chirality and organic acids
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
what are chiral molecules
a molecule that is not superimposable with it’s mirror image
what is the condition of becoming a chiral atom
containing at least one asymmetrically-substituted sp3 carbon atom
what is a stereoisomer (spatial isomer)
a type of isomer where the molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in thr 3D orientation of these atoms in space
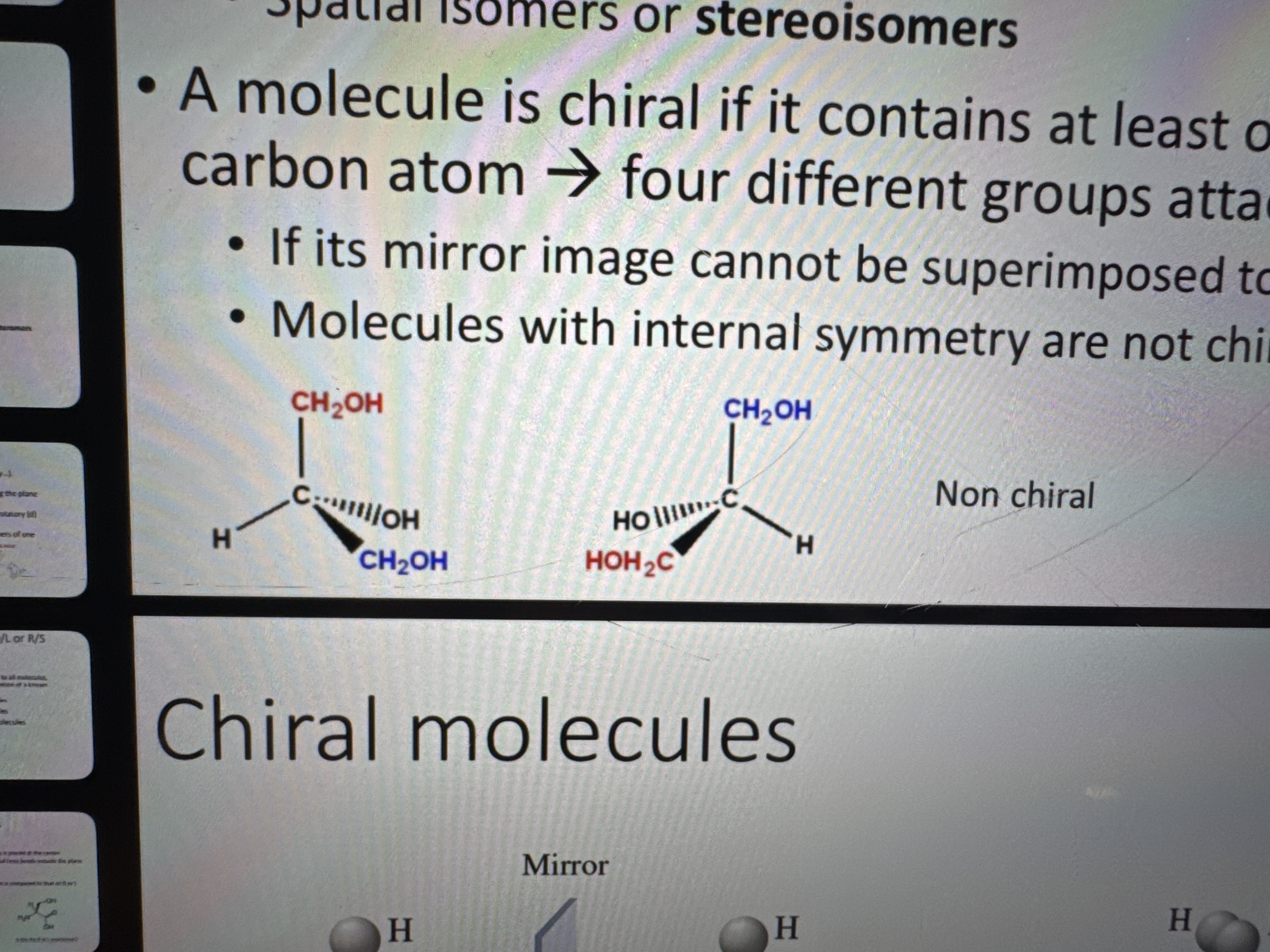
why are these two molecules not chiral
because the central atom doesn’t have four DIFFERENT groups attached to it
what is an enantiomer
optical isomer meaning two molecular entities that are mirror images pf each other but not super imposable
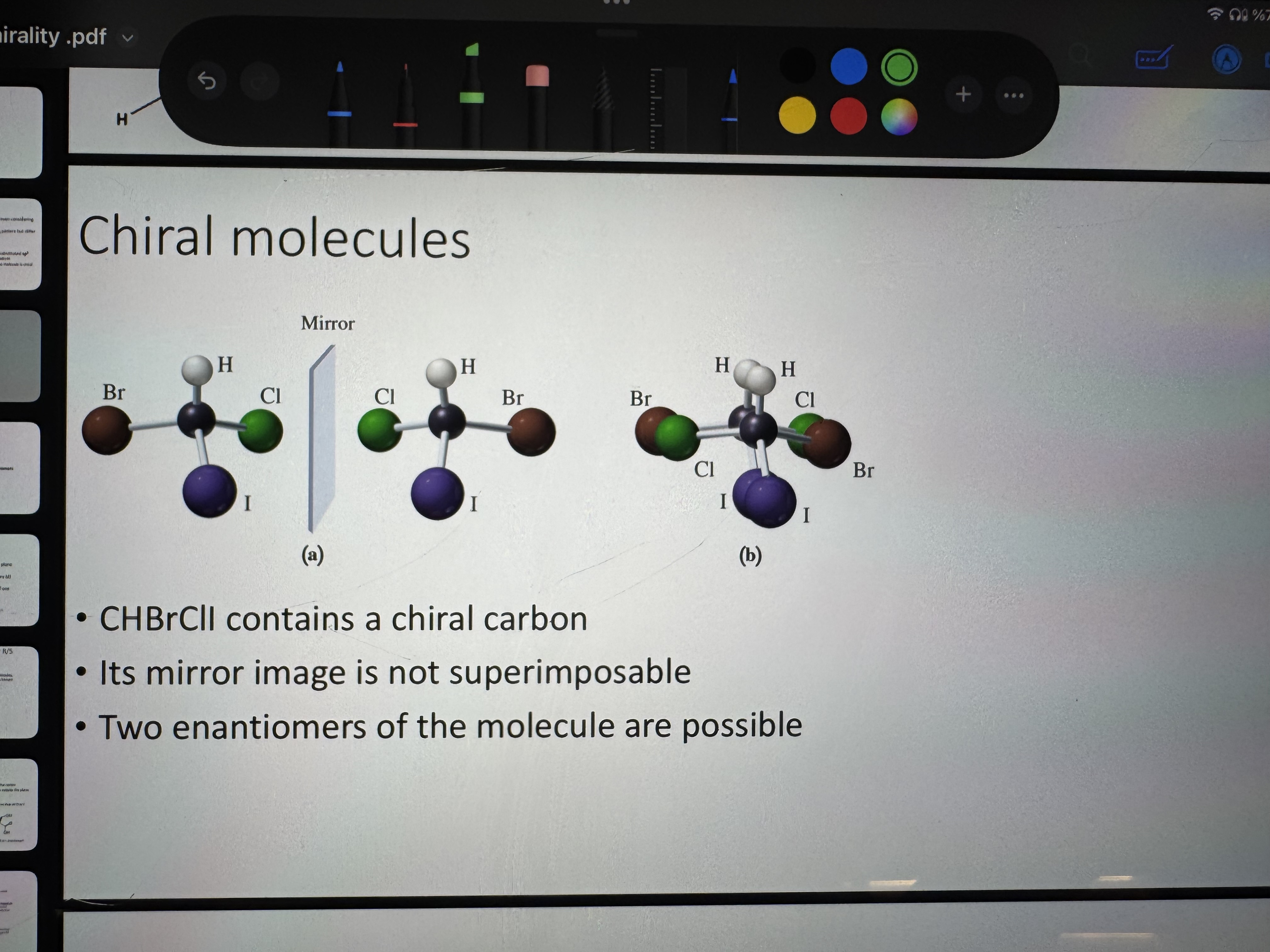
how do we calculate the number of stereoisomers
a molecule with N chiral centers can be represented by2^n stereoisomers
