P4: Electric circuits
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
What does electrical charge need to flow through a closed circuit?
Circuit must have a source of PD
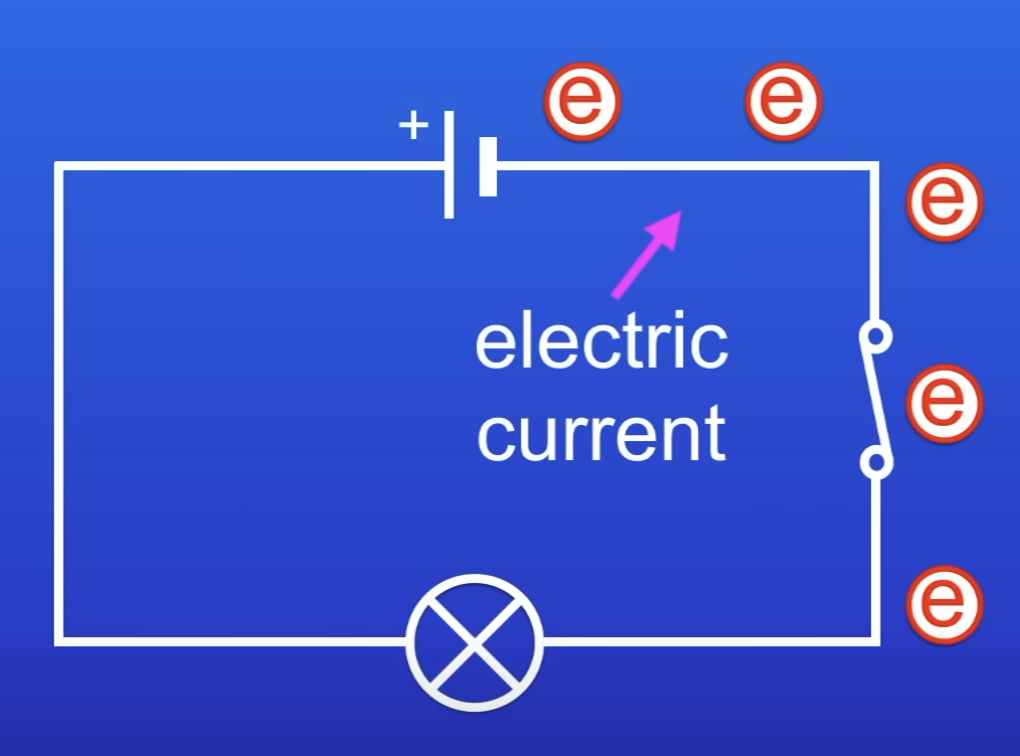
What happens when you close the switch of a circuit?
Electrons flow out of the cell
They move around the circuit
Charge
Group of electrons
Electric current
Flow of electrons
Size of electric current =
Rate of flow of electrical charge
In what direction does electric current flow?
Negative to positive end of cell
Are electrons positive or negative?
Negative
What are elctrons carrying?
Energy from cell
What do electrons do with the energy from the cell they are carrying?
Pass energy to components
What happens to the energy transferred to a lamp?
Electrical energy transferred to thermal + light energy
When electrons return to the positive end of the cell, are they carrying more or less energy than when they left the negative end?
Less
What direction is conventional current drawn in?
Positive to negative
What is electrical charge measured in?
Coulomb (C)
1 Amp current =
1 coulomb of charge flowing per s
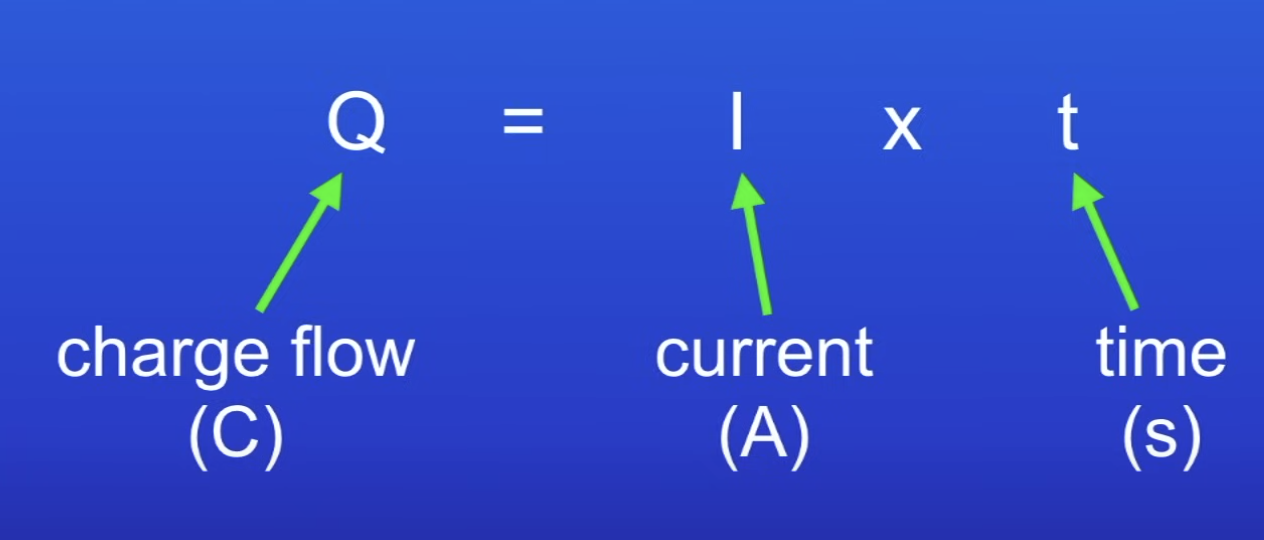
Charge flow equation
charge flow = current × time
Q = It
Unit of electric current
Ampere (Amp)
What is used to measure current in a circuit?
Ammeter

Is current used up in a circuit?
No-never
In a series circuit (single closed loop) current is…
Same value at any point
Series circuit
No branches, single closed loop
In a series circuit, current can only flow in…
1 path
Parallel circuit
Has branches
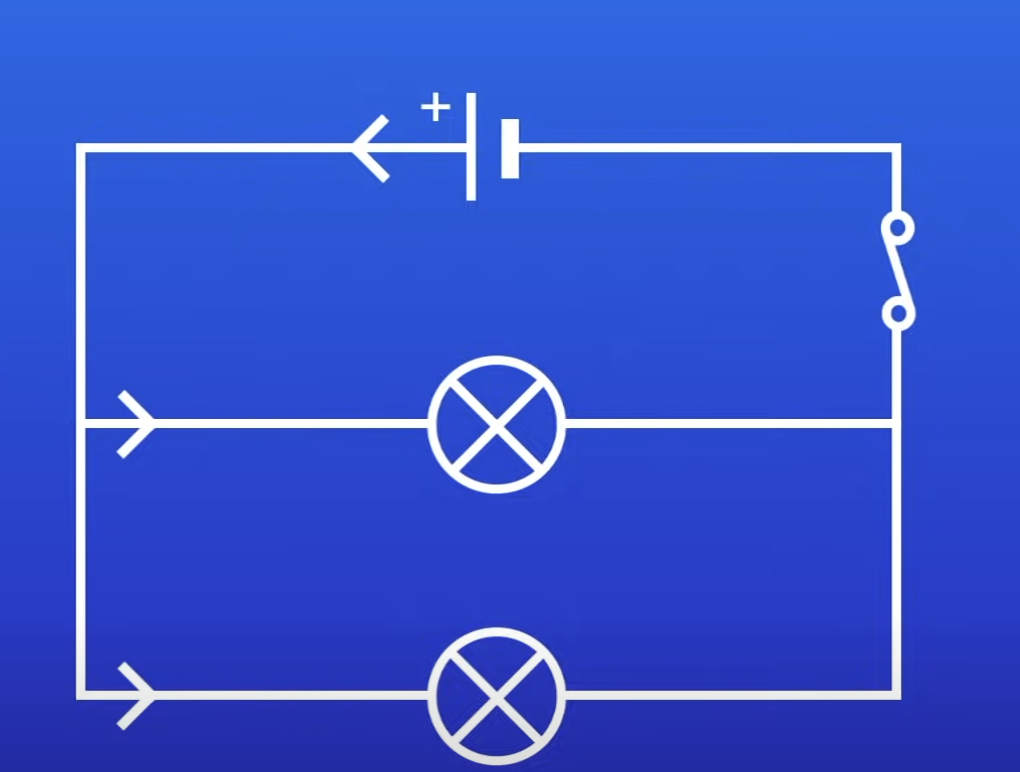
How does current flow in a parallel circuit?
Current splits
Some passes thru both branches
How does current behave in a parallel circuit?
Current in branches adds up to total current leaving the cell
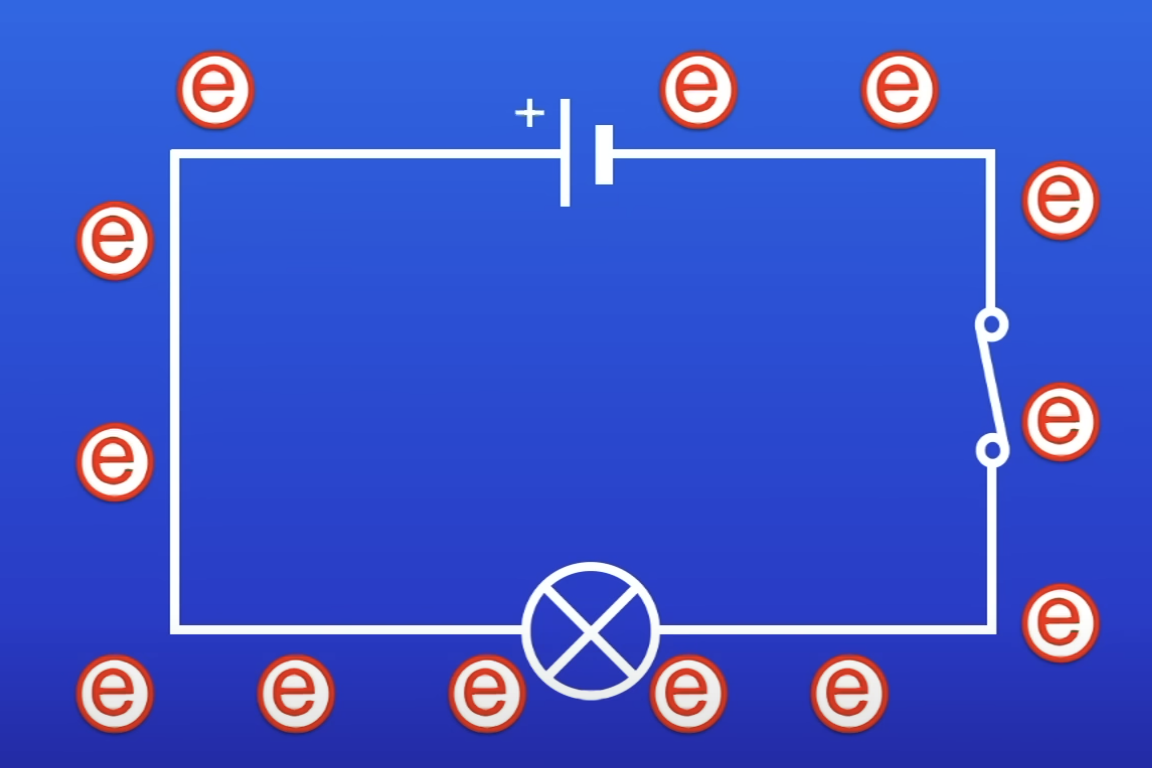
Energy transfers involved in this?
Cell has chemical energy store
Transferred to electrical energy + carried out by electrons (current) passing out the cell
Electrons pass thru components, EE transferred to other forms of energy
If lamp, EE transferred to TE + LE
Potential difference (voltage)
Measure of WD / energy transferred to a component by each coulomb of charge that passes thru it
PD of 1 volt =
1 joule of energy transferred to each coulomb of charge moving thru the circuit
How is PD measured in a circuit?
Voltmeter

How is a voltmeter connected in a circuit?
In parallel to the component you want to measure the voltage of
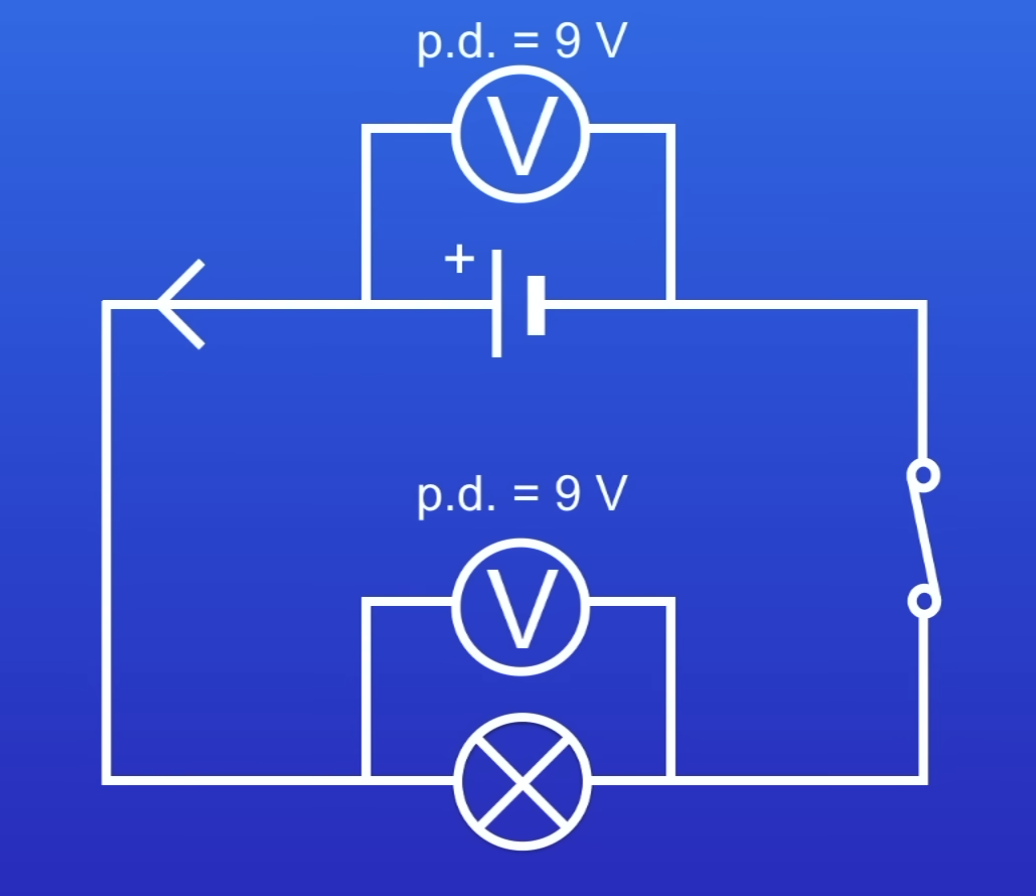
How is a ammeter connected in a circuit?
