AP Psychology: Testing and Individual Differences
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Standardized Test
One that is administered, scored, and interpreted in the same way no matter when or where it is used

Norms
Established rules of behavior or standards of conduct

Standardization sample
A large group of people that is representative of the entire population of potential test takers and establish the norms

Reliability
Ability of a test to yield very similar scores for the same individual over repeated testings

Validity
The extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to.

Aptitude test
Estimates the probability that a person will be successful in learning a specific new skill (ACT test)
Achievement test
A test designed to assess what a person has learned (AP tests)

Intelligence
the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations

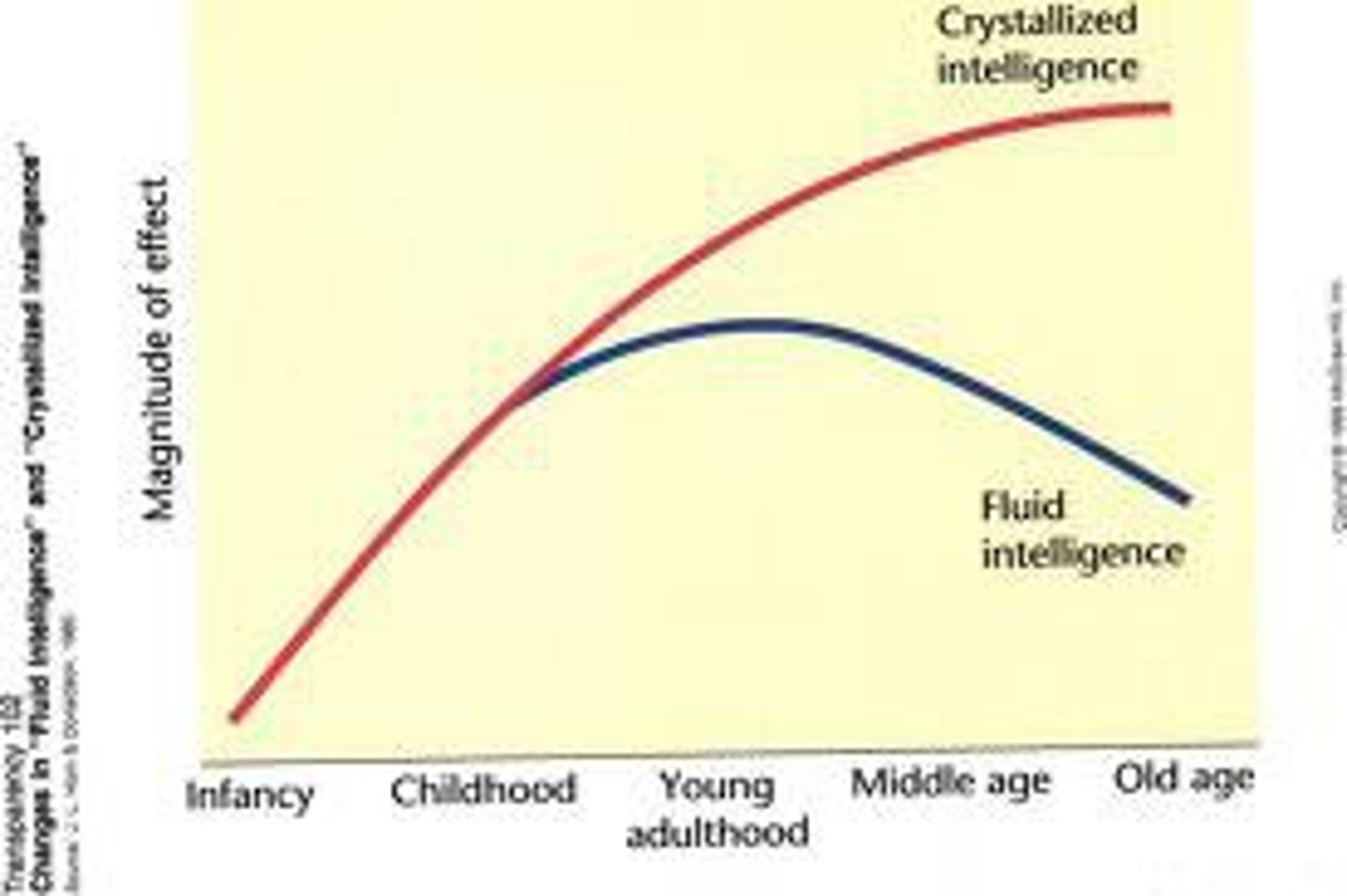
