ERT II Unit 3: Medication Administration
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Info on drug label
Brade/Trade name
Generic name
Strength
Total amount or volume in container
Form of drug
Manufacturer
Directions/storage
Expiration date
Lot #
National Drug Code (NDC)
Brand/Trade name
Name used by manufacturer of drug
Capitalized & sometimes bold
Name followed by ® symbol indicating copyright
Generic name
Name used by all manufacturers who market that drug
Lower case, smaller font, below brand name
Strength
Amount of drug contained in identified unit
Ex: mg/mL, units/mL, mg/tab
Directions/storage
Directions: “See package insert”
Storage: is drug heat or light sensitive? does it need to be refrigerated?
Lot #
Identifies drug by batch
Needed if recalled
Required documentation with vaccines
National Drug Code (NDC)
10-digit number that identifies each drug (starts with NDC)
Required by federal law
Decimals
Tenths (0.1)
Hundredths (0.01)
Thousandths (0.001)
Solid medication
If tablet is scored for easy divisionin halves, you can round to the nearest ½ tablet
Ex: 0.4 tab rounded to 0.5 (1/2) tablet
Never give partial dose unless tablet is scored

Liquid medication
Usually rounded to the nearest tenth
Syringes are calibrated in tenths and/or hundredths
Ex: 1.76 mL rounds to 1.8 mL
Systems of measurement
Metric system (medical setting)
Household system (usually home setting)
Systems measure 3 things
Weight: mass or heaviness
Volume: amount of space occupied
Length: linear distance from one point to another
Metric system
Decimal system
Based on multiples of 10
Basic units of measurement
Weight (grams)
Volume (liters)
Length (meters)
Prefixes
Micro-: 1/1,000,000 (0.000001)
One-millionth
Milli-: 1/1,000 (0.001)
One-thousandth
Centi-: 1/100 (0.01)
One-hundredth
kilo-: 1,000 (1000)
Common uses of metric measurements
mL: often used to give liquid medication orally or by injection
mg: is often used to give medications such as tablets, powder, or topical preparations
cm: is often used to measure a wound, head or chest circumference of an infant, diameter of swollen limb, etc.
kg: often used to measure infant wieght or to calculate pediatric medication dosage
Household measurements
Least accurate
Basic units of measurement
Drop/drops (gtt/gtts), teaspoon (t, tsp), tablespoon (T, tbsp, tbs)
ounce (oz), pound (lb)
quart (qt), pint (pt)
cup (c )
Mostly used for patient use at home to measure medication (drop, tsp, tbsp)
May be used in healthcare to measure weight (pounds) & hight (ft & in), eye drops, or ear drops
Conversions
Changing from one unit of measurement to another
Includes:
Converting units within the same measurement system
Converting units from one measurement system to another
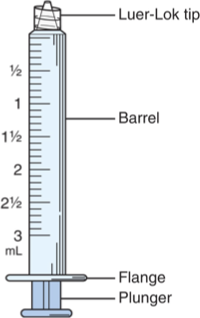
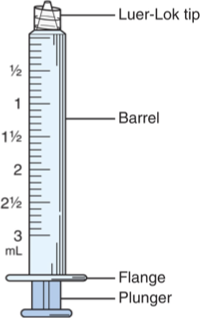
Syringe
Plastic disposable part containing medication
May have safety device
Separate or combined with needle
Type used depends on type of injection and amount of medication being administered
Parts
Barrel: holds meds, calibrated in cc/mL or units
Flange: rim that stabilizes syringe during injection
Plunger: drawns meds, pushes meds
Types
Hypodermic: calibrated in tenths (0.10) of cc/mL, administer IM injections, 1-3 cc/mL capacity
Insulin: calibrated in units (U), used to administer insulin, U-50 or U-100 capacity
