Kines 566 UW Madison Final
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Health Promotion
the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health
Broader approach that includes creating supportive environments to enable healthy behaviors.
Health education
providing accurate health information and teaching health skills to help people make healthy decisions
Goes beyond learning experiences that provide people with knowledge and skills to improve their health behaviors.
PRECEDE-PROCEED Model
Comprehensive health planning model that addresses both behavioral and environmental facotrs inlfuencing health
Precede: identifies the root cuase of health issues by analyzing social, epidemiological, and education factors
Proceed: focuses on policy implementation and program evaluation
SMART objectives
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time-bound
Theory of Planned Behavior
Intention drives behavior: attitude, social norms, and perceived control.
Health intervention
an act performed for, with or on behalf of a person or population whose purpose is to assess, improve, maintain, promote or modify health, functioning or health conditions
Ecologial Model
Focuses on multiple layers of influence (individual, interpersonal, community, societal) that effect health behavior
Application: encourages designing interventions that address various levels of influences, beyond just individual behaviors.
Social Cognitive Theory
Behavioral change results from self-efficacy, observational learning, and outcome expectations.
→ people learn from others and self: self-efficaicy, observational learning, and outcome expectations
Health Belief Model
What is it? Explains and predict individual health behvaiors by focusing on attidues and beliefs of people.
How it works? Suggests that a person's belief in a personal threat of an illness or diseasr, together with their belief in the effectivness of the recommended health behavior, will predcit the likelihood of adopting behavior.
Community-based health intervention
Programs and initiatives that aim to improve the health and well-being of specific population groups within a local community by preventing dysfunction and promoting well-being, often involving community participation and collaboration
Cultural Adaptation in Health Intervention
using specific languages, styles of music, dance styles, etc. in order to make the population feel culturally involved
Intervention Mapping
Framework for designing helath behvaior intervention based on theory and evidence
1. Needs Assessment
2. Changes Objectives
3. Theories and Methods
4. Program design
5. Implementaiton
6. Evaluation
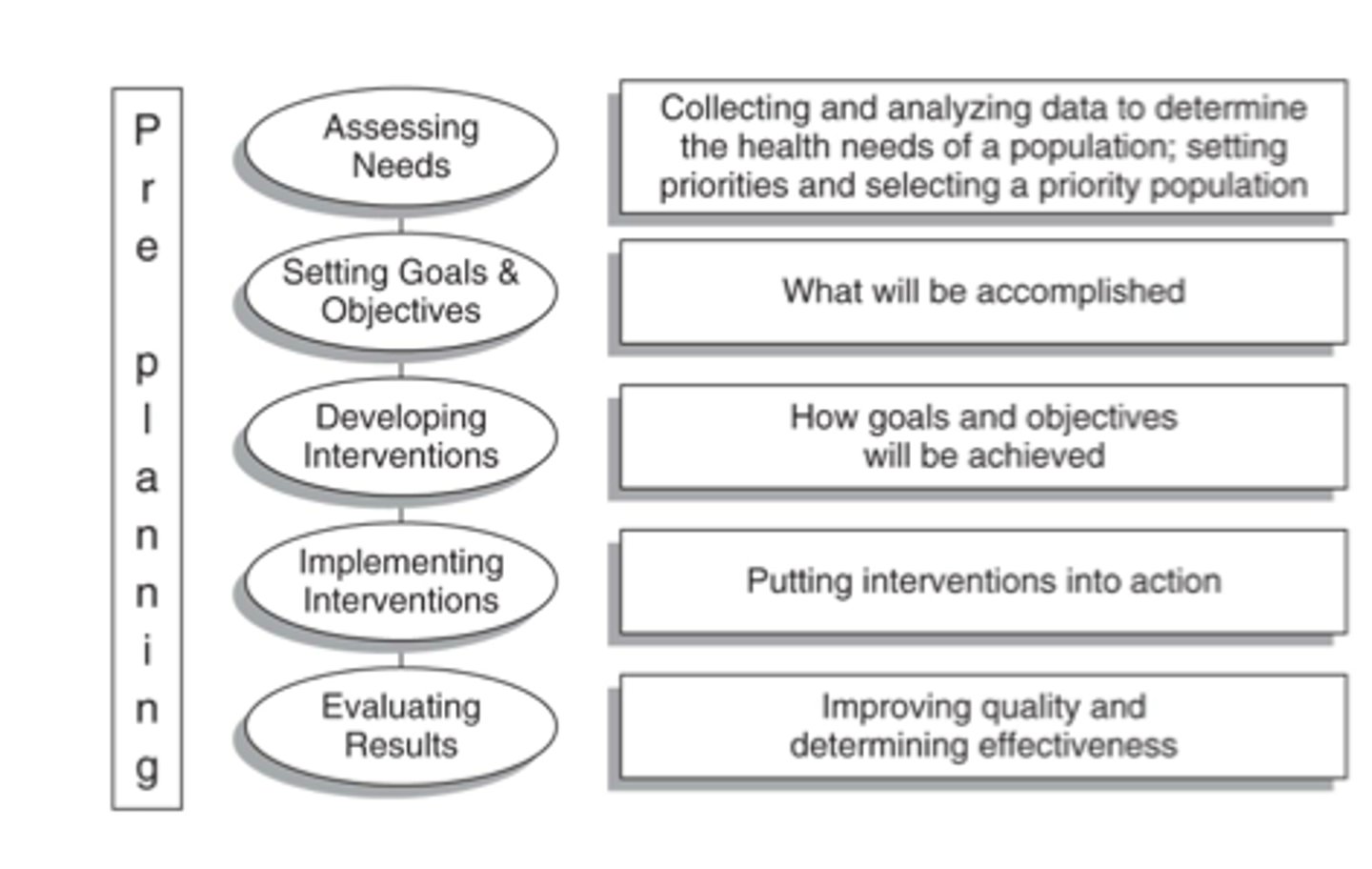
Generalized Model
1. assessing needs
2. setting goals and objectives
3. developing interventions
4. implementing interventions
5. evaluating results
Health Promotion characteristics
Focuses on community-level or policy changes that make healthy choices more accessible
Includes environmental, organizational, and policy efforts
Goal - make healthy behaviors easier and more widespread
Community Engagement Strategies
Engage key stakeholders, government, healthcare providers to ensure the intervention is uspported and has necessary resources.
