Visceral Anatomy - Pelvis and Perineum
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
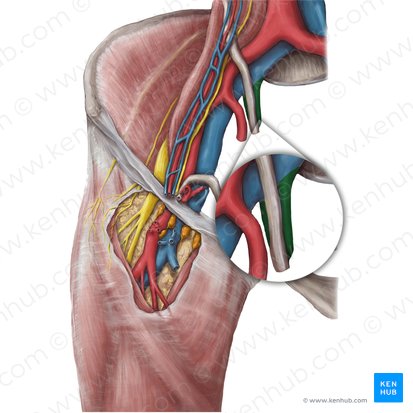
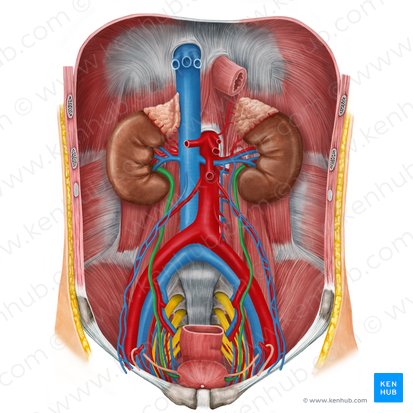
internal iliac artery
courses inferiorly into the pelvic cavity posterior to the ureter and anterior to the internal iliac vein
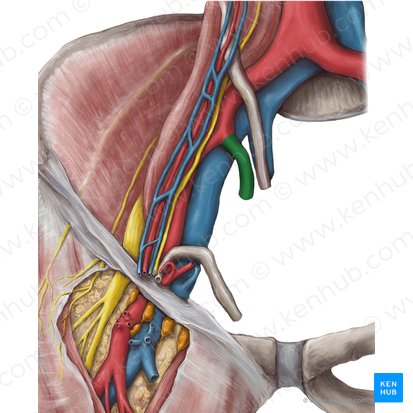
superior gluteal artery
inferior gluteal artery
Name the 2 important branches of internal iliac artery
common iliac artery
Internal iliac artery is a branch of which artery?
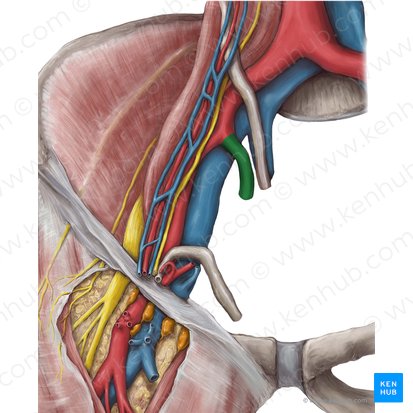
superior gluteal artery
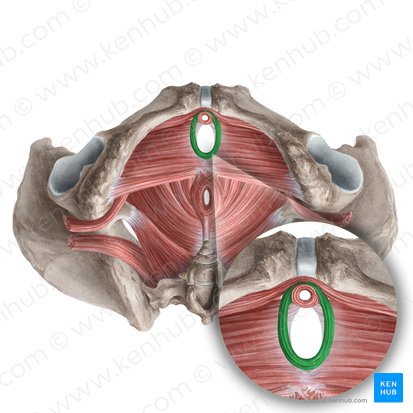
exits from pelvic cavity into gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen, specifically the suprapiriform foramen
inferior gluteal artery
exits from the pelvic cavity into the gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen, specifically the infrapiriform foramen
greater sciatic foramen
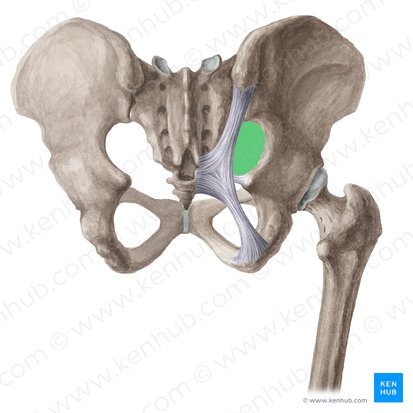
internal iliac vein
lies between the lateral pelvic wall and the internal iliac artery
joins the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein
medial cluneal nerves DPR S1-S3
DPR S4-S5 and coccygeal nerves
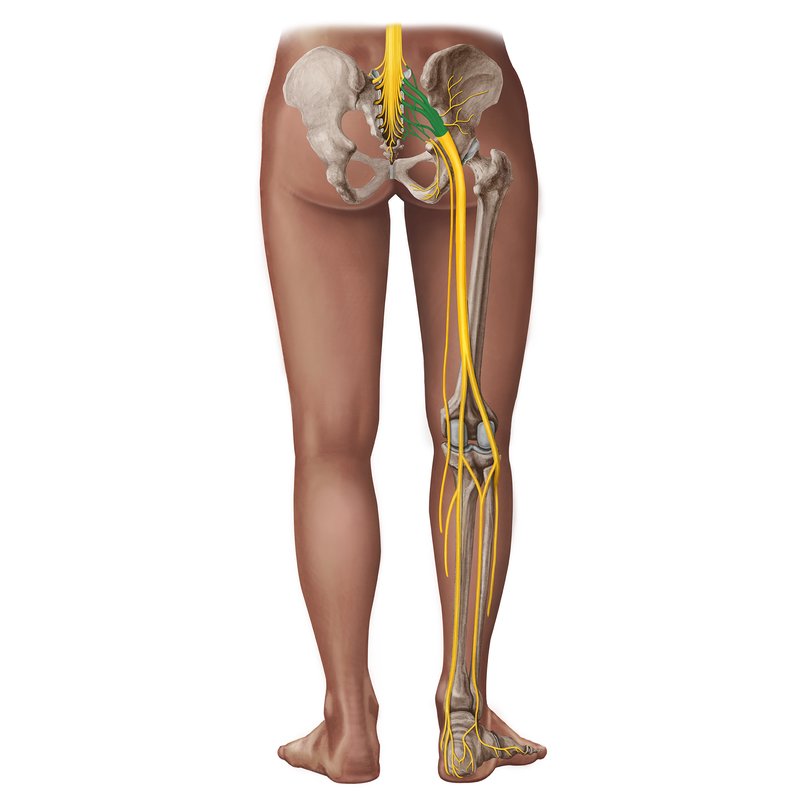
sacral plexus
takes form on the posterior wall of the pelvis
formed by the lumbosacral trunk (L4, L5) and VPR of S1-S3 and descending part of S4
