Unit 3.8 Animal Reproduction
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:02 AM on 12/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
1
New cards
Animal Reproduction
1. **Asexual & Sexual Reproduction**
* Mechanisms of Asexual Reproduction
a. Invertebrates
b. Parthenogenesis
* Variations in patterns of sexual reproduction
* Reproductive cycles
* Evolutionary enigma
\
2. **Fertilization**
* Types of fertilization
* Ensuring the survival of offspring
* Gamete production and delivery
\
3. **Reproductive Organs**
* Male anatomy
a. Testes
b. Ducts
c. Accessory glands
d. Penis
* Female anatomy
a. Ovaries
b. Oviducts & Uterus
c. Vagina & Vulva
d. Mammary glands
* Gametogenesis
a. Spermatogenesis
b. Oogenesis
\
4. **Tropic and Sex Hormones**
* Human sexuality
* Hormone control in males
* Hormone control in females
a. Ovarian cycle
b. Uterine (menstrual cycle)
c. Menopause
d. Menstrual vs estrous cycles
* Human sexual response
\
5. **Embryonic Development**
* Conception, Embryonic Development,
and Birth
* Maternal Immune Tolerance of the
Embryo and Fetus
* Contraception and Abortion
* Modern Reproductive Technologies
2
New cards
**zygote,** meiosis, egg, sperm
**Sexual reproduction**
* The fusion of haploid gametes form a diploid cell, the **_____**
* The animal that develops from a zygote can in turn give rise to gametes by _____
➔ Has two gametes
* **___:** large and nonmotile female gamete
* **_____:** generally much smaller and motile male gamete
* The fusion of haploid gametes form a diploid cell, the **_____**
* The animal that develops from a zygote can in turn give rise to gametes by _____
➔ Has two gametes
* **___:** large and nonmotile female gamete
* **_____:** generally much smaller and motile male gamete
3
New cards
mitotic
**Asexual reproduction**
* New individuals are generated without the fusion of egg and sperm
* For most asexual animals, reproduction relies entirely on ______ cell division
* New individuals are generated without the fusion of egg and sperm
* For most asexual animals, reproduction relies entirely on ______ cell division
4
New cards
**Asexual & Sexual Reproduction**
* Mechanisms of Asexual Reproduction
a. Invertebrates
b. Parthenogenesis
* Variations in patterns of sexual reproduction
* Reproductive cycles
* Evolutionary enigma
a. Invertebrates
b. Parthenogenesis
* Variations in patterns of sexual reproduction
* Reproductive cycles
* Evolutionary enigma
5
New cards
Invertebrates
1. Budding
2. Fission
3. Fragmentation and Regeneration
6
New cards
Budding
* New individuals arise from outgrowths of existing ones
* **EX.** stony corals, buds form and remain attached to the parent
* Eventually results in a colony more than 1 m across, consisting of thousands of connected individuals
* **EX.** stony corals, buds form and remain attached to the parent
* Eventually results in a colony more than 1 m across, consisting of thousands of connected individuals

7
New cards
**Fission**
The splitting and separation of a parent organism into two individuals of approximately equal size
8
New cards
Fragmentation and regeneration
* **______,** the breaking of the body into several pieces, followed by _______, regrowth of lost body
par
* If more than one piece grows and develops into a complete animal, the effect is reproductionts
* annelid worms, corals, sponges, cnidarians, and tunicates
par
* If more than one piece grows and develops into a complete animal, the effect is reproductionts
* annelid worms, corals, sponges, cnidarians, and tunicates
9
New cards
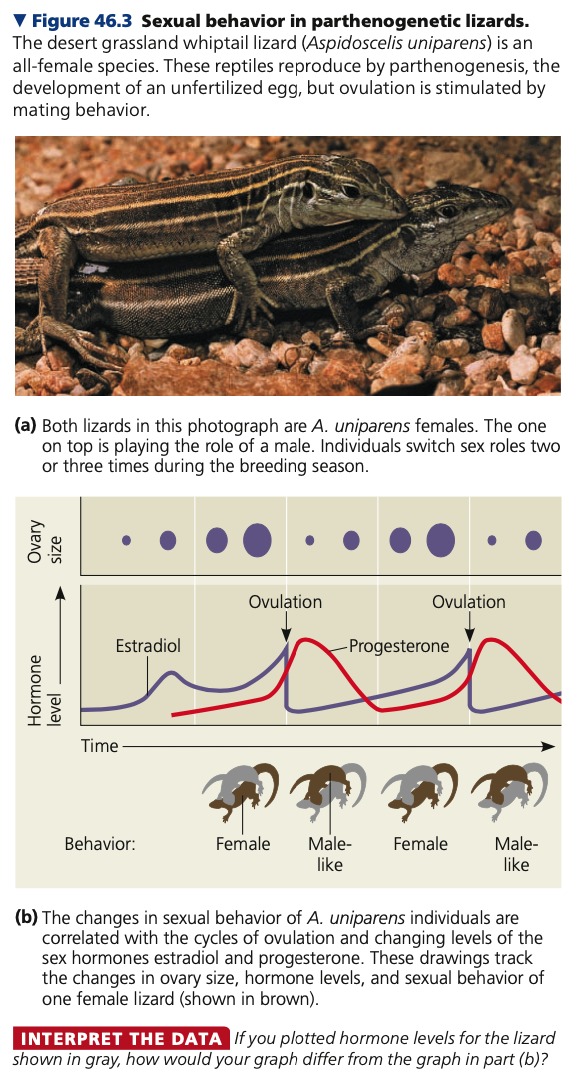
Parthenogenesis
* An egg develops without being fertilized
* Occurs in both vertebrate and invertebrate animal species
* Occurs in both vertebrate and invertebrate animal species
10
New cards
bees, haploid
**Parthenogenesis (invertebrates)**
* Occurs in certain species of ___ (honey bees), wasps, and ants
* Either _____ or diploid offspring
* Occurs in certain species of ___ (honey bees), wasps, and ants
* Either _____ or diploid offspring
11
New cards
low
**Parthenogenesis (vertebrates)**
* Thought to be a rare response to ___ population density
* **EX.** female Komodo dragons, hammerhead sharks, and zebra sharks have been observed to produce offspring when kept in captivity apart from males of their species
* Thought to be a rare response to ___ population density
* **EX.** female Komodo dragons, hammerhead sharks, and zebra sharks have been observed to produce offspring when kept in captivity apart from males of their species
12
New cards
Variations in patterns of sexual reproduction
1. Hermaphroditism
2. Sex reversal
13
New cards
sessile, corals
**Hermaphroditism**
* Each individual has both male and
female reproductive systems
* The term *hermaphrodite* merges the
names of Hermes and Aphrodite, a
Greek god and goddess
* Particularly common among ____ (stationary) animals, such as barnacles, burrowing animals, such as clams, and some parasites, including tapeworms
* In some species, including many ____, hermaphrodites can also self-fertilize
* Each individual has both male and
female reproductive systems
* The term *hermaphrodite* merges the
names of Hermes and Aphrodite, a
Greek god and goddess
* Particularly common among ____ (stationary) animals, such as barnacles, burrowing animals, such as clams, and some parasites, including tapeworms
* In some species, including many ____, hermaphrodites can also self-fertilize

14
New cards
wrasse, oyster
**Sex reversal**
* The sex (gonadal and secondary sexual characteristics) of an organism is altered from one gender to another
* Occurs in bluehead __ and certain ____ species
* Done to maximize successful reproduction and produce more offspring
* The sex (gonadal and secondary sexual characteristics) of an organism is altered from one gender to another
* Occurs in bluehead __ and certain ____ species
* Done to maximize successful reproduction and produce more offspring
15
New cards
seasons, hormones, ovulation
**Reproductive cycles**
* Exhibited by most animals, whether asexual or sexual
* Often related to changing ______
* Controlled by _____, whose secretion is in
turn regulated by environmental cues
* Animals expend resources to reproduce only when sufficient energy sources are available and when environmental conditions favor the
survival of offspring
* **______**: the production and release of
mature eggs
* Exhibited by most animals, whether asexual or sexual
* Often related to changing ______
* Controlled by _____, whose secretion is in
turn regulated by environmental cues
* Animals expend resources to reproduce only when sufficient energy sources are available and when environmental conditions favor the
survival of offspring
* **______**: the production and release of
mature eggs
16
New cards
number, combinations, adaptation
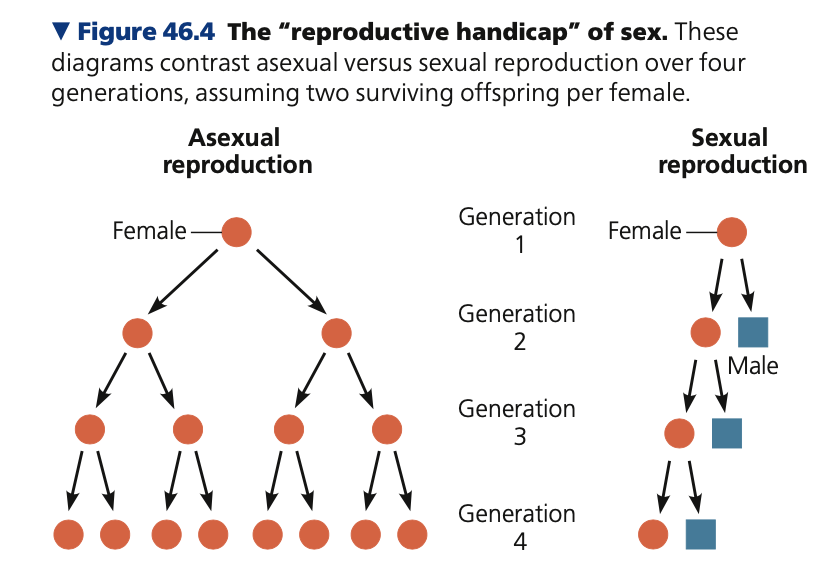
**Evolutionary enigma**
* The existence of sexual reproduction is puzzling
* Asexual condition will increase in frequency at each generation
* Sex has a “twofold cost”: the _____ of sexual offspring will remain the same at each generation because both a male and a female are required to reproduce
\
* Hypotheses on the advantages of sexual reproduction
* The unique ______ of parental genes formed during meiotic recombination and fertilization
* Beneficial gene combinations arising through
recombination might speed
up _______
* Might allow a population to
rid itself of sets of harmful
genes more readily
* **Varied genotype offspring**: may
enhance the reproductive success of parents when environmental factors, such as pathogens, change relatively rapidly
* **Asexual reproduction**: expected to be most advantageous in stable, favorable environments because it can perpetuate successful genotypes precisely
* The existence of sexual reproduction is puzzling
* Asexual condition will increase in frequency at each generation
* Sex has a “twofold cost”: the _____ of sexual offspring will remain the same at each generation because both a male and a female are required to reproduce
\
* Hypotheses on the advantages of sexual reproduction
* The unique ______ of parental genes formed during meiotic recombination and fertilization
* Beneficial gene combinations arising through
recombination might speed
up _______
* Might allow a population to
rid itself of sets of harmful
genes more readily
* **Varied genotype offspring**: may
enhance the reproductive success of parents when environmental factors, such as pathogens, change relatively rapidly
* **Asexual reproduction**: expected to be most advantageous in stable, favorable environments because it can perpetuate successful genotypes precisely
17
New cards
Fertilization
* Types of fertilization
* Ensuring the survival of offspring
* Gamete production and delivery
* Ensuring the survival of offspring
* Gamete production and delivery
18
New cards
Types of fertilization
1. External fertilization
2. Internal fertilization
19
New cards
moist, **Spawning,** positive, **courtship**
1. **External fertilization**
* The female releases eggs into the environment, where the male fertilizes them
* Almost always requires a ___ habitat
* To prevent the gametes from drying out
* To allow the sperm to swim to the eggs
* Many aquatic invertebrates simply
shed their eggs and sperm into the surroundings, and fertilization occurs without the parents making physical contact
* **Timing** is crucial
* **______:** individuals
clustered in the same area release their gametes into the water at the same time
* Chemical signals (_____ feedback)
* Environmental cues (e.g. temperature or day length)
* When external fertilization is not synchronous across a population, individuals may exhibit specific **“_____” behaviors** leading to the fertilization of the eggs of one female by one male

20
New cards
**copulation**
2. **Internal fertilization**
* Enables sperm to reach an egg even
when the external environment is dry
* Typically requires sophisticated and
compatible reproductive systems, as well as cooperative behavior that leads to **_____**
* The male copulatory organ delivers sperm
* The female reproductive tract often has receptacles for storage and delivery of sperm to mature eggs
21
New cards
Chemicals, water
**Pheromones**
* May occur in either type of fertilization
* _____ released by one organism that influence the physiology and behavior of other individuals of the same species
* Small, volatile or _____-soluble molecules that disperse into the environment and are active at very low concentrations
* Many function as mate attractants
* Controversial existence in humans
* May occur in either type of fertilization
* _____ released by one organism that influence the physiology and behavior of other individuals of the same species
* Small, volatile or _____-soluble molecules that disperse into the environment and are active at very low concentrations
* Many function as mate attractants
* Controversial existence in humans
22
New cards
fewer, eggshell, Marsupial, Eutherian, membranes
**Ensuring the survival of offspring**
* **Internal fertilization** produces ____ gametes, but has a higher zygote survival.
1. Fertilized eggs are sheltered from potential predators
2. Mechanisms that provide greater protection of the embryos and parental care of the young
* Secreting a protective ____ (birds and other reptiles)
* Retaining the embryo for a portion of its development within the female’s reproductive tract
* _____ mammals: kangaroos and opossums
* they then crawl out and complete development attached to a mammary gland in the mother’s pouch
* _____ (placental) mammals: zebras and humans
* nourished by the mother’s blood supply through a temporary organ, the placent
* In contrast, the eggs of fishes and amphibians have only a gelatinous coat and lack internal ______.
* **Internal fertilization** produces ____ gametes, but has a higher zygote survival.
1. Fertilized eggs are sheltered from potential predators
2. Mechanisms that provide greater protection of the embryos and parental care of the young
* Secreting a protective ____ (birds and other reptiles)
* Retaining the embryo for a portion of its development within the female’s reproductive tract
* _____ mammals: kangaroos and opossums
* they then crawl out and complete development attached to a mammary gland in the mother’s pouch
* _____ (placental) mammals: zebras and humans
* nourished by the mother’s blood supply through a temporary organ, the placent
* In contrast, the eggs of fishes and amphibians have only a gelatinous coat and lack internal ______.

