Physics - electricity and circuits (10,11)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
current
the flow of electric charge, measured in amps
potential difference / voltage
the difference in potential energy per unit charge between two points in a circuit, measured in volts
Ohm’s law
V = IR, voltage = current x resistance
resistance
how much an object resists the flow of current, measured in ohms
series circuit
all components are connected in one loop. Current is the same throughout it.
parallel circuit
connected across parallel branches, so that the current can flow through each branch independently. The voltage across each component is the same
how to calculate total resistance in a series circuit
sum of all individual resistances
how to calculate total resistance in parallel circuit
1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + …
formula for power
P = IV, power = current x voltage
static electricity
the buildup of electric charge on the surface of objects, usually caused by friction
what causes an object to become electrically charged
when it gains or loses electrons
charging by friction
two objects are rubbed together, causing the electrons to transfer from one object to another. One object becomes positively charged while the other becomes negatively charged.
color of live wire
brown
color of earth wire
green yellow
color of neutral wire
blue
alternating current / AC
a type of electrical current where the flow of charge periodically reverses direction
direct current / DC
a type of electrical current where the flow of charge always moves in the same direction
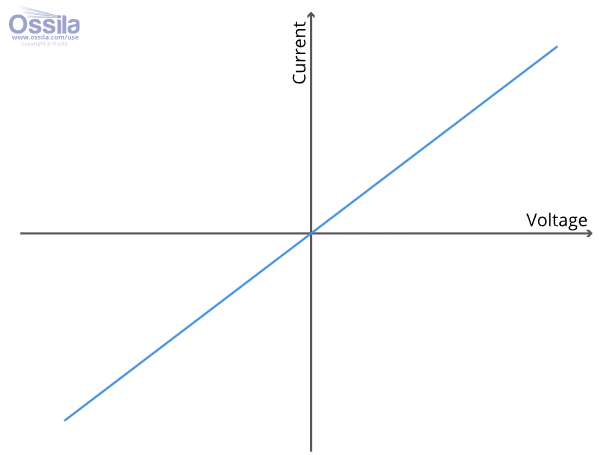
IV graph of a resistor
straight line which passes through the origin
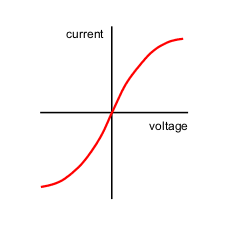
IV graph of a bulb
curves upward because as the current increases, the resistance increases
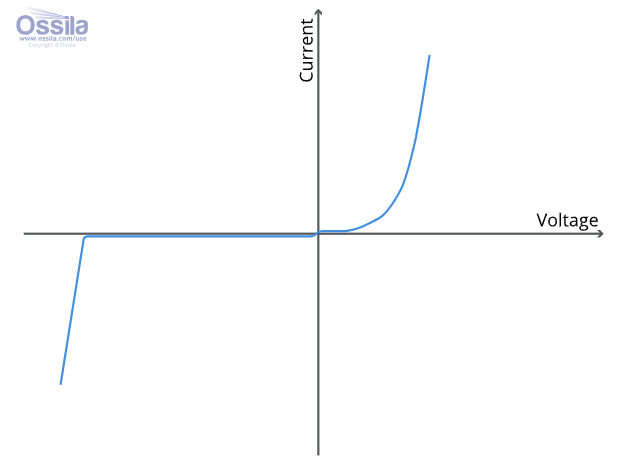
IV graph of a diode
zero current in reverse direction as component does not work in reverse, and current only increases after voltage reaches a threshold
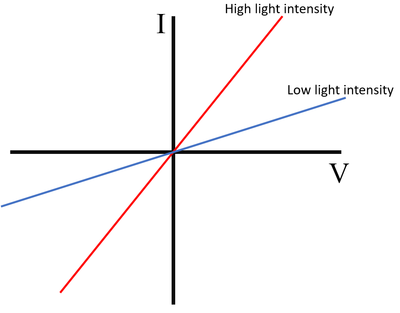
IV graph of LDR
straight line but changes gradient based on intensity of light