lab 12: gastrointestinal system
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
why doesnt the stomach normally digest itself
the stomach does not digest itself because of the secretion of mucus from the gastric glands
mucus protects the lining of the stomach from acidic contents of the stomach lumen
microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells "the brush border"
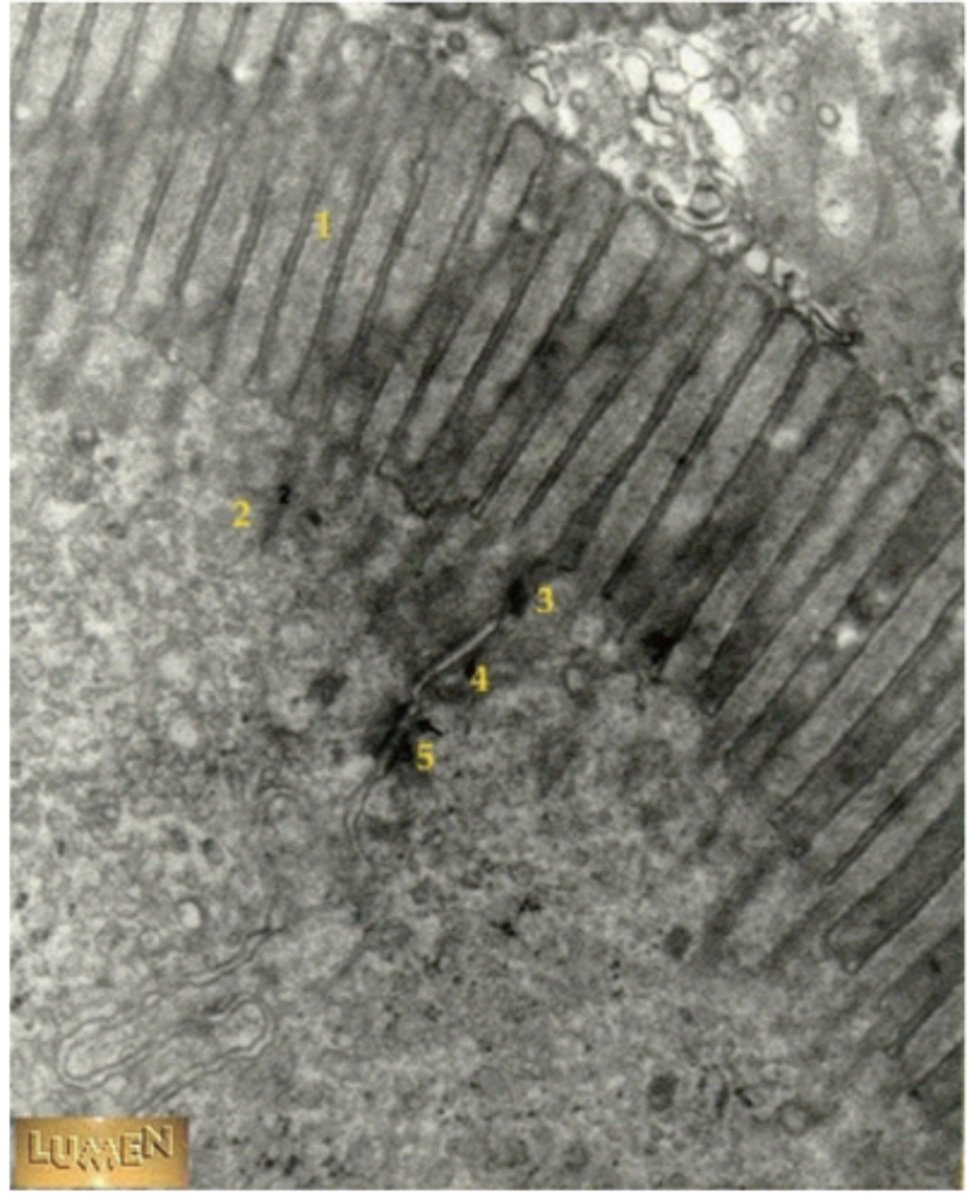
describe the structural adaptations of the small intestine that help increase the rate at which the products of digestions can be absorbed
plicae: folds in the wall of the digestive tract
villi: folds in the epithelium
microvilli: folds in the cell membrane of the intestinal cells
ALL INCREASE SURFACE AREA
acinar cells and islets of langerhans
liver lobule
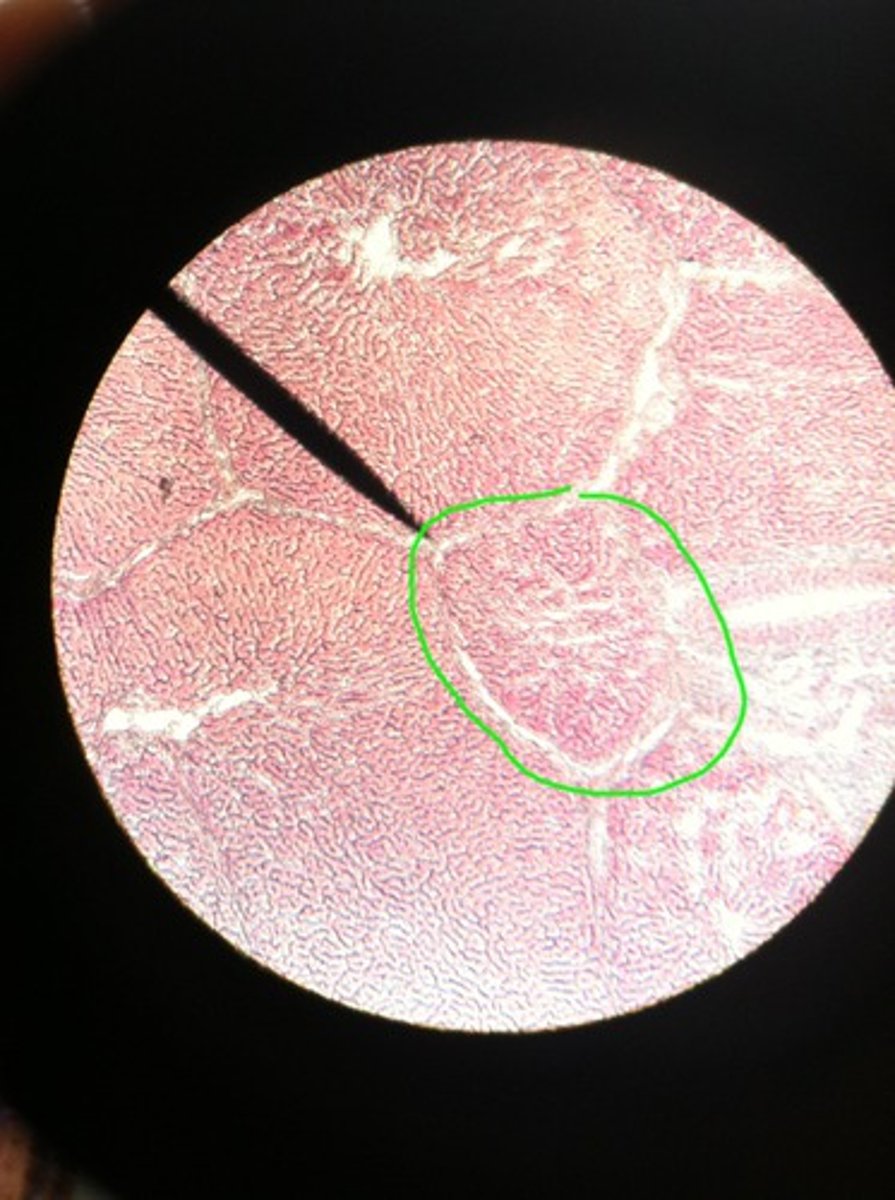
