ANAT 3001 blood vessels
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
walls of blood vessels
3 layers common to arteries and veins
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica externa
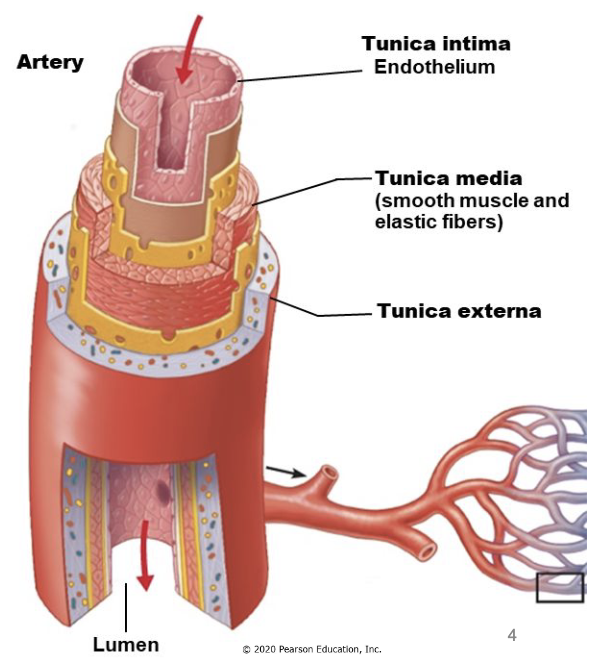
tunica intima
inner layer
simple squamous epithelium (endothelium)
tunica media
middle layer
contains smooth muscle to control blood flow
thicker in arteries than veins
tunica externa (“adventitia”)
outer layer
connective tissue anchors vessels to other structures
vasoconstriction
contract smooth muscle in tunica media
decrease blood flow through lumen
vasodilation
relax smooth muscle in tunica media
increases blood flow through lumen
arteries
elastic arteries, muscular arteries, arterioles
carry blood away from heart (oxygenated and deoxygenated)
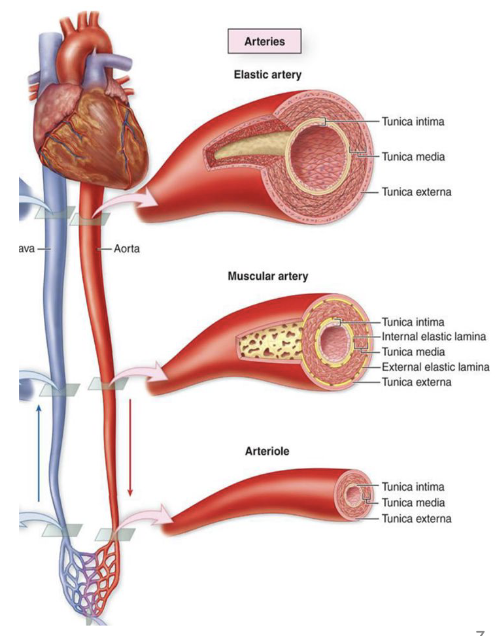
elastic arteries
largest (2.5-1cm)
closest to heart, conduct blood away from heart
elastic fibers allow expansion when blood is pumped
ex. aorta, pulmonary, brachiocephalic, common carotid, subclavian, and common iliac arteries
branch into muscular arteries
muscular arteries
medium sized arteries distribute blood to organs and tissues
less elastic tissue and relatively thicker tunica media
control flow of blood with smooth muscle
branch into arterioles
arterioles
smallest arteries