how do we calculate the number of enantiomeric pairs (enantiomers)2^{n-}
a molecule with n chiral centers will have 2^{n-1} enantiomers
what are diasteromers
it’s a type of stereomer. stereomers that are not mirror images of each other
do enantiomers and diastereomers have identical physical properties
enantiomers do diastereomers dont
what are the two types of enantiomers
dextrorotatory (d) and levorotatory (l)
how do dextrorotatory and levorotatory enantomers rotate light
dextrorotatory rotates the light clockwise
levorotatory rotates the light counter clockwise
a 50% mixture of the d and l enantiomers doesn’t rotate the plane of a polarized light
what is the difference between diastereomers and enantiomers
they are both stereomers but diastereomer is not the mirror image and enantiomer is the mirror image (enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other)
what are the two configurations of chiral centers
the D/L system and the R/S system
the d/l system representation
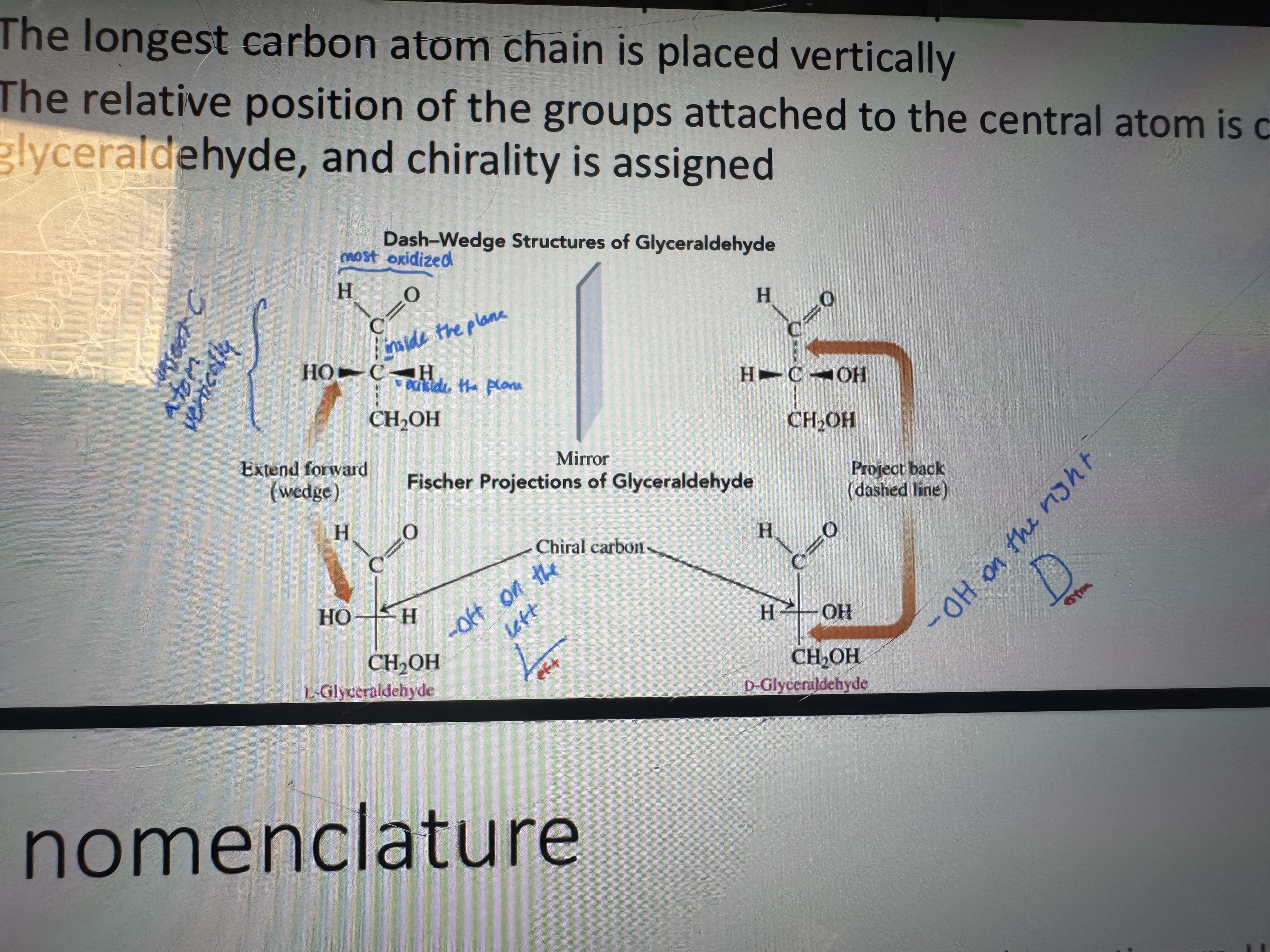
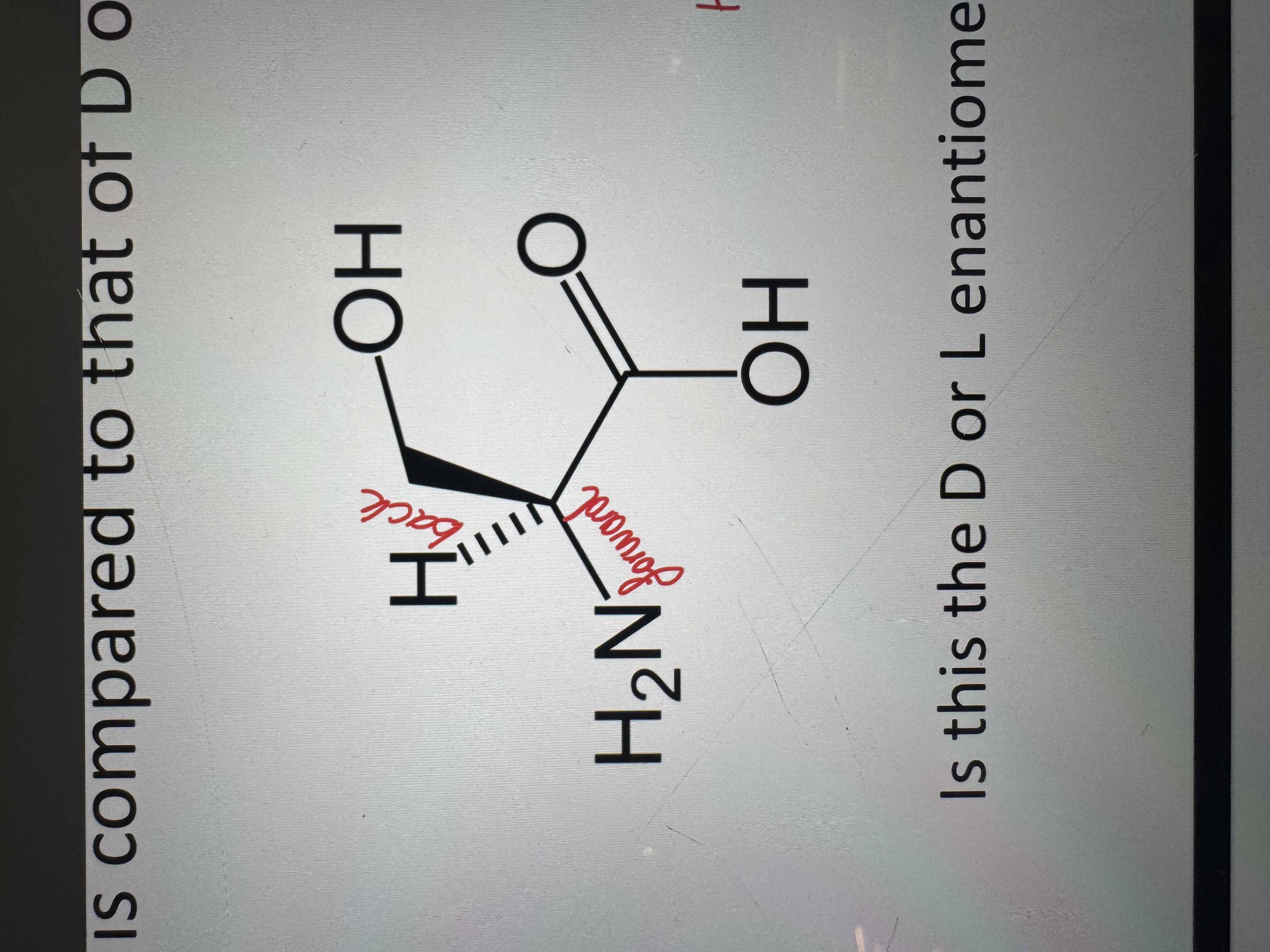
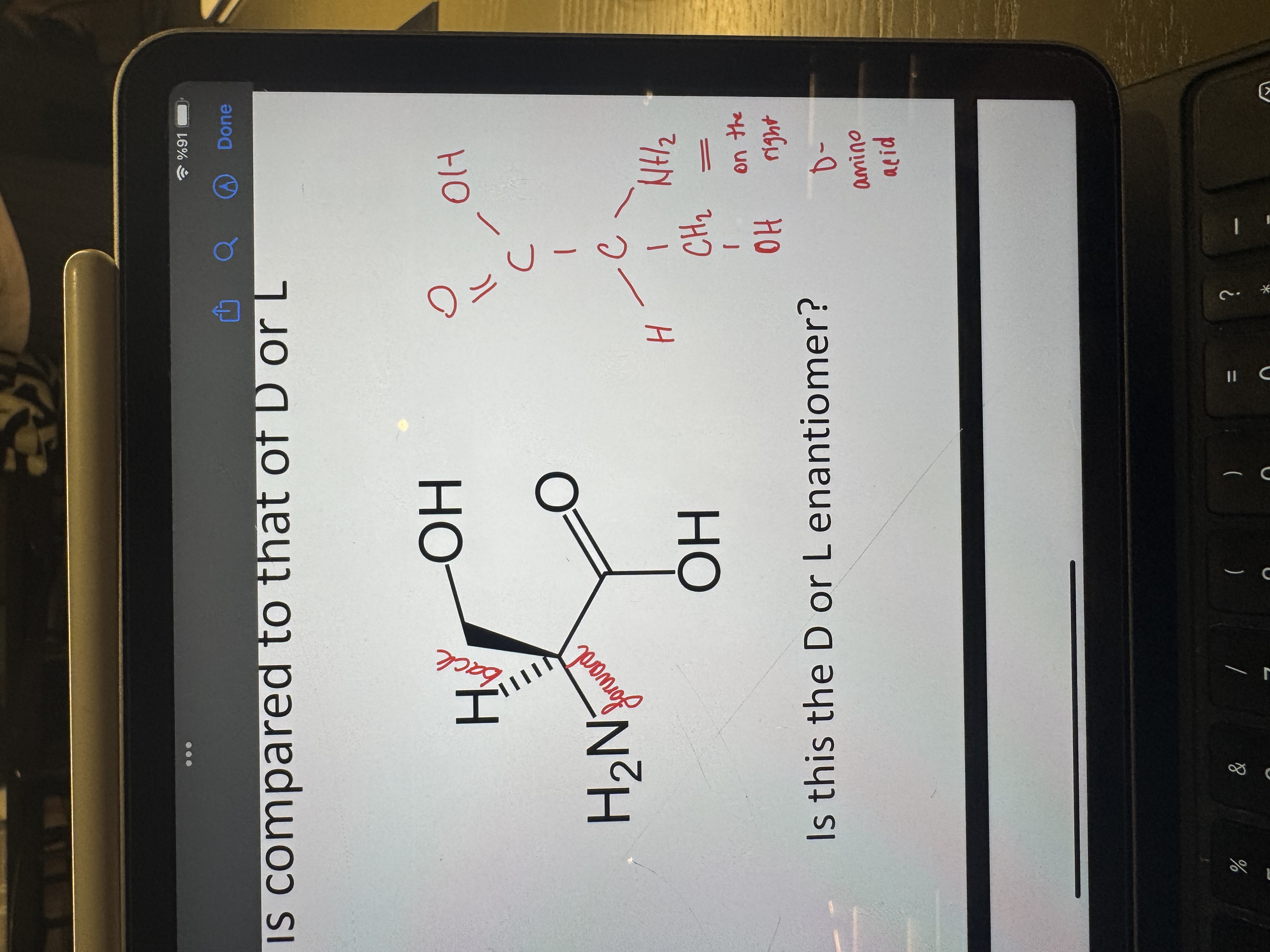
is this a d or l enantiomer
d-amino acid
what is the d/l system estanlished for
carbohydrates
how to do the r/s configuration

when is a molecule not chiral
when the carbon atom has two identical substituents
what is a molecule that isn’t chiral bur can become chiral with a chemical reaction called
prochiral carbon atom
when is an enantiomer s and when is it r
R when it’s numbered clockwise
S when it’s numbered counter clockwise
what is used for the synthesis of proteins
only L-amino acids
how many in 20 proteins have chiral centers
19 of them have at least one chiral center
how many chiral centers does a ribose have
3 or 4 chiral centers
what is a racemic mixture
