Bio 2 Lab Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:06 AM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
1
New cards
Taxonomy
using anatomical, functional, and genetic relationships to classify and name organisms
2
New cards
Taxon
any group or rank in a biological classification into which related organisms are classified
3
New cards
Dichotomy
the division into two mutually exclusive, opposed, or contradictory groups
4
New cards
Couplets
two choices in each step of a dichotomous key
5
New cards
Binomial nomenclature
system in which the latin names for individual species are written
6
New cards
Phylogenetic tree
branching diagram or tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species
7
New cards
Clade
group of taxa that share the same common ancestor
8
New cards
Character table
determine in which lineage a character first appeared
9
New cards
In-group
taxa of interest
10
New cards
Out-group
taxon that diverged early on in the lineage and will not have shared characteristics with in groups
11
New cards
Rooted phylogenetic tree
all taxa descend from one ancestor lineage
12
New cards
Polytomy
branch point with more than two descendants
13
New cards
Theory of maximum parsimony
states that the polygenetic tree should be drawn with the fewest evolutionary events
14
New cards
Basic characteristics of bacteria
naming is partly based on cell shape
small in size
no membrane-bound organelles
unicellular
small in size
no membrane-bound organelles
unicellular
15
New cards
Bacillus subtilius
gram positive bacillus
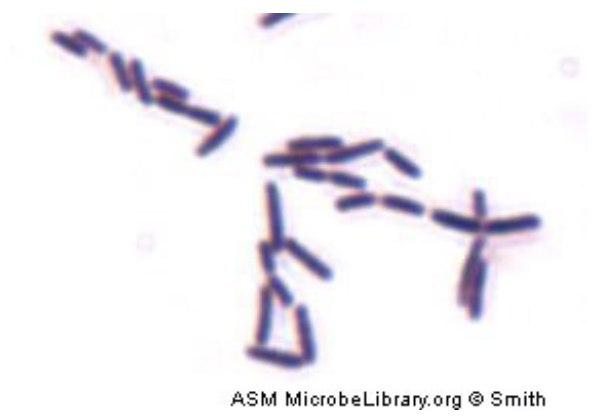
16
New cards
E coli
gram negative bacillus
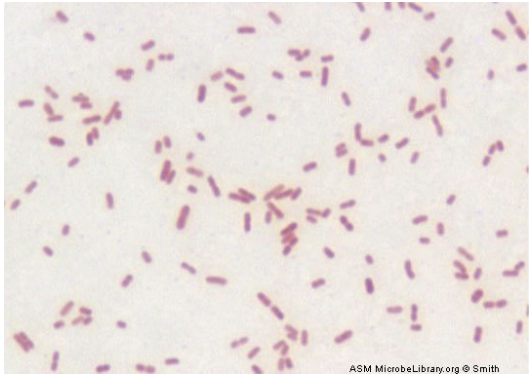
17
New cards
Staphylococcus epidermis
gram positive coccus
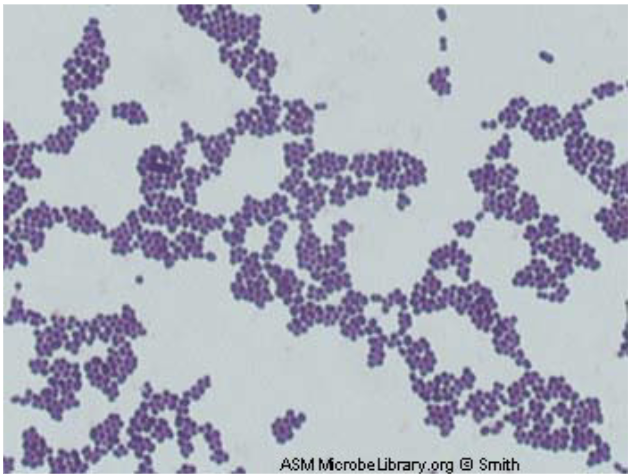
18
New cards
A bacteria stains gram positive if
It has a lot of peptidoglycan
19
New cards
Crystal violet is used for…
primary stain
20
New cards
When gram staining iodine is used for…
locking in the purple, fixant
21
New cards
When gram staining acetone alcohol is used for…
removes purple from some cells
22
New cards
When gram staining safranin is used as a…
counterstain
23
New cards
What are basic characteristics of fungi?
