DSA08 Benign & Malignant Diseases of the Breast - Pathology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
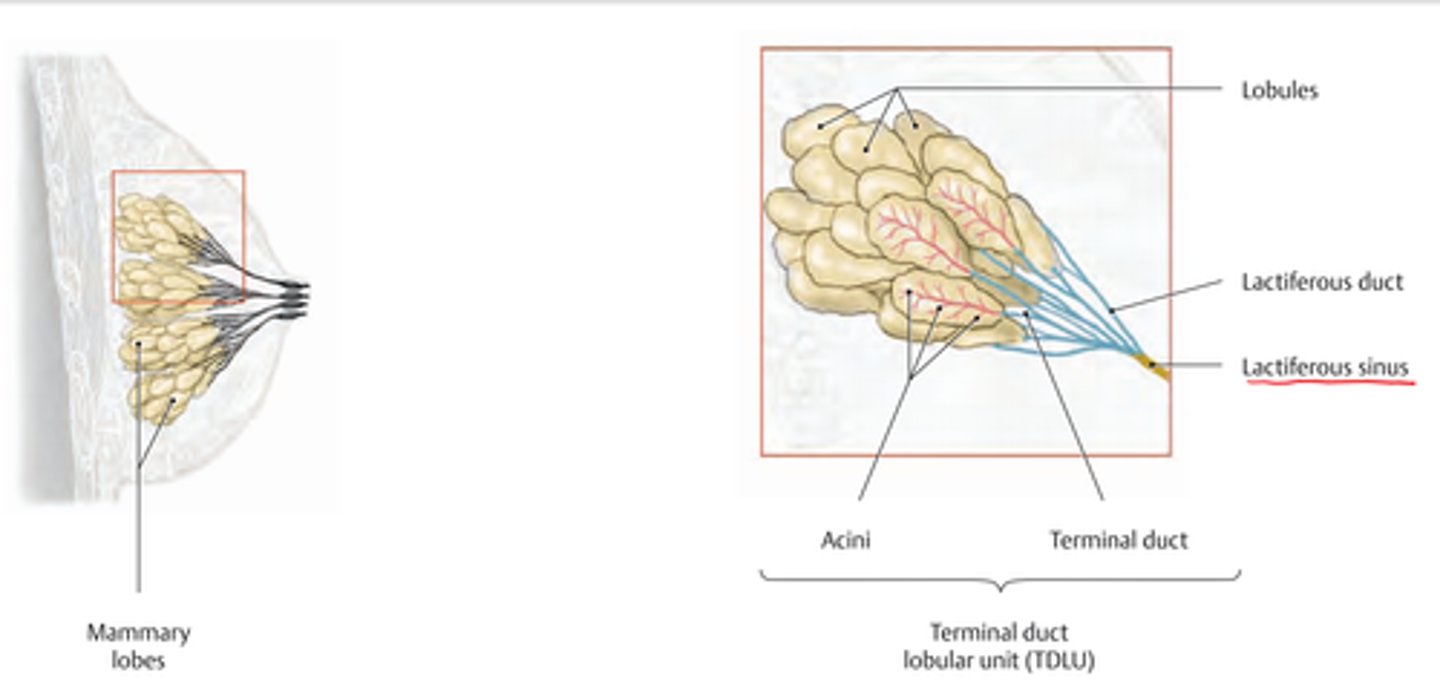
Terminal Ductal Lobular Unit (TDLU) - small acini
What is the functional unit of the breast and what is it made of?
Luminal epithelial cells
What cells in the INNER cell layer of the lobules of the TDLU produce milk?
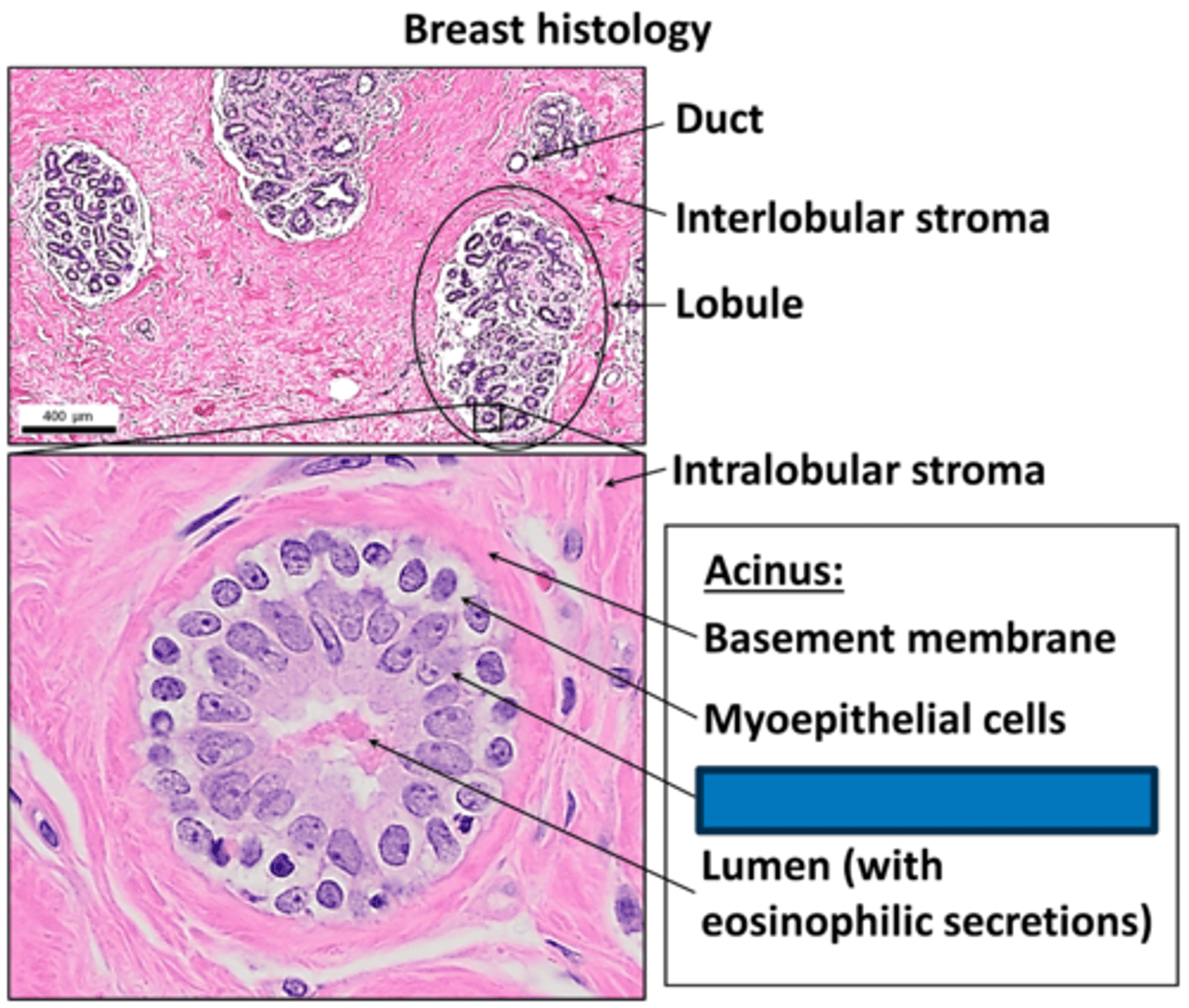
Myoepithelial cells
What cells in the OUTER cell layer of the lobules of the TDLU that contract to propel milk?
