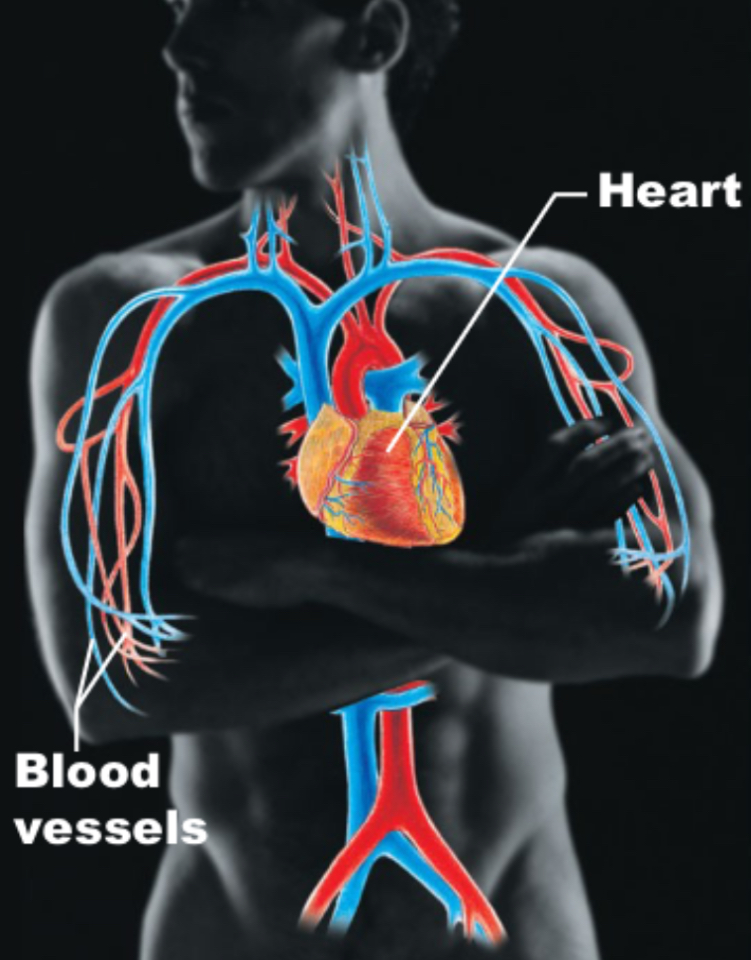
Cardiovascular
Heart, blood vessels; transport blood via blood vessels, carries O2, CO2, and waste
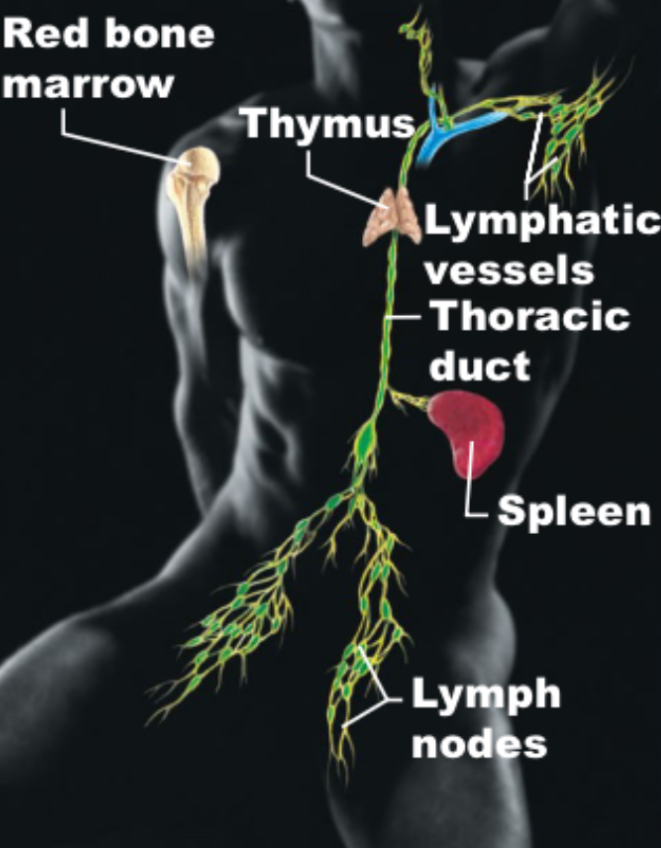
Lymphatic
Red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, lymph nodes; returns excess fluid from blood vessels to blood, houses lymphocytes, immune response
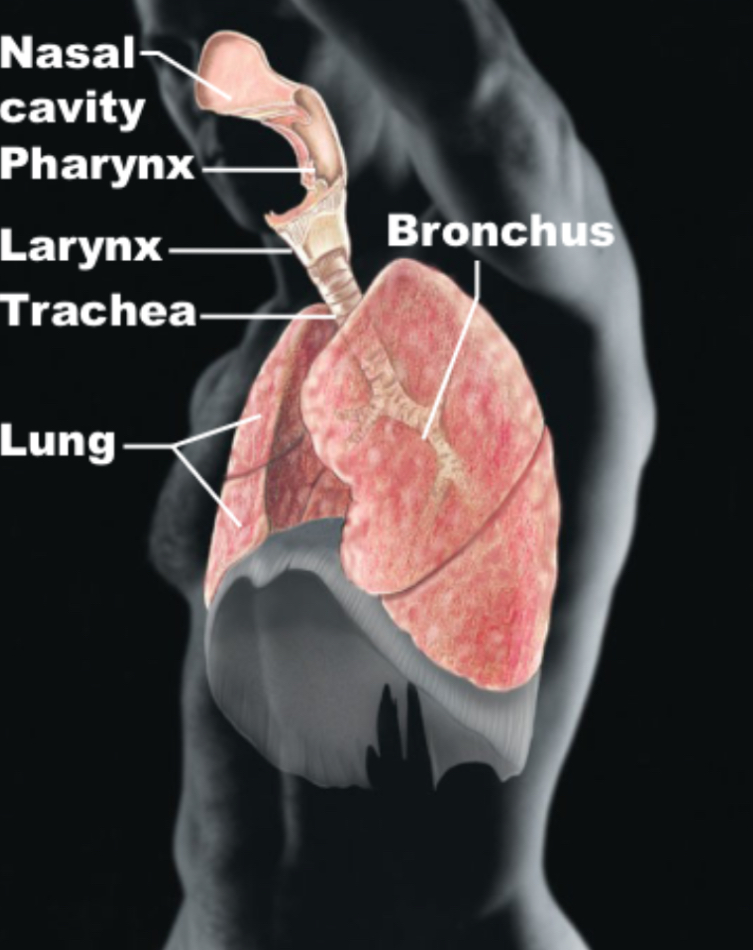
Respiratory
Lungs, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus; supports blood with O2, exchanges gas
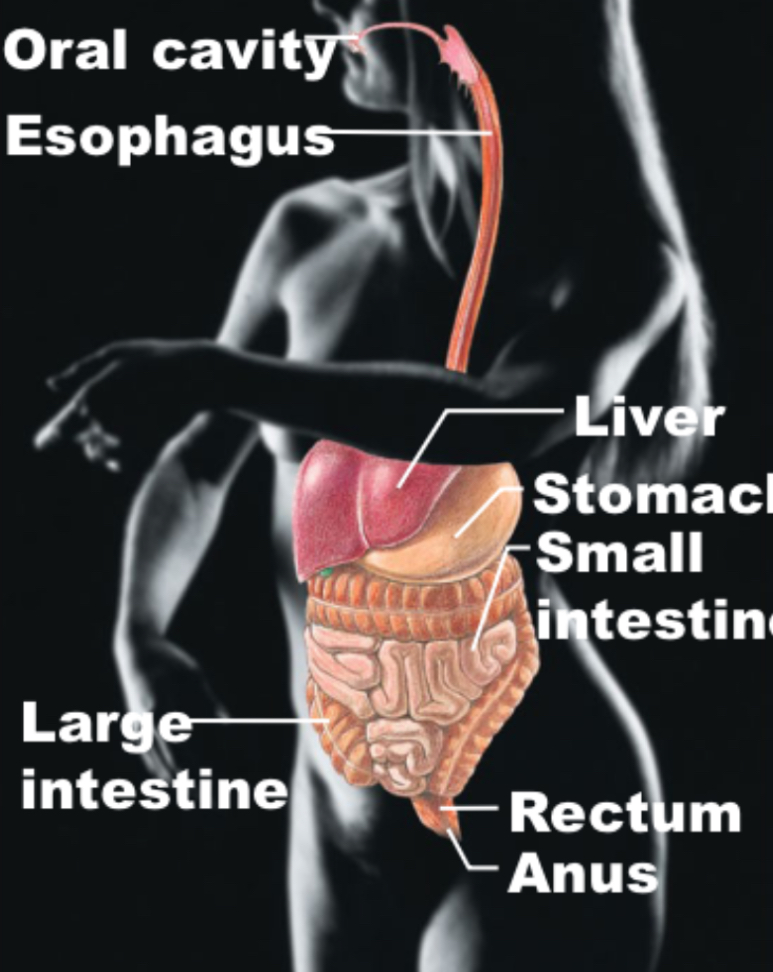
Digestive
Oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, small and large intestine, rectum, anus; break down and expel food
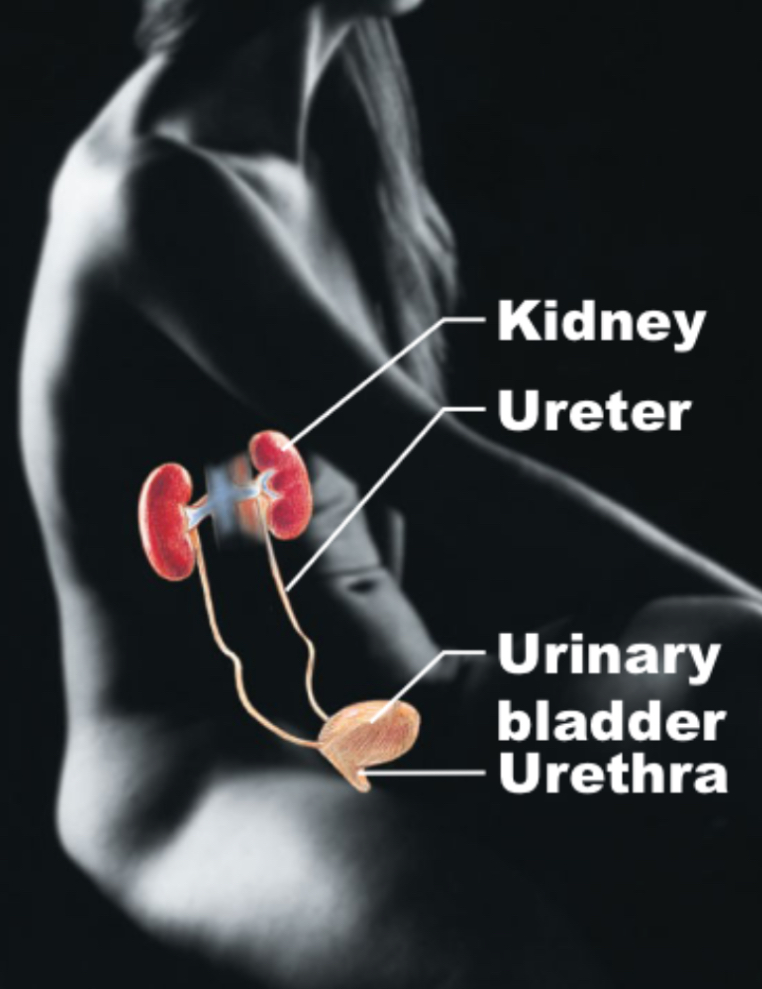
Urinary
Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra; regulate H2O, electrolytes, filter through kidneys
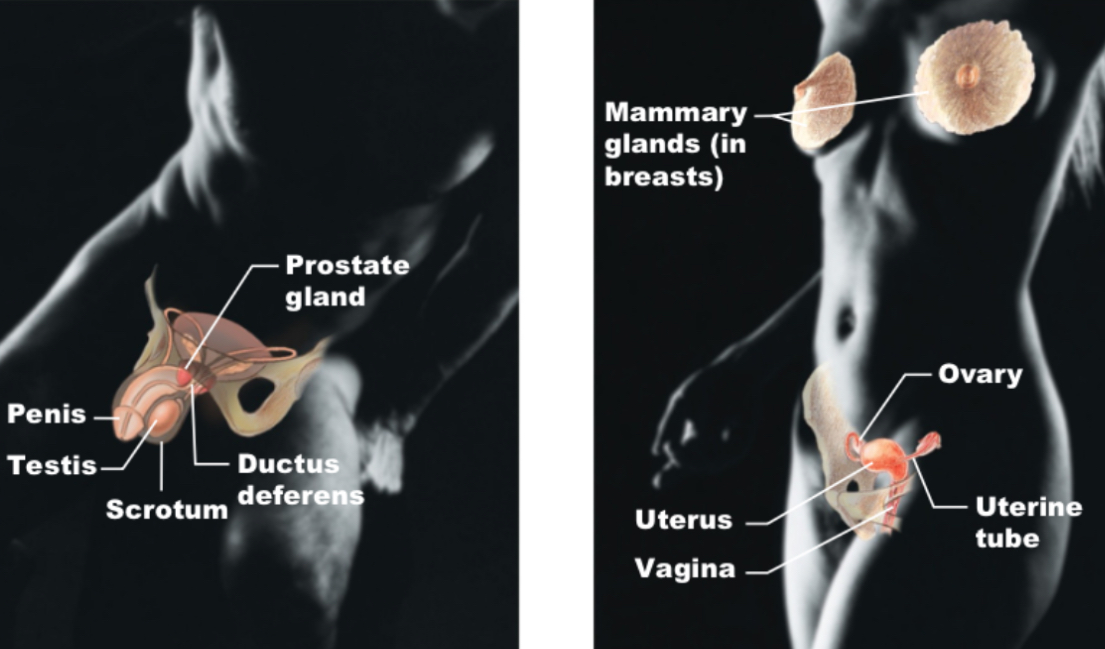
Reproductive
Prostate, penis, tested, scrotum, ductus deferens, mammary gland, ovary, uterus, uterine tube, vagina; produce sperm and egg
Anatomical position
Body erect, feet apart, palms forwards
Superior
Cephalad, cranial, caudel; towards the head
Inferior
