PPT 4: Proximal Joints - An In-Depth Study of Elbow and Distal Radioulnar Movement Mechanics
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What are the characteristics of a synovial joint? (4)
1. Freely movable
2. A joint capsule lined by synovial membrane
3. Synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid
4. Joint surfaces lined with articular cartilage
What are three ways to classify a synovial joint?
1. Number of Articulating Surfaces
2. Shape of Articulating Surfaces
3. Degrees of Freedom
Simple joint
Two articulating surfaces
Compound joint
More than two articulating surfaces
What is a ball and socket joint?
joint movement that provides the widest range of motion in all planes (ex. shoulder and hip)
Complex joint
Two or more articulating surfaces and fibrocartilage disc or meniscus
What is a condyloid joint?
joint movement that goes forward-backward and side to side movement and does not allow rotation (ex. joint between radius and carpal bones of wrist)
What is a planar joint?
joint movement that is gliding, often with articulating surfaces that are flat, or curved (ex. joint between tarsal bones)
What is a saddle joint?
Two bones that fit together like a rider in a saddle; allows for flexion/extension and abduction/adduction (ex. between trapezium carpal bone and 1st metacarpal bone)
What is a hinge joint?
Joint movement that is limited to extension and flexion (ex. elbow and knee)
What is a pivot joint?
Joint movement that allows only rotary movement around a single axis (ex. between CV1 and CV2)
What is uniaxial DOF?
movement in one plane (ex. elbow joint - hinge)
What is biaxial DOF?
movement in two planes (ex. condyloid or saddle joints)
What is triaxial DOF?
movement in three plans (ex. ball and socket joints)
What is the sternoclavicular joint comprised of? (3)
1. Medial end of clavicle
2. Clavicular notch of manubrium
3. Cartilage of first rib
What is the number of articulating surfaces of the sternoclavicular (SC) joint?
Complex joint; 2 or more articulating surfaces + articular disc
What is the shape of articulating surfaces of the SC joint?
Saddle or modified ball and socket
What is the degrees of freedom of the SC joint?
Tri-axial, 3 DOF, 6 movements
What are the movements of the SC joint (clavicle)?
1. Elevation/Depression (Anterior-Posterior axis)
2. Anterior/Posterior rotation (Medial-Lateral axis)
3. Retraction/Protraction (vertical axis)
What is the ligamentous support to the SC joint?
1. Interclavicular ligament
2. Anterior Sternoclavicular
3. Posterior Sternoclavicular
4. Costoclavicular (anterior & posterior lamina (plate))
How common are SC joint dislocations?
Very rare due to the strong ligamentous support and disc
What is the acromioclavicular joint comprised of? (2)
1. Lateral end of the clavicle
2. Medial margin of acromion of scapula
What is the function of the acromioclavicular joint? (2)
1) To maintain relationship between clavicle and scapula
2) To allow additional ROM during shoulder motions
What are the number of articulating surfaces of the acromioclavicular joint?
Complex: Two articulating surfaces + articulating disc often present
What is the shape of articulating surfaces of the acromioclavicular joint?
Planar (gliding joint)
What are the degrees of freedom in the acromioclavicular joint?
Tri-axial, 3 DOF, 6 Movements
What are the movements of the AC joint?
1. Elevation/Depression
2. Anterior/Posterior Translation (occurs during Protraction/Retraction of scapula)
3. Anterior/Posterior Rotation (occurs during humeral elevation)
What is the ligamentous support of the AC joint? (3)
1. Acromioclavicular ligament
2. Coracoacromial ligament
3. Coracoclavicular ligament (conoid & trapezois)
What does the acromioclavicular ligament do?
Strengthens anterior and inferior aspect of joint; capsular thickenings
What does the coracoclavicular ligament do?
- Extrascpaular (situates outside of capsule)
- Critical, limits large excursion and medial displacements. - Comprised of conoid and trapezoid
What does the coracoacromial ligament & arch do?
Provides a protective roof over G/H joint, muscles, tendons, and bursae, but may be a site for impingement
What is an impingement of the AC joint?
When you elevate your arm overhead, structures can get pinched
What is a dislocation of the AC joint?
Mainly from contact sports, blow to shoulder, may occur with fracture of the coracoid process
What is impingement syndrome?
Entrapment of the 1) supraspinatus tendon or 2) rotator cuff mechanism or 3) subacromial-deltoid bursa; and/or 4) the biceps tendon between the humeral head and coracoacromial arch
What does impingement often occur with?
