Toxicology: Chapters 10
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Formic acid
The toxic compound that causes urticaria after it is injected into your skin by nettle cells of Stinging nettle
You need repeated exposure to it to activate the immune system to get an allergic reaction
Urushiol is the plant toxin in Poison Ivy. What is the specific toxicity of this compound?
They are agonists or antagonists of the acetylcholine receptor
Many plant alkaloids are neurotoxins; what is the specific mechanism of these alkaloids
The active compound in the plant makes your pupils dilate, which is considered to make females look more attractive
How did the plant Belladonna get its name?
Organophosphorous pesticides inhibit the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which prolongs the residence time of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft; atropine blocks the acetylcholine receptor, thus reducing overstimulation caused by too much neurotransmitter
The plant alkaloid atropine is used to treat patients who suffer from overdoses of organophosphorous compounds. How does this work?
they both are acetylcholine receptor AGONISTS
Cytisine is a plant toxin found in Laburnam; the mechanism of toxicity is comparable to nicotine, which is:
Monocrotaline
Example of a plant alkaloid that is NOT a neurotoxin.
It causes veno-occlusive disease: a pathology of the liver that results in cirrhosis
What is the toxic action of monocrotaline?
They have complex molecular structures that makes it very difficult to synthesize them
Pennyroyal is an example of a group of plants that produce terpenoids; what are these compounds known for?
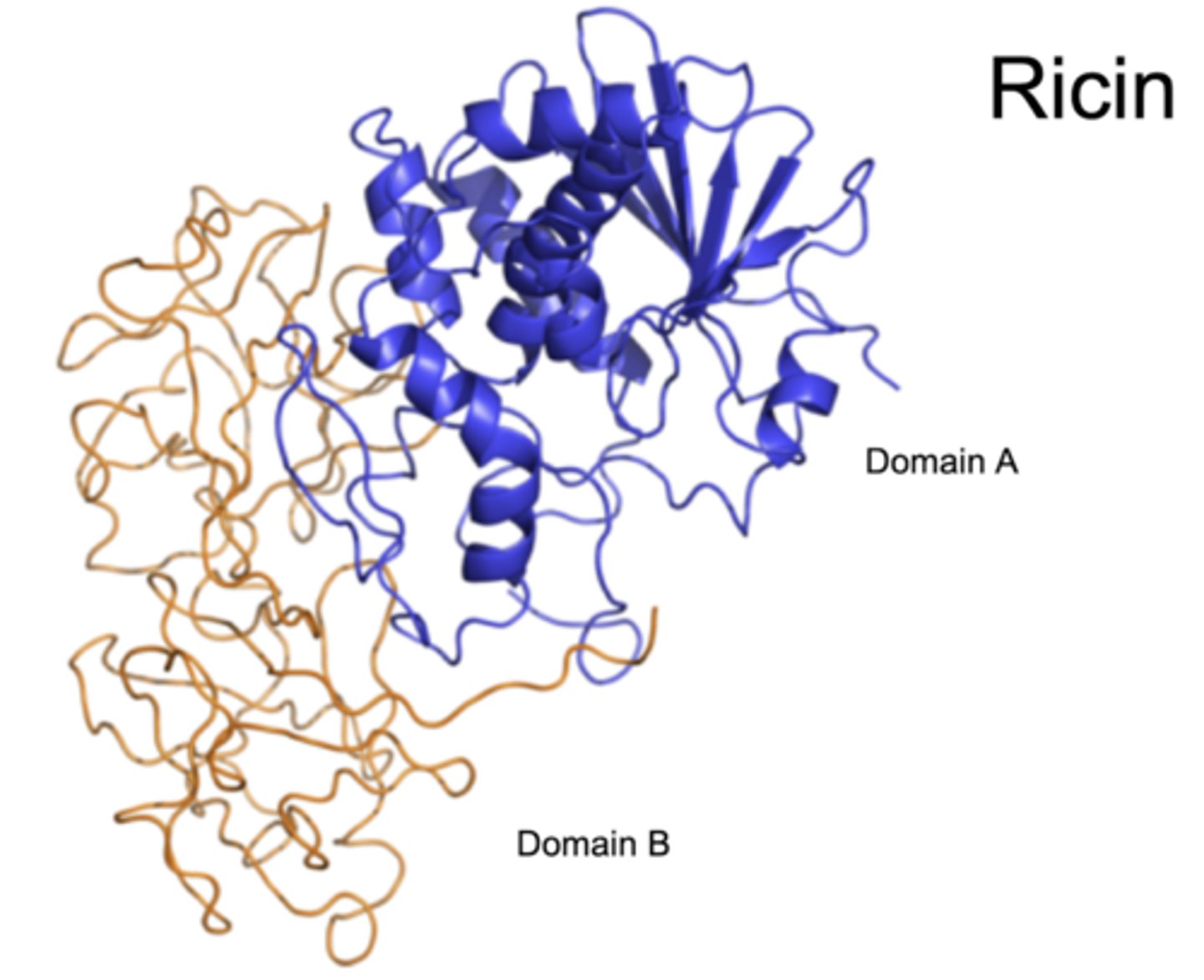
The toxic action consists of non-specific inhibition of protein synthesis, which is essential for all living cells
Ricin is a plant toxin derived from Castor oil beans; it is very toxic because:
Because it is difficult to disperse, and humidity and UV light quickly destroy the compound when released into the environment
Ricin was investigated for use as an agent in chemical warfare. Despite its high toxicity ti was deemed not suitable for large scale war applications. Why was that?
Stomach cancer and vitamin B1 deficiency
What are the 2 potential toxic effects of eating Braken Fern?
Because toxic mushrooms may look like edible ones, which can lead to unintentional poisoning
Why is eating wild mushrooms not without risk?
Enzymes that paralyze prey species
Snake venoms are species-specific mixtures of what kind of compounds?