In series
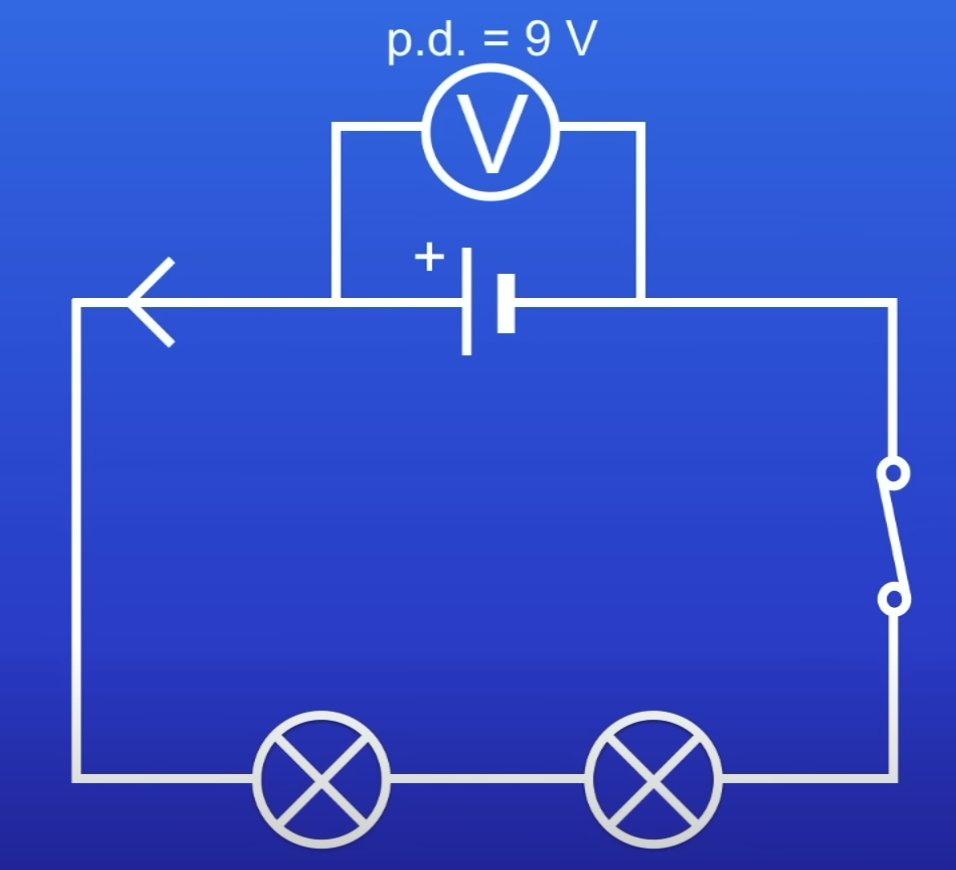
In series, why are both lamps dimmer than if there were just 1?
PD in each lamp is lesser
Total energy carried by current in shared betw 2 lamps
So lesser electrical energy transferred to light energy
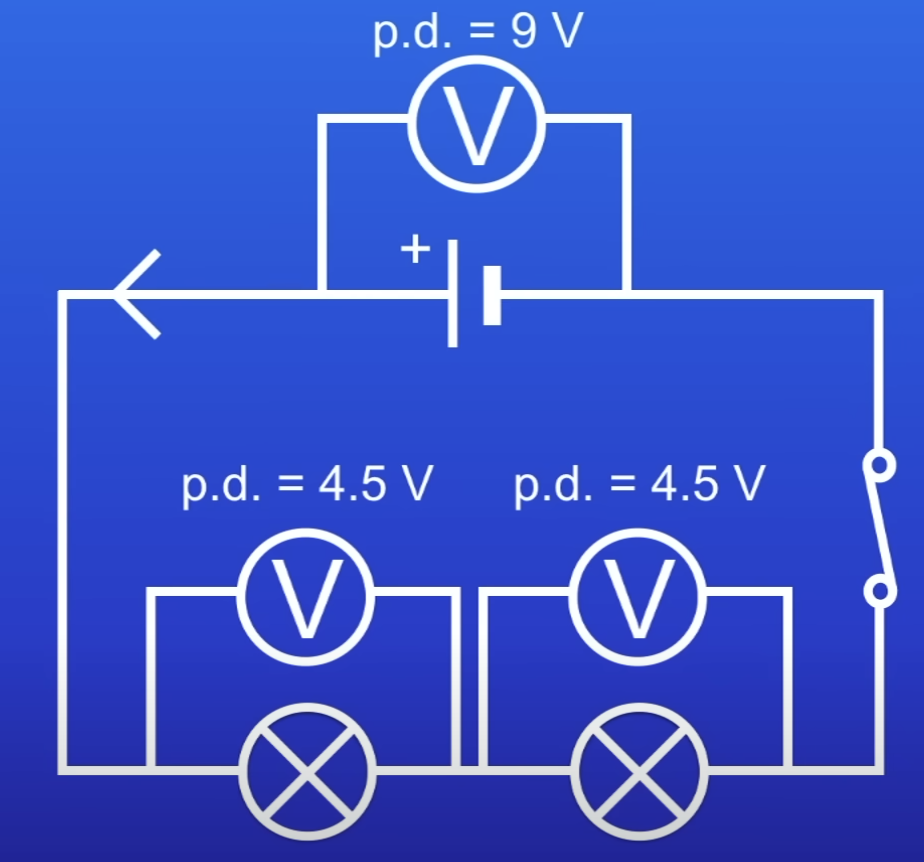
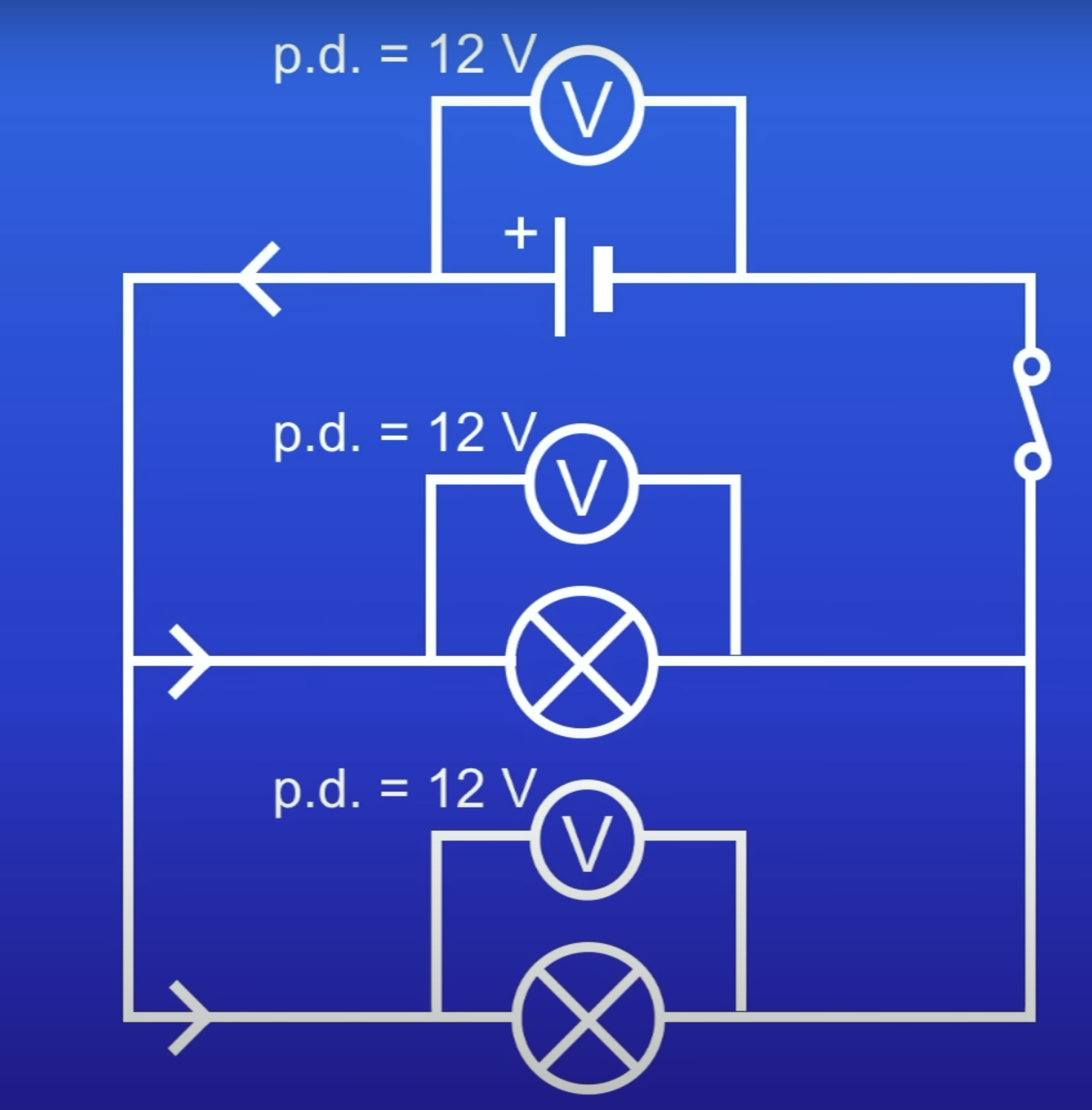
How does voltage behave in a series circuit?
Shared
Total PD across components = total PD across cell
Voltage (PD)
Amt of energy transferred to each coulomb of charge moving thru a circuit
What does a PD of 6V show us?
Current carrying 6J of energy per coulomb of charge
How does PD behave in a parallel circuit?
For components connected in parallel, the PD across each component is the same
Battery
2 or more cells connected tog
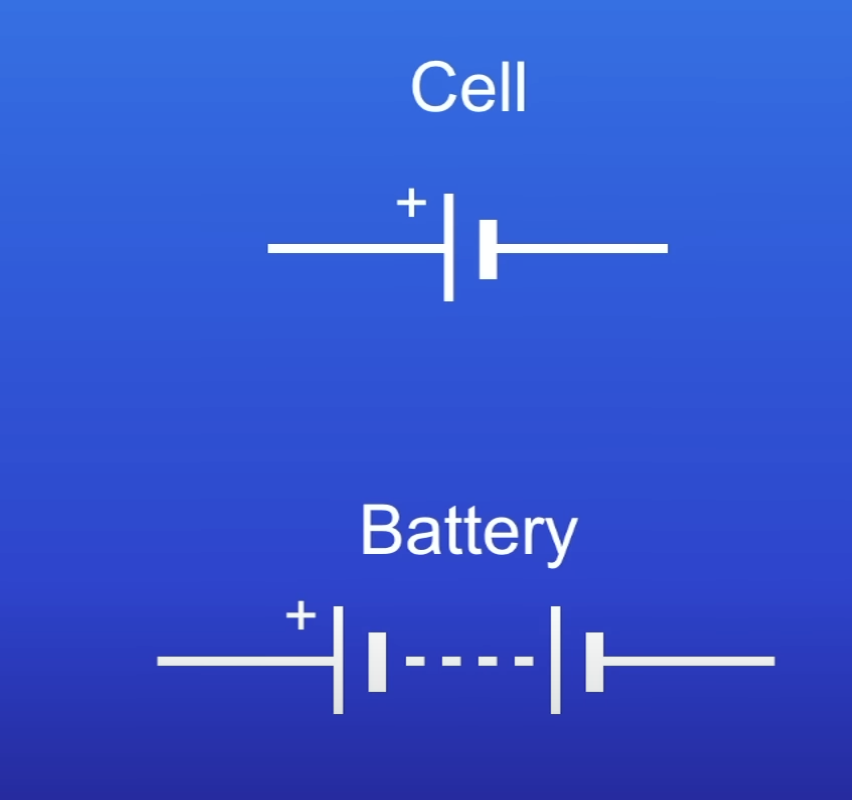
The cells in a battery must be…
Connected in the same direction
Eg positive ends both pointing left
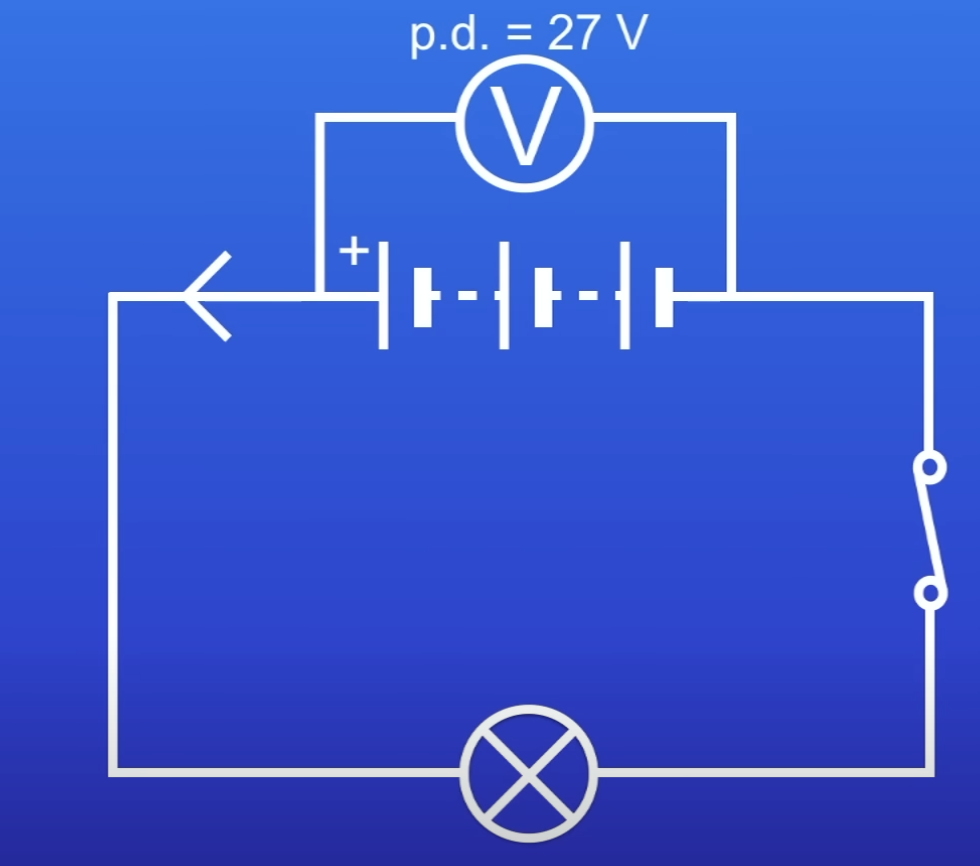
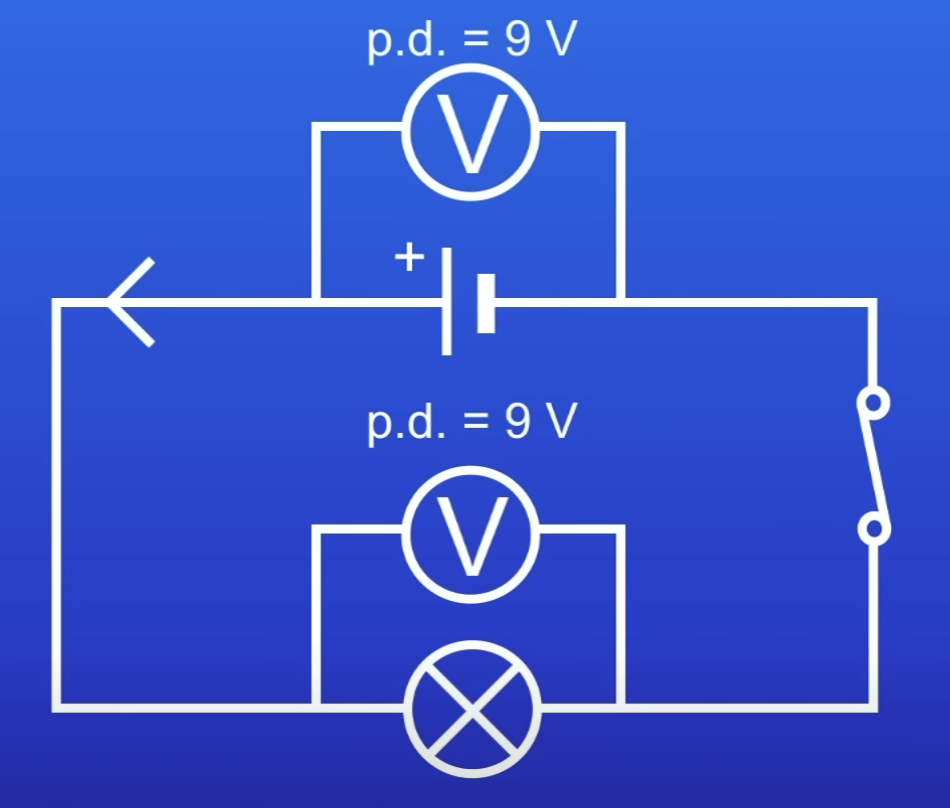
If each cell has a PD of 9V, what is the overall PD of the battery?
