Biology Module 4
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
c. protein with calcium and phosphorus compound
1. Bones connect at joints. Cartilage reduces friction at the joints and prevents the bone ends from grinding away.
Bone is made up of________.
a. fat with protein and phosphorus compounds
b. tendons and ligaments
c. protein with calcium and phosphorus compound
d. dead epidermis skin
b. To bind with troponin, changing its shape so that the
actin filament is exposed
2. The role of calcium in muscle contraction is…
a. To break the cross bridges as a co-factor in the
hydrolysis of ATP
b. To bind with troponin, changing its shape so that the
actin filament is exposed
c. To transmit the action potential through the transverse
tubules
d. To spread the action potential through the transverse
tubules.
c. Skeletal muscles are neurogenic while cardiac muscles
are myogenic.
3. Skeletal and cardiac muscles are two different types of
muscles. Which statement is correct?
a. Both skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles are nonstriated.
b. Both skeletal muscles and cardiac muscles are
multinucleated.
c. Skeletal muscles are neurogenic while cardiac muscles
are myogenic.
d. Skeletal muscles are cross-linked fibers while cardiac
muscles are shaped like long fibers.
c. 5
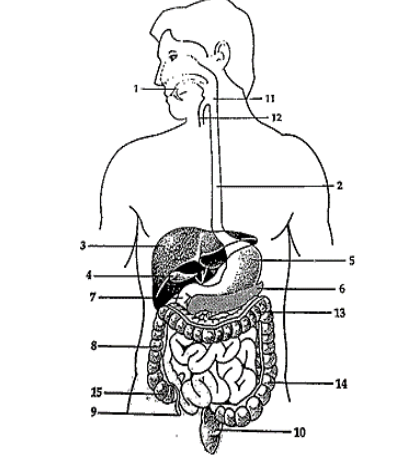
For numbers 4, refer to the following figure.
4. Digestion is the breakdown of complex food molecules
into smaller components. At which site does digestion of
proteins begin?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 5
d. 7
b. He will digest fats slower than usual.
5. Jejomar had his gall bladder removed last week because of severe inflammation caused by gallstone accumulation. What would most likely happen to Jejomar's body metabolism?
a. He cannot digest fats anymore.
b. He will digest fats slower than usual.
c. There will be no change in digestion.
d. Absorption of glucose could be affected.
d. Active transport
6. All of the following facilitate gas exchange in the lungs
EXCEPT
a. Thin alveolar surfaces
b. Moist alveolar surfaces
c. Differences in the partial pressures O2 and CO2
d. Active transport
b. Glucose is reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
7. Why is glucose found in glomerular filtrate but NOT in the urine?
a. Kidney cells require glucose because energy is needed
for active transport.
b. Glucose is reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
c. Glucose is converted to amino acids in the kidney.
d. Glucose molecules are too large to pass through the
tubules.
c. Follicle formation, ovulation, corpus luteum,
menstruation
8. The typical sequence in the human menstrual cycle is
a. Ovulation, menstruation, corpus luteum, follicle
formation
b. Ovulation, follicle formation, corpus luteum,
menstruation
c. Follicle formation, ovulation, corpus luteum,
menstruation
d. Follicle formation, corpus luteum, menstruation,
ovulation
c. chemoreceptors
9. Which of the ff. receptors are NOT present in human
skin?
a. thermoreceptors
b. pressure receptors
c. chemoreceptors
d. pain receptors
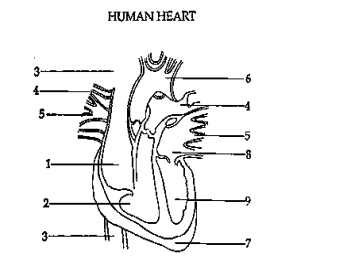
c. 3-1-2-4-5-8-9-6
10. Using the diagram below, which sequence is the correct flow of blood through the heart?
a. 3-8-9-4-5-1-2-6
b. 1-2-3-5-4-8-9-6
c. 3-1-2-4-5-8-9-6
d. 3-1-2-3-4-5-8-9
b. Oxygenated blood toward the heart
11. In pulmonary circulation in mammals, the veins carry
a. Oxygenated blood away from the heart
b. Oxygenated blood toward the heart
c. Deoxygenated away from the heart
d. Deoxygenated blood toward the heart
b. Arteries; capillaries
12. Blood pressure is highest in _____, and the blood moves most slowly in ______.
a. Arteries; veins
b. Arteries; capillaries
c. Veins; arteries
d. Capillaries; veins
d. A defective semilunar valve
13. When the doctor listened to Janet’s heart, he heard
“lubb-hiss, lubb-hiss” instead of the normal “lubb-dupp’
sounds. This hiss is most likely due to ______
a. A clogged coronary artery
b. A defective atrioventricular valve
c. A damaged pacemaker
d. A defective semilunar valve
c. Humoral immune response
14. Lymphocytes, a subclass of white blood cells, are
divided into two types: B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes.
