chapter 3: overview of diseases of the periodontium
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
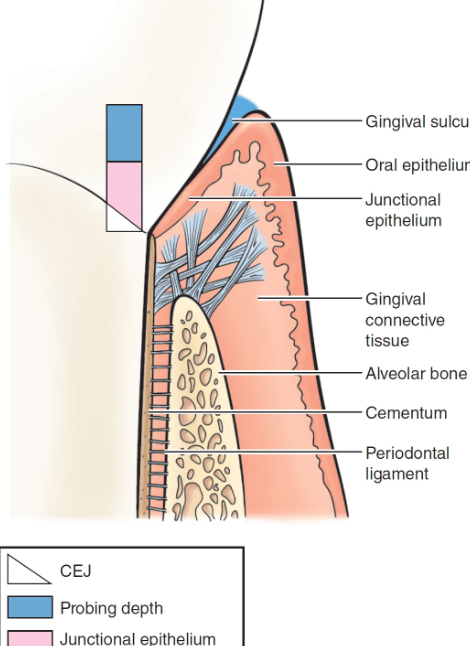
characteristics of healthy periodontium
clinical: pink, firm interdental papillae, no bleeding, 1-3 mm probing depth
histological: JE coronal to the CEJ, supragingival fibers intact, alveolar bone intact, periodontal ligament intact
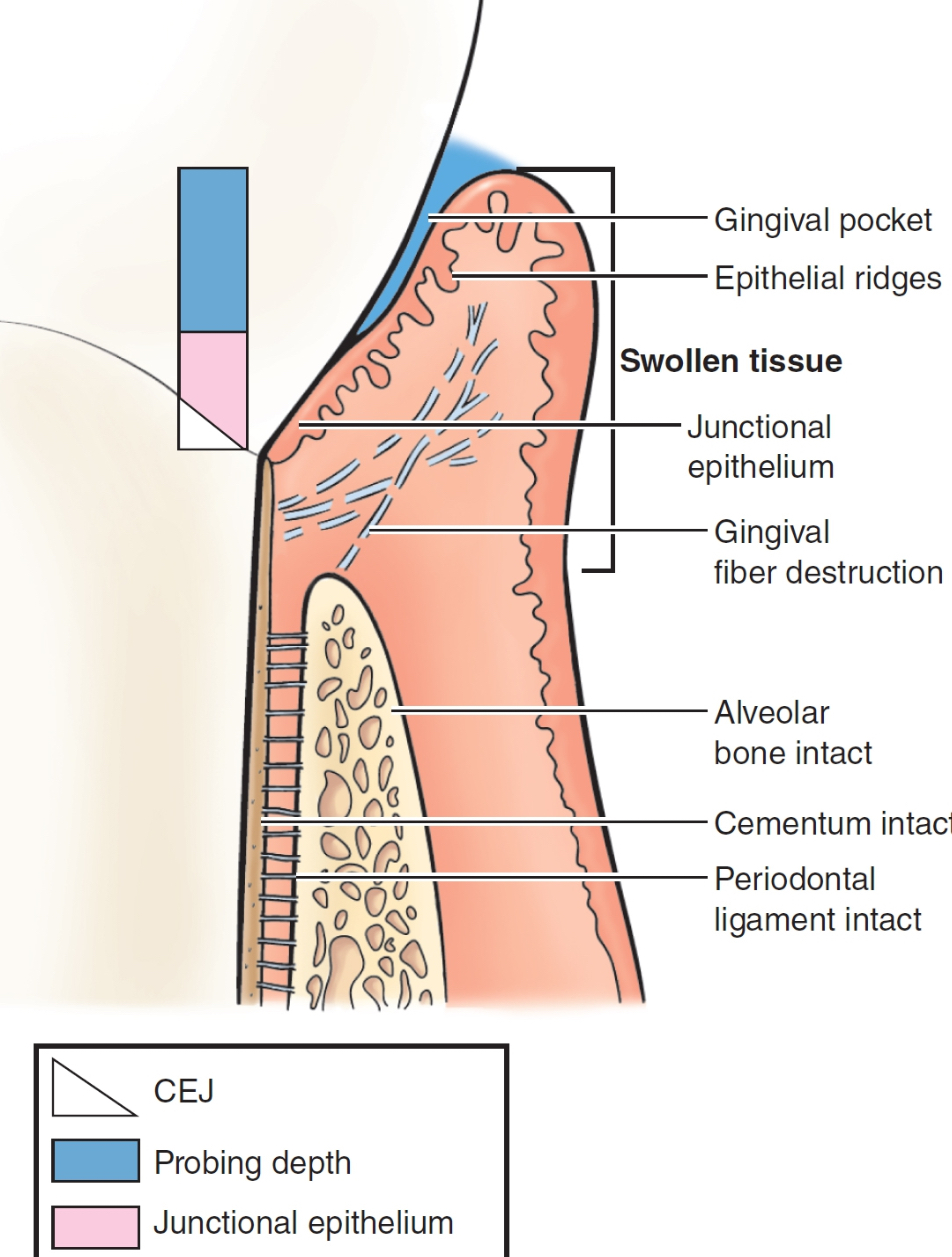
characteristics of gingivitis
some reversible tissue damage
clinical: red, swollen (edematous), bleeding likely, sulcus depth 3mm+
histological: JE at CEJ, supra-gingival fiber destruction, alveolar bone intact, periodontal ligament intact
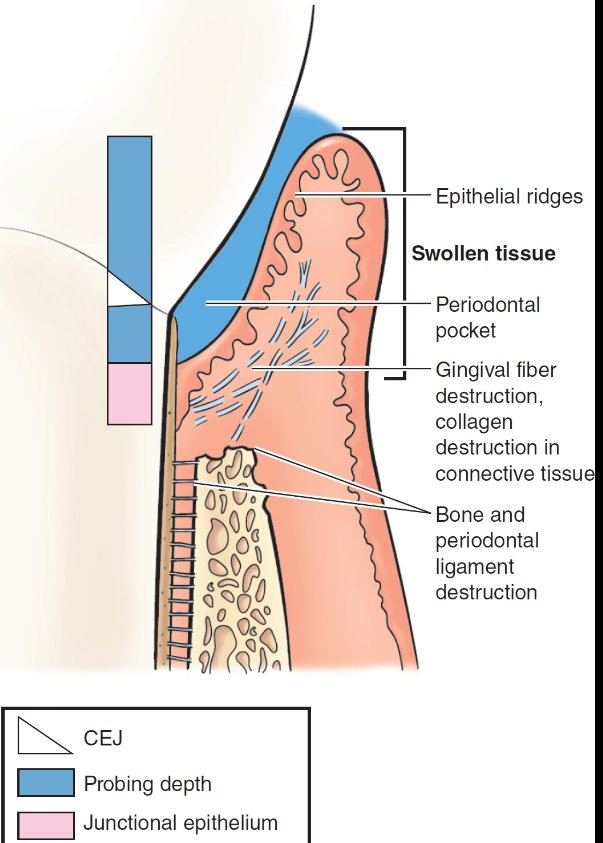
characteristics of periodontitis
permanent destruction
clinical: pink or purplish, swollen (edematous) or fibrotic, bleeding or pus, probing depths 4mm+
histological: JE on cementum (APICAL MIGRATION), supragingival fibers destruction (makes it easier for JE to migrate), alveolar bone destruction, periodontal ligament destruction
gingivitis is observed clinically ____ days after plaque biofilm accumulates in the gingival sulcus
4-14
gingival tissue enlargement
caused by acute and chronic gingivitis