23
New cards
precursors, gametes
**Gamete production and delivery**
* Sexual reproduction in animals relies on sets of cells that are _____ for eggs and sperm
* Cells dedicated to this function are often established early in the formation of the embryo and remain inactive while the body plan takes shape
* Cycles of growth and mitosis then increase, or amplify, the number of cells available for making ____—eggs or sperm
* Sexual reproduction in animals relies on sets of cells that are _____ for eggs and sperm
* Cells dedicated to this function are often established early in the formation of the embryo and remain inactive while the body plan takes shape
* Cycles of growth and mitosis then increase, or amplify, the number of cells available for making ____—eggs or sperm
24
New cards
**Gamete production and delivery**
1. Gonads
2. Accessory tubes and glands
3. Cloaca
25
New cards
polychaete
1. **Gonads (primary reproductive organs)**
* Organs the produce gametes
* Found in many but not all animals
* Exceptions include palolo and most other ______ worms
* eggs and sperm develop from undifferentiated cells lining the coelom (body cavity)
26
New cards
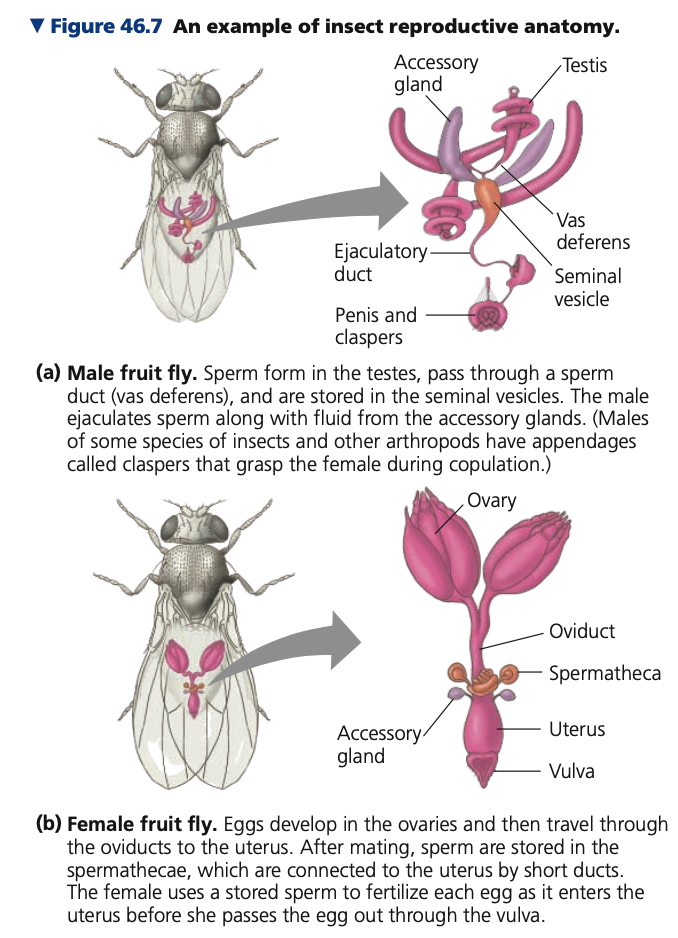
***Spermathecae,*** insect
2. **Accessory tubes and glands**
* Found in more elaborate reproductive
systems
* Carry, nourish, and protect the
gametes and sometimes the
developing embryos
* ***_______***: sacs in which sperm
may be kept alive and stored for extended periods found in the female reproductive system in many ____ species
27
New cards
Common, mammals
3. **Cloaca**
* Found in many nonmammalian vertebrates
* _____ opening for the digestive, excretory, and reproductive systems
* Probably present in the ancestors of all vertebrates
* Lacking a well-developed penis, males of these species instead release sperm by turning the cloaca inside out
* _____ generally have separate openings and thus lack a cloaca
28
New cards
Reproductive Organs
* Male anatomy
a. Testes
b. Ducts
c. Accessory glands
d. Penis
* Female anatomy
a. Ovaries
b. Oviducts & Uterus
c. Vagina & Vulva
d. Mammary glands
* Gametogenesis
a. Spermatogenesis
b. Oogenesis
a. Testes
b. Ducts
c. Accessory glands
d. Penis
* Female anatomy
a. Ovaries
b. Oviducts & Uterus
c. Vagina & Vulva
d. Mammary glands
* Gametogenesis
a. Spermatogenesis
b. Oogenesis
29
New cards
External reproductive organs (male)
Scrotum, penis
30
New cards
Internal reproductive organs (male)
gonads (testes), accessory glands, ducts
31
New cards
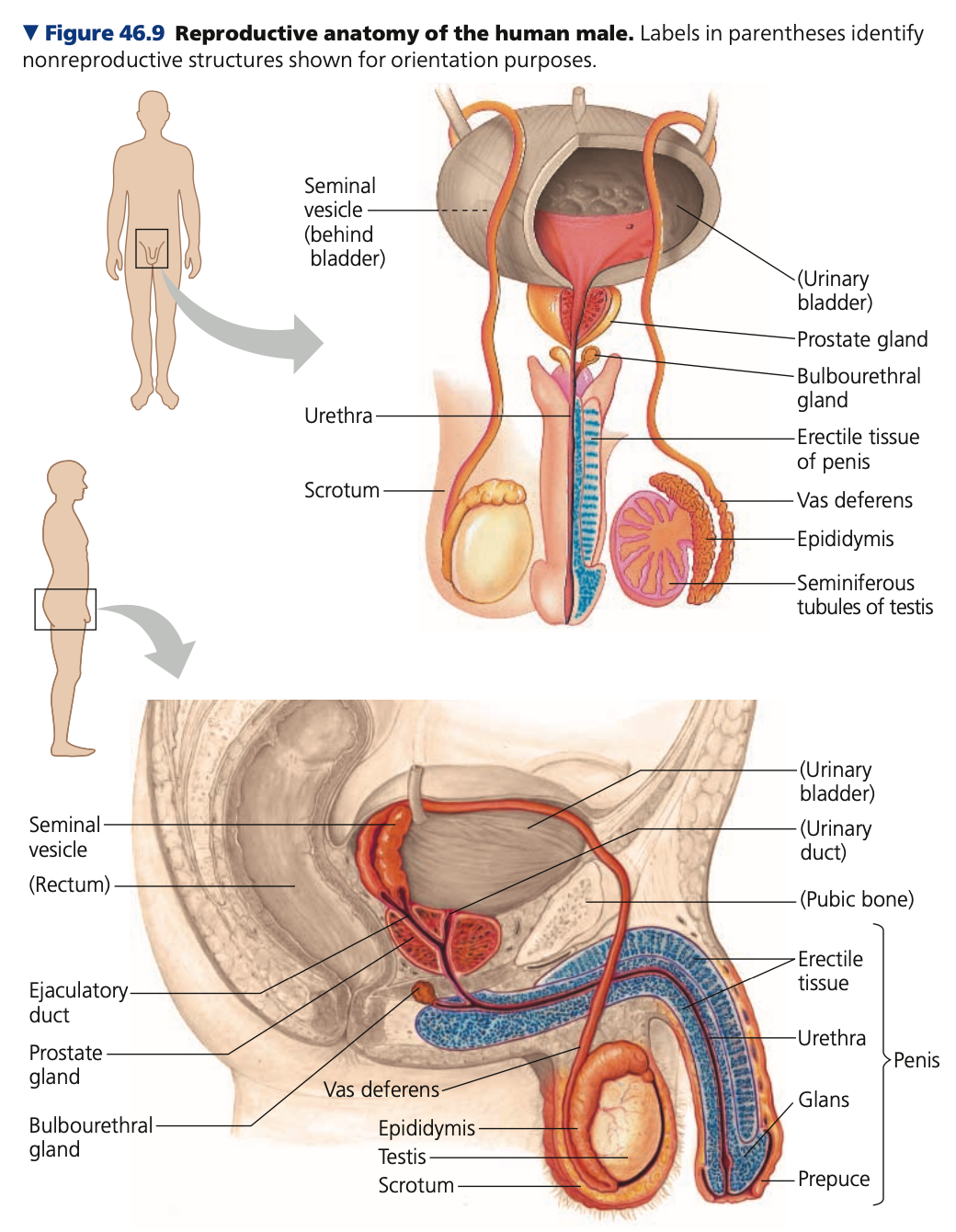
Male anatomy
a. Testes
b. Ducts
c. Accessory glands
d. Penis
b. Ducts
c. Accessory glands
d. Penis
32
New cards
**seminiferous, scrotum, testicle**
**Testes**
* Male gonads that produce sperm in highly coiled tubes called **_______ tubules**
* **_____**: a fold of the body wall that keeps testis temperature cooler than the rest of the body (about 2°C below the core body temperature) for proper sperm production
* Develop in the abdominal cavity and descend into the scrotum just before birth
* **____**: a testis within a scrotum
* Variations in animals include:
* **Rodents:** the testes are drawn back into the cavity between breeding seasons, interrupting sperm maturation
* **Low-body temperature mammals:** retain the testes in the abdominal cavity at all times (whales and elephants)
* Male gonads that produce sperm in highly coiled tubes called **_______ tubules**
* **_____**: a fold of the body wall that keeps testis temperature cooler than the rest of the body (about 2°C below the core body temperature) for proper sperm production
* Develop in the abdominal cavity and descend into the scrotum just before birth
* **____**: a testis within a scrotum
* Variations in animals include:
* **Rodents:** the testes are drawn back into the cavity between breeding seasons, interrupting sperm maturation
* **Low-body temperature mammals:** retain the testes in the abdominal cavity at all times (whales and elephants)
33
New cards
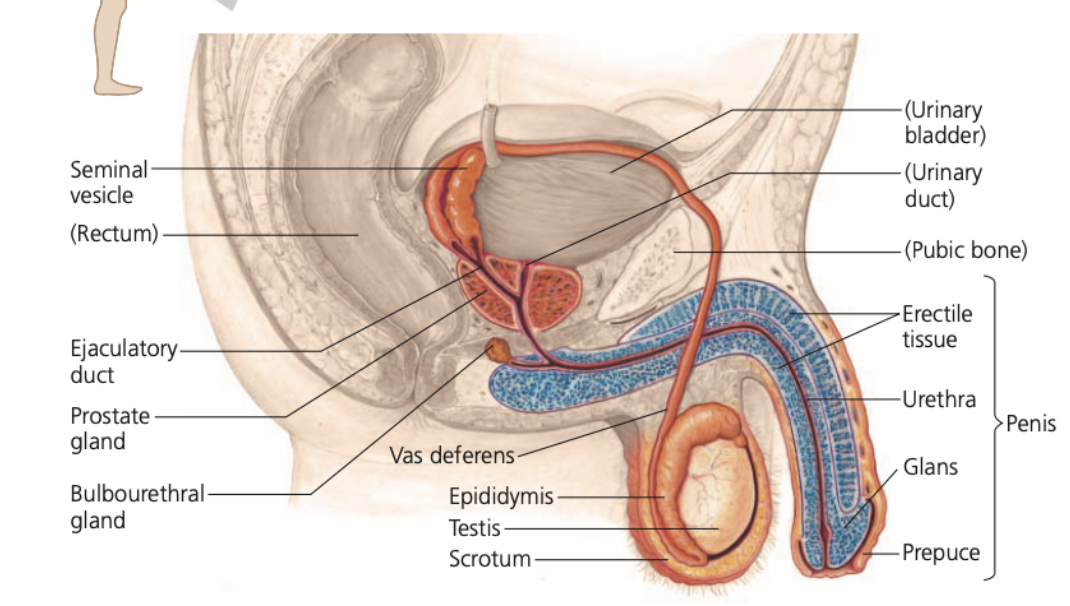
**Epididymis,** Coiled, **deferens, ejaculation,** seminal, **Urethra**
**Ducts**
1. **_______**
* ____ duct that sperm pass into from the seminiferous tubules of a testis
* Takes three weeks for sperm to travel the 6-m length of this duct, during which time the sperm complete maturation and become motile
2. **Vas ______**
* A muscular duct that propels sperm from each epididymis during **______**
* Each vas deferens (one from each epididymis) extends around and behind the urinary bladder, where it joins a duct from the ______ vesicle, forming a short ejaculatory duct that opens into the urethra
3. **______**
* The outlet tube for both the excretory system and the reproductive system
* Runs through the penis and opens to the outside at the tip of the penis
1. **_______**
* ____ duct that sperm pass into from the seminiferous tubules of a testis
* Takes three weeks for sperm to travel the 6-m length of this duct, during which time the sperm complete maturation and become motile
2. **Vas ______**
* A muscular duct that propels sperm from each epididymis during **______**
* Each vas deferens (one from each epididymis) extends around and behind the urinary bladder, where it joins a duct from the ______ vesicle, forming a short ejaculatory duct that opens into the urethra
3. **______**
* The outlet tube for both the excretory system and the reproductive system
* Runs through the penis and opens to the outside at the tip of the penis
34
New cards
Semen
* The fluid that is ejaculated
* Formed by secretions from the three
sets of accessory glands that combine with sperm
* Formed by secretions from the three
sets of accessory glands that combine with sperm
35
New cards
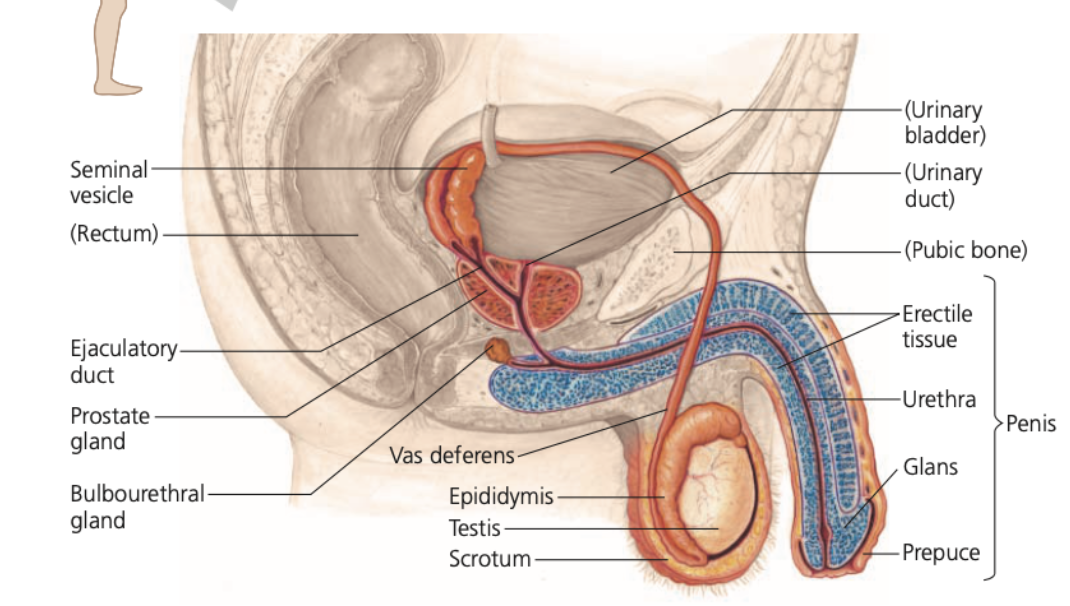
alkaline, **prostaglandins,** milky, citrate, clear, neutralizes,
**Accessory glands**
1. **Pair of seminal vesicles**
* Make up about 60% of the total semen volume
* Thick, yellowish, and _____ fluid
* Contains mucus, fructose, a coagulating enzyme, ascorbic acid, and local regulators called **_____** (stimulate female uterine contractions to help move semen to the uterus)
2. **Prostate gland**
* Secretes its products directly into the urethra through small ducts
* Thin, fluid containing anticoagulant enzymes and _____ (a sperm nutrient)
3. **Pair of bulbourethral glands**
* Small glands along the urethra below the prostate
* Secrete __ mucus that ____ any acidic urine remaining in the urethra before ejaculation
* Carries some sperm released before ejaculation, which may contribute to the high failure rate of the withdrawal method of birth control (coitus interruptus)
1. **Pair of seminal vesicles**
* Make up about 60% of the total semen volume
* Thick, yellowish, and _____ fluid
* Contains mucus, fructose, a coagulating enzyme, ascorbic acid, and local regulators called **_____** (stimulate female uterine contractions to help move semen to the uterus)
2. **Prostate gland**
* Secretes its products directly into the urethra through small ducts
* Thin, fluid containing anticoagulant enzymes and _____ (a sperm nutrient)
3. **Pair of bulbourethral glands**