It blocks the Na channels on axons and leads to respiratory failure
Tetrodotoxin is a natural poison that is found in a variety of marine species. What is the mode of action?
A cyanide-containing compound which tastes like almonds (amygdalin)
The toxin in seeds of peaches and apples consists of:
The root is ground up, which releases an enzyme that breaks down the linamarin; the toxic cyanide group is then washed out and remaining cassava pulp is used in food preparation
Linamarin is a toxic compound in cassava root, which is a food staple in many African countries. How is the cassava root made edible?
The toxin produced by the Tetanus bacterium
Lockjaw is a very severe neurological disease. What causes it?
When they are filtering water that contains large amounts of toxic dinoflagellate algae, especially during algal blooms in coastal waters that receive excessive amounts of nutrients
Seafood, and especially shellfish like oysters and mussels, can create a human health issue when they contain toxins like brevetoxin and domoic acid. Under what conditions do these toxins accumulate in shellfish?
Painful vasoconstriction in toes and fingers
Ergot is a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. The toxin that is produced by this fungus causes:
Because ragwort contains alkaloids that can be broken down to reactive metabolites, causing hepatocyte damage and liver cirrhosis
Ragwort (Senecio jacobea) is sometimes used in herbal teas. Why do you want to be careful with drinking this tea?
The main categories of natural toxins
Bacterial, molds/fungi, plants, and animals.
How do plant toxins typically function in nature?
They provide protection against herbivores.
Common effects of plant toxins on the skin
Allergic reactions and dermatitis.
What organ systems can be affected by plant toxins?
Skin, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, liver, kidneys, nervous system.
Name three well-known plant toxins.
Nicotine, caffeine, and opium/morphine.

What is urushiol and what plant is it associated with?
Urushiol is a toxin in poison ivy that causes contact allergies.
What is the mechanism of action of atropine?
It is an acetylcholine receptor antagonist that blocks parasympathetic nerves.
What are the effects of coniine, found in hemlock?
It is a neurotoxin that causes muscle paralysis.

What is monocrotaline and its effects?
A pyrrolizidine alkaloid that can cause veno-occlusive disease and liver cirrhosis.
What is ricin and its lethal dose?
A protein toxin with an LD50 of 0.2 mg in humans, causing severe diarrhea and vomiting.