smallest arterioles have only endothelium and single layer of smooth muscle
branch into capillaries
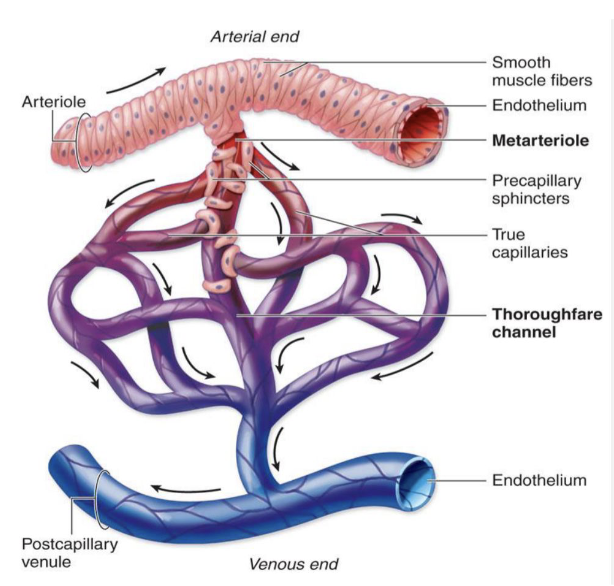
capillaries
smallest blood vessels
only one RBC can pass through a capillary at a time
form a bed or branching vessels for exchange of gases and nutrients
composed of tunica intima (endothelium and basement membrane)
veins
venules, medium veins, large veins
carry blood to the heart (oxygenated and deoxygenated)
superficial veins travel in subcutaneous tissue
deep veins travel between skeletal muscles
open multiple veins per artery
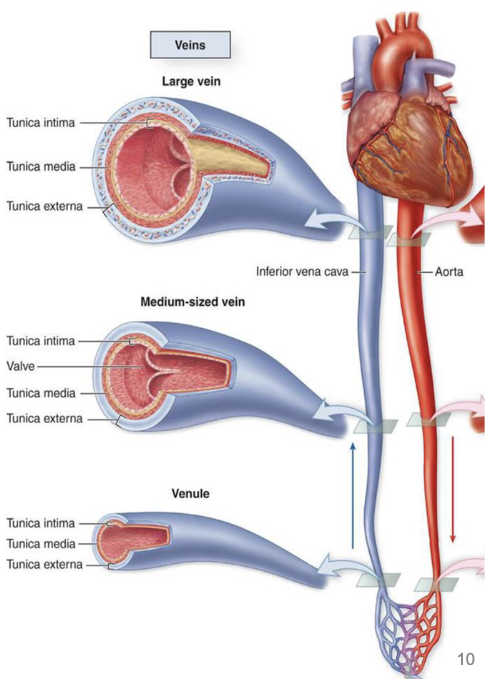
venules
smallest of veins, run with arterioles
have thin layer of smooth muscle, little ability to vasoconstrict
merge to form larger venules, then veins
medium veins
~1 cm in diameter
have all 3 tunics, externa is thickest
run with muscular arteries
low pressure in veins, need valves for one way flow
large veins
up to 3 cm in diameter
have all 3 tunics, externa is thickest
run with elastic arteries
lack valves
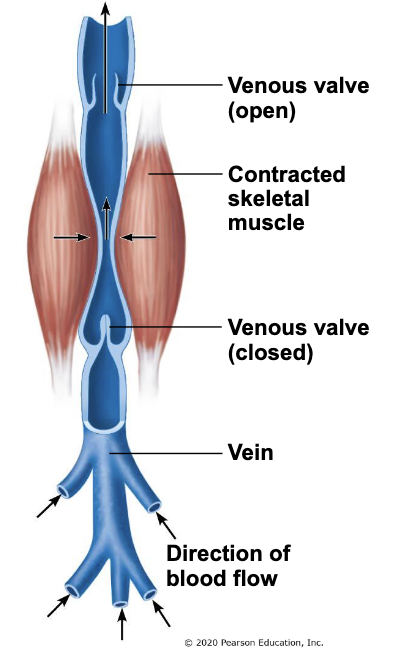
skeletal muscle pump
skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation helps move venous blood
muscles squeeze veins, push blood towards heart
inactivity results in greater risk of clot formation
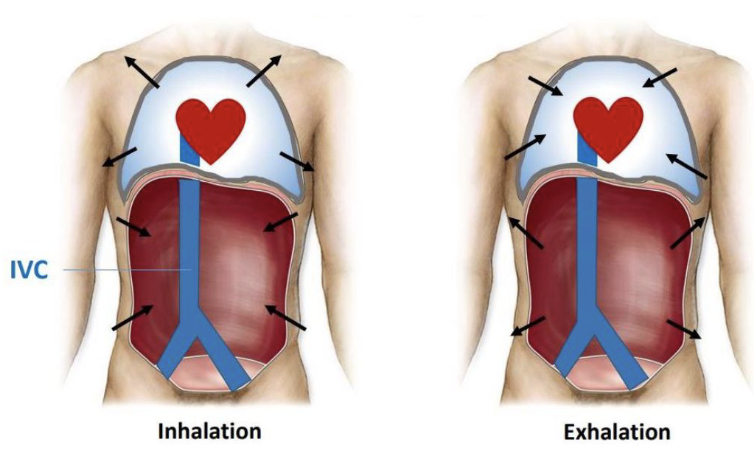
respiratory pump