50% mixture of d and l enantiomers
give an example of chirality used in medicine
talidomide: ipnotic to fight nausea
it is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers (R-talidomide and S enantiomer)
R is sedative and S is teratogenic but they interconvert due to keto-enol tautomerism
what is the common name of methanoic acid and ethnoic acid
methanoic acid: formic acid
ethanoic acid: acetic acid
what is the hybridization of carboxylic acids
sp2
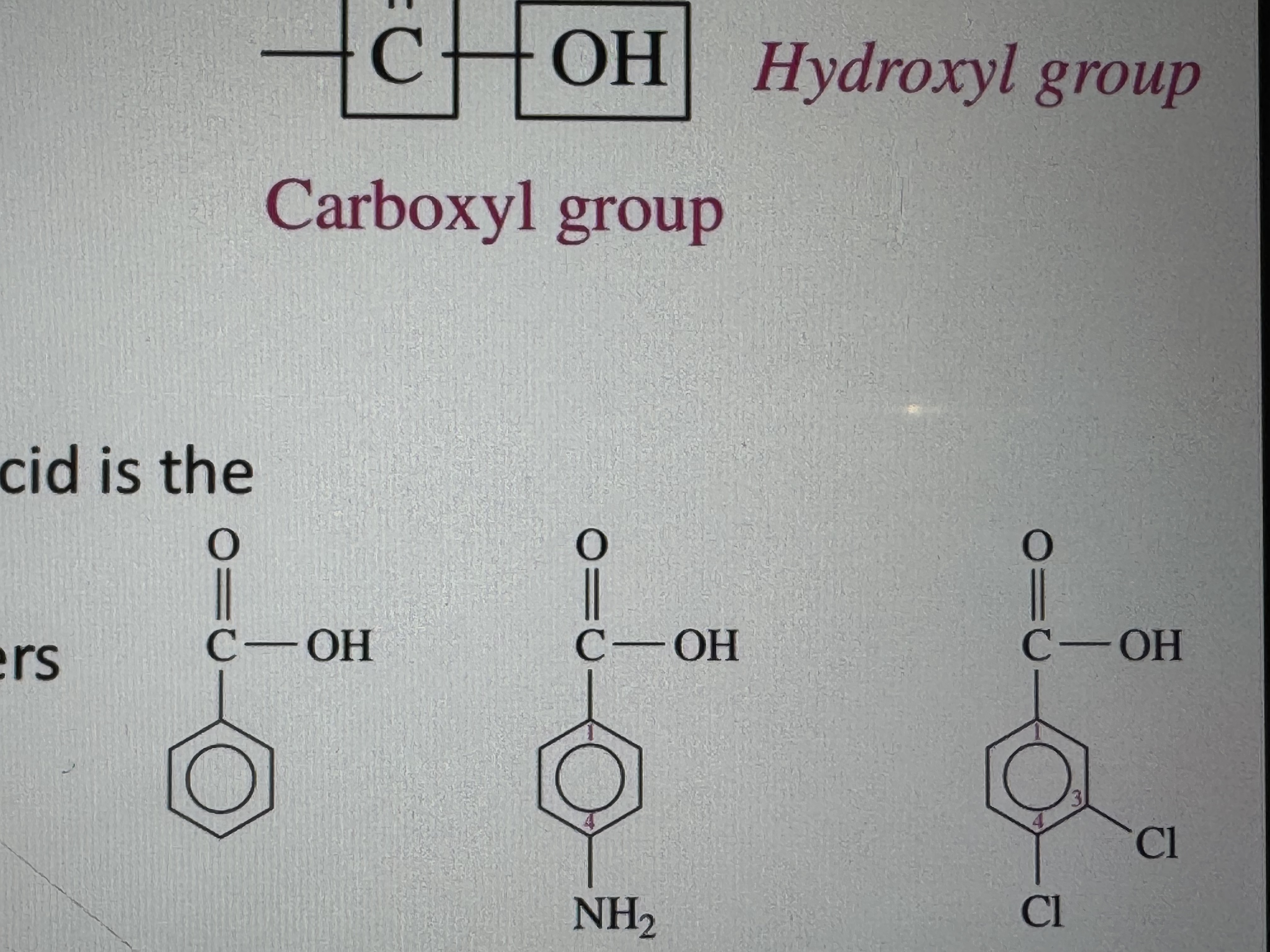
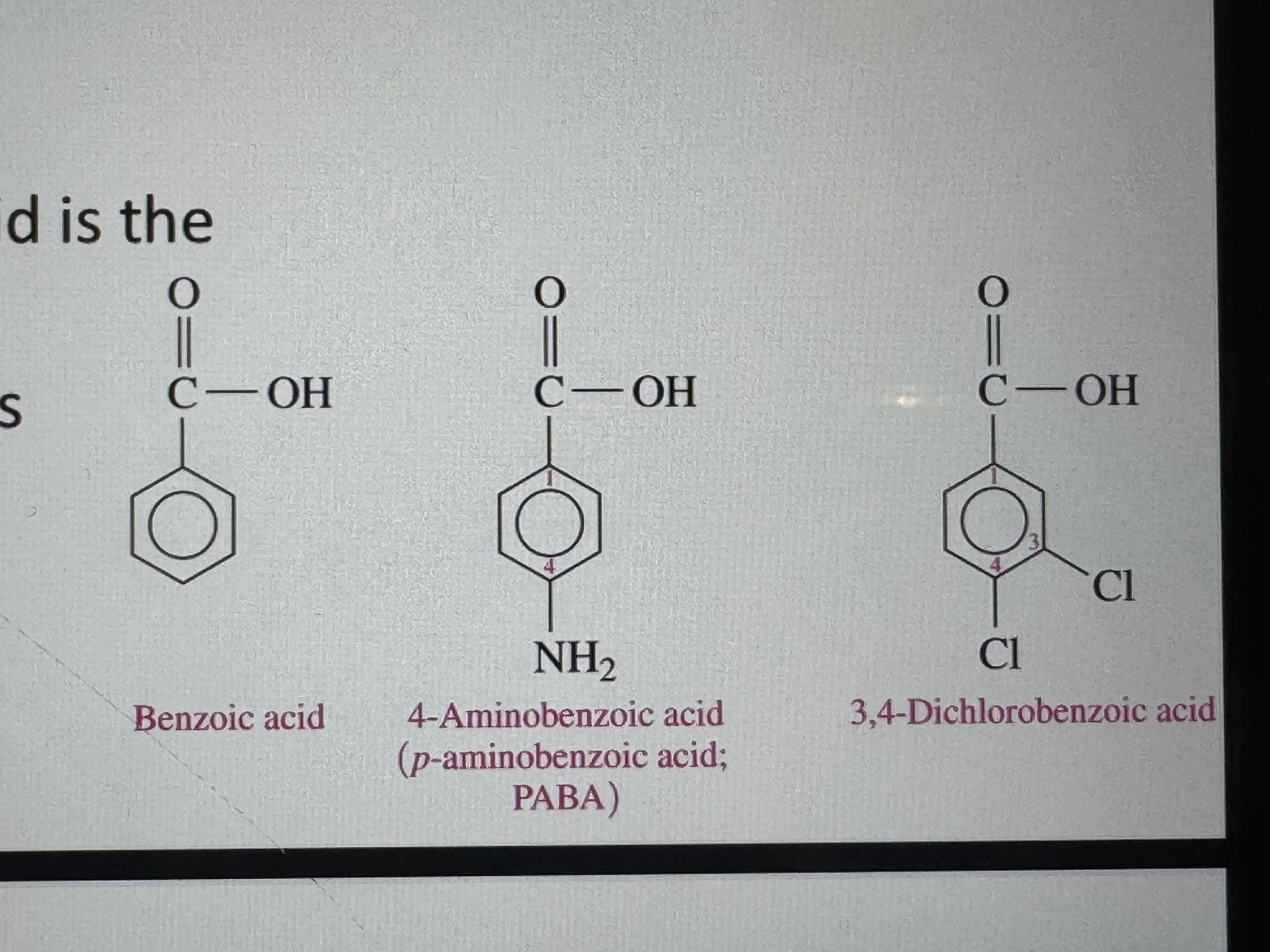
name these
what do we get when we oxide an aldehyde
carboxylic acid
how does ethanol become ethanoic acid (acetic acid)
we oxidize ethanol to get acetaldehyde (ethanal) then oxidize it again to get ethanoic acid = we oxidized it twice
are carboxilic acids soluble in water
yes but it becomes less soluble as chain gets longer (>5 carbons)