Fit Families Program
Addresses the underdeveloped FMS in children with ASD, 12-week family oriented program to improve FMS in children with ASD. Parents are brought on as coaches and learn how to teach their child-specific FMS skills.
SMART Goals
Specific, measurable steps: How do we measure success?
Define what you want to achieve, but they must connect to the instruments used for measurement.
Needs assessment inform Smart goals→ identify key challenges, health disparities, and resource gaps in a population
Environmental Health Intervention
Focus on preventing disease and promoting health by creating healthy environments, encompassing actions like providing safe water, air, and food, and addressing hazards like toxic waste and lead.
Steps of Health Promotion Intervention
1. Conduct→ needs assessment
2. Identify → health issue and population of interest
3. Set → clear goals and measurable objectives
4. Design → intervention
5. Develop → budget and allocate resources
6. Plan → data collection and evaluation
7. Implement → intervention and monitor progress
Social Determinants of Health
The conditions in which people live, work, learn, and play that influence their health and well-being
Importance of planning models in health
Provide a structured, systematic approach to designing, implementing, and evaluating programs, ensuring they are evidence-based, effective, and address the needs of the target population
Role of Community Engagement in health interventions
Community members should play an active role in the health iniative
They should serve as a cocreators, advocates, and liasions, helping to shape the programs design, promote it's adoption and provide ongoing feedback.
They can share thoughts and ideas to help make sure the program fits their needs and values
Essential for making the program culturallyt relevant and ensuring that the prgram lasts longer because it resonates with the community.
Ethical considerations in health interventions
fully informed, informed consent, define purpose, making sure everyone knows what is happening
Environmental Structuring - Restructuring
modifying the physical environment to influence behavior or promote sustainability, ranging from simple changes to complex infrastructure projects
Self-Monitoring
a personality trait and a strategy that involves observing and recording one's own behaviors, thoughts, and emotions to gain awareness and potentially modify them
Mechanism of Action
describes how a drug or other substance exerts its effects in the body
Behavior change Technique
strategies used to help individuals modify their behaviors to promote better health or achieve specific goals
Barrier Identification & Problem Solving
involves recognizing obstacles that hinder progress and then developing strategies to overcome them, often through a structured process of definition, diagnosis, solution implementation, and sustainment
Needs assessment
A systematic process used to identify and understand the health problems, gaps, and priorities of a target population in order to guide program planning and intervention design.
Process evaluation
An evaluation that examines how an intervention is implemented, including whether activities are delivered as planned, reach the intended audience, and operate efficiently.
Gantt charts
Visual project management tools that display tasks, timelines, and deadlines, showing when activities start and end and how they overlap over time.
Health equity
The principle of ensuring everyone has a fair and just opportunity to attain their highest level of health by addressing social, economic, and structural barriers to health.
Outcome evaluation
An evaluation that measures the short- and medium-term changes in knowledge, behaviors, attitudes, or skills that result from an intervention.
Formative evaluation
Evaluation conducted during program development or early implementation to improve design, materials, and delivery before full-scale implementation.
Health intervention strategies
Planned actions or approaches used to improve health outcomes, such as education, policy change, environmental modifications, or community-based programs.
Evidence based interventions
Programs or strategies that are supported by scientific research demonstrating their effectiveness through rigorous studies or systematic reviews.
Quantitative data collection method
A method of collecting numerical data that can be statistically analyzed, such as surveys, questionnaires, biometric measures, or attendance records.
Impact evaluation
An evaluation that assesses the long-term effects of an intervention and determines whether observed changes can be attributed directly to the program.
Budget
A financial plan that outlines estimated costs and funding sources required to implement and sustain a program or intervention.
Self determination Theory (SDT)
A behavioral theory that emphasizes the role of autonomy, competence, and relatedness in motivating individuals to adopt and maintain healthy behaviors.
Ecological interventions
Interventions that target multiple levels of influence on health—individual, interpersonal, organizational, community, and policy—to create sustainable behavior change.