IVC ascends in abdomen and thorax
does not have skeletal muscle pump, assist from diaphragm
inhalation - diaphragm flattens
increases abdominal pressure
lowers thoracic pressure
blood in IVC pushed towards heart
aorta
carries oxygenated blood away from the heart
3 parts
ascending aorta
aortic arch
descending aorta
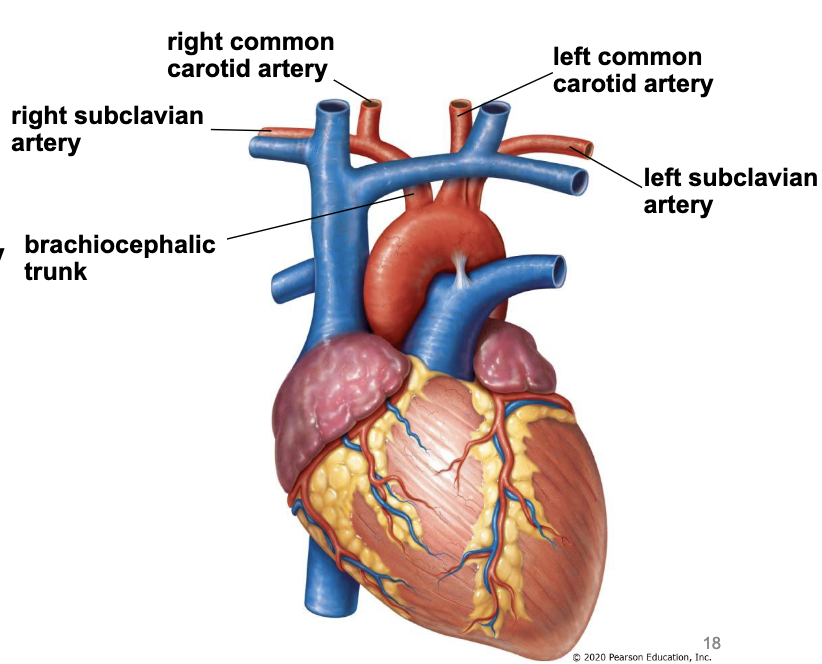
aortic arch
aortic arch gives off 3 branches that supply the head, neck, and upper limbs
brachiocephalic trunk
right common carotid artery - supply head and neck
right subclavian artery - supply upper limbs
left common carotid artery
left subclavian artery
arteries to head and neck
common carotid artery splits into…
internal carotid artery - travels into cranial cavity to supply brain
external carotid artery - remains outside of skull to supply superficial structures of head and neck
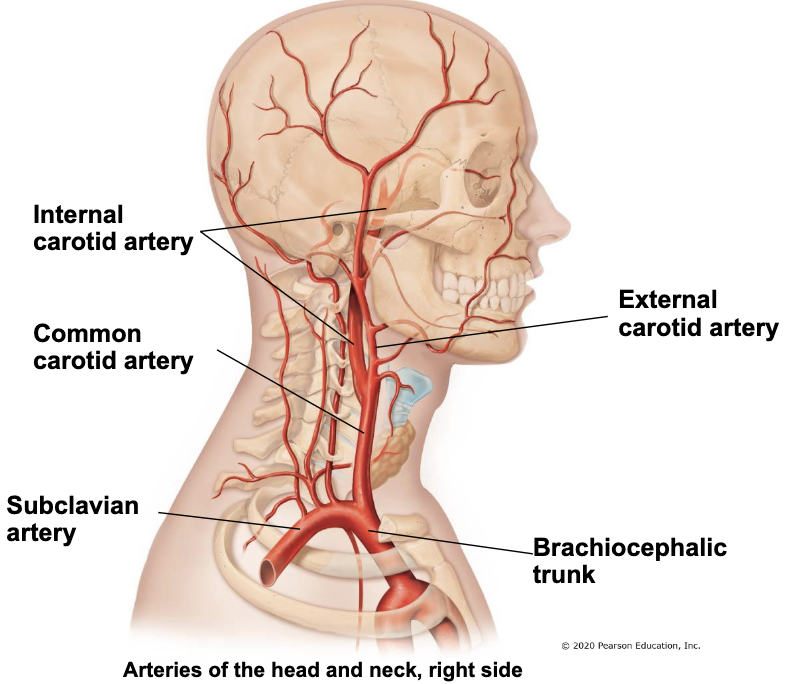
branches of external carotid artery
superior thyroid a. - supply thyroid gland
lingual a. - supply tongue
facial a. - supply face
occipital a. - supply back of head
maxillary a. - supply muscles of mastication and teeth
superficial temporal a. - supply scalp
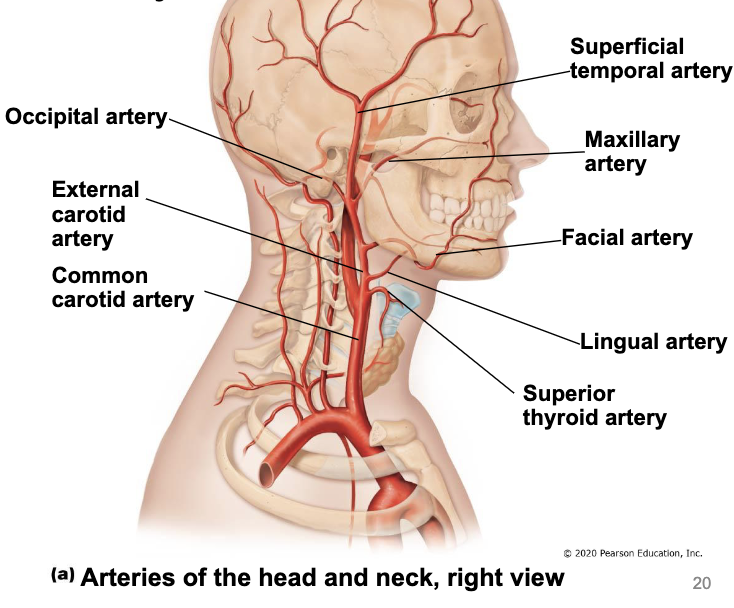
vertebral arteries
branch from subclavian arteries
travel superiorly in transverse foramina in cervical vertebrae
enter cranium through foramen magnum