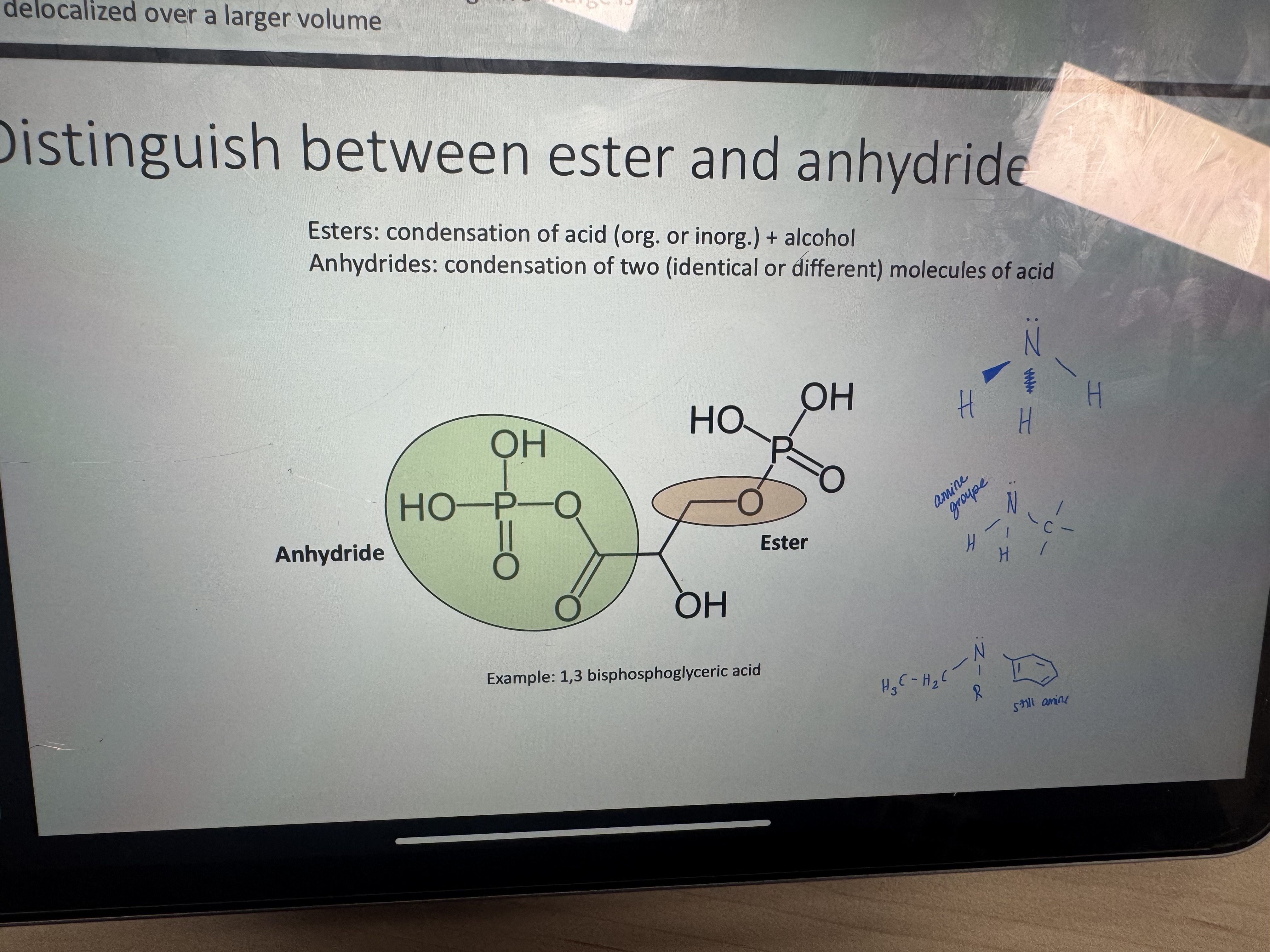
how is an anhydride formed
when two molecules of acid undergo condensation amd lose a water molecule (can be symmetric if it’s two molecules of same acid or asymmetric)
why are anhydrides highly reactive with nucleophiles (including water)
to give two molecules of acid in a highly exergonic reaction
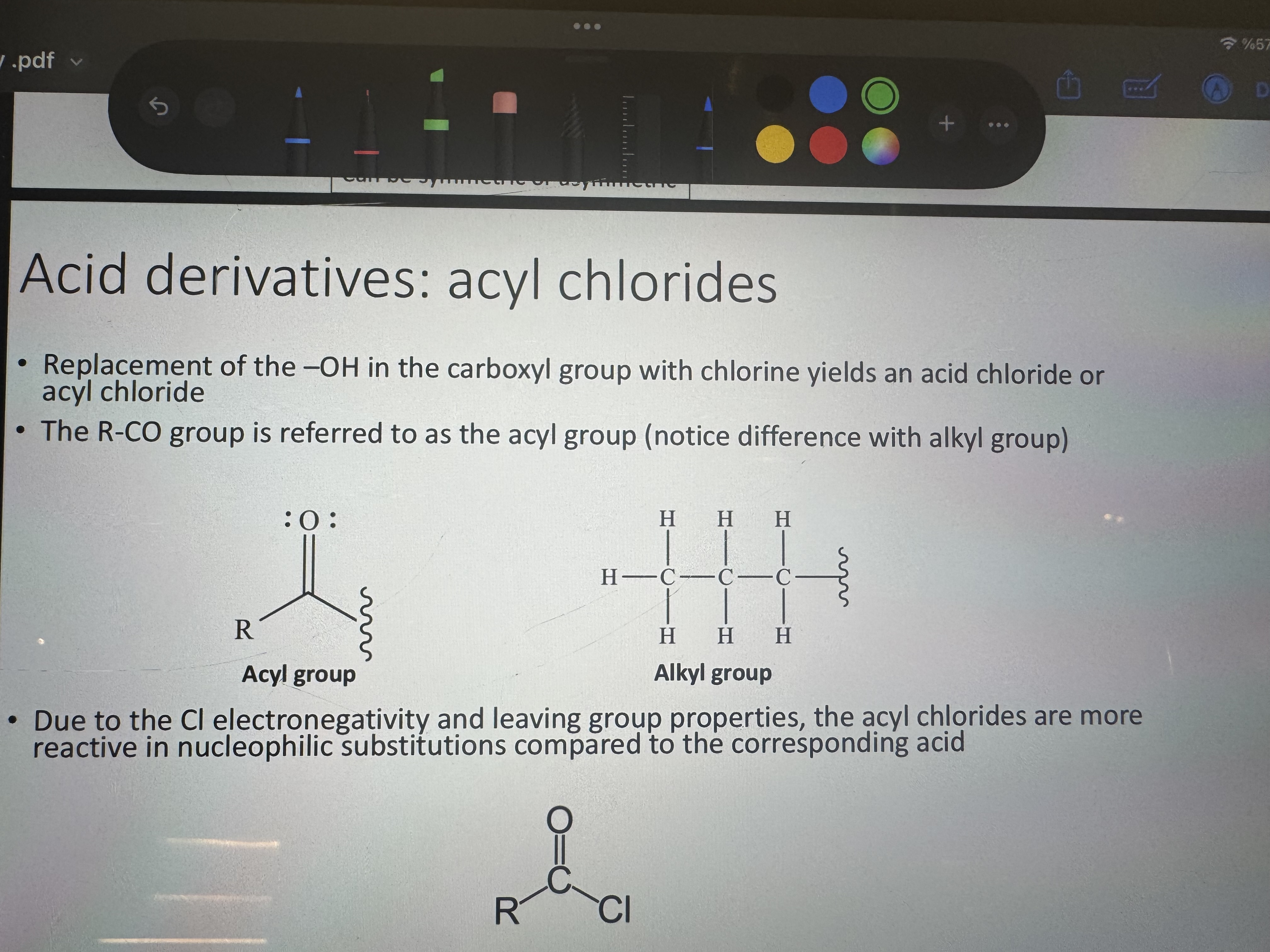
what do we replace in the carboxyl group with what to get an acyl chloride or an acid chloride
replacement of -OH in the carboxyl group with chlorine
acyl and alkyl group representation
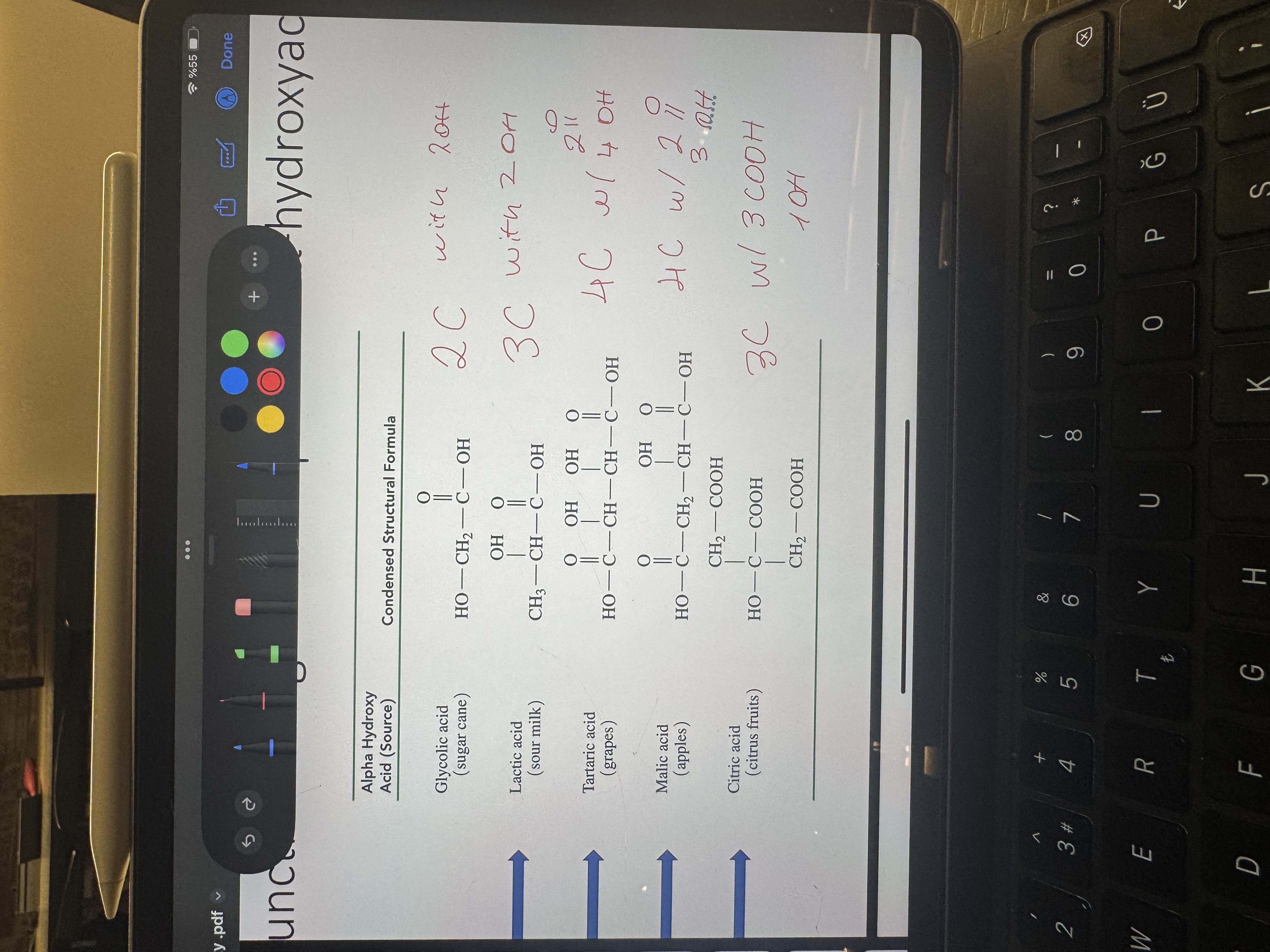
alpha hydroxyacids table
what are dicarboxilix acids
organic molecules containing two -COOH groups
dicarboxilic acids to memorize their names and structures

what is an alpha ketoacid
a carboxylic acid that have a keto group directly attached to the COOH