Non-mobile, non-photosynthetic, cell walls made of chitin
24
New cards
Phylum Oomycota
ex) water mild, saprolegnia
Repro structure: oogonium
Spore: oospore
Protists
Repro structure: oogonium
Spore: oospore
Protists
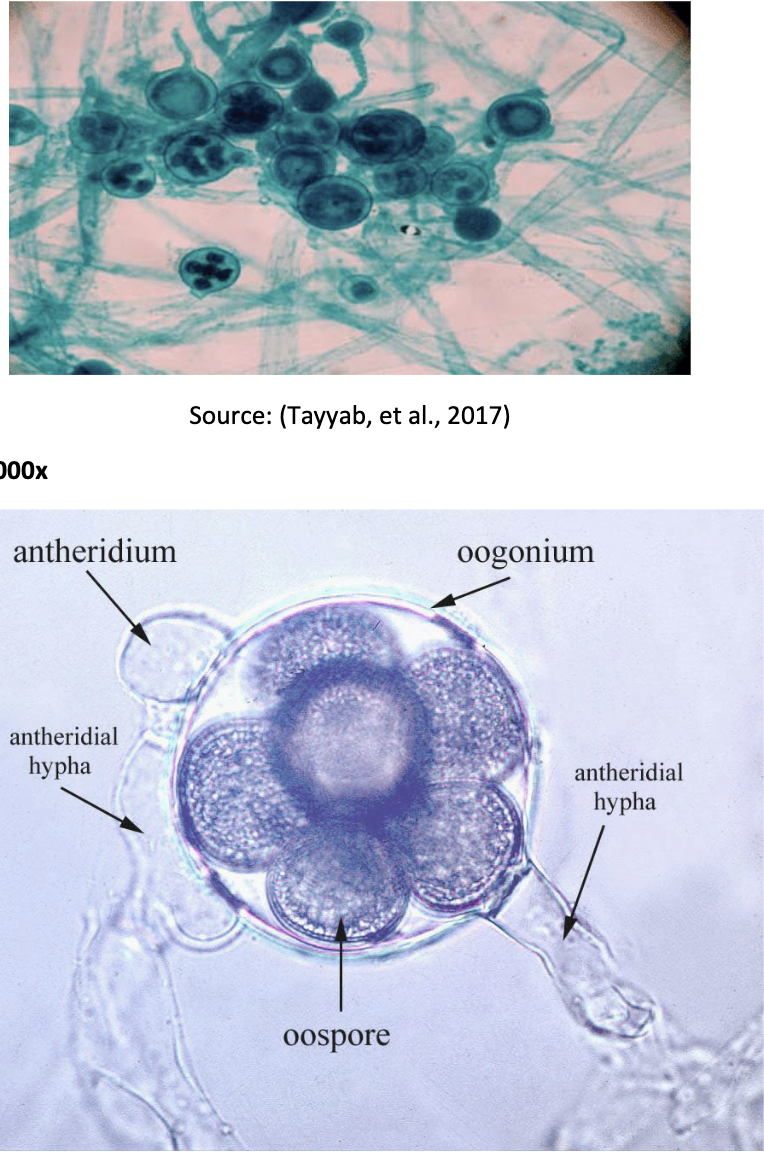
25
New cards
Zygomycota
ex) Rhizopus
asexual repro structure: sporangiophore
asexual Spore: sporangiospore
sexual repro structure: sporangium
sexual spore: zygospore