What is the role of B-lymphocytes?
a. Chemical defense
b. Non-specific defense
c. Humoral immune response
d. Cell-mediated immune response
c. The opening of voltage-gated K+ channels.
15. The hyperpolarization at the end of a normal action
potential results from
a. The opening of voltage-gated Na+ channels.
b. The closing of voltage-gated Na+ channels.
c. The opening of voltage-gated K+ channels.
d. The closing of voltage-gated K+ channels.
a. Cerebellum
16. Freddy, a tourism student, went to a bar to celebrate his coming-out party. His friends were spoon-feeding him different types of alcohol the whole night. When he stood up, he had a hard time balancing himself. Which part of the brain is involved in Freddy’s loss of control when he
drinks alcohol?
a. Cerebellum
b. Cerebrum
c Medulla oblongata
d. Hypothalamus
d. It includes the vagus nerve.
17. Which of the following statements concerning the
somatic division of the peripheral nervous system is
INCORRECT?
a. Its pathways innervate skeletal muscles.
b. Its pathways are usually voluntary.
c. Some of its pathways are referred to as reflex arcs.
d. It includes the vagus nerve.
b. II and III
18. In an autonomic nervous system, which of the
following is an effect of sympathetic division?
I. The penis erects.
II. The heart rate increases.
III. The liver is stimulated to release glucose.
IV. The muscular contractions of stomach increase.
a. I, II and III
b. II and III
c. III only
d. I, III and IV
a. Reproductive system
19. Which organ-system do you think is not vital to the
survival of an individual organism?
a. Reproductive system
b. Digestive system
c. Muscular system
d. Nervous system
c. Stimulation of a nerve cell causes sodium ions to leak
into the cell and the sodium influx triggers the inward
leaking of even more sodium.
20. Which physiological response is an example of positive
feedback?
a. An increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood
stimulates the pancreas to secrete insulin, a hormone that
lowers blood glucose concentration
b. A high concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood
causes deeper, more rapid breathing which expels CO2.
c. Stimulation of a nerve cell causes sodium ions to leak
into the cell and the sodium influx triggers the inward
leaking of even more sodium.
d. The pituitary gland secretes a hormone called TSH
which stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete another
hormone called thyroxine. A high concentration of
thyroxine suppresses the pituitary’s secretion of TSH.
c. insulin – stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver
21. Which of the following hormones is incorrectly paired
with its action?
a. oxytocin - stimulates uterine contraction in the child
birth
b. thyroxine – stimulates metabolic processes
c. insulin – stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver
d. ACTH – stimulates the release of glucocorticoids by
adrenal cortex
d. Anterior Pituitary Gland →TSH → Hypothalamus
22. Cell signaling is important for regulation of
physiological processes. It comes in three steps: release of
chemical messenger from the signaling cell, transport of
chemical messenger and communication of signal to
target cell. Which of the following does not have a correct
endocrine pathway?
a. Hypothalamus→ CRH → Anterior Pituitary Gland
b. Anterior Pituitary Gland → Prolactin→ Mammary Gland
c. Posterior Pituitary Gland → ADH→ Kidney
d. Anterior Pituitary Gland →TSH → Hypothalamus
b. cretinism
23. Thyroid hormone deficiency may result in
a. acromegaly
b. cretinism
c. gigantism
d. hyperthyroidism
c. Decreased recovery of water from the urine
24. Antidiuretic hormone affects the kidney by increasing
the water permeability of the distal convoluted tubule and
collecting duct, thus increasing the osmolarity of the urine.
When levels of ADH are low, which of the following will be
the direct result?
a. Decreased recovery of sodium from the urine
b. Increased recovery of sodium from the urine
c. Decreased recovery of water from the urine
d. Increased recovery of water from the urine
a. Aldosterone
25. Which hormone triggers your body to retain NaCl,
especially during periods of heat?
a. Aldosterone
b. Progesterone
c. ACTH
d. Epinephrine