left and right arteries join to form basilar artery
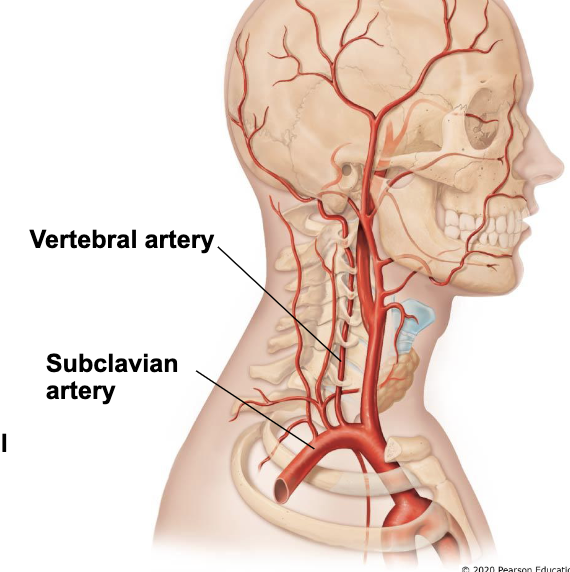
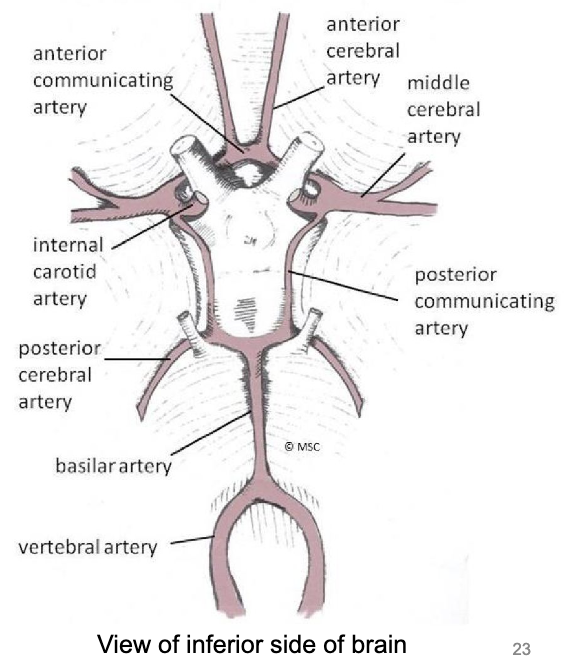
blood supply to the brain: internal carotid arteries
branch into anterior and middle cerebral arteries
anterior cerebral arteries connect via anterior communicating arteries
blood supply to the brain: vertebral arteries
join to form basilar artery
basilar artery gives off left & right posterior cerebral arteries
posterior cerebral arteries connect to internal carotid arteries through posterior communicating arteries
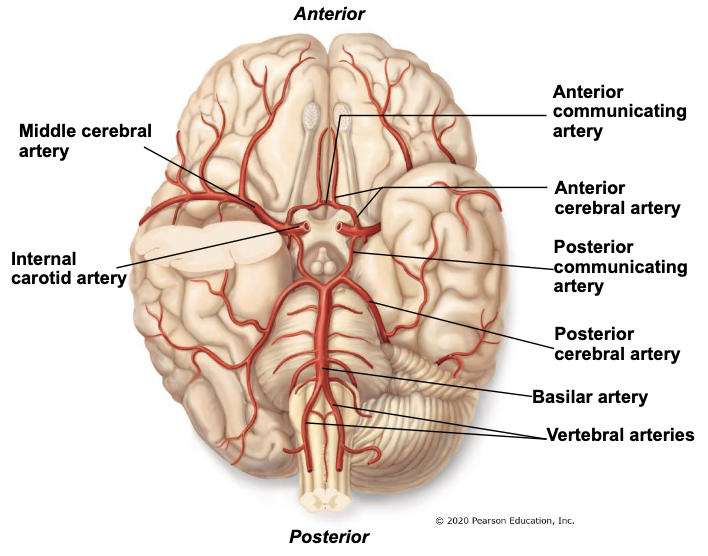
circle of willis
circle of arteries supplying the brain
formed by posterior cerebral, posterior communicating, internal carotid, anterior cerebral, and anterior communicating arteries
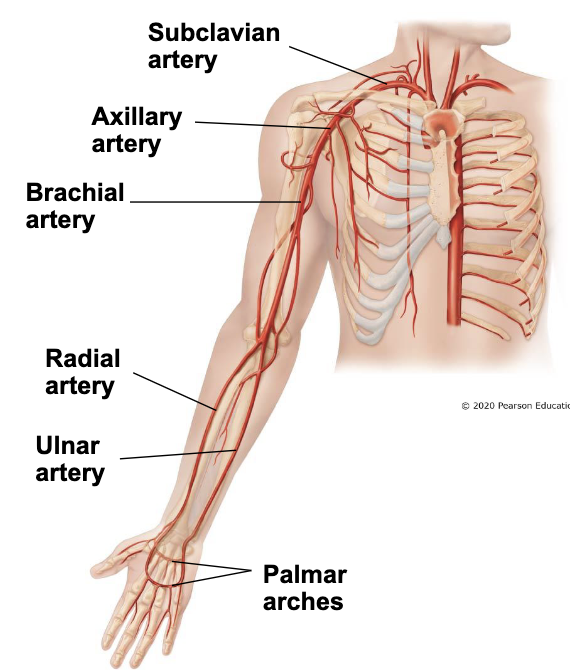
blood supply to upper limbs
subclavian artery
travels between first rib and under clavicle to become axillary artery
axillary artery
becomes brachial artery
brachial artery
after passing elbow, splits into radial and ulnar arteries
radial & unlar arteries
form palmer arches in the hand
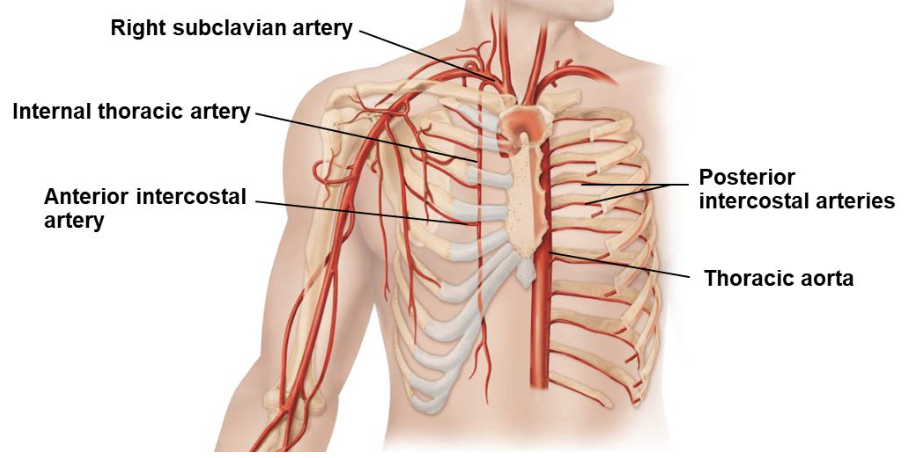
blood supply to thorax
thoracic aorta
gives off posterior intercostal arteries
internal thoracic arteries
either side of the sternum
branch from subclavian arteries