asexual repro structure: sporangiophore
asexual Spore: sporangiospore
sexual repro structure: sporangium
sexual spore: zygospore
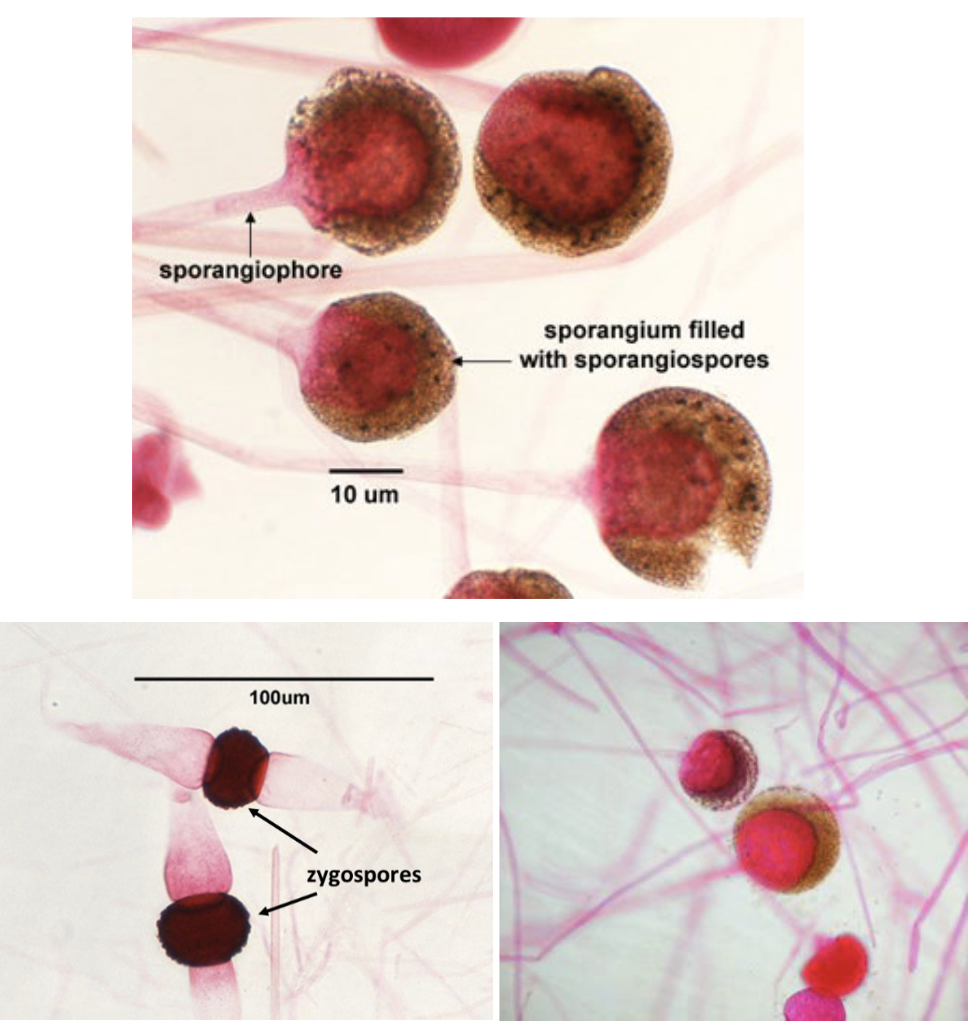
26
New cards
Phylum Basidiomycota
ex) Coprinus
repro structure: basidiocarp
spore: basidiospore
repro structure: basidiocarp
spore: basidiospore
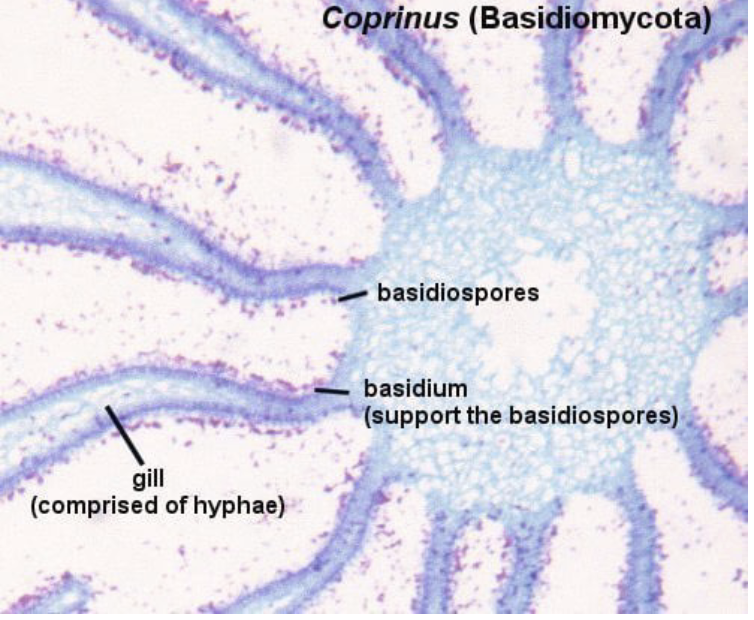
27
New cards
Phylum Ascomycota
ex) Peziza
repro structure: ascocarp