* Small glands along the urethra below the prostate
* Secrete __ mucus that ____ any acidic urine remaining in the urethra before ejaculation
* Carries some sperm released before ejaculation, which may contribute to the high failure rate of the withdrawal method of birth control (coitus interruptus)
36
New cards
3, **shaft, glans, Prepuce, Foreskin**
**Penis**
* Contains the urethra as well as __ cylinders of spongy erectile tissue
* The main **___** of the penis is covered by relatively thick skin
* The head of the penis, the male **____**, has a much thinner outer layer and is much more sensitive to stimulation
* **____**: a fold of skin that covers the glans of humans
* **____**: male prepuce that is removed in circumcision
* Contains the urethra as well as __ cylinders of spongy erectile tissue
* The main **___** of the penis is covered by relatively thick skin
* The head of the penis, the male **____**, has a much thinner outer layer and is much more sensitive to stimulation
* **____**: a fold of skin that covers the glans of humans
* **____**: male prepuce that is removed in circumcision
37
New cards
veins,
**Erection**
* During sexual arousal, the erectile
tissue fills with blood from the
arteries
* As this tissue fills, the increasing
pressure seals off the ____ that drain the penis, causing it to engorge with blood
* The resulting erection enables the penis to be inserted into the vagina
* During sexual arousal, the erectile
tissue fills with blood from the
arteries
* As this tissue fills, the increasing
pressure seals off the ____ that drain the penis, causing it to engorge with blood
* The resulting erection enables the penis to be inserted into the vagina
38
New cards
Viagra, vasodilating
**Erectile dysfunction**
* Inability to have an erection
* Due to alcohol consumption, certain drugs, emotional issues, and aging
* ____: promote the _____ action of the local regulator nitric oxide, resulting in the relaxation of smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis that enhance blood flow into the erectile tissues.
* Inability to have an erection
* Due to alcohol consumption, certain drugs, emotional issues, and aging
* ____: promote the _____ action of the local regulator nitric oxide, resulting in the relaxation of smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis that enhance blood flow into the erectile tissues.
39
New cards
Baculum
* A bone that helps stiffen the penis
* Found in the penis of dogs, raccoons,
walruses, and several other mammals
* Found in the penis of dogs, raccoons,
walruses, and several other mammals
40
New cards
Female anatomy
a. Ovaries
b. Oviducts & Uterus
c. Vagina & Vulva
d. Mammary glands
b. Oviducts & Uterus
c. Vagina & Vulva
d. Mammary glands
41
New cards
External reproductive organs (female)
Clitoris, two sets of labia
42
New cards
Internal reproductive organs (male)
gonads (ovaries), ducts & chambers
43
New cards
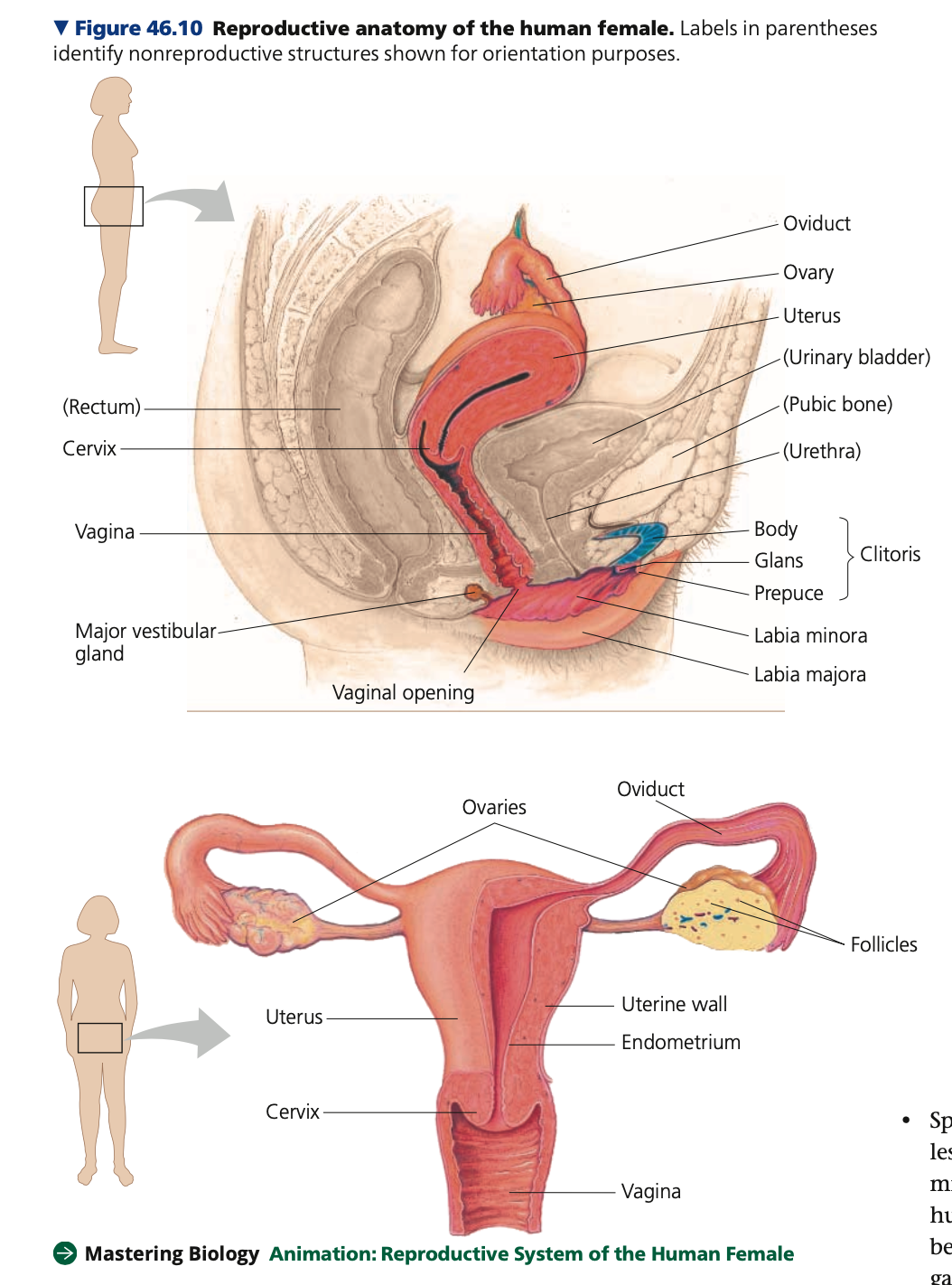
ligaments, follicles, oocyte, support
**Ovaries**
* Female gonads
* a pair of ovaries that flank the uterus
* Held in place in the abdominal cavity by ______
* Outer layer of each ovary
* Packed with __ consisting of __a partially developed egg surrounded by ____ cells
* Surrounding cells nourish and protect
oocyte during formation and development
* Female gonads
* a pair of ovaries that flank the uterus
* Held in place in the abdominal cavity by ______
* Outer layer of each ovary
* Packed with __ consisting of __a partially developed egg surrounded by ____ cells
* Surrounding cells nourish and protect
oocyte during formation and development
44
New cards
hair, Cilia, fluid, wavelike
**Oviducts / Fallopian Tubes**
* Extends from uterus toward funnel-like opening at each ovary
* Dimensions of tube vary along its length
* Inside diameter near uterus is as narrow as human __
* During **ovulation**
* ___ on epithelial lining of oviduct begin beating
* Motion draws ___ from body cavity into oviduct bringing the egg
* Further motion + _____ contractions of oviduct help the egg down the duct to the uterus
* Extends from uterus toward funnel-like opening at each ovary
* Dimensions of tube vary along its length
* Inside diameter near uterus is as narrow as human __
* During **ovulation**
* ___ on epithelial lining of oviduct begin beating
* Motion draws ___ from body cavity into oviduct bringing the egg
* Further motion + _____ contractions of oviduct help the egg down the duct to the uterus
45
New cards
Endometrium, Cervix
**Uterus / Womb**
* Thick, muscular organ that can expand during pregnancy to accommodate 4kg fetus
* ________
* Inner lining which is richly supplied with blood vessels
* _____
* Neck of uterus
* Opens to vagina
* Thick, muscular organ that can expand during pregnancy to accommodate 4kg fetus
* ________
* Inner lining which is richly supplied with blood vessels
* _____
* Neck of uterus
* Opens to vagina
46
New cards
elastic, birth
**Vagina**
* Muscular but _____ chamber
* Site for insertion of the penis and deposition of sperm during copulation
* Serves as the ____ canal through which baby is born
* Muscular but _____ chamber
* Site for insertion of the penis and deposition of sperm during copulation
* Serves as the ____ canal through which baby is born
47
New cards
**external, majora, minora, Hymen, Prepuce,** vestibular
**Vulva**
* Collective term for **_____ female genitalia**
* Where opening of vagina is found
1. **Labia _____**
* Thick , fatty ridges
* Enclose and protect rest of the vulva
\
2. **Labia ____**
* Pair of slender skin folds
* Contains
* Vaginal opening
* Separate opening of the urethra
\
3. **_____**
* Thin piece of tissue
* Partly covers vaginal opening at birth
* Wears away through physical activity
\
4. **Clitoris**
* Located at the top of labia minora
* Erectile tissue supporting rounded glans/head
* **____**
* Small hood of skin covering glans
* Richly supplied with nerve endings
* One of the most sensitive points of sexual stimulation
\
* **During sexual arousal**
* the clitoris, vagina, and labia minora all engorge with blood and enlarge
* Induces ______ glands near vaginal opening to secrete lubricating mucus, facilitating intercourse
* Collective term for **_____ female genitalia**
* Where opening of vagina is found
1. **Labia _____**
* Thick , fatty ridges
* Enclose and protect rest of the vulva
\
2. **Labia ____**
* Pair of slender skin folds
* Contains
* Vaginal opening
* Separate opening of the urethra
\
3. **_____**
* Thin piece of tissue
* Partly covers vaginal opening at birth
* Wears away through physical activity
\
4. **Clitoris**
* Located at the top of labia minora
* Erectile tissue supporting rounded glans/head
* **____**
* Small hood of skin covering glans
* Richly supplied with nerve endings
* One of the most sensitive points of sexual stimulation
\
* **During sexual arousal**
* the clitoris, vagina, and labia minora all engorge with blood and enlarge
* Induces ______ glands near vaginal opening to secrete lubricating mucus, facilitating intercourse
48
New cards
epithelial, **connective, adipose**
**Mammary glands**
* Present in both sexes
