Neuroanatomy (Lec. 3)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
degenerative brain disease associated with repeated hits to the brain
commonly found in athletes of contact sports (e.g. football and boxing)
diagnoised after death
chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) symptoms
memory loss
depression
aggressive behaviour
(sometimes) suicidal thoughts
how CTE occurs
tau (protein) builds up over time in certain patterns
the tau clumps strangle brain cells, diminishing their ability to function
affecting the dorsolateral frontal cortex (responsible for cognition and executive function - working memory, planning & abstract reasoning
dura mater
outermost layer
connected to the skull (outter layer)
covers the gyri in foldings of the brain (inner layer)
white covering aroudn the brain
arachnoid mater
middle spider-like layer
attaches tightly to the inner dural layer
ensuring room for cerebrospinal fluid to flow
what suports the brain & spinal cord
bone (skull verta)
meninges
cerebrospinal fluid (found in the gap between the brain and the skull)
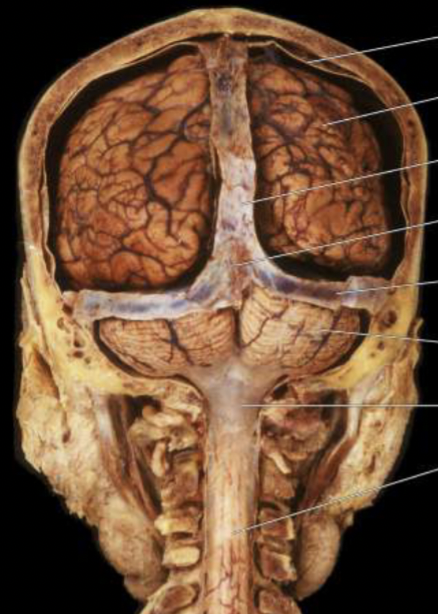
pia mater
innermost layer
adheres tightly to the brain followign gyri and sulci
falx cerebri
cresecent shape (following the lognitudinal fissure)
descends vertically in the longitudinal fissure, separating the 2 CEREBRUM hemispheres
tentorium cerebelli
“tent of the cerebellum”
U-shaped
parallel to the floor
runs between the occipital lobe and the cerebellum
falx cerebelli
a small midline fold that runs in the space between the 2 CEREBELLUM hemispheres
subarachnoid space
located between the arachnoid and pia mater
filled with cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) and major cerebral arteries
anterior fossa
ventral apsect of the frontal lobe
middle fossa
much of the temporal lobe
posterior fossa
brainstem and cerebellum
foramen magnum (aka “great hole”)
oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull
the spinal cord passes through when exiting the cranial cavity
cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)
the fluid that fills the brain’s ventriclar spaces
freuqent bleeding after trauma/cerbral artery rupture
meningiomas
benign tumours arising from the dura mater
meningiomas symptoms
vision changes
headaches
hearing loss
memory loss
loss of smell
laguage difficulty
arms & legs weakness
meningitis
an infection and inflammation of the 2 inner menial layers
major functions of the ventricular system
protects the brain - shock absorber
provides buoyancy - reducing brain weight
provides a medium for the exchange of materials between blood vessels and brian tissue
lateral ventricles
aka 1st and 2nd ventricles
1 is located in each hemisphere
spans all 4 lobes
third ventricle
a narrow midline space between the right and left ventricle diencephalon (thalamus
hypothalamus)
fourth ventricle
betwene the dorsal brainstem adn cerebellum
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricle
septum pellucidum
a thin membrane separting the fontal horns and body of the L and R ventricles
choroid plexus
modified vascular structure lining the ventricles producing CSF by filtering blood
circulation of CSF
lateral ventricles
3rd ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
4th ventricle
subarachnoid space
arachnoid granulations
venous circulation
arachnoid granulations
specialized portions of the arachnoid
protrudes through the inner layer of the dura matter and superior agittal sinus
CSF passes through here and returned to the venous circulation in the superior agittal sinus
hyrdocephalus
when there is an abnormal buildup (in cerebral abduct) of CSF in the ventricles due to an obstruction
can lead to an enlargement of the ventricles —> compression of the brain
commonly found in kids
the brain’s energy consumption
consumes >20% of the ody’s energy at rest