spore: ascospore
repro structure: ascocarp
spore: ascospore
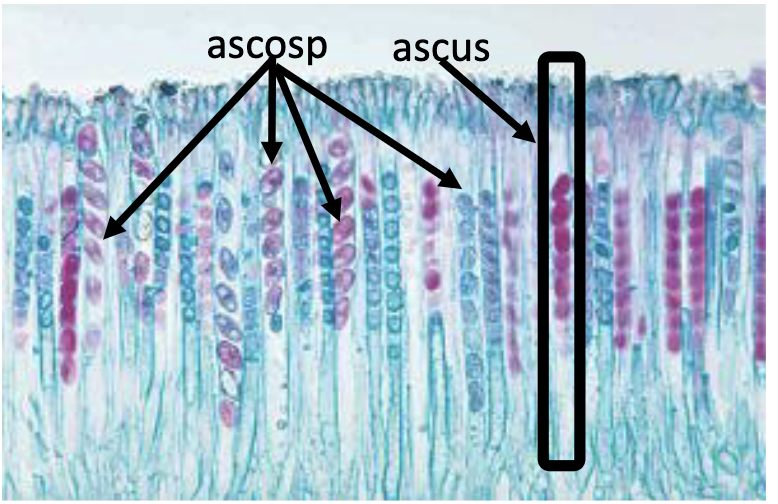
28
New cards
Ascomycota
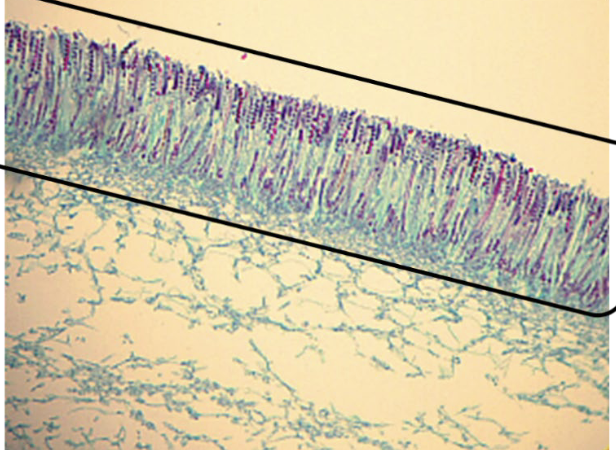
29
New cards
Phylum Ascomycota “Imperfect Fungi”
ex) Aspergillus
repro structure: condidiophore
spore: conidia
repro structure: condidiophore
spore: conidia
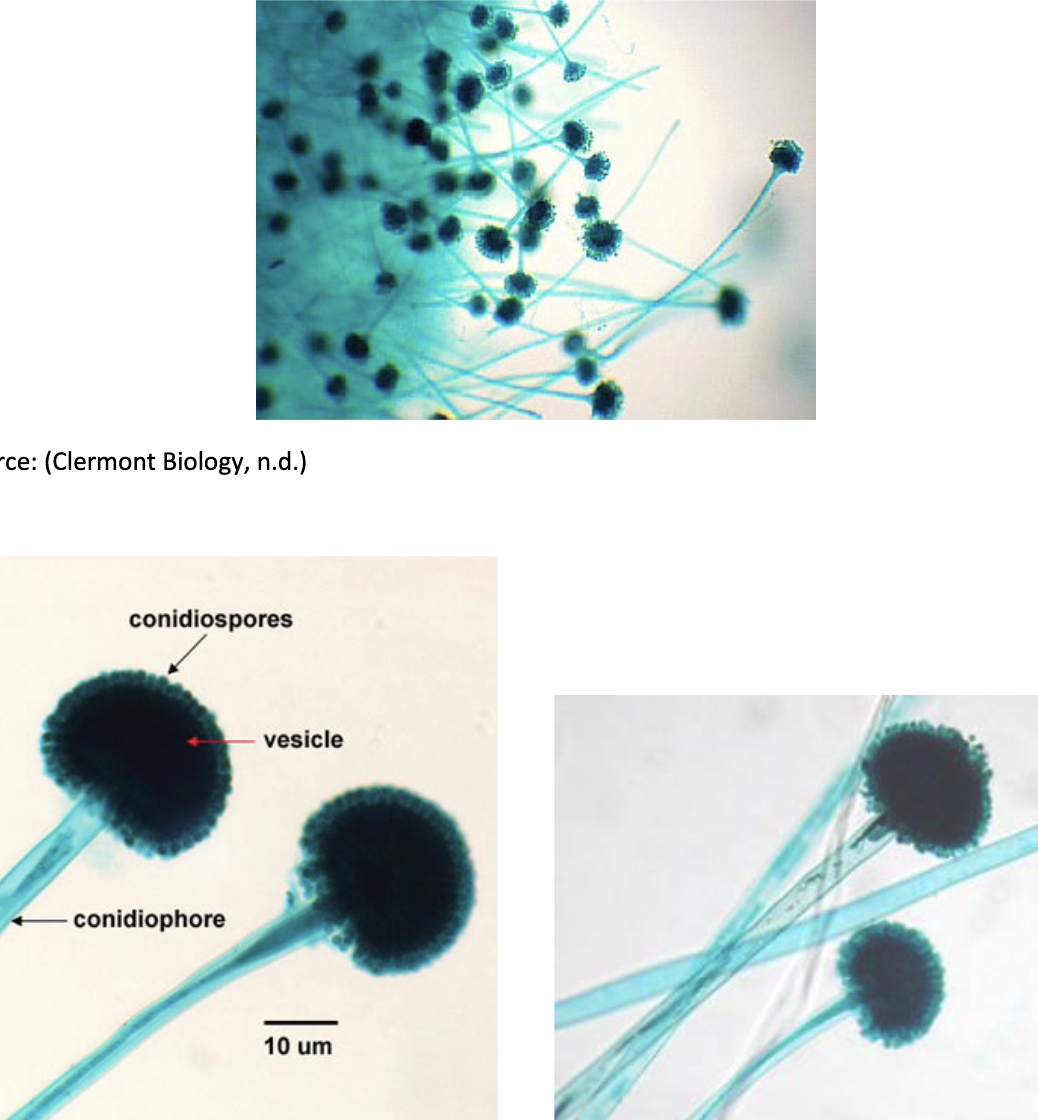
30
New cards
Phylum Ascomycota “Imperfect Fungi”
ex) Penicillium