located on anterior aspect of piriformis muscle and covered with fascia of piriformis
course inferolaterally into gluteal region through the greater sciatic foramen, specifically the suprapiriform foramen
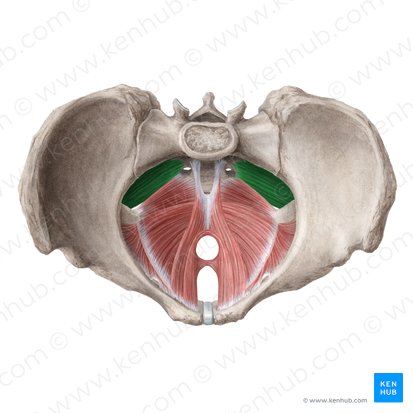
piriformis
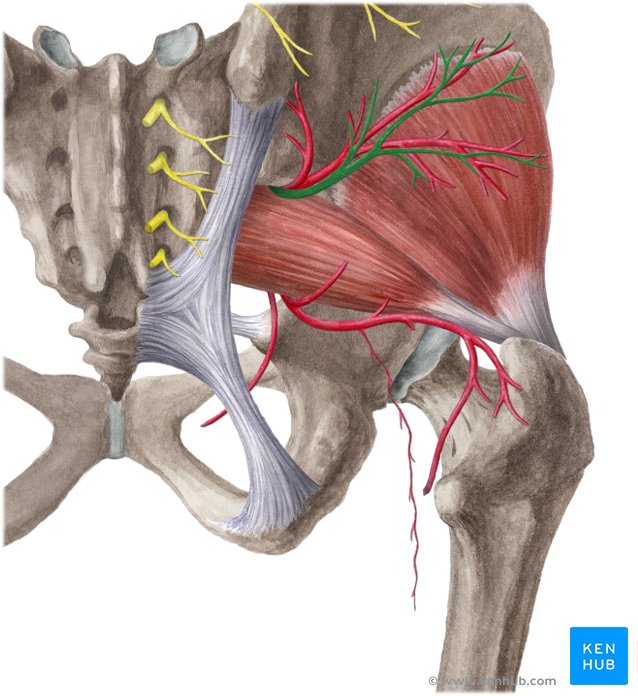
superior gluteal nerve
passes through the greater sciatic foramen superior to the piriformis muscle
motor
Is superior gluteal nerve sensory, motor, or mixed?
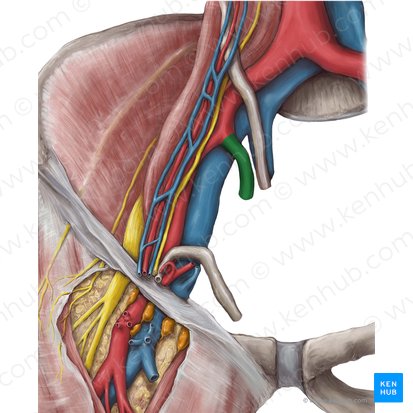
inferior gluteal nerve
passes through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle
motor
Is inferior gluteal nerve sensory, motor, or mixed?
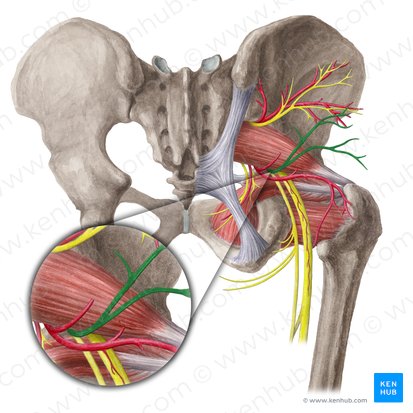
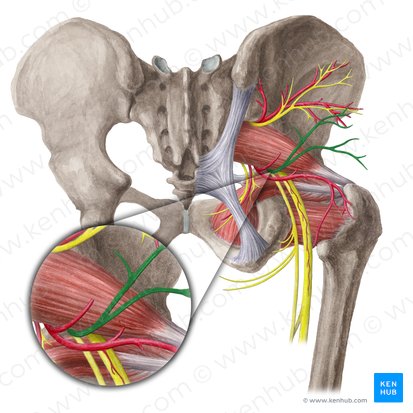
nerve to piriformis
motor
Is nerve to piriformis sensory, motor, or mixed?
nerve to quadratus femoris
mixed
Is nerve to quadratus femoris sensory, motor, or mixed?
nerve to obturator internus
mixed
Is nerve to obturator internus sensory, motor, or mixed?
pudendal nerve
mixed
Is pudendal nerve sensory, motor, or mixed?
nerves to levator ani and coccygeus
motor
Are nerves to levator ani and coccygeus sensory, motor, or mixed?
sciatic nerve
passes through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis
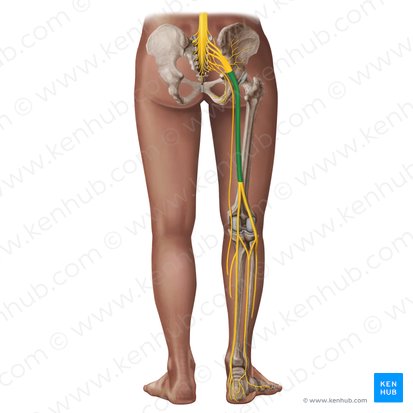
mixed
Is sciatic nerve sensory, motor, or mixed?
