Academic Earth/Space Science : Midterm Exam Study Guide
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
Oxygen, silicon, aluminum, calcium, iron, magnesium, sodium, and potassium.
What are the major elements of Earth’s crust?
2
New cards
Relation between elements and minerals
elements make up minerals
3
New cards
Isotope
an atom that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
4
New cards
compound
consists of two or more elements that are chemically combined in specific proportions
5
New cards
covalent bonds
form when atoms share electrons
6
New cards
metallic bonds
form when metal ions share electrons
7
New cards
ionic bonding
forms between negative and positive ions
8
New cards
Characteristics of a mineral
crystalline structure, chemical compound, solid, naturally occurring, and inorganic
9
New cards
silicon-oxygen tetrahedron
the building blocks of all silicates
10
New cards
What is a mineral’s streak?
the color of the powder of a mineral
11
New cards
Which mineral property is least useful?
color
12
New cards
Why would a mineral cleave?
In the atomic structure of a mineral, some bonds are weaker than others. These weak bonds are places where a mineral will break when it’s stressed.
13
New cards
density formula
d=m/v
14
New cards
How are rocks classified?
By how they form
15
New cards
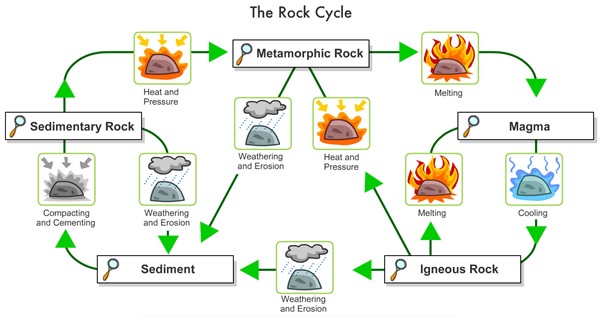
Rock Cycle
16
New cards
slow cooling
underground causes large grains
17
New cards
fast cooling
above ground causes smaller grains
18
New cards
What are the various changes that occur during metamorphism?
new minerals grow with different sizes, shapes, and orientations than those of other minerals.
19
New cards
Contact metamorphism
intruding magma causes localized areas of elevated temperature that alter rock
20
New cards
regional metamorphism
occurs over large areas of Earth’s crust, usually during mountain building, and is associated with very high temperatures and pressure
21
New cards
placer deposits
minerals that fall into the cracks of creek beds
22
New cards
Advantages of solar energy
free, clean, renewable source
23
New cards
Nuclear fusion
a uranium atom is split in a controlled reaction, which creates energy, which generates heat, which boils water, which creates steam that spins a turbine
24
New cards
How does hydroelectric power create energy?
water spins a turbine
25
New cards
point source pollution
pollution from a known and specific location, such as factory pipes
26
New cards
non-point source pollution
pollution that doesn’t have a specific point or origin
27
New cards
When were the most anti-pollution laws passed?
1970s
28
New cards
What is the most important law for air pollution?
Clean Air Act
29
New cards
mechanical weathering
occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller and smaller pieces without changing the rock’s mineral composition
30
New cards
frost wedging
the mechanical breakup of rock caused by the expansion of freezing water in cracks and crevices
31
New cards
What type of weathering is most effective in mid-latitudes?
frost wedging
32
New cards
What affects the rate of weathering?
rock characteristics and climate
33
New cards
In which climate is weathering the most effective?
hot, wet climate
34
New cards
what are the various components of soil
mineral matter, or broken-down rock; humus, which is the decayed remains of organisms; water; and air.
35
New cards
What determines a soil’s texture?
grain size, sand (large), silt, and clay (small)
36
New cards
What is the main source of organic matter in soil?
plants
37
New cards
A horizon
loose and partly decayed mineral matter)
38
New cards
B horizon
clay transported from above
39
New cards
C horizon
partially weathered parent material
40
New cards
pedalfer
usually form in temperate areas that receive more than 63 cm of rain every year. This soil is present in much of the forested areas in the eastern area of the states. The B horizon in this type of soil usually contains a large amount of iron oxide, making it a red-orange color.
41
New cards
pedocal
found in the western US in areas that have grasses and bush vegetation. Since chemical weathering is slower in drier climates, they usually contain less clay than pedalfers. They contain calcite, or calcium carbonate, and are typically a light-gray brown.
42
New cards
laterite
form in hot, wet, tropical areas. Chemical weathering is intense. The large quantity of water that passes through these soils removes most of the calcite and silica. Iron oxide and aluminum are left behind and the iron oxide gives it it’s distinct red color.
43
New cards
soil erosion rates today vs the past
The soil erosion rates are faster today because of human and biological removal of plant life and vegetation
44
New cards
How do humans impact soil erosion?
Human activities that remove natural vegetation, such as farming, logging, and construction, have greatly accelerated erosion
45
New cards
What are the various trigger of mass movements?
saturation of surface materials with water, over steepening of slopes, removal of vegetation, and earthquakes.
46
New cards
over-steepened slope
a steepened slope that exceeds over 40 degrees
47
New cards
What is the general seed of the various mass movements?
creep is the slowest, mudslide is the fastest
48
New cards
fault
a fracture in the earth where movement has occurred
49
New cards
focus
the point where an earthquake starts
50
New cards
foreshock
a small earthquake that can happen days or years before an earthquake
51
New cards
aftershocks
after an earthquake and can happen for weeks or months after the initial quake
52
New cards
P waves
the fastest, can travel through solids, liquids, and gasses
53
New cards
S waves
come second, and can only travel through solids
54
New cards
surface waves
come last and are the most destructive
55
New cards
What are the various scales used to measure earthquakes?
richter scale, seismograph, modified mercalli scale, and momentum magnitude
56
New cards
seismograph
instrument that records earthquake waves
57
New cards
seismogram
comes from the seismograph
58
New cards
How does the Richter scale measure earthquakes?
based on the height of the largest seismic wave based on a seismograph
59
New cards
tsunami
triggered by an earthquake, occurs where a slab of the ocean floor is displaced vertically along a fault
60
New cards
Layers of the Earth defined by physical properties
Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Lower Mantle, Inner core, Outer Core
61
New cards
Layer of the Earth defined by Composition
Crust, Mantle, Core
62
New cards
Core
below mantle and composed of iron-nickel alloy
63
New cards
mantle
has the igneous peridodite
64
New cards
crust
thin, rocky layer that is mostly made out of granite
65
New cards
lithosphere
crust and uppermost mantle
66
New cards
asthenosphere
below the lithosphere and has the upper mantle
67
New cards
lower mantle
consists of rocks that are very hot and capable of gradual flow
68
New cards
outer core
liquid layer surrounding the inner core
69
New cards
inner core
behaves like a solid due to extreme pressures