what are the other names of alpha-ketopropionic acid and alpha-ketoglutaric acid
pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate
when we reduce the ketone group what do we get
hydroxyl
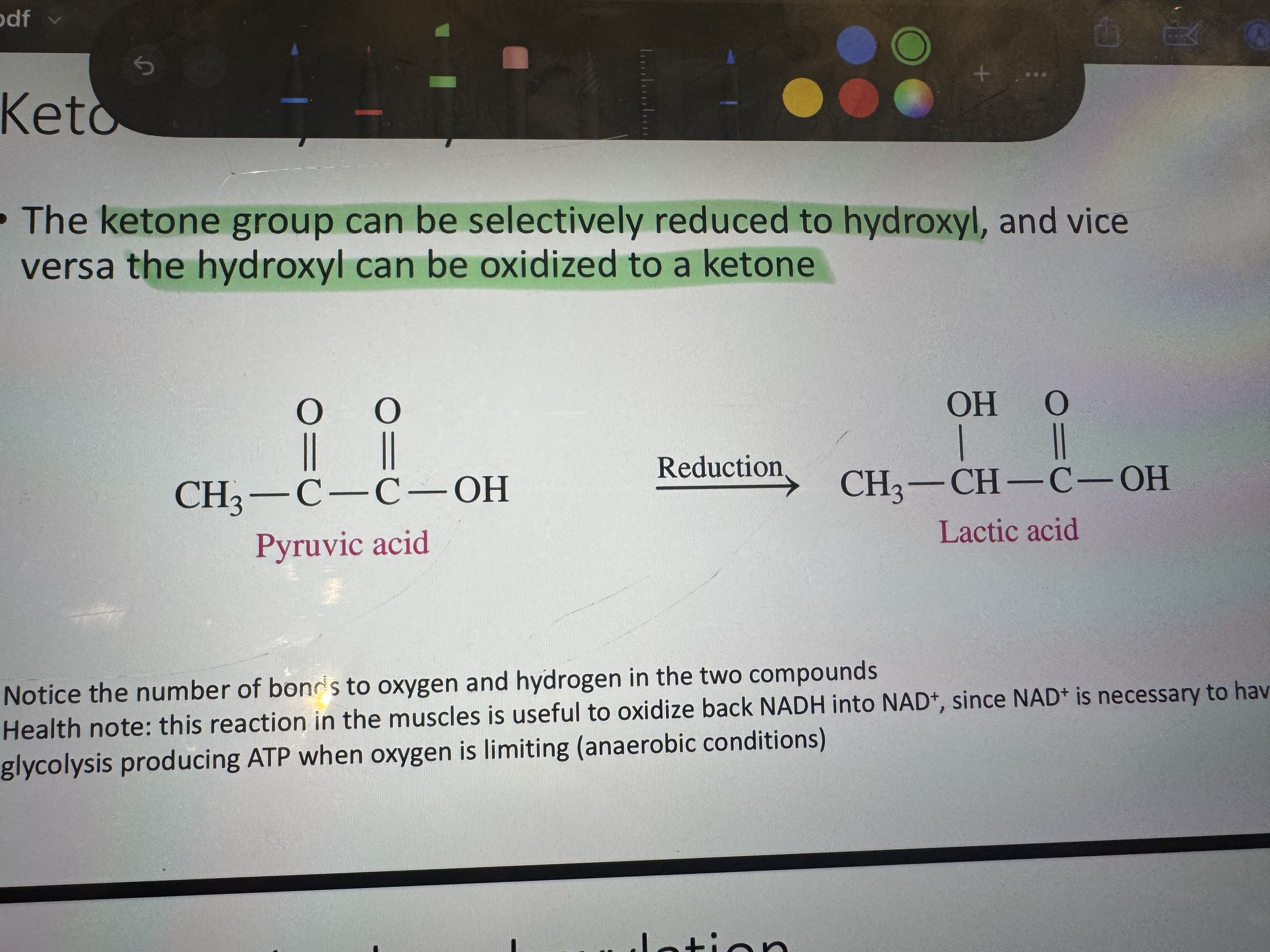
where in our body do we see the reducing of ketone group to hydroxyl as pyruvic acid turning into lactic acid
this reaction in the muscles is useful to oxidize back NADH to NAD+
what is the common name of 3-oxobutanoic acid or beta-ketobutanoic acid
acetoacetic acid
decarboxylation, loss of CO2 in acetoacetic acid
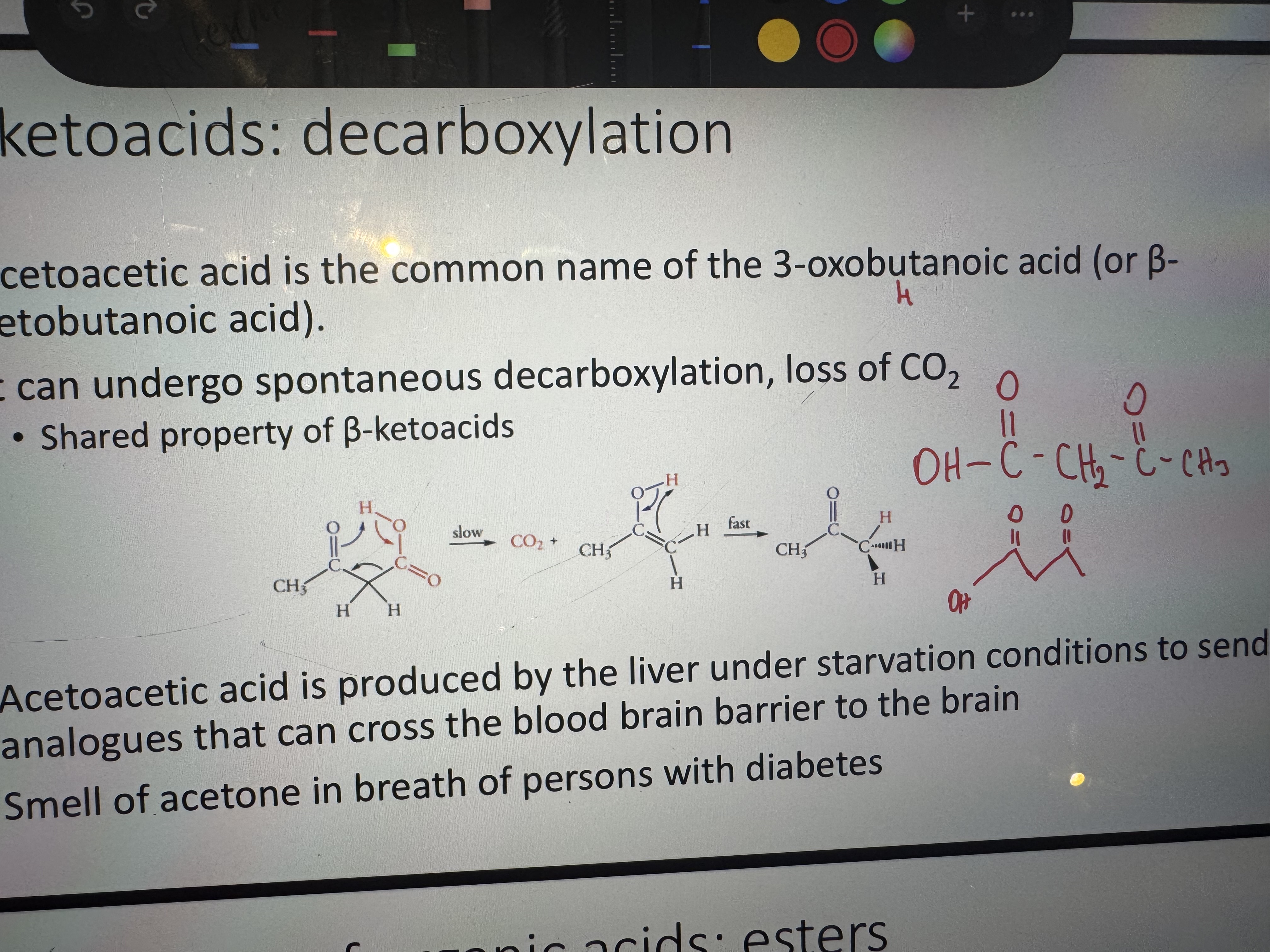
why is acetoacetic acid produced
it’s produced by the liver under starvation conditions to send lipid analogues that can cross the blood brain barrier to the brain
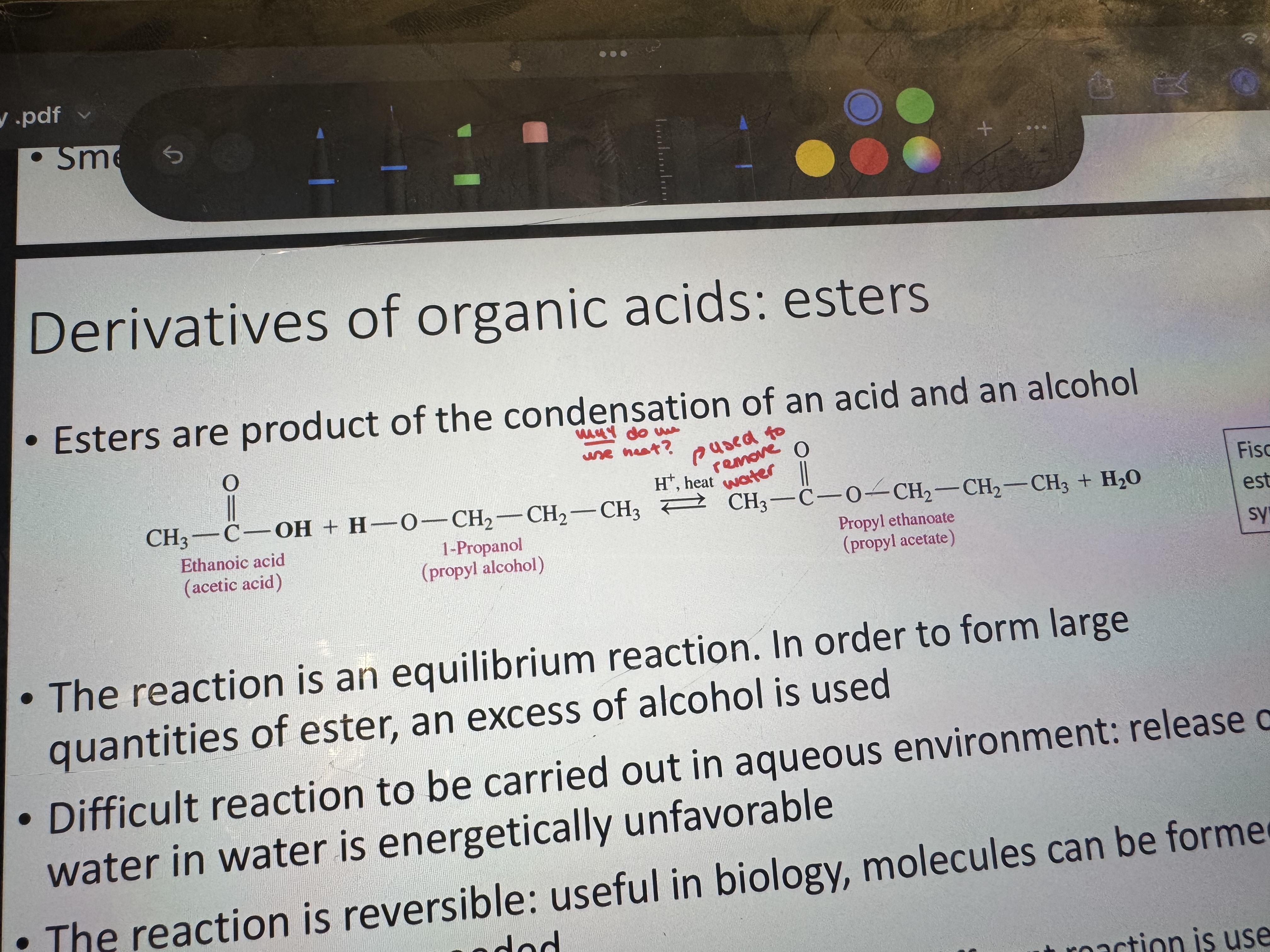
what is the product of condensation of an acid and an alcohol
an ester
why do we use heat for the condensation of alcohol and an acid