Fluid intelligence
Ability to acquire knowledge quickly and adapt effectively to new situations.
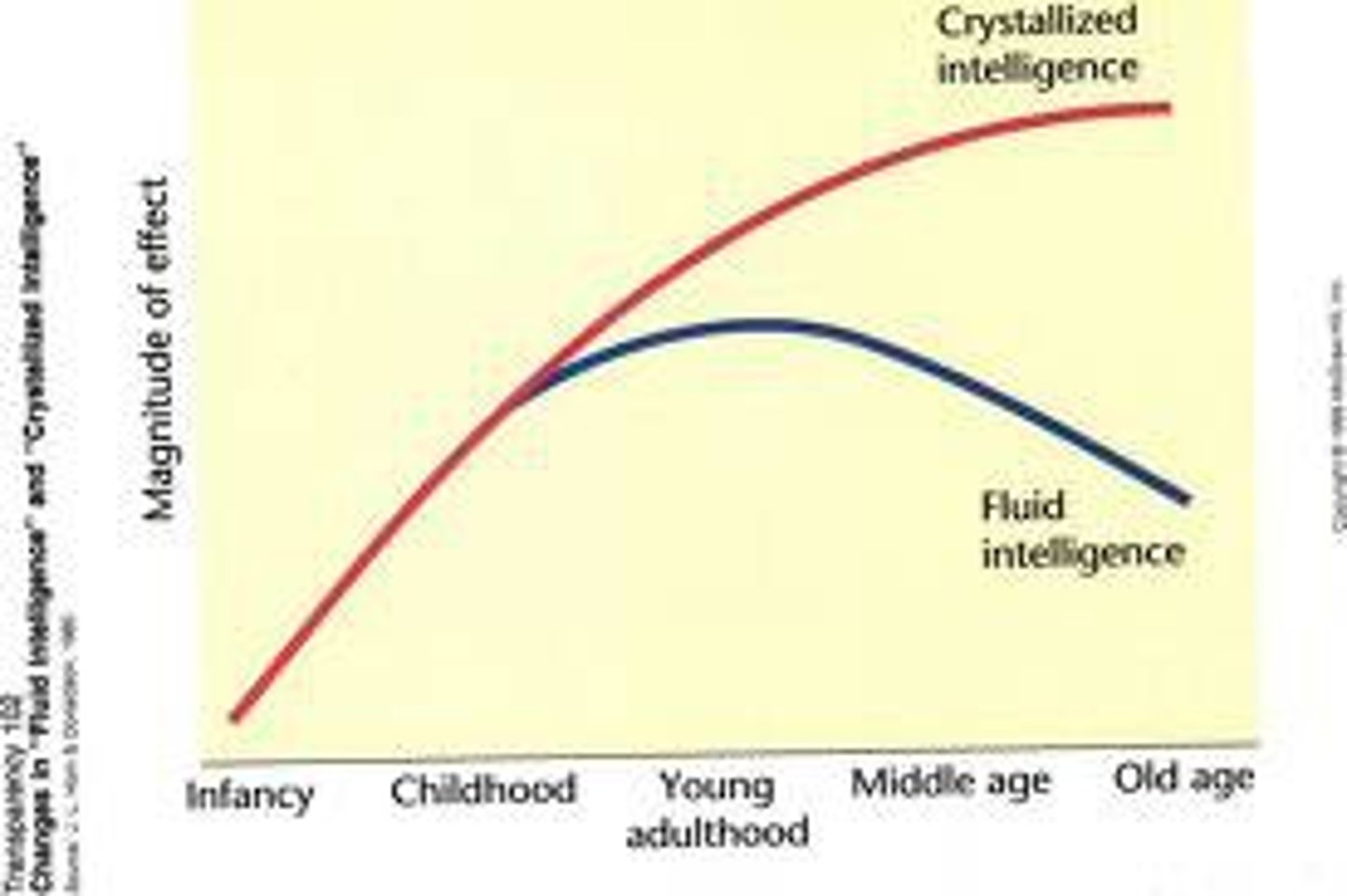
Crystallized intelligence
Knowledge and skills accumulated from prior experience, schooling, and culture.
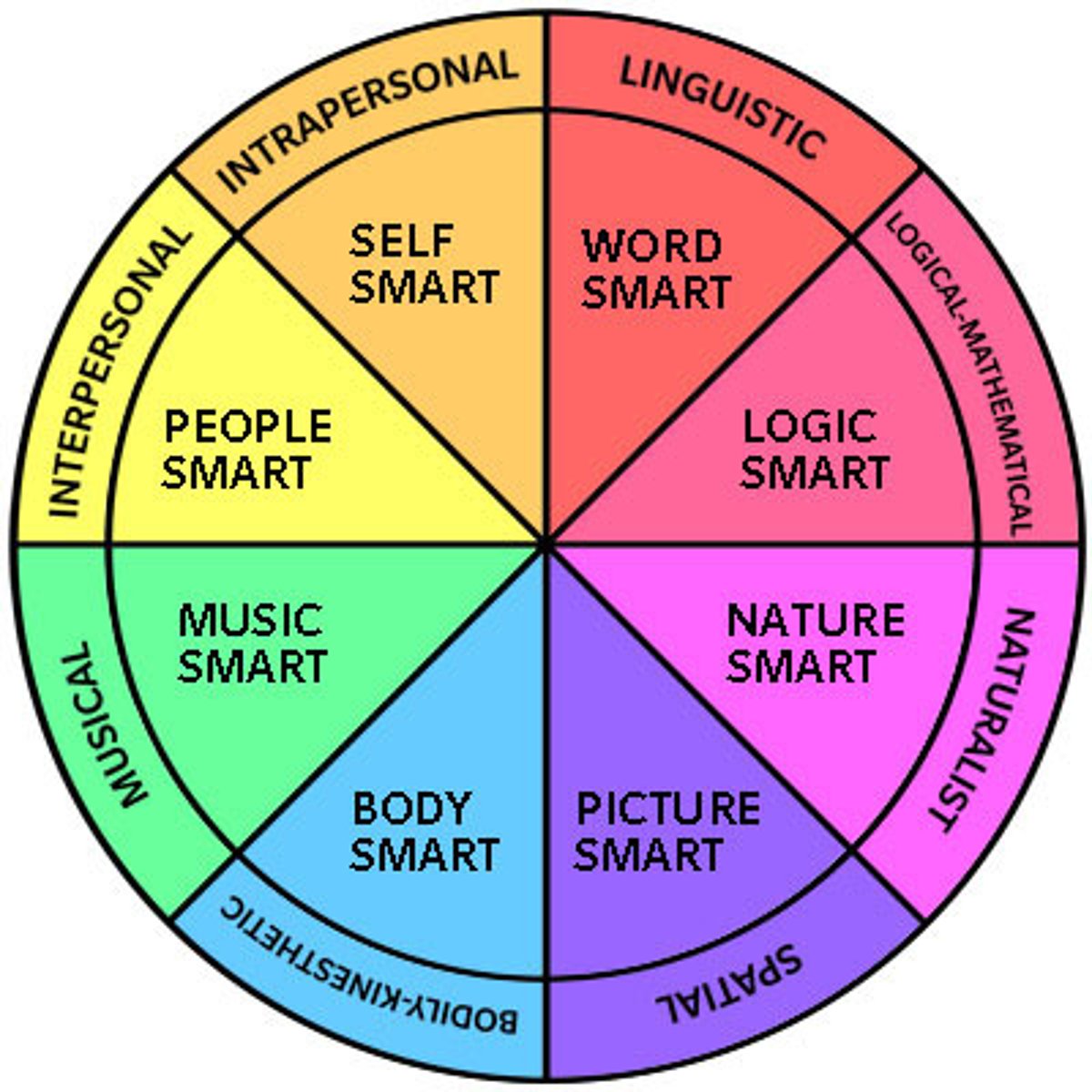
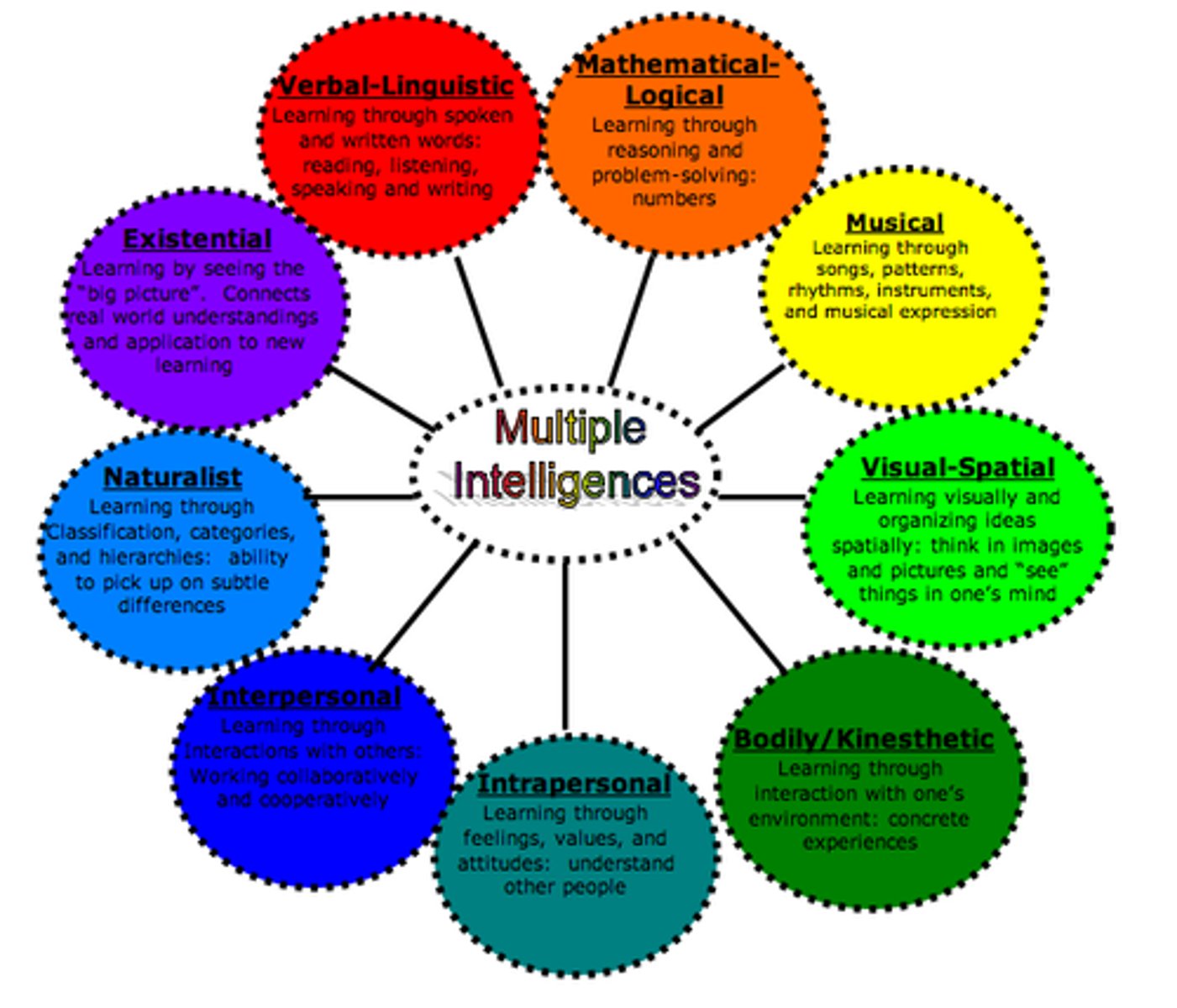
Multiple intelligence
Intelligence is more than IQ and everyone has a different recipe of intelligence (assessment)