caudal, toward the tail
Anterior
ventral, front of body
Posterior
dorsal, back of body
Superficial
external, on surface of body
Deep
internal, toward organs
Proximal
close to point of attachment
Distal
away from point of attachment
Medial
toward midline
Lateral
away from midline, to side
Cranial Cavity
Contains the brain
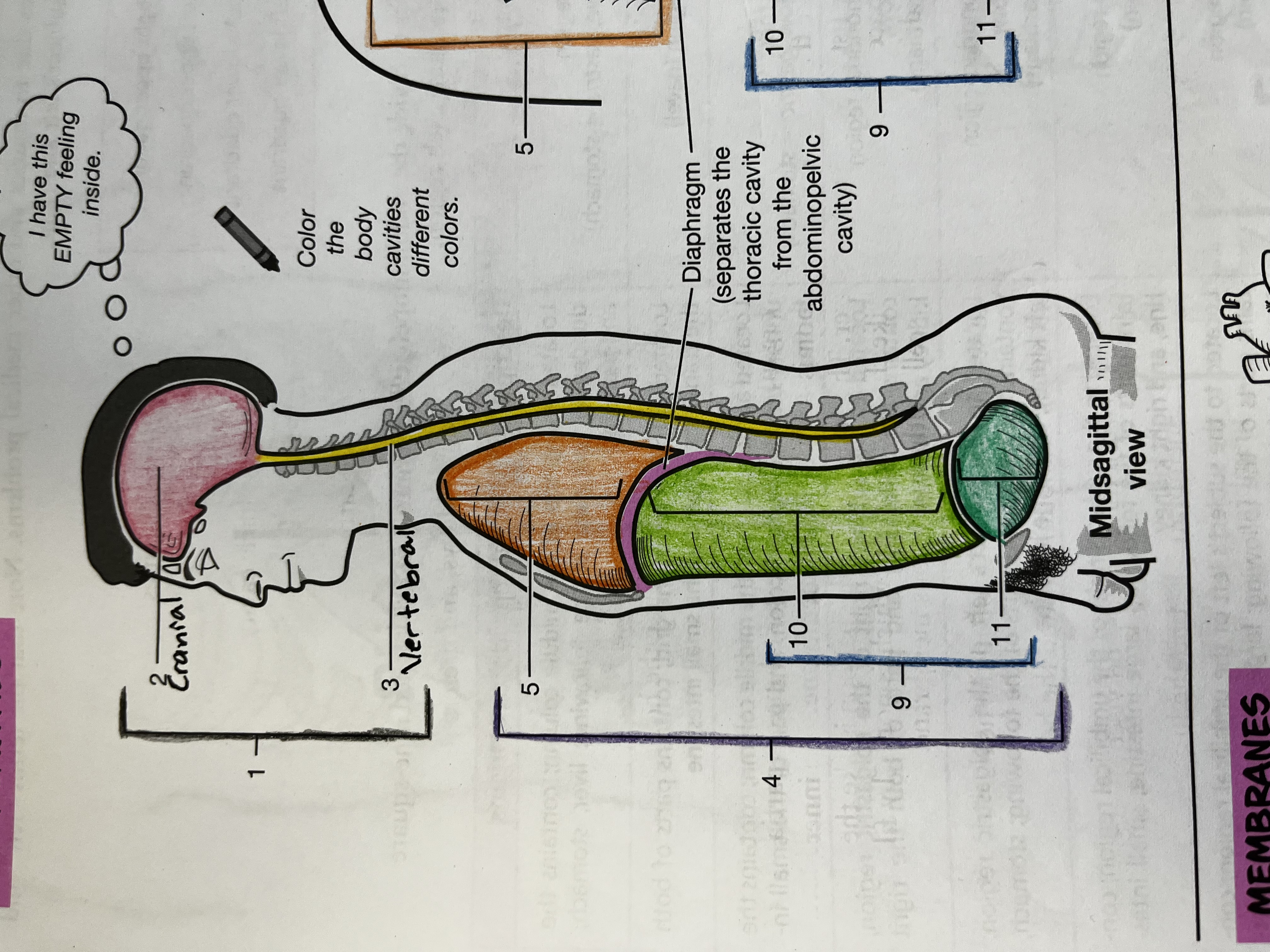
Vertebral Cavity
Contains the spinal cord
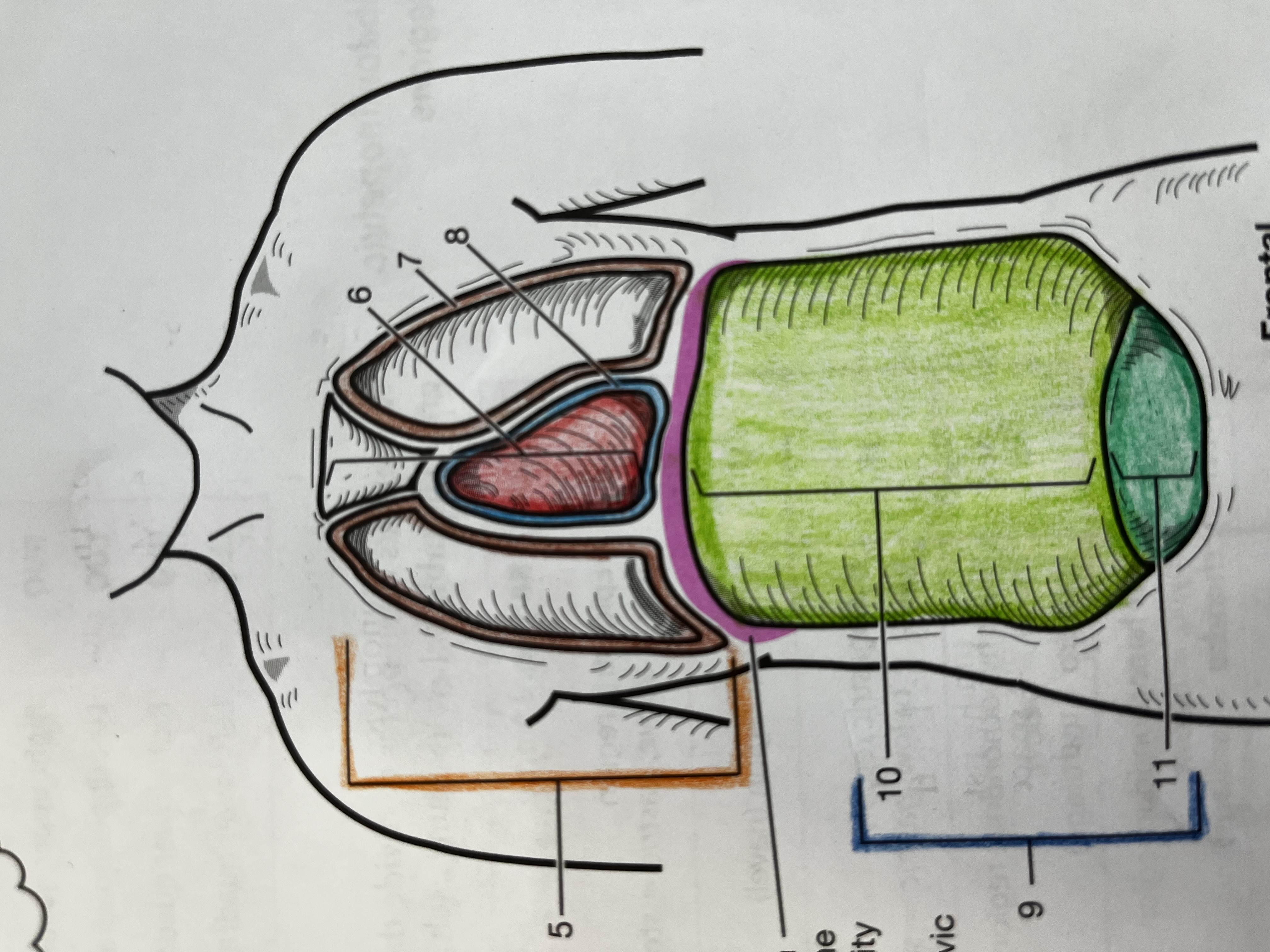
Thoracic cavity
contains the heart and lungs
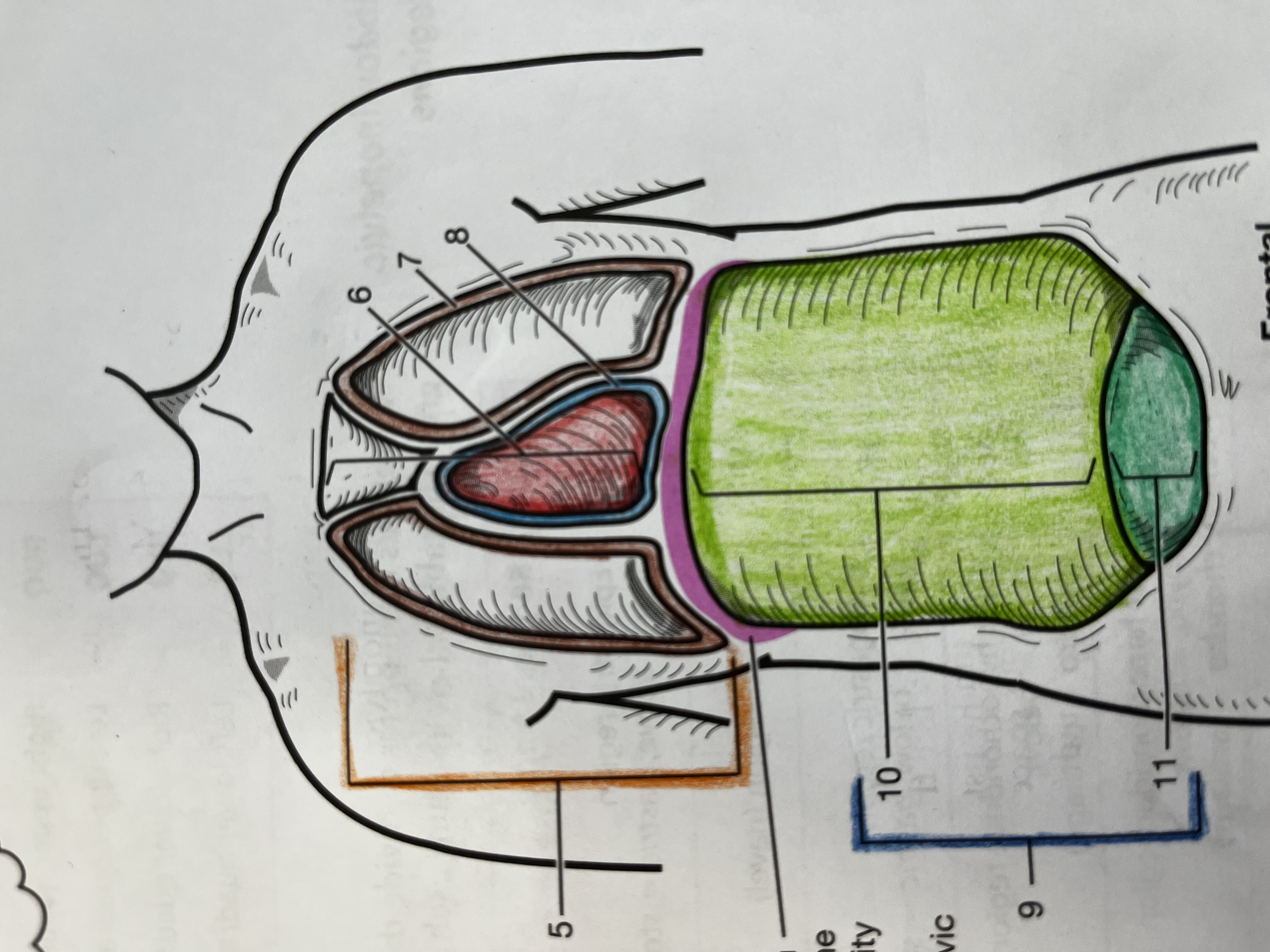
Mediastinum
Median compartment of the thoracic cavity
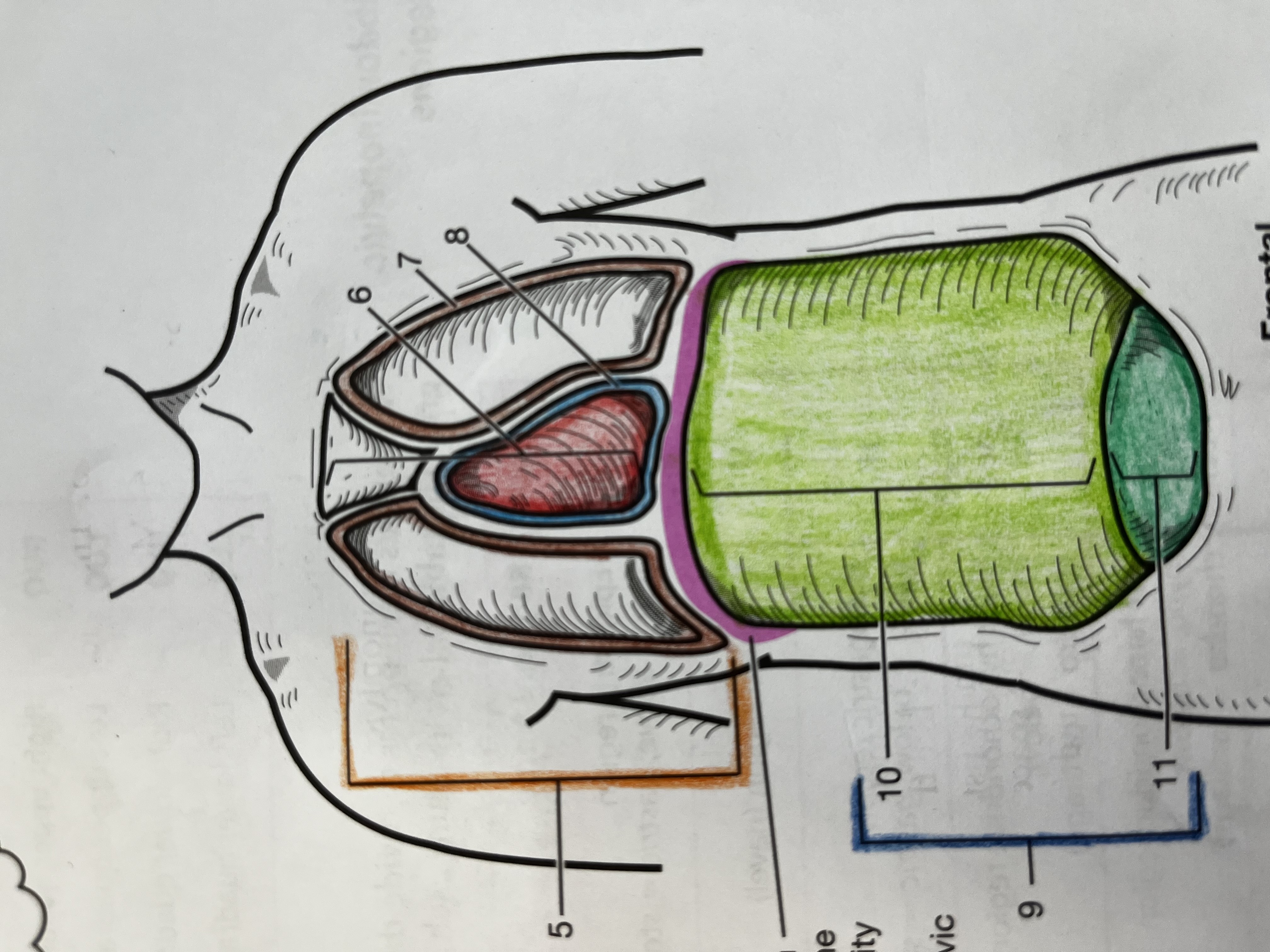
Pleural cavity
Fluid filled space around the lungs
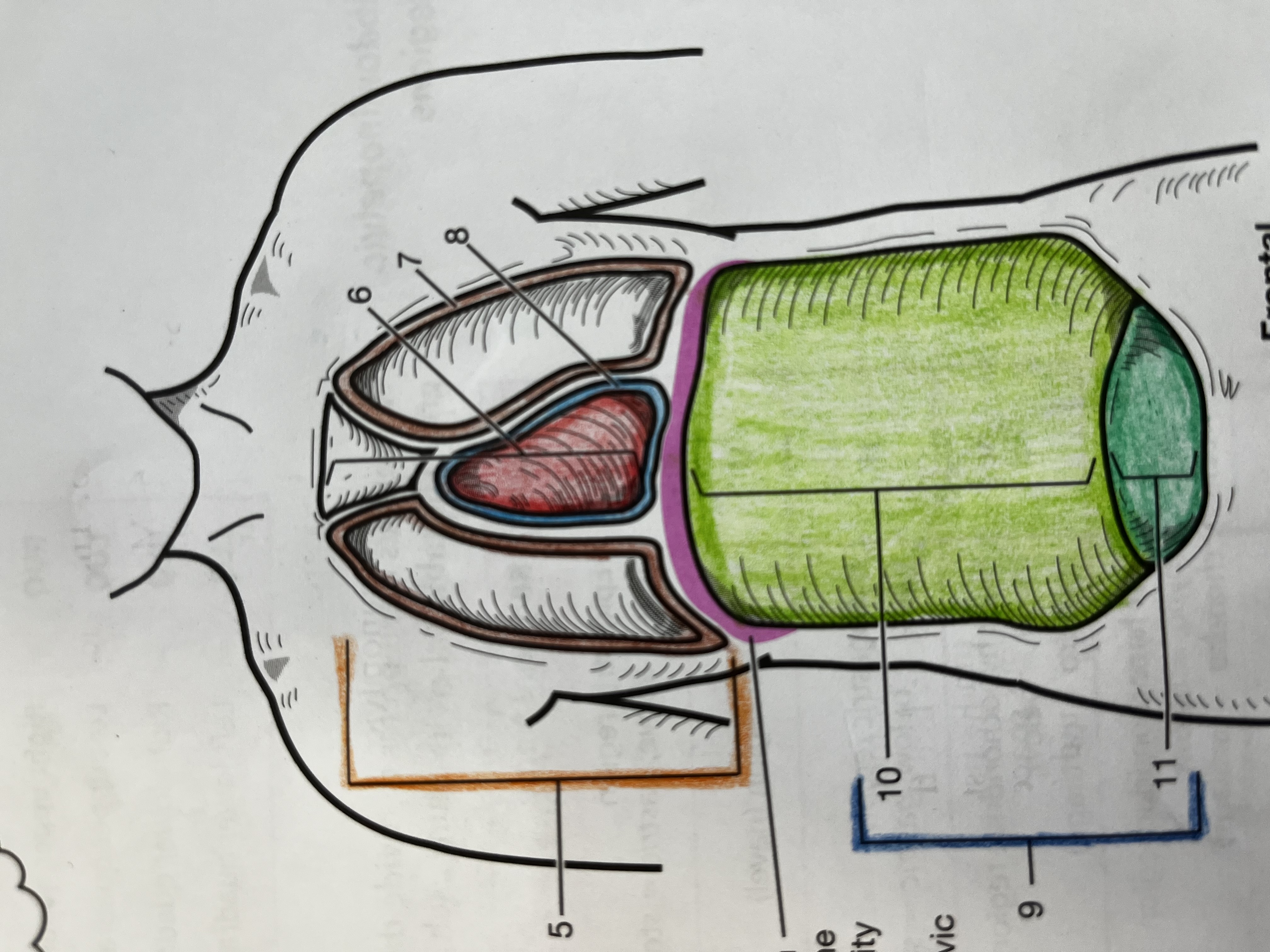
Pericardial Cavity
Fluid filled space around the heart
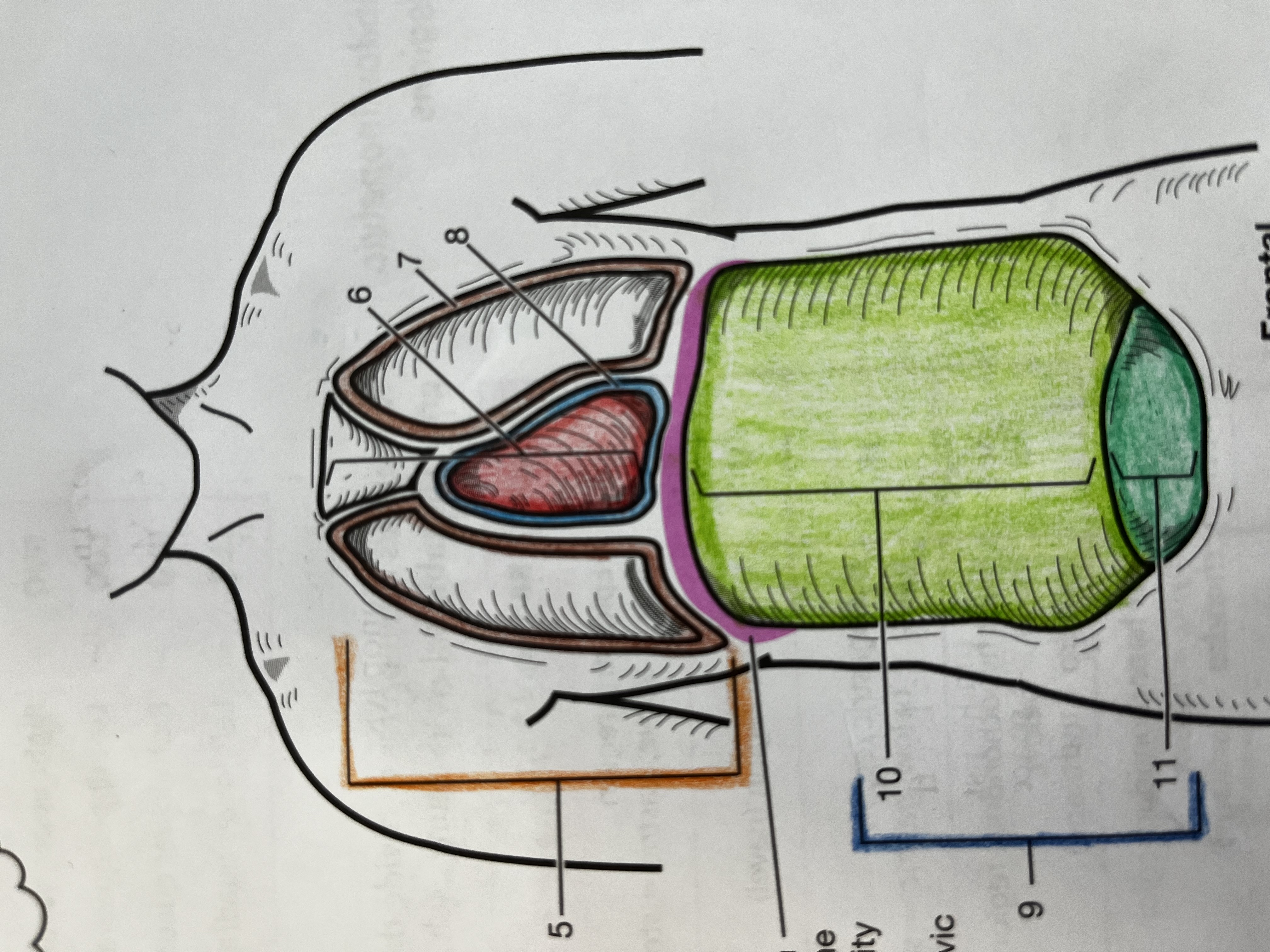
Abdominopelvic cavity
consists of the abdominal and pelvic cavities
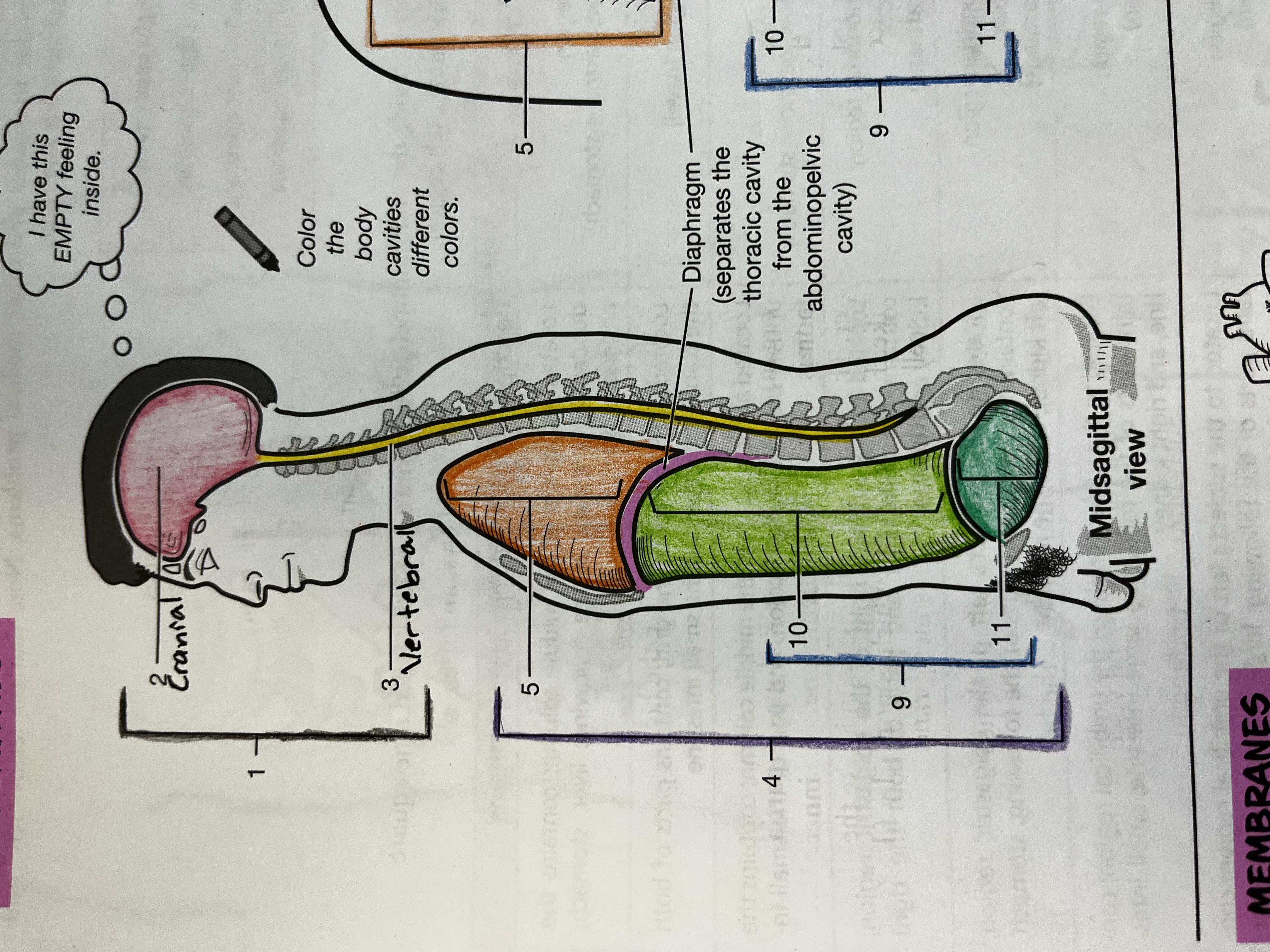
Abdominal cavity
Contains the digestive organs, kidneys, and ureters
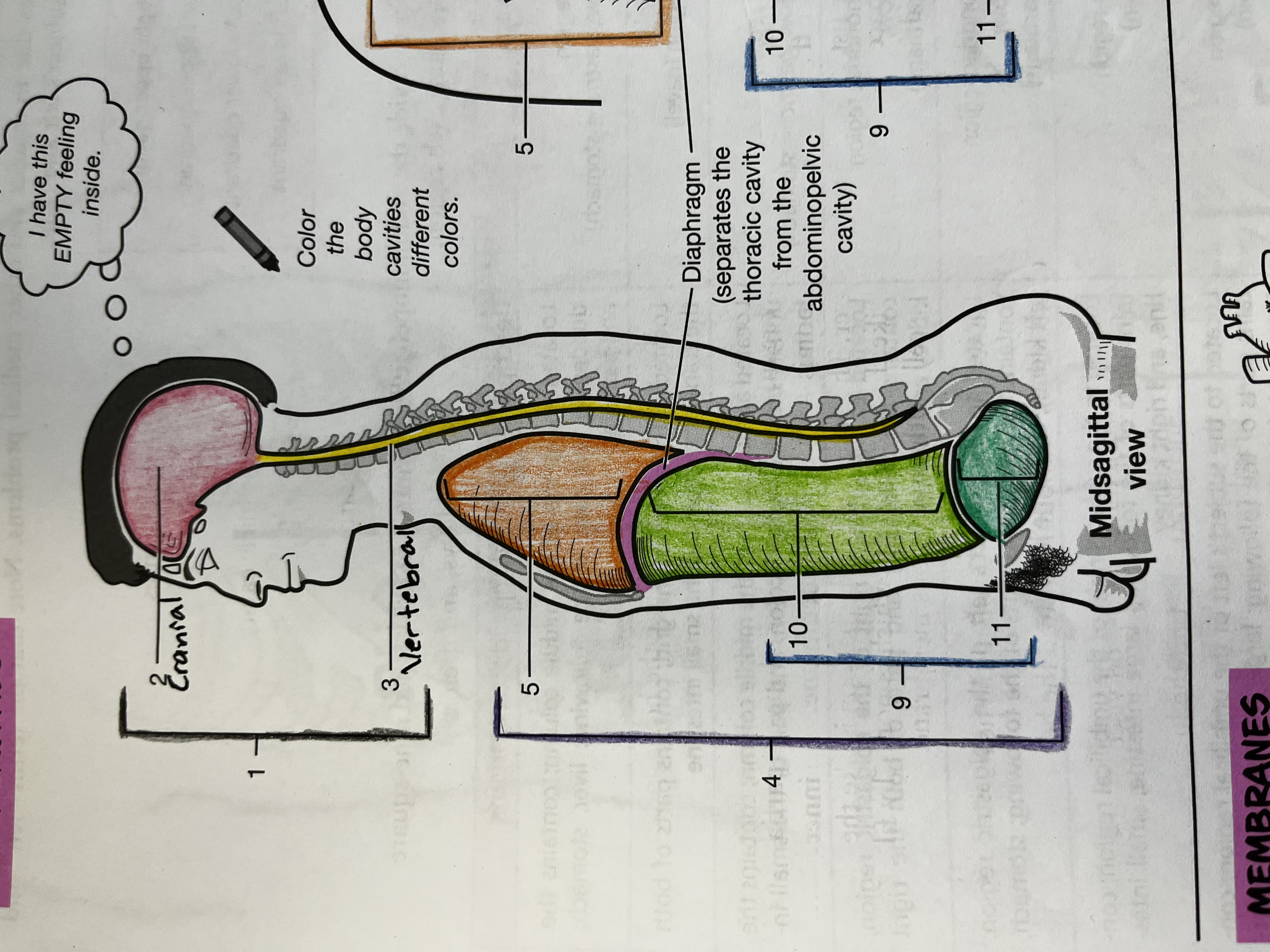
Pelvic cavity
Contains the urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs, and the rectum
RUQ