a stroke
sudden loss of brain function caused by a sudden lockage or rupture if a blood brain vessel
stroke symptoms
loss of balance/headache/dizziness
blurred vision
half of face is drooping
1 arm/leg weakness
speech difficulty
how a stroke occurs
blood flow to the brain is blocked/sudden bleeding in the brain
ishchemic strokes
blocked blood vessels
thrombotic: blockage due to fatty plaque build-up on cerebral vessels
embolic: blood clots ofmred somewhere else in the body, traveling through bloodstream to the brain
hermorrhagic strokes
rupruted blood vessel
bleeding within/around the brain
transient ischemic attack (TIA)
warning stroke signs (temporary blockage)
blood supply of the brain and spinal cord from aorta
internal carotid
verteral arteries
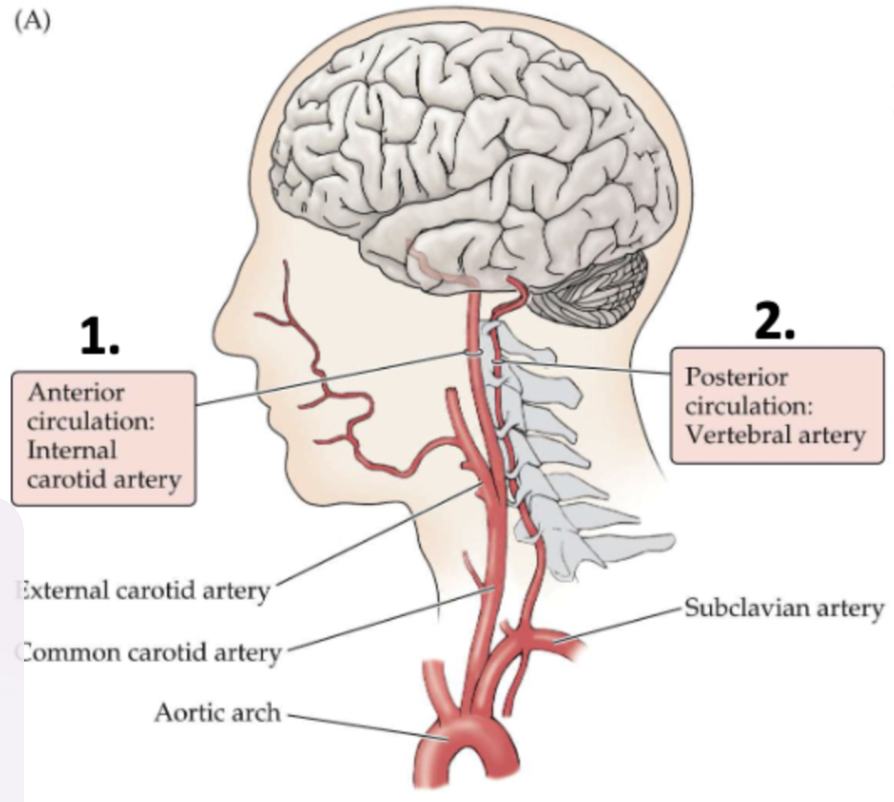
carotid arteries
ascend up the L and R sides of the neck
branch into the external and internal carotid arteries
vertebral arteries
ascend up eahc side of the cervical vertebrae
fuse together within the skull to form the basilar artery
anterior circulation
supplies the forebrain (cerebral hemispheres and diencephalon)
posterior ciurcualtion
supplies the brainstem, cerebellum, and upper portion of the spinal cord
also supplies to the brainstem, cerebellum, and upper portion of the spinal cord
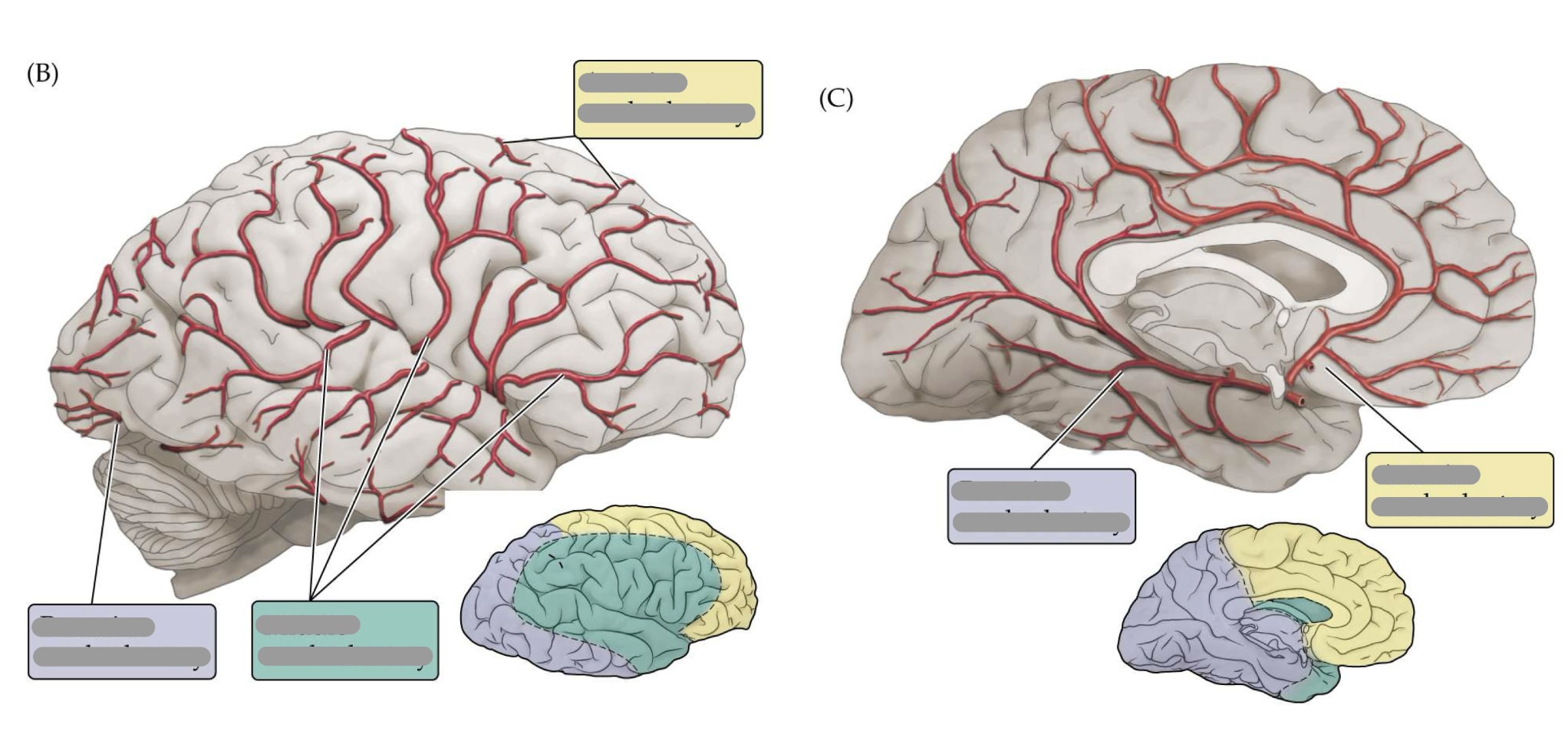
they supply 2nd/3rds of the cerebrum (arteries)
the interanl arteries branch to form the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and middle cerrebral artery (MCA)
anterior cerebral arteries
travel anterior (forward) from the internal carotid artery
towards the medial longitudinal fissure
middle cerebral arteries
travel out laterally from the internal carotid artery towards the lateral (sylvian) fissure
what do anterior cerebral arteries supply?
supplies regions in the medial aspect and dorsal margins of the frontal lobe
what do middle cerebral arteries supply?
