searching for, enhancing and reocvering fingerprints from crime scenes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what are fingerprints?
Ridges on tips of fingers
Folds in outer layer of skin, the epidermis
how do fingerprints adhere to surfaces?
Along tops of ridges are minute pores from which sweat is exuded
Transfers/adheres to surface touched
why do we have fingerprints?
Friction helps grip objects and sense of touch, help protect from injury
at crime scene
Plastic-impressed marks
Patent - visible contaminant/residue, contrast against background
Latent - require enhancement, not readily visible
Sequential scene examination- always done at end as powder is contaminant
Visual examination
Use of oblique lighting
Photography-non-destructive
Recovery of any forensic material - trace, DNA and other forensic evidence
Enhancement
Recovery
Clean down
visible (patent) fingerprints
See with naked eye
Transparent material e.g. oil grease
Contaminated impressions
Impressions in dust
Impressions in soft material / putty /easter egg
Impressions caused by reaction between surface and fingerprint e.g. on silverware
fingerprints left:
Fingerprints in blood-patent can find latent aswell
Fingerprints left on surfaces
Fingerprint in soft material e.g. putty, blue tack, putty
latent fingerprints
Must be enhanced
Where found?
Where has offender touched? e.g. point of entry
How do we locate them? - put ourselves in offenders shoes
enhancement types of powder
Flake - thin layers
Granular - tiny circular beads
Fluorescent - granular
Magnetic (flake and granular)
flake powders
Metallic flake introduced in 1970
Best for smooth, clean, dry surfaces
Aluminium or magenta
Bronze/gold
Can be lifted due to nature of flat surface
Applied with carbon fibre - zephyr brush
granular powders
Available in black and white
Resemble ball bearing coated in carbon
Practice varies on lifting or not lifting and photography
Should be use on flaky paint and textured surfaces
Applied with an animal-hair or synthetic brush
Some don’t lift because it can squash the 'balls' and only photograph
magnetic powders
Granular or flake
Applied using magnetic wand
Instant results on paper, but less sensitive than chemicals
Photographed or lifted - flake or granular
fluorescent powders
Granular
Applied with animal-hair or synthetic brush
Magnetic fluorescent powders available
Fluoresce using UV light source
Useful when surface is contaminated or is multi-coloured
application of magnetic powder
Load magnetic wand with powder
Cascade powder over area- use powder as brush
Do not let wand touch area
Use clean brush to lightly 'clean out' mark
Photograph and/or lift using fingerprint tape/gel and secure to an acetate sheet
fingerprint brushes

how do we recover and what?
Photography
Use a gel lifter or J-Lar lifting tape
3D marks can be cast (Provil)
Blurred or partial marks should be lifted
Several fingerprints from same hand can be lifted together
Articles baring forensic evidence should have this evidence recovered before fingerprinting
lifting fingerprints/friction ridge detail

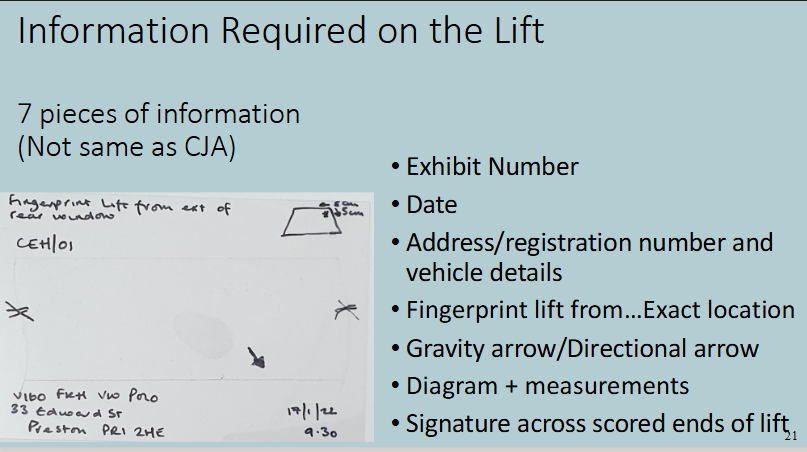
information required on lift
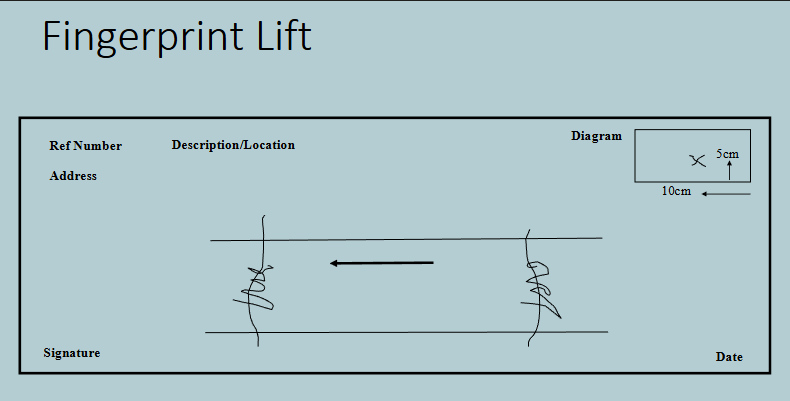
fingerprint lift
documented recovered marks
Make accurate record of where prints were found
Gravity marks or directional arrows should be included to indicate orientation of lift
Gravity arrows on portable items should point to bottom of item
Diagrams with measurements to fixed points
'score' edges of tape on acetate and sign
items recovered for chemical treatment
Porous surfaces(absorbent materials)
Paper: documents, letters, books, envelopes
Cardboard: boxes, packaging
Wood (unfinished): furniture, crates
Semi-porous surfaces (treated/finished surfaces)
Painted wood: doors, furniture
Flossy magazines or photos
Plastic- coated paper
Miscellaneous items
Weapons and tools: knives, guns, screwdrives
Money and coins: paper bills, coins (metal)
Electronic devices: phones, tablets, remote controls
Containers: jars, bottles, cans
chemical treatment
Amido black
Proteins in blood and body fluids
Porous and non-porous (high colour on some porous backgrounds)
Ninhydrin and DFO
Amino acids
Paper and porous surfaces
Small particle reagent (SPR)
Fatty constituents of fingerprint
Non-porous surfaces
Superglue (cyanoacrylate vapour)
Water and possibly other constituents of fingerprint
Non-porous surfaces (rough surfaces, vinyl + rubbers)
IF CHOOSE NOT TO LIFT OR DEVIATE FROM SOP THEN DOCUMENT IN MO SECTION and note reason