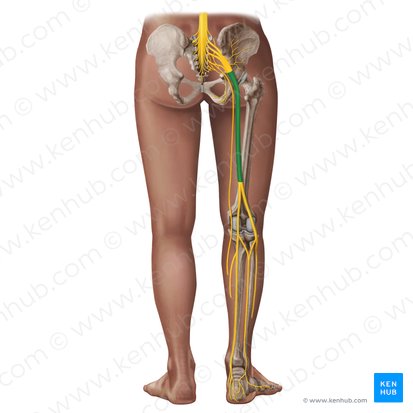
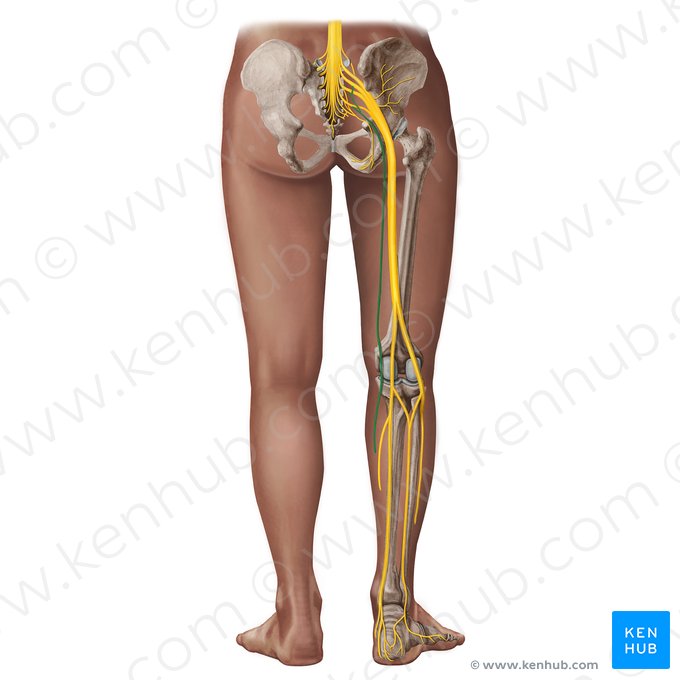
posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S1-S3)
passes through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to piriformis
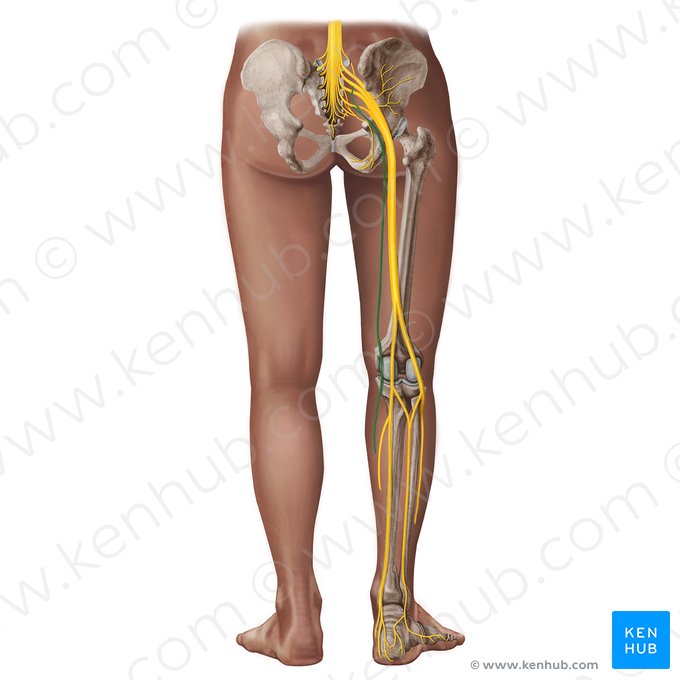
sensory
Is posterior femoral cutaneous nerve sensory, motor, or mixed?
vas deferens
thick-walled tubes in the male reproductive system that transports sperm cells from the epididymis, where the sperm are stored prior to ejaculation
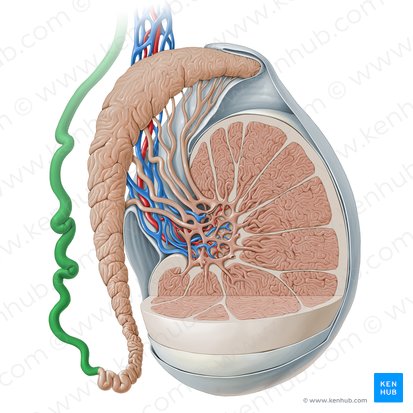
ductus deferens
What is another name for the vas deferens?
