Building Blocks - Amino Acids, Carbohydrates, and Vitamins
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
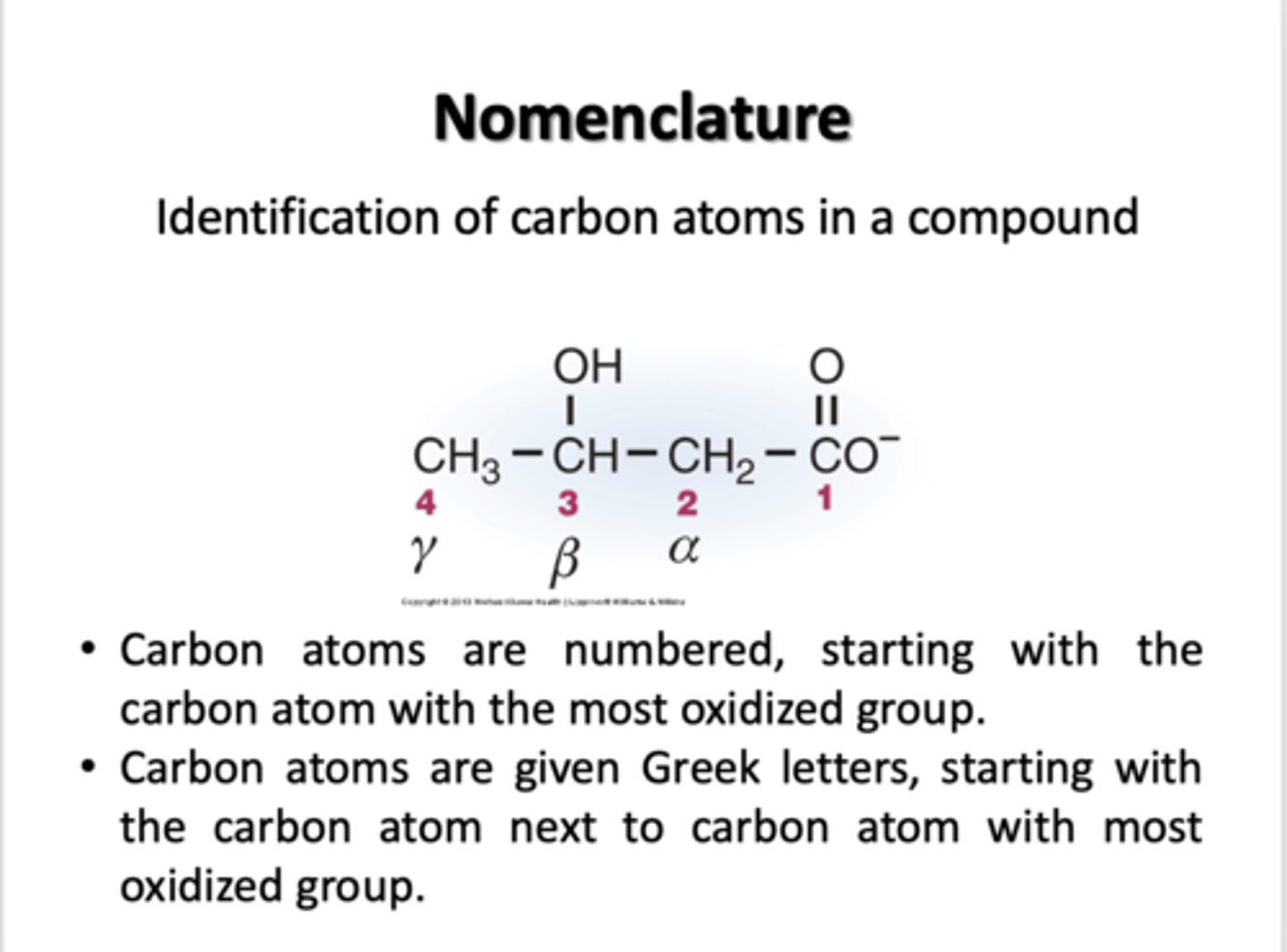
How are carbon atoms identified in a compound?
- Carbon atoms are numbered, starting with the carbon atoms with the most oxidized group
- Carbon atoms are given Greek letters, starting with the carbon next to carbon atom with most oxidized group
What are the simplest carbohydrates known as?