27V
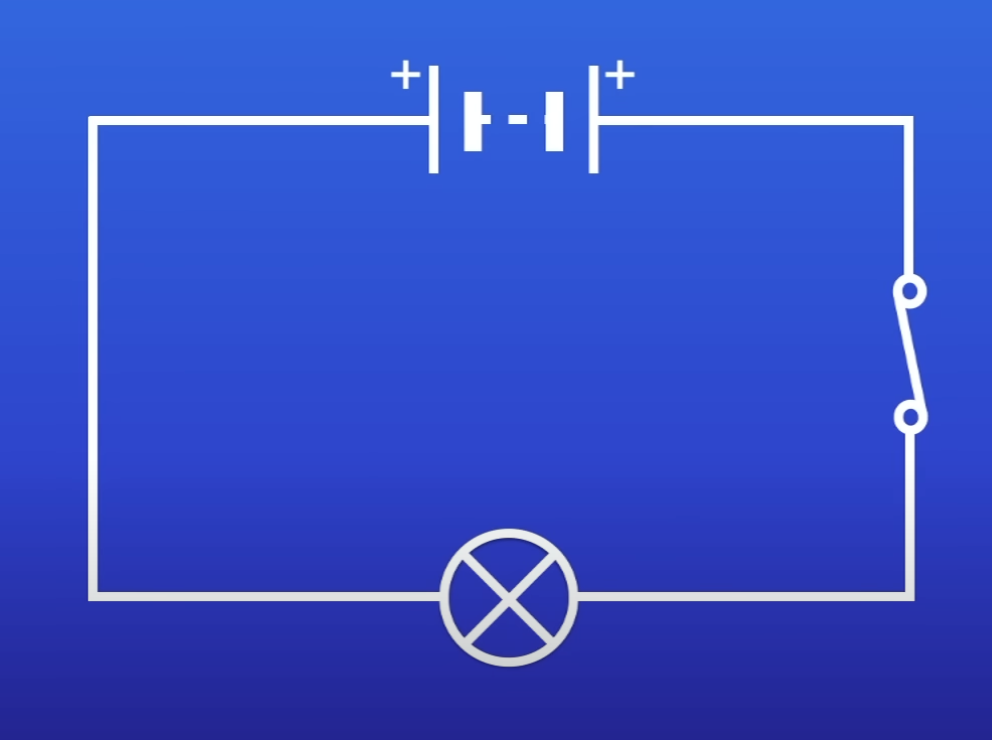
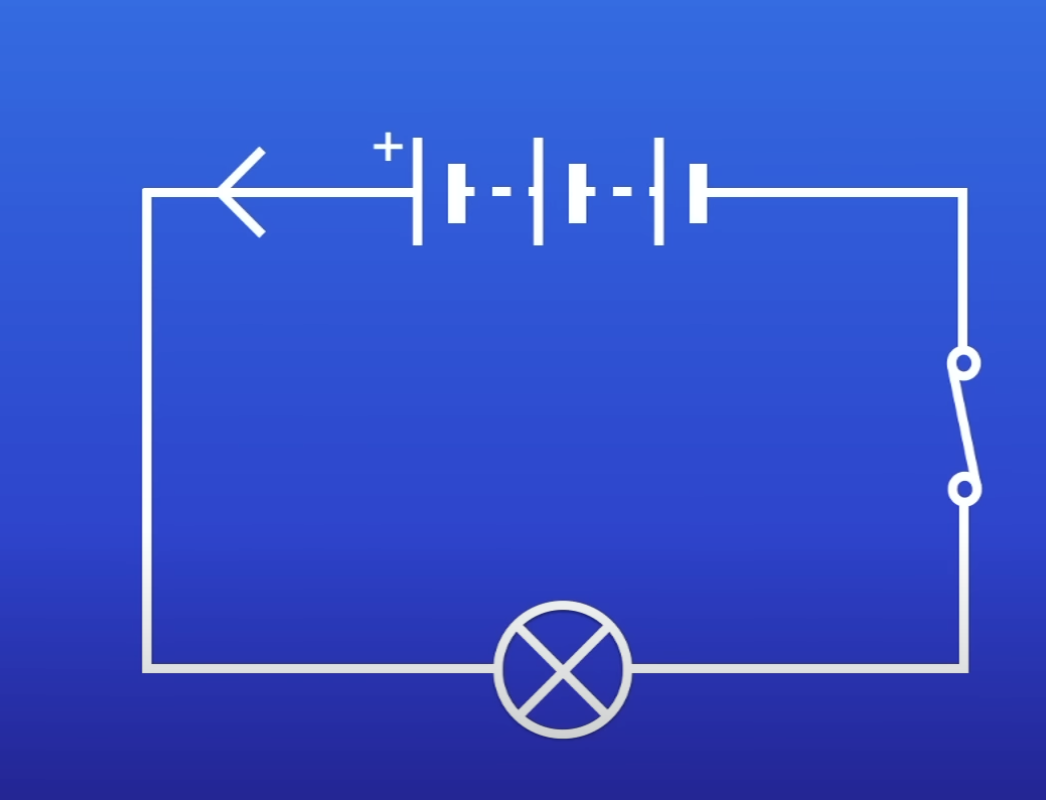
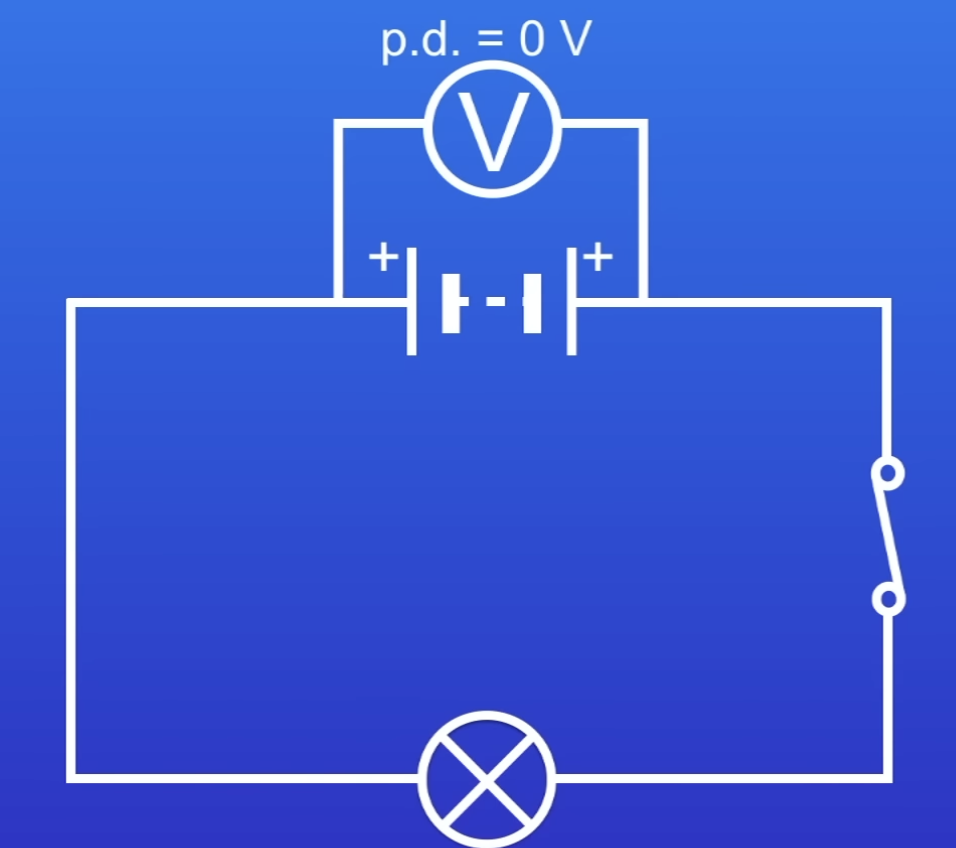
PD of this battery
0V
Cells pointing in diff directions → PD of each cells cancel out
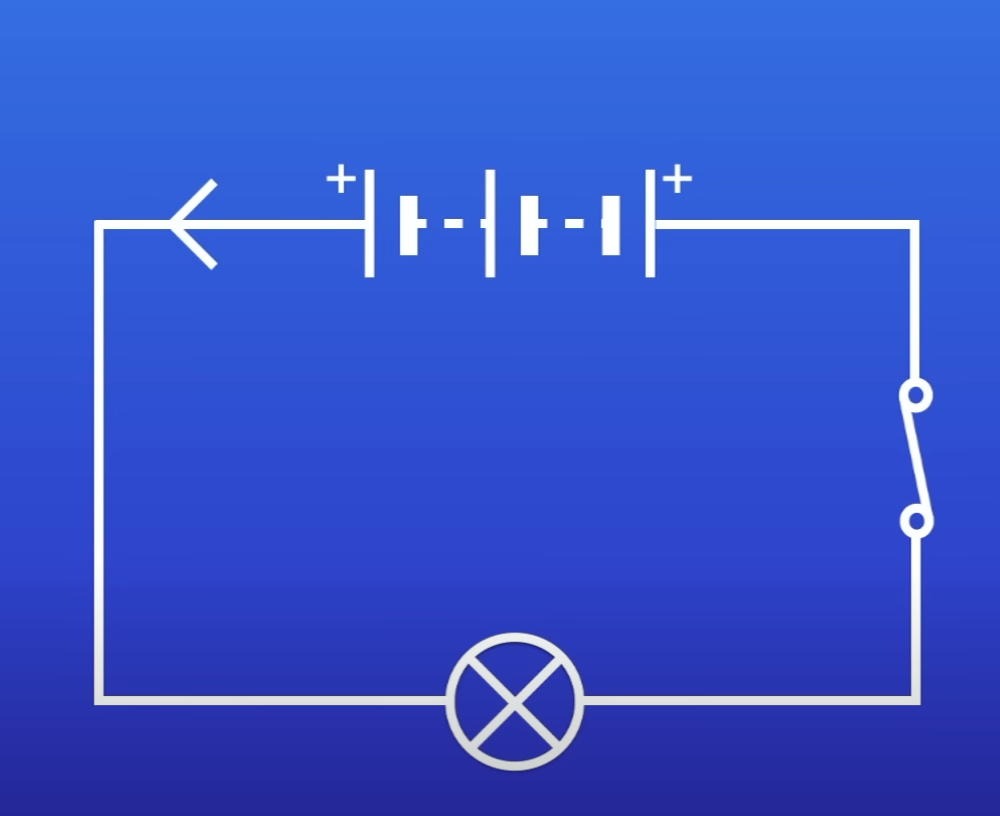
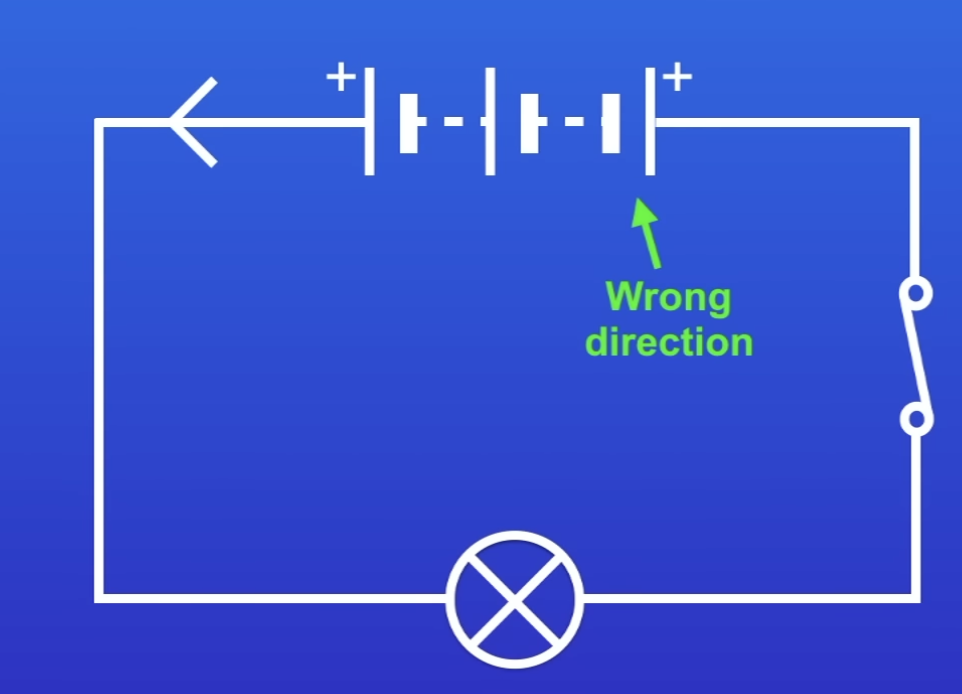
PD of each battery if each cell has a PD of 9V
9V
2 × 9 = 18
18 - 9 9
What happens whenever charge flows in a circuit?