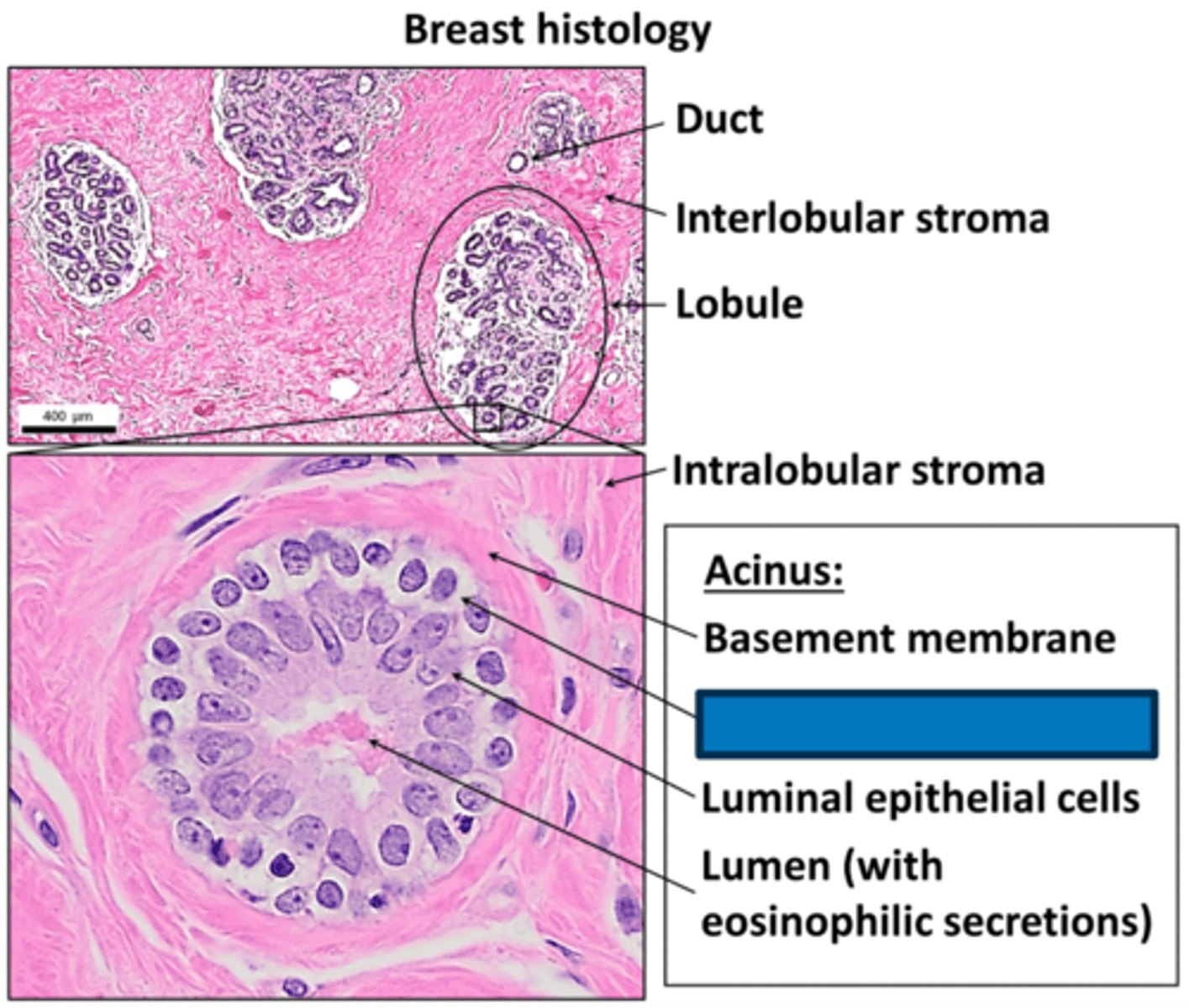
Galactorrhea
Define Condition:
Milk production outside of lactation
-Hx:
> Prolactinoma
> Chronic nipple (neurogenic) stimulation (often from poorly fitting bra)
> Dopamine antagonists
-Path: D/t PRL/Dopamine (PIF) imbalance (More PRL, less Dopa); PRL --> milk production
Gynecomastia
Define Condition:
Benign enlargement of male breast (unilateral/bilateral) - usually subareolar
-Hx:
> May be a/w Galactorrhea
> Physiologic:
>> Newborn male babies (placental transfer of male estrogen)
>> Male puberty (transient androgen to estrogen conversion in periphery)
>> Elderly men (More fatty tissue --> converts androgens to estrogen, less testosterone)
> Other Causes:
>> Cirrhosis (Chronic EtOH)
>> Hypogonadism
>> Exogenous steroids
-Path: Due to estrogen/androgen imbalance (↑estrogen, ↓androgen)
Acute Mastitis (Lactational Mastitis)
Define Condition:
Bacterial Infex while breastfeeding
-Path: MCC = S. aureus via fissures and cracks in nipples
-Sx/PE:
> Red, swollen, painful breast
> FEVER
> Malaise
-Tx: Uncomplicated = Abx & Breastfeed (helps prevent milk stasis)
-Prog: Complication --> Abscess
Periductal Mastitis
Define Condition:
Squamous metaplasia of lactiferous ducts inflammation of subareolar ducts
-Hx/Path: SMOKING (90%)
> Toxic to ducts
> Relative Vit A def (needed for differentiation of specialized epithelial surfaces) in ducts --> Squamous metaplasia
-Dx: Histo = Columnar luminal cells -> squamous metaplasia -> keratin plugs in ducts -> obstruction and inflammation -> peri-areolar mass