Monosaccharides
What is the empirical formula for monosaccharides?
CnH2nOn
Monosaccharides with 3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 carbon atoms are known as....
Trioses, tetroses, pentoses, hexoses, and heptoses
Simplest sugars can either be...
ketoses or aldoses
What is an isomer?
Compounds composed of the same elements, in the same number, but organized differently through bonding or 3-D spatial arrangement.
What is a chiral center?
A carbon atom with four different functional groups attached to it (asymmetrical center)
What two forms can a simple sugar exist in?
D or L enantiomers (stereoisomers).
What is an enantiomer?
Non superimposable mirror images
Sugars in the human tissue are in the ____ form
D
What are epimers?
Stereoisomers that differ in the position of the hydroxyl group at only one of the asymmetric carbons
Monosaccharides form _______ structures
ring
Six member rings structures of hexoses are knows as __________, while five member ring structures of pentoses and fructose are known as _________.
pyranoses
furanoses
Which carbon is known as the anomeric carbon?
Carbon 1
When the hydroxyl group bound to the anomeric carbon is below the plane, it is in the ______ form.
alpha
When the hydroxyl group of the anomeric carbon is above the plane, it is in the _______ form.
beta
What is it called when alpha and beta forms exist in equilibrium?
Mutarotation
Disaccharides contain two monosaccharides joined together by a......
Glycosidic link
How are glycosidic linkages formed?
The hydroxyl group of the anomeric carbon can react with OH or NH group to form a glycosidic linkage (O or N linked)
What types of glycosidic linkages are there?
1-6, 1-2, or 1-4 linkage. Alpha or Beta.
What is sucrose made up of?
Glucose and fructose joined by a 1a - 2B glycosidic linkage.
What is lactose made up of?
Galactose and glucose joined by a Beta 1-4 glycosidic linkage.
What is maltose made up of?
Two glucose molecules joined by an Alpha 1-4 glycosidic linkage.
What is an oligosaccharide
3 - 12 units of monosaccharides linked together
What is a polysaccharide?
- Linear or branched structures.
- More than 12 units.
- Examples: Starch, glycogen, cellulose
What are the 3 common modifications of carbohydrates?
Methylation, amination, and phosphorylation
What are Glycoproteins?
- Sugars attached to proteins.
- Found in cell membranes
- Functions in cell adhesion
Where do the sugars of glycoproteins attach to on the protein?
The amide nitrogen of asparagine or the oxygen atom of serine or threonine residues.
What are Proteoglycans?
- Repeating units of glycosaminoglycans (disaccharide containing a derivative of an amino sugar)
- Attached to protein - known as proteoglycans
What are proteoglycans important components of?
Cartilage
What are vitamins?
Organic molecules that are needed in small amounts in the diets of some higher animals. (Can not be synthesized in some higher organisms).
What can vitamin deficiency cause?
Diseases
How are vitamins grouped?
According to whether they're soluble in water or in nonpolar solvents. (water soluble and fat soluble vitamins).
Many enzyme cofactors are derived from....
water soluble vitamin precursors
What is the importance of cofactors?
They are required for some enzymes to function
Thiamine (B1)
Aldehyde Transfer
Consequence of Thiamine (B1) defficiency?
Beriberi (weight loss, heart problems, neurological disfunction)
Riboflavin (B2)
Oxidation-reduction
Consequence of Riboflavin (B2) deficiency?
Cheliosis and angular stomatitis (lesions of the mouth), dermatitis
Pyridoxine (B6)
Group transfer to or from amino acids
Consequence of Pyridoxine (B6) deficiency?
Depression, confusion, convulsions
Nicotinic acid (niacin) (B3)
Oxidation-reduction
Consequence of Nicotinic acid (niacin) (B3) deficiency?
Pellagra (dermatitis, depression, diarrhea)
Pantothenic acid (B5)
Acyl-group transfer
Consequence of Pantothenic acid deficiency?
Hypertension
Biotin (B7)
ATP-dependent carboxylation and carboxyl-group transfer
Consequence of Biotin (B7) deficiency?