gives off anterior intercostal arteries which join with posterior intercostal arteries
blood supply to the abdomen
thoracic aorta passes the diaphragm to become the abdominal aorta
3 branches
renal arteries supply the kidneys
gonadol arteries supply gonads (testes or ovaries)
abdominal artery splits into left and right common iliac arteries
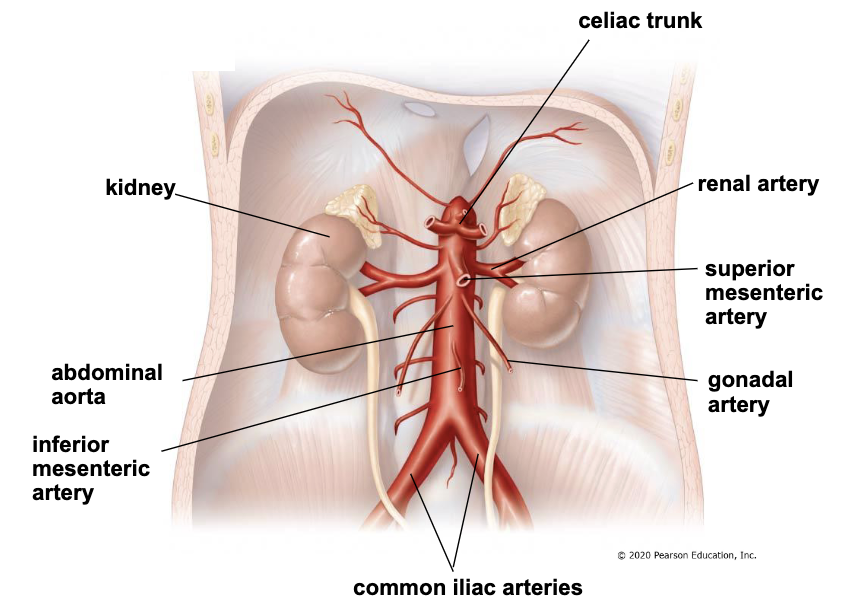
3 unpaired, central branches of the abdominal aorta
celiac trunk
superior mesenteric artery
inferior mesenteric artery
celiac trunk
supplies stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, pancreas, and duodenum
superior mesenteric artery
supplies jejunum, ileum, appendix, ascending colon, and transverse colon
inferior mesenteric artery
supplies descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum
iliac arteries
common iliac arteries enter pelvis and divide into internal and external iliac arteries
internal iliacs supply pelvic organs, gluteal region, and external genitalia
external iliacs leave pelvis to become femoral arteries in the thigh
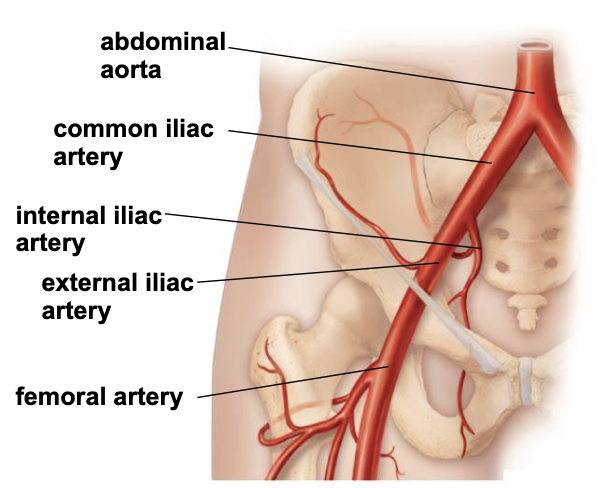
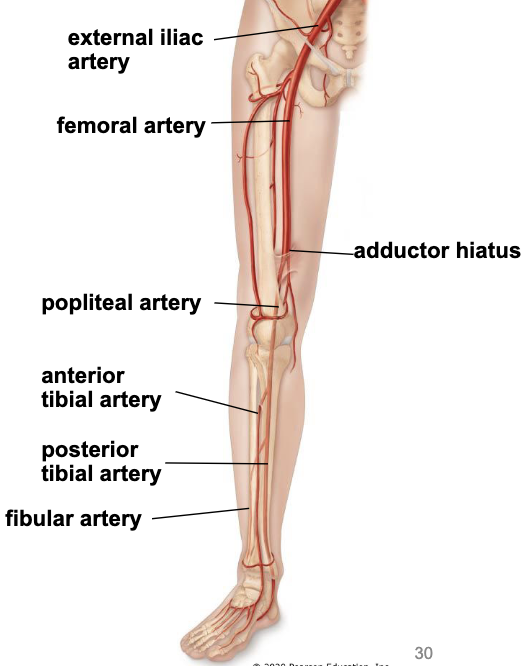
arteries in lower limb
femora artery - supplies the muscles of the thich
passes through the back of the knee to become the popliteal artery
popliteal artery branches into
anterior tibial artery - supply anterior compartment of leg and dorsum of foot