Right Upper quadrant
RLQ
Right lower quadrant
LUQ
Left upper quadrant
LLQ
Left lower quadrant
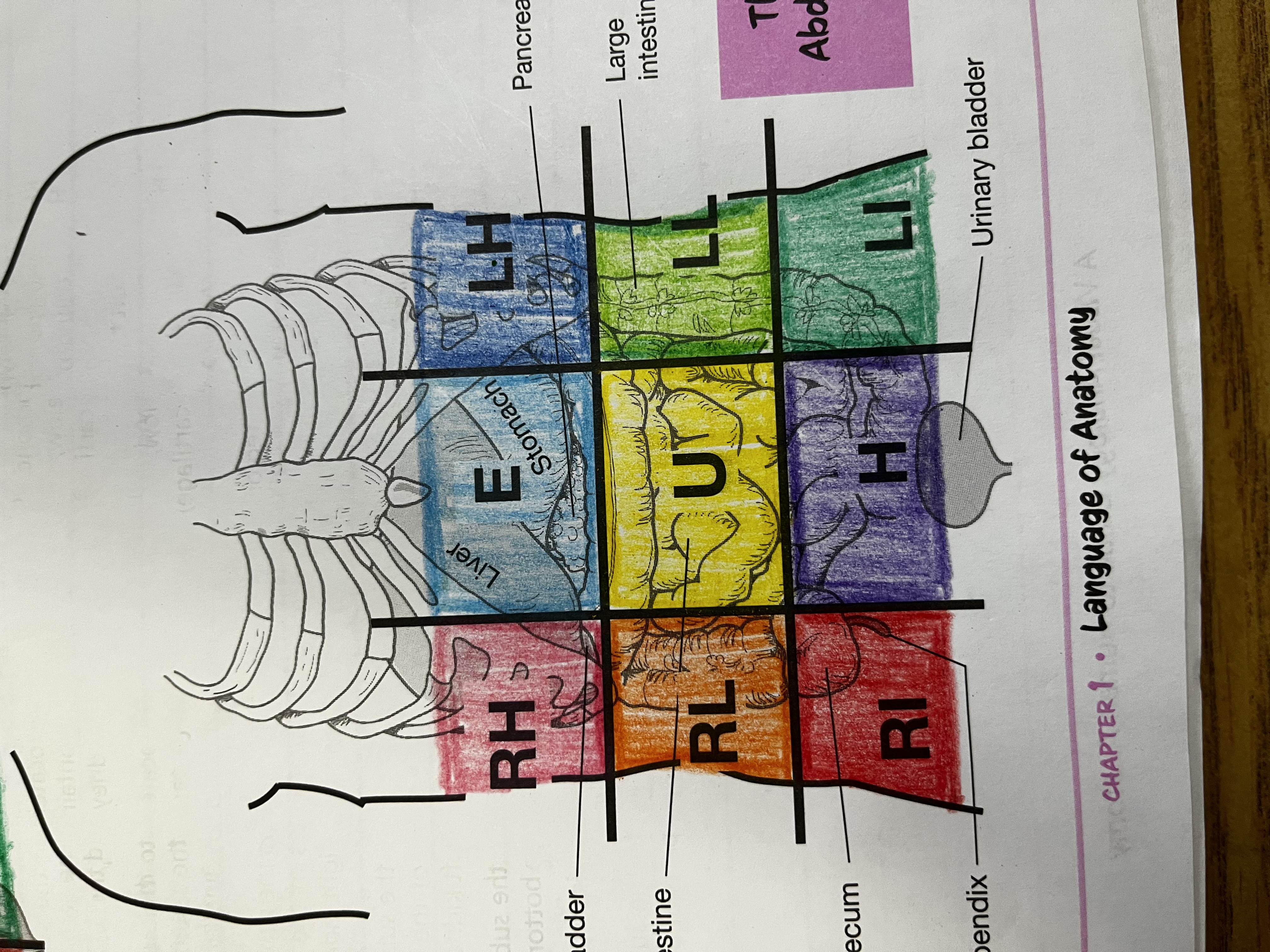
Right Hypochondriac Region
right of the epigastric region, contains gallbladder, right kidney & liver
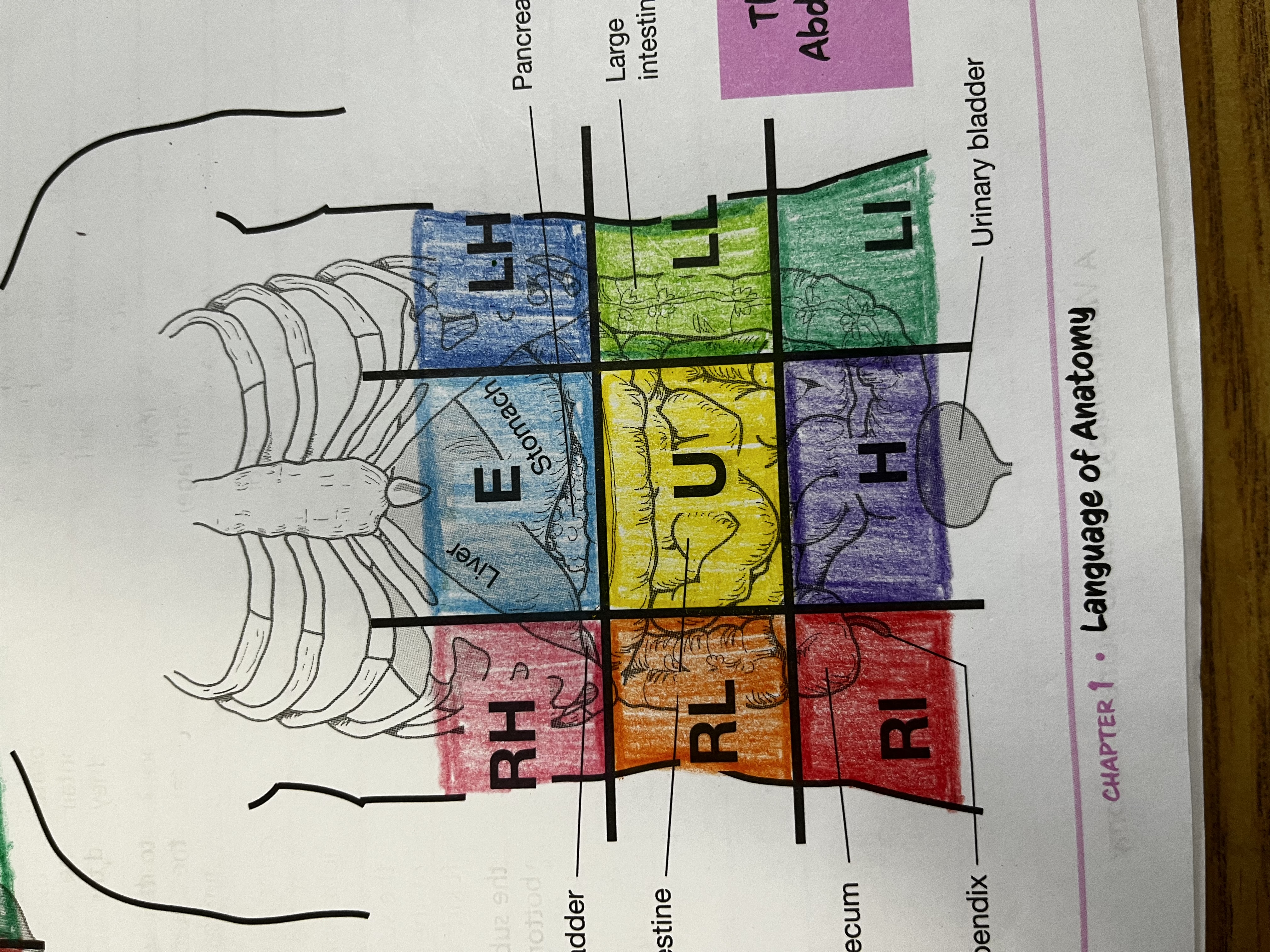
Epigastric region
Contains duodenum & parts of liver, stomach and pancreas
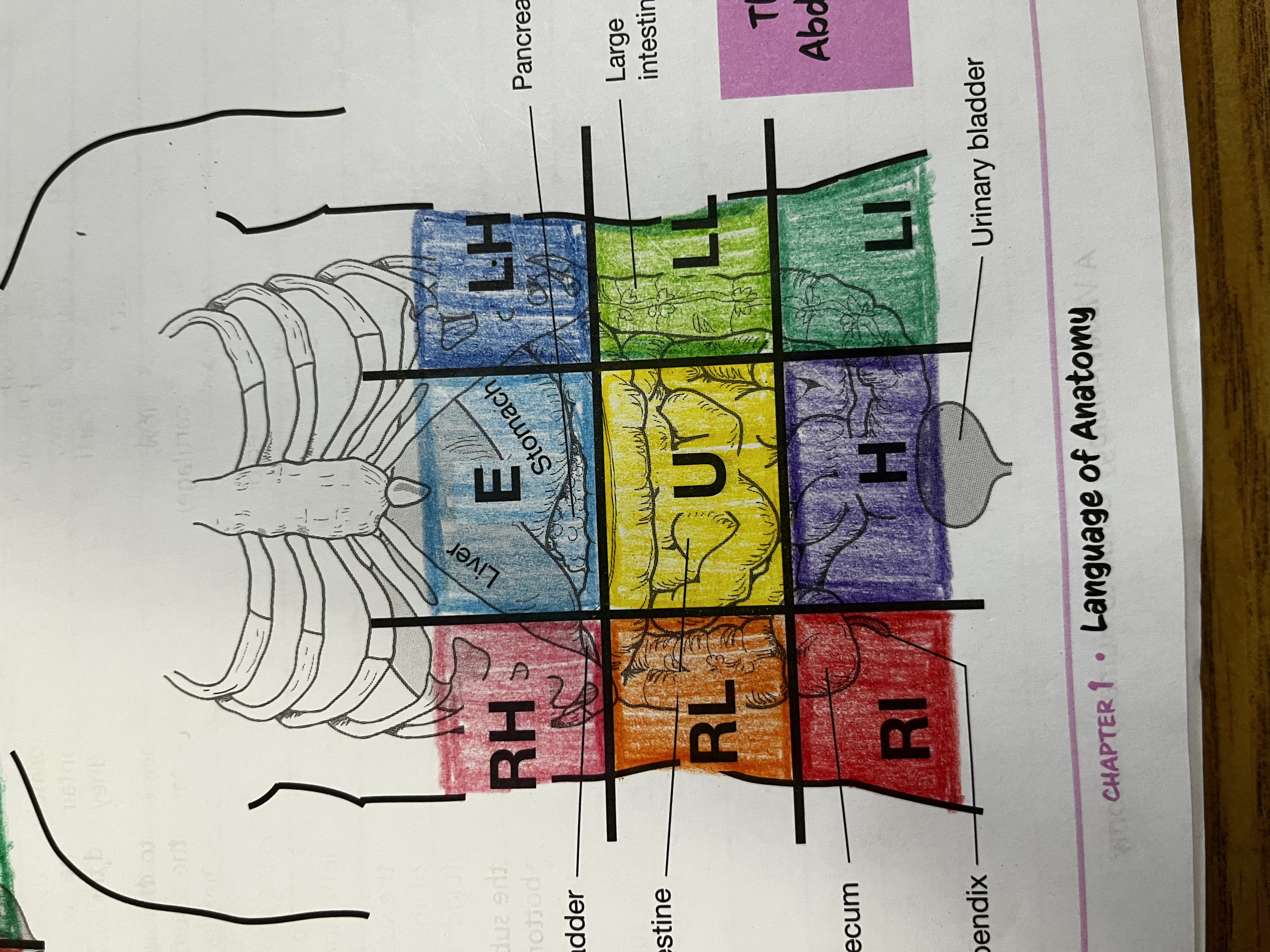
Left hypochondriac region
Left of epigastric region, contains spleen and parts of stomach, left kidney and large intestine
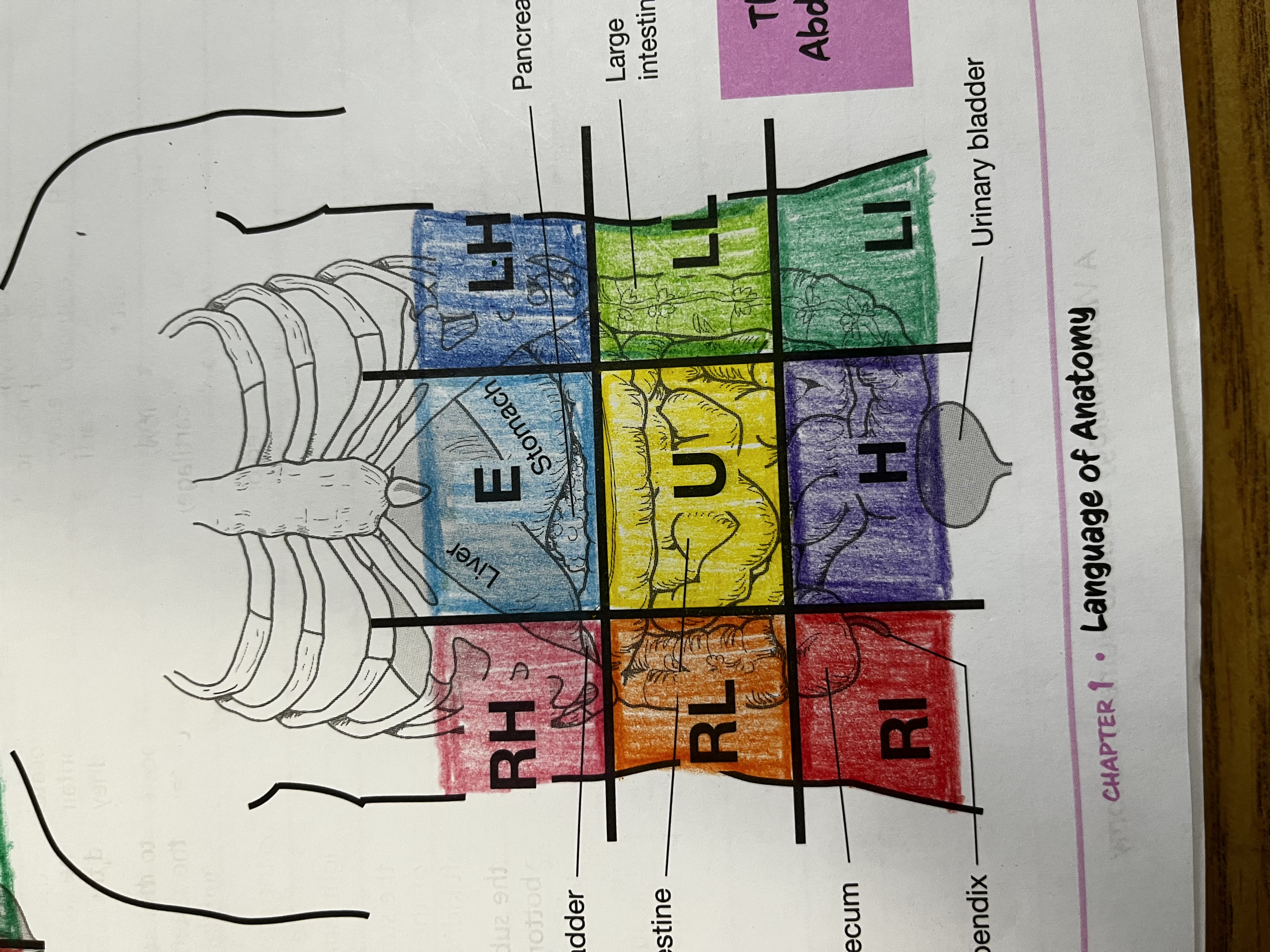
Right lumbar region
Right of the umbilical region, contains large intestine, small intestine and right kidney
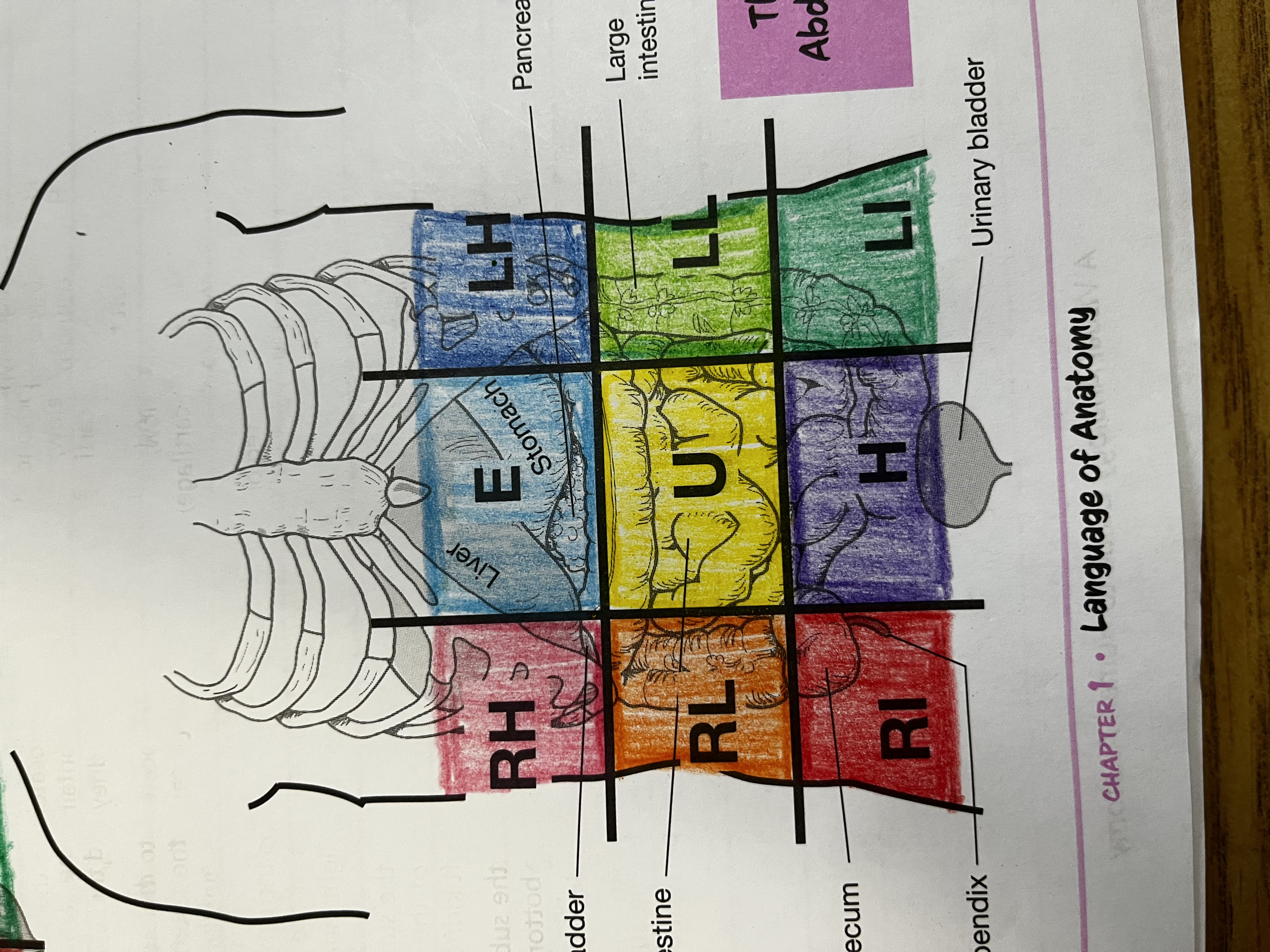
Left lumbar region
Left of umbilical region, contains large intestine, small intestine, and left kidney
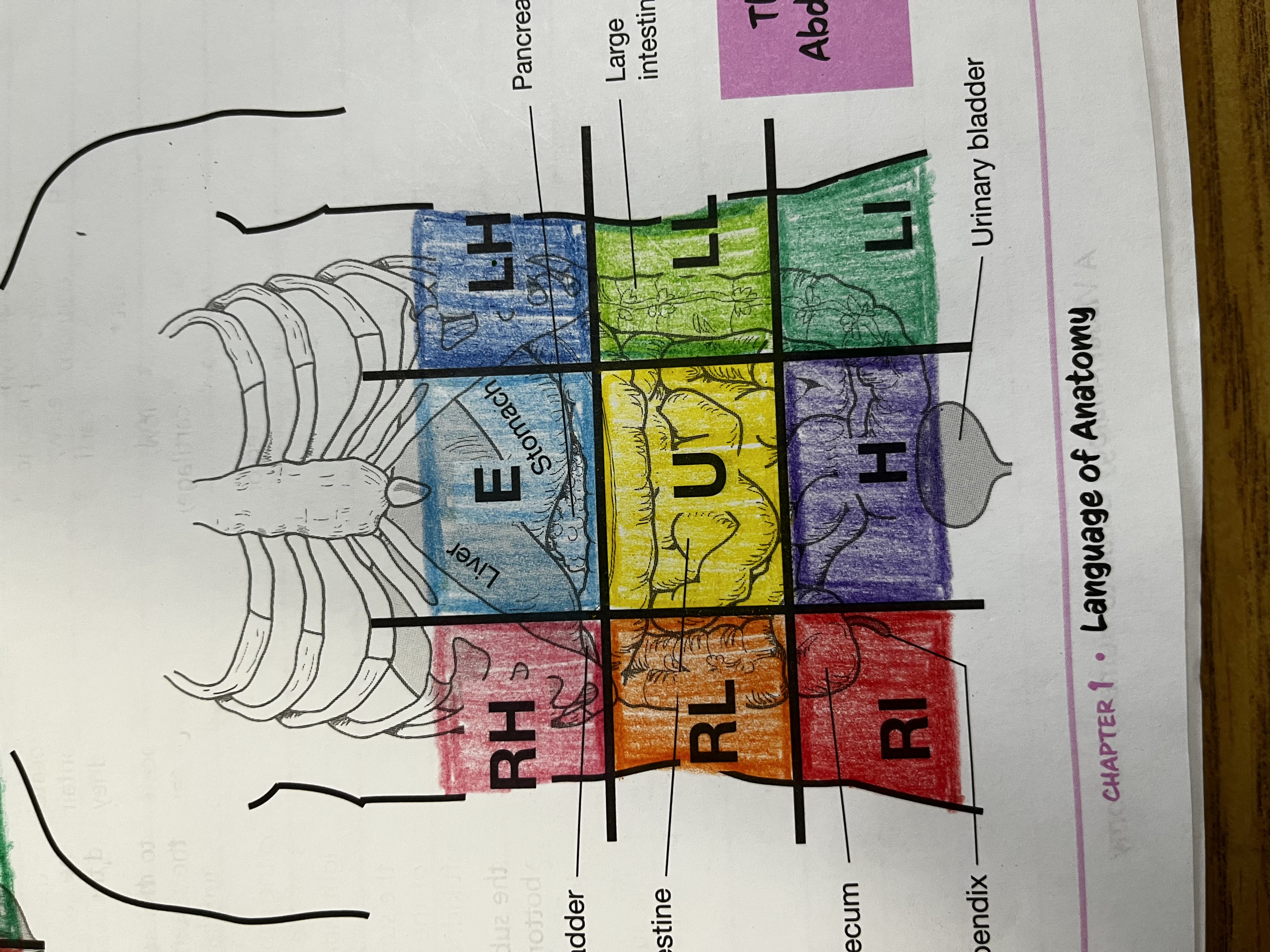
Umbilical region
Center of grid, contains transverse colon and small intestine
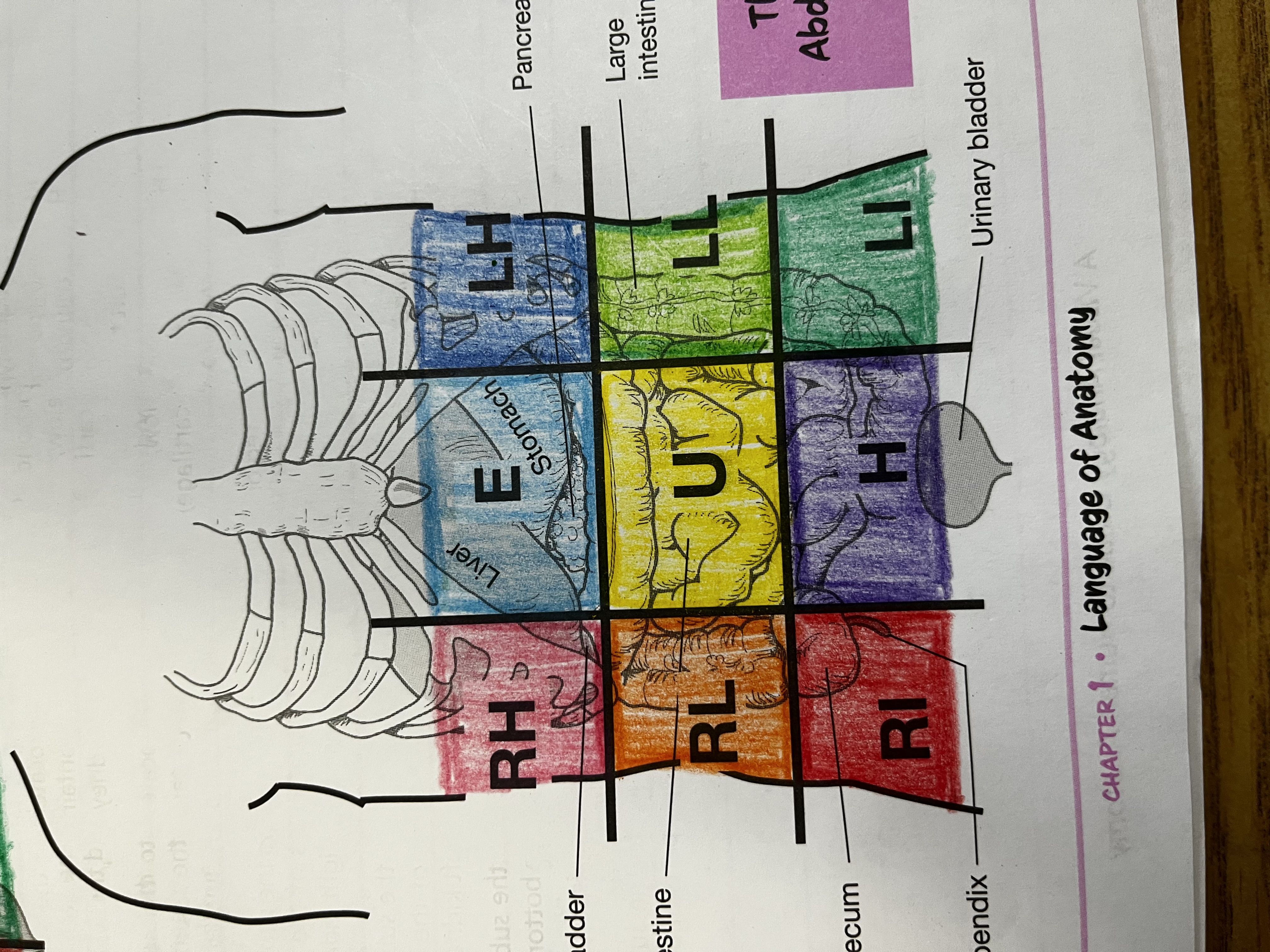
Right iliac region
Right of hypogastric region, contains cecum, appendix, and part of small intestine
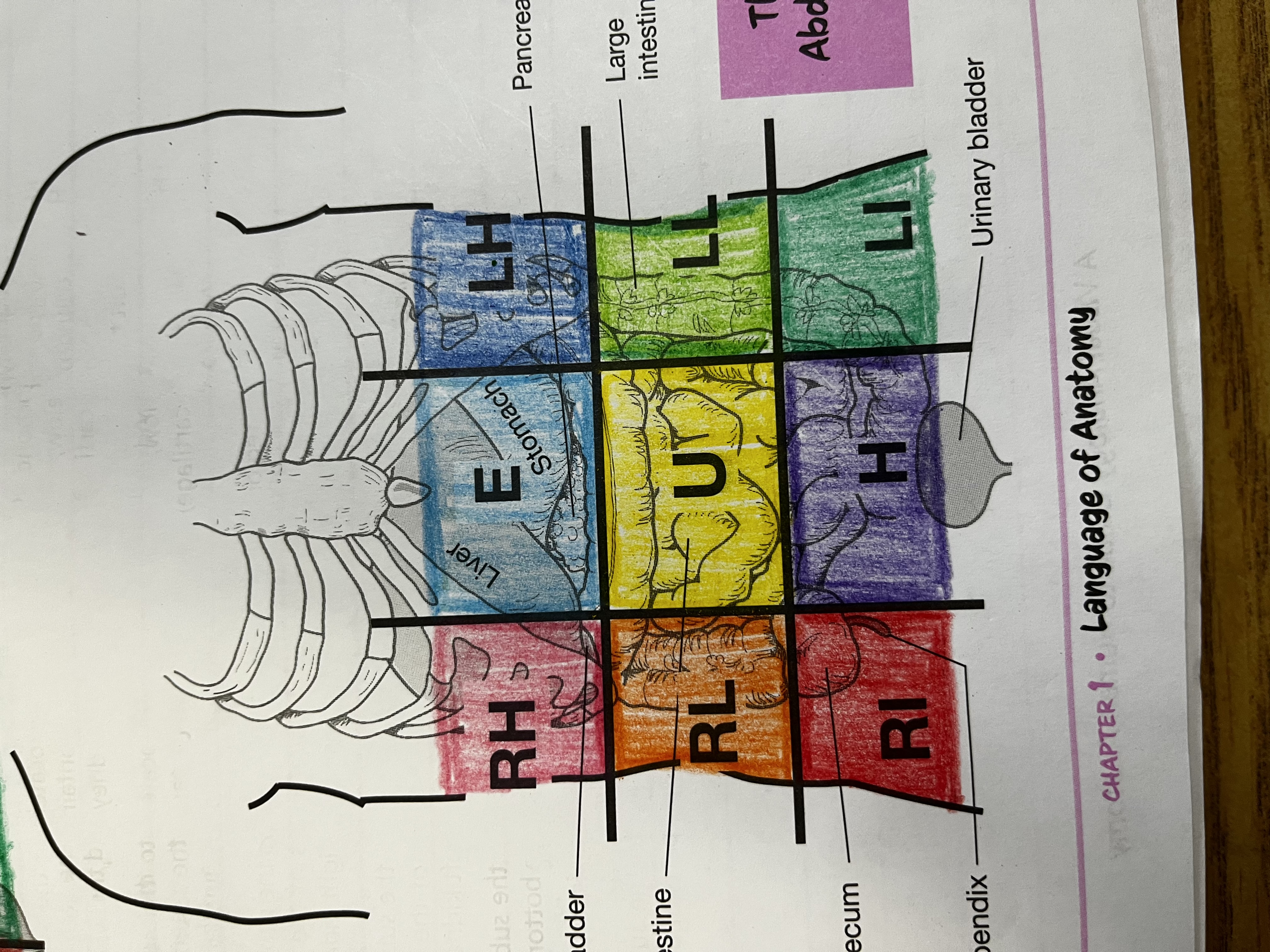
Hypogastric region