supplies extensive region of the central and lateral cerebral hemispheres
sensorimotor
language
posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
supply regions in the posterior partietal, inferior temporal, and occipital lobe
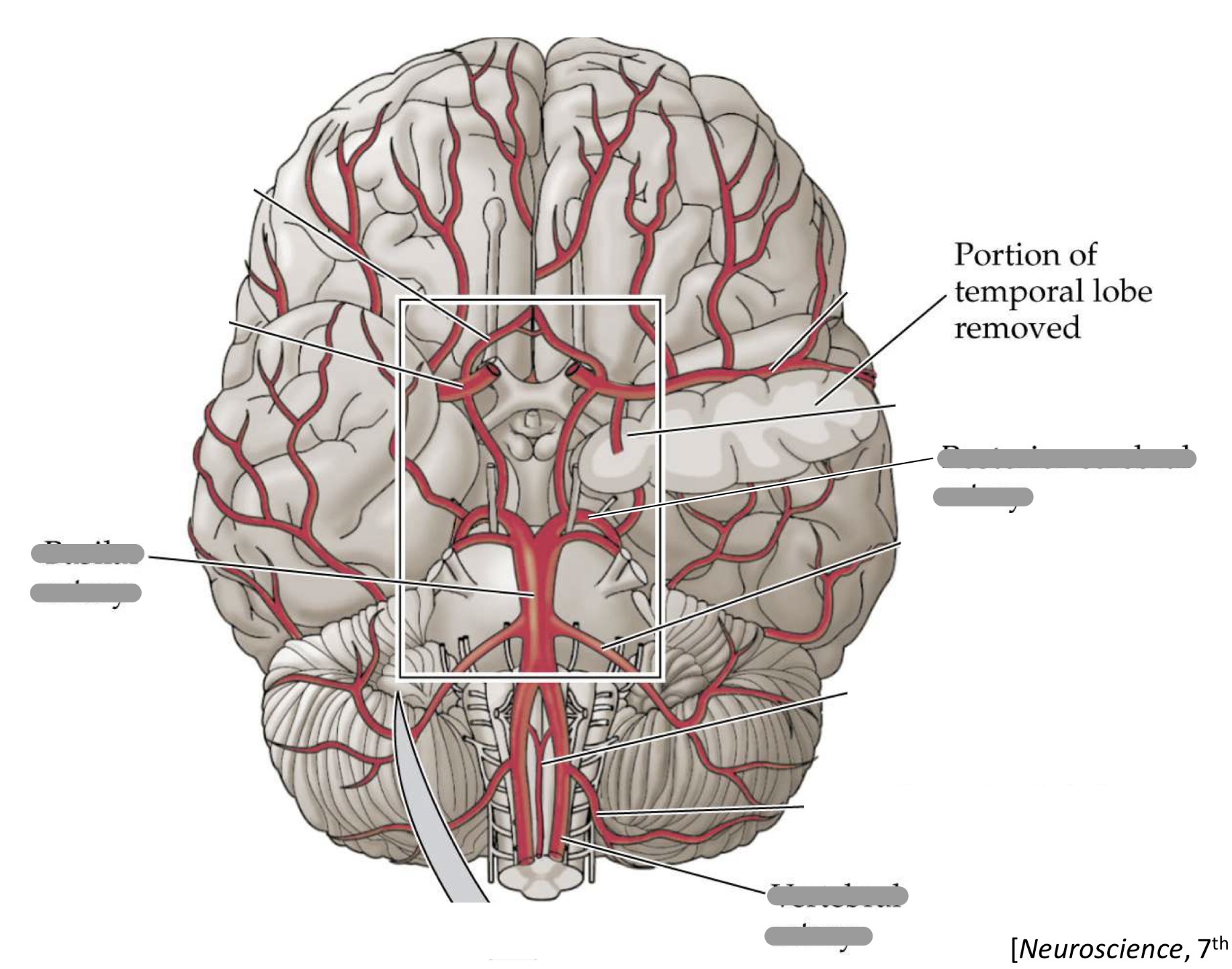
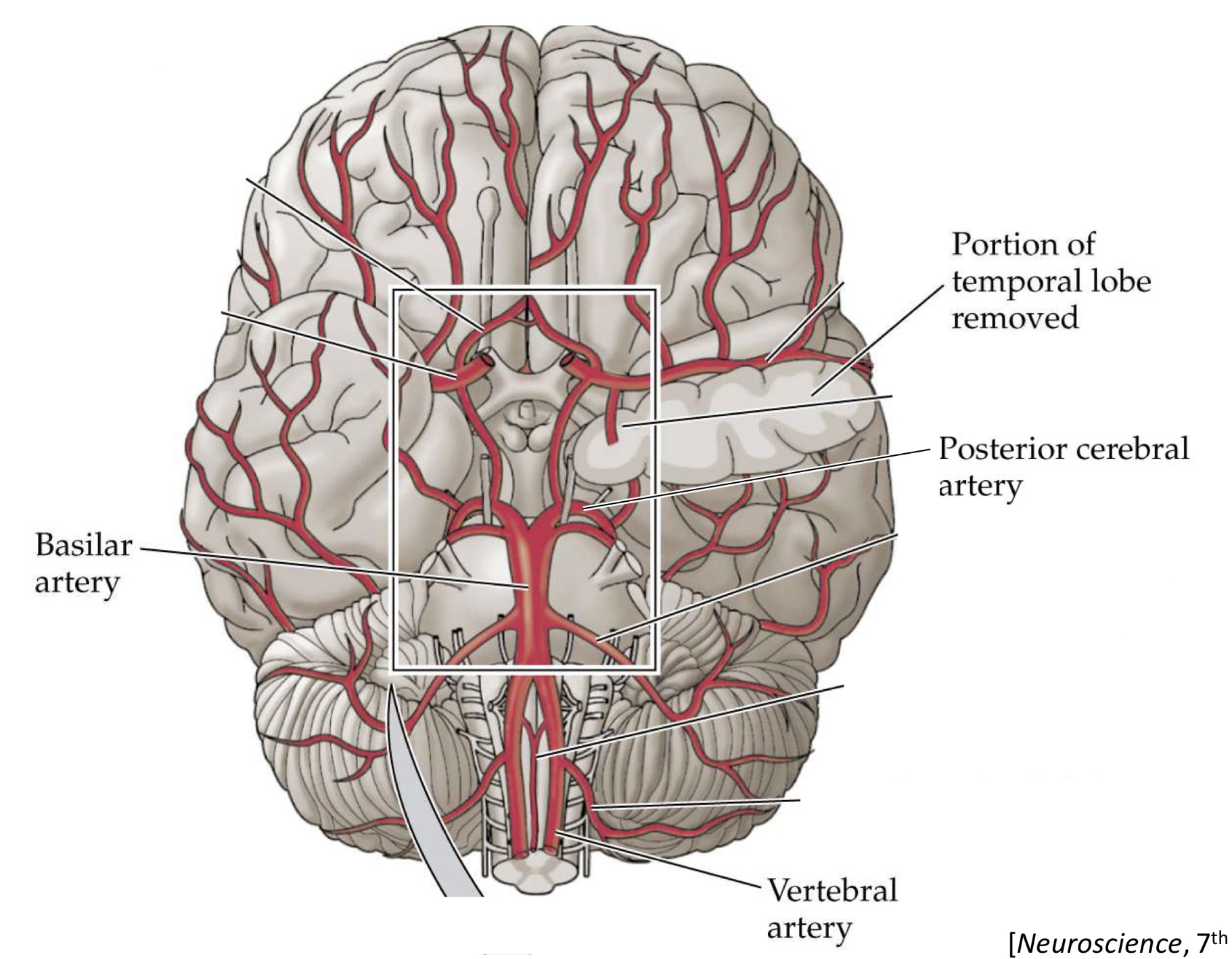
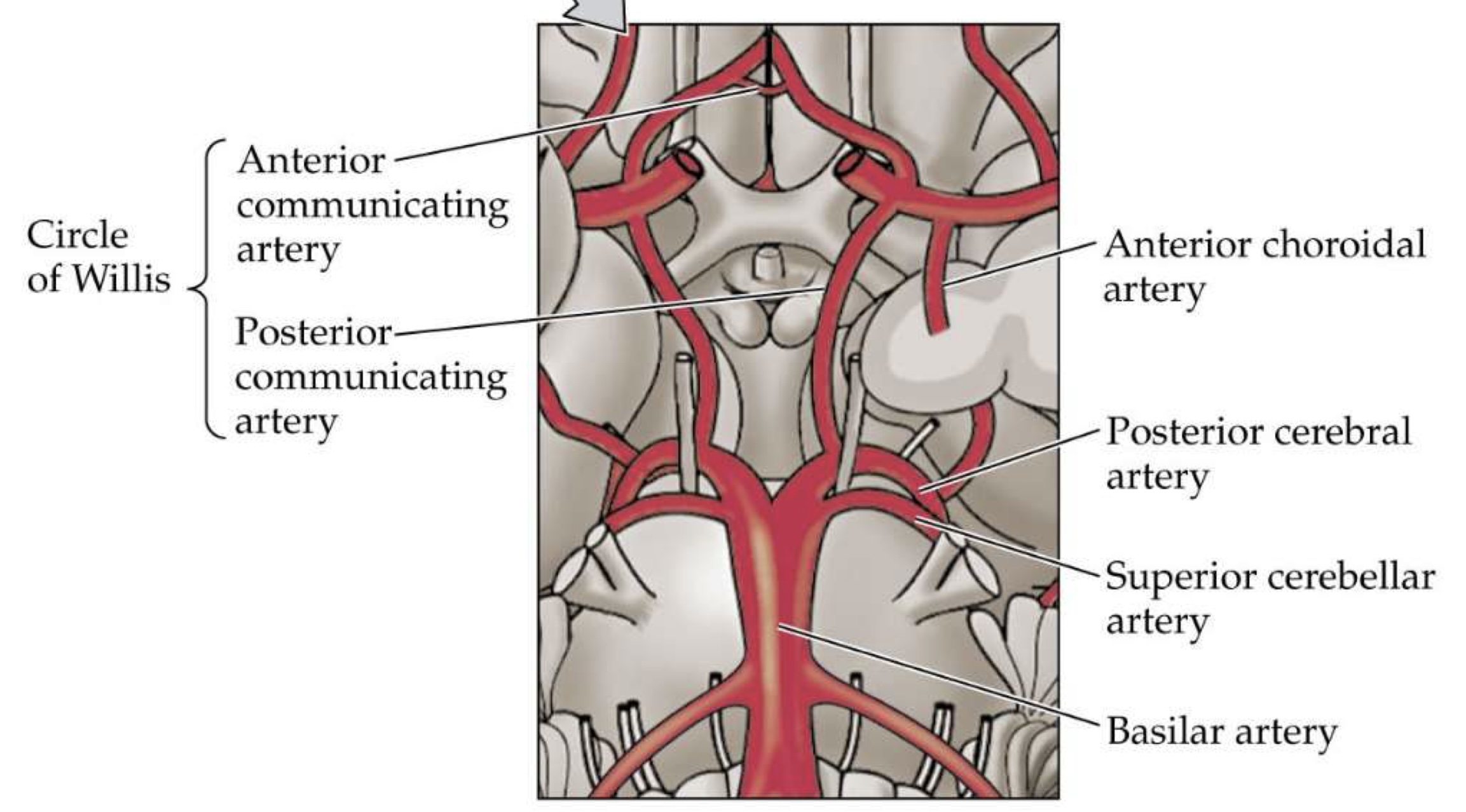
what arteries form the circle of willis?
posterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating artery
internal carotid artery
anterior cerebral artery
anterior communicating artery
where is the circle of willis located?
at the base of the brain
what is found within the center of the circle of willis?
the optic chaism
lenticulostriate arteries
deep-penetrating branches of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) that supplies MOST of the basal ganglia
small diameter & sharp R angle —> easy for rupture/occlusion —> stroke symptoms
posterior cerebral arteries
supplies posterior hypothalamus, most of thalamus
why lenticulostriate arteries are referred to as “end arteries”
the regions they supply do not have significant alternative supply to rely on
the artery from the vertebral supply that goes to the cerebral hemispheres