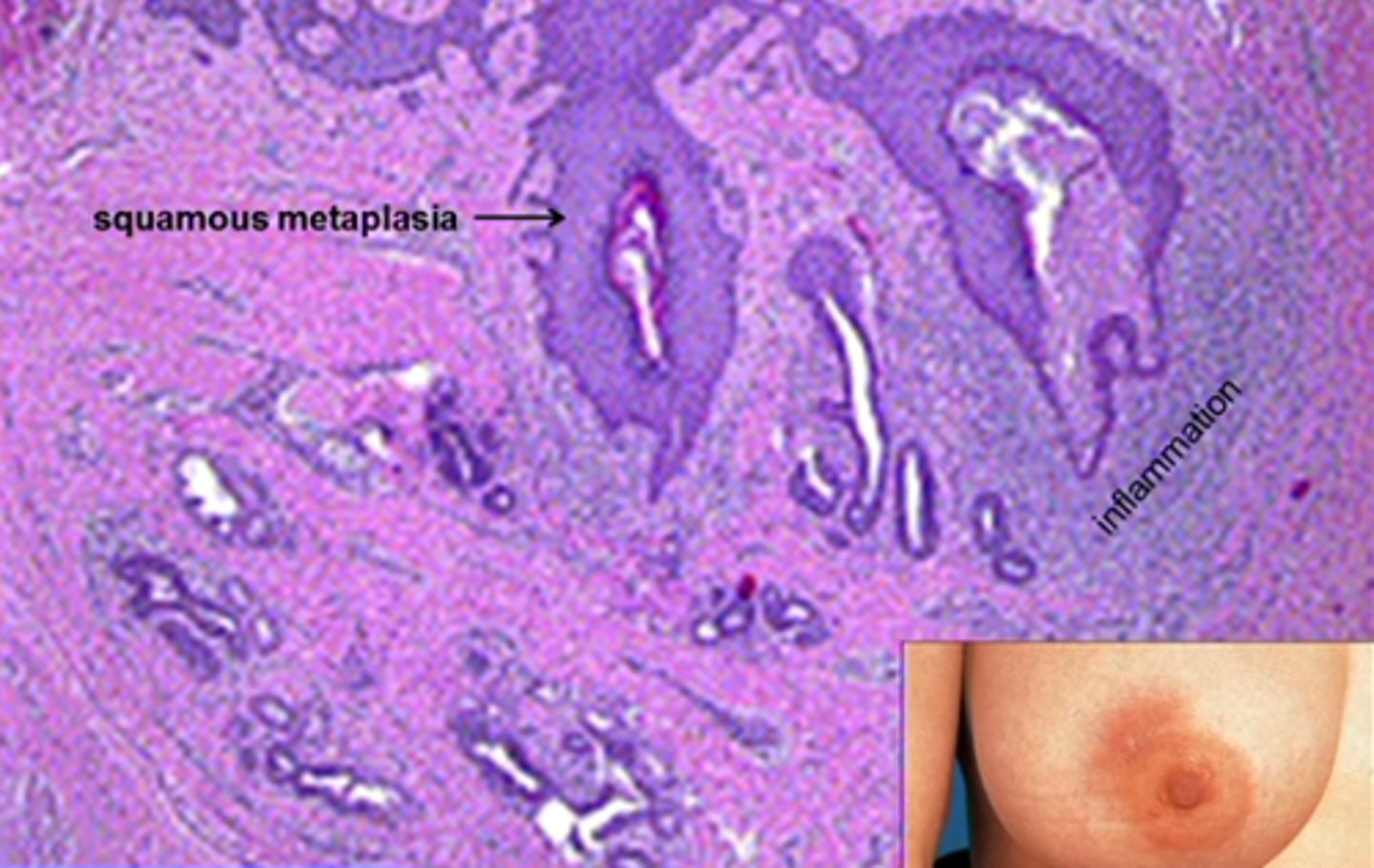
Mammary Duct Ectasia
Define Condition:
Benign inflammatory condition w/ dilation of the subareolar ducts
-Hx: Multiparous postmenopausal women
-Path: Duct walls weaken with age -> ducts fill up with debris -> chronic inflammation and fibrosis
-Sx/PE:
> Dirty white, green-brown nipple discharge (inflammatory debris)
> Palpable, periareolar mass, inverted nipple (MIMICS malignancy)
Fat Necrosis
Define Condition:
Necrosis of breast fat - benign, inflammatory process
-Hx: Usually related to trauma (sports injury, seatbelt injury)
-Sx/PE: Mass on physical exam
-Dx:
> Mamm = Abnormal calcification (d/t saponification)
> Histo = Necrotic fat with associated calcifications, histiocytes, and multinucleated giant cells
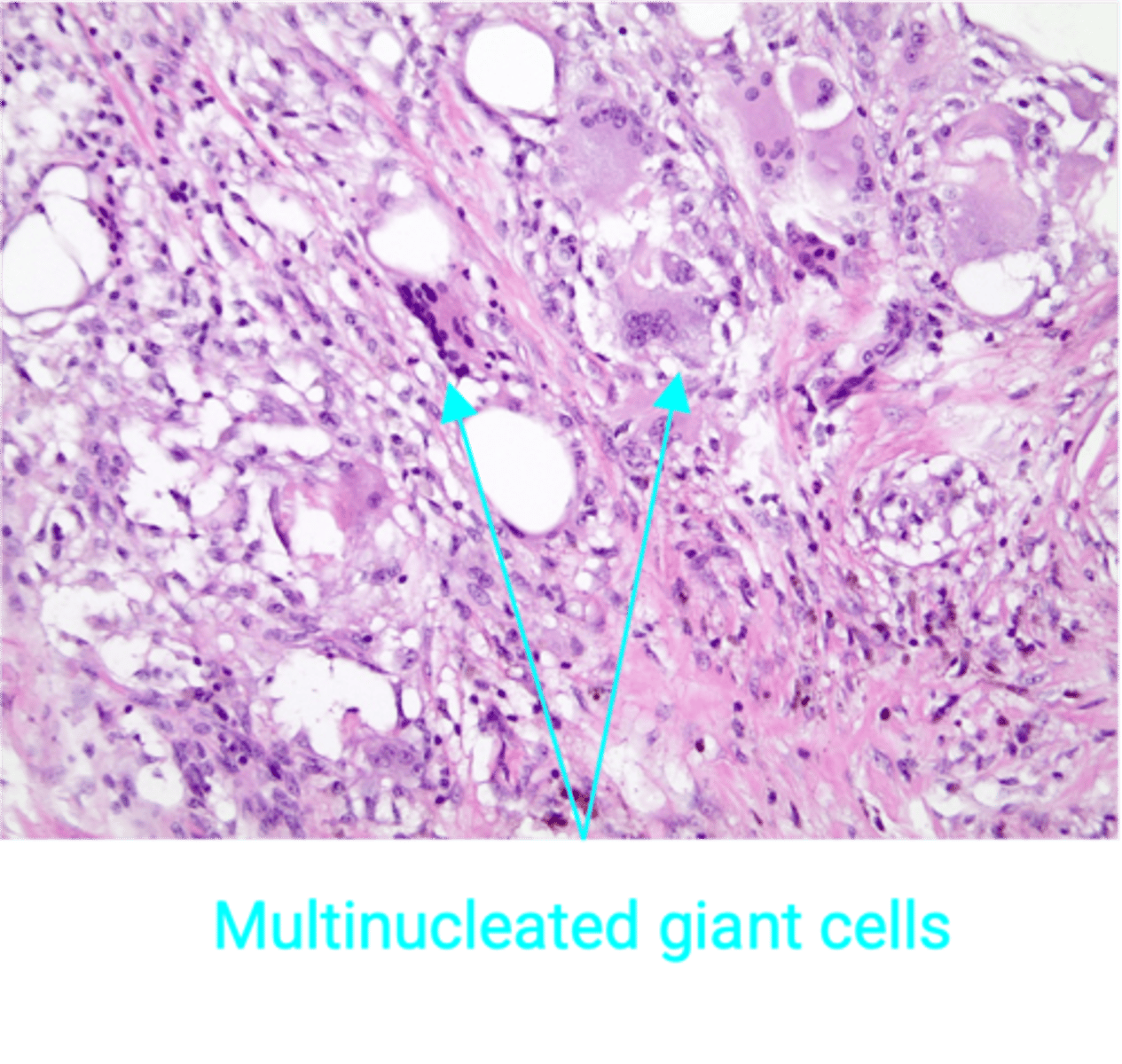
NON-PROLIFERATIVE Fibrocystic Change to Breast
Define Condition:
MC Benign Breast Lesion - Group of benign breast changes/lesions that have fibrosis or cysts in breast
-Hx: MC in Premenopausal Women (20-50 y/o)
-Path: Hormone mediated (cyclic/a/w menstrual cycle)
-Sx/PE:
> Lumpy bumpy breast
> Breast Tenderness
> Bilateral & Multifocal
-Prog: NO INC RISK OF CANCER
> Cysts
>> Dilated fluid filled cysts in TDLU
>> Gross = "Blue Dome"
> Stromal Fibrosis = Cysts rupture -> inflammation and fibrosis
> Apocrine Metaplasia/Change = Duct epithelial cells have abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm
> Adenosis = Increased acini per lobule
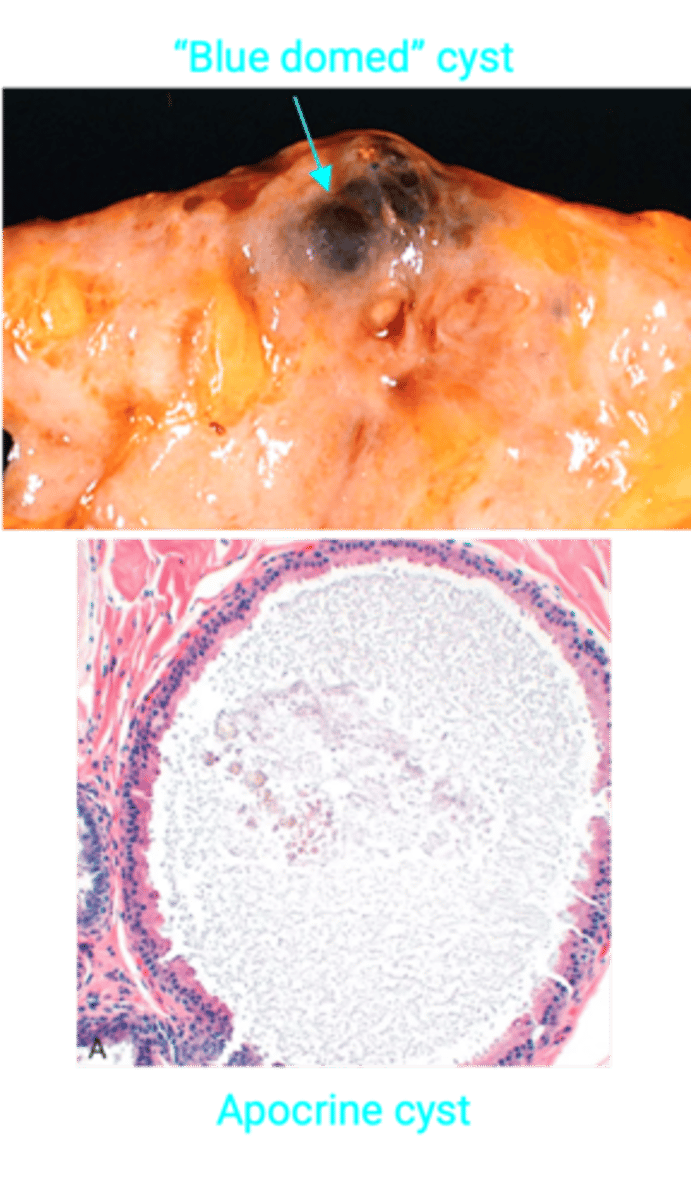
PROLIFERATIVE Fibrocystic Change to Breast
Define Condition:
