[N108] LEC 3.1 - Anxiety, Anxiety Disorders, and Panic Disorders
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
False; anxiety doesn't have a stimulus. Minsan, hindi known yung source of anxiety
True or false? Anxiety comes from an external stimulus
Alarm stage
Resistance stage
Exhaustion stage
What are the 3 stages of the General Adaptation Syndrome?
Alarm stage
Stage in the General Adaptation Syndrome wherein fight or flight reactions are triggered
Resistance stage
Stage in the General Adaptation Syndrome wherein the body tries to cope with anxiety
Mild
Moderate
Severe
Panic
What are the 4 levels of anxiety?
Mild
The following psychological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Wide perceptual field
Sharpened senses
Increased motivation
Moderate
The following psychological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Perceptual field narrowed to immediate task
Selectively attentive
Cannot connect thoughts or events independently
Severe
The following psychological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Perceptual field reduced to one detail or scattered
Cannot complete task
Panic
The following psychological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Distorted perceptions
Loss of rational thought
May be suicidal
Mild
The following physiological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Restlessness
Fidgeting
GI “butterflies”
Difficulty sleeping
Severe
The following physiological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Severe headache
Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
Vertigo
Chest pain
Panic
The following physiological responses manifest in which level of anxiety?
Dilated pupils
Increased BP and pulse
Fight, flight, or freeze
Patient safety
What should be the priority during the severe and panic stages of anxiety?
Selective mutism
Diagnosed in children when they fail to speak in social situations even though they are able to speak
Anxiety disorder to another medical condition
Diagnosed when the prominent symptoms of anxiety (e.g., panic attacks) are judged to result directly from physiological condition (i.e. thyroid disease, mitral valve prolapse)
Substance/medication-induced anxiety disorder
Anxiety directly caused by drug abuse, a medication, or exposure to a toxin
Separation anxiety disorder
Excessive anxiety concerning separation from home or persons, parents, or caregivers
GABA
Which neurotransmitter regulates anxiety?
Serotonin
Which hormone regulates anxiety?
Harry Stack Sullivan
Who created the interpersonal theory?
15 to 30
Panic disorder is composed of discrete episodes of panic attacks lasting for _____ to _____ minutes of rapid, intense, escalating anxiety, a storm of emotions of fear, and physiologic discomfort
1 MONTH
A person diagnosed with panic disorder has periodic, unanticipated panic attacks followed by AT LEAST _____ of persistent anxiety or concern about future attacks.
Peaks in late adolescence and the mid-30s
When is the clinical onset of panic disorder?
Agoraphobia
Type of anxiety disorder: “fear of the marketplace" or fear of being outside
False; others can leave the house but feel safe from the anticipatory fear of having a panic attack only within a limited area
True or false? People with agoraphobia cannot leave the house
True
True or false? Agoraphobia can also occur alone WITHOUT panic attacks
Secondary gain
The attention received from others as a result of anxiety-driven behaviors
Natural environmental phobias
Type of specific phobia: fear of storms, water, heights, or other natural phenomena
Blood-injection phobia
Type of specific phobia: fear of seeing ones' own or others blood, traumatic injury, or an invasive medical procedure such as injection
Situational phobia
Type of specific phobia: fear of being in a specific situation such as on a bridge or in a tunnel, elevator, small room, hospital, or airplane
Animal phobia