* Normally only produce milk in **females**
* Not part of reproductive system but important to reproduction
* Small sacs of _____ tissue secrete milk
* Drains into series of ducts that open at the nipple
* **Breasts**
* Contain ___ and fatty (_____) tissue in addition to the mammary glands
* Present in both sexes
* Normally only produce milk in **females**
* Not part of reproductive system but important to reproduction
* Small sacs of _____ tissue secrete milk
* Drains into series of ducts that open at the nipple
* **Breasts**
* Contain ___ and fatty (_____) tissue in addition to the mammary glands
49
New cards
**haploid, Support**
**Gametogenesis**
* Production of **gametes** (sperm and egg cells)
* Close relation between gonad structure and function
* **Similarities between spermatogenesis (sperm production) and oogenesis (oocyte production)**
* Generate **____ gametes** via meiotic divisions of dedicated diploid cells
* **____ cells in gonad** play essential role in both spermatogenesis and oogenesis
* Production of **gametes** (sperm and egg cells)
* Close relation between gonad structure and function
* **Similarities between spermatogenesis (sperm production) and oogenesis (oocyte production)**
* Generate **____ gametes** via meiotic divisions of dedicated diploid cells
* **____ cells in gonad** play essential role in both spermatogenesis and oogenesis
50
New cards
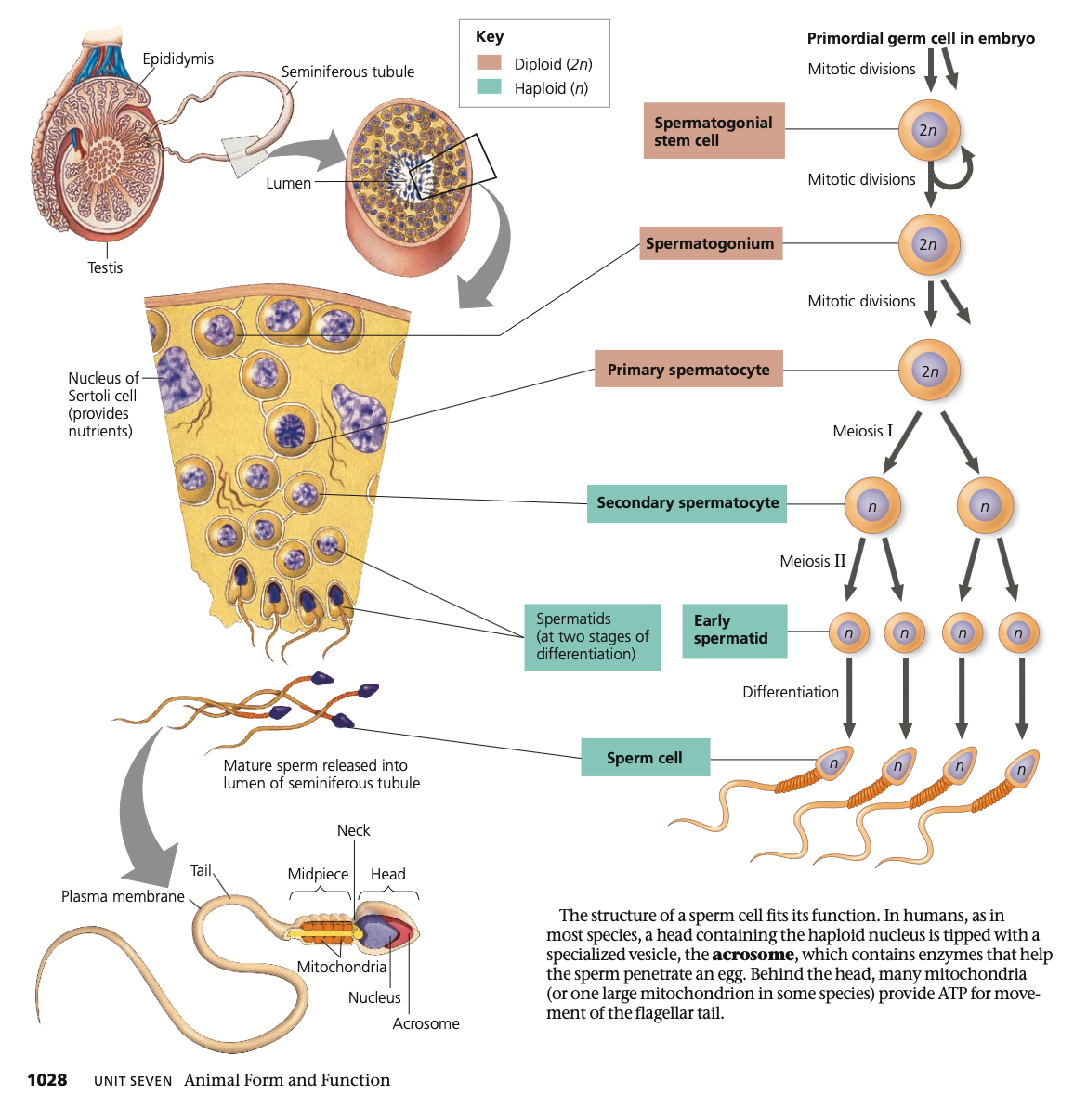
Continually, continuous, **seminiferous, day, 4**
**Spermatogenesis**
* ______ occurs throughout adolescence and adulthood
* Produces mature sperm from precursor cells in _____ sequence
* Cell division and maturation occur throughout the **______ tubules**
* Hundreds of millions of sperm produced **each ___**
* For a single sperm, the process takes about **seven weeks**
* _ products of meiosis develop into **mature gametes**
* ______ occurs throughout adolescence and adulthood
* Produces mature sperm from precursor cells in _____ sequence
* Cell division and maturation occur throughout the **______ tubules**
* Hundreds of millions of sperm produced **each ___**
* For a single sperm, the process takes about **seven weeks**
* _ products of meiosis develop into **mature gametes**
51
New cards
birth, interruptions, **ovary, years, unequal**
**Oogenesis**
* Mitotic divisions complete before ___
* Production of mature gametes stops at around age 50
* Has long ______ in between precursor cell creation and maturity
* Immature eggs form in the ____ of the female embryo
* Development not complete until **____, and often decades**, later
* Cytokinesis during meiosis is **______**
* Almost all the cytoplasm segregated to a **single daughter cell**
* Large cell becomes egg;
* Smaller cells (polar bodies)
degenerate
* Mitotic divisions complete before ___
* Production of mature gametes stops at around age 50
* Has long ______ in between precursor cell creation and maturity
* Immature eggs form in the ____ of the female embryo
* Development not complete until **____, and often decades**, later
* Cytokinesis during meiosis is **______**
* Almost all the cytoplasm segregated to a **single daughter cell**
* Large cell becomes egg;
* Smaller cells (polar bodies)
degenerate
52
New cards
**outer,** inward, **motile, spermatogonia, spermatocytes, sperm**
**Spermatogenesis**
* Stem cells that give rise to sperm are on the **____ edge** of the seminiferous tubules
* Move _____ as they pass through **spermatocyte** and **spermatid** stages
* Sperm released into lumen (fluid-filled cavity) of the tubule
* Sperm travels along tubule into
epididymis and **becomes ___**
* **In mature testes**
1. **Stem cells** divide mitotically to form **_______**
2. **Spermatogonia divide to create _______**
3. Each spermatocyte divides to create **four spermatids**
1. Reduces chromosome number to 23 (haploid)
4. Spermatids undergo extensive changes as they differentiate into **____**
* Stem cells that give rise to sperm are on the **____ edge** of the seminiferous tubules
* Move _____ as they pass through **spermatocyte** and **spermatid** stages
* Sperm released into lumen (fluid-filled cavity) of the tubule
* Sperm travels along tubule into
epididymis and **becomes ___**
* **In mature testes**
1. **Stem cells** divide mitotically to form **_______**
2. **Spermatogonia divide to create _______**
3. Each spermatocyte divides to create **four spermatids**
1. Reduces chromosome number to 23 (haploid)
4. Spermatids undergo extensive changes as they differentiate into **____**
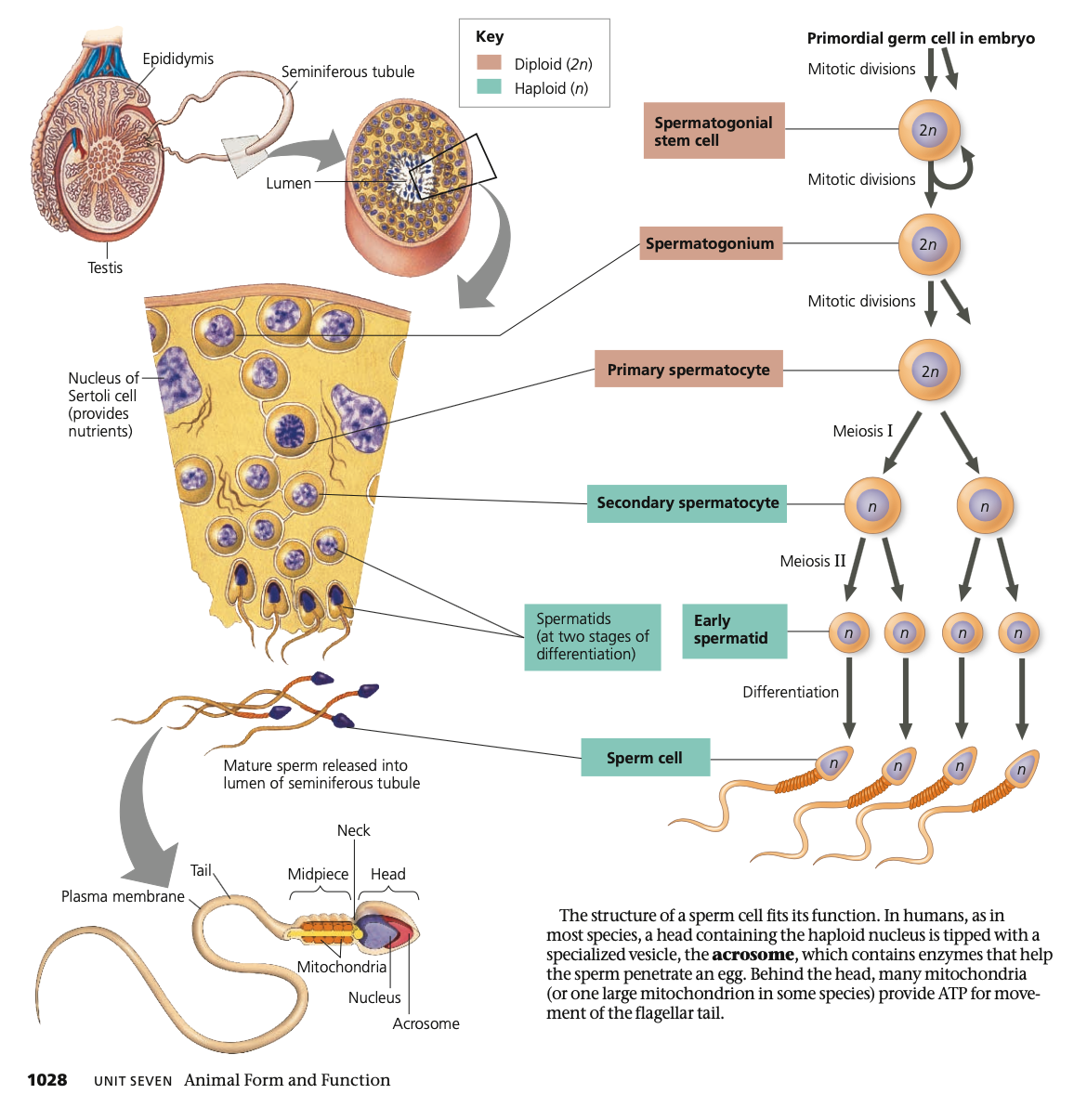
53
New cards
**Acrosome,** mitochondria
**Sperm Structure & Function**
* **Head**
* Contains haploid nucleus
* **_______**
* Specialized vesicle in sperm head which contains enzymes that help sperm penetrate egg
* **Behind the head**
* Many _____/One large mitochondrion provide ATP for movement of flagellar tail
* **Head**
* Contains haploid nucleus
* **_______**
* Specialized vesicle in sperm head which contains enzymes that help sperm penetrate egg
* **Behind the head**
* Many _____/One large mitochondrion provide ATP for movement of flagellar tail
54
New cards
primary, 500
**Oogenesis**
* Begins in the female embryo
* At birth ovaries contain 1-2 million _____ oocytes
* Between puberty and menopause
* ○ ___ fully matured oocytes
* Begins in the female embryo
* At birth ovaries contain 1-2 million _____ oocytes
* Between puberty and menopause
* ○ ___ fully matured oocytes
55
New cards
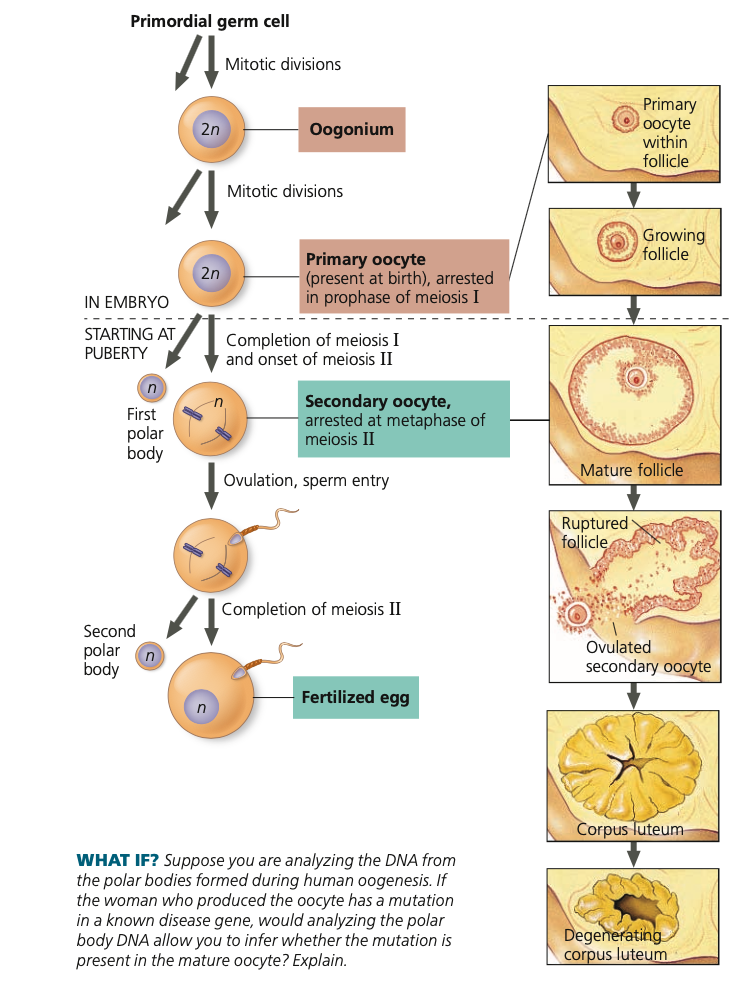
germ, oogonia, **prophase I,** oocytes, follicle, FSH, meiosis I, meiosis II, secondary, ovulation
**Oogenesis**
1. Primordial ___ cells produce ____
2. Oogonia divide mitotically to form cells that begin meiosis but stop at **_______** before birth
1. Primary ___ (the developmentally arrested cells) each reside within a small ____ (cavity lined with protective cells)
3. At puberty, follicle stimulating hormone (___)
stimulates small number of follicles to resume growth and development
1. One follicle fully matures per month
2. Primary oocyte completes ____
3. Second meiotic division begins but stops at metaphase
4. Arrested in ____,__ ______ oocyte is
released at ______ (follicle breaking open)
1. Primordial ___ cells produce ____
2. Oogonia divide mitotically to form cells that begin meiosis but stop at **_______** before birth
1. Primary ___ (the developmentally arrested cells) each reside within a small ____ (cavity lined with protective cells)
3. At puberty, follicle stimulating hormone (___)
stimulates small number of follicles to resume growth and development
1. One follicle fully matures per month
2. Primary oocyte completes ____
3. Second meiotic division begins but stops at metaphase
4. Arrested in ____,__ ______ oocyte is
released at ______ (follicle breaking open)
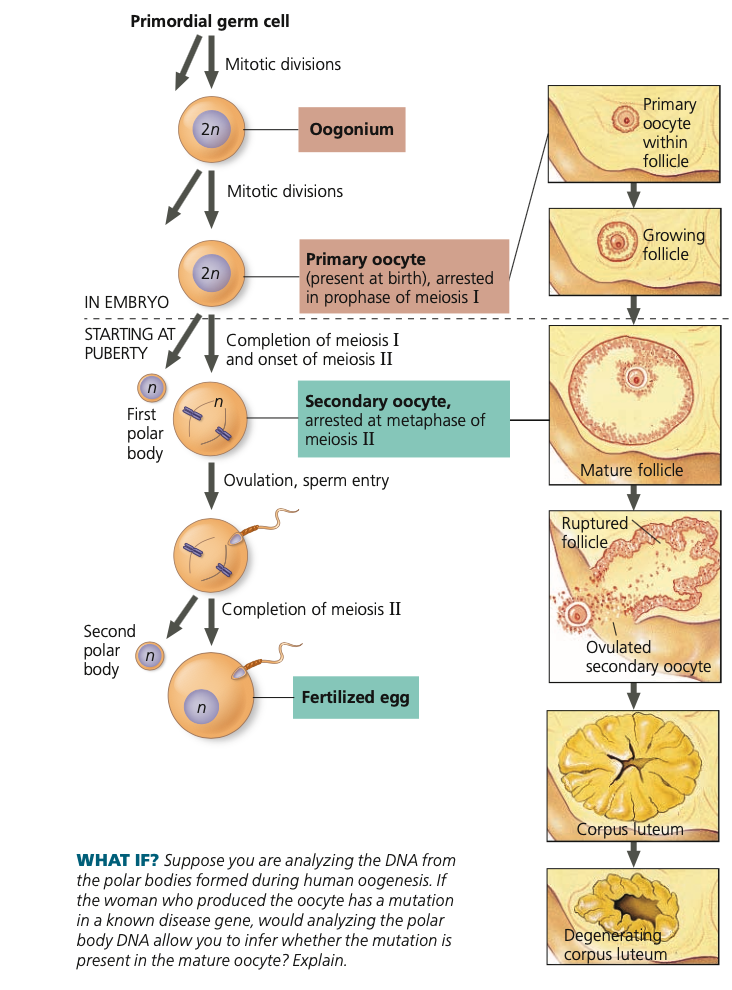
56
New cards
sperm, unequal
**Oogenesis**
5. Only if ____ penetrates oocyte
1. Meiosis II resumes
2. (Some animal species have sperm enter earlier or later)
6. The two meiotic divisions involve ____ cytokinesis
1. Smaller cells become polar bodes
which degenerate (first polar body
may or may not divide again).