How does ptaquiloside from bracken fern affect health?
It is a carcinogen linked to throat and stomach cancer.
What is the role of cyanides in toxicity?
Cyanides inhibit the electron transport chain.
What is the significance of ergot (Claviceps purpurea)?
It produces lysergic acid, a precursor for LSD, and causes vasoconstriction.
What are the effects of alpha-amanitin from Amanita phalloides?
It inhibits RNA polymerase, leading to liver and kidney failure.
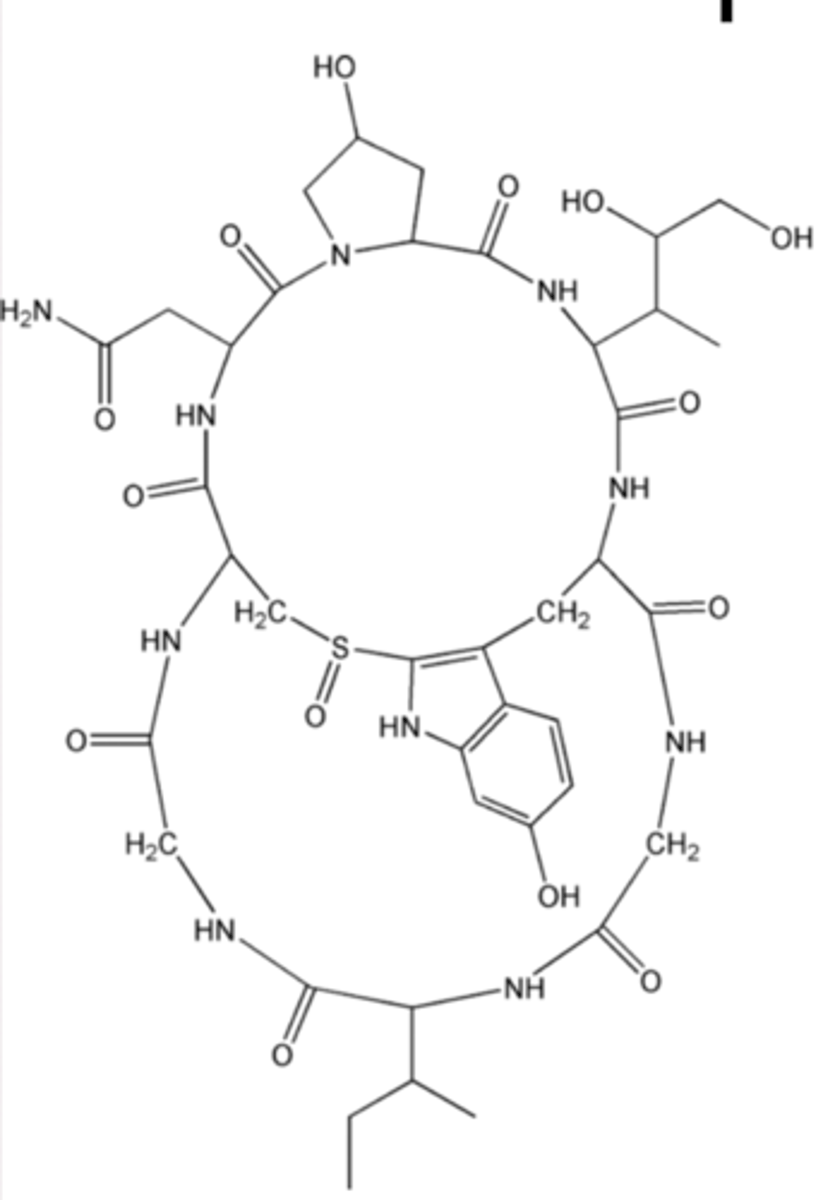
What is the function of snake venom?
It contains enzymes that affect the cardiac system and muscle control of prey.