posterior tibial artery - supply posterior compartment of leg and plantar foot
fibular artery - supply lateral compartment of leg
veins of the head and neck
external jugular vein
internal jugular vein
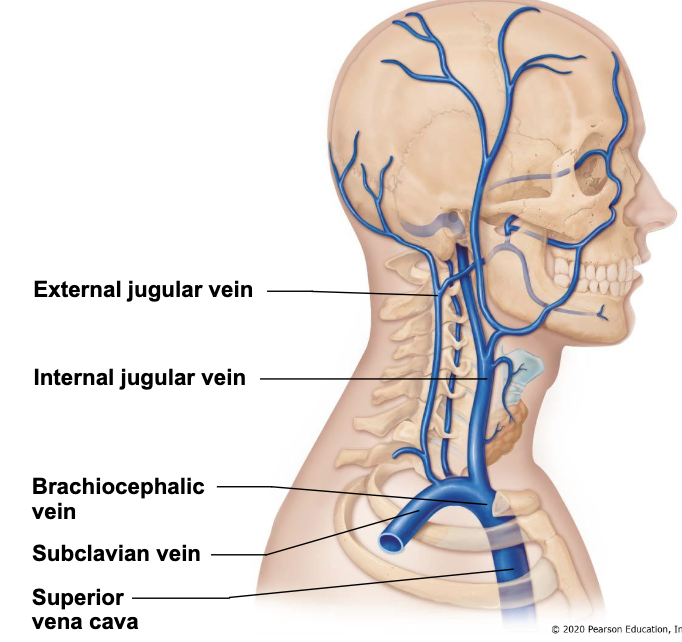
external jugular vein
superficial to sternocleidomastoid
carries blood from neck and superficial head
joins with internal jugular vein or subclavian vein at base of neck
internal jugular vein
begins at jugular foramen (base of skull)
carries blood from brain (dural sinuses), orbit, and face
deep to sternocleidomastoid
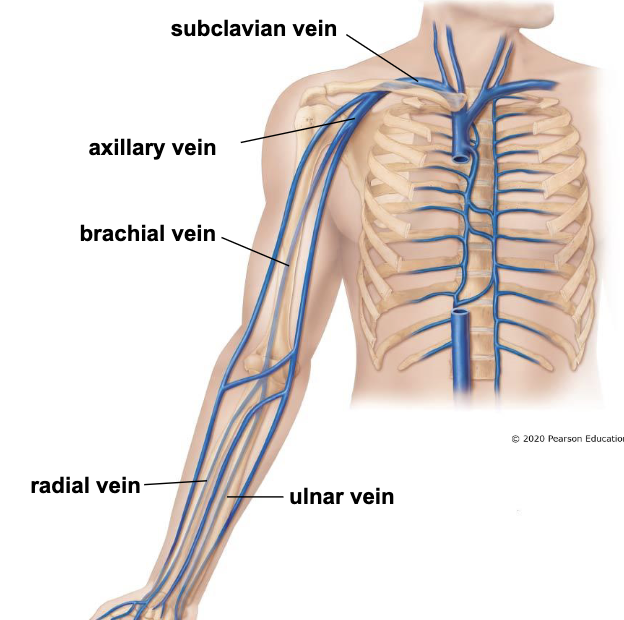
deep veins of upper limb
*run with arteries with the same name
radial & ulnar veins
drain blood from hand and forearm
join near the elbow as the brachial vein
brachial vein
drains blood from arm
becomes axillary vein in the axilla
axillary vein
receives blood from shoulder, lateral thoracic wall, and upper extremity
becomes subclavian vein under clavicle
subclavian vein
joins with internal jugular vein to become the brachiocephalic vein
superficial veins of upper limb
*also called cutaneous veins (in hypodermis)
basilic vein - medial side of arm and forearm, joins axillary vein
cephalic vein - lateral side of arm and forearm, joins subclavian vein
medial cubital vein - connects cephalic and
common site for venipuncture