7. Functional product of complete oogenesis is
a single mature egg containing a sperm head
5. Only if ____ penetrates oocyte
1. Meiosis II resumes
2. (Some animal species have sperm enter earlier or later)
6. The two meiotic divisions involve ____ cytokinesis
1. Smaller cells become polar bodes
which degenerate (first polar body
may or may not divide again).
7. Functional product of complete oogenesis is
a single mature egg containing a sperm head
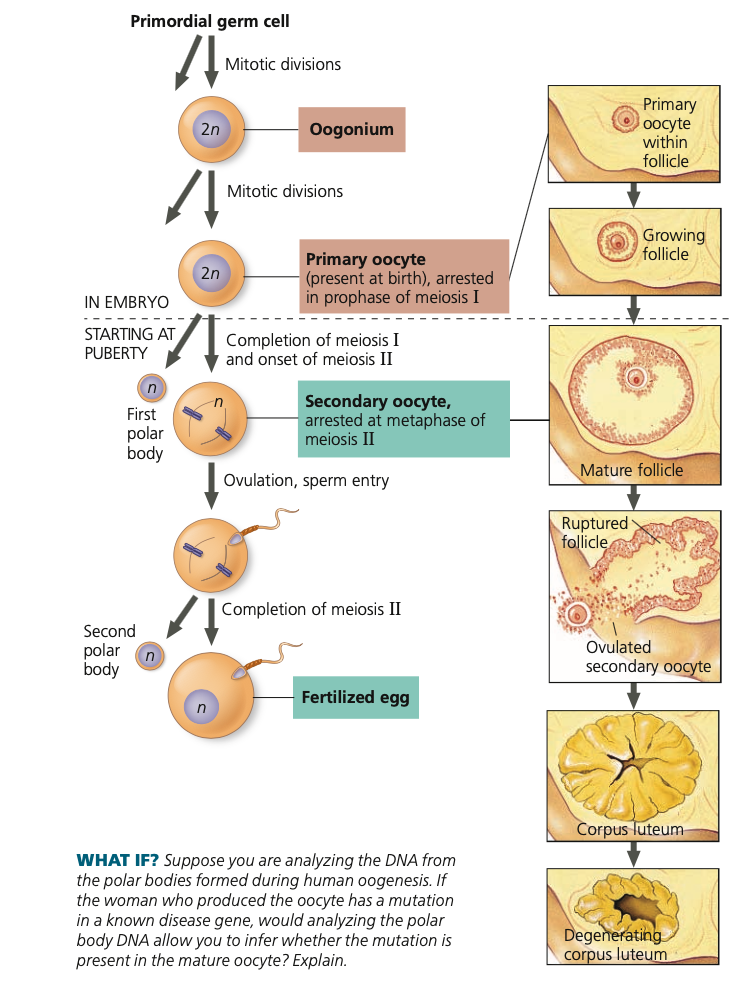
57
New cards
haploid
**Fertilization**
* defined strictly as the fusion of the
_____ nuclei of the sperm and
secondary oocyte,
* term is often used loosely to mean
the entry of the sperm head into the
egg
* defined strictly as the fusion of the
_____ nuclei of the sperm and
secondary oocyte,
* term is often used loosely to mean
the entry of the sperm head into the
egg
58
New cards
ruptured, estradiol, progesterone
Corpus luteum
* Developed _____ follicle left
behind
* Secretes
* ______
* _________
* a hormone that helps maintain the uterine lining during pregnancy
* If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum degenerates, and a new follicle matures during the next cycle
* Developed _____ follicle left
behind
* Secretes
* ______
* _________
* a hormone that helps maintain the uterine lining during pregnancy
* If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum degenerates, and a new follicle matures during the next cycle
59
New cards
Tropic and Sex Hormones
* Human sexuality
* Hormone control in males
* Hormone control in females
a. Ovarian cycle
b. Uterine (menstrual cycle)
c. Menopause
d. Menstrual vs estrous cycles
* Human sexual response
* Hormone control in males
* Hormone control in females
a. Ovarian cycle
b. Uterine (menstrual cycle)
c. Menopause
d. Menstrual vs estrous cycles
* Human sexual response
60
New cards
hypothalamus, GnRH, FSH, LH, endocrine, gonadotropins, Adrenal
**Tropic and Sex Hormones**
* coordinated actions of hormones from the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and gonads.
* Endocrine control of reproduction begins with the ____ secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (____).
* Directs the anterior pituitary to secrete the gonadotropins follicle-stimulating hormone (__) and luteinizing hormone (__)
* are tropic hormones, meaning that they regulate the activity of ______ cells or glands.
* are called ______ because they act on the male and female gonads.
* FSH and LH support gametogenesis
* ______ glands also secrete sex hormones in small amounts.
* coordinated actions of hormones from the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, and gonads.
* Endocrine control of reproduction begins with the ____ secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (____).
* Directs the anterior pituitary to secrete the gonadotropins follicle-stimulating hormone (__) and luteinizing hormone (__)
* are tropic hormones, meaning that they regulate the activity of ______ cells or glands.
* are called ______ because they act on the male and female gonads.
* FSH and LH support gametogenesis
* ______ glands also secrete sex hormones in small amounts.
61
New cards
Androgens
testosterone
62
New cards
Estrogens
estradiol, progesterone
63
New cards
concentrations, secondary, dimorphism, calcium
**Tropic and Sex Hormones**
* All three hormones are found in both males and females, but at quite different ________.
* The concentration of testosterone in the blood is roughly 10X higher in males
* Blood estradiol level is about 10X higher in females than in males
* Sex hormones in human males and females induce formation of ______ sex characteristics
* physical and behavioral differences between males and females that are not directly related to the reproductive system.
* often lead to sexual _____, the difference in appearance between the
male and female adults of a species
1. **Androgens**
1. voice to deepen, facial and pubic hair to develop, and muscles to grow
2. specific sexual behaviors and sex drive, increase in general aggressiveness
2. **Estrogens**
1. breast and pubic hair development
2. female sexual behavior, induces fat deposition in the breasts and hips
3. increases water retention, alters _____ metabolism.
* All three hormones are found in both males and females, but at quite different ________.
* The concentration of testosterone in the blood is roughly 10X higher in males
* Blood estradiol level is about 10X higher in females than in males
* Sex hormones in human males and females induce formation of ______ sex characteristics
* physical and behavioral differences between males and females that are not directly related to the reproductive system.
* often lead to sexual _____, the difference in appearance between the
male and female adults of a species
1. **Androgens**
1. voice to deepen, facial and pubic hair to develop, and muscles to grow
2. specific sexual behaviors and sex drive, increase in general aggressiveness
2. **Estrogens**
1. breast and pubic hair development
2. female sexual behavior, induces fat deposition in the breasts and hips
3. increases water retention, alters _____ metabolism.
64
New cards
*SRY ,* **Cis, Trans**
**Human sexuality**
* **Biological sex**
* reflects the genitals present at birth and the child’s chromosome
* Y chromosome carries a gene called *__* that directs development of the gonad into a testis
* XX embryos, which lack the Y and hence lack *SRY*, the gonad becomes an ovary.
* **__gender**
* a person having a gender identity in line with their assigned sex
* **___gender**
* a mismatch between their gender identity and their assigned sex
* **Sexual orientation**
1. Heterosexual
2. Homosexual
3. Bisexual
4. Asexual
* **Biological sex**
* reflects the genitals present at birth and the child’s chromosome
* Y chromosome carries a gene called *__* that directs development of the gonad into a testis
* XX embryos, which lack the Y and hence lack *SRY*, the gonad becomes an ovary.
* **__gender**
* a person having a gender identity in line with their assigned sex
* **___gender**
* a mismatch between their gender identity and their assigned sex
* **Sexual orientation**
1. Heterosexual
2. Homosexual
3. Bisexual
4. Asexual
65
New cards
Sertoli, seminiferous, Leydig, connective, testosterone, Testosterone, *inhibin,* FSH
**Hormone control in males**
* In directing spermatogenesis, FSH and LH act on two types of cells in the testis
* FSH stimulates __ cells, located within the ___ tubules, to nourish developing sperm
* LH causes ____ *cells*, scattered in ____ tissue between the tubules, to produce _____ and other androgens, which promote spermatogenesis in the tubules.
* Negative feedback mechanisms:
1. _______ regulates the blood concentration of GnRH, FSH, and LH through inhibitory effects on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary.
2. *__*, a hormone that in males is produced by Sertoli cells, acts on the anterior pituitary gland to reduce ____ secretion
* In directing spermatogenesis, FSH and LH act on two types of cells in the testis
* FSH stimulates __ cells, located within the ___ tubules, to nourish developing sperm
* LH causes ____ *cells*, scattered in ____ tissue between the tubules, to produce _____ and other androgens, which promote spermatogenesis in the tubules.
* Negative feedback mechanisms:
1. _______ regulates the blood concentration of GnRH, FSH, and LH through inhibitory effects on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary.
2. *__*, a hormone that in males is produced by Sertoli cells, acts on the anterior pituitary gland to reduce ____ secretion
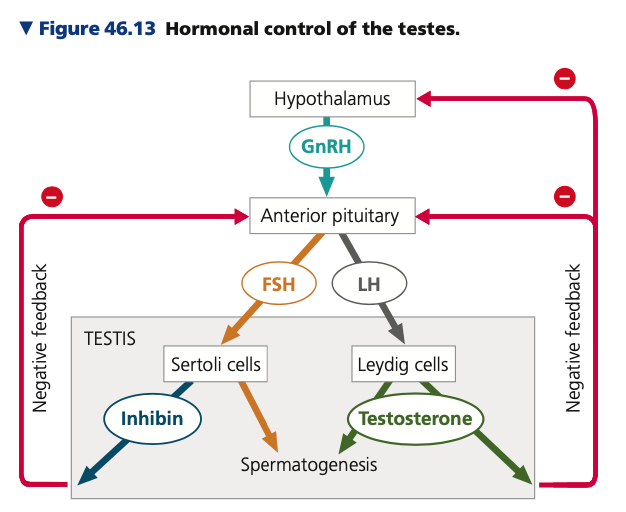
66
New cards
local, renin, angiotensin, corticotropin, prostaglandins
**Hormone control in males**
* Leydig cells have other roles
* secrete small quantities of many other hormones and __ regulators, (oxytocin, __,____, ____-releasing factor, growth factors, and _______)
* These signals coordinate the activity of reproduction with growth, metabolism, homeostasis, and behavior.
* Leydig cells have other roles
* secrete small quantities of many other hormones and __ regulators, (oxytocin, __,____, ____-releasing factor, growth factors, and _______)
* These signals coordinate the activity of reproduction with growth, metabolism, homeostasis, and behavior.
67
New cards
follicle, oocyte, endometrium
**Hormone control in females**
* two closely linked reproductive cycles in human females:
* **Ovarian cycle**
* Once per cycle a _____ matures and an _____ is released
* **Uterine (menstrual cycle)**
* the _______ thickens and develops a rich blood supply before being shed through the cervix and vagina if pregnancy does not occur.