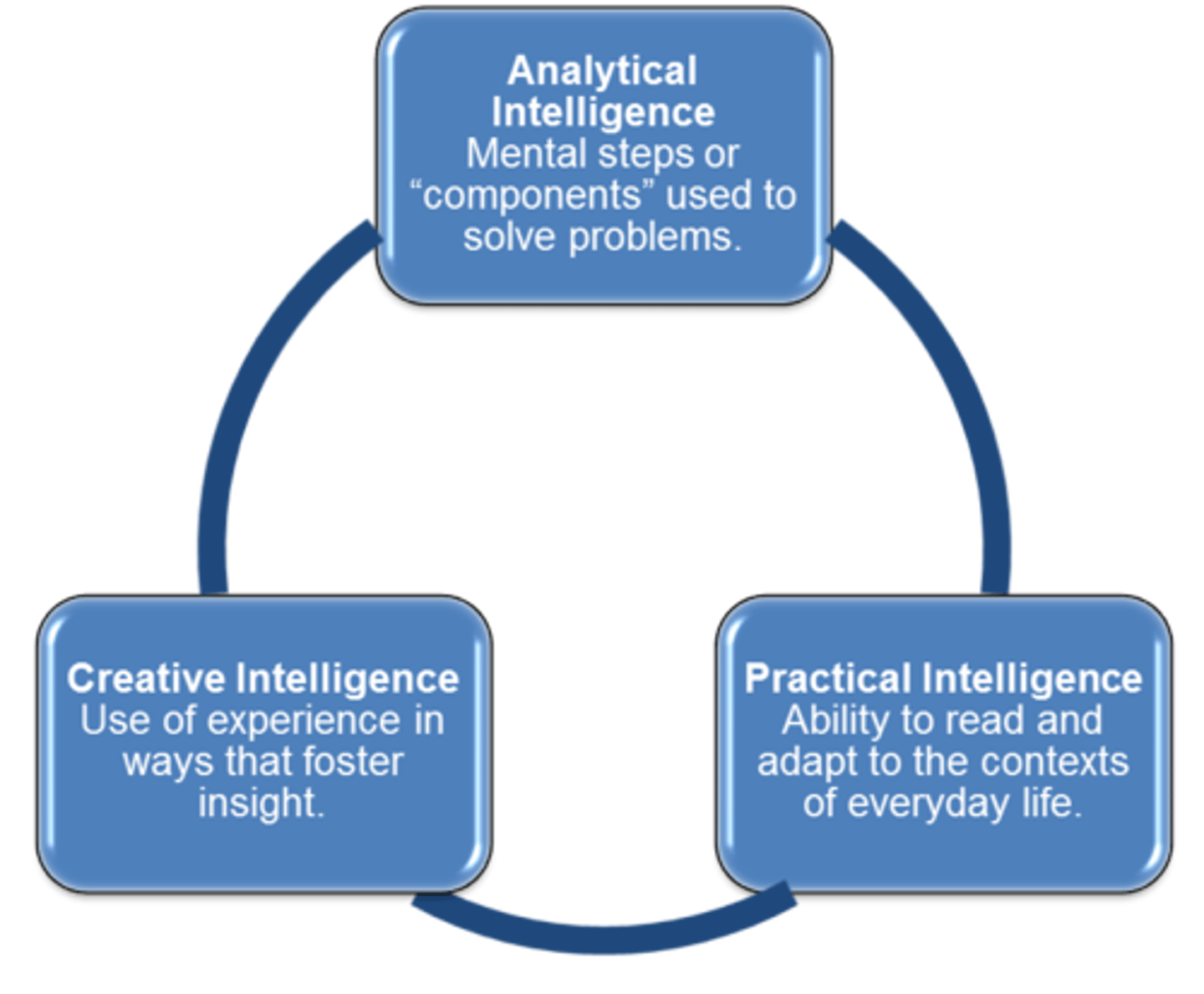
Triarchic theory of intelligence
Sternberg's theory that there are three kinds of intelligence: analytical, creative, and practical
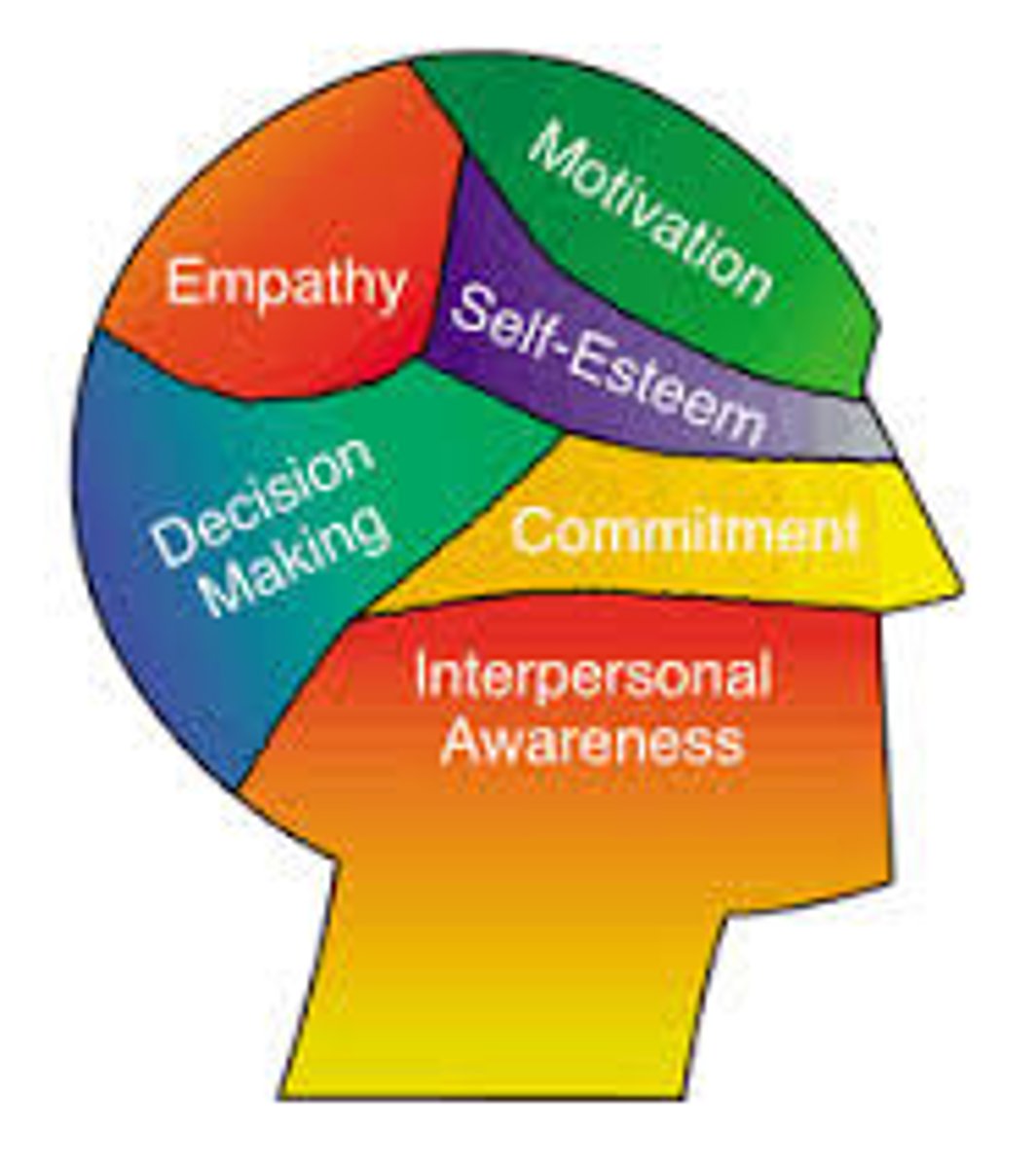
Emotional intelligence
The ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
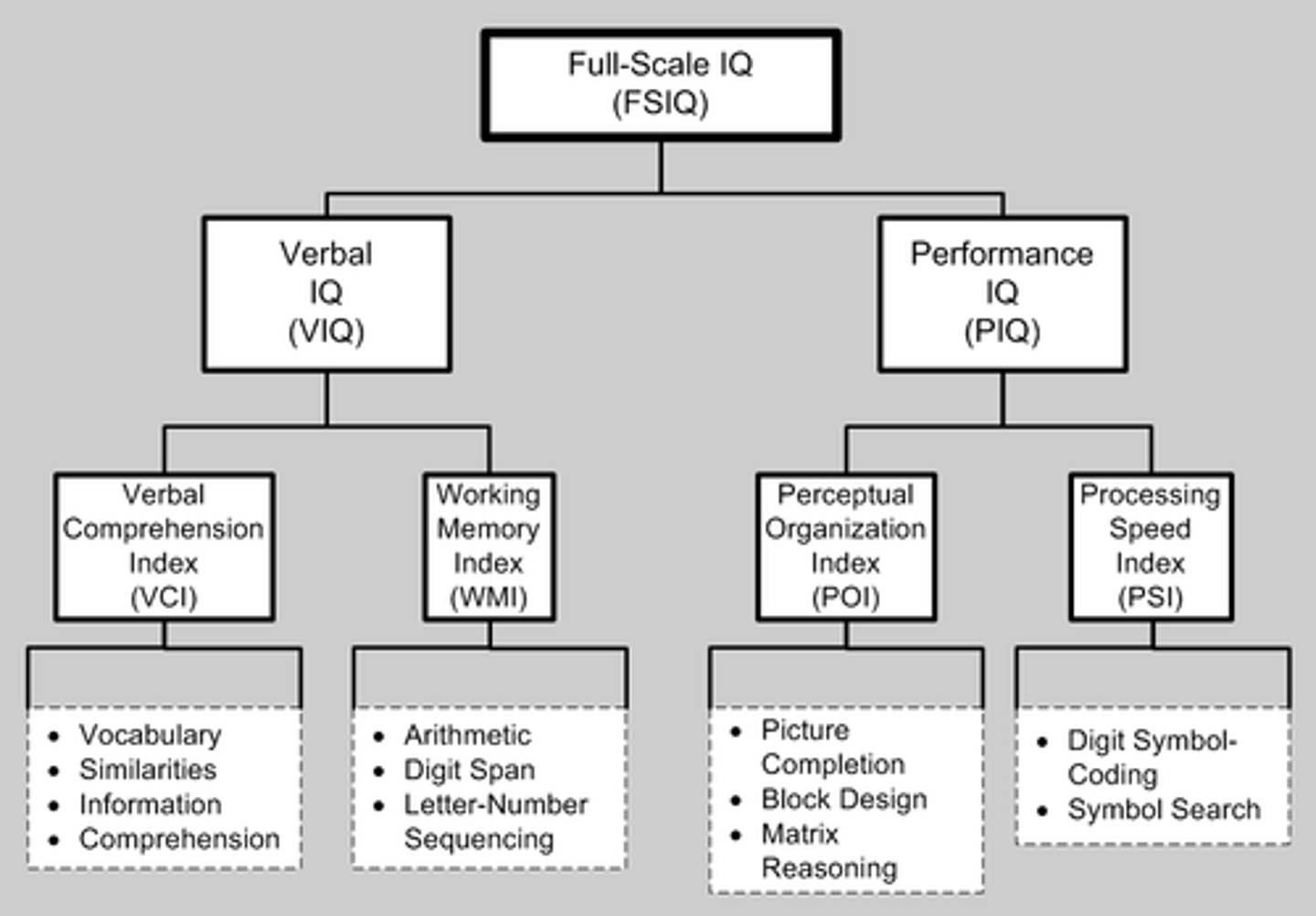
Stanford-Binet IQ test
Standardized test used to test intelligence
IQ = (mental age) / (chronological age) X 100