Work is done (ET)
Energy transferred equation
E = QV
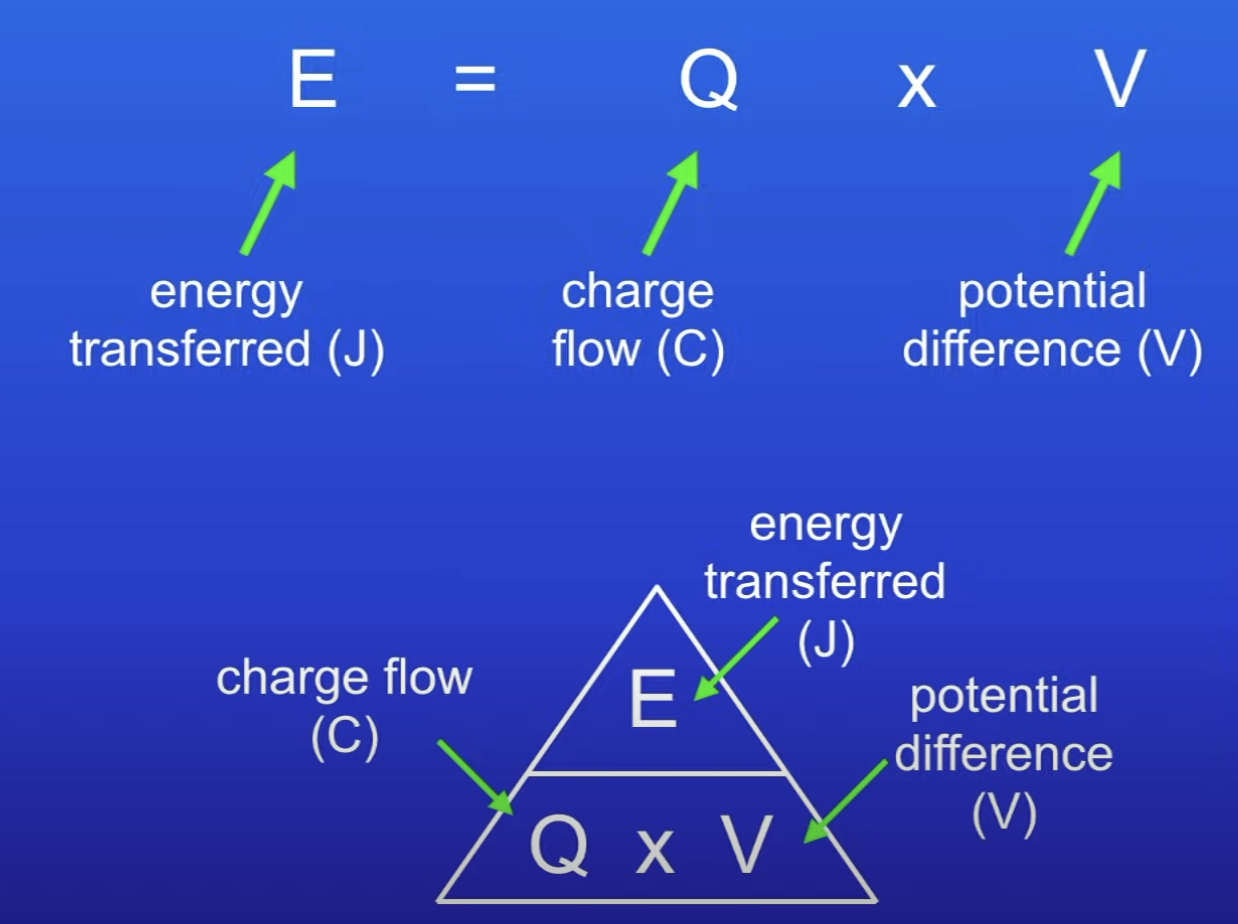
What does this show in terms of energy?
All electrical energy carried by current is transferred by lamp to other forms of energy
What about components causes them to transfer energy?
Resistance
Electric current
Flow of electrons thru a conductor (eg metal wire)
What does resistance tell us?
PD needed to drive a current thru a component
How much energy needed to push a coulomb of charge thru
Resistance
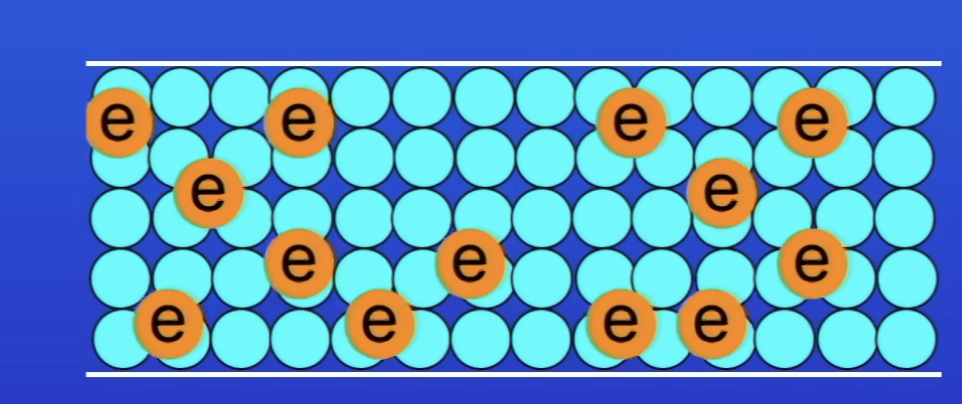
What happens as electrons move thru a conductor (metal wire)?
e- collide w atoms in the metal
So electrical energy transferred to other forms of energy (eg thermal)
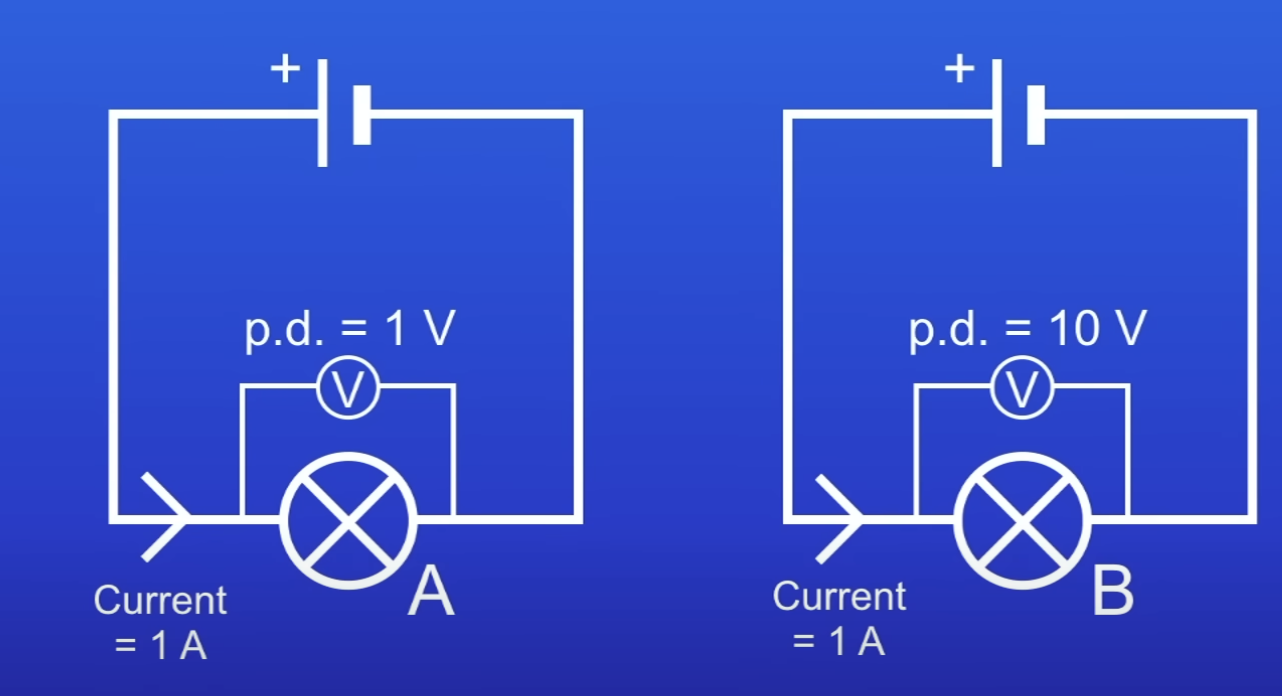
Which lamp has a lower resistance and why?
Lamp A = lower resistance
Current being driven by PD of only 1V
So only small amt of energy needed to drive the current thru the lamp
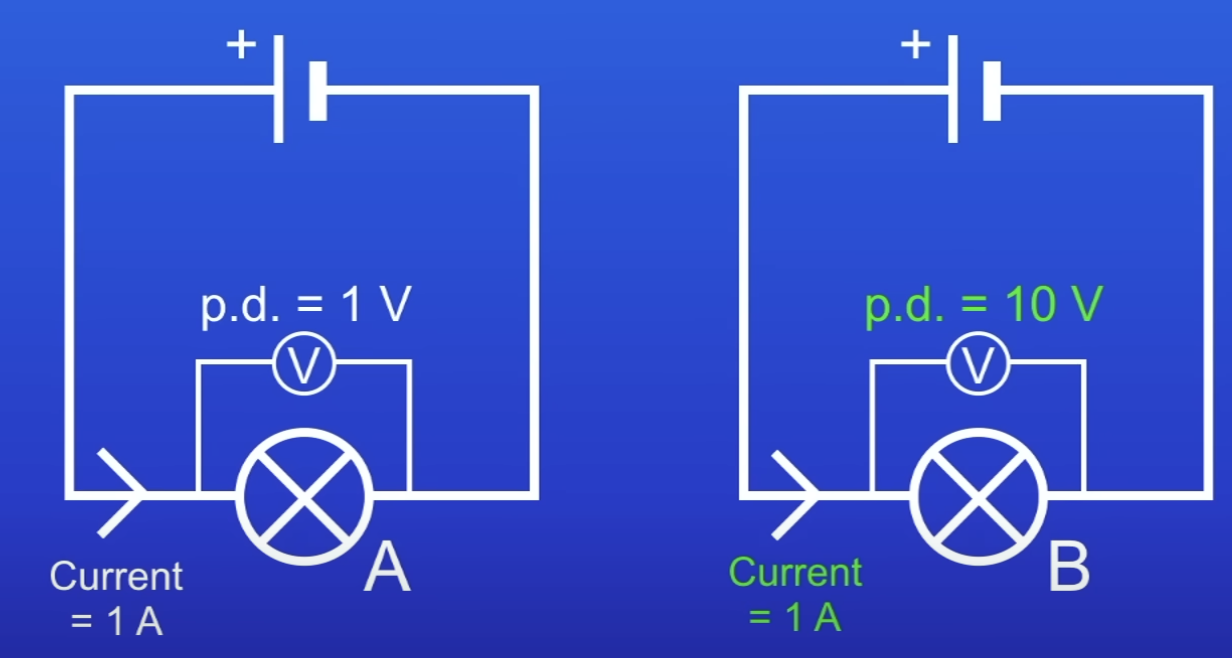
Which lamp has a higher resistance and why?