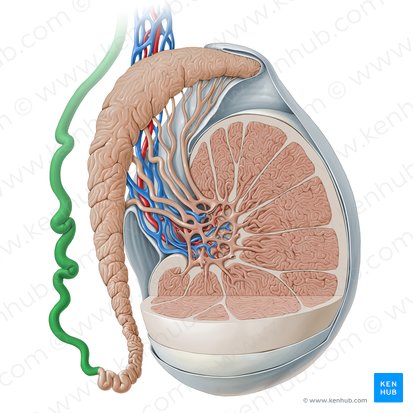
seminal vesicles
secrete a thick alkaline fluid with fructose (energy source for sperm) and a coagulating agent that mixes with the sperm as they pass into the ejaculatory ducts and urethra
seminal glands
What is another name for the seminal vesicles?
ejaculatory ducts
a slender tube formed by the duct of the seminal gland joining the vans deferens
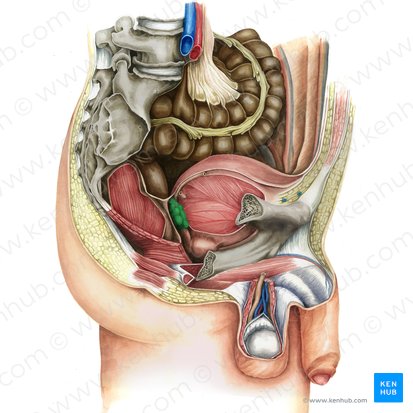
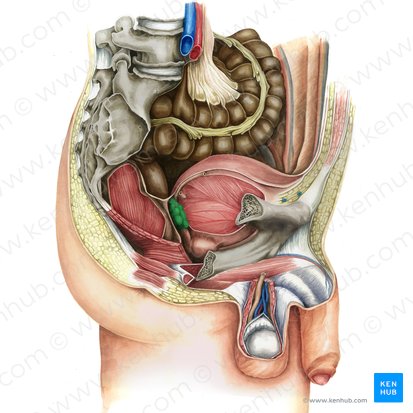
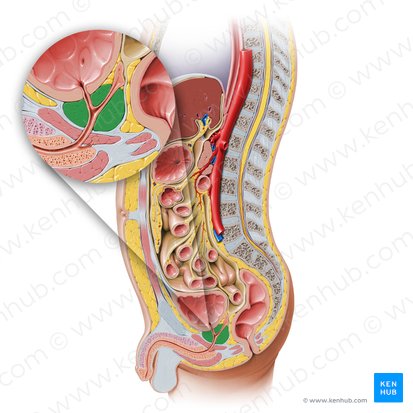
prostate gland
largest accessory gland of the male reproductive system (produces prostatic fluid that helps to nourish and transport sperm)
firm, walnut shaped
surrounds the prostatic urethra
base closely related to the neck of the bladder
posterior to the pubic symphysis
anterior to the rectum
superior to the levator ani
benign prostatic hyperplasia
What does BPH stand for?
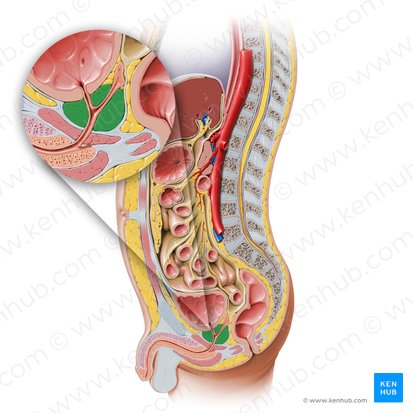
prostate gland enlargement
What is BPH also known as?
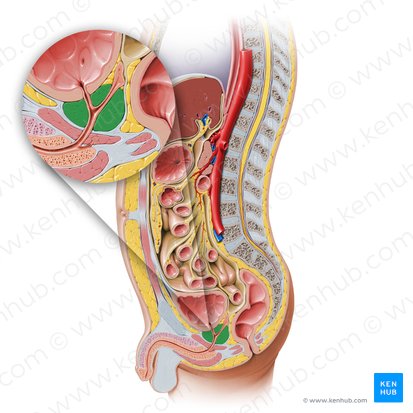
bulbourethral glands
pea-sized, embedded within the external urethral sphincter
contribute to the final volume of semen by producing a lubricating mucus secretion
kidneys
ureters
urinary bladder
urethra
Name the 4 organs of the urinary system
ureters
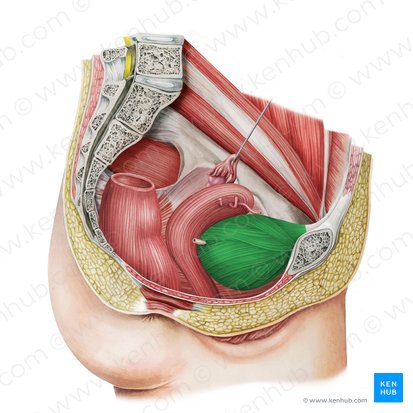
female urinary bladder
hollow muscular organ
temporary reservoir for urine that usually fills at a constant rate