MC Benign Breast Lesion - Group of benign breast changes/lesions that have fibrosis or cysts in breast
-Hx: MC in Premenopausal Women (20-50 y/o)
-Path: Hormone mediated (cyclic/a/w menstrual cycle)
-Sx/PE:
> Lumpy bumpy breast
> Breast Tenderness
> Bilateral & Multifocal
-Prog:
WITHOUT Atypia --> Slight Inc Risk of Cancer (1.5-2x)
> Sclerosing Adenosis = Inc number of compressed acinin w/ dense stroma; may have calcifications
> Epithelial Hyperplasia = Inc luminal/myoepithelial cells in ducts/lobules --> lumen filled w/ cells
WITH Atypia --> MODERATE Inc Risk of Cancer (4-5x)
> Atypical Hyperplasia = Epithelial Hyperplasia + Atypia
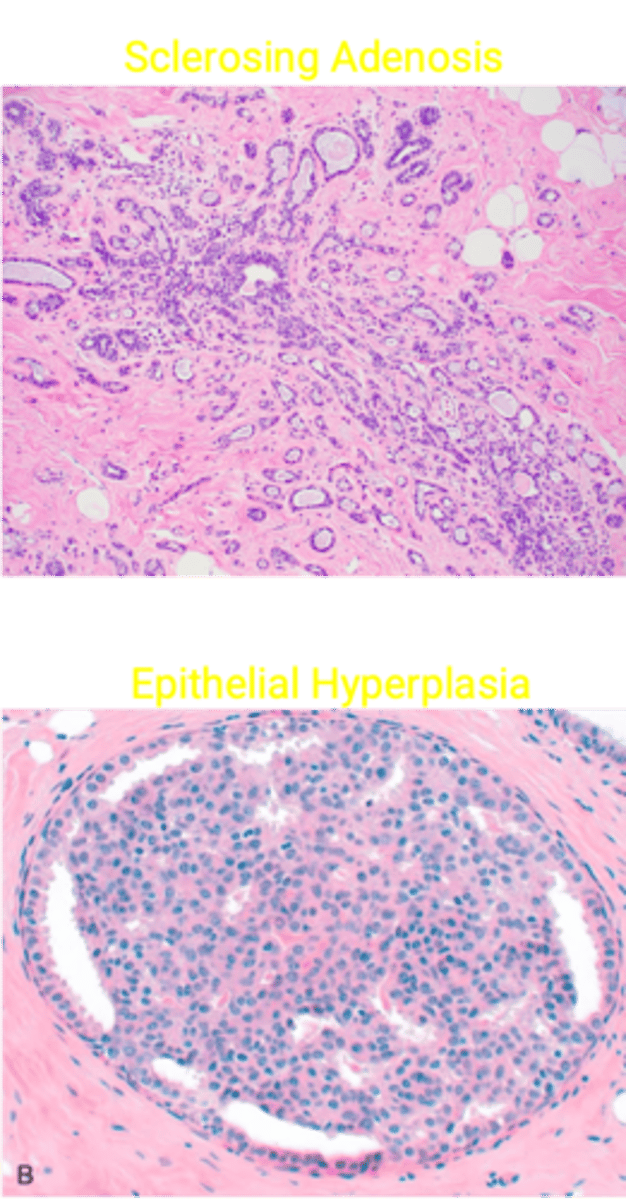
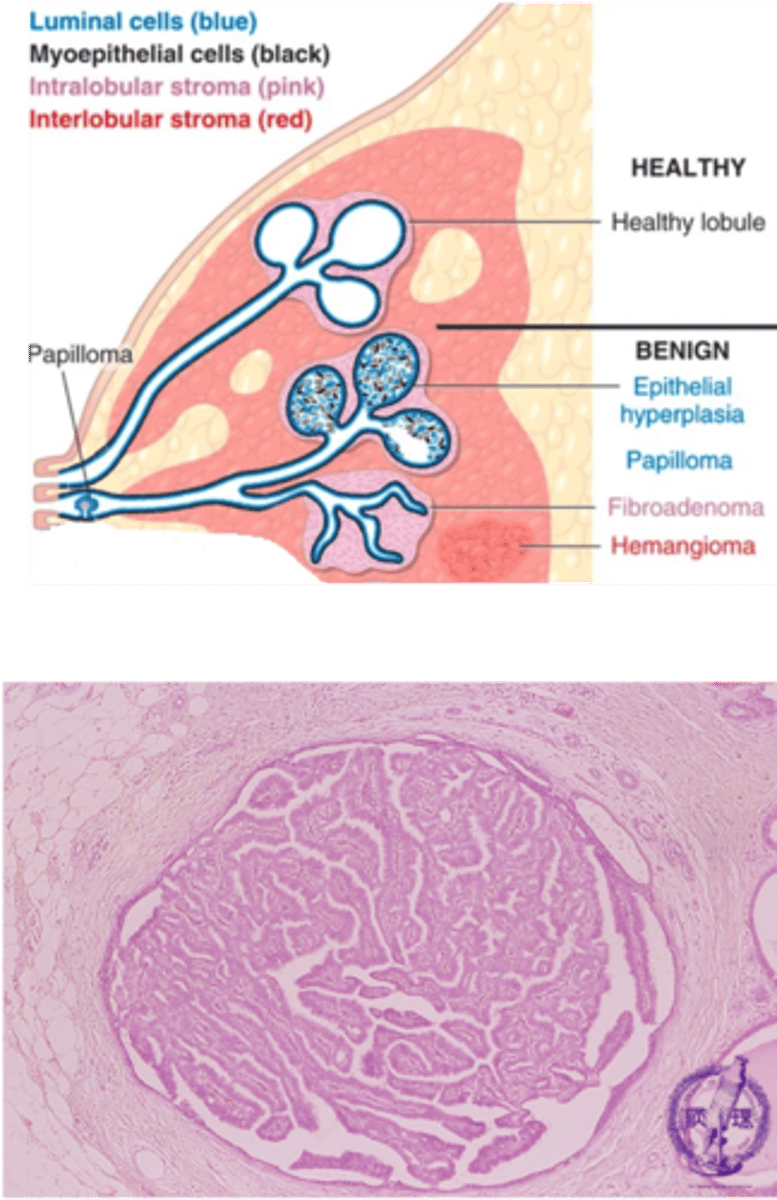
Intraductal Papilloma
Define Condition:
Papillary growth of ductal epithelial cells, usually into a large duct
-Hx: Premenopausal Women
-Sx/PE: bloody nipple discharge
-Dx: fibrovascular projections (papillae) lined by both epithelial (luminal) and MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS (diff from Papillary Carcinoma)
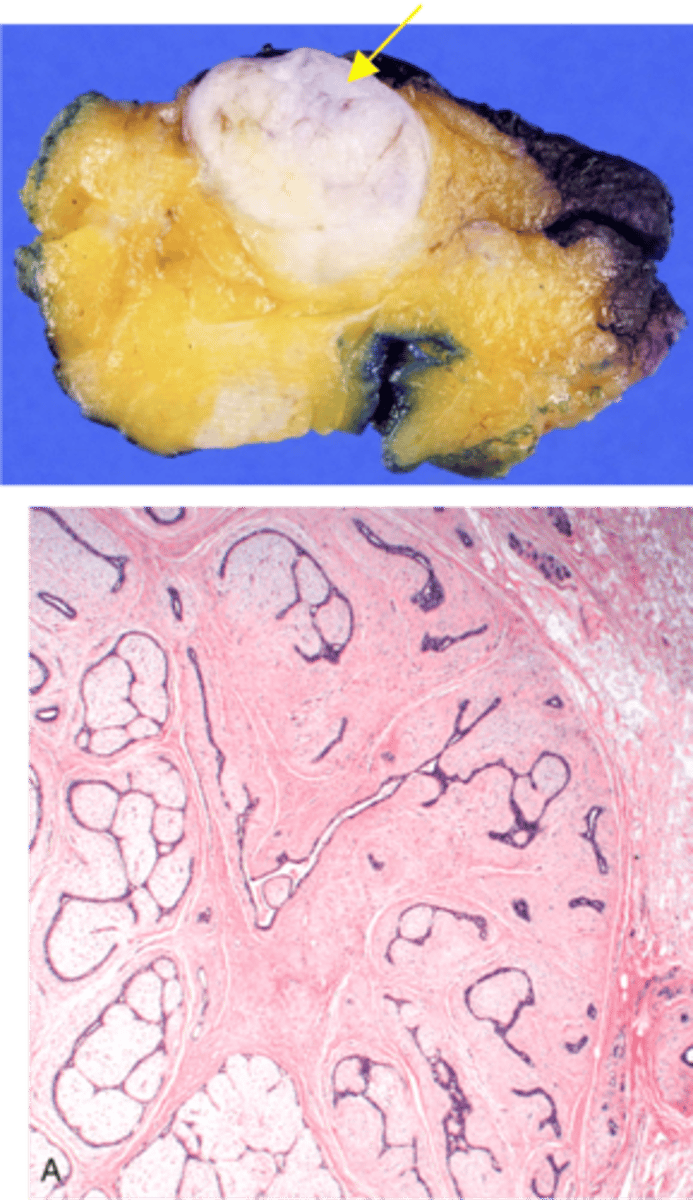
Fibroadenoma
Define Condition:
MC BENIGN Neoplasma of Breast - Tumor of fibrous tissue and glands (fibroepithelial tumor)
-Hx: Premenopausal Women
-Sx/PE:
> Well-circumscribed, mobile marble-like mass
> May grow during pregnancy & cause pain during menstrual cycle (estrogen sensitive)
-Dx:
> Gross = well-circumscribed tan white nodule
> Histo = Biphasic tumor with compressed epithelial lined spaces and uniform stromal cells that have low stromal cellularity