Repetitive overhead activities, which are common among painters, plumbers, and construction workers
What are the glenoid of scapula characteristics in the G/H joint? (3)
1) One shallow pear shaped conacavity, deepened by glenoid labrum
2) Superior/inferior axis longer than medial/lateral axis
3) Faces laterally, anterior & superior in scapular plane
What are the head of the humerus characteristics in the G/H joint? (2)
1. One rounded ball shaped convexity angled 135 degrees superiorly
2. Faces medially, slightly posterior & superior
What is the number of articulating surfaces in the G/H joint?
Complex: possesses a labrum
What is the shape of articulating surfaces in the G/H joint?
Ball and socket
What is the degrees of freedom in the G/H joint?
Tri-axial, 3 DOF, 6 movements
What does the G/H joint labrum do?
It circles periphery of glenoid fossa to make the joint more stable
Where is the G/H joint capsule located?
Attaches medially to the margins of the glenoid and laterally to anatomical neck of humerus
What does the G/H joint capsule do?
It encloses the proximal attachment of long head of biceps
Where are the two openings in the G/H joint capsule?
1) Passage of long head of biceps
2) Anteriorly (subscapular bursa and synovial cavity)
What is the ligementous support at the G/H joint?
1) Glenohumeral ligaments (capsular ligaments)
2) Coracohumeral Ligament
3) Transverse Humeral Ligament
What is the glenohumeral ligaments comprised of?
Superior, middle, and inferior bands that strengthen anteriorly
What is the Foramen of Weitbrecht?
The space for potential dislocation between superior and middle bands of glenohumeral ligament
What is the coracohumeral ligament comprised of?
Capsular ligament to strengthen G/H joint superiorly
What does the transverse humeral ligament do?
Attaches from greater to lesser tubercle to hold the tendon of the long head of the biceps in place
What is a bursa?
a fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid, located at points of friction between muscles
What is synovial fluid?
- viscous solution found in synovial joints
- reduces friction between articular cartilage
- lubricates the joint and provides nourishment to joint via diffusion
Where is the subscapularis bursa?
Between the tendon of subscapularis muscle and the G/H joint capsule
Where is the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa?
Superficial to the supraspinatus tendon and distal muscle belly, and deep to acromion and deltoid muscle
Where is the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa susceptible to impingement?
Under coracoacromial arch
Where does a labral tear occur?
Superiorly or inferiorly
What is a SLAP lesion?
Superior labrum, anterior to posterior tear, may also include biceps tendon
What is a Bankart lesion?
Tear of inferior labrum, also involves the inferior glenohumeral ligament
What are labral tears comorbid with?
Shoulder dislocations
How can a labral tear occur? (2)
1) Direct fall or blow to the arm resulting in abnormal movement of the humerus
2) Repetitive trauma between greater tubercle and rotator cuff under the coracoacromial arch
What would happen if labral tear is left untreated?
It will start to cause harm to articular cartilage, then could cause arthritis
What is at the distal end of the humerus?
2 articulating surfaces facing 45 degrees from humeral shaft (trochlea and capitulum)
What is the trochlea articulating surface?
Medial, spindle shaped with a central depression. It's concave from medial to lateral and convex from anterior to posterior
What is the capitiulum articulating surface?
Lateral; 1 spheroidal rounded convexity
What is the proximal radius articulating surface?
1 shallow concavity
What is the proximal ulna articulating surface?
1 deep concavity; longer Superior-Inferior than Medial-Lateral; ridges located superior and inferior
What are the articulating surfaces of the elbow joint?
Compound: 1) capitulum 2) trochlea 3) radius 4) ulna
What is the shape of articulating surfaces of the elbow joint?
Hinge or ginglymus
What are the degrees of freedom of the elbow joint?
Uni-axial; 1 DOF; 2 movements
What are the movements of the elbow joint?
Flexion and extension (Medial-lateral)
Does the elbow joint have a joint capsule?
Yes, an extensive one
Where are the three fat pads in the elbow joint?
1) Olcecranon fossa
2) Coronoid fossa
3) Radial fossa
What is the ligamentous support of the elbow joint?
1) Ulnar collateral ligament
2) Radial collateral ligament
What are the characteristics of the ulnar collateral ligament?
- Medial ligament
- Triangular shaped
- Three bands (anterior, oblique, posterior)
What does the ulnar collateral ligament do?
Provides reinforcement for the humeroulnar articulation against valgus joint stress, with the anterior band being the primary stabilizer
What are the characteristics of the radial collateral ligament?