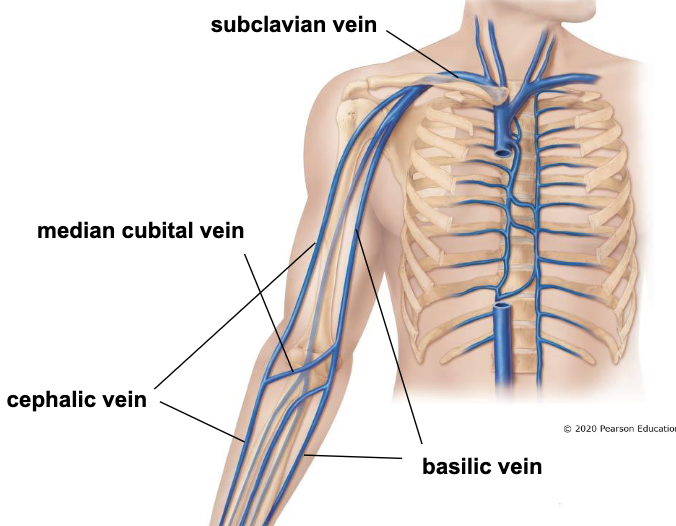
veins of the thorax
posterior intercostal veins drain blood from intercostal spaces
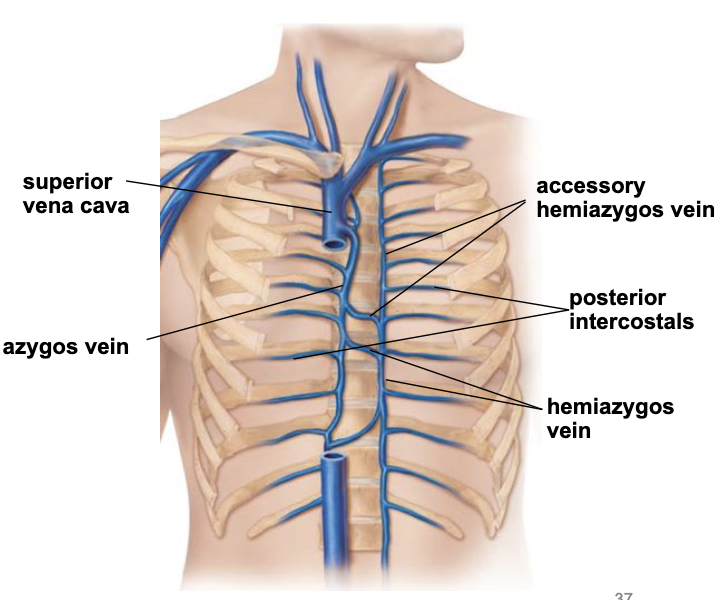
veins of the thorax - right side
azygos vein collects blood from the posterior intercostals
returns blood to the superior vena cava
veins of the thorax - left side
lower left region - hemiazygos vein collects blood from posterior intercostals
upper right region - accessory hemiazygos vein collects blood from posterior intercostals
both return blood to the azygos vein
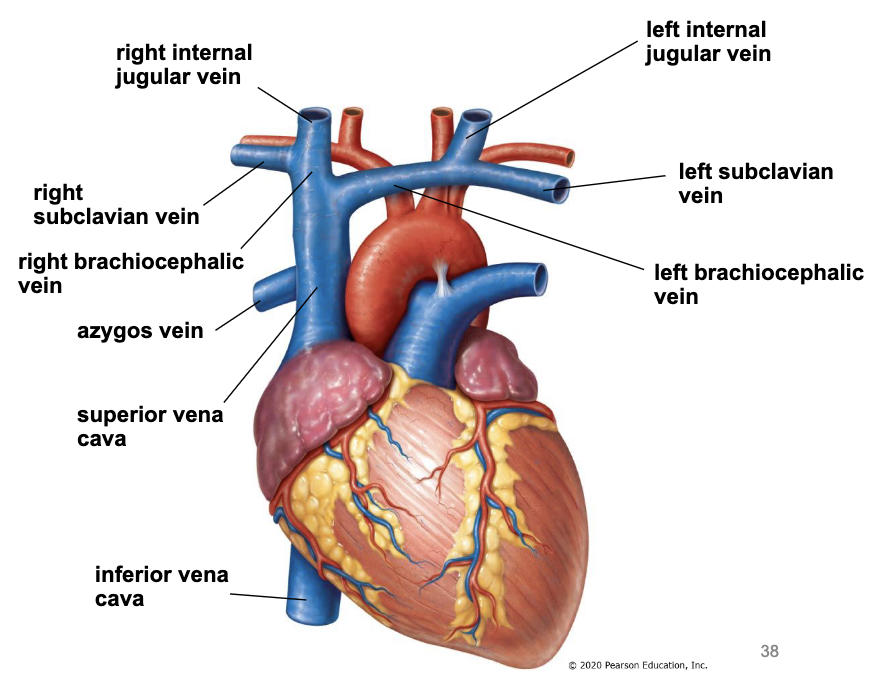
veins to the heart
internal jugular veins & subclavian veins join to form brachiocephalic veins
brachiocephalic veins join to form SVC
azygos vein joins the back of SVC
IVC returns blood from the abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs
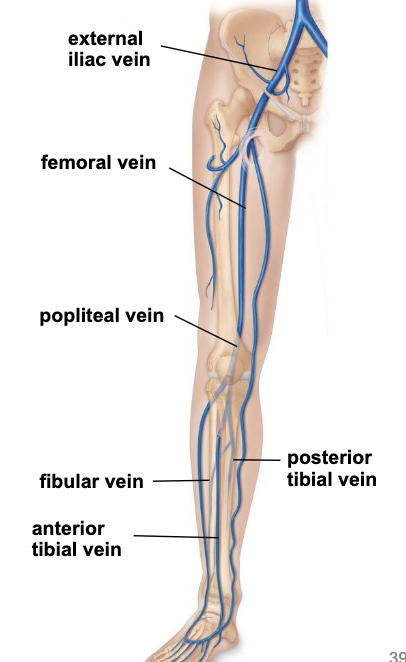
deep veins of lower limb
posterior tibial vein drains blood from the foot and posterior compartment of the leg
anterior tibial vein drains blood from the anterior compartment of the leg and foot
fibular vein drains blood from the lateral compartment of the leg
all 3 veins join to form the popliteal vein behind the knee
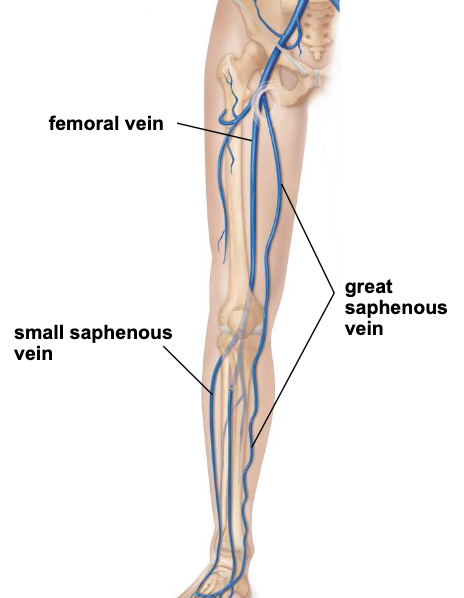
popliteal vein moves around the medial side of the thigh to become the femoral vein that drains the thigh