Tuberculin: calibrated in tenths (0.10) and hundredths (0.01) of cc/mL, used to administer small dosages or PPD, 1 cc/mL capacity
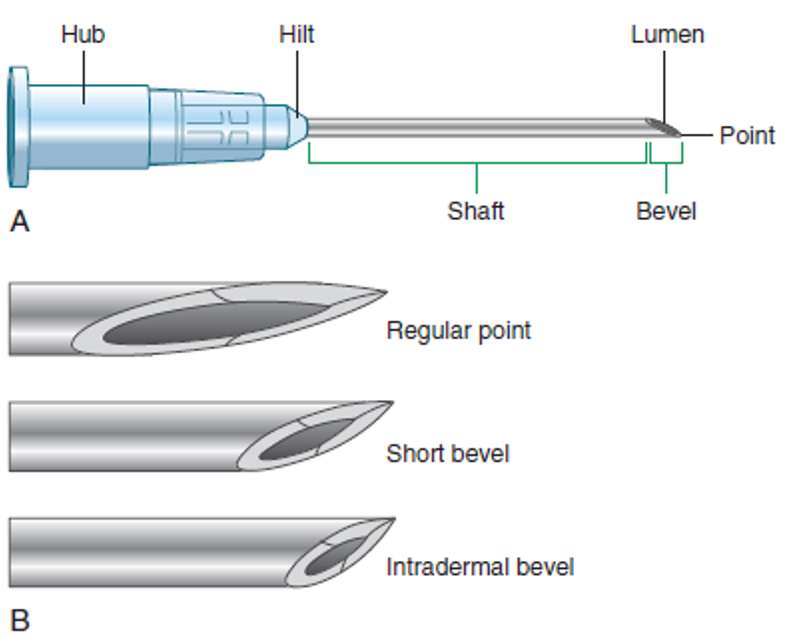
Parts of a Needle
Hub
Connects needle to syringe (Leur-Lok)
Shaft
Inserted into tissue
Measured in inches (3/8-3 inches)
Length varies by type of injection, site, and size of pt
Tip is tapered/slanted (bevel)
Lumen
Hollow shaft medication flows through
Measured in “gauge”: diameter (width) of lumen
As gauge number increases, diameter decreases
Solid drugs
Tablet: solid formed by compressed powdered medication; may be coated, various sizes & shapes
May be chewable or scored for easy splitting
Caplet: coated, oval tablet
Capsule: medication contained in gelatin shell
Enteric coated (protects stomach, dissolves in small intestine rather than stomach), sustained-release SR or extended-release ER or XL (gradual, continuous release)
Lozenge: disk, possible sweetened, contained medication
Semi-solid drugs
Cream: medication in non-greasy base
Ointment: medication in greasy base
Suppository: medication in oil base like cocoa butter, solid at room temp, but dissolves at body temp; instilled into rectum
Liquid drugs
Swallowed, rubbed into skin, or instilled in ears/eyes/nose
Elixir: medication particle dissolved in liquid containing alcohol
Syrup: medication particles dissolved in sugar and water
Suspension: medication particles suspended in liquid; shake before administration
Aerosol: medication suspended in a gas
Lotions
Sprays
Route of administration
Depends on drug, dosage, intended action, response time desired
Oral: mouth
Sublingual (SL): dissolves under tongue; rapid absorption
Buccal: between gum and cheek; rapid absorption
Inhalation: lungs; medication reaches alveoli where it is absorbed; Ex: MDIs and nebulizer medications
Topical: medication applied to skin; local effect; aerosols held 3-6 inches form skin; apply to wounds with sterile swab
Transdermal: medication applied to skin and absorbed into bloodstream; systemic effect; may use patch to deliver medication; write name and date when patch applied; wear gloves
Nasal/intranasal: medication breathed in through nose and absorbed in nasal mucosa; blow nose first; sitting position
Ocular: instilled by liquid drop or ointment into eye; labeled ophthalmic; do not touch eye with applicator tip
Otic: instilled into ear; treat infection, reduce pain, or soften cerumen
Rectal: rectum; suppositories; medication absorbed slowly through rectal mucosa; used when pt cannot tolerate oral meds; need water-soluble gel (K-Jelly) to ease insertion; use gloved, lubricated ringer to insert 3-4 inches in adults; use little finger to insert in small children 2 inches
Vaginal: vagina; local effects; suppositories inserted 3-4 inches with finger; creams, ointments, or foams usually come with applicator; most used at hs when pt is lying flat
Parenteral: outside GI tract; injection
Intradermal (ID): dermis
Subcutaneous (Subcut): hypodermis/fat
Intramuscular (IM): muscle
Intravenous (IV): vein
Rights of drug administration
Right patient
State name and verify DOB
Right drug
Verify three time (when retrieving from storage, when preparing, before administration)
Never administer drug prepared by another person
Right route
Right time (ex: q2h, TID, @hs)
Right dose
Check label for concentration and compare with provider’s orders
Is dosage appropriate range?