Lamb B = higher resistance
Current being driven by PD of 10V
So large amt of energy needed to drive current thru lamp B (more needed than A)
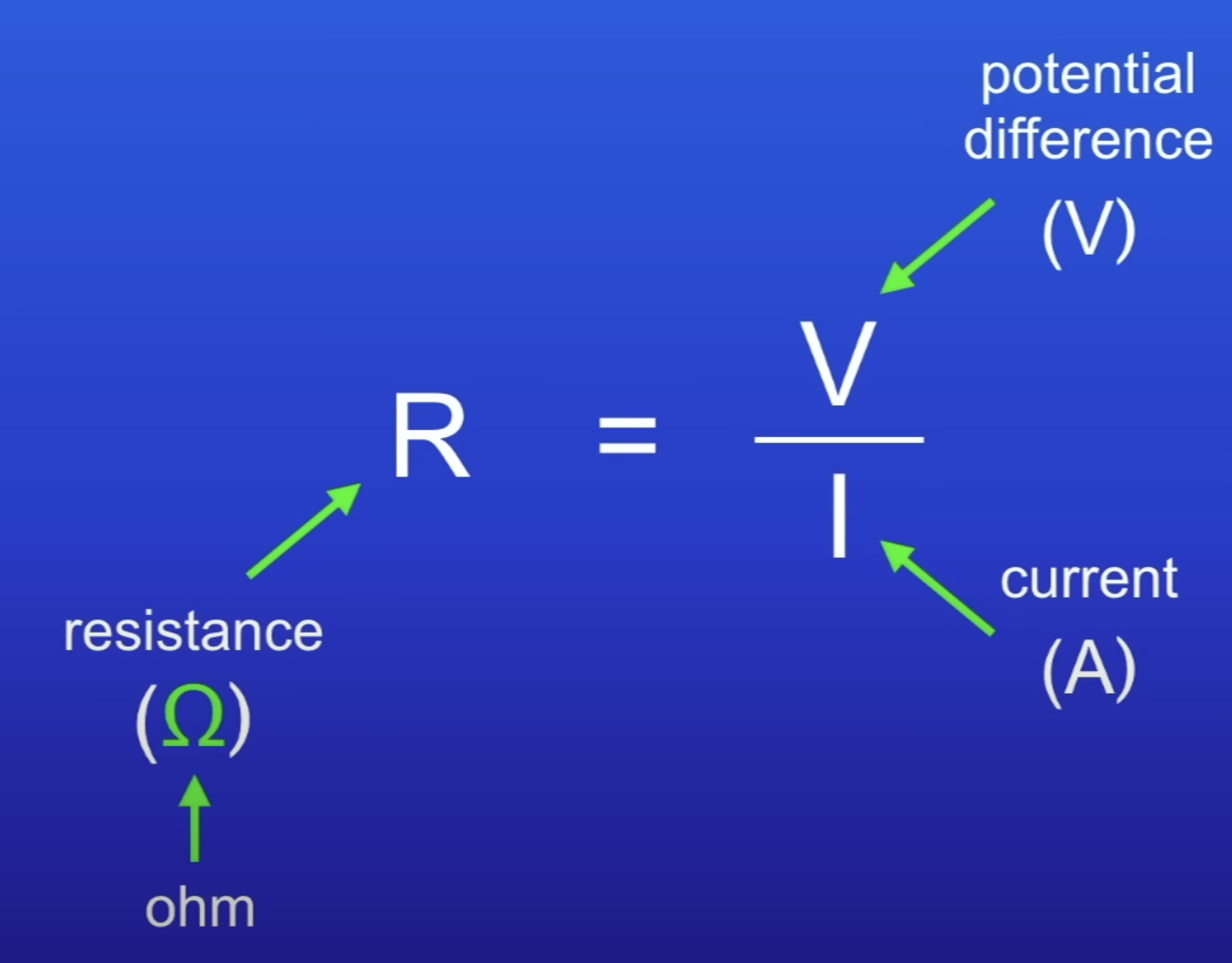
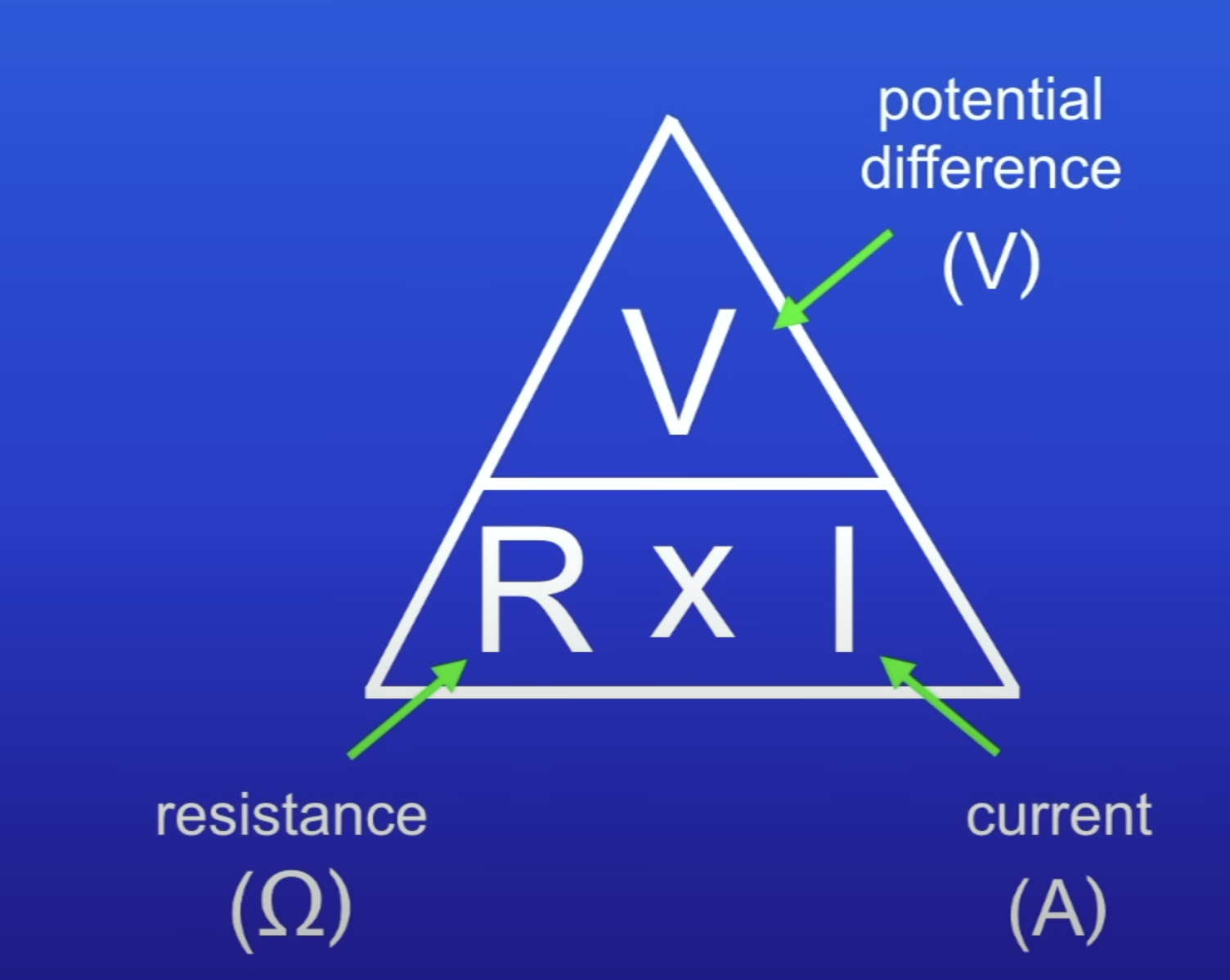
Resistance equation
R = V/I
Unit for resistance
Ohm
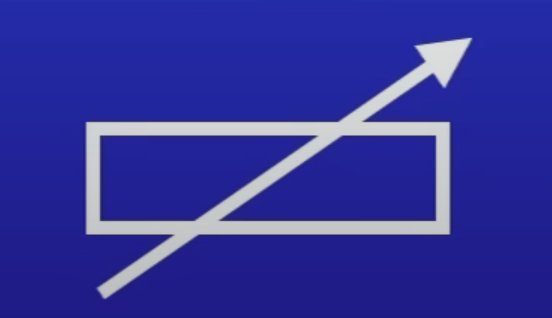
How does a variable resistor work?
Contains long piece of wire in a coil
Use slider to change length of wire current runs thru → hence ↑ or ↓ resistance
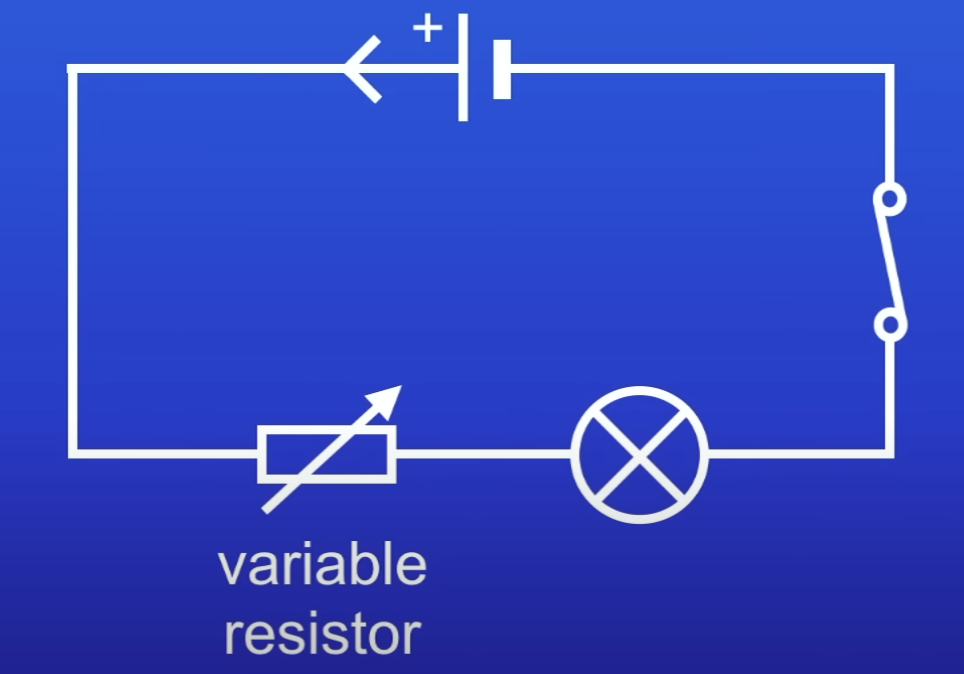
What is a variable resistor used for in this circuit?
To control PD across lamp
Increase resistance → makes lamp dimmer
Ohm’s law
Current thru a resistor at a constant temp is directly proportional to PD across the resistor
What does current thru a component depend on?
Resistance of component
PD across component
Higher resistance means…
More energy transferred as the curent moves
When is resistance useful?
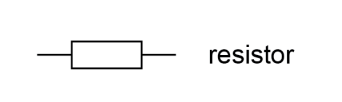
Resistor
Device that limits the flow of electrical current in a circuit
The greater the resistance of the component…
The smaller the current for a given PD across the component
Factors affecting resistance
Thickness, length, temperature of wire
How do thicker wires decrease resistance?
Moving electrons have more space to move
How do shorter wires decrease resistance?
Moving electrons have a shorter distance to travel
How do hotter wires increase resistance?
Metal atoms in wire move faster
So electrons collide more with them
When is a resistor used?
When want to add resistance into a circuit
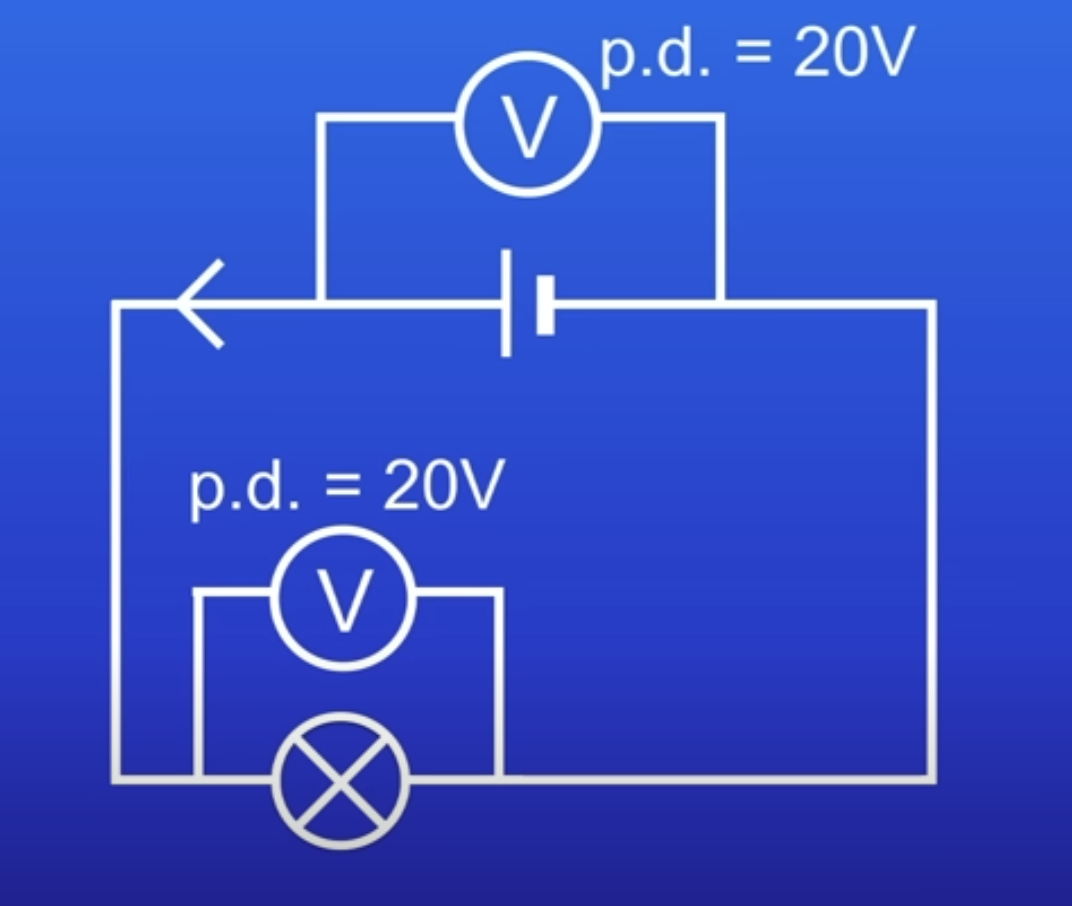
The lamp is very bright (20V), how can you make the lamp dimmer?