* two closely linked reproductive cycles in human females:
* **Ovarian cycle**
* Once per cycle a _____ matures and an _____ is released
* **Uterine (menstrual cycle)**
* the _______ thickens and develops a rich blood supply before being shed through the cervix and vagina if pregnancy does not occur.
68
New cards
**Menstruation, 28**
**Hormone control in females**
* If an oocyte is not fertilized and pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining is sloughed off, and another pair of ovarian and uterine cycle begins.
* **________**
* cyclic shedding of the blood-rich endometrium from the uterus
* average __ days but can range from about 20 to 40 days
* If an oocyte is not fertilized and pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining is sloughed off, and another pair of ovarian and uterine cycle begins.
* **________**
* cyclic shedding of the blood-rich endometrium from the uterus
* average __ days but can range from about 20 to 40 days
69
New cards
**Hormone control in females**
a. Ovarian cycle
b. Uterine (menstrual cycle)
c. Menopause
d. Menstrual vs estrous cycles
b. Uterine (menstrual cycle)
c. Menopause
d. Menstrual vs estrous cycles
70
New cards
Ovarian Cycle
1. Follicular phase (Days 0-14)
2. Ovulation (Day 14)
3. Luteal phase (Days 15-28)
71
New cards
hypothalamus, GnRH, FSH, LH, inhibits, GnRH
**Ovarian cycle**
* ovarian cycle begins when the ___ releases ____, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete small amounts of ___ and __.
* FSH & LH: stimulates follicle growth
* Cells of the growing follicles: estradiol
1. **Follicular phase (Days 0-14)**
* Follicles grow and oocytes mature
* Low estradiol: ______ secretion of pituitary hormones, keeping the concentration of FSH and LH relatively low
* High estradiol: stimulates gonadotropin secretion by causing the hypothalamus to increase output of ____
* Follicle enlarges to form a bulge at the surface of the ovary
* ovarian cycle begins when the ___ releases ____, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete small amounts of ___ and __.
* FSH & LH: stimulates follicle growth
* Cells of the growing follicles: estradiol
1. **Follicular phase (Days 0-14)**
* Follicles grow and oocytes mature
* Low estradiol: ______ secretion of pituitary hormones, keeping the concentration of FSH and LH relatively low
* High estradiol: stimulates gonadotropin secretion by causing the hypothalamus to increase output of ____
* Follicle enlarges to form a bulge at the surface of the ovary
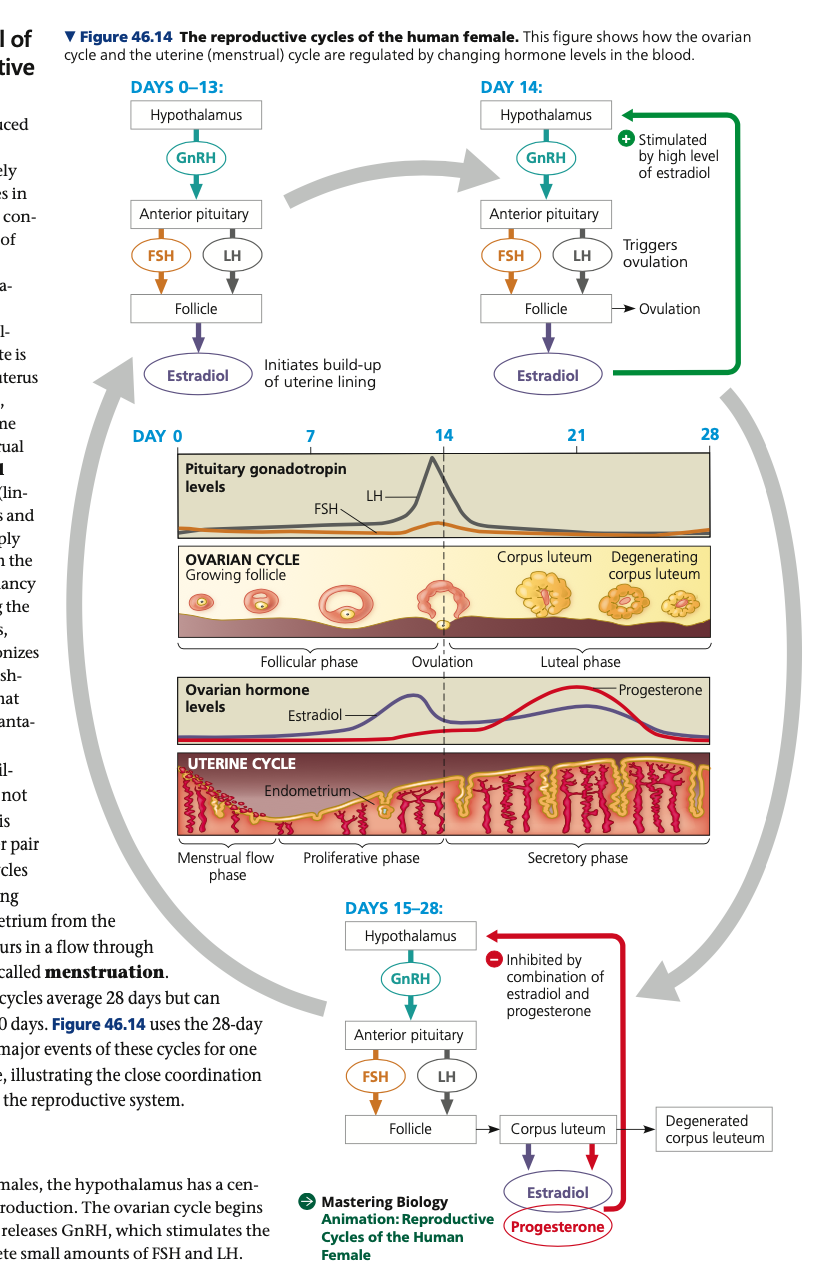
72
New cards
secondary, corpus, progesterone, gonadotropin
**Ovarian cycle**
2. **Ovulation (Day 14)**
* In response to FSH and the peak in LH level, the follicle and adjacent wall of the ovary rupture, releasing the _____ oocyte
* Women may feel a pain in the lower abdomen
\
3. **Luteal phase (Day 15-28)**
* LH stimulates the remaining follicular tissue to form the _____ luteum, a glandular structure
* Secretes ______ and estradiol, which in combination exert negative feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary.
* If pregnancy does not occur, the low ______ concentration cause the corpus luteum to disintegrate, triggering a sharp decline in estradiol and progesterone concentration
* liberates the hypothalamus and pituitary from negative feedback
2. **Ovulation (Day 14)**
* In response to FSH and the peak in LH level, the follicle and adjacent wall of the ovary rupture, releasing the _____ oocyte
* Women may feel a pain in the lower abdomen
\
3. **Luteal phase (Day 15-28)**
* LH stimulates the remaining follicular tissue to form the _____ luteum, a glandular structure
* Secretes ______ and estradiol, which in combination exert negative feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary.
* If pregnancy does not occur, the low ______ concentration cause the corpus luteum to disintegrate, triggering a sharp decline in estradiol and progesterone concentration
* liberates the hypothalamus and pituitary from negative feedback
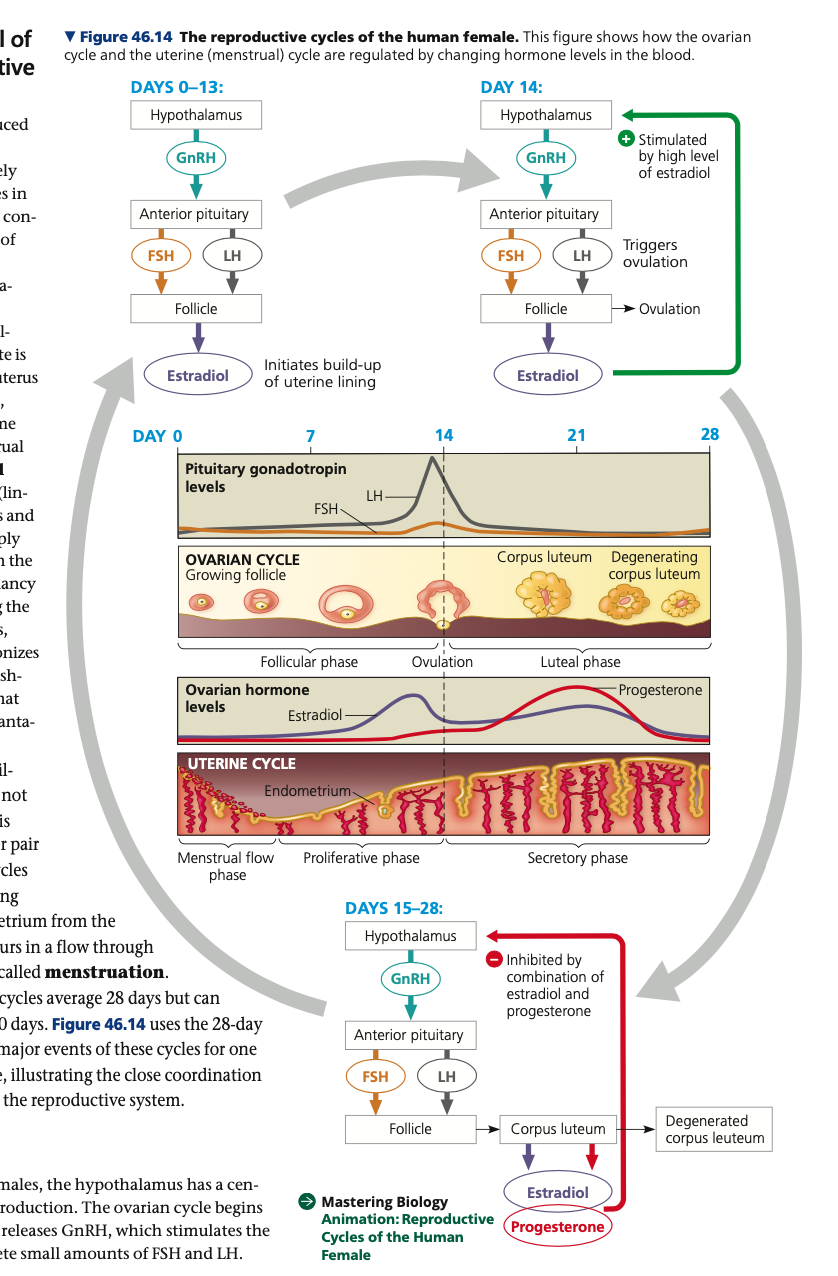
73
New cards
Uterine (menstrual) cycle
1. Proliferative phase (Days 6-14)
2. Secretory phase (Days 15-28)
3. Menstrual flow phase (Days 1-5)
74
New cards
follicular, estradiol, Progesterone, constrict, follicles
**Uterine (menstrual cycle)**
* Ovarian steroid hormones stimulate the uterus to prepare for support of an embryo
\
1. **Proliferative phase (Days 6-14)**
* Coordinated with _____ phase
* _____ secreted in increasing amounts by growing follicles signals the endometrium to thicken.
\
2. **Secretory phase (Days 15-28)**
* After ovulation (coordinated with ____ phase)
* ______ secreted by the corpus luteum stimulate maintenance and further development of the uterine lining
* Enlargement of arteries and growth of endometrial glands
\
3. **Menstrual flow phase (Days 1-5)**
* rapid drop in ovarian hormone concentration causes arteries in the endometrium to _____
* uterine lining largely disintegrates (menstruation)
* new set of ovarian _____ begin to grow
* Ovarian steroid hormones stimulate the uterus to prepare for support of an embryo
\
1. **Proliferative phase (Days 6-14)**
* Coordinated with _____ phase
* _____ secreted in increasing amounts by growing follicles signals the endometrium to thicken.
\
2. **Secretory phase (Days 15-28)**
* After ovulation (coordinated with ____ phase)
* ______ secreted by the corpus luteum stimulate maintenance and further development of the uterine lining
* Enlargement of arteries and growth of endometrial glands
\
3. **Menstrual flow phase (Days 1-5)**
* rapid drop in ovarian hormone concentration causes arteries in the endometrium to _____
* uterine lining largely disintegrates (menstruation)
* new set of ovarian _____ begin to grow
75
New cards
Endometriosis
* Some cells of the uterine lining migrate to an abdominal location that is abnormal (ectopic)
* Like the uterine endometrium, the ectopic tissue swells and breaks down during each ovarian cycle, resulting in pelvic pain and bleeding into the abdomen
* Like the uterine endometrium, the ectopic tissue swells and breaks down during each ovarian cycle, resulting in pelvic pain and bleeding into the abdomen
76
New cards
Cessation
**Menopause**
* After about 500 cycles (ages 46-54)
* ______ of ovulation and menstruation
* Ovaries lose their responsiveness to FSH and LH, resulting in a decline in estradiol production
* An unusual phenomenon in animal kingdom
* After about 500 cycles (ages 46-54)
* ______ of ovulation and menstruation
* Ovaries lose their responsiveness to FSH and LH, resulting in a decline in estradiol production
* An unusual phenomenon in animal kingdom
77
New cards
before, absorbs, **Estrus**
**Menstrual vs estrous cycles**
1. **Menstrual**
* Humans and other primates
* We bleed sadge
\
2. **Estrous**
* Other animals
* Uterus re______ the endometrium in the absence of a pregnancy, and no extensive fluid flow occurs
* Usually copulate only during the period surrounding ovulation
* **Estrus**: only time when female is receptive to mating (“heat”)
* length, frequency, and nature of estrous cycles vary
1. **Menstrual**
* Humans and other primates
* We bleed sadge
\
2. **Estrous**
* Other animals
* Uterus re______ the endometrium in the absence of a pregnancy, and no extensive fluid flow occurs
* Usually copulate only during the period surrounding ovulation
* **Estrus**: only time when female is receptive to mating (“heat”)
* length, frequency, and nature of estrous cycles vary
78
New cards
shared, Vasocongestion, Myotonia
**Human sexual response**
* a number serve similar functions in arousal, reflecting their _____ developmental origin
* embryonic tissues give rise to the scrotum and the labia majora
* General pattern of human sexual response is similar in males and females
* ________
* filling of a tissue with blood
* _______
* increased muscle tension
* a number serve similar functions in arousal, reflecting their _____ developmental origin
* embryonic tissues give rise to the scrotum and the labia majora
* General pattern of human sexual response is similar in males and females
* ________
* filling of a tissue with blood
* _______
* increased muscle tension
79
New cards
Sexual Response Cycle
1. Excitement
2. Plateau
3. Orgasm
4. Resolution
80
New cards
Coitus
Sexual intercourse
FUCKING!!!! D
FUCKING!!!! D
81
New cards
congestion, lubricated, myotonia
**Sexual Response Cycle**
1. **Excitement**
* Vaso______ is particularly evident in erection of the penis and clitoris and in enlargement of the testicles, labia, and breasts
* vagina becomes ___, and _____ may occur, as evident in nipple erection or tension of the limbs
1. **Excitement**
* Vaso______ is particularly evident in erection of the penis and clitoris and in enlargement of the testicles, labia, and breasts
* vagina becomes ___, and _____ may occur, as evident in nipple erection or tension of the limbs
82
New cards
uterus, heart
**Sexual Response Cycle**
2. **Plateau**
* Sexual responses continue as a result of direct stimulation of the genitalia
* Females: outer third of the vagina becomes vasocongested, while the inner two-thirds slightly expands
* Elevation of the _____, forms a depression for receiving sperm at the back of the vagina
* ____ rate rises, sometimes to 150 beats per minute
* caused by physical activity & autonomic nervous system
2. **Plateau**
* Sexual responses continue as a result of direct stimulation of the genitalia
* Females: outer third of the vagina becomes vasocongested, while the inner two-thirds slightly expands
* Elevation of the _____, forms a depression for receiving sperm at the back of the vagina
* ____ rate rises, sometimes to 150 beats per minute
* caused by physical activity & autonomic nervous system
83
New cards
contractions, Emission, Ejaculation
**Sexual Response Cycle**
3. **Orgasm**
* rhythmic, involuntary ______ of the reproductive structures in both sexes
* shortest phase
* **Males**
1. ______
* glands and ducts of the reproductive tract contract, forcing semen into the urethra
2. _____
* urethra contracts and the semen is expelled
* **Females**
* uterus and outer vagina contract, but the inner two-thirds of the vagina does not.