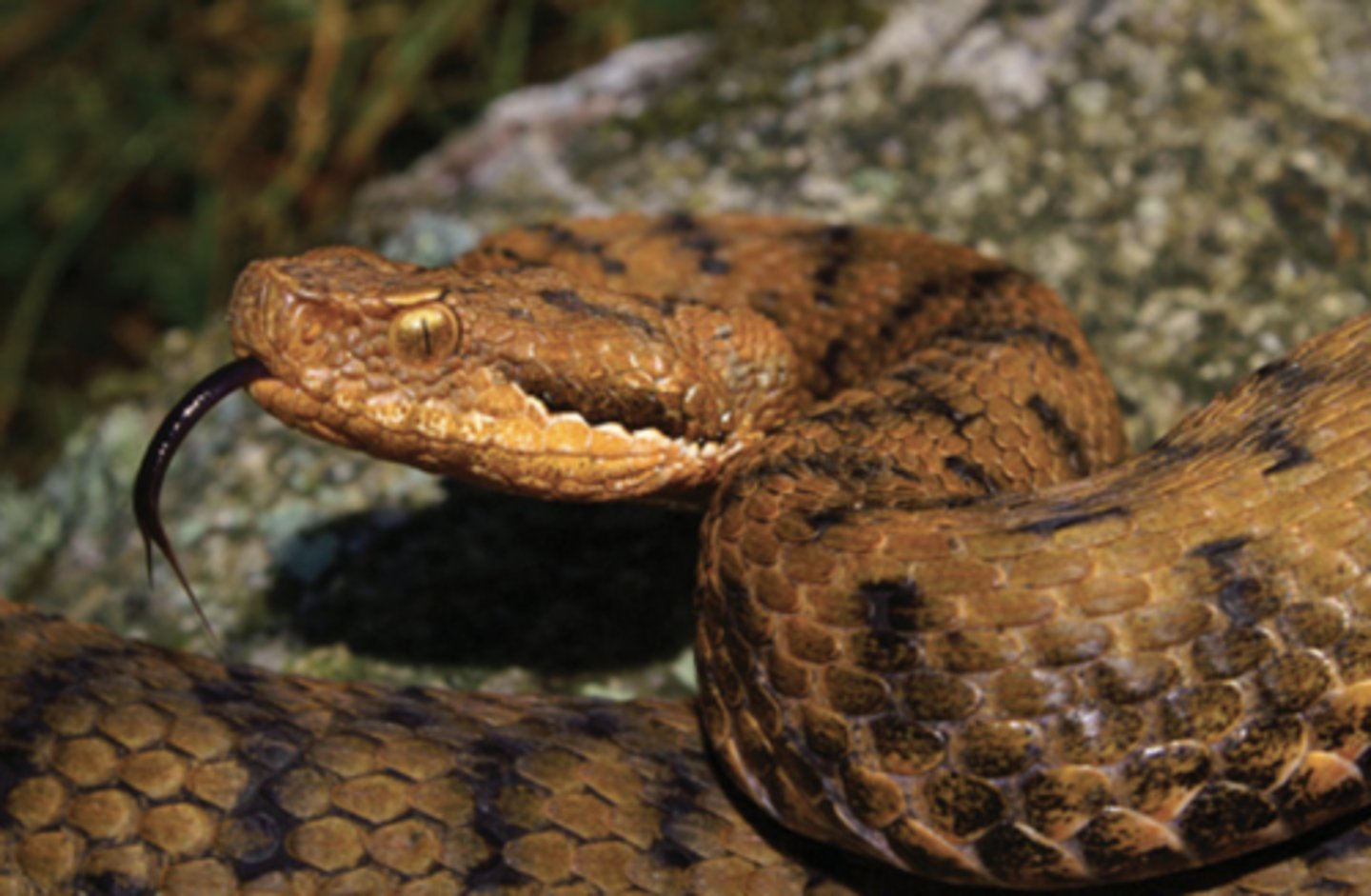

Phosphodiesterases
Affect prey's cardiac system, mainly to lower the blood pressure.
Cholinesterase
Inhibitors, to make the prey lose control of
its muscles.
Hyaluronidase
Increases tissue permeability to increase the rate that other enzymes are absorbed into the prey's tissues.
What is tetrodotoxin and its source?