excess collagen fibers (body’s attempt to repair the tissue damage) → deeper probing depths/pseudopocket (JE remains in its normal position) (also known as gingival pocket)
cyanotic gingiva
reddish-blue color of gingivitis
blood flow increases → blood vessels become congested → slows flow of oxygenated blood to tissues and the flow of unoxygenated blood away from the tissues → unoxygenated blood pools in the gingival tissues
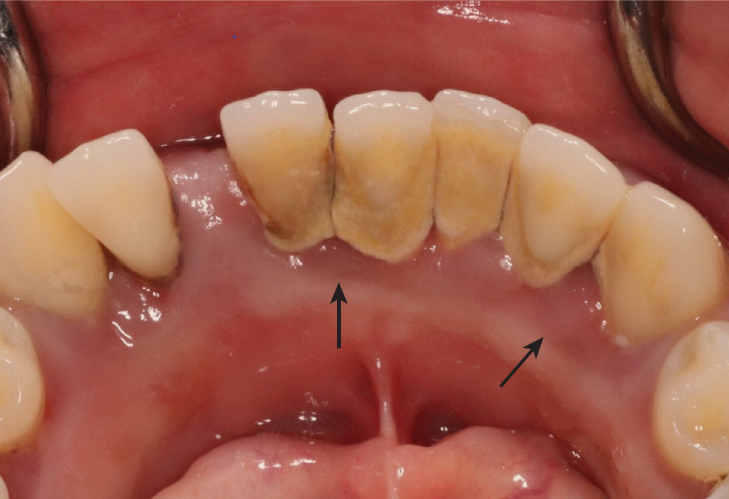
fibrotic tissue
common in periodontitis
firm, light pink with a leathery consistency
transseptal fiber bundles
resilient bands of gingival ligament fibers that run from one tooth to another across the crest of the bone (can usually withstand periodontal inflammation)
if inflamm is severe enough to overcome these fibers, tooth displacement/pathologic tooth migration occurs
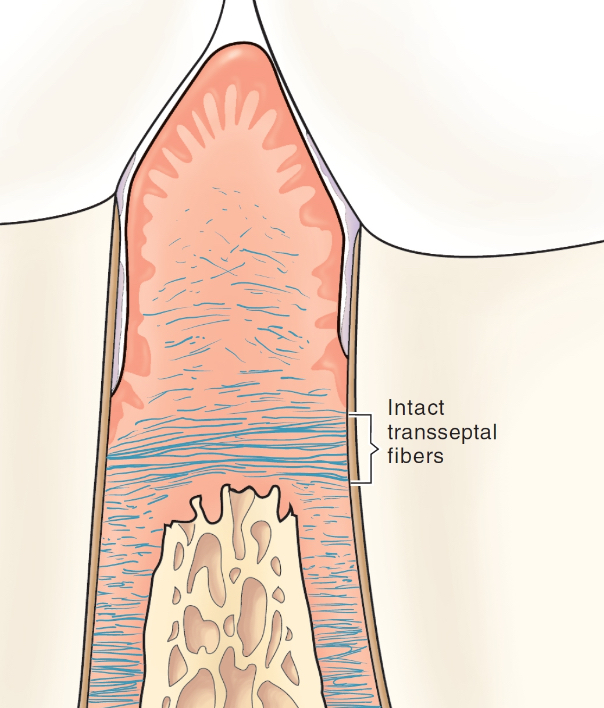
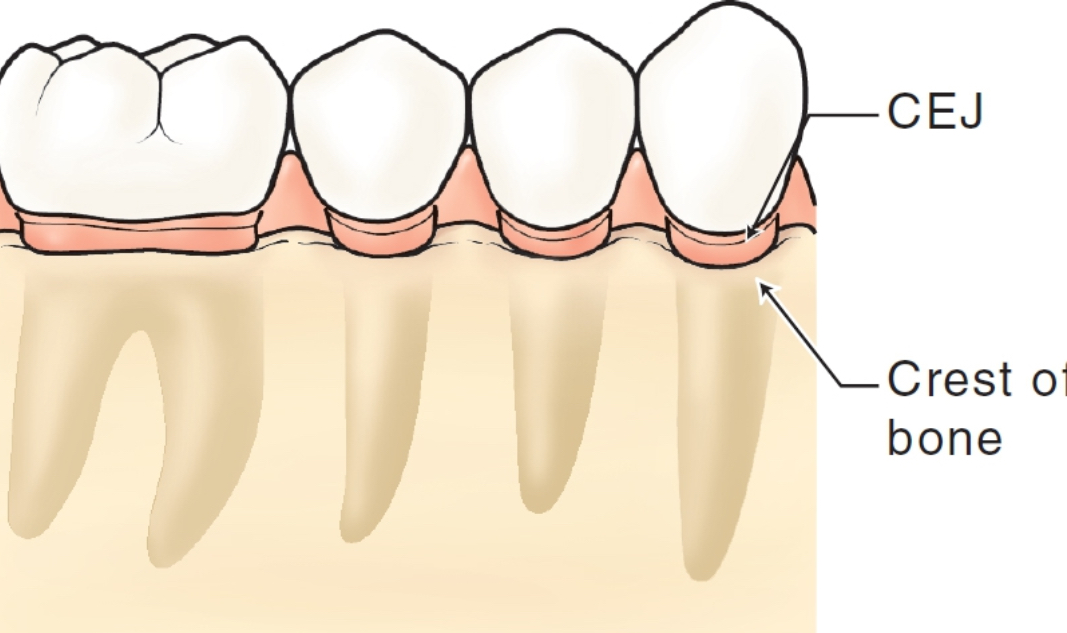
in health and gingivitis, the crest of the alveolar bone is located approximately ____ to the CEJ
2-3 mm apical
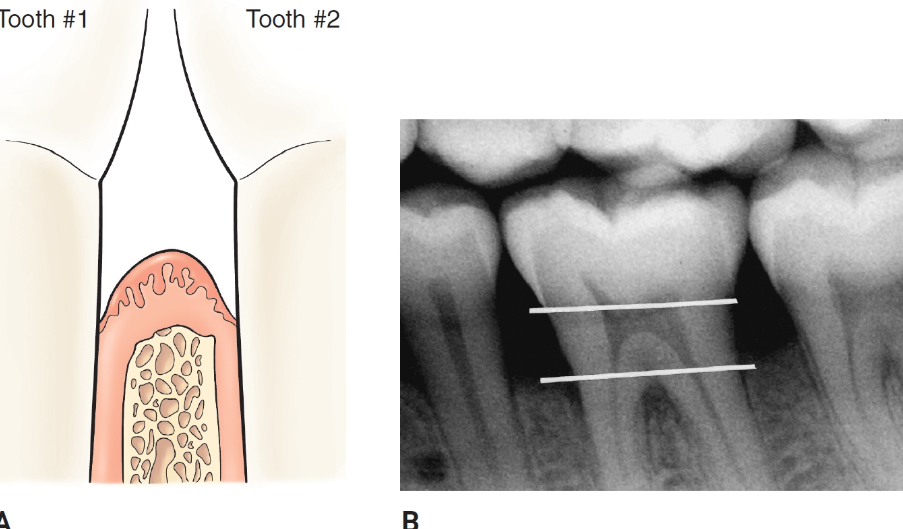
horizontal bone loss
alveolar bone is reduced in height, but the crest margin remains perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth
vertical bone loss
uneven reduction in the height of alveolar bone. resorption is more rapid next to the root → trench-like areas