Right documantation
Right to be educated
Explain drug that will be given, verify allergies, discuss possible side effects
Right to refuse
Patient has legal right to refuse but must be informed of consequences of refusal…document!
Oral administration
Medication is given by mouth in solid or liquid form
After swallowing, absorption occurs mainly in small intestine (route that takes the longest time to absorb)
Use medical asepsis to administer
Most convenient, most common route
Should not be used if difficulty swallowing or absorption problems
Oral meds that coat throat should not be followed immediately with water
Many meds should be swallowed with glass of water, not sip
Straw should be used with meds that could stain teeth (tetracycline)
Liquid meds should be measured with plastic med cup or med syringe
Prescribed dose is gently tapped into lid of med container
Dose is then placed in med cup
Parenteral administration
Injectable meds in sterile, liquid form
After injection, med is absorbed into bloodstream
Absorption is more rapid than oral route
Includes:
Intradermal
IM
Subcut
IV
Use sterile technique to administer (invasive)
Prep of parenteral meds
Available in various dispensing units
Ampules
Vials
Prefilled syringes/cartridges
Ampule
Small sealed glass container containing single dose of med
Prep
Verify order
Perform calculations if necessary
Assemble equipment and sanitize hands
Compare order with label on vial
Check expiration date
Tap narrow top of ampule to settle med to bottom of ampule
Disinfect neck of ampule with alcohol wipe
Place ampule breaker or gauze over top of ampule
Hold covered ampule between thumb and fingers
Break at neck, away from you, using one quick motion
Place broken top in sharps container
Using a filter needle, withdraw ordered dose of med
Discard ampule in sharps
Remove filter needle and place in sharps
Place appropriate needle for administration on syringe and recap
Vial
Closed container with rubber stopper
Single or multi-dose
Prep
Roll vial between hands if requires mixing
Inject equal amount of air into vial to prevent a vacuum from forming in vial
When withdrawing, keep needle below fluid level to prevent entrance of air bubbles into syringe
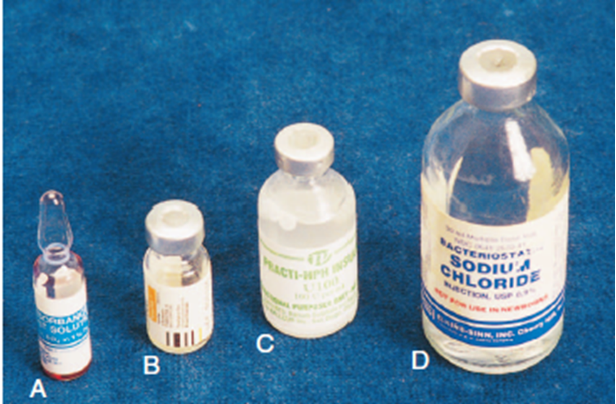
Prefilled disposable syringes or cartridges
Used with reusable Tubex injector
Drug info printed on cartridge
Reconstitution of powdered drugs
Adding liquid (usually normal saline-NS or sterile water) to a powdered drug
Prolongs shelf-life
Prep