- Lateral ligament
- fan shaped
What does the radial collateral ligament do?
Provides reinforcement for the humeroradial articulation against varus stress (resists medially directed force)
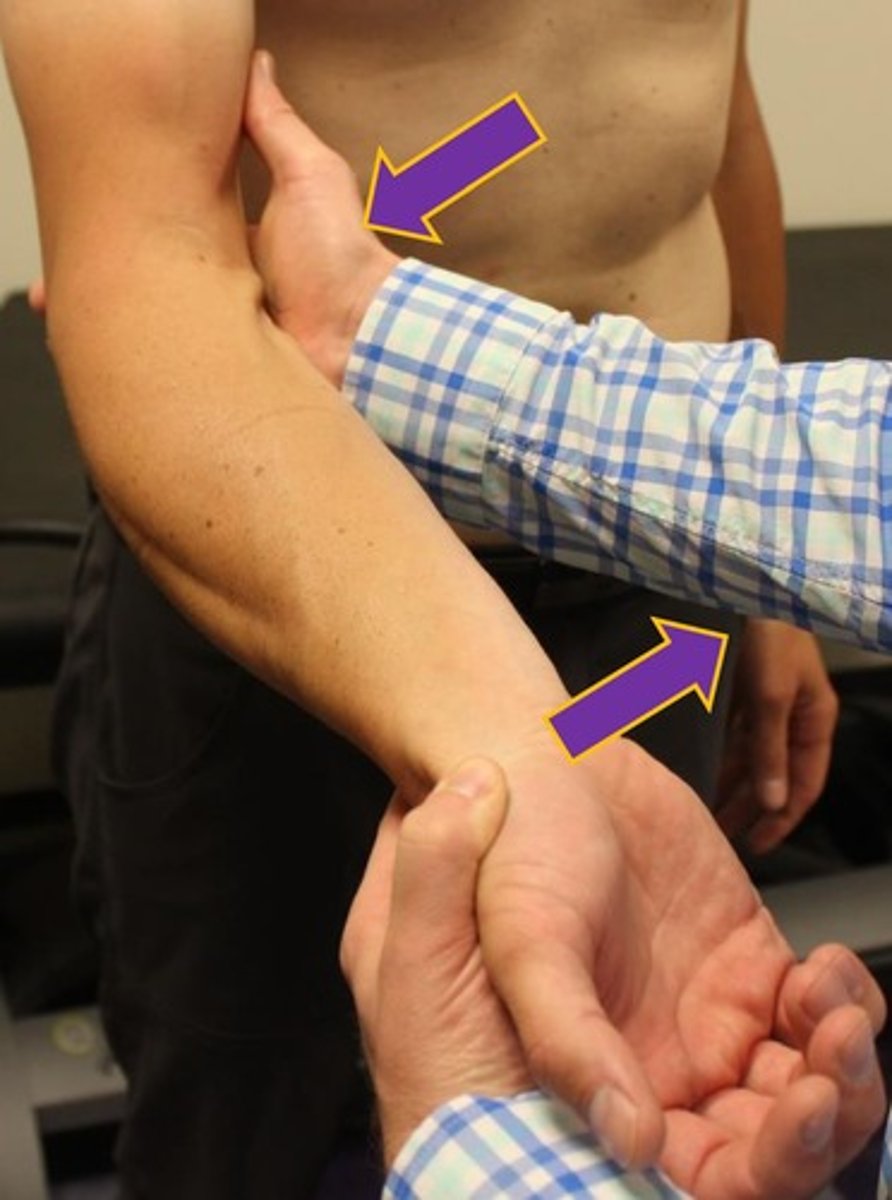
What is a valgus stress?