repro structure: condidiophore
spore: conidia
repro structure: condidiophore
spore: conidia
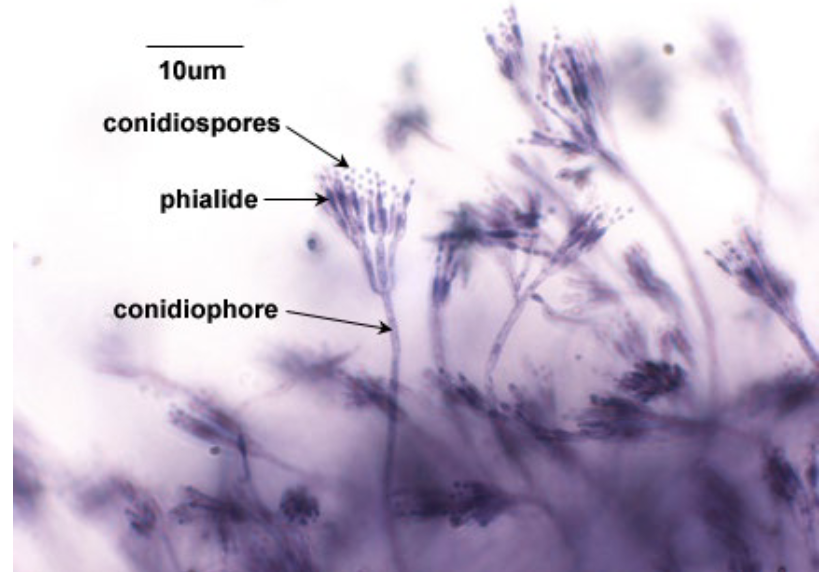
31
New cards
Lichen
mutualistic relationship between fungi and photosynthetic (algal) organisms
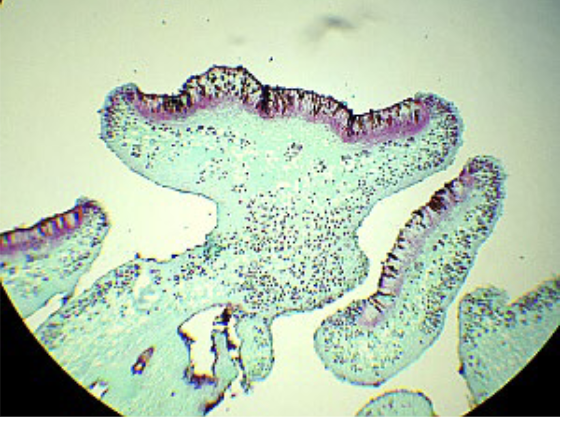
32
New cards
Phylum Ascomycota
ex) yeast
Yeast reproduce asexually by budding. Yeast also reproduce sexually by forming an ascus and eight ascospores.