Rash about the eyebrows, muscle, pain, fatigue (rare)
Folic acid (B9)
Transfer of one-carbon components - thiamine synthesis
Consequence of Folic acid (B9) deficiency?
Anemia, neural-tube defects in development
Cobalamin (B12)
Transfer of methyl groups; intramolecular rearrangements
Consequence of Cobalamin (B12) deficiency?
Anemia, pernicious anemia, methylmalonic acidosis
What cofactors are involved in Carbonyl/Acyl group transfer reactions?
Pantothenate (B5) and Thiamine (B1)
What cofactors are involved in oxidation-reduction reactions?
Nicotinic acid (B3) and Riboflavin (B2)
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino Acids
How many amino acids are there?
20 standard amino acids
Only ____ amino acids are incorporated into proteins
L
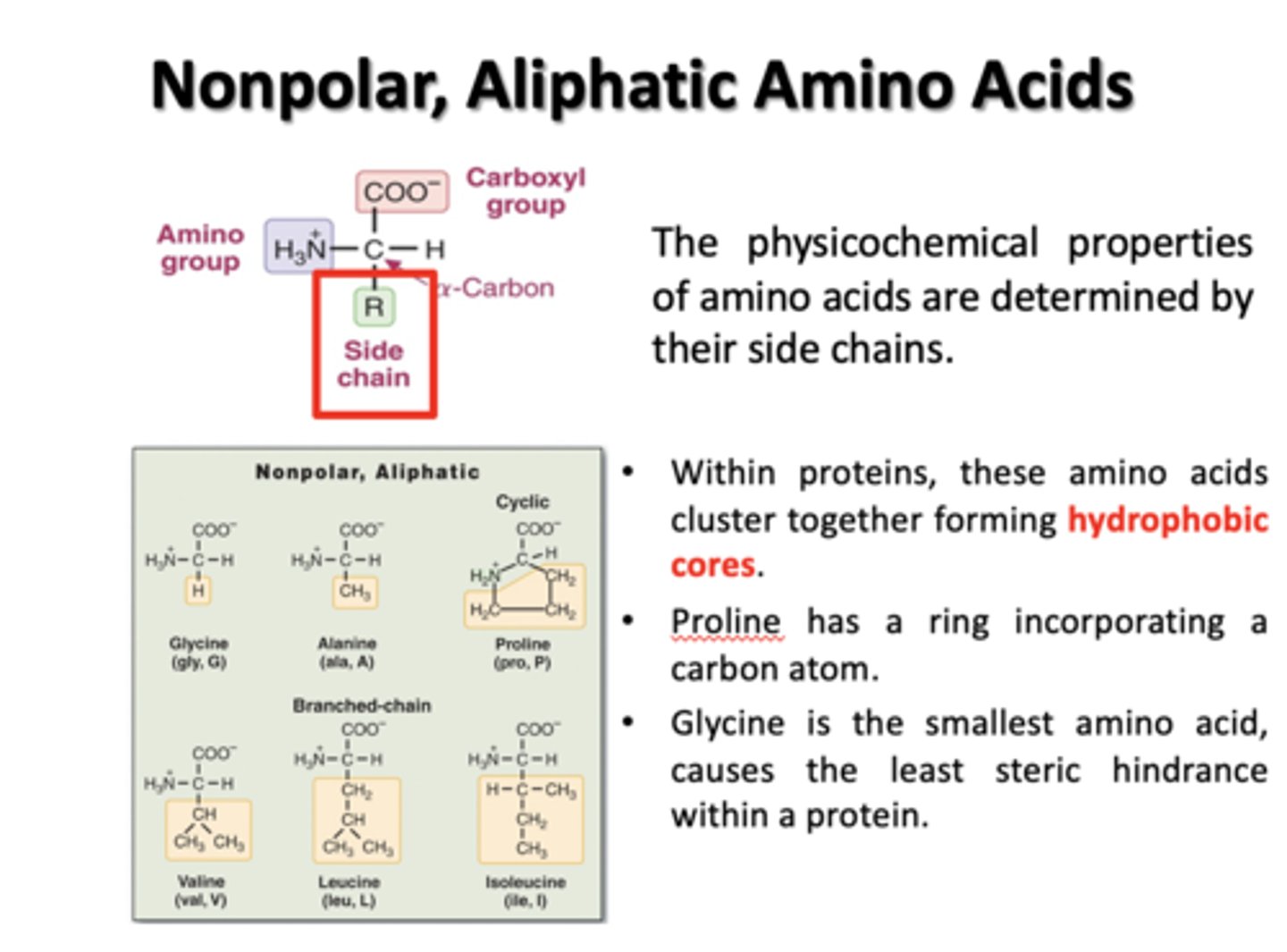
Nonpolar, Aliphatic Amino Acids
Glycine, Alanine, Proline, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine
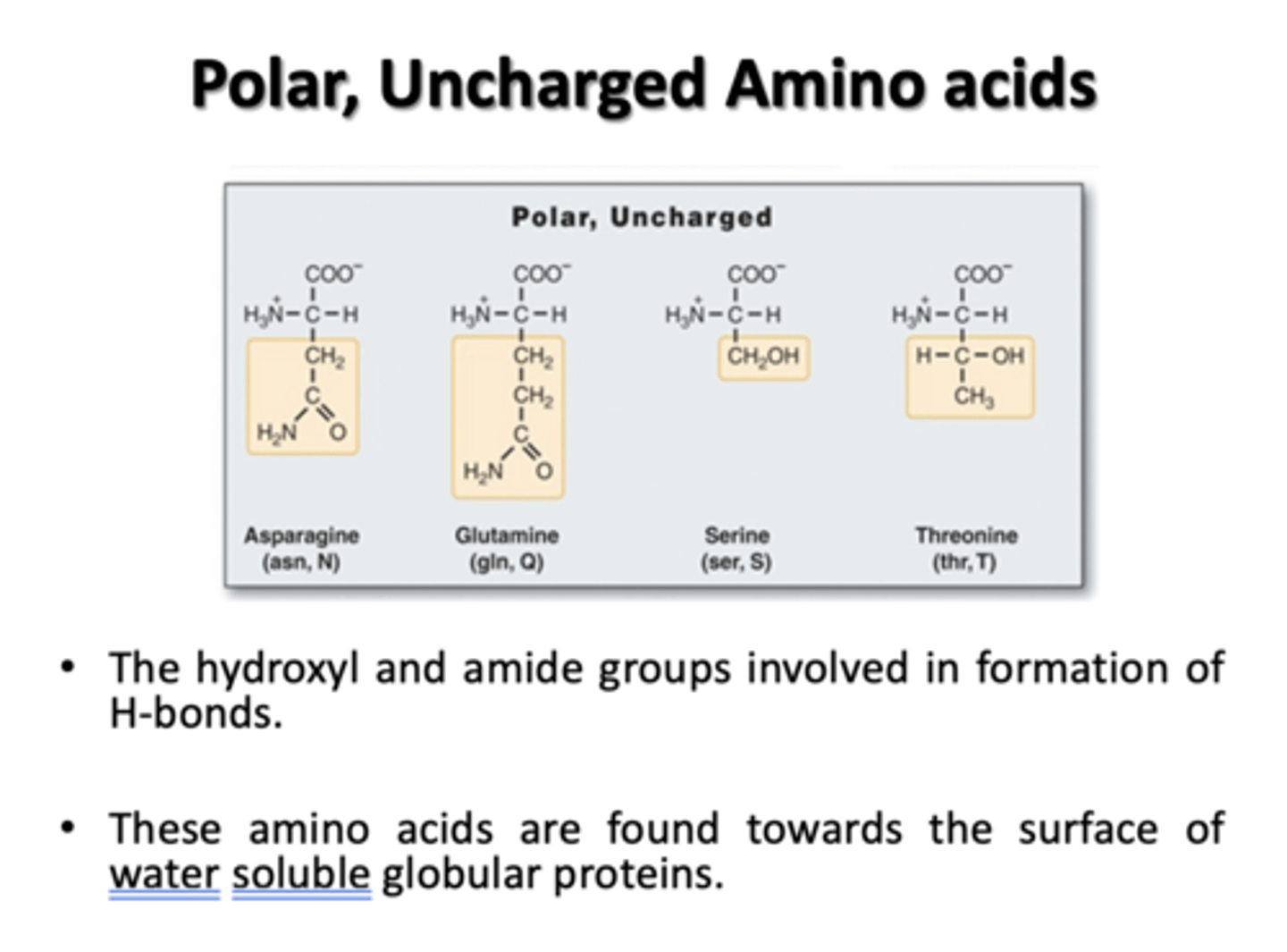