A potent neurotoxin found in puffer fish that blocks sodium channels.
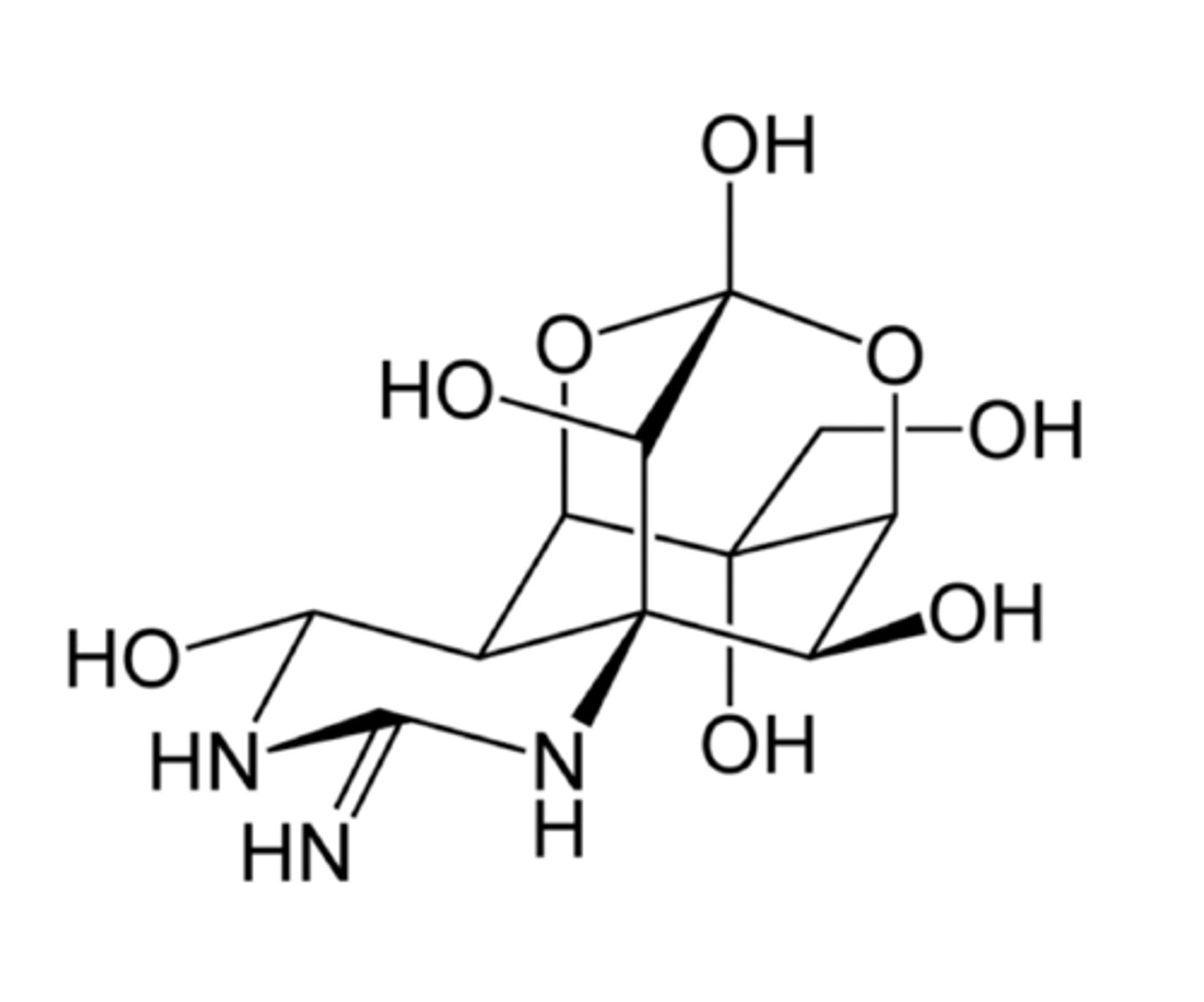
What is the medical use of botulinum toxin?
It is used in Botox for cosmetic procedures.