medially directed force at elbow, and laterally directed force at wrist
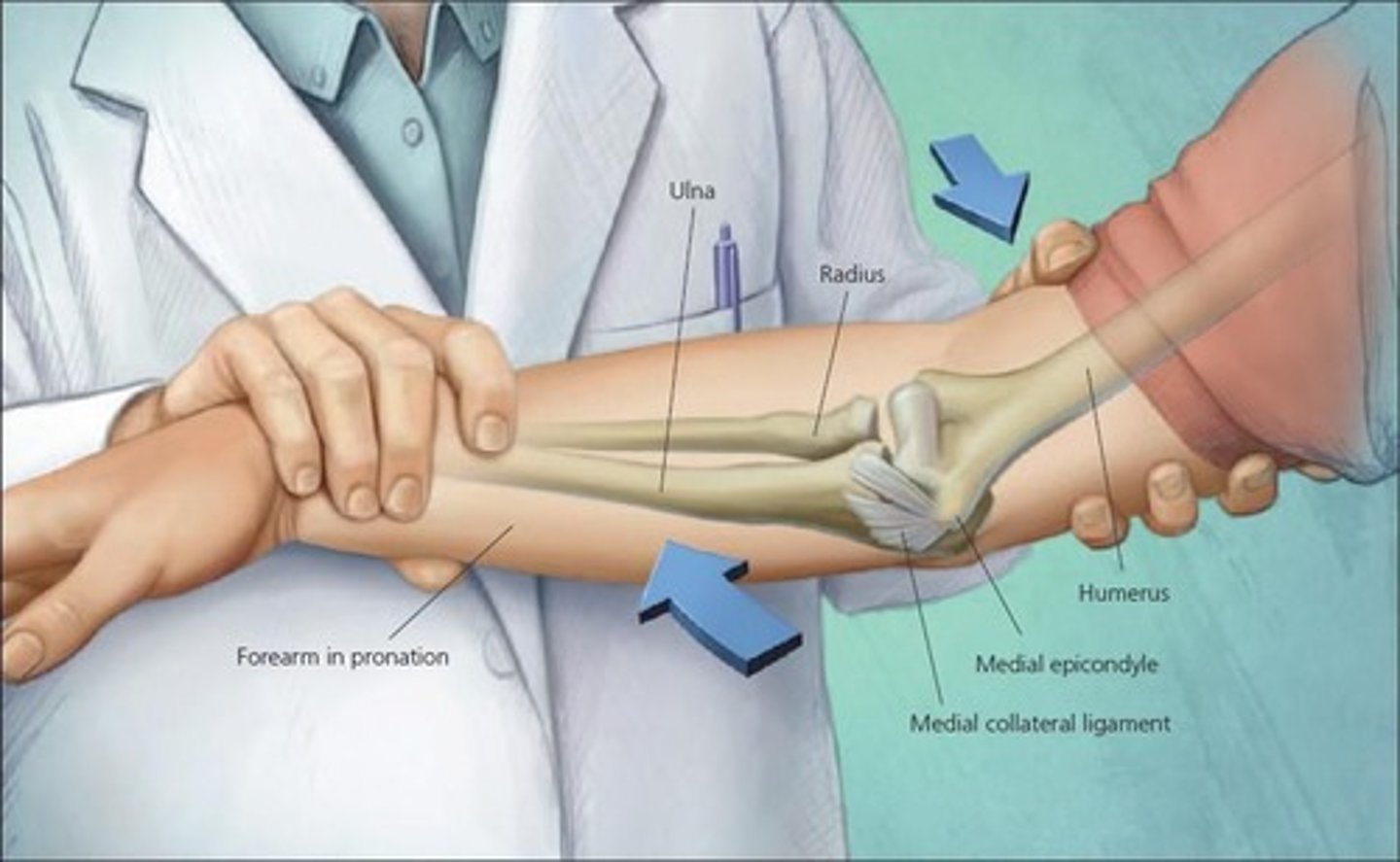
What is a varus stress
laterally directed force at elbow, and medially directed force at wrist
What is more common valgus or varus stresses at elbow?
Valgus
What is Tommy John surgery?
Reconstruction of the ulnar collateral ligament with the tendon from the palmaris longus; common contracture of severe valgus stress
What is the proximal radioulnar joint comprised of? (3)
1. Radial notch of ulna
2. Head of radius
3 .Annular ligament
What is the number of articulating surfaces of proximal radioulnar joint?
Compound; 2 or more articulating surfaces
What is the shape of articulating surfaces of the proximal radioulnar joint?
Pivot
What is the degrees of freedom of the proximal radioulnar joint?
Uniaxial; 1 DOF
What are the movements of the proximal radioulnar joint?
Pronation/supination (longitudinal axis)
What is the distal radioulnar joint comprised of?
1. Ulnar notch of radius
2. Articular disc
3. Head of the ulna
What is the number of articulating surfaces of the distal radioulnar joint?
Complex; more than two and presence of articular disc
What is the shape of articulating surfaces of the distal radioulnar joint?
Pivot
What is the degrees of freedom of the distal radioulnar joint?
Uniaxial; 1 DOF
What are the movements of the distal radioulnar joint?
Pronation/supination (longitudinal axis)
How does a subluxation or disclocation of radial head occur?
Sudden jerking of child's pronated forearm, causing annular ligament to tear