Use cell with lower PD
Add extra resistance into circuit
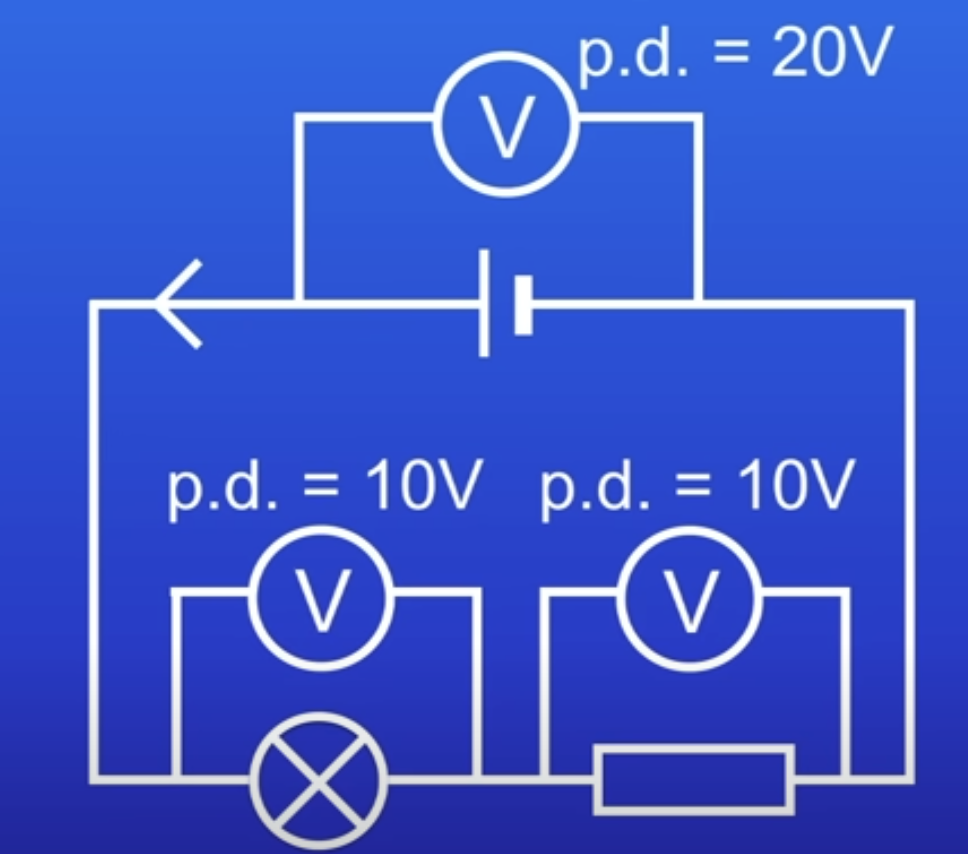
How can you make this lamp dimmer by adding extra resistance into the circuit?
Add resistor in series with the lamp → PD shared betw lamp + resistor
So less electrical energy transferred to lamp → not as bright
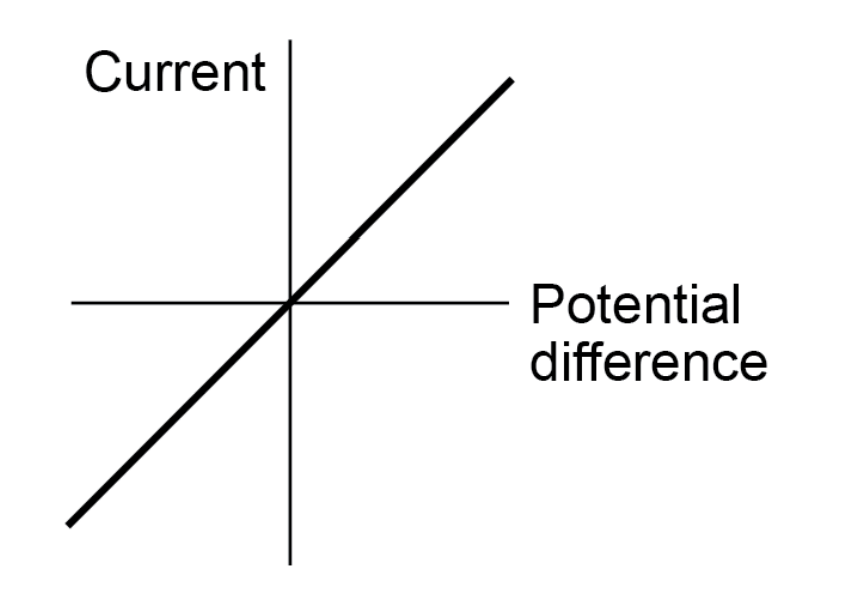
Current thru a resistor is…
Directly proportional to PD
What does it mean if current thru a resistor is DP to PD?
Resistance is constant (R doesn’t change if current changes)
Straight line
Ohmic conductor
Components (resistors) that follow Ohm’s law
Conductor for which PD + I are DP → R = constabt
Fixed resistors, wires
A resistance will only stay constant if?
Temp is constant
Current thru an ohmic conductor (at a constant temp) is?
DP to PD across the resistor
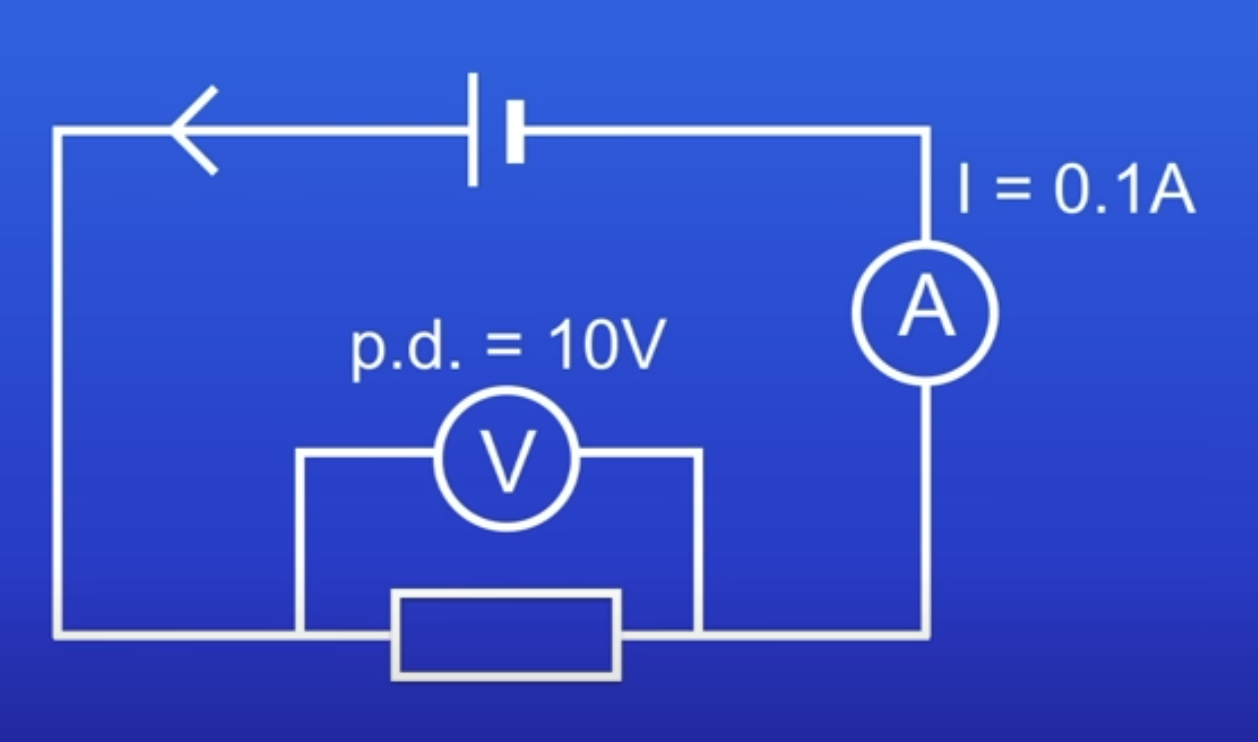
What happens to current flowing thru a resistor if PD is increased?
Increases
Why does a PD of 0V give a current of 0 amps?
If PD is 0, electrons have no energy → can’t move thru resistor
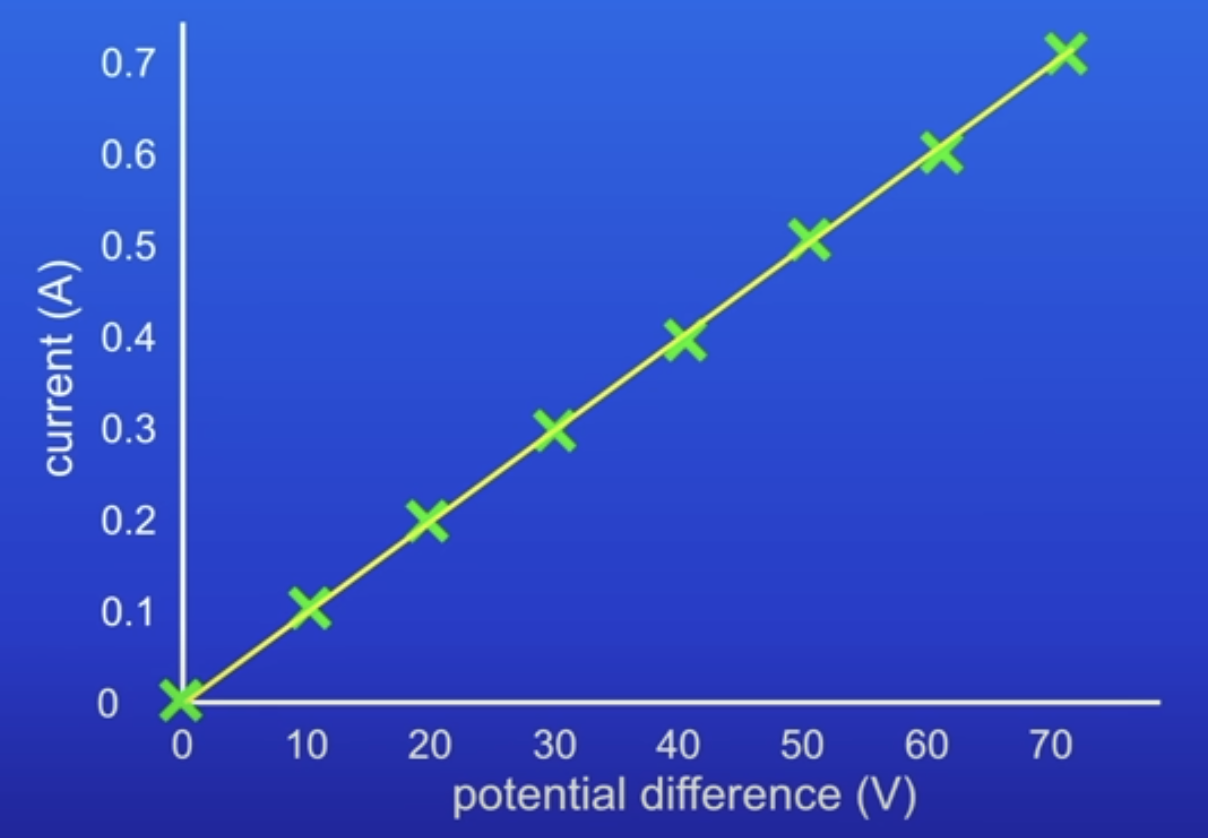
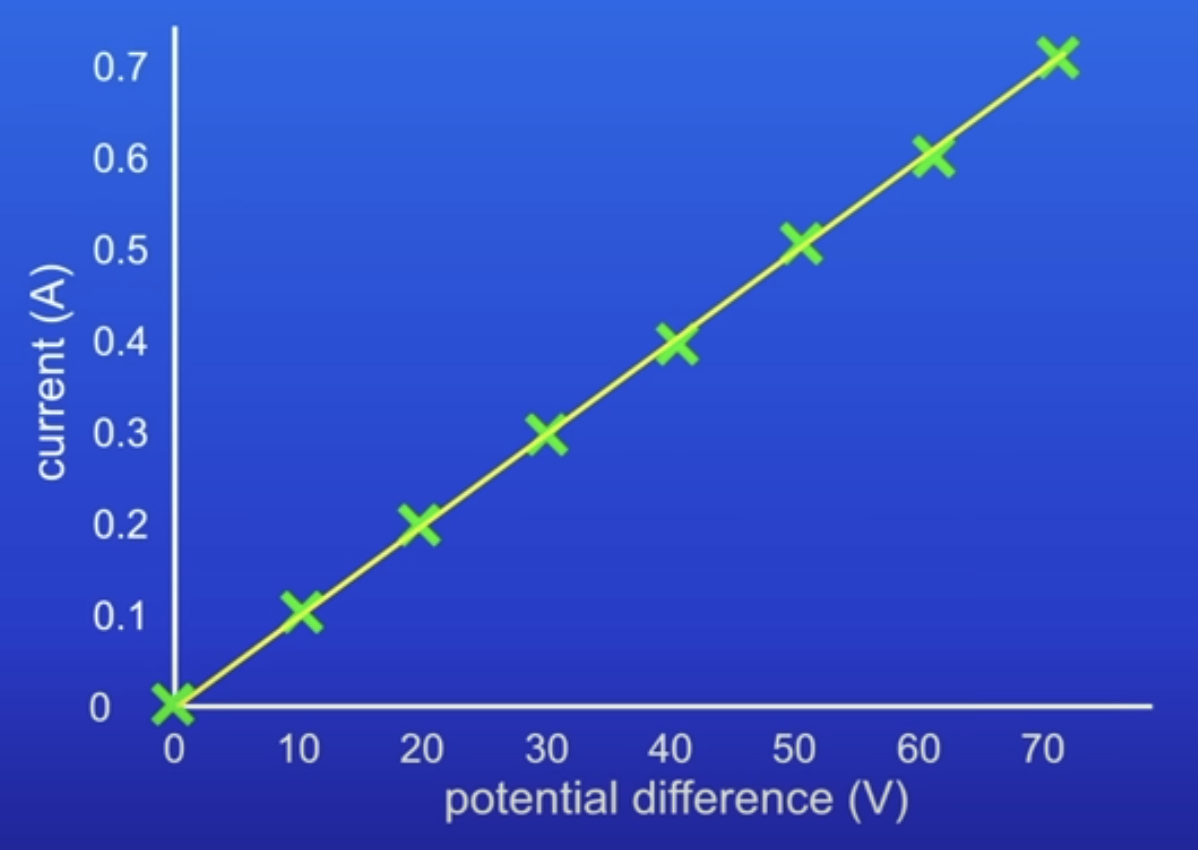
How does this graph show that current thru a resistor is DP to PD?
Straight line passing thru origin
IV graph for an ohmic conductor
When are resistors used in circuits?