to remove h2o
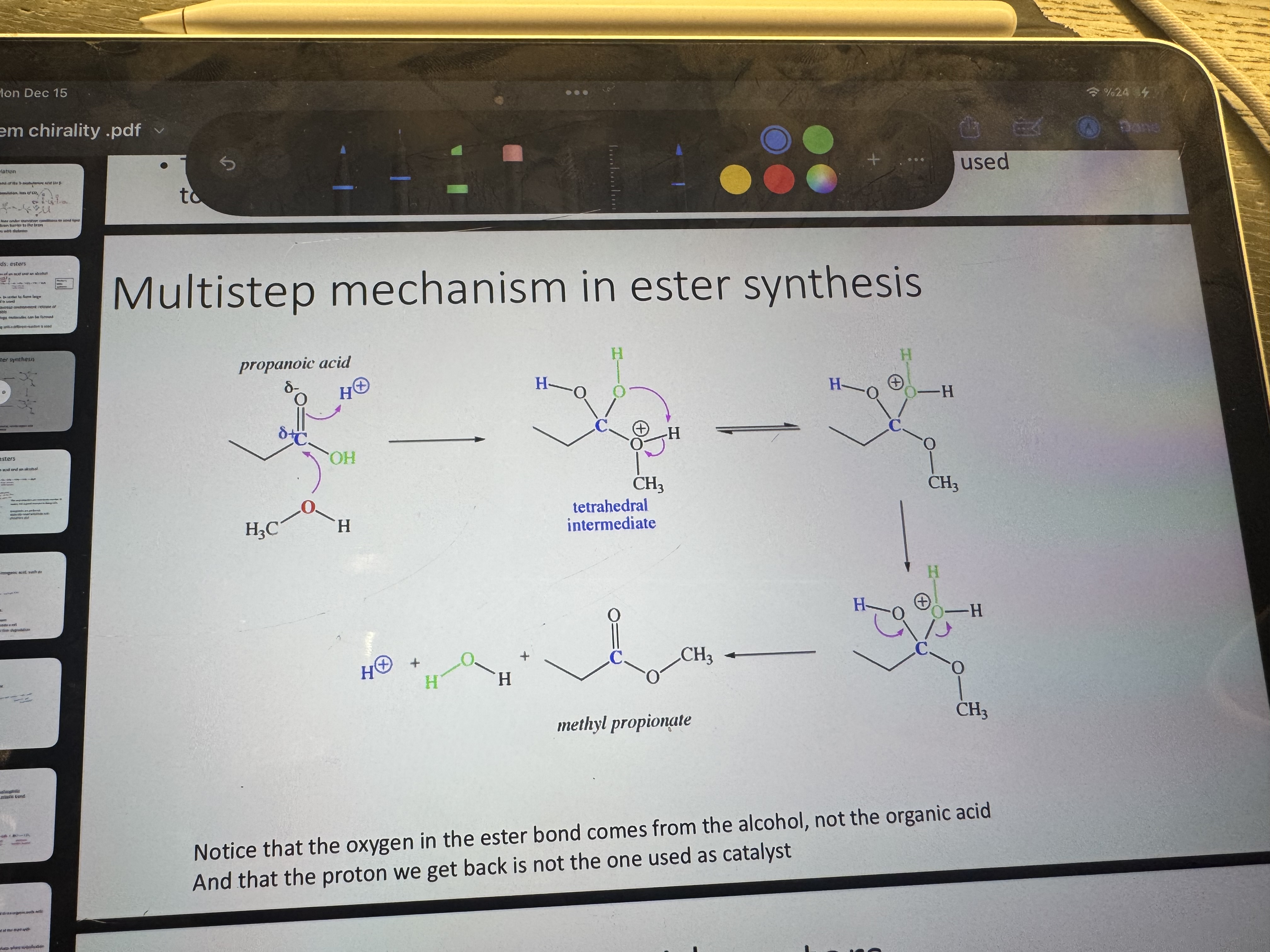
multistep mechanism in ester synthesis
phosphate esters are used to:

naming esters
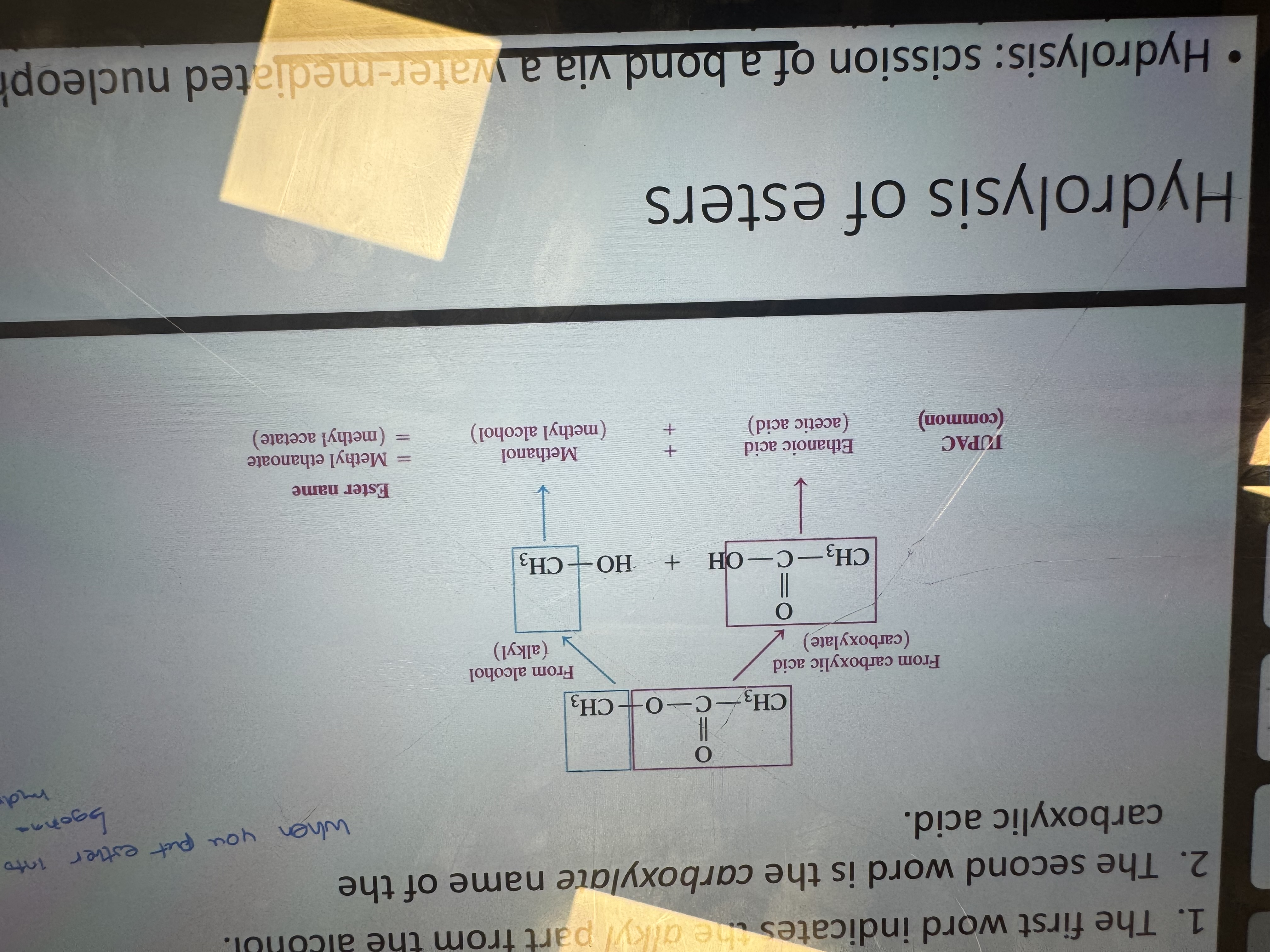
what happens in the hydrolysis of esters
-it’s the opposite of the synthesis from acid and alcohol and is catalyzed by acids or bases.
-scission of a bond via a water-mediated nucleophilic attack
-C-C bonds are hyrolyzed slowly if at all
-C-O bonds can be hydrolyzed
examples of esters in biology
tryacylglycerides, phospholipids and phosphorylated amino acids (serine, threonine, tyrosine)q
what is a thioester
product of condensation between an acid and a thiol (sulfur containing alcohol)
why is it important that sulfur is bigger in size than oxygen
because it’s easier to hydrolyse the thioester and it has a longer bond
what is a thioester used for
to activate carboxyl-containing compounds for reactions