Read label to determine correct amount of diluent to add to create dose ordered by provider
Disinfect top of each vial with alcohol wipe
Draw up correct amount of air to inject into diluent
Insert needle into center of rubber stopper and inject air
Invert diluent vial and withdraw correct amount of diluent
Remove needle from diluent
Inject needle into center of rubber stopper of drug vial and inject diluent
Remove needle from vial and discard into sharps
Roll vial between palms to mix thoroughly
Place air into new syringe equal to amount of med to be administered
Inject air into vial, invert vial, and withdraw ordered amount of med
Mark with reconstitution date if multi-dose vial
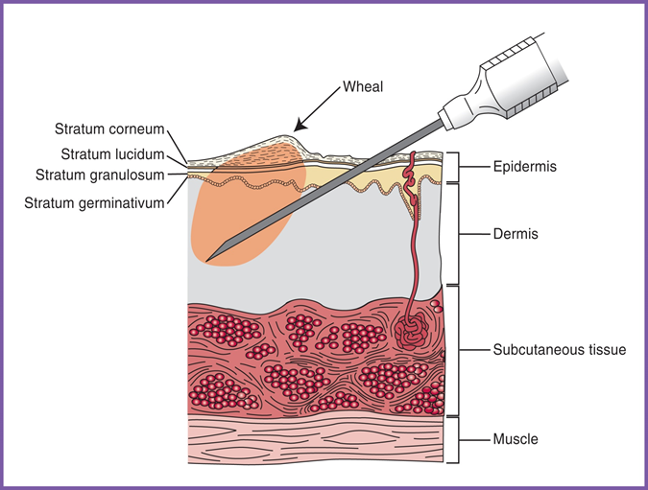
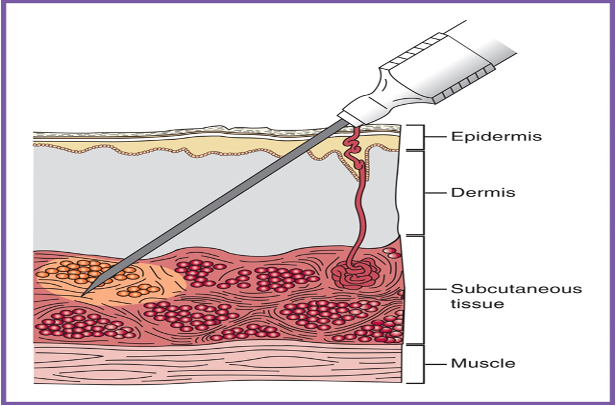
Intradermal injection (ID)
Given just under the epidermis
Almost parallel angle (10-15º)
Small amount of med only (0.01-0.1 mL)
Nerves exist here, so may cause burning sensation when med is dispersed
Common ID injections include
Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST)
Intradermal flu vaccine (Fluzone)
Allergy testing
Tuberculosis (TB) ID injection
TB is an infectious, bacterial disease caused by tubercle bacillus
Usually affects lungs
S&S: fatigue, weight loss, fever, night sweats, productive cough, chest pain
Latent TB
No active disease, no s/s, not contagious, but TB test will be positive
Latent TB can become active TB when immune system is weakened
Will need tx antibiotics (INH) six months to one year
Why do we do screening? To identify pts who:
are infected with TB
might develop TB
would benefit from treatment of latent TB
Two types of tests have been approved by FDA to screen tuberculosis
Skin test (TST)
Blood test called QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube test (GFT-GIT)
T-SPOT TB Test (T-Spot)
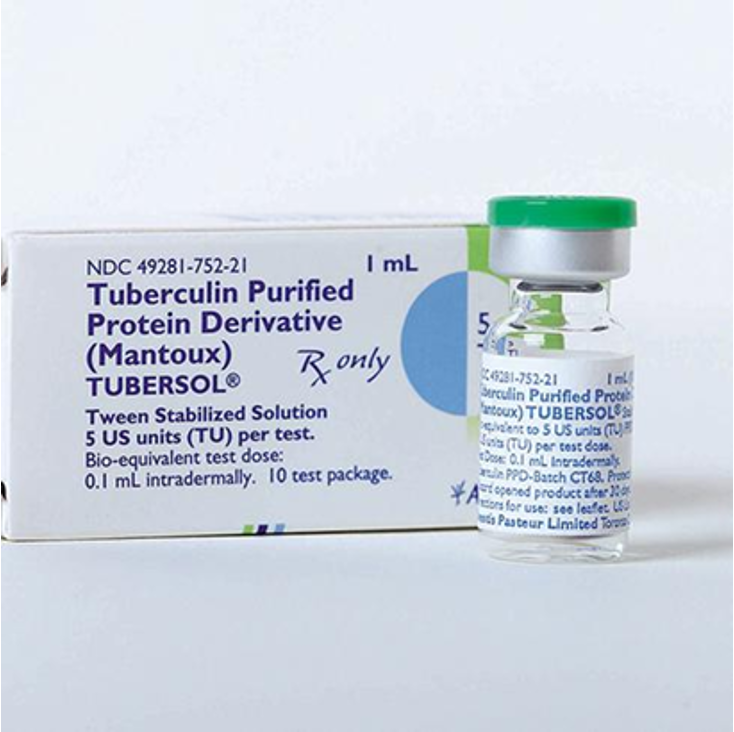
TST (TB skin test)
MA responsibilities
Administer TST
Read results
Can be given to
Pts with prior BCG vaccination (notify provider, may want blood test instead)
Pts with mild illness
Female pts who are pregnant or breastfeeding
Pts immunized with any vaccine ON THE SAME DAY as TST
Pts immunized with inactivated vaccines
Contraindications
Prior, documented positive TST
Prior, severe reaction/allergy to TST
Prior, documented treatment for active TB
Pts under 6 months who have received vaccination with live virus such as MMR vaccine within past month (can interfere with cell mediated response to PPD)
Procedure
Screen: can pt have TST?
