BIO 201: Chapter 4.2 Gross Anatomy of the Central Nervous System - The Spinal Cord
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
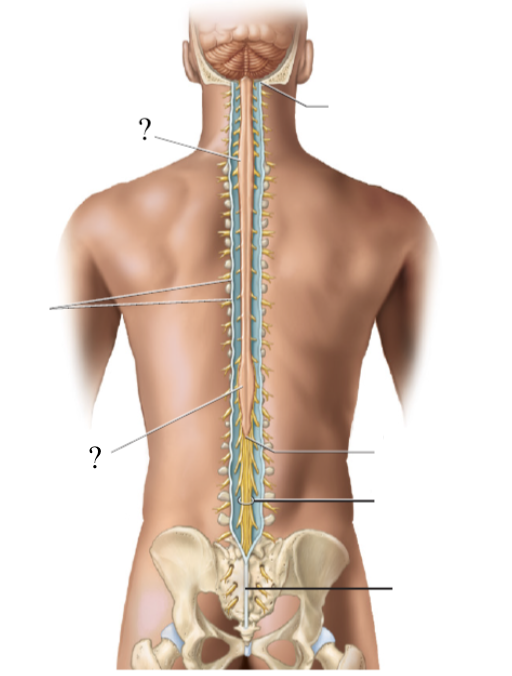
conus medullaris
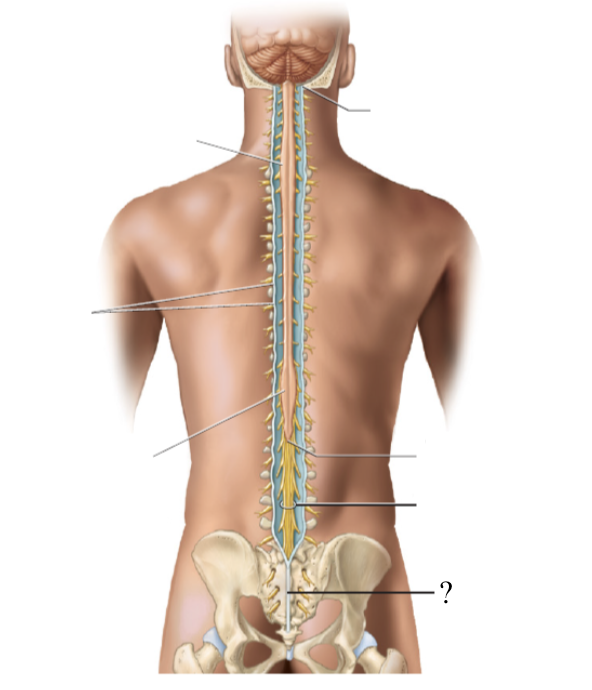
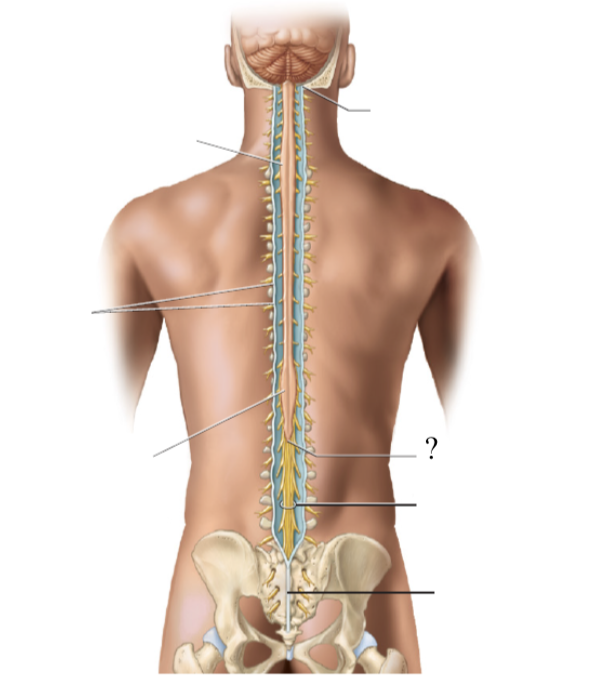
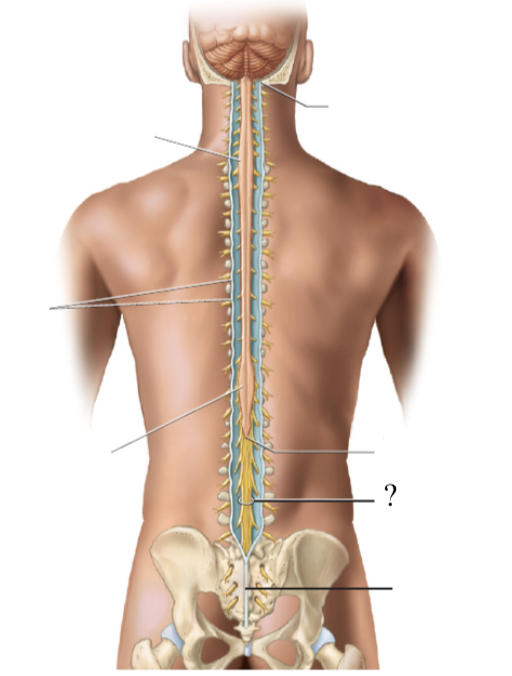
the spinal cord extends to the region of L1 and L2 vertebrae (where the spinal cord stops) and thins down in this cone-shaped region
cauda equina
bundle of nerve roots that resemble a horse’s tail that fill the rest of the vertebral column from L2 to S4 vertebrae
innervates the pelvis organs and lower extremity
anterior median fissure
anterior deep groove of the spinal cord
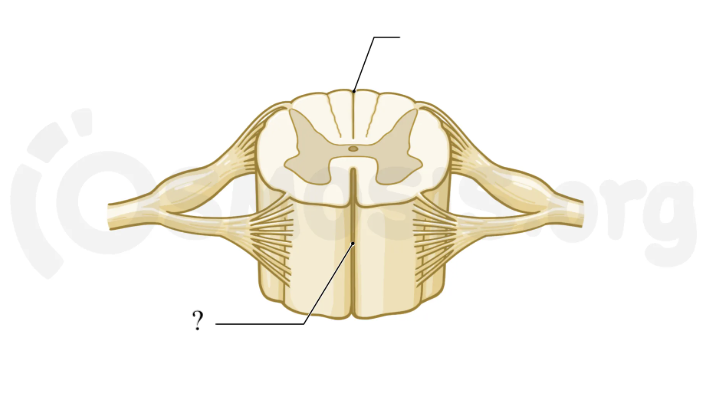
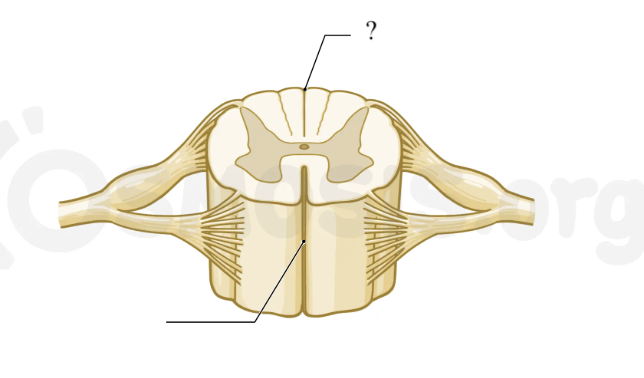
posterior median sulcus