pathway of inflammation into alveolar bone
horizontal bone loss (path of least resistance): gingival connective tissue → alveolar bone → PDL
vertical bone loss: gingival connective tissue → PDL (too weak to act as a barrier) → alveolar bone
disease sites
area of tissue destruction, just bc a pocket is present does not mean the patient has an active disease
inactive- stable
active- continued apical migration of the junctional epithelium over time
periodontal pocket
apical migration of the JE
destruction of periodontal ligament fibers
destruction of the alveolar bone
suprabony pocket
base of the pocket is coronal to the crest of the alveolar bone
horizontal bone loss
infrabony pocket
base of the pocket is apical to the crest of the bone
vertical or angular bone loss
infrabony defects
classified by the number of bony walls surrounding the tooth
three-wall: three bony walls remain and one is missing
two-wall: two bony walls remain and two are missing, interdental crater most common
one-wall: one bony wall remains and three are missing, hemiseptum (only the buccal or lingual wall remains)
osseous crater
when bone loss occurs in the interdental alveolar bone, the contour of the bone from facial to lingual dips apically
affects two adjacent root surfaces to a similar extent
furcation involvement
on a multi-rooted tooth when periodontal infection invades the area between and around the roots, resulting in a loss of alveolar bone between the roots of a multirooted tooth
continuous disease model of disease progression
(prior to 1980)
periodontal disease worsened throughout the entire mouth in a slow and constant rate; all cases of untreated gingivitis led to periodontitis
intermittent disease progression theory
current research- periodontal disease is characterized by periods of disease activity and inactivity; destruction does not occur in all parts of the mouth at the same time (susceptibility to periodontitis varies)
incidence
the number of new disease cases in a population that occur over a given period
prevalence
number of all cases (both old and new) of a disease that can be identified within a specified population at a given point in time
variables associated with the prevalence of periodontal disease
gender, race, socioeconomic status, age, behavior (like tobacco use), access to dental care
examples of commonly used periodontal indices
CPITN- community and periodontal index of treatment needs
EIBI- Eastman interdental bleeding index
GBI- gingival bleeding index
GI- gingival index
PSR- periodontal screening and recording