Use 1 mL syringe with 1/4-5/8 inch, 25-27-gauge needle
Draw up 0.1 mL of PPD (purified protein derivative of tuberculin) from vial (Tubersol 5 TU/0.1 mL)
Have pt extend forearm, palm up
Identify site on mid-anterior forearm (2-4 inches below elbow)
Disinfect skin at site with alcohol and allow to dry
Remove cover from syringe/needle and hold it with dominant hand using thumb and index finger
Ensure that bevel is pointing upward
Hold skin taught at site with non-dominant hand
At 5-15º angle (almost parallel to skin), slowly insert needle until bevel is covered with skin
Lower needle to be parallel with skin and anchor it in place with dominant hand
Move non-dominant hand to slowly inject all of PPD (0.1 mL) until 6-10 mm wheal is created
No wheal, withdraw needle & administer new injection in new location
Withdraw needle and activate safety device using one hand
Discard syringe/needle into sharps
Document (include lot # and exp date)
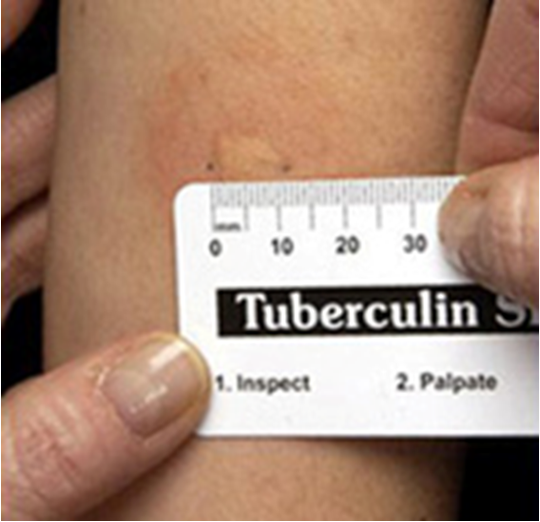
Reading results
Use inspection & palpation to read results
Results are read 48-72 hours after administration
Use mm ruler to read at diameter horizontally (induration only, redness is not significant)
If person was infected with TB, immune system has developed antibodies that will react to injection by causing swelling (induration)
Will cause induration in person with latent or active TB (does not differentiate between two types)
Induration ≥ 15 mm in patient with no known risk factors is considered positive
Induration of ≥ 5-15 mm in patient with certain risk factors is considered positive
Positive TB is followed with chest x-ray
TST (two step-TB)
Who needs two-step TST?