posterior shallow groove of the spinal cord
central canal
pathway traveling with the spinal cord located in the midline and center of the spinal cord where CSF flows as wells
closed in adults but open in children
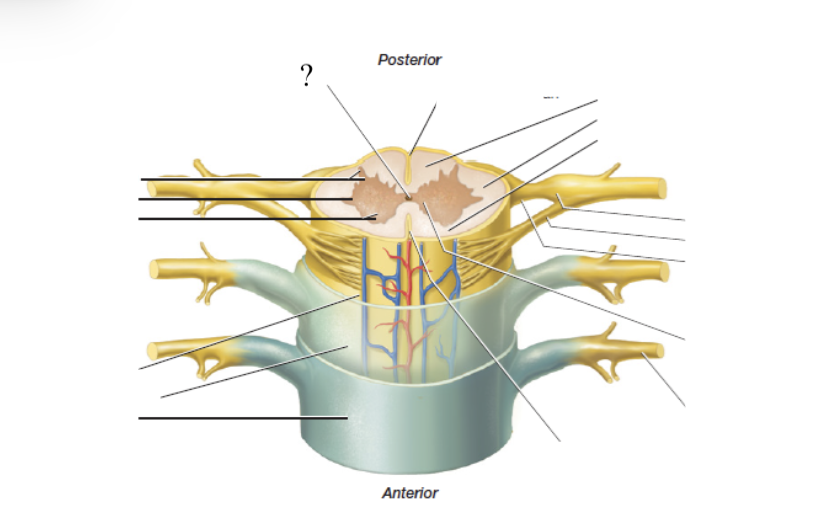
spinal gray matter
butterfly-shaped and deep and made up of three horns
anterior horn
made up of cell bodies of the lower motor neurons of the spinal cord, and axons of these nerves exit via the anterior (ventral) spinal nerve roots
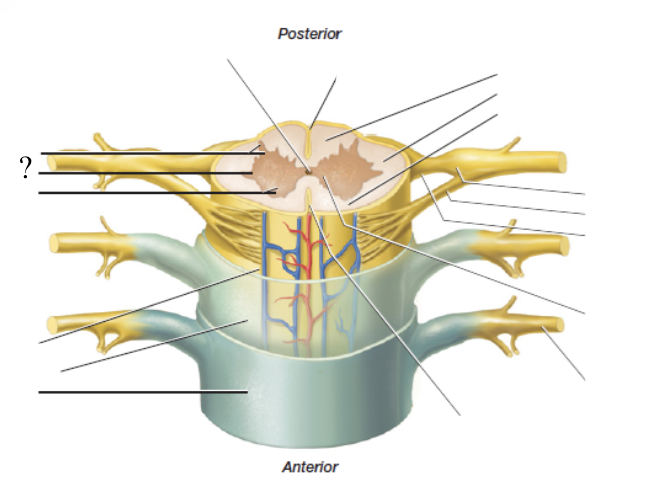
posterior horn
receive axons from the dorsal root ganglia which house the cell bodies of the sensory neurons and are housed just outside the cord
lateral horn
only present in thoracic and lumbar regions, contains cell bodies of the sympathetic division (fight or flight) of the autonomic nervous system
gray commissure