describe several functions of the liver and its anatomical connection to the alimentary canal
production of bile
storage of fat [triglycerides]
storage of carbs [glycogen]
conjugation of toxins to water-soluble molecules
bile stored in gallbladder and delivered to small intestine for emulsification of fat
describe the sources of digestive enzymes along the alimentary canal
salivary glands: amylase, lipase
gastric glands: pepsin
intestinal epithelium: brush border enzymes
pancreas: pancreatic enzymes
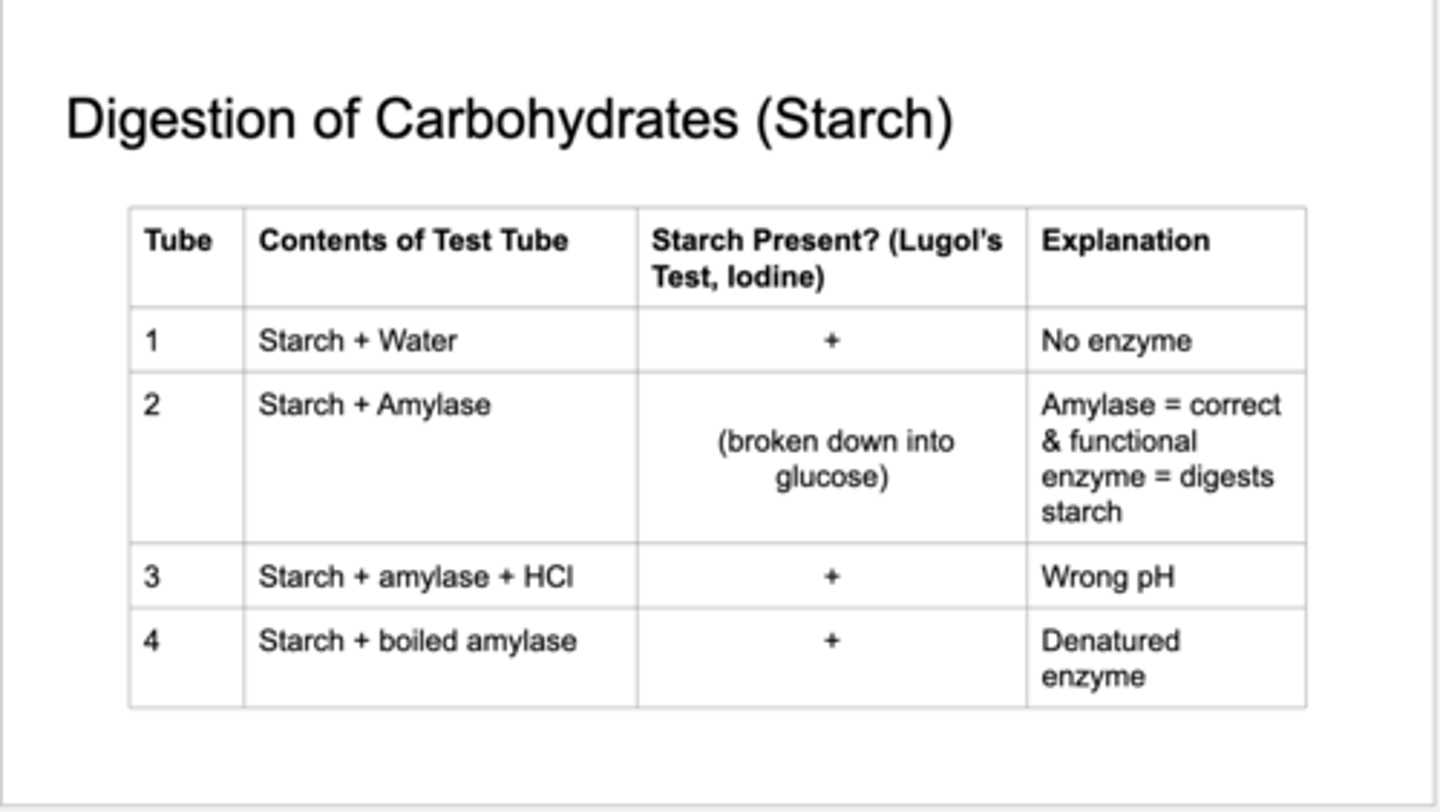
digestion of carbohydrates [starch]
digestion of protein [egg albumin]
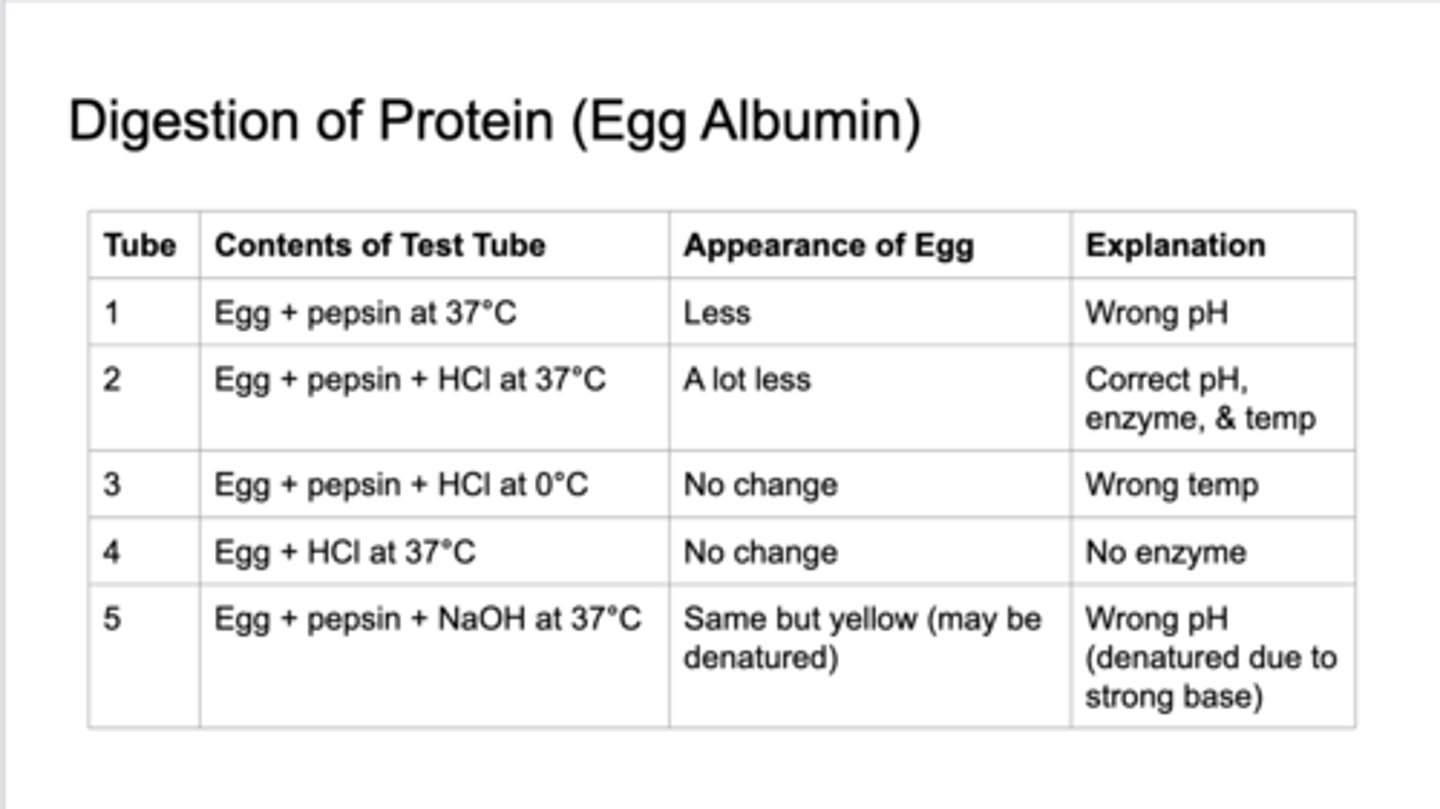
compare the effects of HCl on protein digestion by pepsin vs the effects of HCl on starch digestion by salivary amylase