Type of specific phobia: fear of animals or insects (usually the specific type)
Social anxiety disorder
Social phobia is also known as _____
Social phobia
Type of anxiety disorder: the person becomes severely anxious to the point of panic or incapacitation when confronting situations involving people
Generalized anxiety disorder
Type of anxiety disorder: worries excessively and feels highly anxious at least 50% of the time for 6 MONTHS OR MORE
True
True or false? Patients with generalized anxiety disorder may have one or several social phobias
A. Irritability
B. Muscle tension
D. Fatigue
E. Difficulty thinking
F. Sleep alterations
A person with generalized anxiety disorder has THREE OR MORE of the following symptoms (select all that apply):
A. Irritability
B. Muscle tension
C. Suicidal ideation
D. Fatigue
E. Difficulty thinking
E. Compulsion
F. Sleep alterations
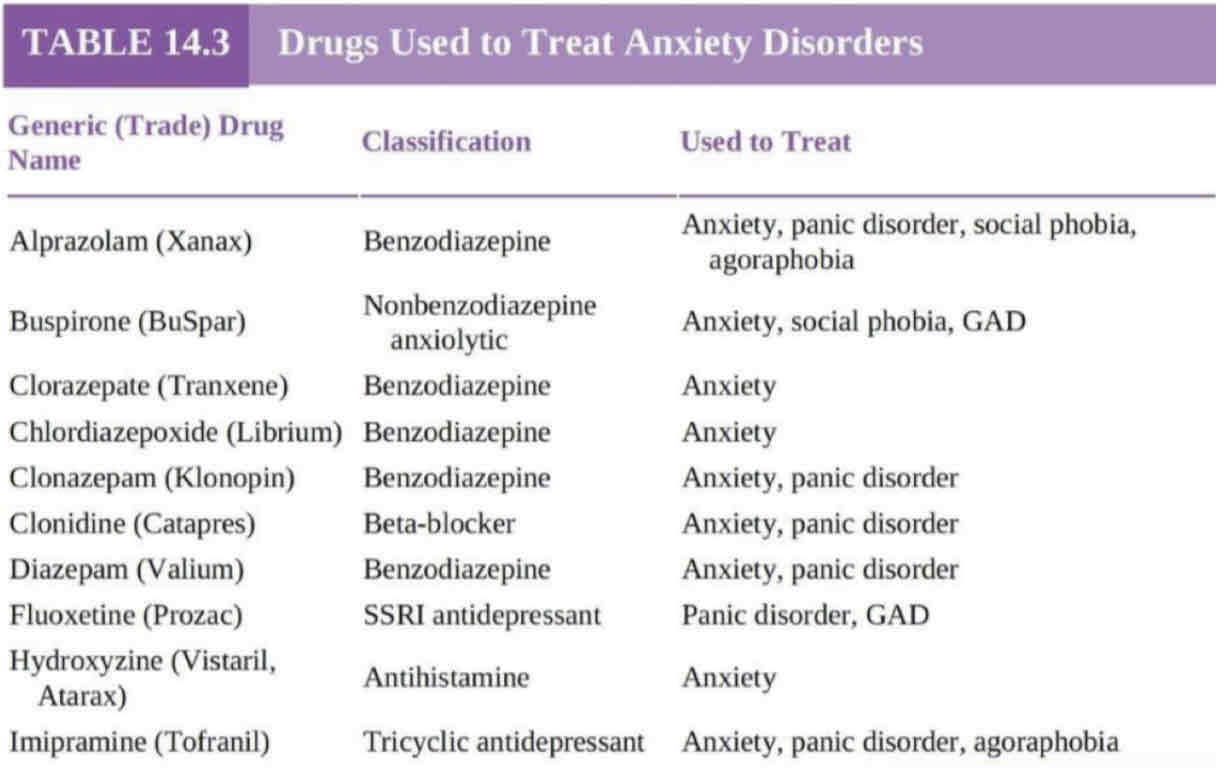
BONUS: drugs used to treat anxiety disorders
Cognitive behavioral therapy
Treatment that focuses on the way the patient thinks
Positive reframing
Decatastrophizing
Assertiveness training
What are the 3 techniques used in CBT?
Positive reframing
Technique in CBT: involves turning negative messages into positive messages
Decatastrophizing
Technique in CBT: involves the therapist's use of questions to more realistically appraise the situation
Assertiveness training
Technique in CBT: aims to help the person negotiate interpersonal situations and foster self-assurance
Behavioral therapy
Treatment that focuses in teaching the client what is anxiety, identifying anxiety responses, teaching relaxation techniques, goals setting, visualization of phobic situations
Desensitization
Flooding
What are the 2 techniques used in behavioral therapy?
Desensitization
Technique in behavioral therapy: involves progressively exposing the client to the threatening object in a safe setting until the anxiety decreases
Flooding
Technique in behavioral therapy: form of rapid desensitization; the behavioral therapist confronts client with phobia object until anxiety is eliminated
A) History of panic attacks in the past
When assessing a patient's history for anxiety, what is important to ask about?
A) History of panic attacks in the past
B) History of family disputes
C) History of medication use
D) History of sleep patterns
C) Increased speech rate, pitch, and volume; difficulty sitting still
During the assessment of general appearance and motor behavior in a client with anxiety, which of the following might be observed?
A) Slow speech and lethargic movement
B) Normal appearance with no signs of anxiety
C) Increased speech rate, pitch, and volume; difficulty sitting still
D) Calm demeanor with steady motor behavior
C) Tearfulness and self-directed anger for "being unable to control myself"
What might a client with anxiety express when discussing their panic attacks?
A) Happiness and relief
B) Anger at others for their condition
C) Tearfulness and self-directed anger for "being unable to control myself"
D) Indifference to the situation
B) Themselves
Clients experiencing panic attacks are at risk for harm primarily towards:
A) Others
B) Themselves
C) Animals
D) Property
B) Problems with sleeping and eating
Which of the following physiological and self-care concerns are commonly reported by clients with anxiety?
A) Improved appetite and sleep
B) Problems with sleeping and eating
C) Excessive physical activity
D) Poor self-care routines
Promoting safety and comfort
Provide a safe environment and privacy
Use of therapeutic communication
Simple and calm communication
Managing anxiety
Teach relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercise and guided imagery
Client and family education
Relaxation techniques
Emphasis on importance on compliance with medication regimen
Importance of participating in the community such as involvement with support groups
Provide at least 2 interventions in managing anxiety