Bottom of middle column, contains urinary bladder, sigmoid colon and part of small intestine
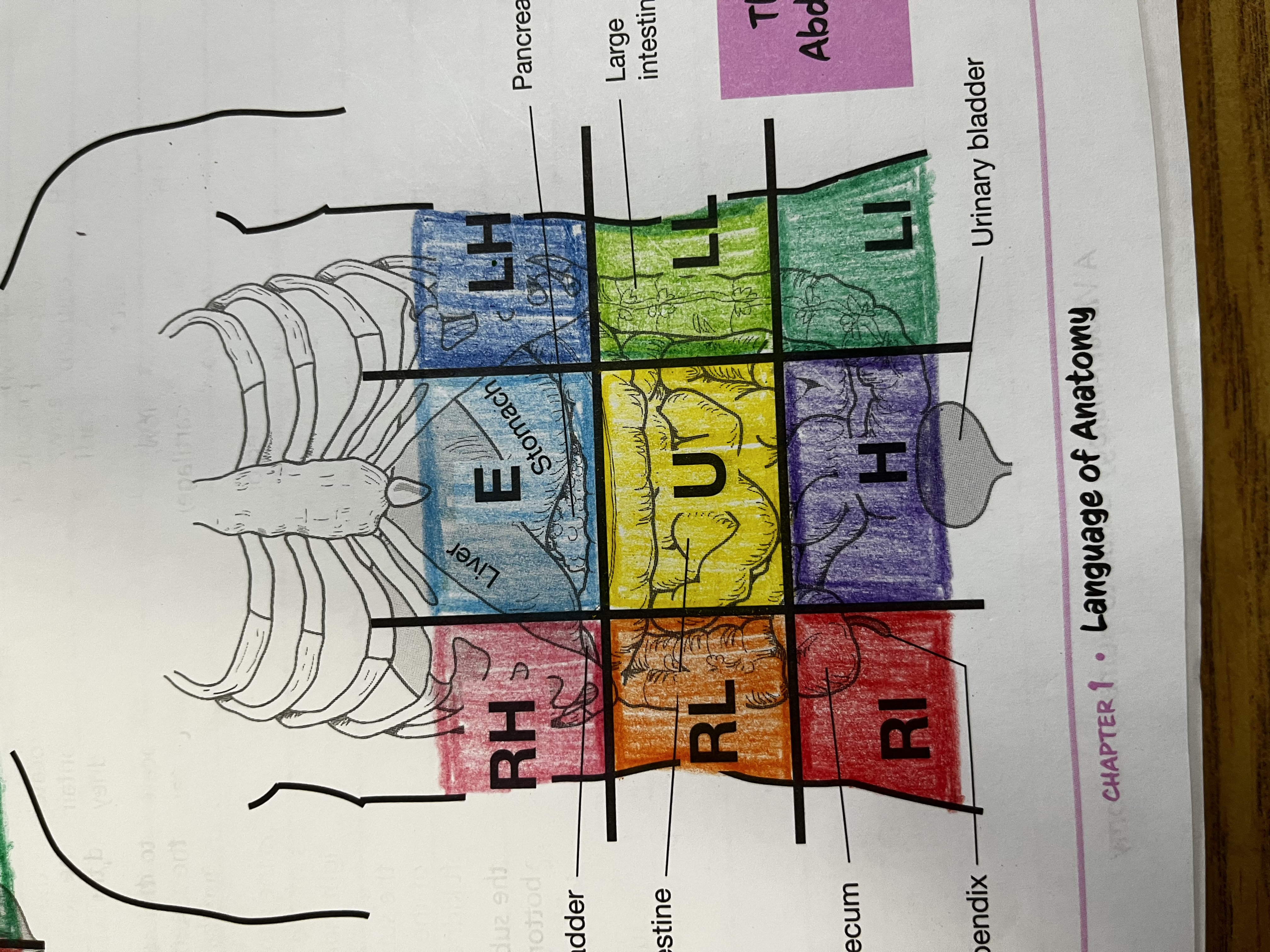
Left iliac region
Left of hypogastric region, contains large and small intestine
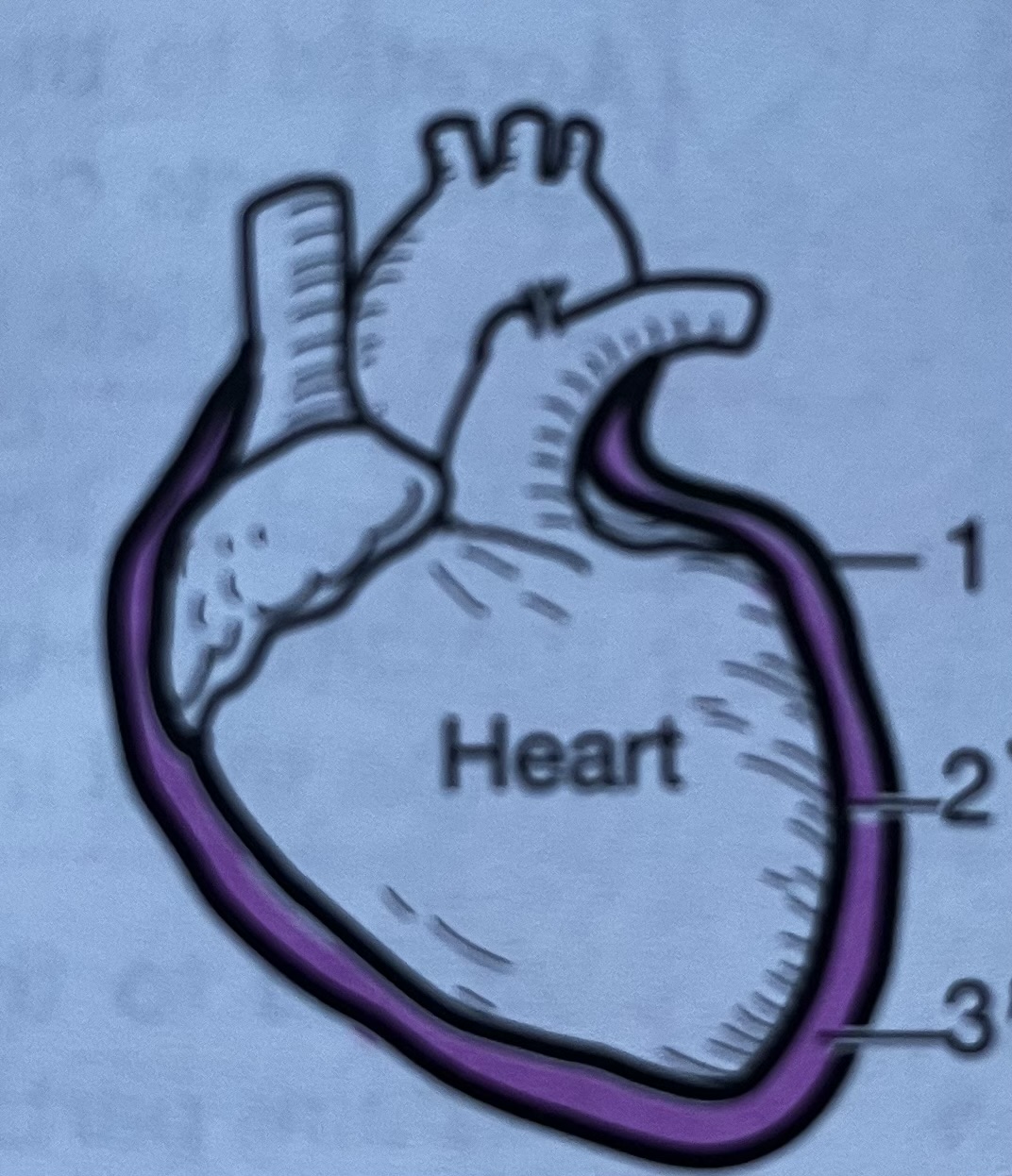
Heart membrane #1
Parietal pericardium, outer serous membrane layer of the heart
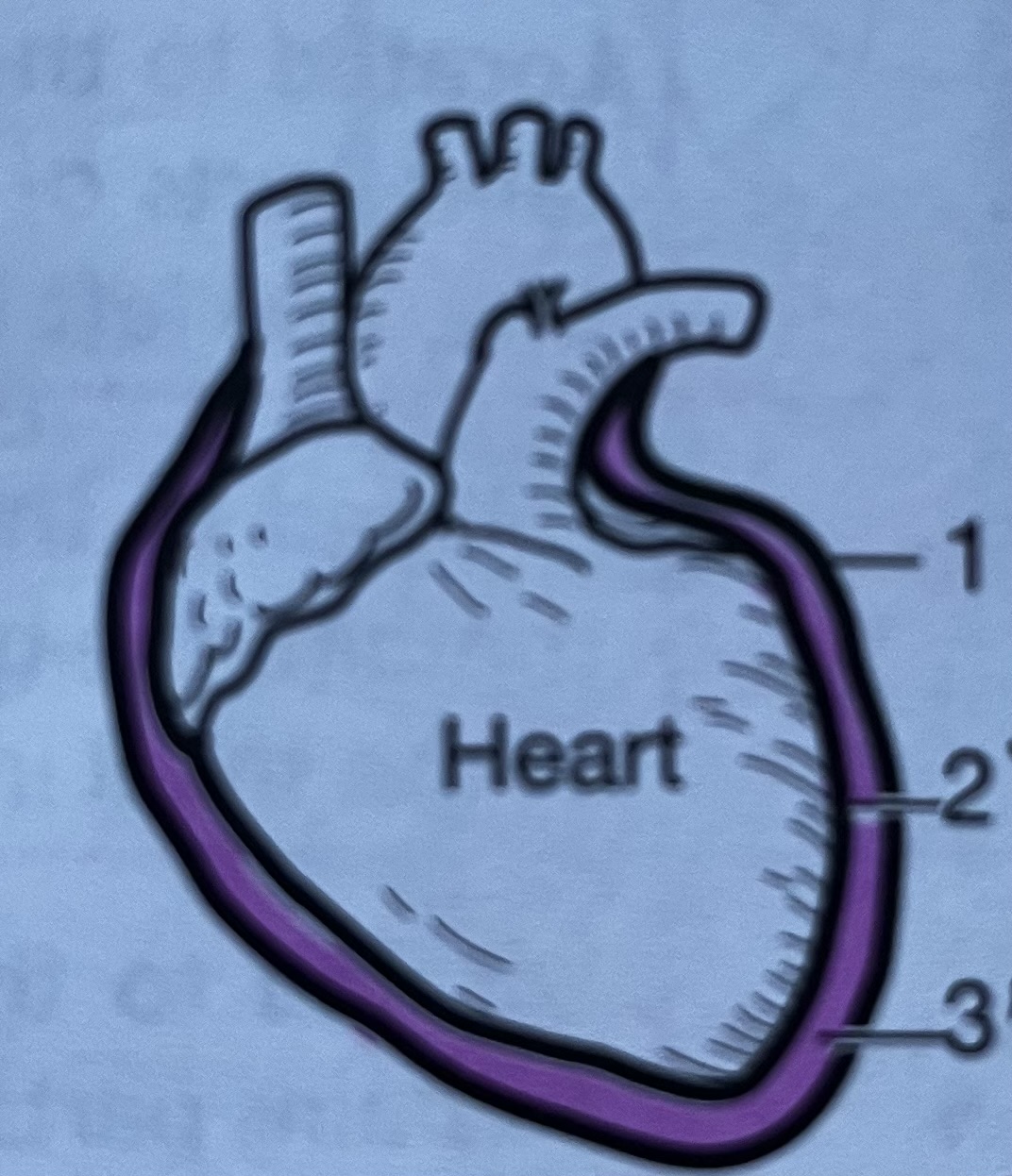
Heart membrane #2
Visceral pericardium, innermost serous membrane of the heart
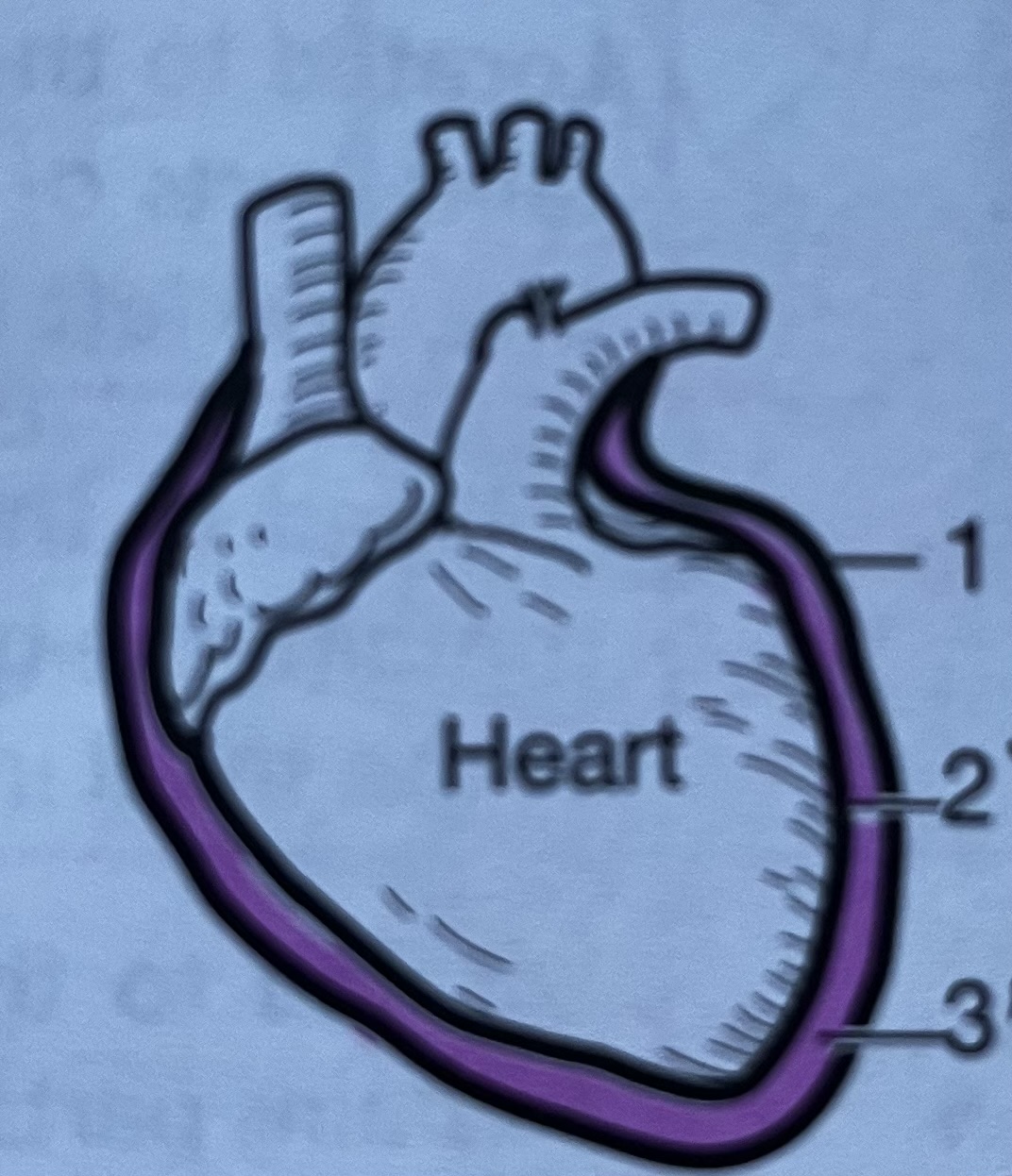
Heart membrane #3
Pericardial cavity, fluid filled space between the parietal and visceral layers
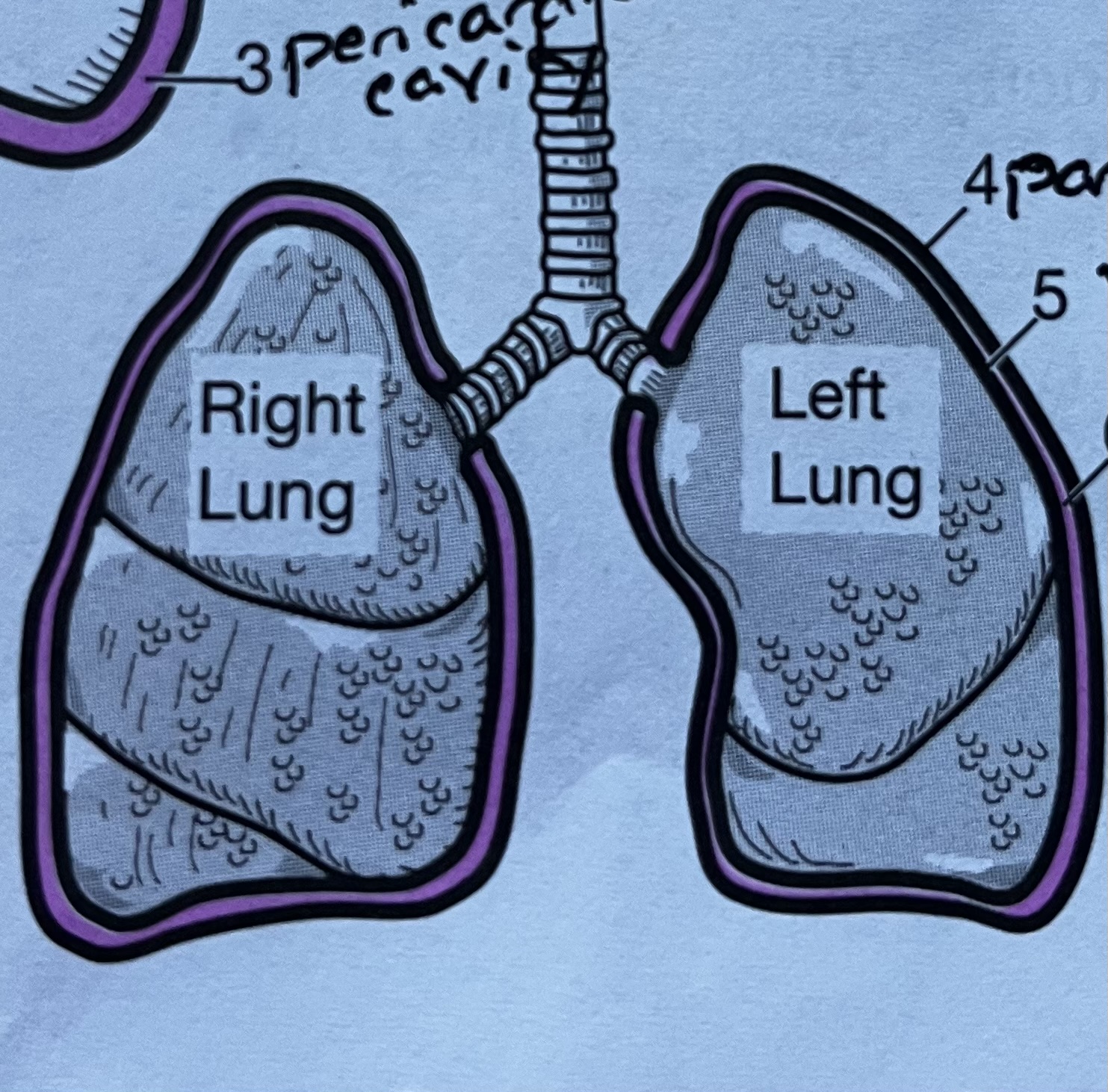
Lung membrane #4
Parietal pleura, outer serous membrane of the lungs
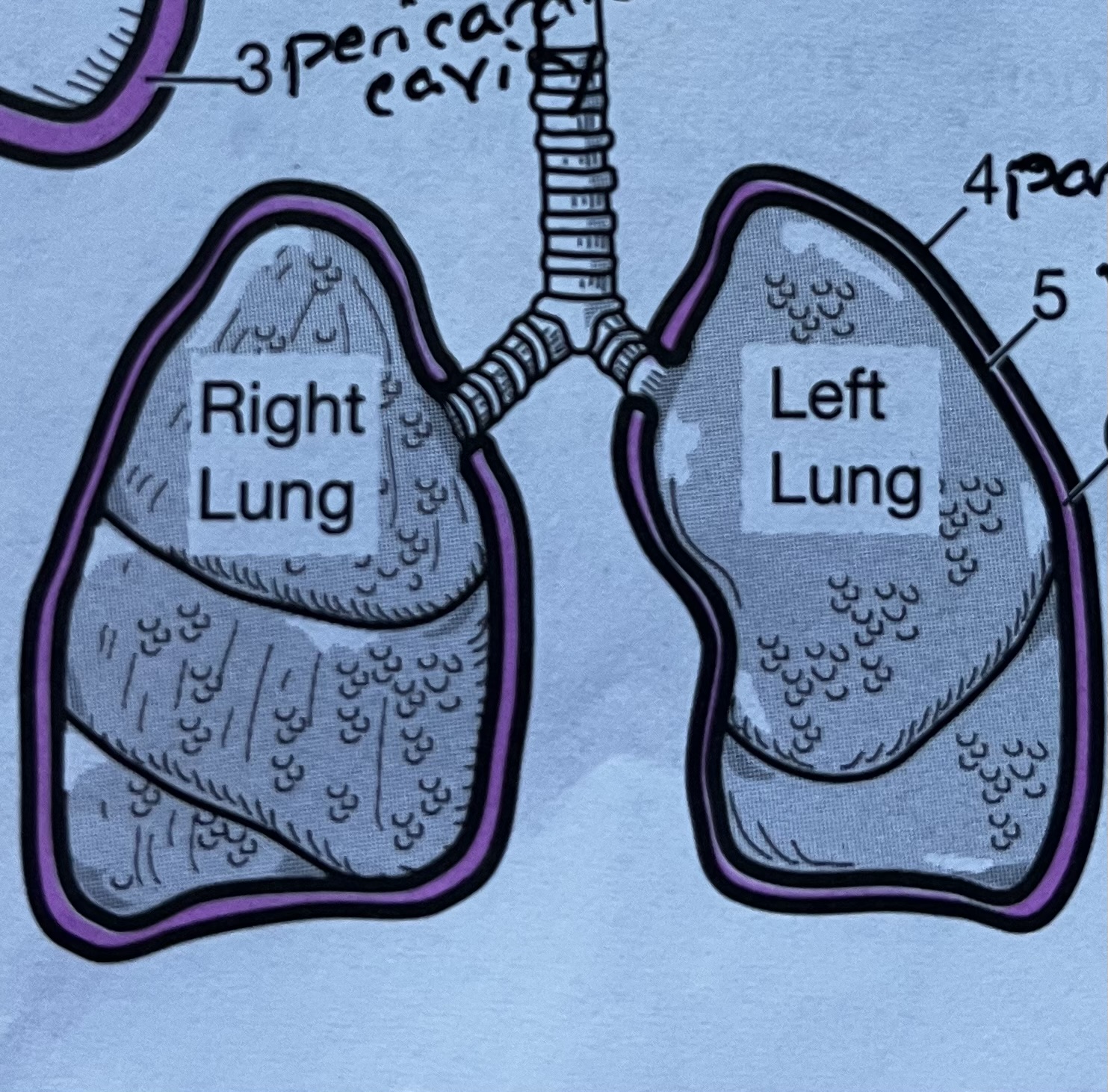
Lung membrane #5
Visceral pleura, innermost serous membrane of the lungs
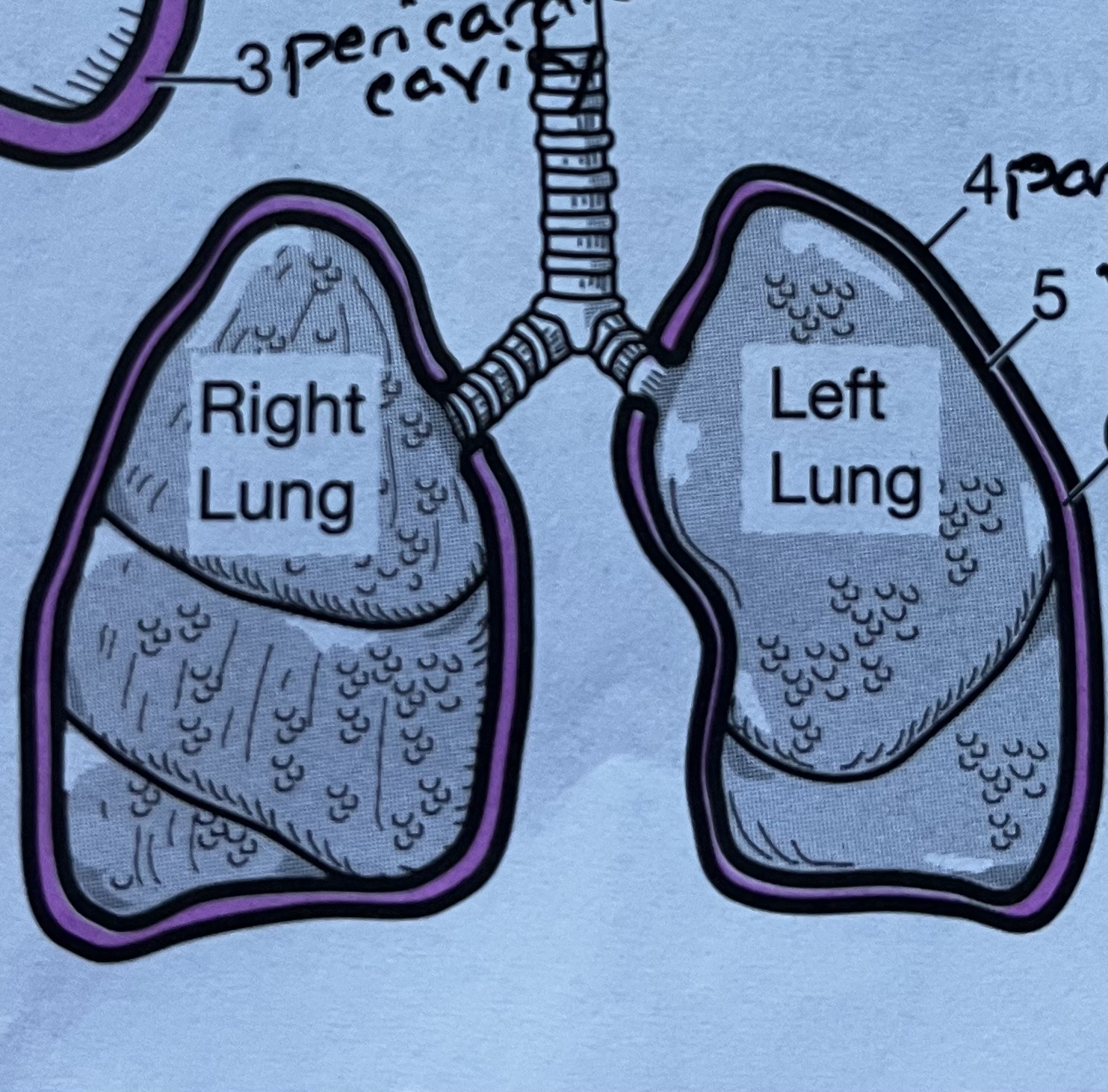
Lung membrane #6
Pleural cavity, fluid filled space between the parietal and visceral membranes
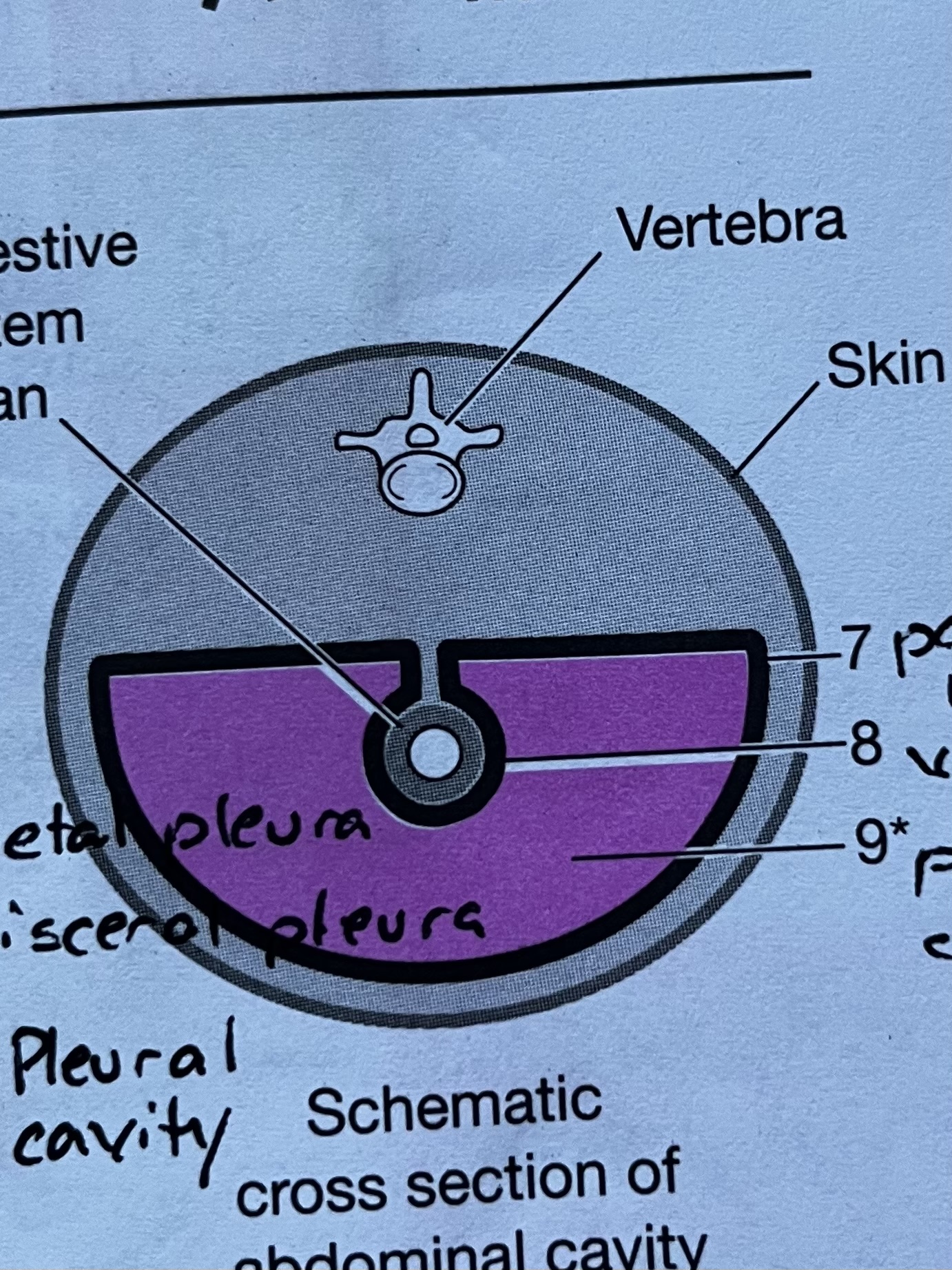
Abdominopelvic Membrane #7
Parietal peritoneum, outermost serous membrane layer of the Abdominopelvic cavity
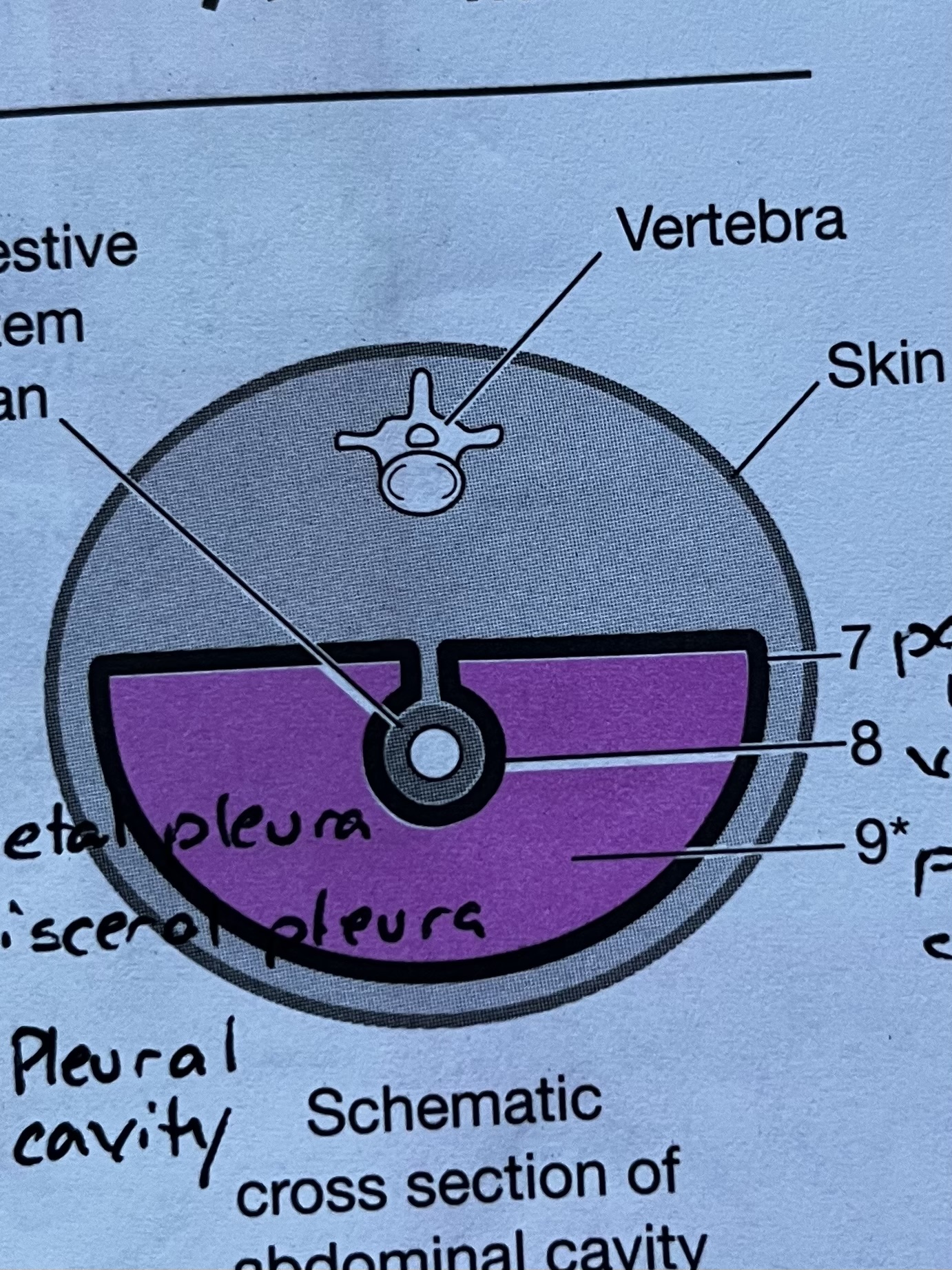