lies mostly inferior to the peritoneum, subperitoneal
occupies the anterior portion of the pelvic cavity and is just superior and posterior to the pubis
resting on the pubic bones and pubic symphysis anteriorly and the anterior wall of the vagina posteriorly
male urinary bladder
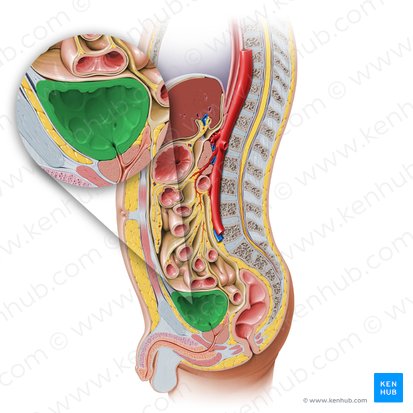
hollow muscular organ
temporary reservoir for urine that usually fills at a constant rate
lies mostly inferior to the peritoneum, subperitoneal
occupies the anterior portion of the pelvic cavity and is just superior and posterior to the pubis
resting on the pubic bones and pubic symphysis anteriorly and the prostate posteriorly
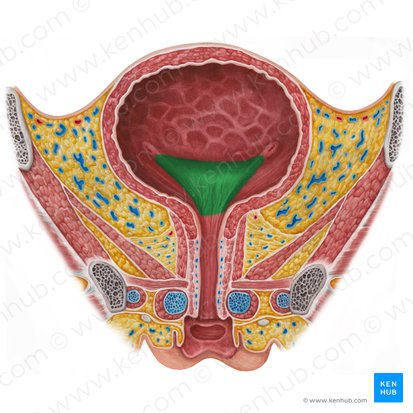
bladder trigone
stabilizes the attachment of the ureters to the bladder
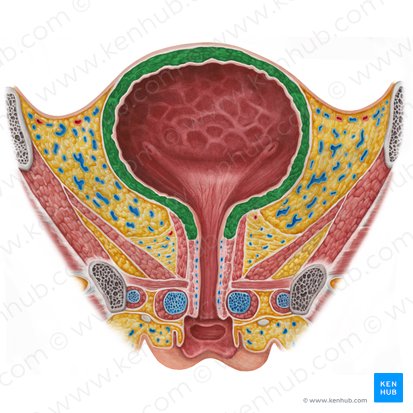
detrusor muscle
a powerful smooth muscle that forms the wall of the bladder
elastic and allows filling by staying relaxed (accommodation)
maintains low bladder pressure
responsible for the involuntary completion of micronutrition once it has begun
female urethra
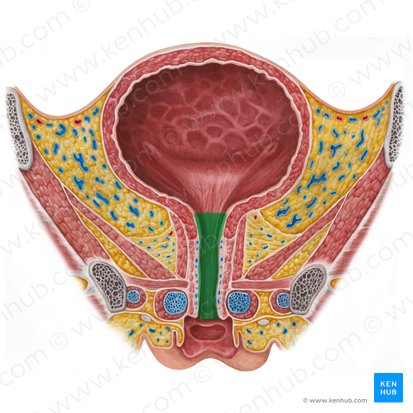
male urethra
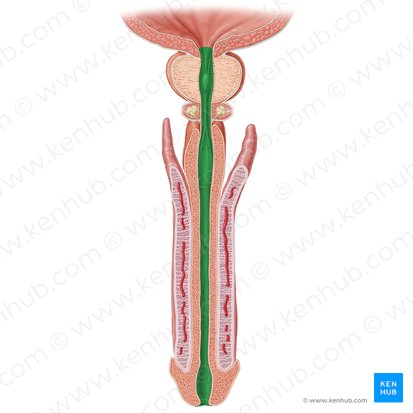
prostatic urethra
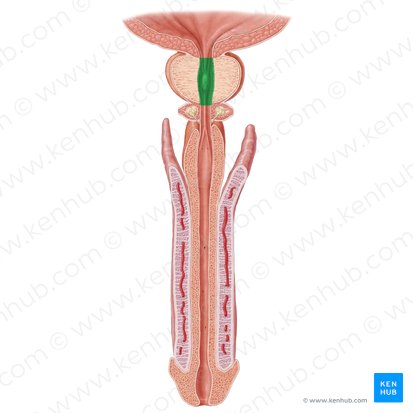
membranous urethra
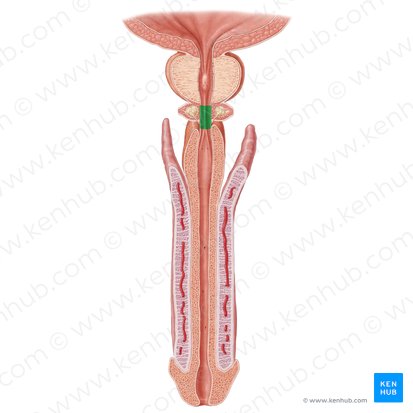
penile urethra
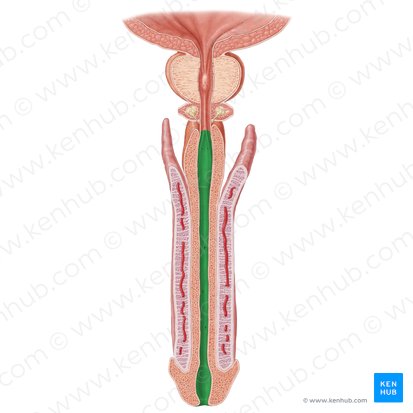
spongy urethra
What is another name for the penile urethra?