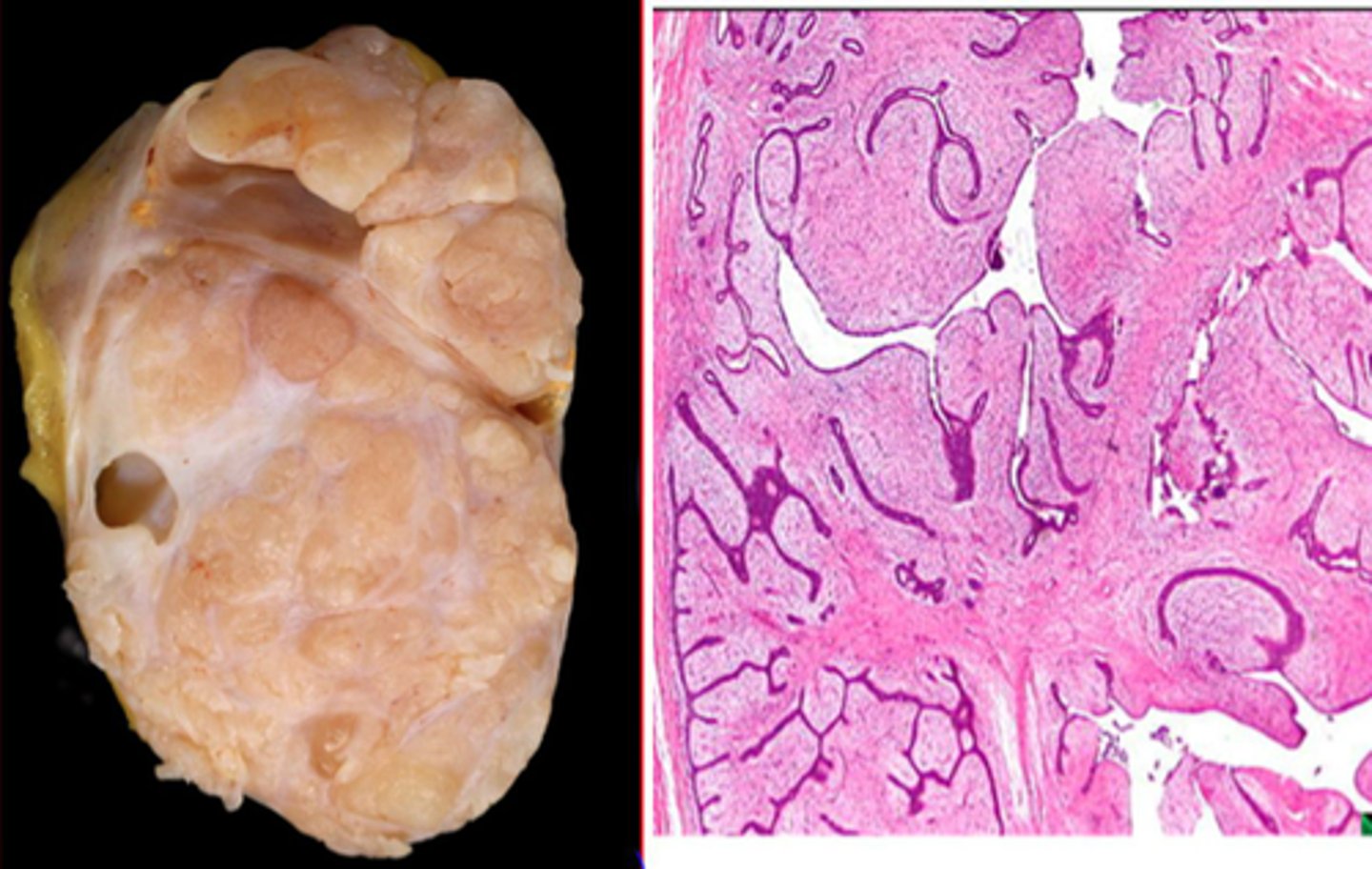
Phyllodes Tumor
Define Condition:
Stromal fibroepithelial tumor (tumor of fibrous tissue and glands but the stromal cells outgrow the epithelial component)
-Hx; Post-Menopausal women
-Path: FAST GROWING tumor; Generally BENIGN, but has potential to be malignant - behavior dependent on histologic grade (High grade lesions (pleomorphic, cellular stroma with high mitotic activity and infiltrative borders) have ↑ risk of mets)
-Dx: Histo = excess fibrous tissue pushes out “leaf-like” projections
Group of abnormal cells that have not spread from the location where they first formed aka the malignant cells have NOT invaded through the basement membrane (BUT has 8-10x Increased risk of Invasive Carcinoma)
Define Carcinoma in Situ (CIS)
When malignant cells have gone through the basement membrane
Define Invasive Carcinoma
Breast Carcinoma
Define Condition:
Most common female malignancy (1/4); Second leading cause of cancer death in women
-Hx:
> 1 in 8 change of developing (40,000 die each year)
> 5x higher in North America and Northern Europe
> Age > 50 y/o
> 5-10% HEREDITARY
>> BRCA gene:
>>> Inc risk of Ovarian Cancer (also higher incidence of prostate, pancreatic, gastric cancers)
>>> If Hereditary = More in PRE-menopausal women
>>> Up to 70% risk developing by age 65
>> Lynch Syndrome
> Nongenetic Factors (MORE ESTROGEN):
>> Early menarche
>> Late menopause
>> Late first pregnancy (after 30)
>> Nulliparity
>> No breast feeding
>> Combination Hormone replacement therapy >5 yrs
>> Obesity