Abdominopelvic Membrane #8
Visceral peritoneum, innermost serous membrane layer lining the digestive organs
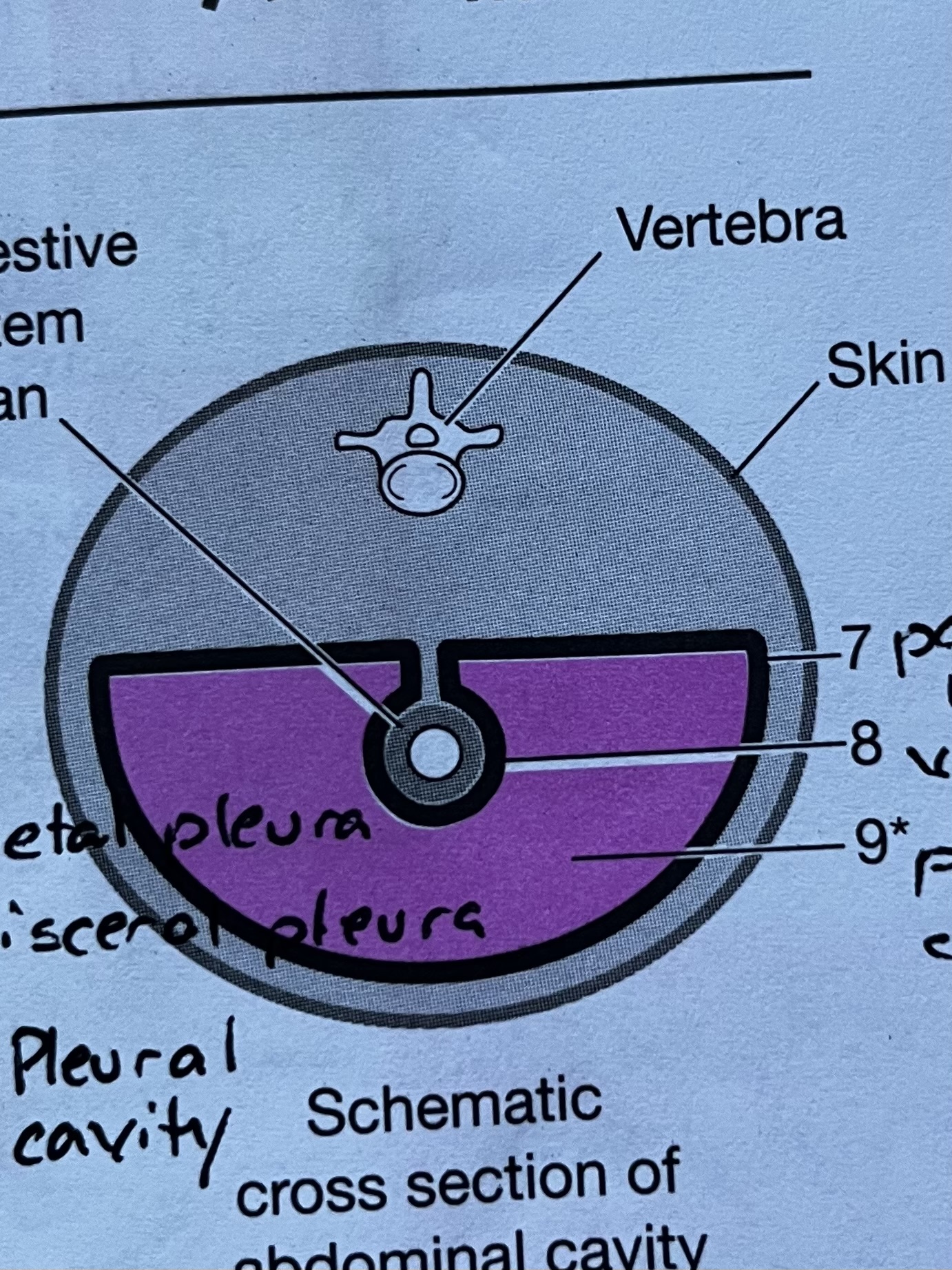
Abdominopelvic Membrane #9
Peritoneal Cavity, fluid filled space between the parietal and visceral layers
Cell
Smallested structural unit with all the characteristics of life
3 Major elements of a cell + functions
Plasma membrane- cell boundary
Cytoplasm- cytosol contains organelles
Nucleus- DNA
Chemical composition of the plasma membrane ?
Biomolcularlayer of lipids( phospholipids & glycolipids) and proteins, keeps membrane stable to separate interstitial fluid from surrounding extracellular fluid
Compare tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions
Tight junctions- impermeable, prevent molecules from passing through intercellular space
Desmosomes-anchor cells together, form a tension reducing fiber network(zipper)
Gap junctions- allow small molecules to pass for intercellular communication
Positive Feedback mechanisms
Caused more of an action to occur
ex. Blood clotting when the lining of a blood vessel is injured
Negative Feedback mechanism