posterior cerebral artery
+ also supplies midbrain of the brainstem
the artery that can also supply medial regions of midbrain and pons
basilar artery
the arteries caudal to the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) that supply regions of the brainstem on their way to supplying blood to the cerebellum
superior cerebellar artery (SCA): midbrain + cerebellum
anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA): pons + cerebellum
posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA): medulla + cerebellum4
what spaces are considered “potential spaces”
subdural space & epidural space
hemorrhage
occurs when an artery in the brain ursts and causes localized bleeding
epidural hemorrhage
blood between the skull and dura mater due to injury
epi = above —> “above the dura”
subdural hemorrhage
blood between the dura mater and arachnoid mater
sub = below —> “below the dura”
subarachnoid hemorrhage
blood within the subarachnoid space and pia mater
due to brain aneurysm
intracerebral hemorrhage
leeding with the brain tissue itself
a series of dural ____ return blood from the brain back to the heart via internal juglar veins
venous sinuses
superior sagittal sinus
runs along the dorsal midline of the hemispheres & drains into the confluence of sinuses
transverse sinus
oriented on horizontal plane
extending laterally from the confluence sinuses
traveling briefly anterior before turning to sigmoid sinuses
list of dural venous sinuses
superior sagittal sinus
inferior sagittal sinus
straight sinus
confluence sinuses
transverse sinus
sigmoid sinuses
cavernous sinus
confluence of sinuses
found at the posterior end of the longitudinal fissure & drains into the L and R transverse sinus
purpose of venous sinuses
to drain blood and CSF from the brain
the blood-brain barrier (BBB)
makes the movement of substances from blood vessels into brain cells difficult
provides protection and homeostasis in the brain
can only cross the blood-brain barrier if
soluble in lipids
special transporters
what the blood brain-barrier allow through it to maintain homeostasis
oxygen
glucose
other critical molecules
glymphatic system
a lymphatic system in the brain to remove wastes and aid movement of nutrients
glymphatic system draining process
CSF flows from subarachnoid space to periarterial space
CSF enters brain tissue via specialized chanels
CSF drains into perivascular space - joining the cirulatory system