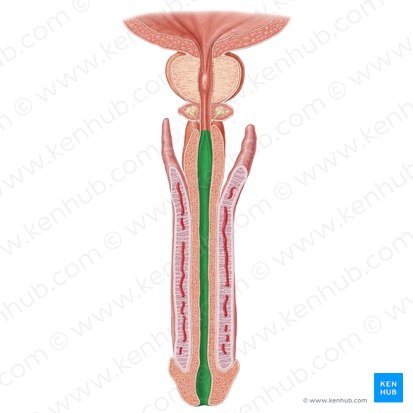
internal urethral sphincters
smooth muscle involuntary
external urethral sphincters
skeletal muscle voluntary
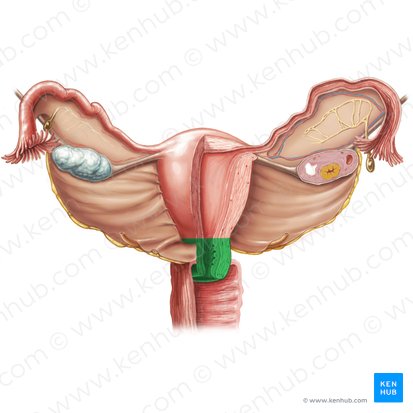
ovaries
small, oval-shaped glands located on either side of the uterus
produce and store eggs (also called ovum) and make hormones that control the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
during ovulation, one of them releases an egg which is swept into the fallopian tube by the finger-like projections of the fimbriae
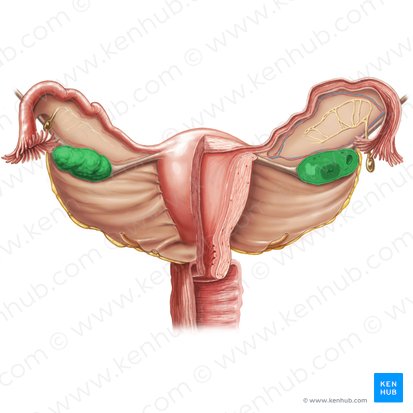
fallopian tubes
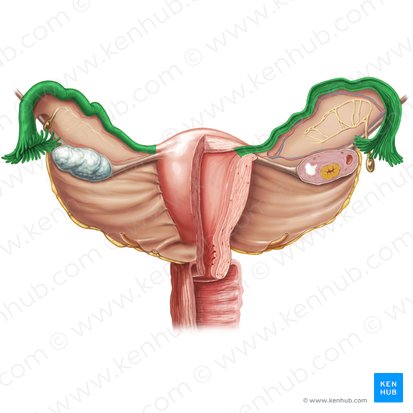
infundibulum of fallopian tube
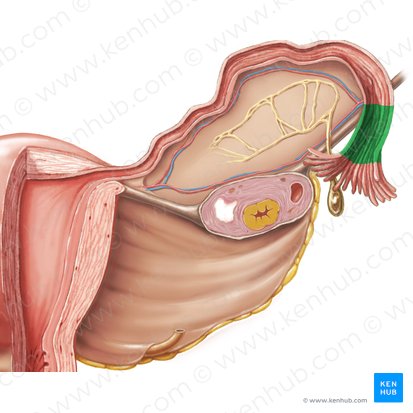
fimbriae of fallopian tube
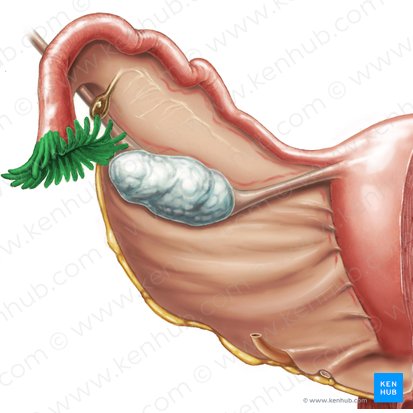
ampulla of fallopian tube
most common site of fertilization of the egg
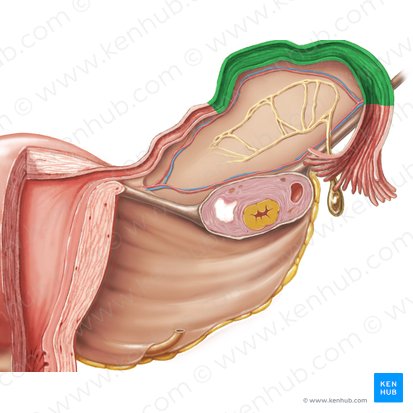
isthmus of fallopian tube
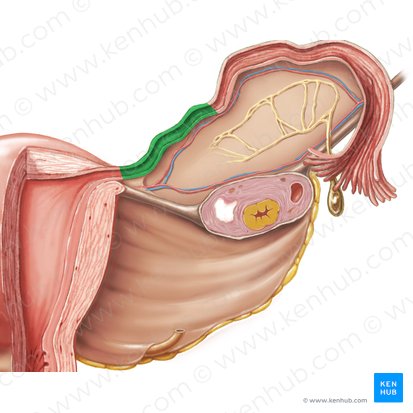
intramural part of fallopian tube
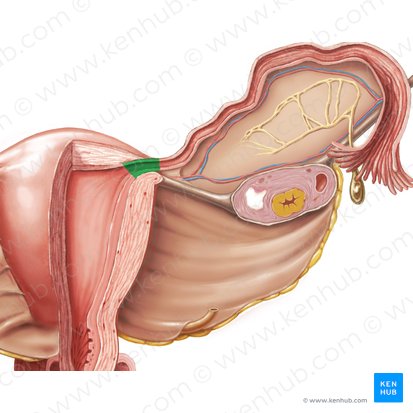
uterus
a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum
ovaries produce eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes; once the egg has left the ovary, it can be fertilized and implant itself in this organ’s lining
cervix
the lower, narrower end of the uterus (womb) that connects the uterus to the vagina
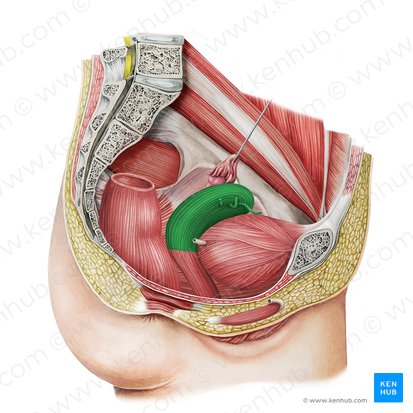
round ligament of uterus
one side of it is attached to the uterus; it then crosses the pelvis through the deep inguinal ring which then traverses the inguinal canal and then enters the labia majora, where it terminates with its fibers blending into the mons pubis
formed from fetal gubernaculum
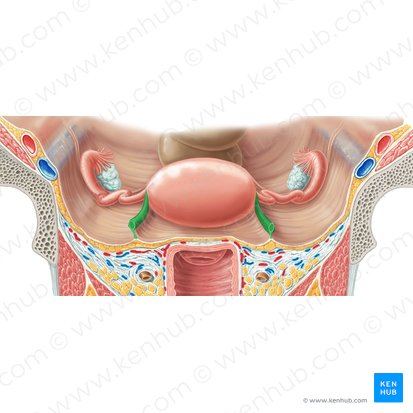
broad ligament
contains blood vessels to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, round ligaments, and uterus
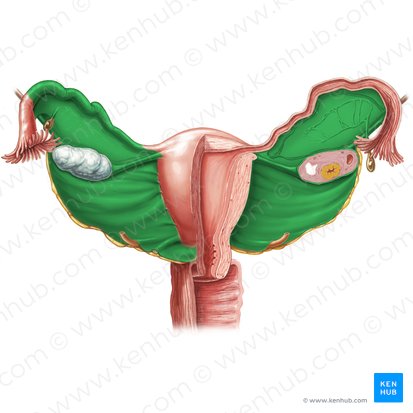
vagina
the passageway through which fluid passes out of the body during menstrual periods
connects the cervix (the opening of the womb, or uterus) and the vulva (the external genitalia)
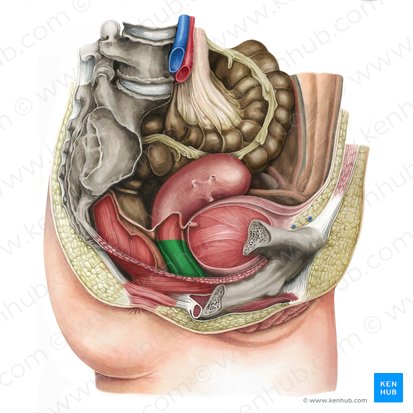
birth canal
What is the vagina also known as?