>> Chest radiation
>> Benign breast disease (atypical hyperplasia)
-Prog:
> Depends on AXILLARY NODE INVOLVEMENT (No nodes = 83% 5 yr; > 4 nodes = 45% 5 yr)
> Better If Diagnosed OLDER
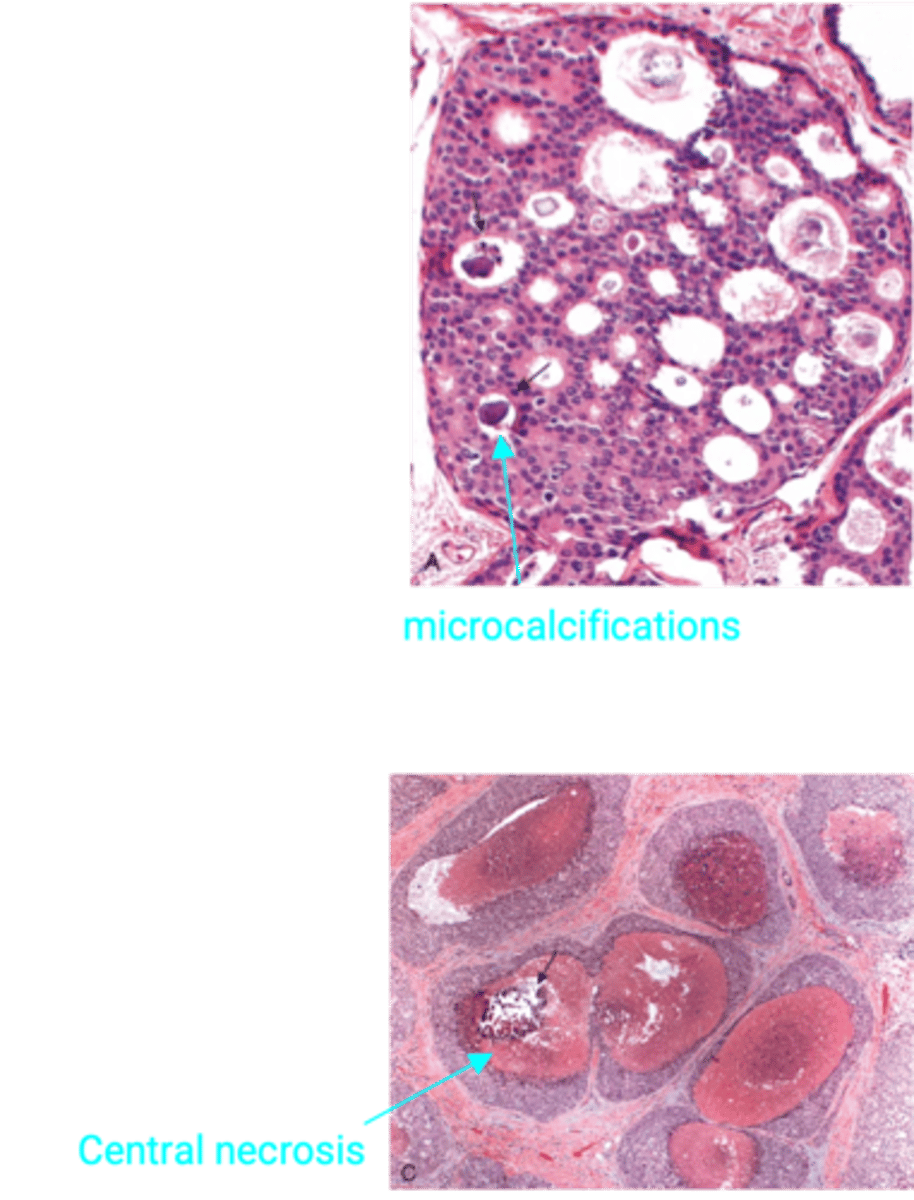
COMEDO Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
Malignant proliferation of cells in ducts with no invasion of the basement membrane
-Dx:
> A/w Microcalcifications (usually no mass, but detected on Mammogram --> get BIOPSY to distinguish btwn benign and malignant)
> Comedonecrosis (Central necrosis) and dystrophic calcifications in center of ducts
-Prog:
> HIGH Risk of cancer progression
> Risk of carcinoma in SAME breast
> Best Predictors for Recurrence/Progression = Nuclear grade & Necrosis
Paget Disease of Nipple (DCIS Subtype)
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
Malignant proliferation of cells in ducts with no invasion of the basement membrane - extends up the lactiferous ducts to involve nipple skin
-Hx: Almost always associated with an underlying DCIS/invasive carcinoma
-Sx/PE: Eczematous/Erythematous change of nipple areolar skin
-Dx: Histo
> Enlarged, polygonal epithelial cells with abundant pale cytoplasm, large nuclei
-Prog:
> Risk of carcinoma in SAME breast
> Best Predictors for Recurrence/Progression = Nuclear grade & Necrosis
Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS)
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
Malignant proliferation of cells in lobules with no invasion of the basement membrane
-Hx: Discovered INCIDENTALLY on biopsy