Homeostatic control mechanism, reduces intensity & inhibits action from continuing to occur
Ex. Sweating to help lower elevated body temp
Axial
Head,neck, and trunk
Appendicular
Limbs
Three components of homeostatic control systems
Effector, receptor (senses the change), and the control center
Mitochondria
creates ATP, contains RNA & DNA, membraneous
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis, 2 types: free & membrane bound, nonmembraneous
ER
2 types: rough & smooth, membraneous
Rough- synthesize integral proteins & phospholipids for plasma membrane
Smooth- lipid metabolism, detoxifies drugs, synthesizes fats, produces steroid hormones
Golgi Apparatus
modifies & packages proteins & lipids, membraneous
ER provides vesicles of proteins/lipids→CIS face→ trans face
Lysosomes
Suicide sacs, contain digestive enzymes to ingest bacteria, viruses, membraneous
Peroxisomes
Detoxifies harmful substances, neutralizes free radicals (electrons not paired), membraneous
Nuclear Envelope
Large molecule transport w/ double membrane barrier
Nucleolus
Involved w/rRNA synthesis & ribosome assembly
Chromatin
Condense into chromosomes during mitosis
Epithelial Tissue
forms boundaries between different environments, protecting, secreting, absorbing, and filtering on the epidermis and lining of the GI tract
List the two main types of epithelium
Covering/lining and glandular
Apical surface
microvili, cilia
Basal surface
bottom surface of a tissue (Reticular + Basal lamina = basement membrane)
Avascular
no blood vessels
Innervated
supplies a body part with nerves
Rate of Regeneration
The time it takes for cells to complete mitosis, high allows quick healing; con is that it can become cancerous
Squamous Epithelium Tissue (thin & flat)
skin, lungs, mouth; simple- filtration & diffusion, stratified-protection
Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue (cube-shaped)
kidney, glands, ovaries; simple- secrete, absorb
Columnar Epithelium Tissue (column-shaped)
upper respiratory, GI tract; simple- secrete, absorb, cilia move mucous
Transitional Epithelium Tissue
distends, cuboidal to columnar shapes
Gland
epithelial tissues specialized to synthesize and secrete a product
Exocrine Gland
hollow organ or duct; action is local (sweat, salivary, mucous, oil), unicellular or multicellular
Endocrine Gland
within the blood stream, travels a great distance to target (pituitary glands, ovary, testes)
Unicellular (single cells)
Mucous-secreting cells are called goblet cells, only unicellular gland in the body, in large and small intestines
Multicellular
Secretory sheets lining the abdomen and chest (abs)
Serous (serosae)
membranes in pleura, pericardium, and peritoneum
Parietal Serosae
line internal body walls
Visceral
cover internal body organs
Connective Tissue
Binding, support, protection, insulation, and transportation of extracellular matrix and cells
Extracellular Matrix Ground Substance
The medium (stuff between 2 cells) where solutes dissolve between blood capillaries & cells, contains interstitial fluid and proteins; has ground substance: either hard & calcified (bones) or liquid (blood/plasma)
Extracellular Matrix of Fibers (3 types)
Collagen (white fibers)- strongest & most abundant fibers
Elastic- networks of long, thin, elastin fibers
Reticular- short, fine, highly branched collagenous fibers (scary Halloween trees)
Blasts
Mitotically active and secretory cells
Cytes
Mature cells