Polar, Uncharged Amino Acids
Asparagine, Glutamine, Serine, Threonine
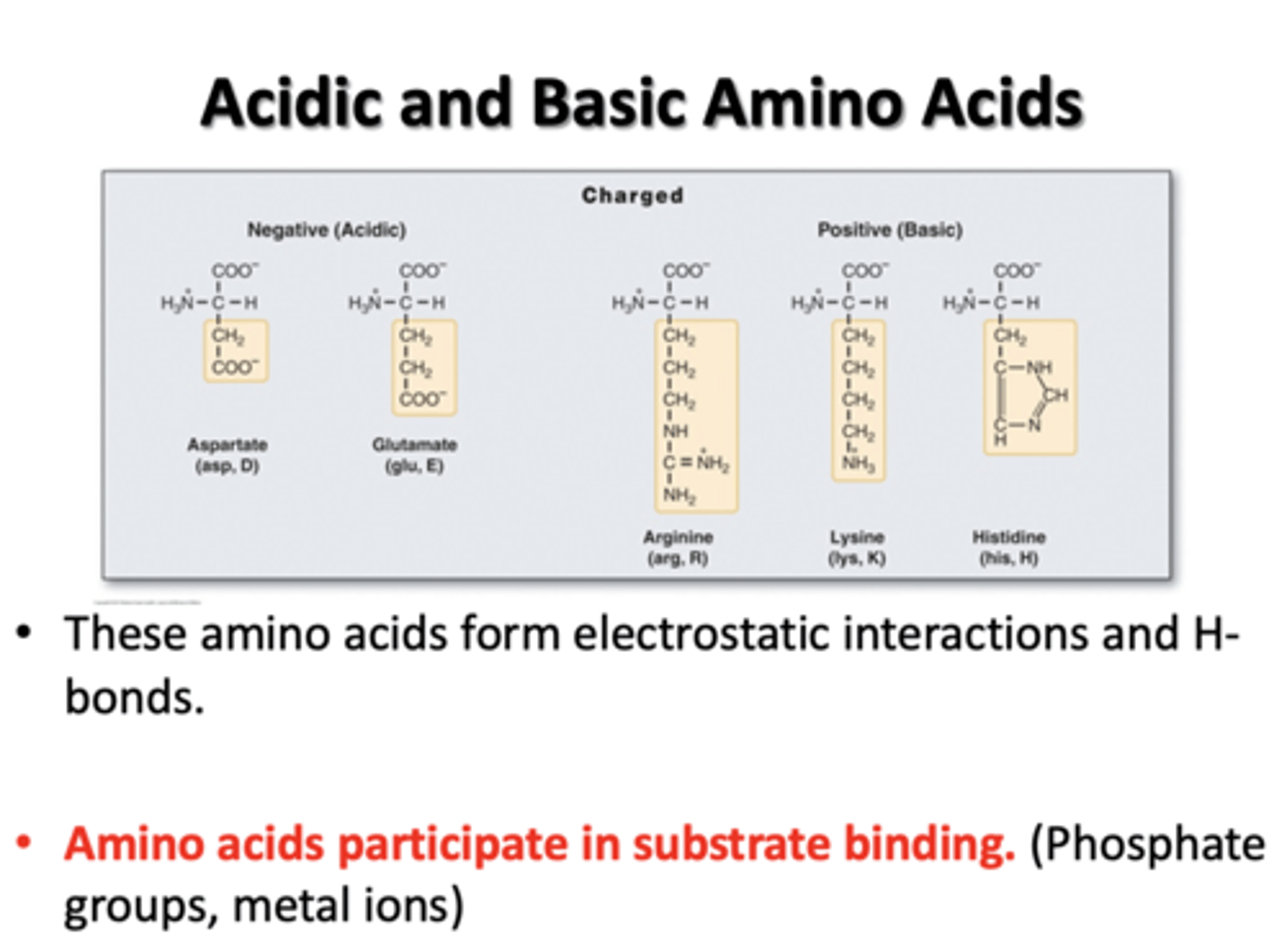
Acids and Basic Amino Acids
Aspartate, Glutamate, Arginine, Lysine, Histidine
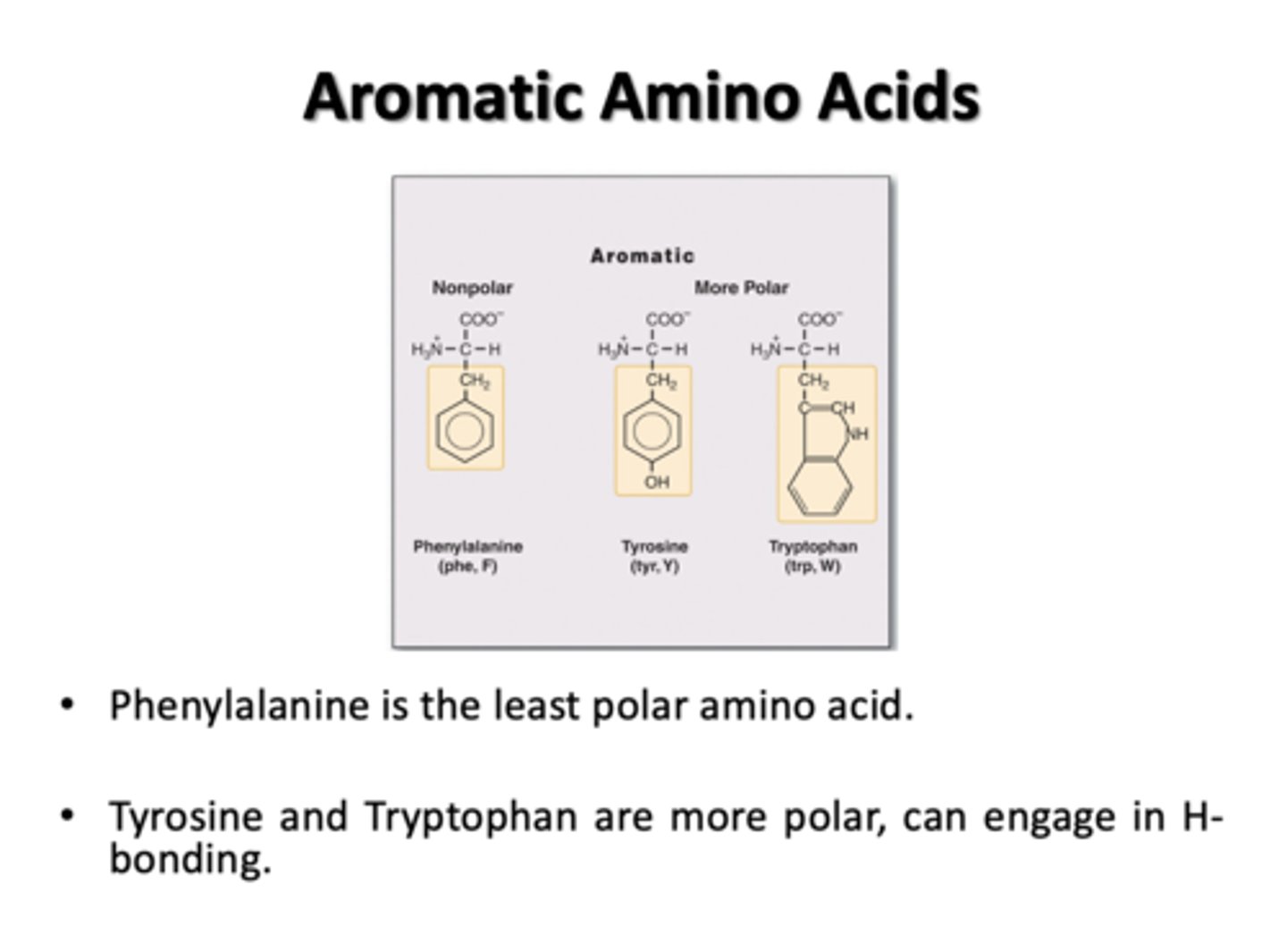
Aromatic Amino Acids
Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
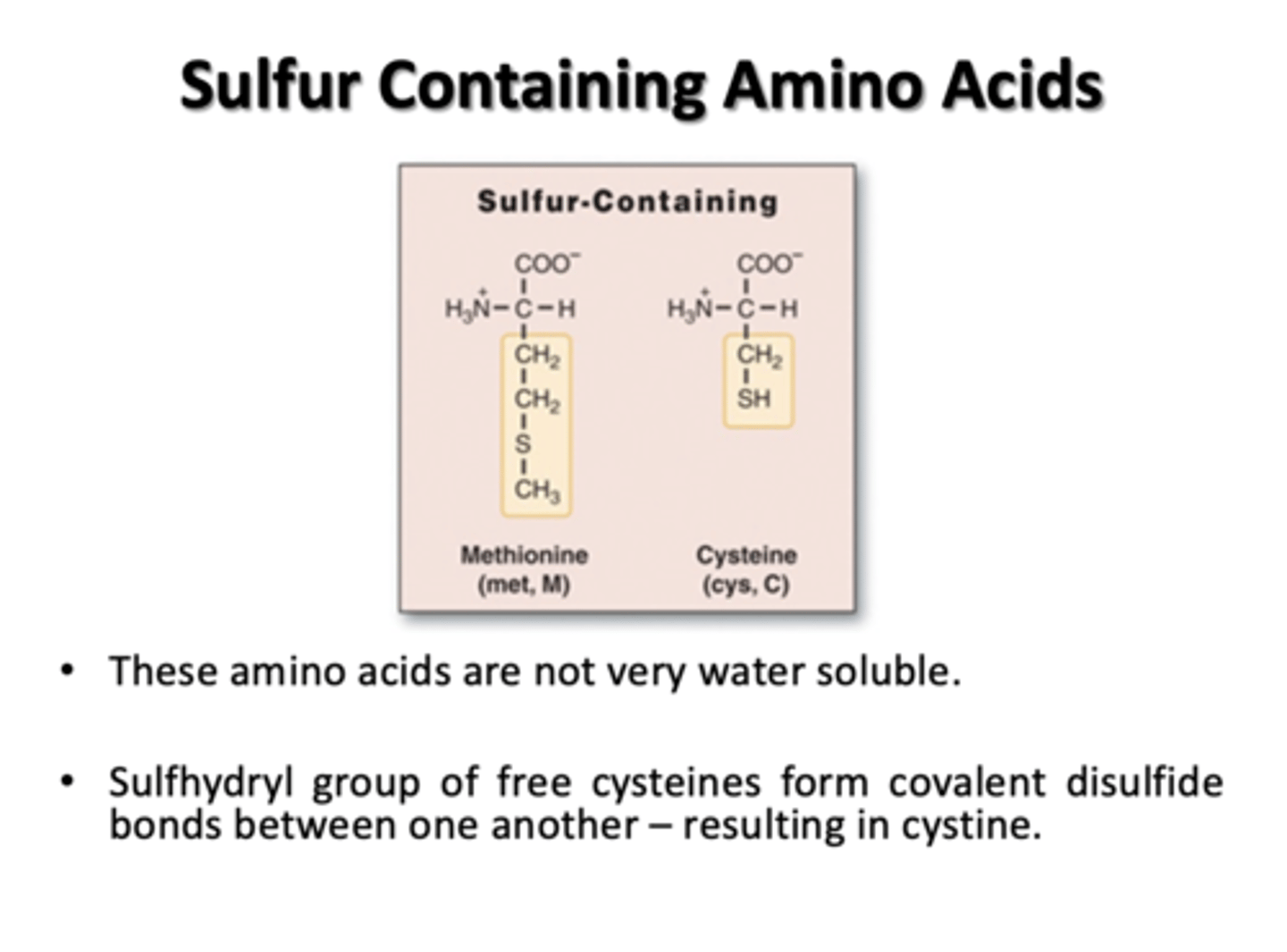
Sulfur Containing Amino Acids
Methionine and Cysteine
Amino acids and heterocyclic rings contain nitrogens, which carry a __________ charge at neutral pH.
positive
Nucleosides consist of a ______________ _______ attached to a sugar.
heterocyclic ring
A nucleoside plus ___________ is a nucleotide
phosphate