-Path: Dyscohesive cells due to loss of E-cadherin adhesion protein
-Dx: Does NOT produce a mass or calcifications
-Prog: Inc risk of carcinoma in EITHER breast
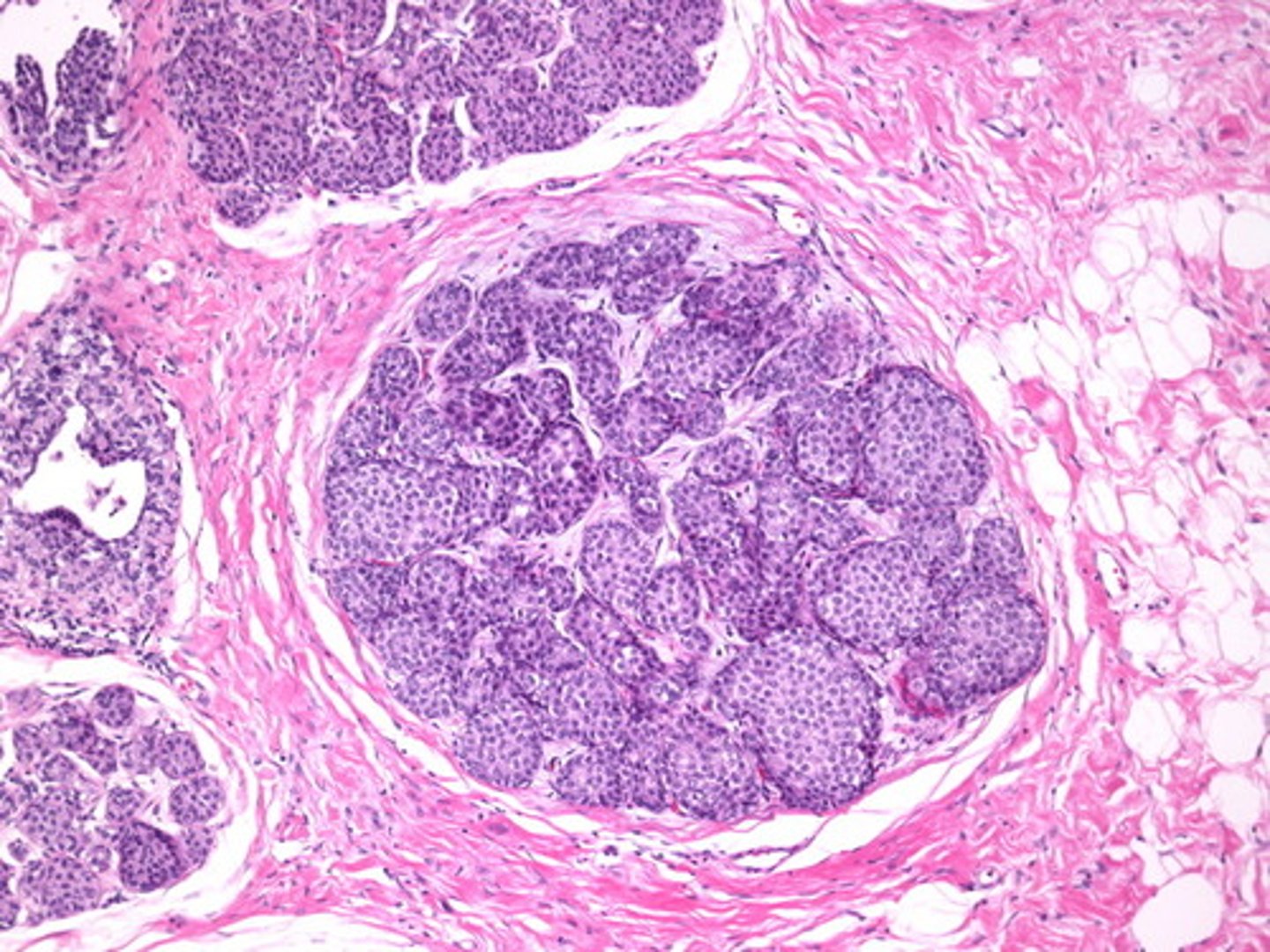
Invasive/Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
MC Morphologic type of invasive carcinoma in breast - classically forms duct-like structures (80% of cases)
-Path:
> Atypical ductal hyperplasia -> DCIS
-Dx:
> Histo
>> A/w calcifications
>> Infiltrating well-differentiated tubules to sheets of pleomorphic (poorly differentiated) tumor cells in desmoplastic stroma; no myoepithelial cell layer
> Mamm: Desmoplastic response --> Firm Mass & Density
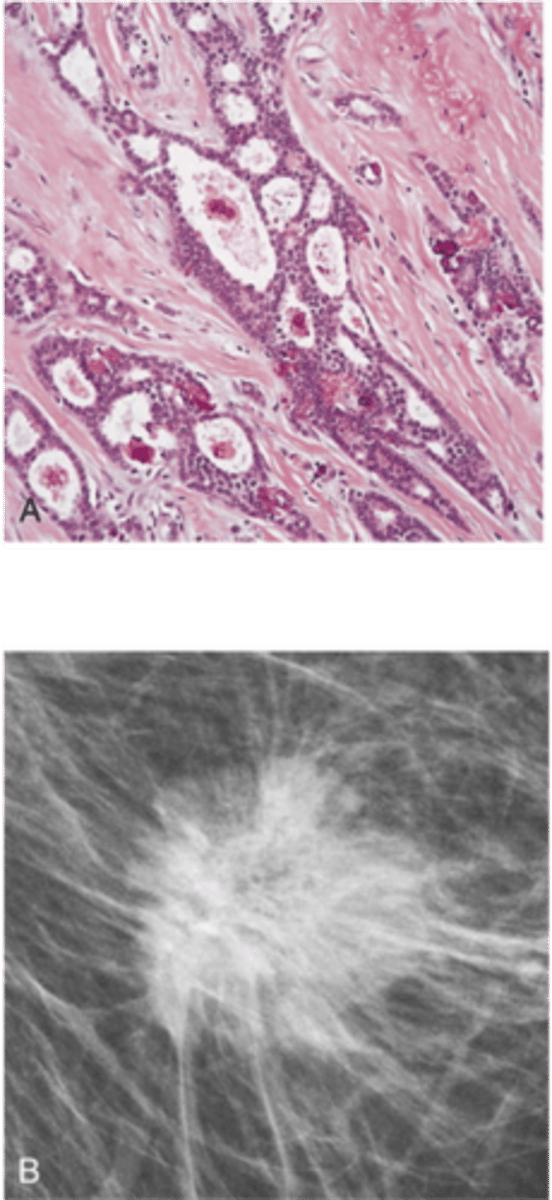
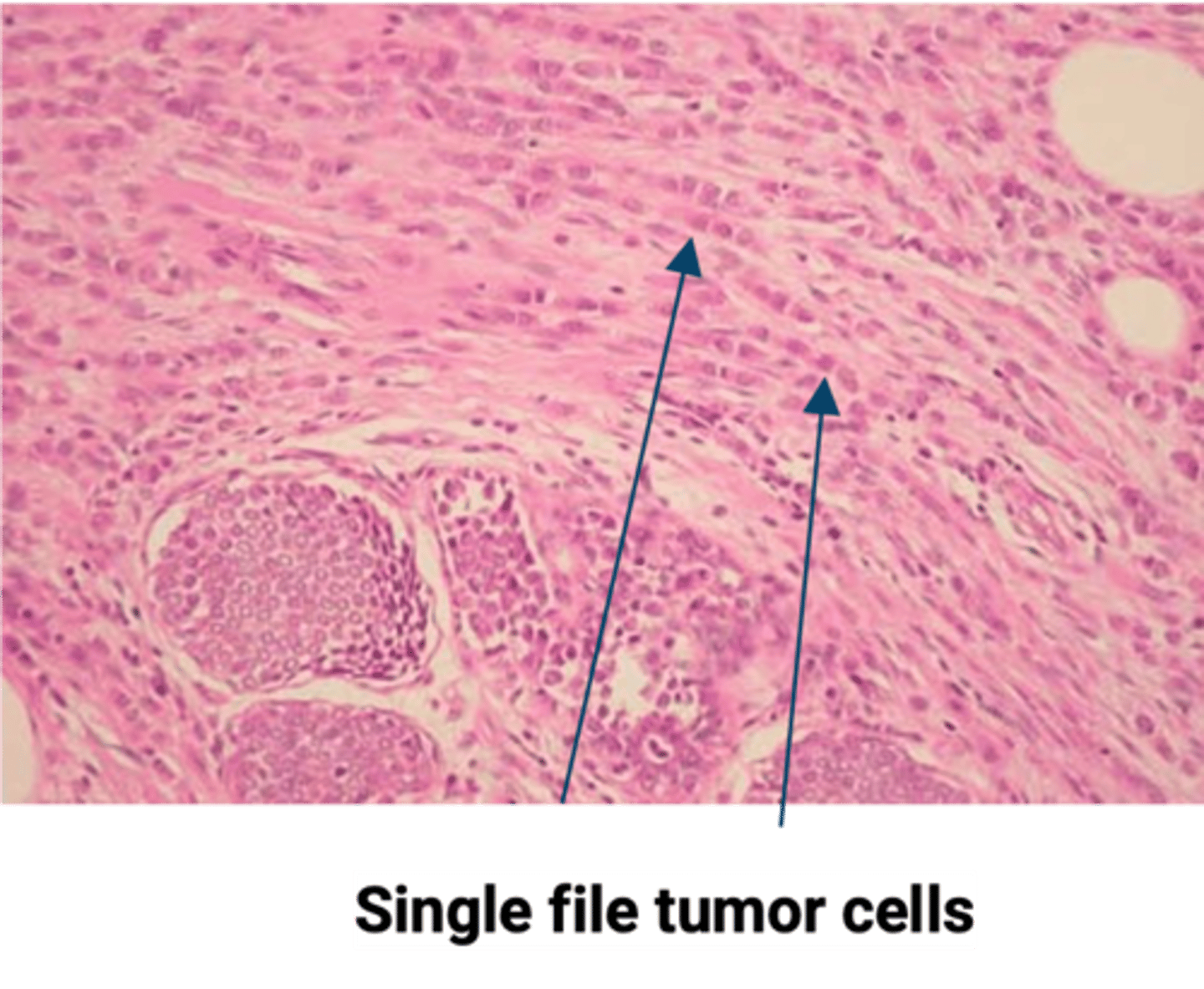
Invasive/Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
-Path: Biallelic loss of CDH1 (E-cadherin)
cell layer
-Dx: Histo: Dyscohesive invading tumor cells in a “single file” and no duct formation; No desmoplastic response
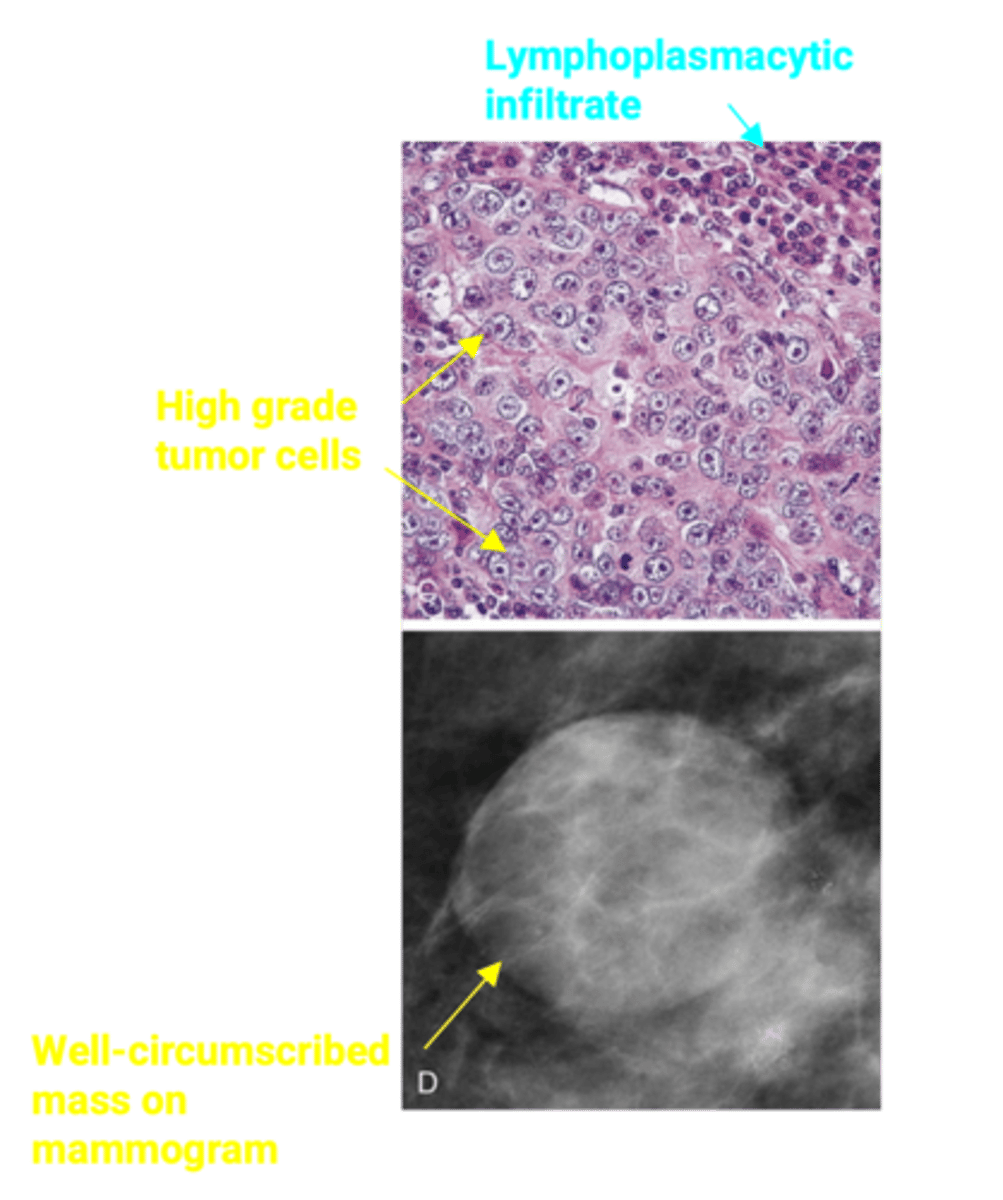
Medullary Carcinoma
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
Well-circumscribed mass that can mimic fibroadenoma on mammography
-Path:
> Triple negative for ER, PR, and HER2
> Increased incidence in BRCA1 carriers
-Dx: Histo:
> Large, high-grade tumor cells growing in sheets with associated lymphocytes and plasma cells
-Prog: GOOD!
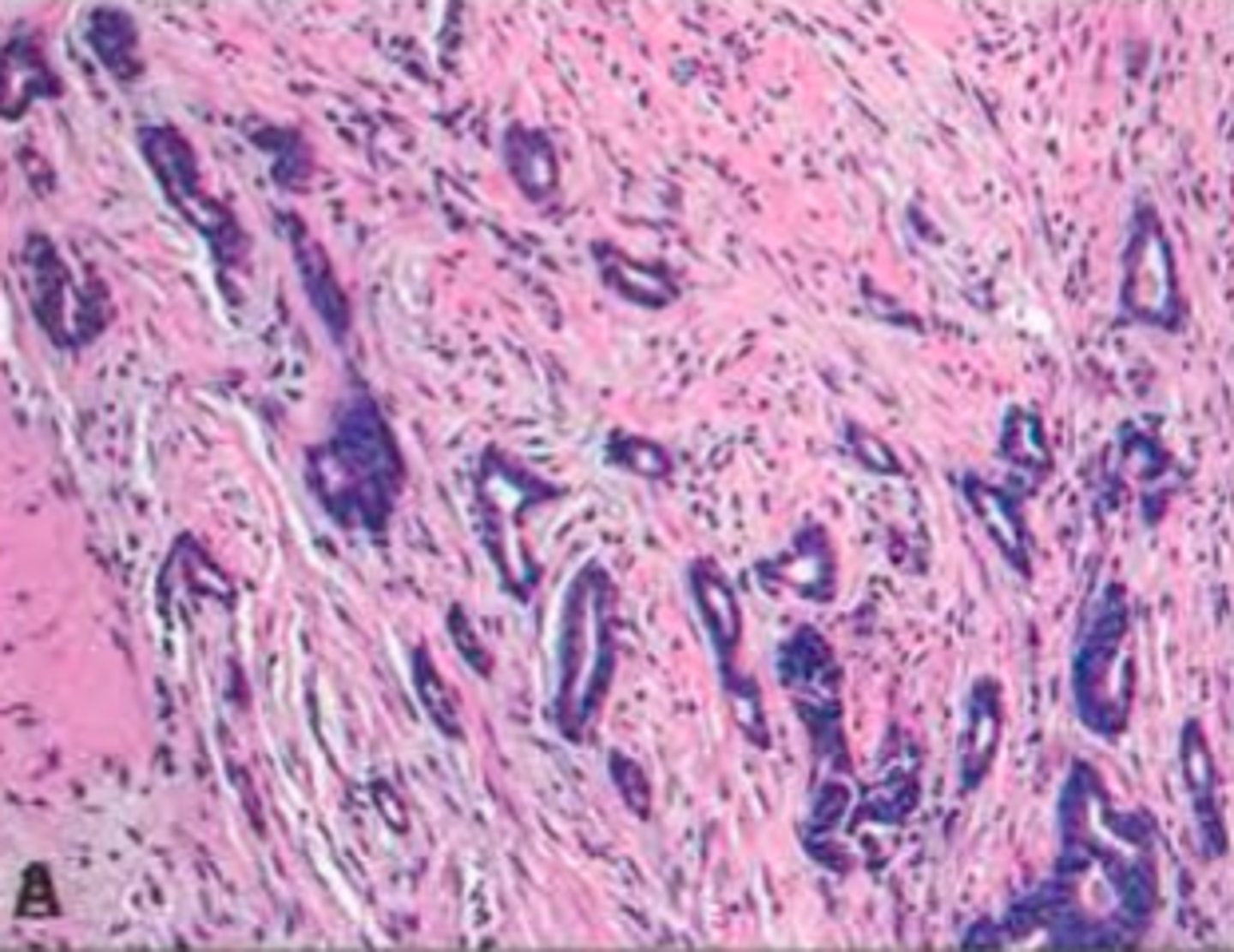
Mucinous Carcinoma
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
D/t abundant extracellular mucin --> Tumor cells floating in mucin pool
-Prog: GOOD!