Wechsler test
advantage over Binet intelligence test both verbal and non-verbal scores
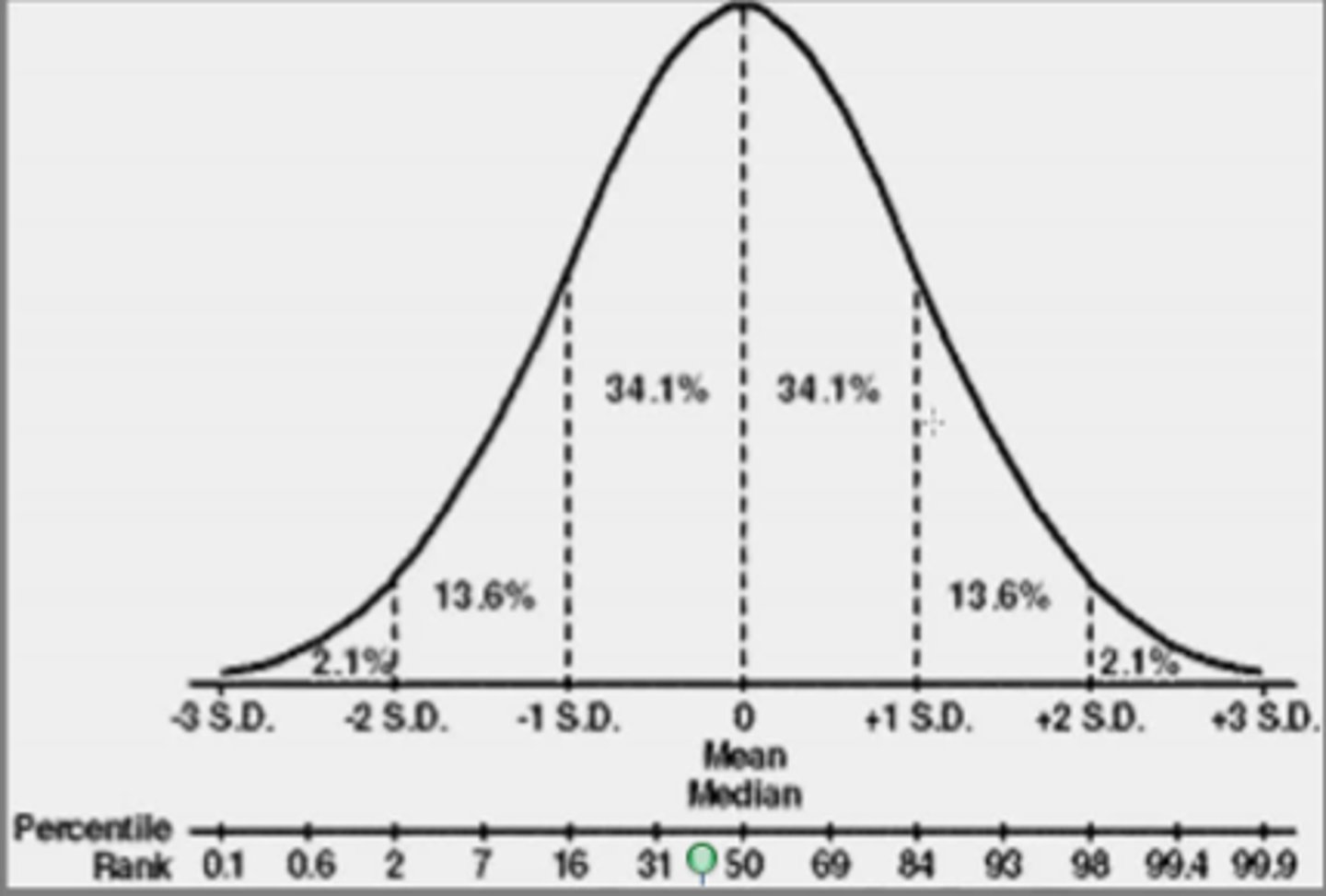
Normal distribution
A bell-shaped curve, describing the spread of a characteristic throughout a population.
Heritability
Ability of a trait to be passed from one generation to the next
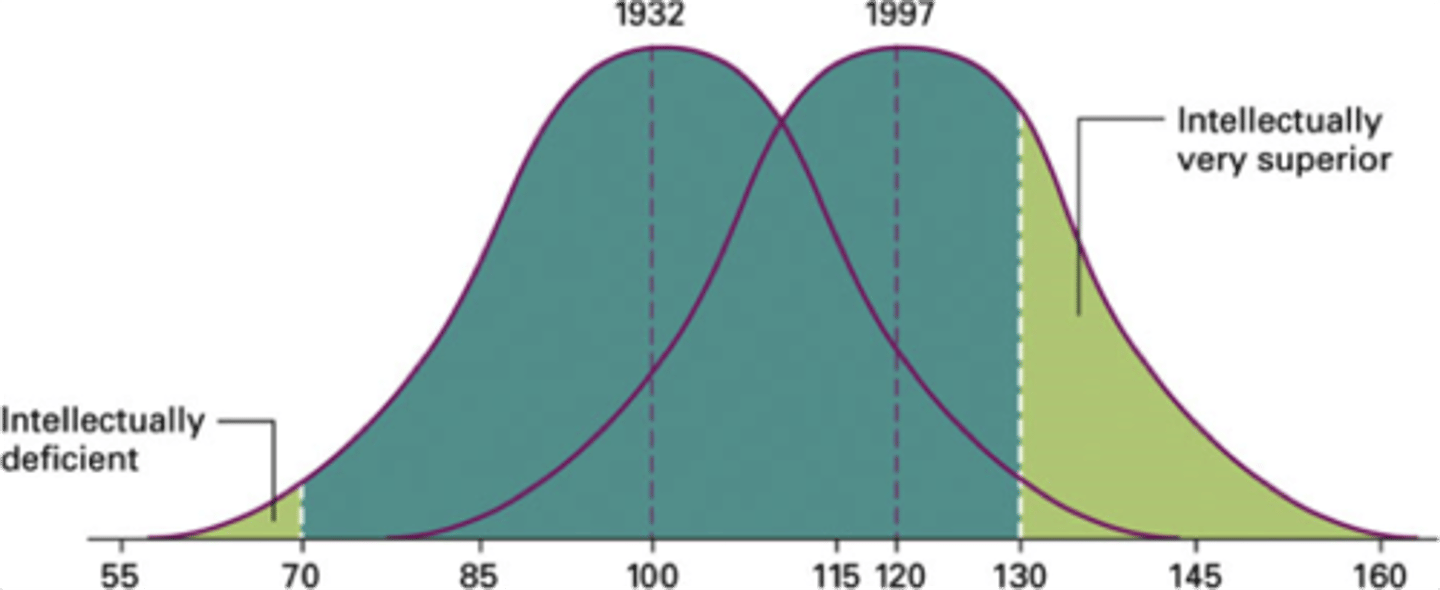
Flynn effect