Residents in long-term care facilities
Healthcare providers
First TST
May be negative if immune system did not immediately identify bacteria
False-negative
Second TST
Done 1-3 weeks after first test was read
Helps trigger immune response to identify those people who have been previously exposed to TB
Booster effect/booster phenomenon
ID flu vaccine
Only ID vaccine
Fluzone contains less antigen than IM flu vaccines
Approved for adults 18-64 years
Administered in deltoid area, but not into muscle
Comes in pre-filled syringe
Insert at 90-degree angle
Subcutaneous injection (Subcut)
Subcut injection is given into adipose (fat) tissue (under epidermis & dermis)
SC, SQ, subQ no longer recommended as abbreviations
Medication is absorbed into capillaries (slower than into muscle) which is beneficial when slow, continuous absorption is needed
Nerves exist here, so may cause discomfort when medication is dispersed
Amount of medication (0.5-1.5 mL); 0.5 mL in children
Common subcut injections include:
Some vaccines (MMR)
Many drugs that must be taken daily, or injected at home, are designed for subcutaneous injection
Examples
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Heparin
Insulin (measured in units)
Allergy injections (NOT TESTING)
Some fertility drugs
Epinephrine
Drugs such as Enbrel for autoimmune diseases
Drugs such as Ozempic for DM
Angle of insertion
Depends upon length of needle
Inserted at 45-degree angle if using 5/8 inch needle
Inserted at 90-degree angle is using ½ inch needle
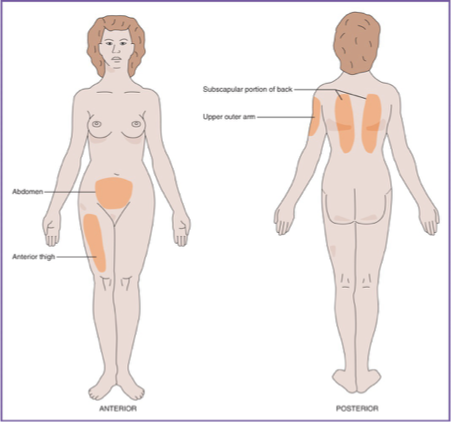
Sites
Upper, lateral-posterior arm for most adults (not into deltoid muscle)
Hand width above elbow, 3 fingers below acromion process
Anterior thigh
One hand above knee, one hand width below greater trochanter
Most often used for infants less than one year or when pt needs to self-administer
Upper back
Abdomen
Two inches away from/around umbilicus
Most often used when pt needs to self-administer (ex: insulin)
Injection
Use 1-3 mL syringe, 5/8 or ½ needle, approx. 25 gauge
Identify site
Disinfect skin at site with alcohol and allow to dry
Remove cover from syringe/needle and hold it with dominant hand using thumb, index finger, and middle finger
Grasp and pinch up tissue with non-dominant hand (lift subcutaneous layer away from underlying muscle)
Insert entire needle at 45- or 90-degree angle, depending on needle length
Using one-handed or two-handed technique, inject medication slowly using plunger
Follow facility/provider recommendation for aspiration (no aspiration for pediatric vaccines, insulin, or heparin)
Release skin
Withdraw needle in same path it entered
Activate safety device with one hand
Discard syringe/needle into sharps (needle first)
Apply gentle pressure to injection site (do not rub)
Monitor pt for adverse reactions
Document
Site rotation
Used for multiple or frequent injections
Easiest to give subsequent injections in circular pattern
One inch apart
Reduces risk of abscesses for pts who require frequent injections
Subcut: Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Enoxaparin is an anticoagulant that helps prevent blood clots (may teach pts how to self administer at home)
When administering subcut enoxaparin, follow these guidelines
Drug should be clear and colorless to pale yellow
Do not push air out of syringe unless you are instructed to do so
Using finger and thumb, pinch skin 1-2 inches away form umbilicus
Push entire needle into skin and inject med while still holding pinched skin
Remove needle
Do not rub or massage
Subcut: Mixing insulin
Insulin is prescribed to type I diabetics, and sometime type II diabetics that require treatment beyond oral hypoglycemic meds
Must be injected (destroyed by stomach)
Comes dissolved or suspended in liquid
Ordered in units
Diabetics sometimes have to take two types of insulin at the same time
Two types can come already combined in premixed solution
Two types may need to be correctly mixed in the same syringe
Make sure syringe chosen is greter than total dosage required (30, 50, or 100 unit syringe?)
Air into cloudy, air into clear…withdraw clear, withdraw cloudy
Intramuscular injection (IM)
Injection into muscle tissue
More rapid absorption than subcutaneous
Used when administering drugs that would irritate or damage subcutaneous tissue
Larger gauge needle used for oil-based medication
Needle length 1-3 inches (1-1 ½ average adult)
Gauge varies with viscosity of med
90-degree angle of insertion always!
3 mL syringe
Inject with moderate speed
Apple pressure, do not massage
Skin is flattened over site with non-dominant hand
Used for: most immunizations, antibiotics, contraceptives (Depo-Provera), vitamin B12, corticosteroids
Aspiration
Air lock technique
Aspiration
Air lock technique
IM injection procedure