found in the midline and functions to connect the left and right portions of spinal gray matter
enlargements
2 thicker/wider sections of the spinal cord
cervical enlargement: gives rise to the nerves of the upper limbs
lumbar enlargement: gives rise to the lumbar and pelvis nerves
spinal white matter
superficial, remaining spinal cord that surrounds the spinal gray matter, made up of fibers grouped in columns called funiculi
anterior, posterior, and lateral funiculi
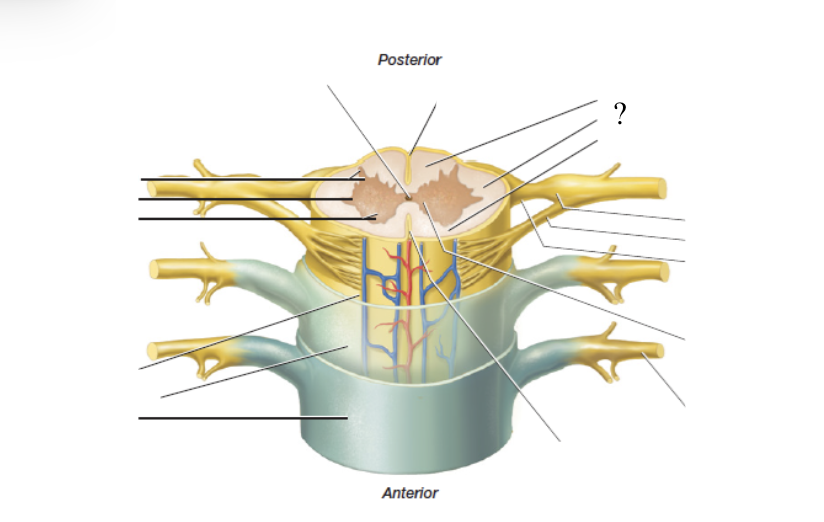
ascending fibers
groups of axons contained in spinal white matter that carry information up the spinal cord
descending fibers
group of axons contained in spinal white matter that carry information down the spinal cord
true
true or false: each spinal nerve arises from 2 points of root attachments to the spinal cord