3. **Orgasm**
* rhythmic, involuntary ______ of the reproductive structures in both sexes
* shortest phase
* **Males**
1. ______
* glands and ducts of the reproductive tract contract, forcing semen into the urethra
2. _____
* urethra contracts and the semen is expelled
* **Females**
* uterus and outer vagina contract, but the inner two-thirds of the vagina does not.
84
New cards
reverses, refractory
**Sexual Response Cycle**
4. **Resolution**
* completes the cycle and _____ the responses of the earlier stages
* Vasocongested organs return to normal size and color, and muscles relax
* male typically enters a _____ period, lasting from a few minutes to hours, when erection and orgasm cannot be achieve
* Females do not have a refractory period, making possible multiple orgasms within a short period of time.
4. **Resolution**
* completes the cycle and _____ the responses of the earlier stages
* Vasocongested organs return to normal size and color, and muscles relax
* male typically enters a _____ period, lasting from a few minutes to hours, when erection and orgasm cannot be achieve
* Females do not have a refractory period, making possible multiple orgasms within a short period of time.
85
New cards
Embryonic development
* Conception, Embryonic Development,
and Birth
* Maternal Immune Tolerance of the
Embryo and Fetus
* Contraception and Abortion
* Modern Reproductive Technologies
a. Infertility & In Vitro Fertilization
b. Detecting Disorders during Pregnancy
and Birth
* Maternal Immune Tolerance of the
Embryo and Fetus
* Contraception and Abortion
* Modern Reproductive Technologies
a. Infertility & In Vitro Fertilization
b. Detecting Disorders during Pregnancy
86
New cards
cervix, liquefy, **blastocyst**
**Conception, Embryonic Development, and Birth**
* When first ejaculated, the semen coagulates, which likely keeps the ejaculate in place until sperm reach the ___.
* Soon after, anticoagulants ___ the semen, and the sperm swim through the cervix and oviducts
\
* **Zygote formation**
1. **Ovulation**
2. **Fertilization / Conception**
1. occurs when a sperm fuses with an egg (mature oocyte) in an oviduct
3. **Cleavage (cell division)**
1. 24 hours after fertilization and after an additional 4 days produces a **______**
4. **Pregnancy / Gestation**
1. embryo implants into the endometrium of the uterus
* When first ejaculated, the semen coagulates, which likely keeps the ejaculate in place until sperm reach the ___.
* Soon after, anticoagulants ___ the semen, and the sperm swim through the cervix and oviducts
\
* **Zygote formation**
1. **Ovulation**
2. **Fertilization / Conception**
1. occurs when a sperm fuses with an egg (mature oocyte) in an oviduct
3. **Cleavage (cell division)**
1. 24 hours after fertilization and after an additional 4 days produces a **______**
4. **Pregnancy / Gestation**
1. embryo implants into the endometrium of the uterus
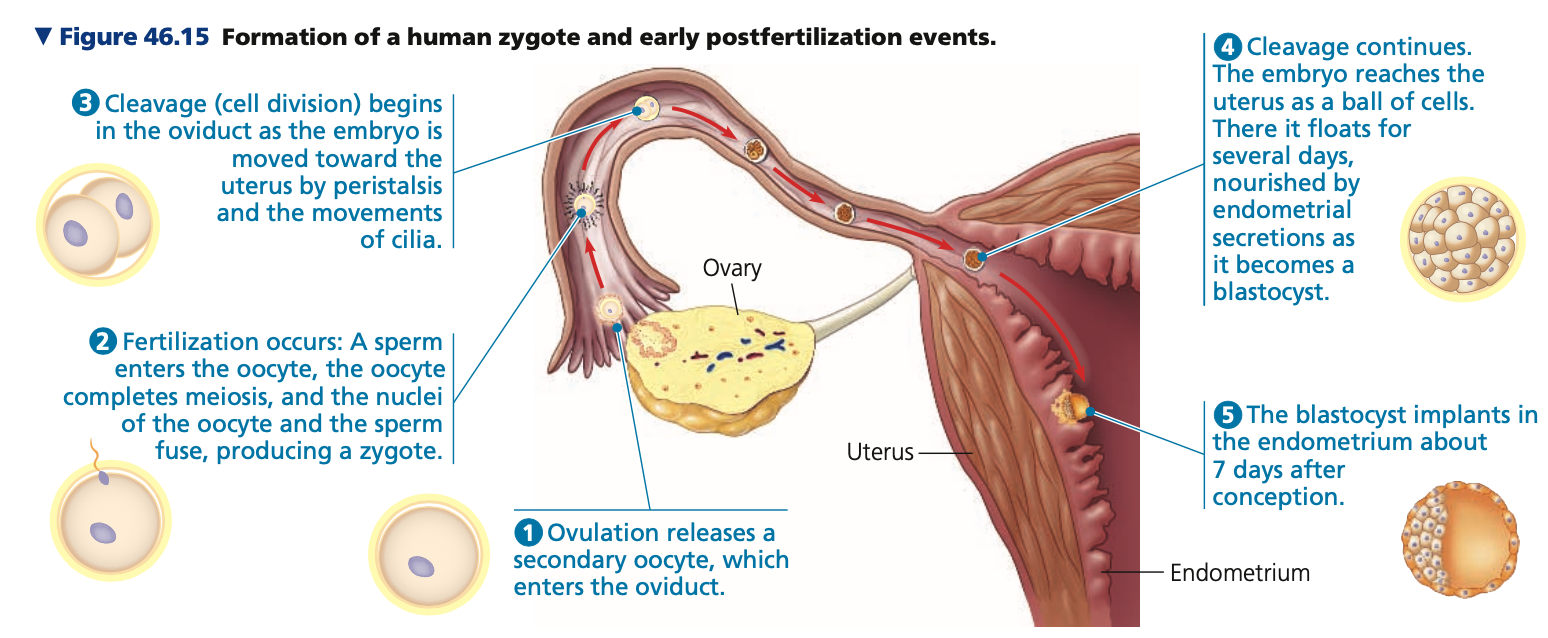
87
New cards
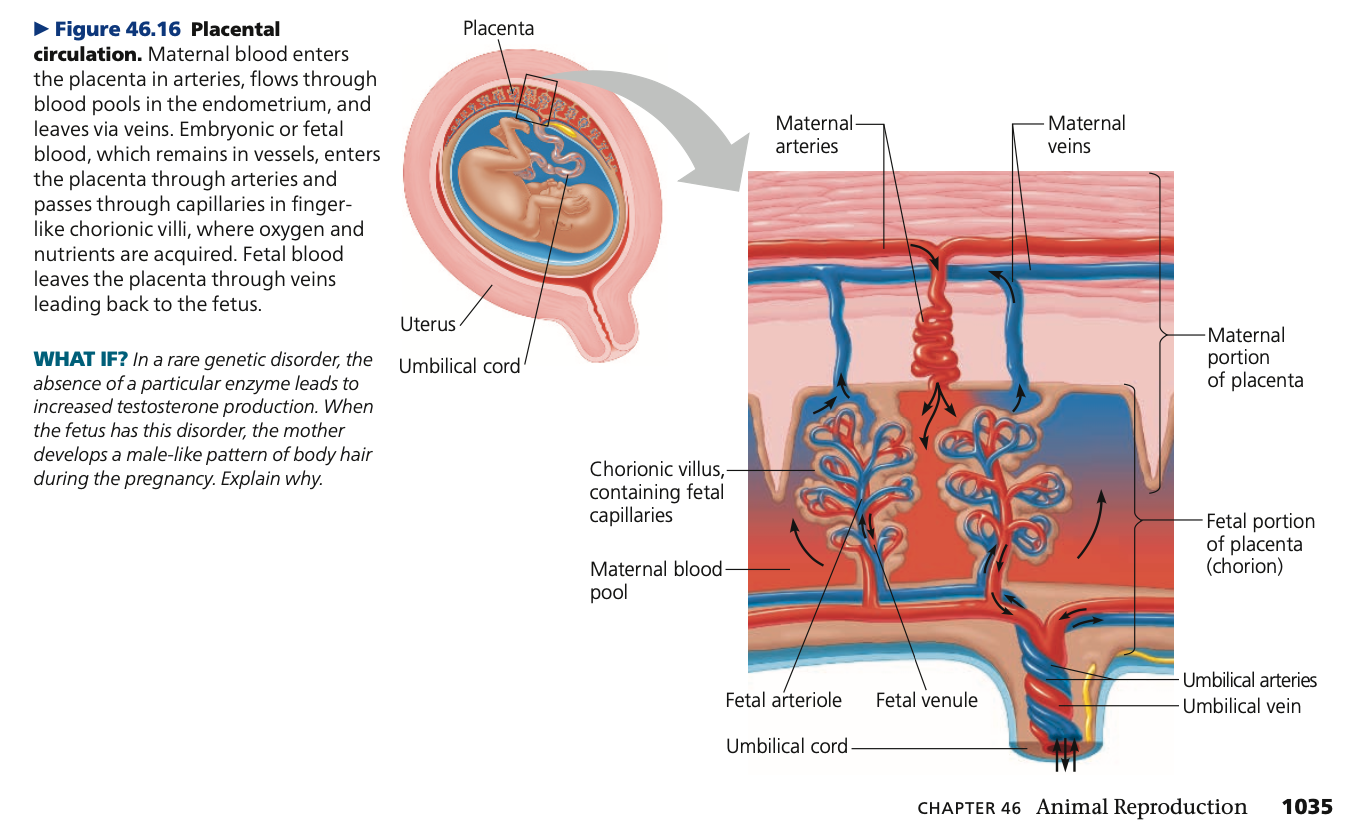
38, **chorionic,** corpus, **trophoblast, placenta,** umbilical
**Human Pregnancy**
* averages 266 days (__ weeks) from fertilization of the egg, or 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual cycle
* Monozygotic embryo: identical twins
* Dizygotic embryo: fraternal twins
\
1. **First trimester**
* embryo secretes hormones that signal its presence and regulate the mother’s reproductive system
* **Human _____ gonadotropin (hCG)**
* acts like pituitary LH in maintaining secretion of progesterone and estrogens by the _____ luteum through the first few months of pregnancy
* detected in pregnancy tests
* Outer layer of the blastocyst, which is called the **____**, grows outward and mingles with the endometrium, eventually helping form the _____
* immune protection, exchanges respiratory gases, and disposes of metabolic wastes for the embryo
* blood flows thru arteries of the _____ cord and returns via the umbilical vein
* averages 266 days (__ weeks) from fertilization of the egg, or 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual cycle
* Monozygotic embryo: identical twins
* Dizygotic embryo: fraternal twins
\
1. **First trimester**
* embryo secretes hormones that signal its presence and regulate the mother’s reproductive system
* **Human _____ gonadotropin (hCG)**
* acts like pituitary LH in maintaining secretion of progesterone and estrogens by the _____ luteum through the first few months of pregnancy
* detected in pregnancy tests
* Outer layer of the blastocyst, which is called the **____**, grows outward and mingles with the endometrium, eventually helping form the _____
* immune protection, exchanges respiratory gases, and disposes of metabolic wastes for the embryo
* blood flows thru arteries of the _____ cord and returns via the umbilical vein
88
New cards
**organogenesis, fetus,** progesterone
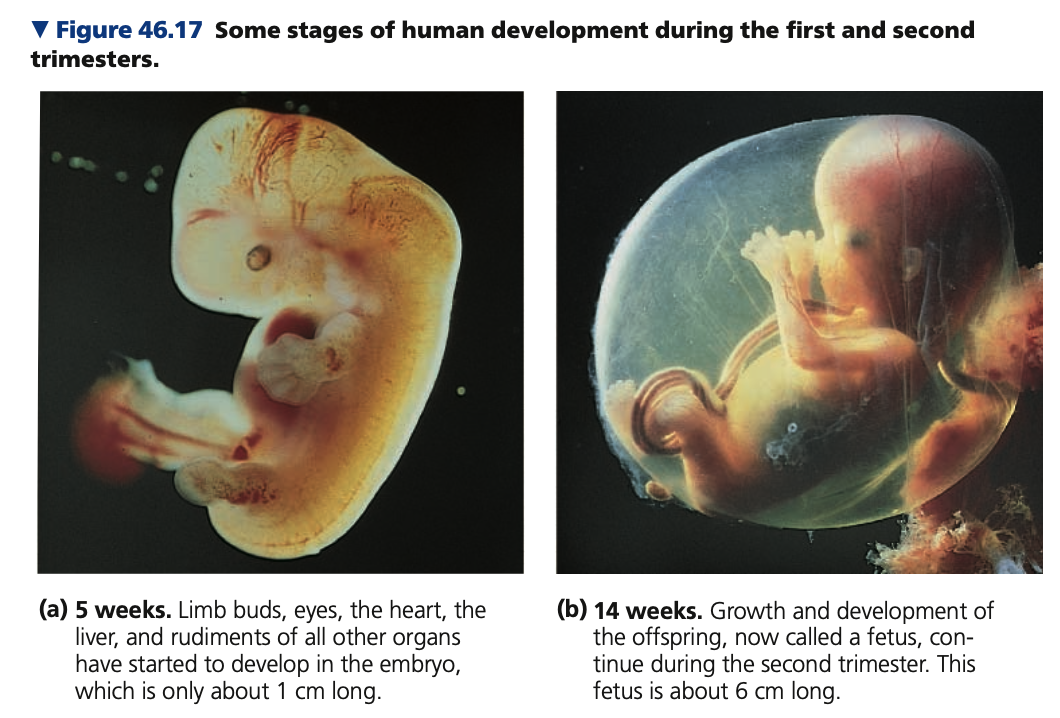
**Human Pregnancy**
1. **First trimester**
* main period of **_______**
* development of the body organs
* heart begins beating by the 4th week; a heartbeat can be detected at 8–10 weeks
* At 8 weeks, all the major structures of the adult are present in rudimentary form, and the embryo is called a _____
* End of first trimester:
* high _______ levels cause:
* Mucus in the cervix forms a plug that protects against infection
* Maternal part of the placenta grows
* Breasts and uterus get larger
* Ovulation and menstrual cycles stop
1. **First trimester**
* main period of **_______**
* development of the body organs
* heart begins beating by the 4th week; a heartbeat can be detected at 8–10 weeks
* At 8 weeks, all the major structures of the adult are present in rudimentary form, and the embryo is called a _____
* End of first trimester:
* high _______ levels cause:
* Mucus in the cervix forms a plug that protects against infection
* Maternal part of the placenta grows
* Breasts and uterus get larger
* Ovulation and menstrual cycles stop
89
New cards
sex, movements, hCG, placenta
**Human Pregnancy**
2. **Second trimester**
* fetus grows to about 30 cm in length
* Development continues, including formation of fingernails, external __ organs, and outer ears
* fetal _____as early as 1 month into the second trimester
* Hormone concentrations stabilize as ___ secretion declines; the corpus luteum deteriorates; and the ______ completely takes over the production of progesterone, the hormone that maintains the pregnancy.
