AUBF_Prelim_Lab: Physical Examination of Urine
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

35 Terms
volume or capacity of a clear container for specime collection and handling
50 mL Capacity
Containers used for
Pediatrics -
24-hour specimens -
Pediatrics - adhesive bags
24-hour specimens - large plastic containers
Information on label that is put on the container
Patient’s name
ID number
Date of Collection
Time of Collection
This must accompany the container
Requisition Form
Other info put on thr label
Type of spx.
Interfering meds
Spx. rejection criteria
Unlabeled containers
Non-matching labels and requisitions
Contaminated specimens - feces, paper
Contaminated containers
Insufficient quantity
Delayed or improper transport
Physical Examination of Urine
It is the first information contained on a routine urinalysis report.
Parameters of Physical Exam of urine
Urine odor
color
transparency
pH
Specific Gravity
Volume
odor of normal urine
faint odor of aromatic compounds
odor of urine as the specimen stands for a longer time
Ammoniacal odorodo
odor of uirn with bacterial infection
foul, pungent odor
odor of urine with diabetic ketosis
sweet or fruity odor
Normal color of urine
Yellow
This gives pigment to the urine to become yellow
Urochrome
Factors that cause variation in urine color
Diet
lifestyle
medication
disease
True
T/F;
a normal yellow urine may also contain analyte that signifies a disease such as glucose, ketones and others.
Transparency
is the general term pertaining to the clarity of the specimen.
Common terms used to eport the appearance of urine are:
clear
Hazy
Slightly cloudy
turbid
milky
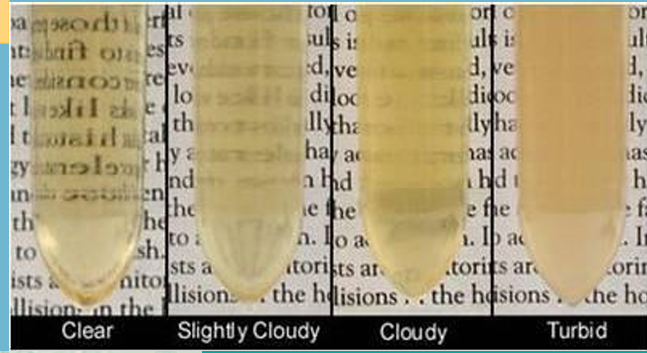
four most common substances that cause turbidity aside from amorphous crystals
WBC
RBC
Epithelial cells
bacteria
white cloudiness in urine appears due to
Amorphous urates
phosphates
carbonates
calcium oxalate
Uric Acid crystal
True
T/F:
The presence of WBC, RBC and bacteria in a freshly voided urine are indicative of pathogenicity and can be a cause for concer
True
T/F:
the degree of turbidity should correspond with the amount of material observed under the microscope
pH
It is the reflection of the ability of the kidney to maintain normal hydrogen ion concentration in plasma and extracellular fluid
usual pH of first morining urine specimen
5-6 pH
Usual pH for urine after eating a meal
4.5-8 pH
Physiologic range of pH of Urine
4.5-8 pH
Tubular secretion of Hydrogen ions
one of the factors (process) that affects the pH of urine
DIfferentiate the Blue and Red Litmus changing their colors
Blue → Red = acid pH
Red → Blue = Alkaline pH
non change = neutral
Normal values of Specific Gravity of Urine during 24 hrs period
1.016 - 1.022
Methods used to measure S.G.
Refractometry (Refractometer)
Reagent strip
Hydrometry (Urinometer)
How many drops of urine is used for refractometer
1-2 drops on the prism surface
True
T/F
The reagent strip reaction is based on the change in pKa (dissociation constant) of a polyelectrolyte in an alkaline medium
What is used to calibrate a refractometer
distilled water
How to remove foam on the hydrometer due to urine bubbling
filter paper
Disadvantage of Urinometer
requires large volume (10-15mL)
Rotating motion
read at lower meniscus