The rise in average IQ scores that has occurred over the decades in many nations
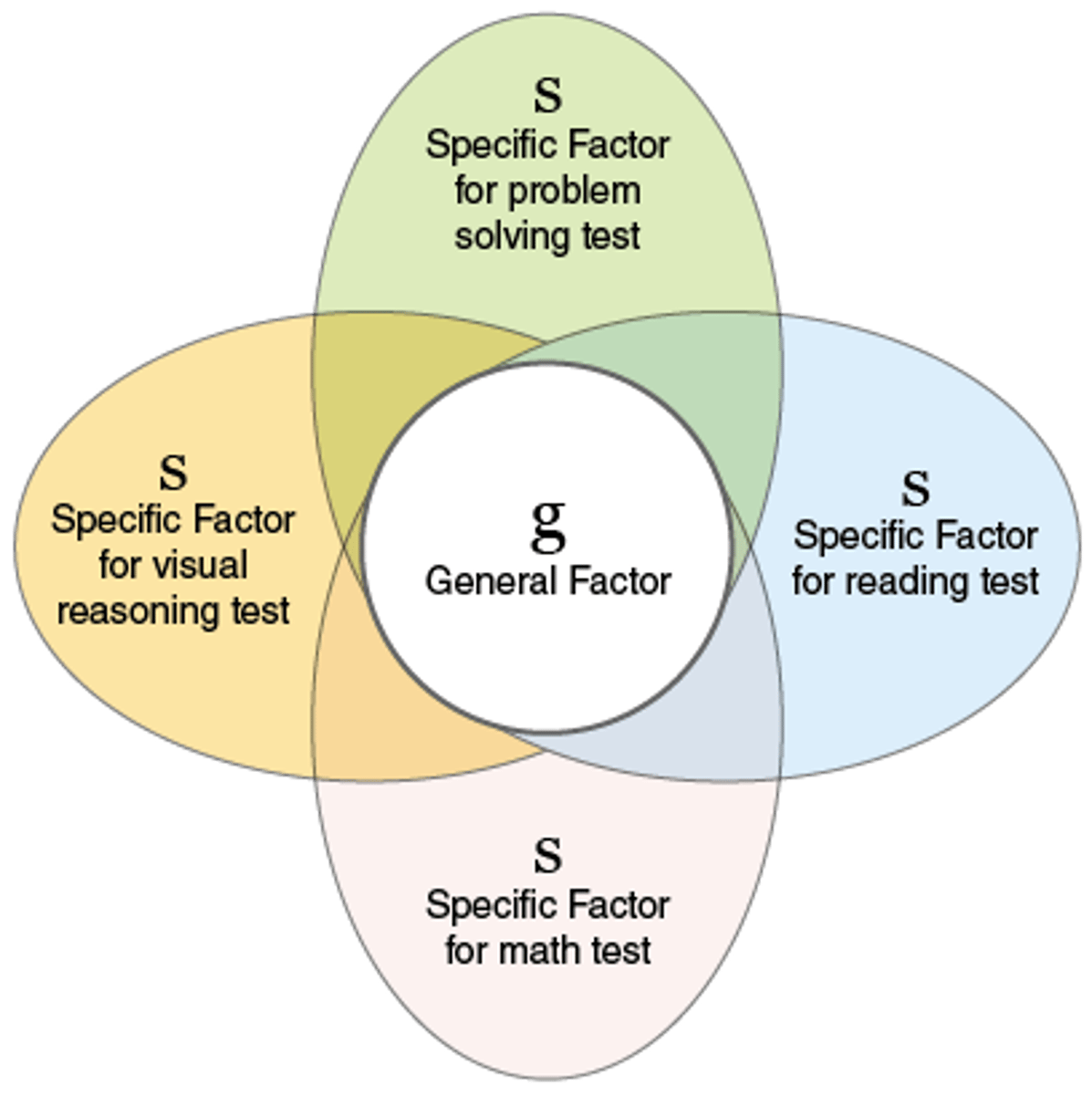
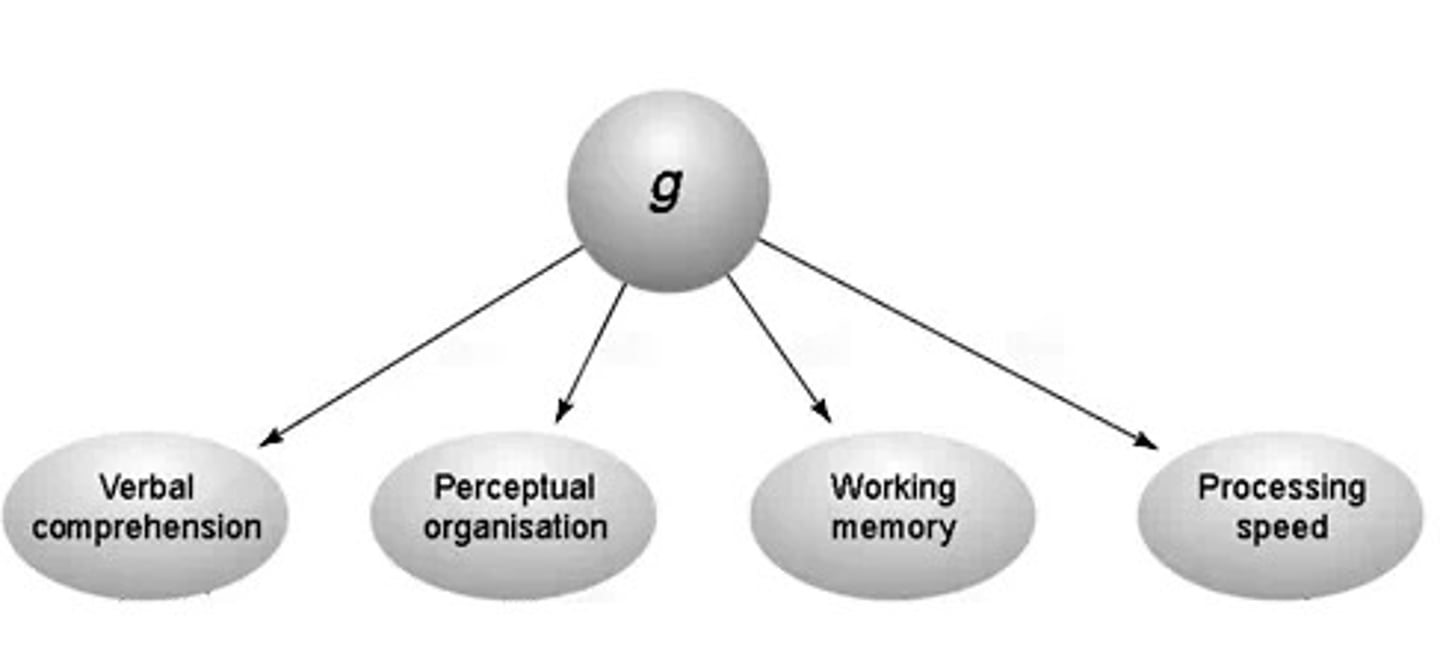
Charles Spearman
creator of "g-factor", or general intelligence, concept
Howard Gardner
Theory of multiple intelligence's
Daniel Goleman
Psychologist associated with the study of emotional intelligence