To control PD across other components
Circuit used to change PD across resistor + measure current flowing thru it
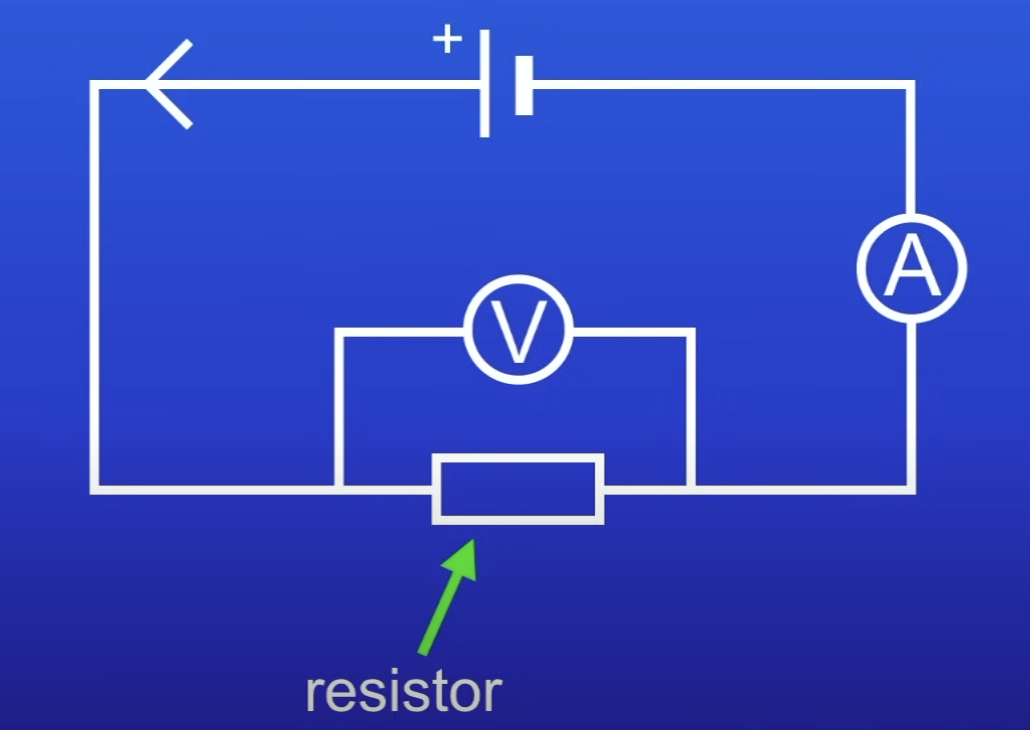
What does it mean if resistance is not constant
Resistance changes w the current through the component
Examples of non-ohmic conductors (resistance isn’t constant)
Filament lamp
Diodes
Thermistors
LDR
Is a filament lamp energy efficient?
No
Filament
Tightly coiled wire
How does a filament lamp work?
Wire gets v hot when electric current passed thru it
Causes it to glow + give out light
IV graph for a filament lamp
As PD increases, current no longer increases as much → R is increasing
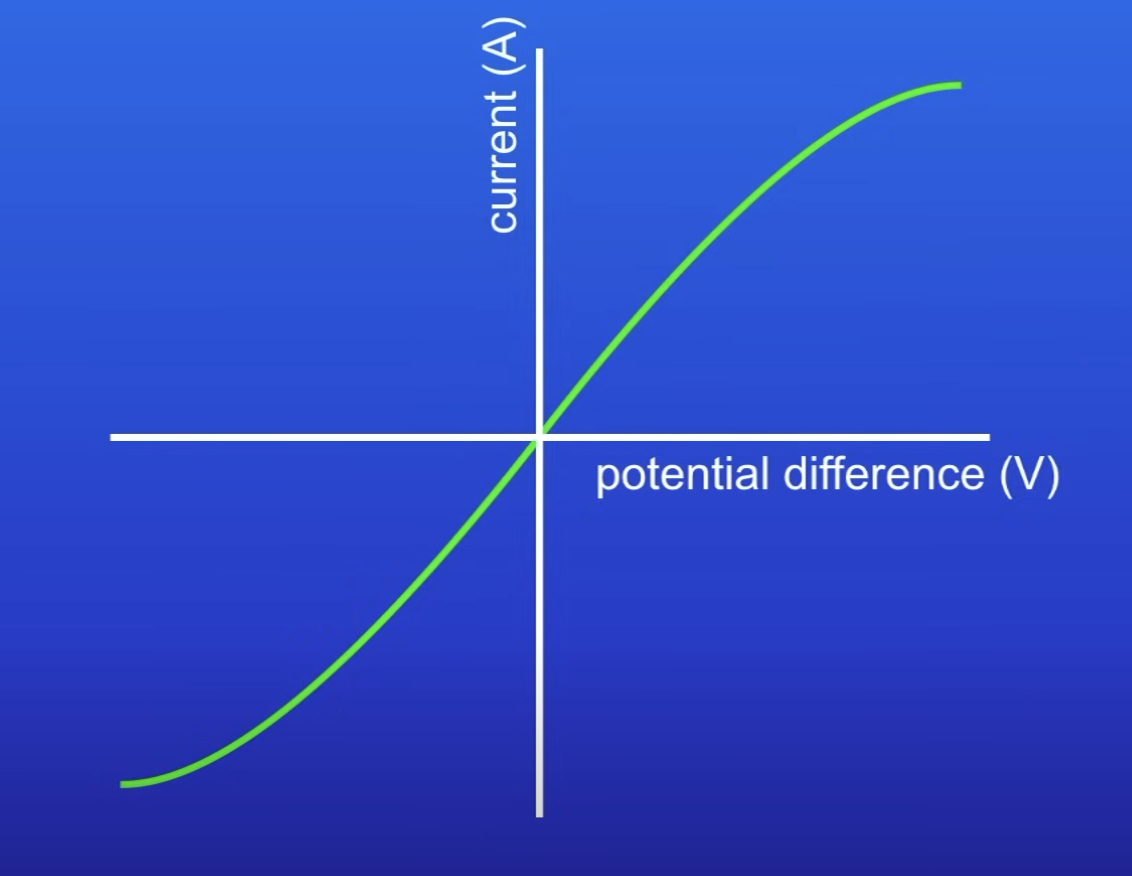
Current thru a filament lamp is…
Not DP to PD
Why is current in a filament lamp not DP to PD (why isn’t resistance constant?)
Filament gets hot → causes R to increase
At high temp, atoms in filament vibrate more
So electrons in current collide more w atoms
So more energy needed to push current thru the filament
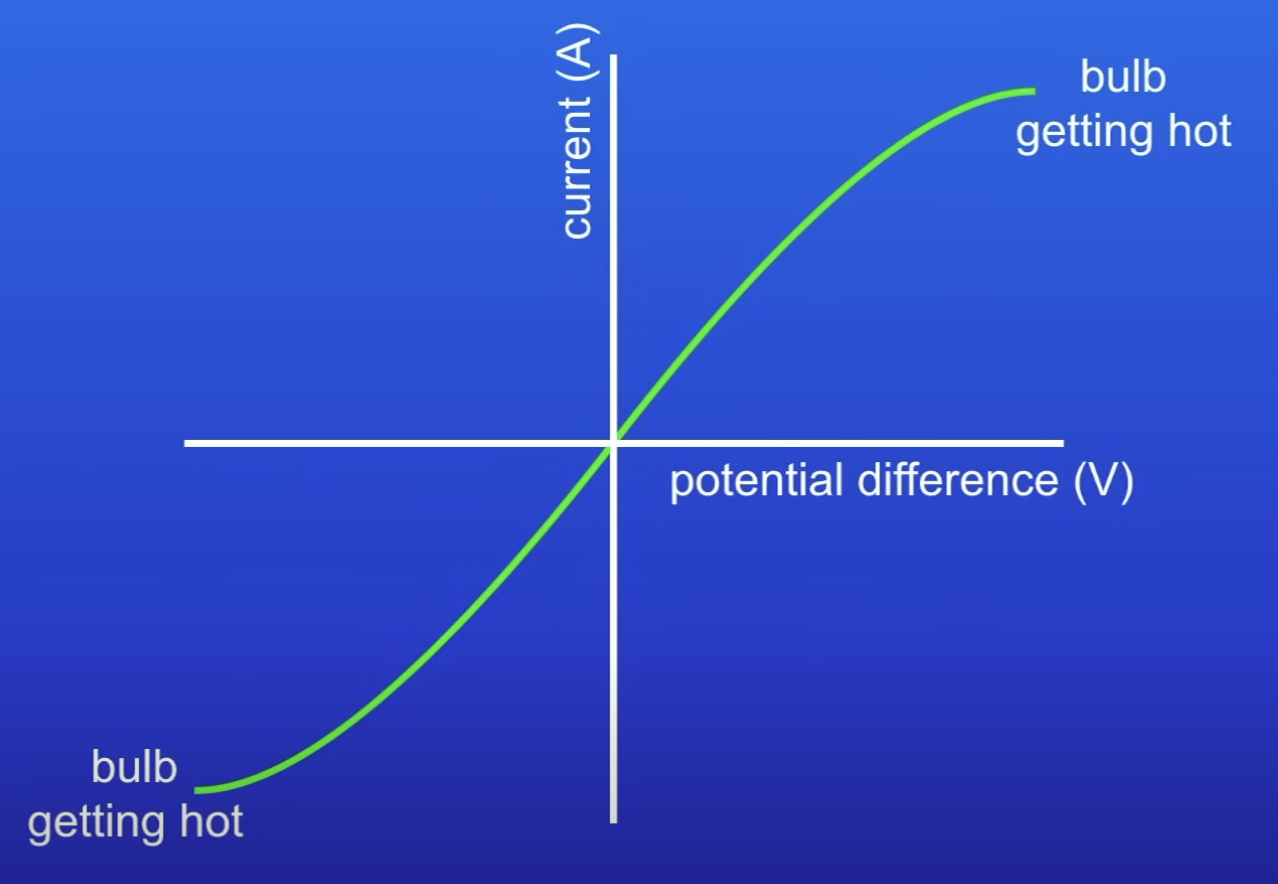
What happens to the resistance of a filament lamp as temp increases?
R increases
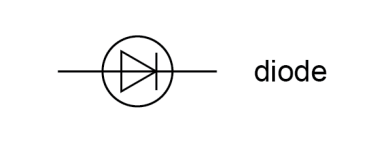
Diode
Non-ohmic conductor that allows current to flow in 1 direction only (forward)
What is special about the current thru a diode?