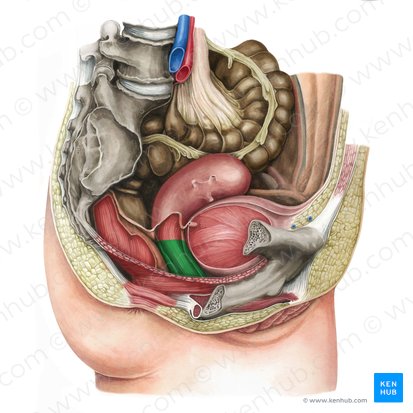
vulva
the outer part of the female reproductive system
also part of the external genitalia
includes the mons pubis
epididymis
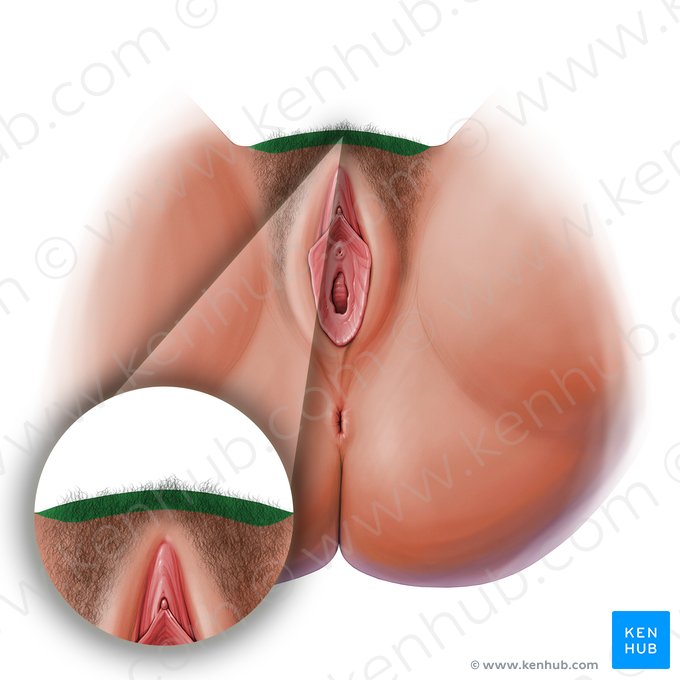
mons pubis
the rounded area
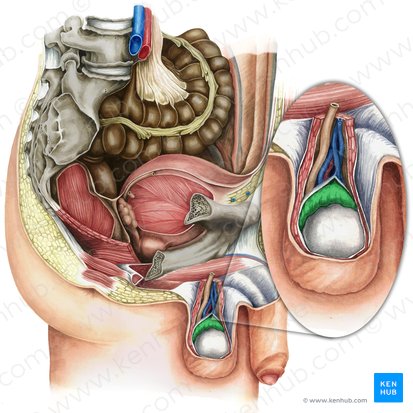
perineum
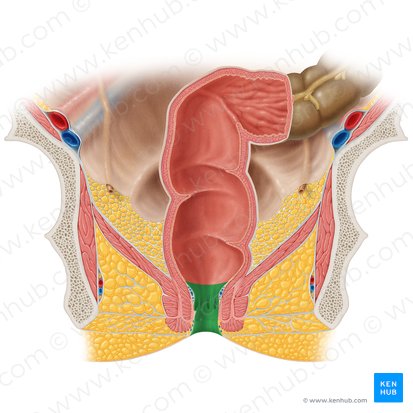
anal triangle
Name the space in red
Name the 3 contents of the anal triangle
anal canal
internal anal sphincter
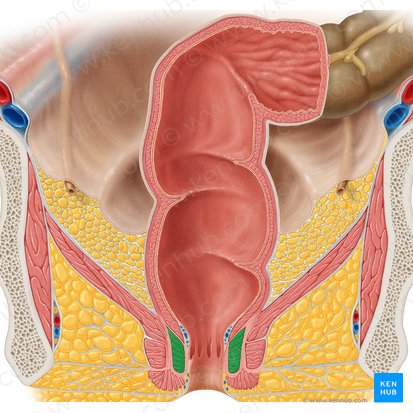
external anal sphincter
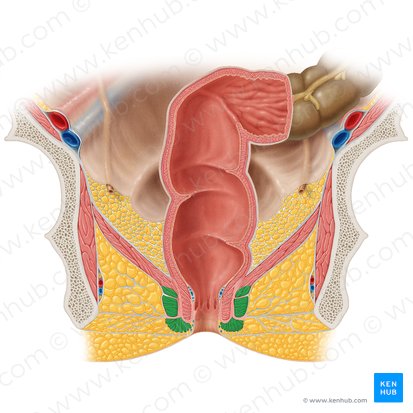
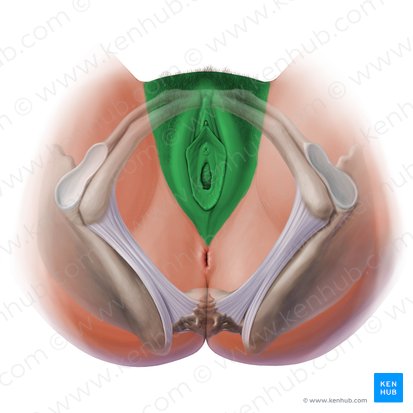