Robert Sternberg
devised the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence (academic problem-solving, practical, and creative)
Alfred Binet
developed intelligence tests to identify slow learners to develop remedial programs

Louis Terman
revised Binet's IQ test and established norms for American children.

David Weschler
established an intelligence test especially for adults (Weschler Intelligence Test for Adults)

Creative intelligence
A form of intelligence that involves the capacity to be intellectually flexible and innovative.

Divergent thinking
Trying to expand the range of alternatives by generating many possible solutions.

Factor analysis
Statistical procedure designed to discover the independent elements (factors) in any set of data
G factor
A general ability proposed by spearman as the main factor underlying all intelligent mental activity
Intelligence Quota (IQ)
a measure of a person's intelligence as indicated by an intelligence test

Mental age
The chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance

Intellectual Disability
indicated by an intelligence score of 70 or below and difficulty in adapting to the demands of life.

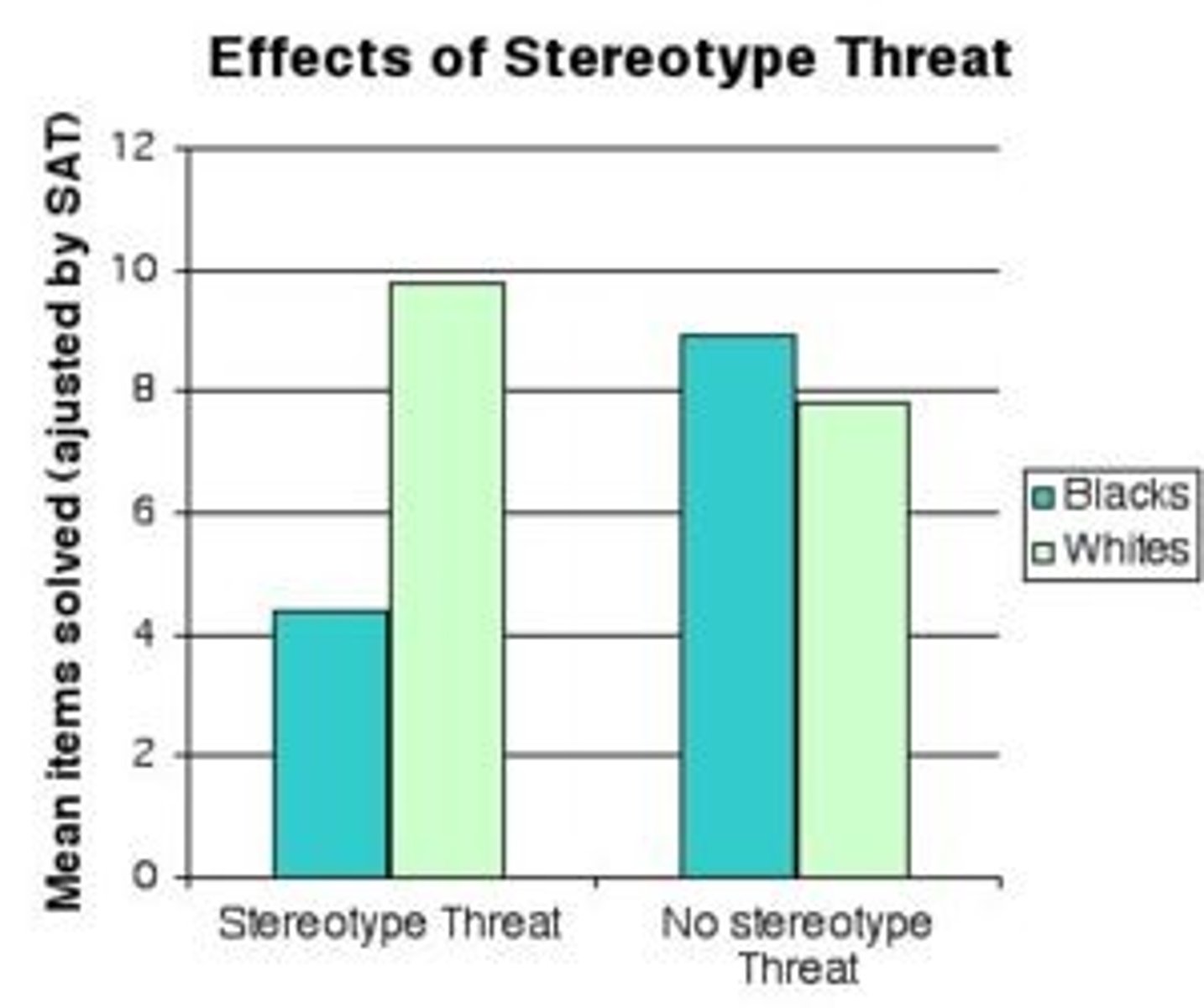
Stereotype threat
A self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
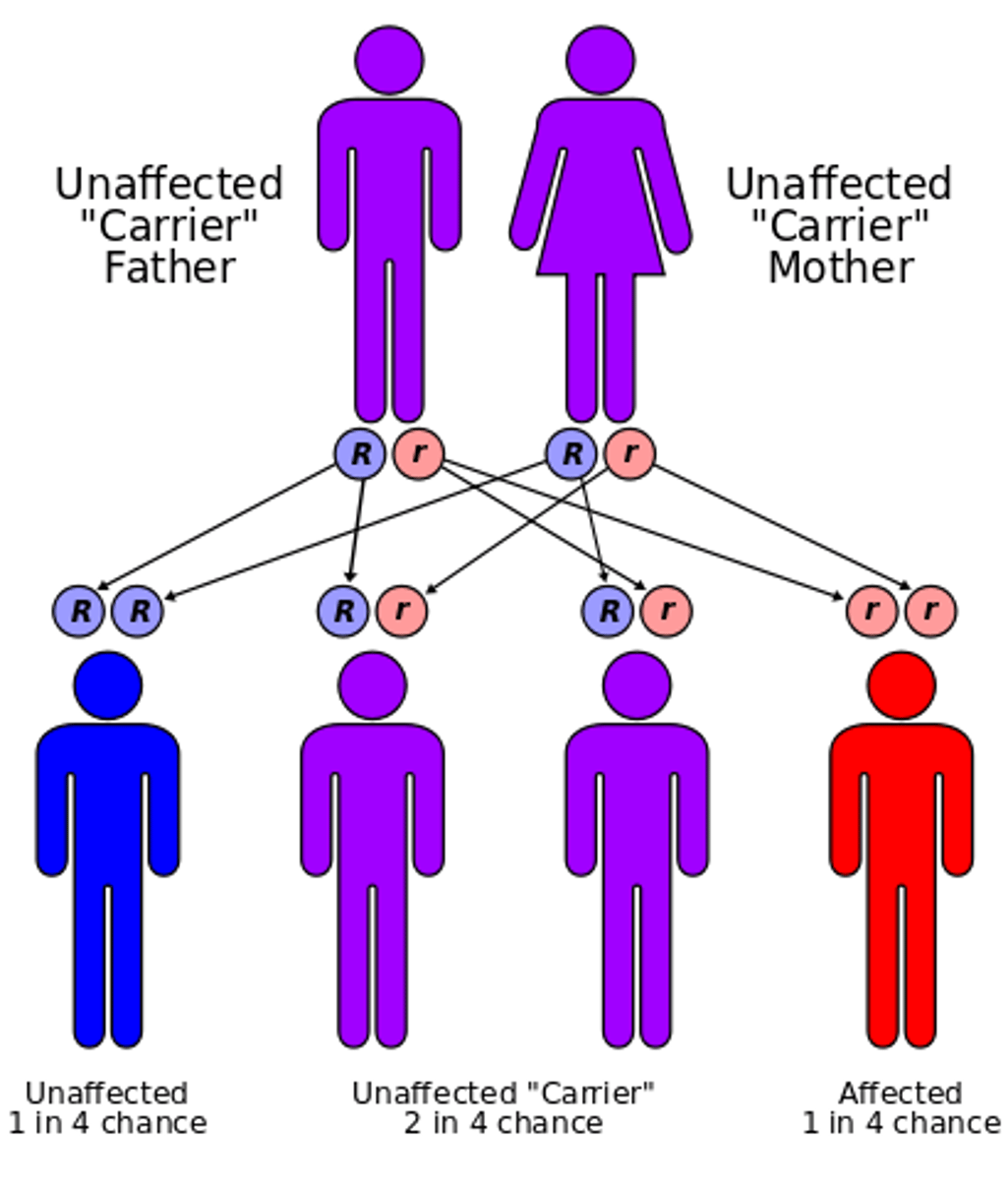
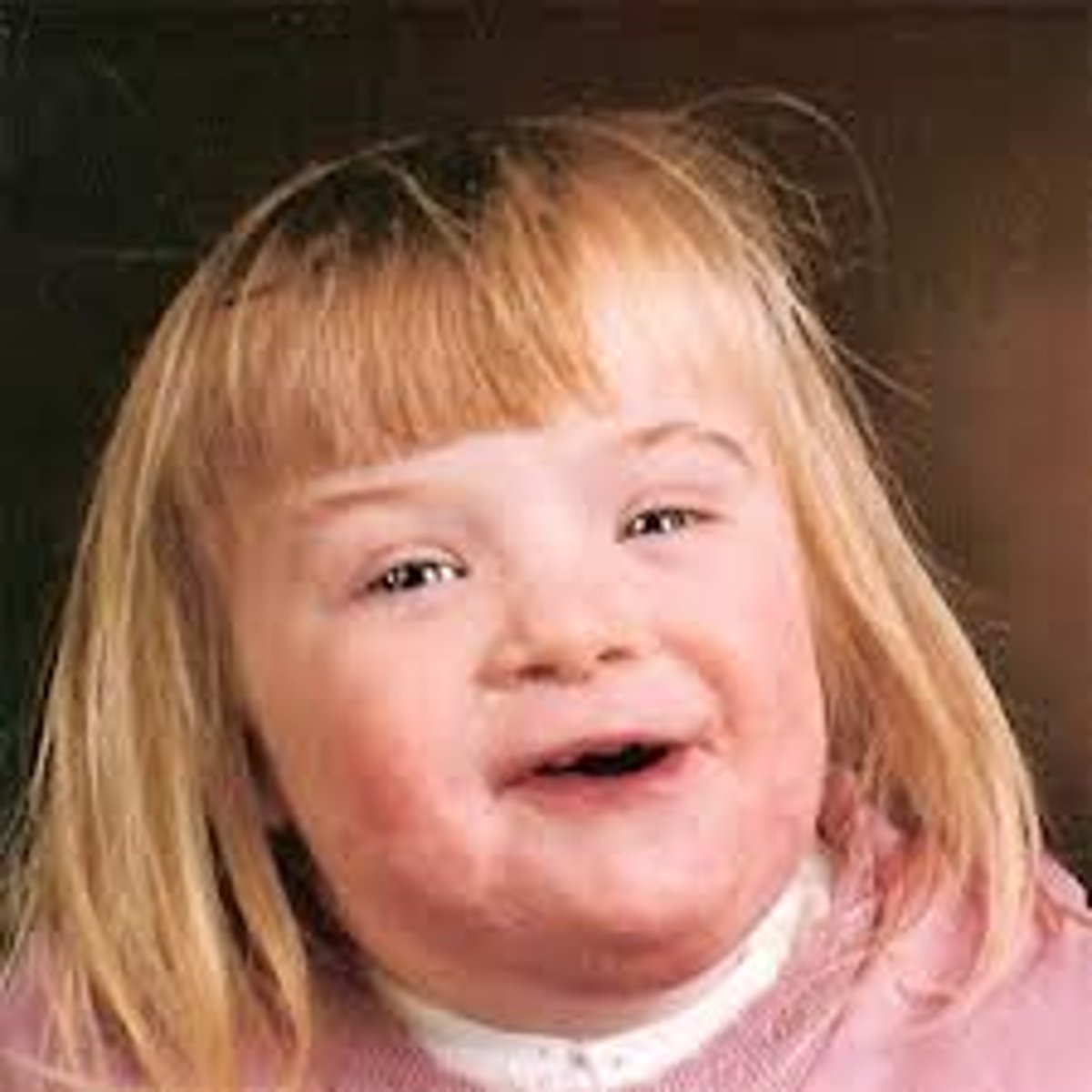
Down syndrome
A genetic chromosome 21 disorder causing developmental and intellectual delays.
Identical twins
Twins who come from one fertilized egg; twins having the same heredity

face validity
extent to which respondents can tell what the items are measuring
construct validity
the extent to which variables measure what they are supposed to measure
predicitive validity
The success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior.
content validity
The degree to which the content of a test is representative of the domain it's supposed to cover.