Photosynthesis Quiz (ATP, Light Dependent, Calvin Cycle)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Energy, ATP, Light Dependent, Calvin Cycle
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Energy
the ability to do work
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Molecule that stores energy
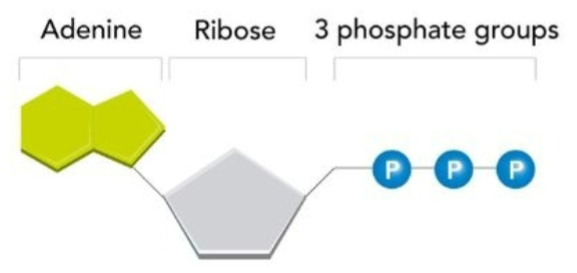
What molecule’s structure is this?
ATP structure
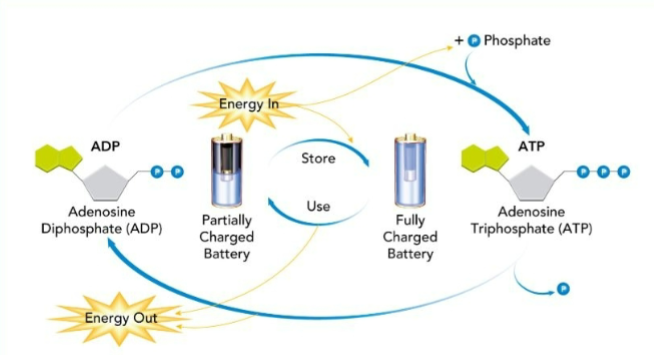
What is this and what does it do?
ATP cycle creates energy from breaking down ATP into ADP
How can cells use ATP?
active transport, protein synthesis, photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Process used by autotrophs to harness sun’s energy and create sugar
Photosynthesis Formula:
6 Carbon Dioxide + 6 water + light —> Glucose + 6 Oxygen
Light Reaction Reactants:
Light, water, NADP+, ADP
Light Reaction Products:
Oxygen, NADPH, ATP
Light Reaction Location:
thylakoid membrane
Calvin Cycle Reactants:
ATP, NADPH, Carbon Dioxide
Calvin Cycle Products:
Sugar, ADP, NADP+
Calvin Cycle Location:
stroma
Chlorophyll reflects this color
green/yellow
Carotenoids reflect this color
orange/yellow
epidermis
surface layer of leaf
cuticle
transparent, waxy covering on leaf
stomata
adjustable pores controlling water movement and gas exchange
mesophyll
layers inside the cells of leaves
Palisade mesophyll
preforms photosynthesis in leaf
Spongy mesophyll
Regulates gas exchange in leaf
xylem
transports water throughout the plant
phloem
transports food across the plant
Bundle sheath cells
Cells that surround xylem and phloem that don’t contain chloroplasts
Is xylem passive or active transport?
passive
Is phloem passive or active transport?
active
Adaptations of aquatic plants
stomata on top of leaves to help regulate transport
Adaptations of Cacti
Stomata closed in day and open in night, thick cuticle, large vacuole, etc.
Adaptations of forest floor plants
Large leaves to capture maximum sunlight
stroma
thick fluid in chloroplast (cytoplasm of chloroplast)
thylakoids
disk-shaped sacs in stroma
Grannum
stacks of thylakodis
Lumen
fruid found in thylakoid membrane or in thylakoids
Which 4 factors affect photosynthesis?
Light, Temperature, Water, Carbon Dioxide
First step of Light Reaction that takes place in PSII
electrons become energized from sunlight and leave to go to electron transport chain (ETC)
How are the electrons replaced from PSII in light dependent reactions?
Water splits and gives it electrons into the PSII, its Hydrogen protons go to the thylakoid lumen to create a electrochemical gradient, and the Oxygen is a byproduct released in the atmosphere
What do electrons do in the cytochrome in light reactions?
Help pump Hydrogen ions across concentration gradient
After being in the cytochrome, where do electrons go in light reactions?
Electrons go to PSI to get re-energized and ready for next steps
After leaving PSI, what do electrons do in light reactions?
Electrons go to the next ETC and convert NADP+ into NADPH
What is the last step in light reactions?
Hydrogen ions flow back and synthesize ATP
3 steps of the Calvin Cycle
Fixation, Reduction, Regeneration
What happens in Carbon Fixation in Calvin Cycle?
RUBISCO allows 3 RuBP + 3 Carbon Dioxide = 6 carbon molecule (unstable) —> splits into 6 PGA
What happens in Reduction in Calvin Cycle?
6 ATP and 6 NADP+ become ADP and NADPH to allow 6 PGA to become 6 G3P —> one G3P leaves to make glucose —> 5 remain
What happens in Regeneration in Calvin Cycle?
The 5 G3P use ATP to become 3 RuBP and allow the cycle to restart