superficial veins of lower limb
located in the hypodermis
great saphenous vein travels along medial leg and thigh collecting superficial blood of lower extremity
empties into femoral vein in upper thigh
small saphenous vein travels along posterior leg collecting superficial blood from leg
empties into popliteal vein
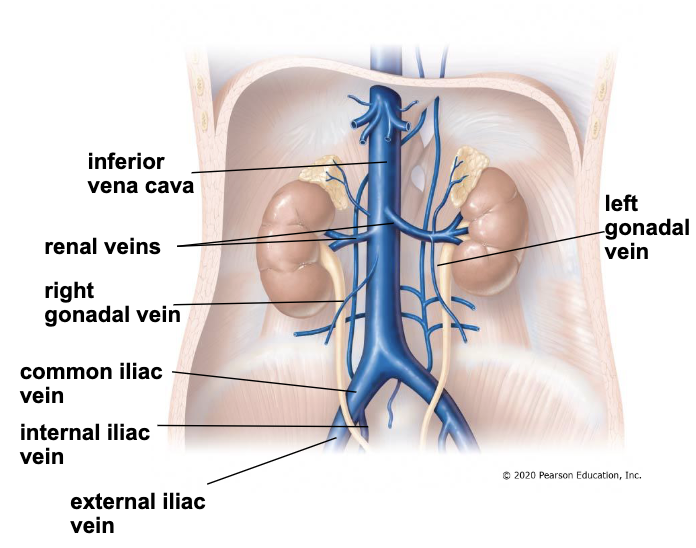
iliac veins
common iliac veins are formed from joining internal and external iliac vein
internal iliac - receives blood from pelvic organs, external genitalia, and gluteal region
external iliac - receives blood from lower extremity, becomes the femoral vein in thigh
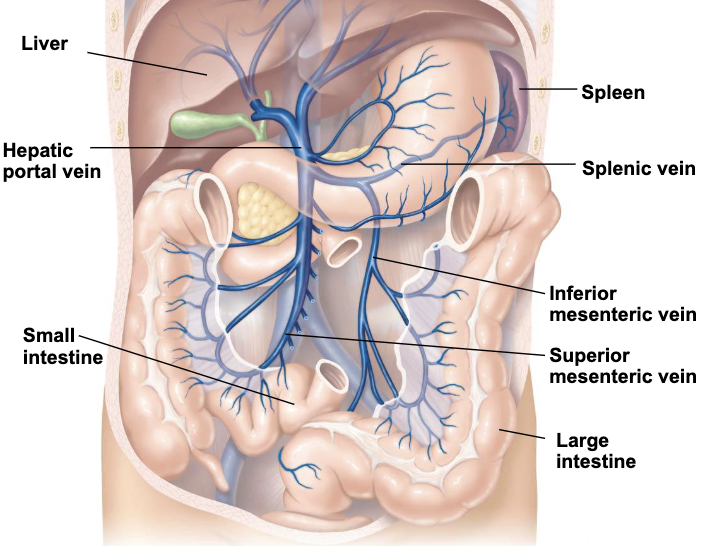
portal vs caval drainage
drainage of venous blood in the abdomen proceeds directly into the inferior vena cava (caval system) or the hepatic portal vein (portal vein)
caval system (IVC)
inferior vena cava receives blood from
renal veins - draining blood from the kidneys
gonadal veins - drain blood from the gonads
common iliac veins
liver
portal system
hepatic portal vein receives blood from the digestive tract and accessory organs to be filtered by liver
nutrients and harmful agents are removed
filtered blood in the liver is sent to the IVC
superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, and splenic veins empty in to the hepatic portal vein