Somatic Nervous System (2)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is myasthenia-like syndrome?
weakness/fatigue that progresses with exertion’
many etiologies (autoimmune attack against NM receptors, paraneoplastic, methimazole tx, congeital)
What does myasthenia-like syndrome cause muscle weakness?
less receptors mean can’t have as great of a response
How does an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor increase muscle contractions?
prevents breakdown of acetylcholine so effect lasts longer
recovers action potential in muscles to recover contraction
What is neostigmine?
IV
reversal of neuromuscular blockage
dx (and tx) of myasthenia-like syndrome (extra label)
tx of GI/bladder atony after SX (sheep, swine, cattle, horses)
What is pyridostigmine?
labeled for management of canine myasthenia-like syndrome
extra label use in cats
PO
Neostigmine/pryidostigmine are examples of ________ antagonists
physiological
do not interact with receptor itself
How is neostigmine used of neuromuscular junction blockage reversal?
increases longevity of acetylcholine so can outcompete atracurium
What is the central compartment of pharmacokinetics?
circulatory system, liver, kidneys, lungs
highly perfused tissues
drug is absorbed into it and then either distributed to peripheral of eliminated
only direct route is IV
The ______ compartment is the only convenient way to sample drug levels
central
What is the peripheral compartment of pharmacokinetics?
all other tissues (ie bone, spleen, brain)
most drugs act here
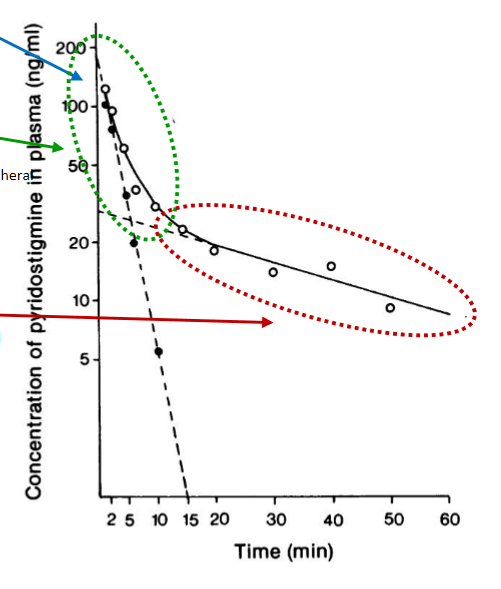
What is characteristic at blue, green, and red arrows?
blue - instant peak concentration after IV dose
green - distribution (initial drop off of drug concentration as moves from central → peripheral compartment)
red - eliminiation (via metabolism or excretion)
The amount of drug bound to target receptors is _______ compared to amount of available drug
negligible
tiny concentration to get effect but need huge concentration to get it to WHERE it causes effect
What is the duration of a drug effect related to?
the time drug is bound to receptor
What happens with decreasing blood levels?
regardless of potency efficacy will also decrease
except with covalently bound drugs or drugs that alter gene expression
What are drug factors that affect absorption?
solubility, dissolution, concentration, and pKa
What are some body factors that affect absorption?
blood flow, absorbing surface, contact time, pH
What is the primary site of enteral absorption?
small intestine
long, well perfused and thin mucosa
Longer GI transit times lead to ________ absorption
greater
cowers longer than cats and vary within species
Once the drug is absorbed by the intestine where does it go first?
enters portal circulation and exposed to liver first
Rank the routes of administration from greatest to best absorption
pulmonary
oral
percutaneous
T/F Elimination depends on administration route
False - only absorption cares about route
What is bioavailability?
fraction of drug absorbed
100% of IV but rarely that much of PO
What are some reasons 100% of PO drugs don’t make it to circulation?
inactivation in GI, transport of drug back into GI lumen, metabolism in GI mucosa/liver (first pass effect)
What is the first pass effect?
drug follows first pass of blood through system
will go into liver via portal system and metabolized then some may make it into circulation
How is bioavailability calculated?
area under curve oral admin X 100
area under curve IV
How do drugs enter the central compartment? Why?
simple diffusion
transporters in membrane are specifc as body regulates what comes into body very carefully
A drug must be what to cross bilayer?
uncharged and nonpolar
most drugs are weak acids/bases and will have charge depending on pH
A weak acidic drug is more acidic medium is what?
less charged
more lipid soluble
more rapidly absorbed
What is the equation to measure the amount of charged/uncharged weak acid?
pH - pKa = log (A-)/(HA)
A weak basic drug in more basic medium is what?
less charged
more lipid soluble
more rapidly absorbed
What is the equation to measure the amount of charged/uncharged weak base?
pH - pKa = log (B)/(HB+)
What is ion trapping?
accumulation of drug on once side of membrane due to pH differences across membrane
weak acids accumulate in basic environments
weak bases accumulate in acidic environments
Carnivores have more ______ stomach while herbivores have more ______ stomach
acidic, basic
dogs/cats - 1-3 pH
equine stomach - 2-6 pH (more acidic towards pylorus)
cows more basic in rumen (7 pH) and acidic i nabomasum (3.5)
How can ion trapping be used to increase drug excretion in urine?
make more acidic urine by ammonium chloride increases base elimination
make more basic urine by sodium bicarbonate increases acid elimination