standing waves
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
How is a standing wave formed?
They are formed when two waves with the same amplitude and frequency superpose on top of each other while travelling in the opposite direction.
2
New cards
What is the total amplitude of a standing wave?
The sum of the individual waves amplitudes.
3
New cards
What is constructive interference?
When the waves superpose to create a larger oscillation.
4
New cards
What is destructive interference?
When the wave superpose to create a smaller oscillation
5
New cards
What is total destructive interference?
When the amplitudes cancel each other out and the net amplitude is zero.
6
New cards
What are the differences between progressive waves (P) and standing waves (S)
P: All points have the same amplitude. S: Amplitude depends on the amount of superposition. P:Energy is transferred along the wave. S: Energy is stored. P:Does not have nodes or antinodes. S: Has both of those. P: Wave speed is the speed that the wave moves throughout a medium. S: Wave speed is the speed that the waves oscillate.
7
New cards
What are nodes?
Points where total destructive interference takes place. There is no displacement or movement.
8
New cards
What are antinodes?
Points where total constructive interference takes place and there is maximum displacement and movement.
9
New cards
What is fixed end wave?
A standing wave that forms when they are two fixed ends. The fixed end always ends on a node.
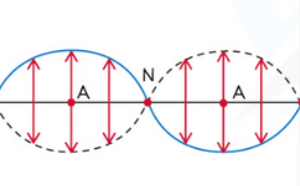
10
New cards
what is the equation for the wavelength of a fixed end wave?
n is the number of harmonics. L is the length of the string.
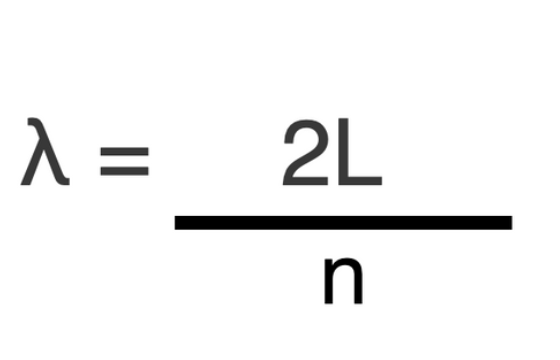
11
New cards
Give an example of a instrument that has a fixed end wave.
Guitar.
12
New cards
What are the harmonics of the guitar string?
The number of frequencies it can naturally vibrate at.
13
New cards
What is the equation for the frequency of a standing wave.
T is tension. µ is the mass per unit length. V is the wave speed.
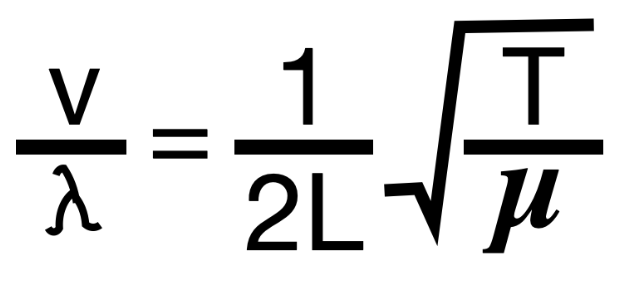
14
New cards
What is a fixed end and an open end wave?
A wave that has a fixed end and an open end. Open ends always end on a node. The number of harmonics is odd.
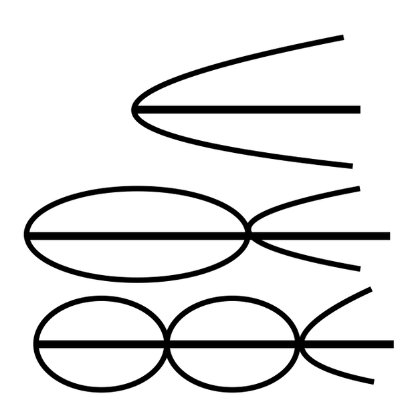
15
New cards
What is the equation for the wavelength of a fixed end and an open end wave?
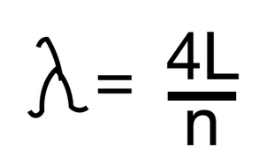
16
New cards
Give an example of an instrument that has a fixed end and open end.
Clarinet.
17
New cards
What is an open end wave?
A wave with two open ends. Each ends an antinode. The end of the waves count as half a harmonic.

18
New cards
What is the equation for the wavelength of an open ended wave?
19
New cards
Give an example of an instrument that has 2 open w