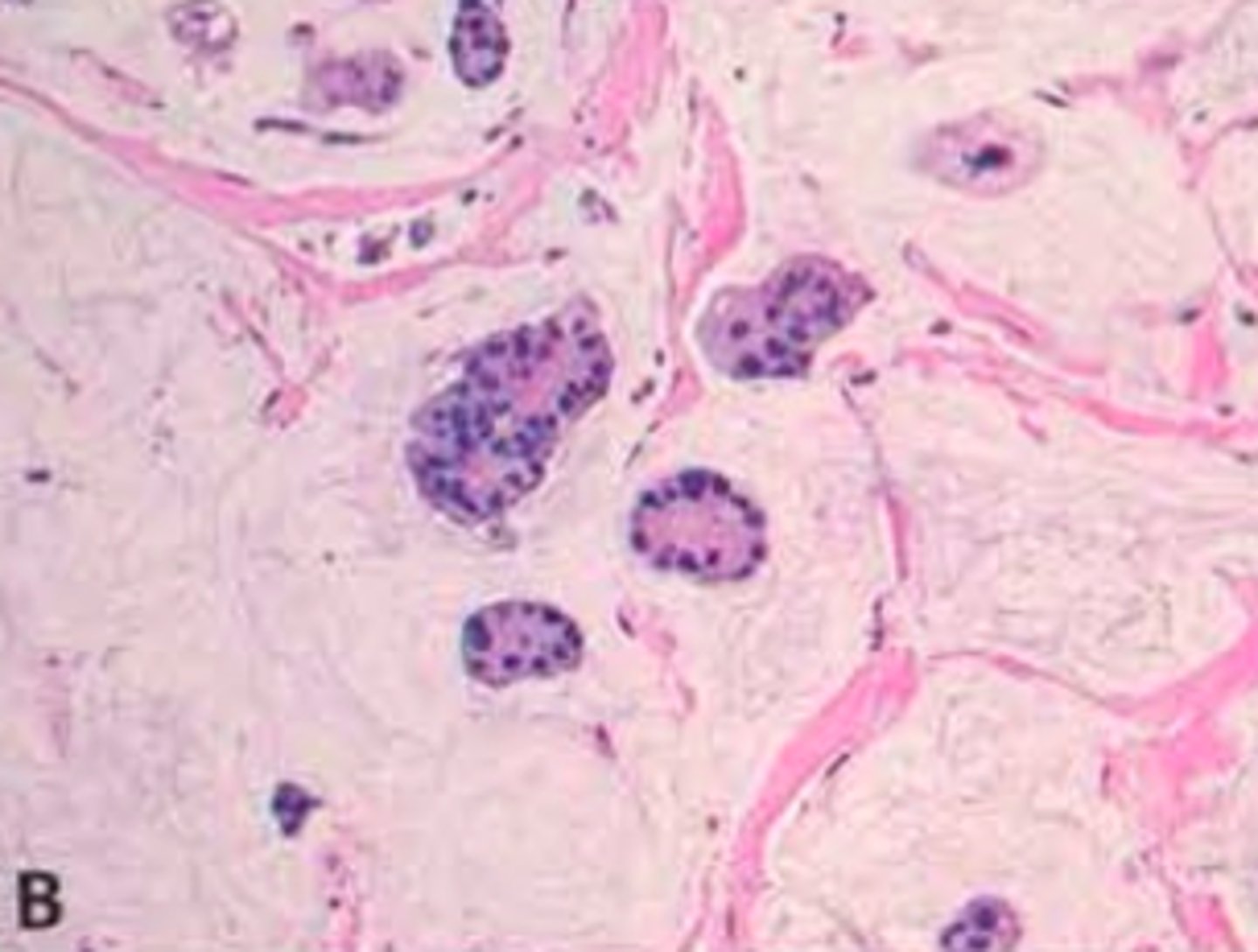
Tubular Carcinoma
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
Well differentiated tubules lacking myoepithelial cells
-Prog: GOOD!
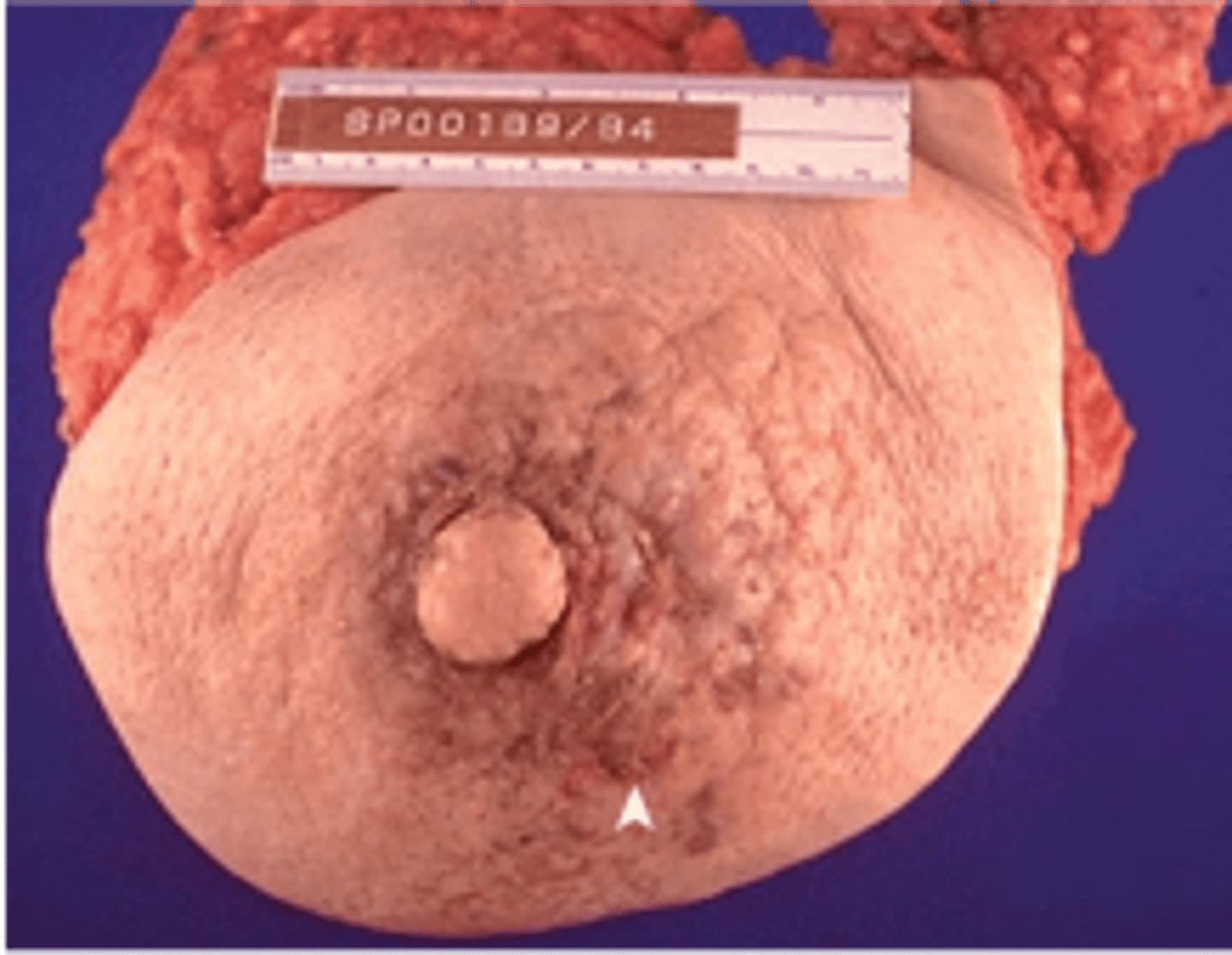
Inflammatory carcinoma
Define Type of Breast Cancer:
Tumor cells invading the dermal lymphatics
-Sx/PE:
> Breast Pain
> Warm, Swollen, Red/Inflamed skin around exaggerated hair follicles giving "Peau d'orange" appearance (orange peel texture)
-Prog: POOR!
MALE Breast Cancer
Define Condition:
1% of all breast cancers (rare)
-Hx: Males, 60-70s
-Path:
> MC Type = IDC
> A/w BRCA2 & Klinefelter syndrome
-Sx/PE: Subareolar mass +/- nipple discharge