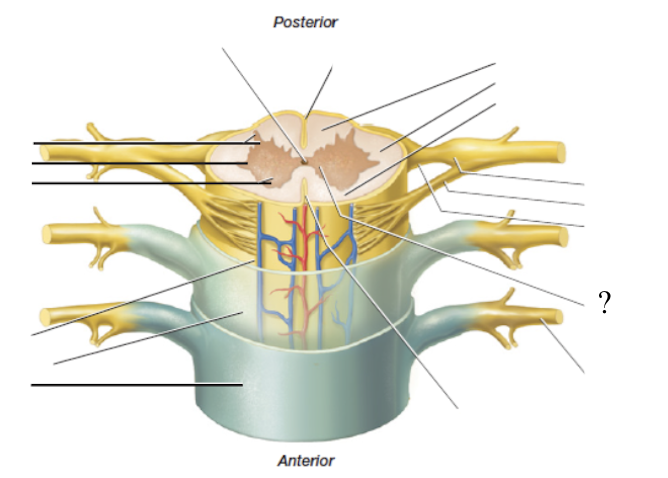
anterior spinal nerve roots
formed by 6-8 anterior/ventral spinal nerve rootlets and function to carry motor axons and efferent signals away from the spinal cord
motor nerves’ neurosoma/cell bodies are found within the spinal cord’s gray matter
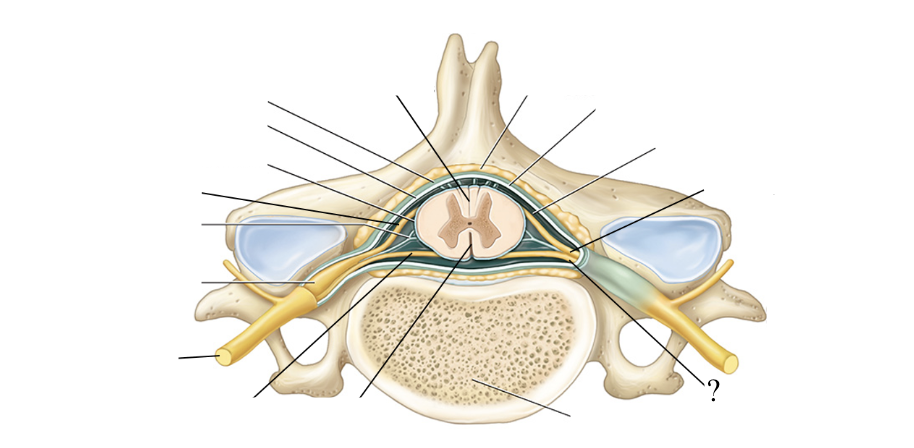
posterior spinal nerve roots
formed by 6-8 posterior/dorsal spinal nerve rootlets and function to carry sensory axons and afferent signals towards the spinal cord
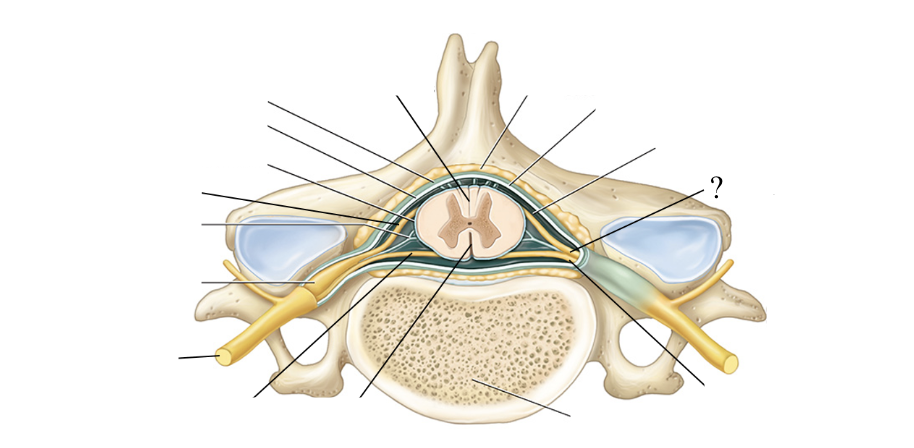
posterior root ganglion
contains the neurosoma/cell bodies of the sensory nerves traveling to the spinal cord
has a bulbous/swollen appearance
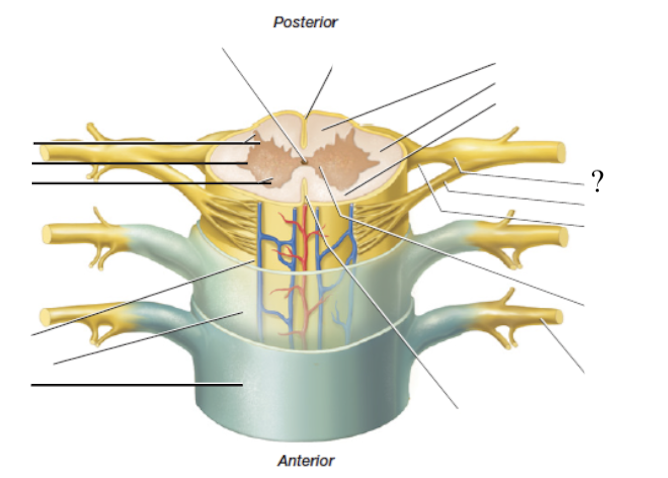
spinal nerves
formed by the fusion of the anterior and posterior spinal nerve roots so it contains both sensory and motor axons