Flows in 1 direction only
Why does the current thru a diode flow in 1 direction only?
Diode has v high resistance in reverse direction, preventing current flow
What does the direction of the arrow in the symbol for a diode show?
Direction conventional current must flow in
For the diode to allow it thru
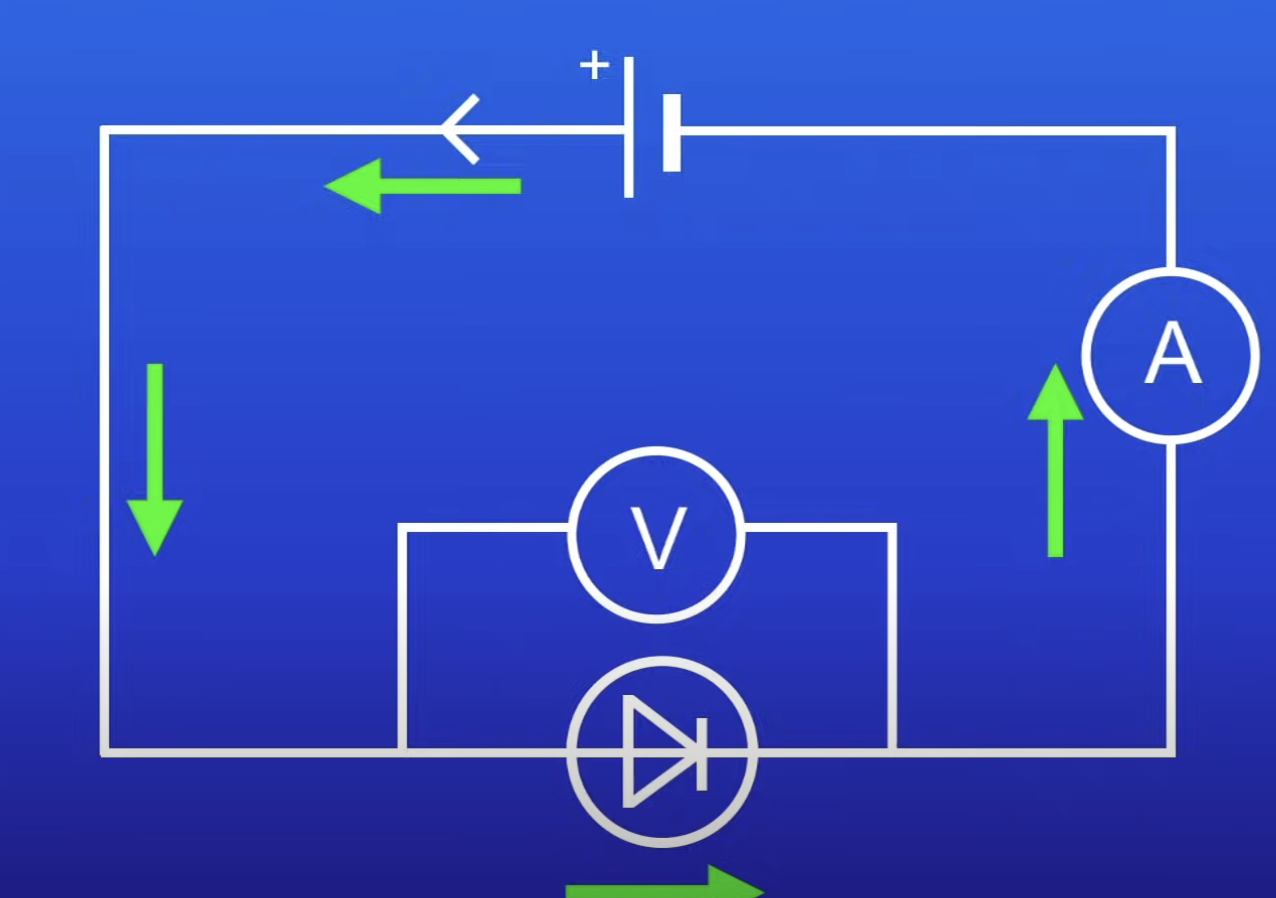
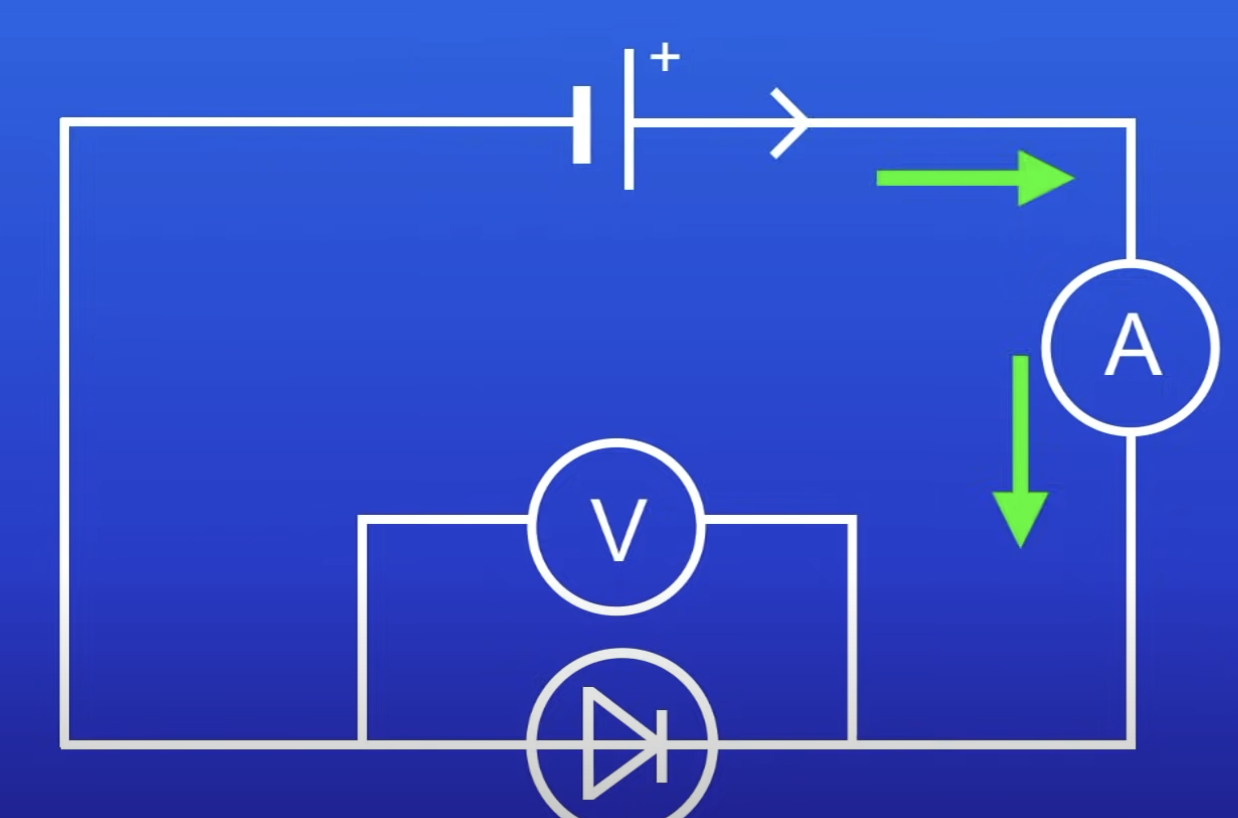
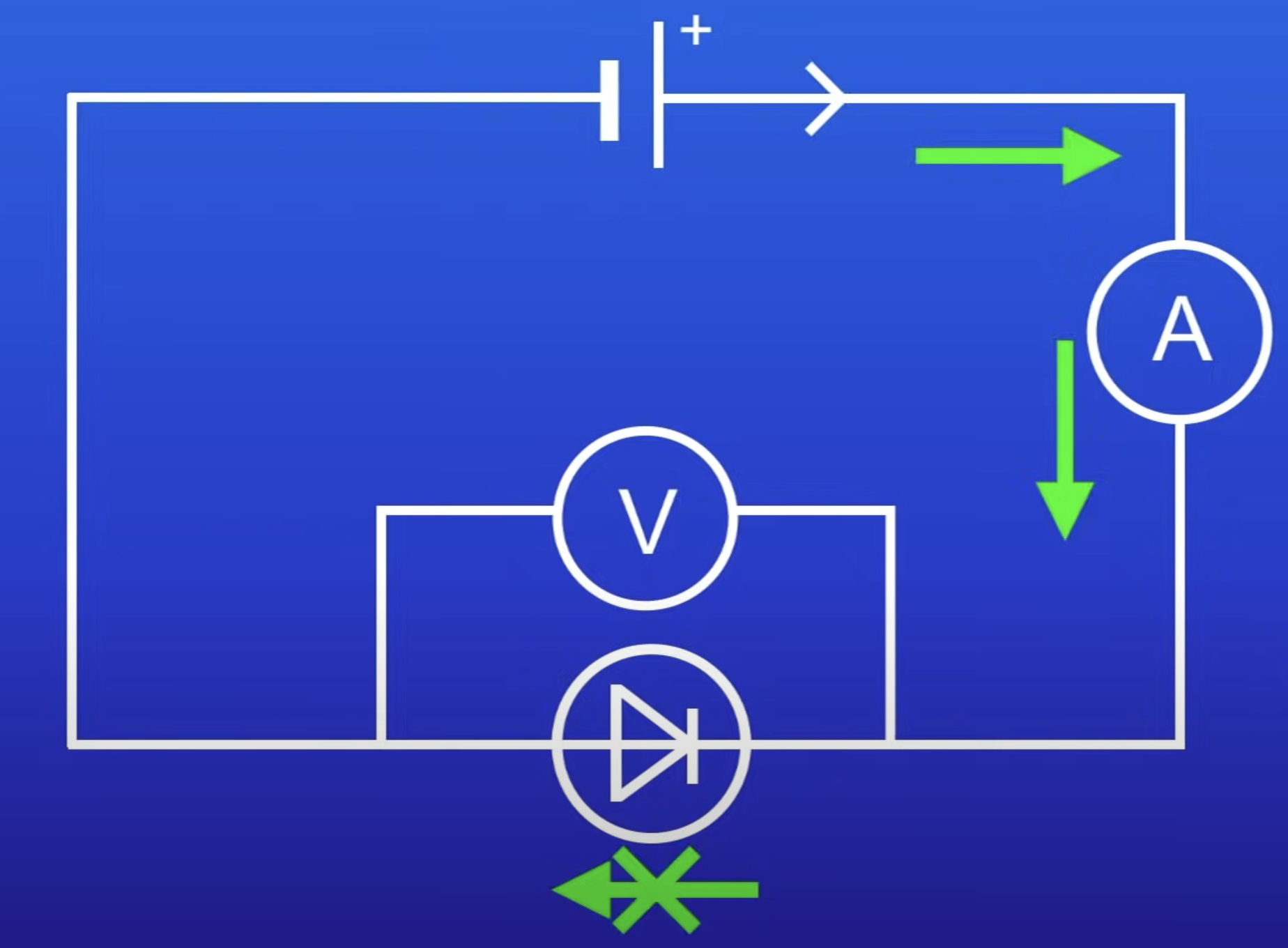
What happens in relation to the diode if the cell is switched around?
Direction of current switches
So diode won’t allow current to pass thru
Due to v high R in reverse direction
IV graph for a diode
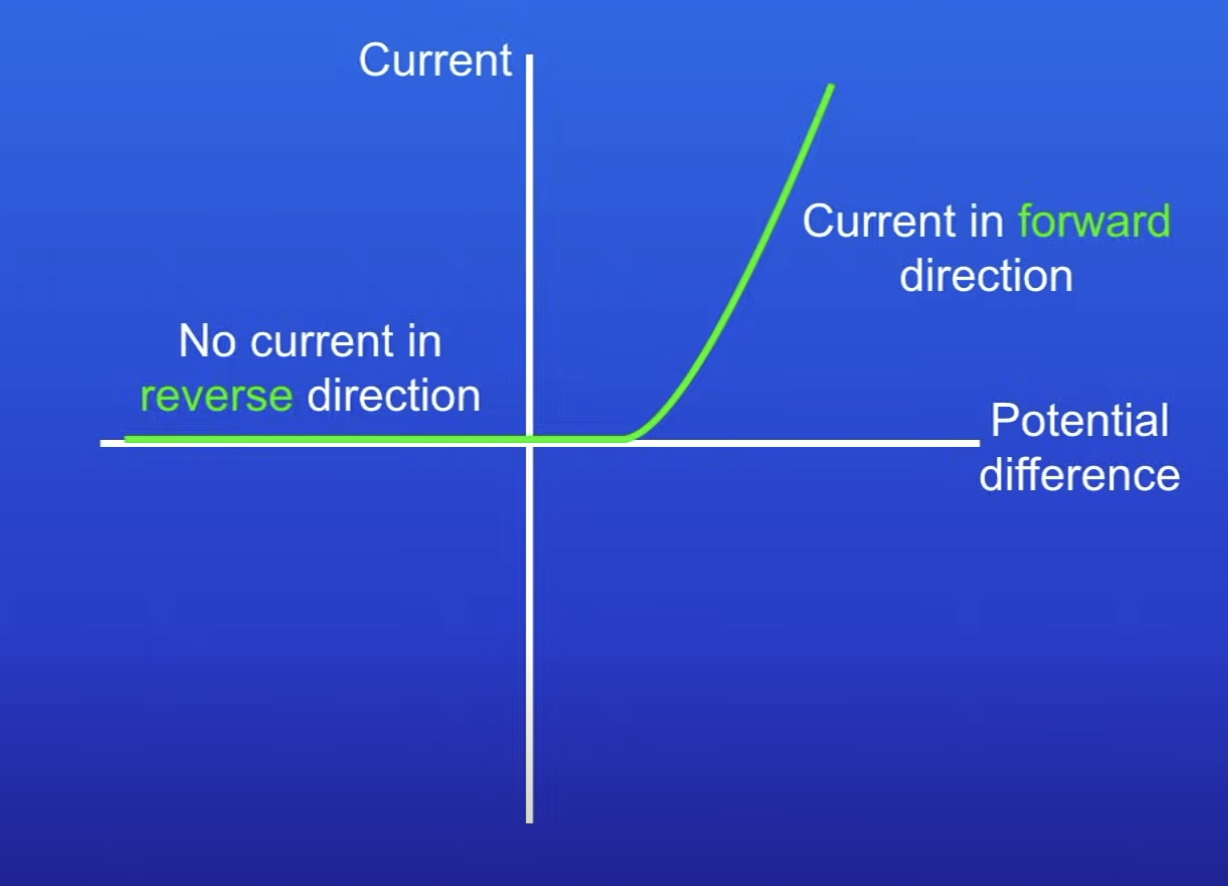
Describe the IV graph for a diode
No current can flow in the reverse direction
In forward direction, current increases as PD increases
What are diodes useful for?
Controlling flow of current in circuits
Light emitting diode (LED)
Gives off light when current flows thru
Only allows current to flow in forward direction
Are LEDs an efficient soure of light?
Yes
What does a diode have in the reverse direction
V high resistance
Resistance of diode in forward + reverse direction
Forward: low
Reverse: high
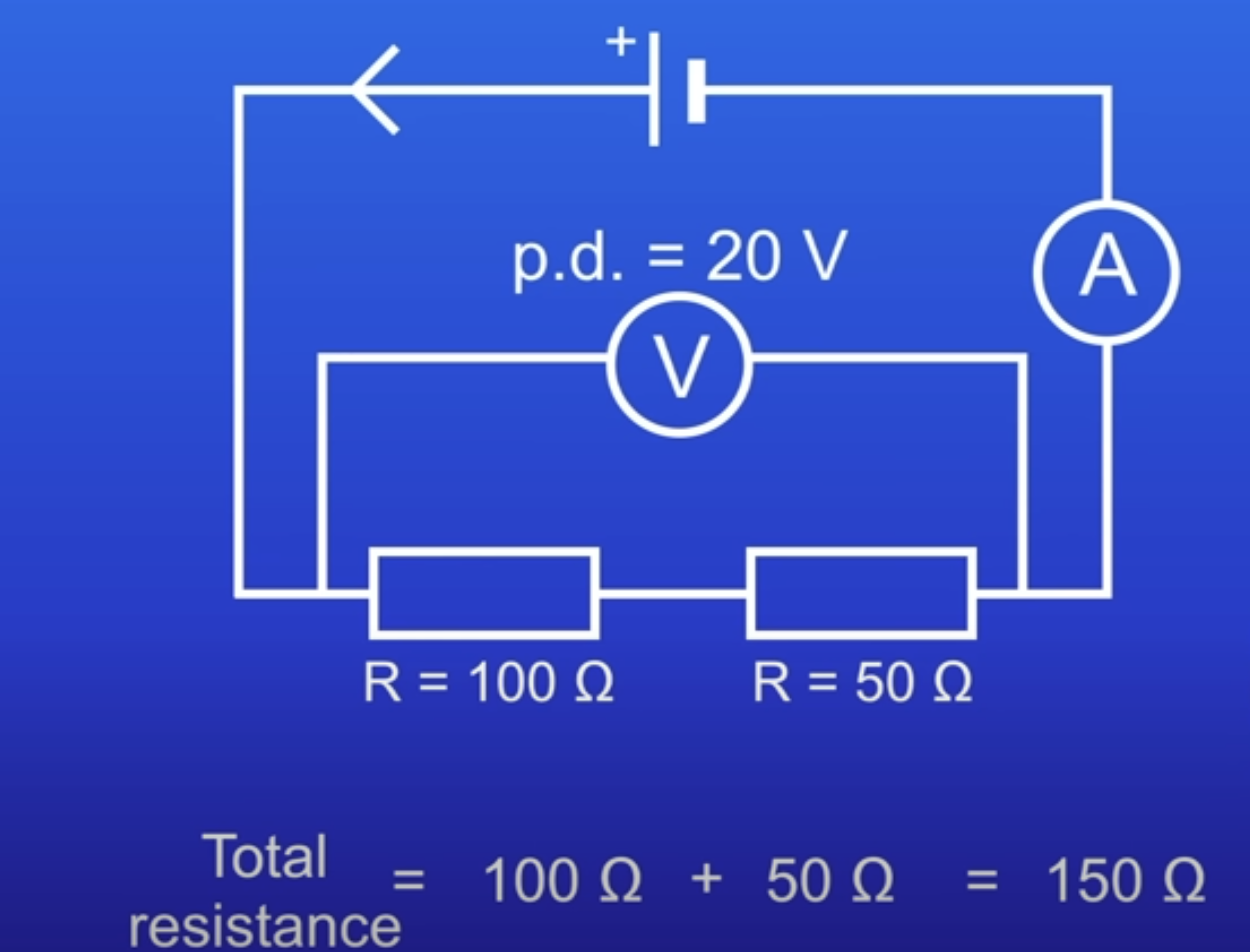
How do resistors in series behave?
Add tog