why are thioesters better than esters transferring an acyl group
Thioesters transfer acyl groups better because they are less resonance-stabilized and have better leaving groups
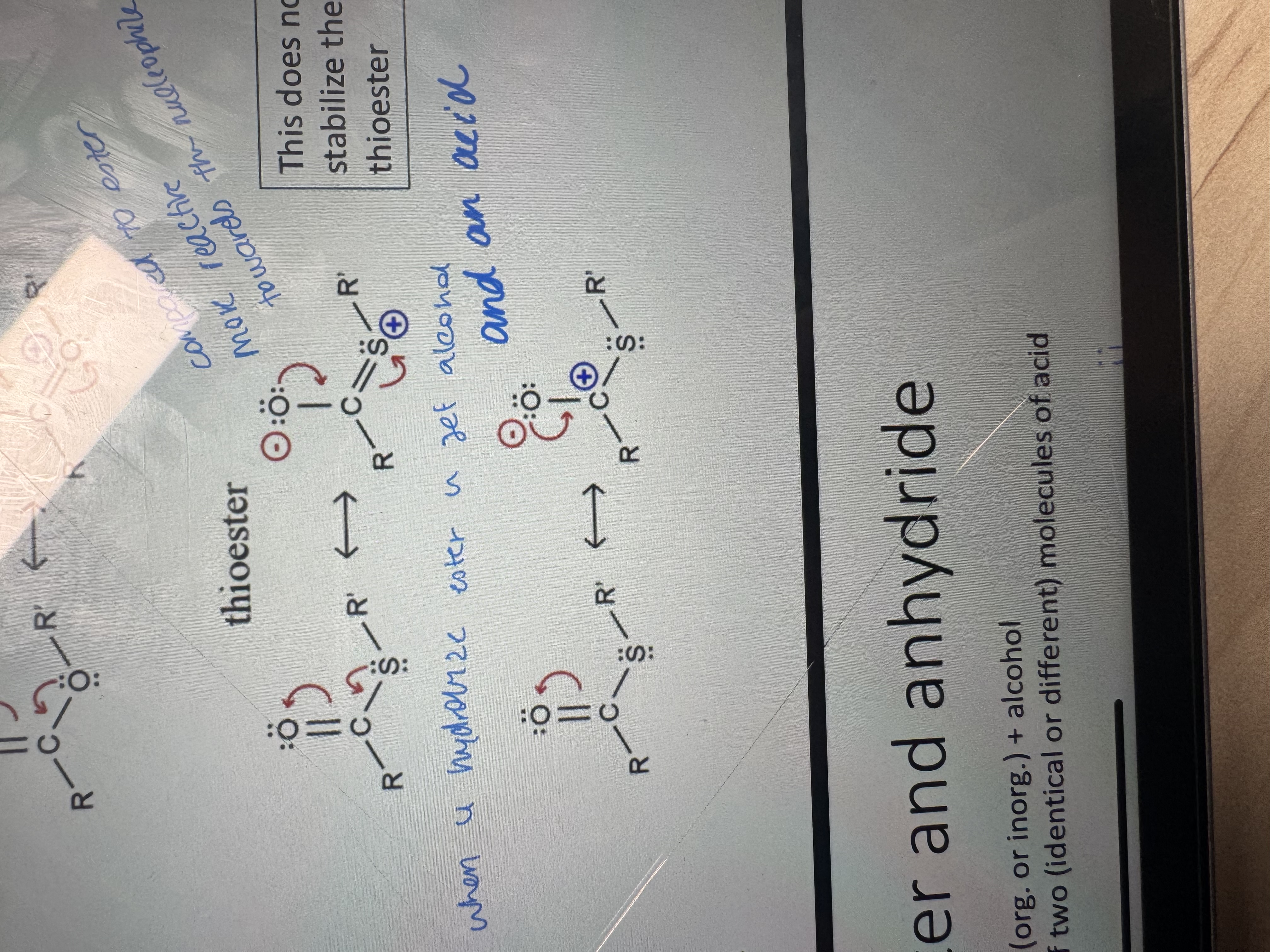
among these two thioesters which one of them is more preferred and stable
on the first one the 2p orbitals of O and 3p orbitals of S don’t superimpose well to form a pi bond due to their different sizes thus the only resonance form one can draw for a thioester is one with a charge separation between O and S like the second one
which one is more reactive an ester or a thioester
thioester is more reactive because the carbonyl carbon has a larger partial positive charge thus more reactive in nucleophilic substitutions
which one is a better leaving group the thiol or or the alcohol group?
thiol is because the negative charge is delocalized over a larger volume
ester vs anhydride