mixed nerves
spinal nerves are ____ that take efferent signals away from the spinal cord/to the body and carry sensory signals from the body to the spinal cord
denticulate ligaments
surrounding fibers that anchor the spinal cord and limit its side to side movements
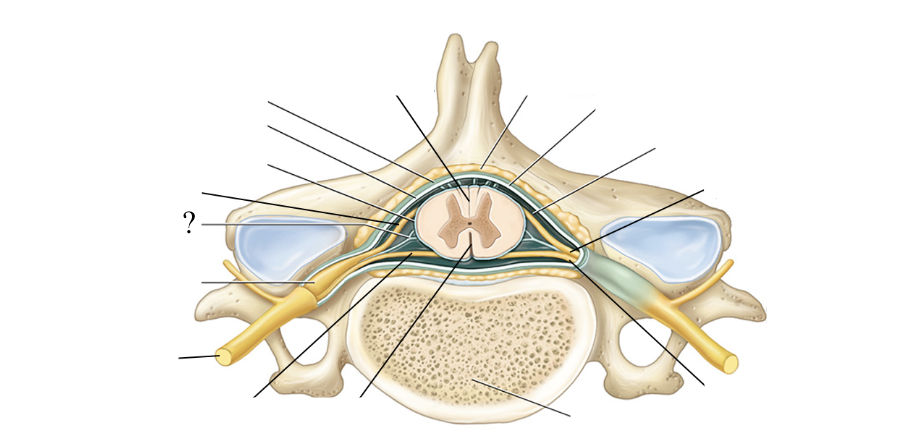
extension
the spinal meninges are an ______ of the cranial meninges
not, space
dura mater is ____ adherent to the vertebrae the way it is in the skull so there is ___ between the dura and spinal column
epidural space
space between the dura and spinal column filled with loose connective tissue, adipose tissue, and blood vessels
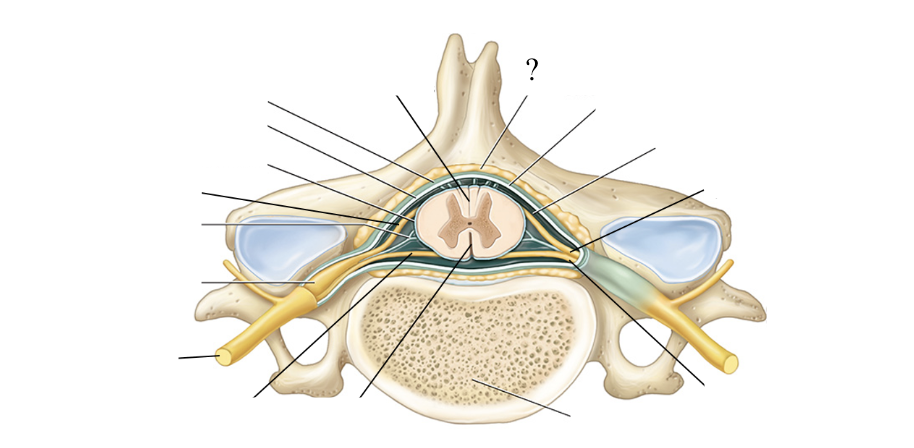
filum terminale
extension of the pia mater that anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx vertebra