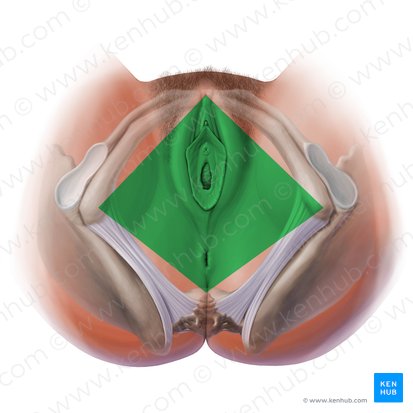
urogenital triangle
Name the space in green
female ischiocavernosus
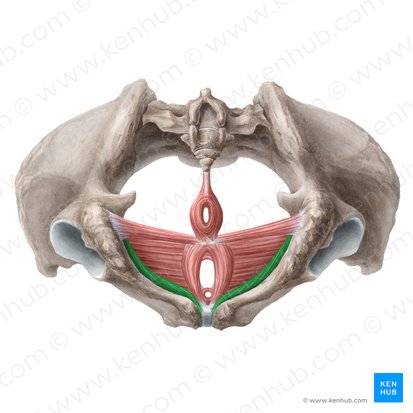
male ischiocavernosus
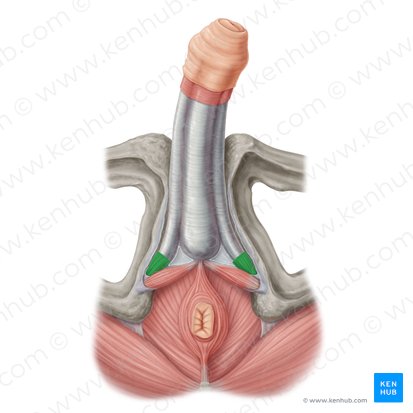
female bulbocavernosus
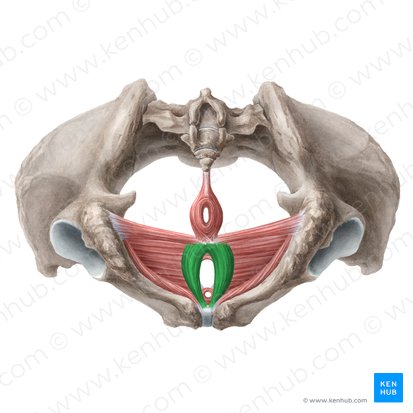
male bulbocavernosus
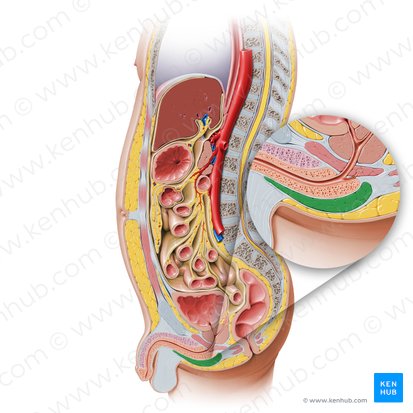
superficial transverse perineum
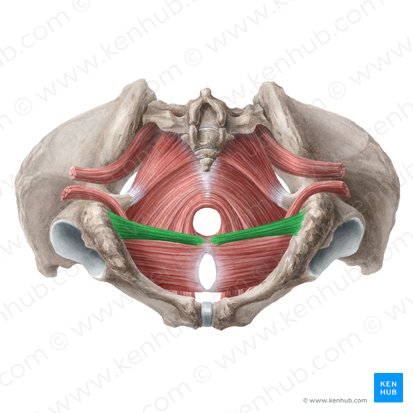
deep transverse perineum
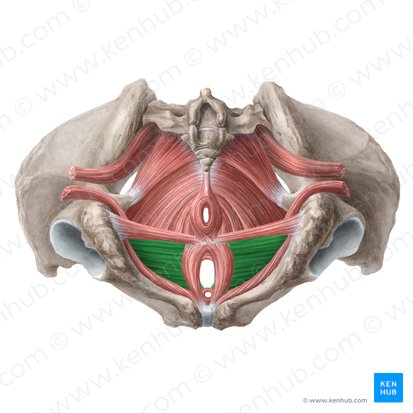
compressor urethrae
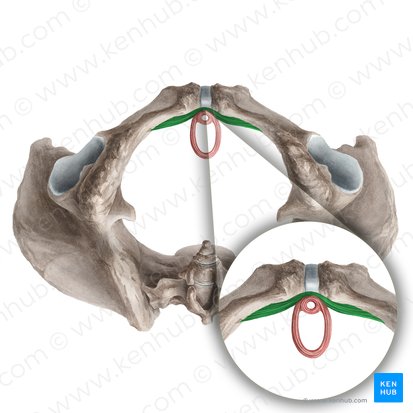
sphincter urethrovaginalis