a low pH environment is essential to the function of pepsin but it prevents the function of salivary amylase
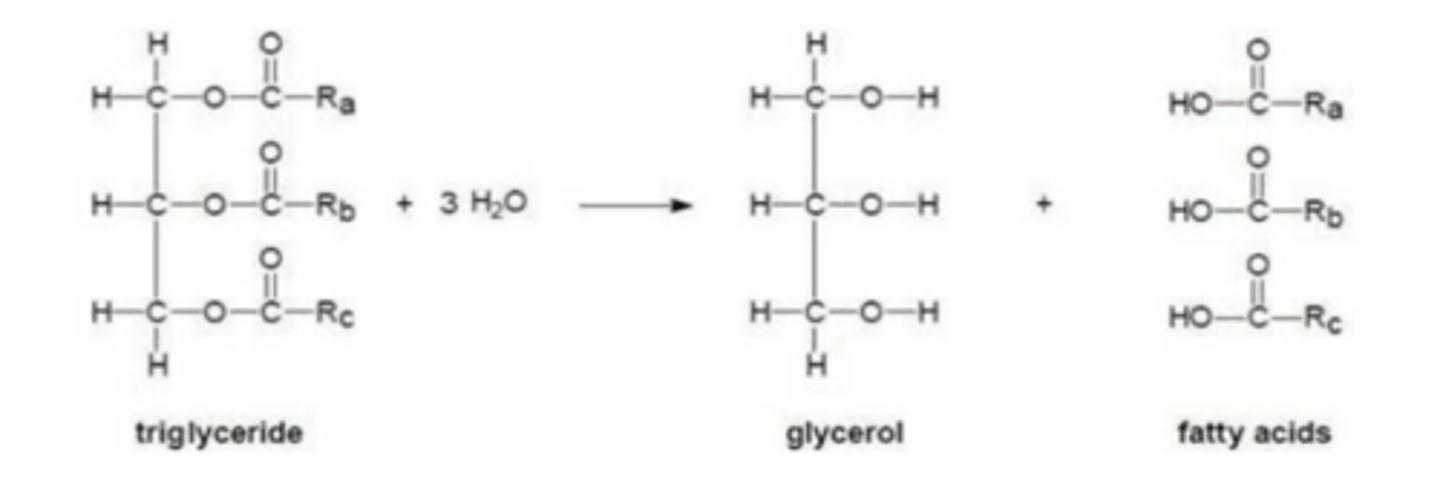
digestion of fat [cream]
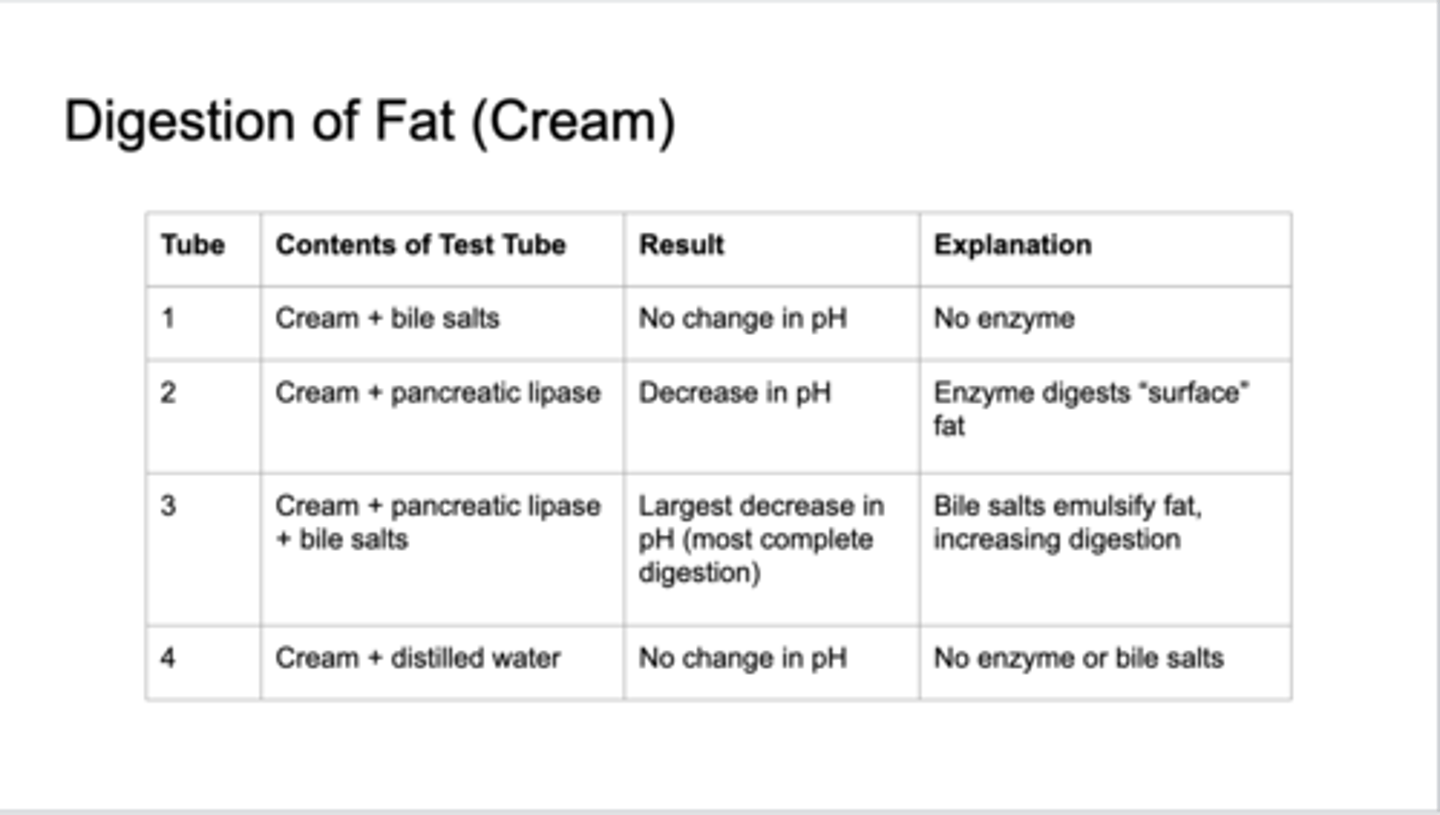
how does fat digestion affect the pH of fluids in the lumen of the alimentary canal?
fat digestion results in the formation of fatty acids and therefore lowers the pH of the lumen of the alimentary canal