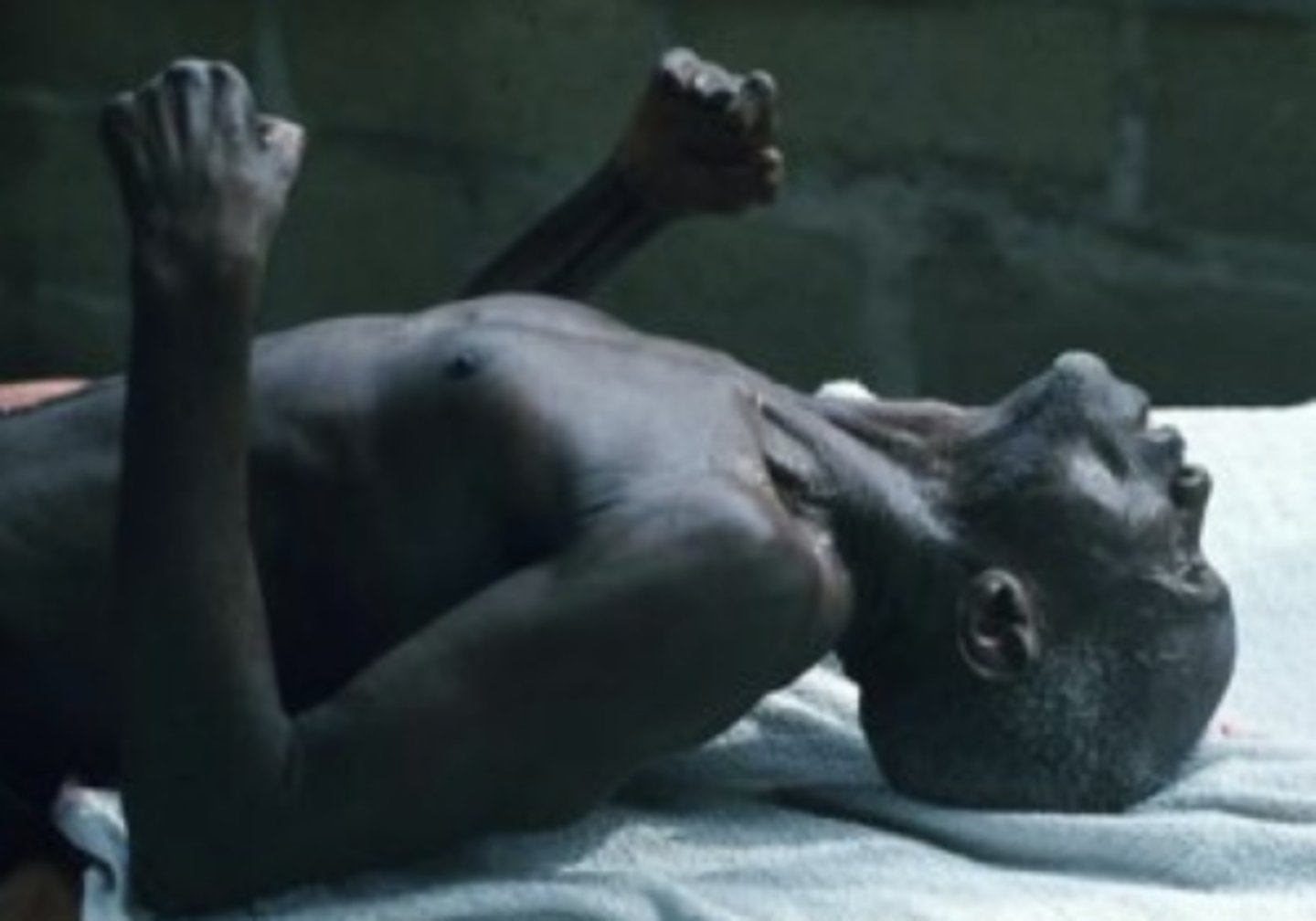
What are the effects of tetanus toxin?
It blocks the release of GABA and glycine, causing muscle spasms.

What are algal toxins and name one example?
Toxins produced by algae; examples include microcystin and saxitoxin.