2. **Second trimester**
* fetus grows to about 30 cm in length
* Development continues, including formation of fingernails, external __ organs, and outer ears
* fetal _____as early as 1 month into the second trimester
* Hormone concentrations stabilize as ___ secretion declines; the corpus luteum deteriorates; and the ______ completely takes over the production of progesterone, the hormone that maintains the pregnancy.
90
New cards
labor, prostaglandins, contractions
**Human Pregnancy**
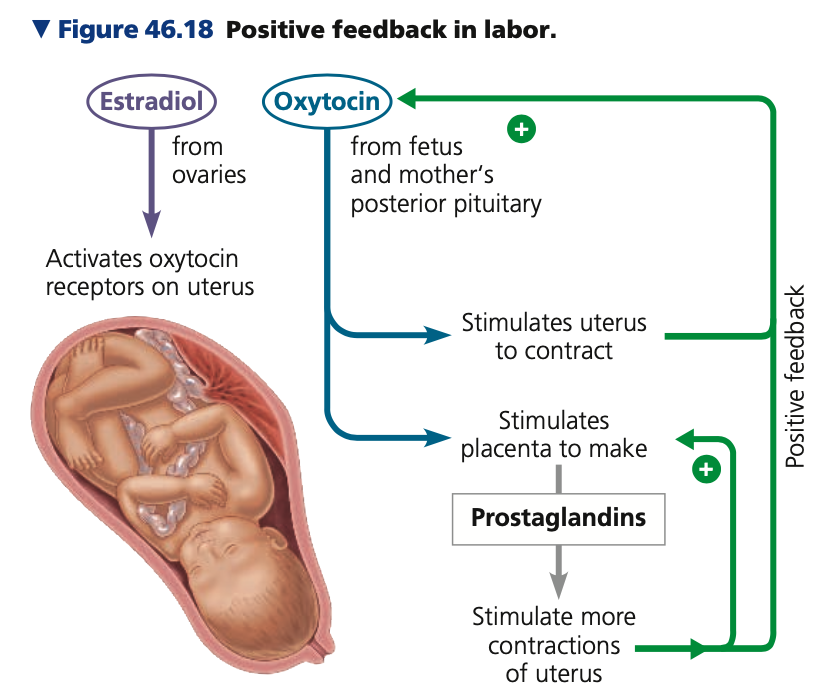
3. **Third trimester**
* grows to about 3–4 kg in weight and 50 cm in length
* mother’s abdominal organs become compressed and displaced
* Childbirth begins with *_____*
* a series of strong, rhythmic uterine contractions that push the fetus and placenta out of the body
* local regulators (_____) and hormones (chiefly estradiol and oxytocin) induce and regulate further _______ of the uterus
* Three stages:
1. Dilation of cervix
2. Expulsion of baby
3. Delivery of placenta
3. **Third trimester**
* grows to about 3–4 kg in weight and 50 cm in length
* mother’s abdominal organs become compressed and displaced
* Childbirth begins with *_____*
* a series of strong, rhythmic uterine contractions that push the fetus and placenta out of the body
* local regulators (_____) and hormones (chiefly estradiol and oxytocin) induce and regulate further _______ of the uterus
* Three stages:
1. Dilation of cervix
2. Expulsion of baby
3. Delivery of placenta
91
New cards
Prolactin, Oxytocin
**Human Pregnancy**
* _____: produce milk
* _____: secrete milk
* _____: produce milk
* _____: secrete milk
92
New cards
autoimmune
**Maternal Immune Tolerance of the Embryo and Fetus**
* half of the embryo’s genes are inherited from the father, many of the chemical markers present on the surface of the embryo are foreign to the mother
* overall regulation of the immune system changes during pregnancy
* relationship between certain _______ disorders and pregnancy
* active area of research for immunologists
* half of the embryo’s genes are inherited from the father, many of the chemical markers present on the surface of the embryo are foreign to the mother
* overall regulation of the immune system changes during pregnancy
* relationship between certain _______ disorders and pregnancy
* active area of research for immunologists
93
New cards
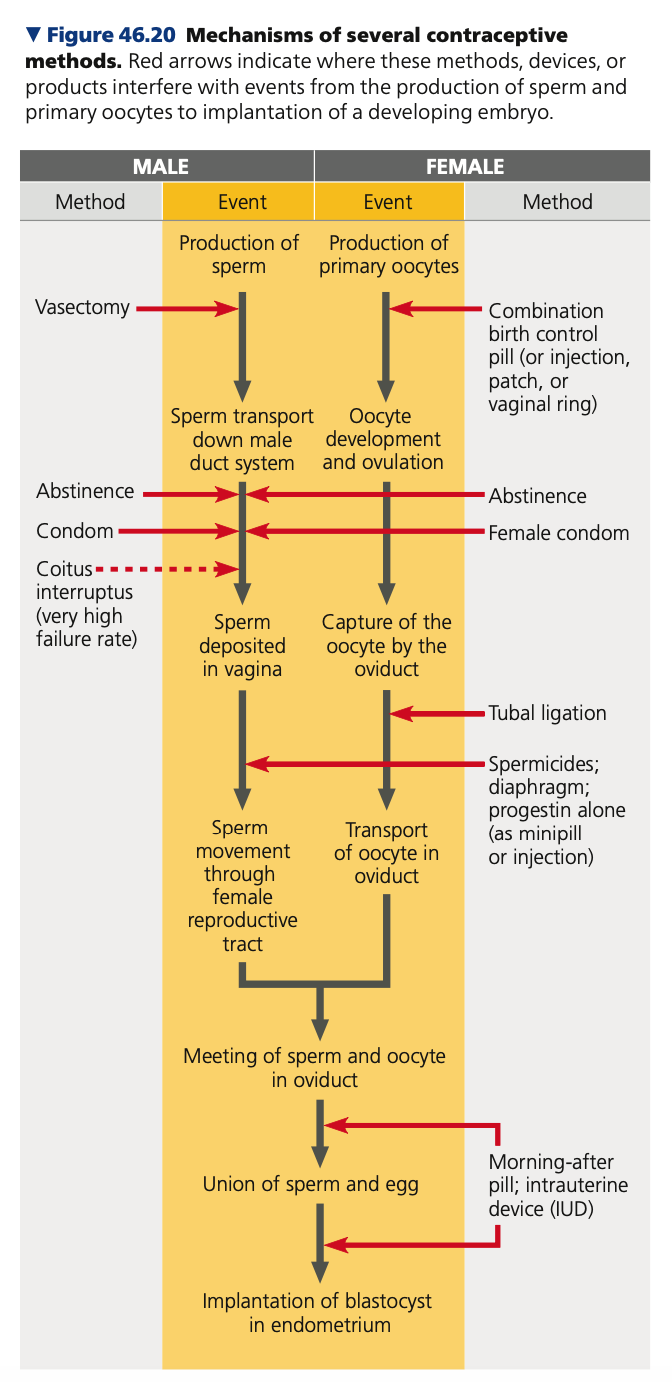
Contraception
the deliberate prevention of pregnancy, can be achieved in a number of ways
\
**Male**
1. Vasectomy
2. Abstinence
3. Condom
1. Highly effective in prevention of STDs
4. Coitus interruptus (pull-out)
1. Unreliable; Sperm from a previous ejaculate may be transferred in secretions that precede ejaculation
\
**Female**
1. Combination birth control pill / injection / patch / vaginal ring
1. Most effective
2. Abstinence
3. Female condom
4. Tubal ligation
5. Spermicides / diaphragm progestin
6. Morning after pill, intrauterine device (IUD)
1. Most effective
2. most commonly used reversible method of birth control
\
**Male**
1. Vasectomy
2. Abstinence
3. Condom
1. Highly effective in prevention of STDs
4. Coitus interruptus (pull-out)
1. Unreliable; Sperm from a previous ejaculate may be transferred in secretions that precede ejaculation
\
**Female**
1. Combination birth control pill / injection / patch / vaginal ring
1. Most effective
2. Abstinence
3. Female condom
4. Tubal ligation
5. Spermicides / diaphragm progestin
6. Morning after pill, intrauterine device (IUD)
1. Most effective
2. most commonly used reversible method of birth control
94
New cards
Progestin
* most commonly prescribed hormonal contraceptives contain a synthetic estrogen and a synthetic progesterone- like hormone called ________
* combination **mimics negative feedback** in the ovarian cycle, stopping the release of GnRH by the hypothalamus and thus of FSH and LH by the pituitary
* By itself, causes thickening of a woman’s **cervical mucus** so that it blocks sperm from entering the uterus
* combination **mimics negative feedback** in the ovarian cycle, stopping the release of GnRH by the hypothalamus and thus of FSH and LH by the pituitary
* By itself, causes thickening of a woman’s **cervical mucus** so that it blocks sperm from entering the uterus
95
New cards
Hormonal contraceptives
* increase the risk of some cardiovascular disorders slightly for nonsmokers and quite substantially
* also decrease the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers
* also decrease the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers
96
New cards
Sterilization
* permanent prevention of gamete production or release
* **Tubal ligation**
* sealing shut or tying off (ligating) of a section of each **oviduct**
* **Vasectomy**
* cutting and tying off of each **vas deferens** to prevent sperm from entering the urethra
* **Tubal ligation**
* sealing shut or tying off (ligating) of a section of each **oviduct**
* **Vasectomy**
* cutting and tying off of each **vas deferens** to prevent sperm from entering the urethra
97
New cards
**Abortion**
* termination of a pregnancy in progress
1. **Spontaneous abortion / miscarriage**
1. very common (33%)
2. **Normal abortion i guess**
1. surgical method
2. **mifepristone**, or **RU486**, can terminate a pregnancy nonsurgically within the first 7 weeks
1. blocks progesterone receptors in the uterus, thus preventing progesterone from maintaining the pregnancy
1. **Spontaneous abortion / miscarriage**
1. very common (33%)
2. **Normal abortion i guess**
1. surgical method
2. **mifepristone**, or **RU486**, can terminate a pregnancy nonsurgically within the first 7 weeks
1. blocks progesterone receptors in the uterus, thus preventing progesterone from maintaining the pregnancy
98
New cards
Infertility
* an inability to conceive offspring
* **increases steadily past age 35**, as well with genetic abnormalities
* prolonged period of time oocytes spend in meiosis
* **sexually transmitted infections (STIs)**
* infected with the chlamydia or gonorrhea bacterium
* inflammatory disorder that can scar the oviduct
* **increases steadily past age 35**, as well with genetic abnormalities
* prolonged period of time oocytes spend in meiosis
* **sexually transmitted infections (STIs)**
* infected with the chlamydia or gonorrhea bacterium
* inflammatory disorder that can scar the oviduct
99
New cards
In Vitro Fertilization
* combining oocytes and sperm in the laboratory
* Fertilized eggs are incubated until they form **eight or more cells** and are then transferred to the woman’s uterus for **implantation.**
* If mature sperm are defective or low in number, a whole sperm or a **spermatid nucleus** may be injected directly into an oocyte
* Fertilized eggs are incubated until they form **eight or more cells** and are then transferred to the woman’s uterus for **implantation.**
* If mature sperm are defective or low in number, a whole sperm or a **spermatid nucleus** may be injected directly into an oocyte
100
New cards
Ultrasound imaging
* generates images using sound frequencies above the normal hearing range
* is commonly used to analyze the fetus’s size and condition
* is commonly used to analyze the fetus’s size and condition