Yeast reproduce asexually by budding. Yeast also reproduce sexually by forming an ascus and eight ascospores.
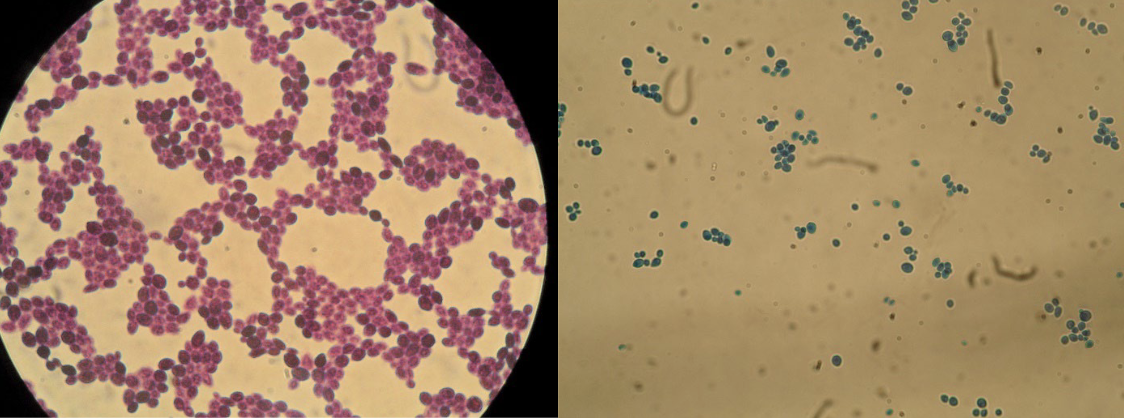
33
New cards
Monocot characteristics
flowering parts in groups of 3
leaves are long and tappered (parallel veins)
1 cotyledon
leaves are long and tappered (parallel veins)
1 cotyledon
34
New cards
Dicot characteristics
flowering parts in groups of 4-5
leaves have branched veins
2 cotyledons
leaves have branched veins
2 cotyledons
35
New cards
Hyphae
each of the branching filaments that make up the mycelium
36
New cards
Mycelium
mesh-like feeding body made of hyphae
37
New cards
Rhizoids
specialized root-like hyphae which anchor the fungi into its substrate
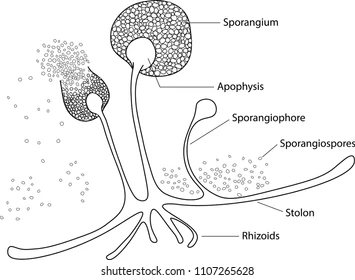
38
New cards
dermal tissue cells and functions
covers and protects plant
constructed of dermal cells, sclerenchyma cells, and collenchyma cells
constructed of dermal cells, sclerenchyma cells, and collenchyma cells
39
New cards
ground tissue cells and functions
responsible for wood repair, photosynthesis, and storage of foood
constructed of parenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, and collenchyma cells
constructed of parenchyma cells, sclerenchyma cells, and collenchyma cells
40
New cards
vascular tissue cells and functions
transports water and food throughout entire plant
divided into xylem and phloem
xylem: transports water and minerals. contains tracheids and vessel elements
phloem: transports food. contains sieve tube cells and companion cells
divided into xylem and phloem
xylem: transports water and minerals. contains tracheids and vessel elements
phloem: transports food. contains sieve tube cells and companion cells
41
New cards
Parenchyma appearance and functions
large, thin cell walls
performs photosynthesis and storage of sugars
performs photosynthesis and storage of sugars
42
New cards
Sclerenchyma appearance and functions
uniformly thick cell walls
provides support to the plant, contains lignin and is fully functional when dead
provides support to the plant, contains lignin and is fully functional when dead
43
New cards
Collenchyma appearance and functions
unevenly thick and thin cell walls
provides mechanical reinforcement to the plant
provides mechanical reinforcement to the plant
44
New cards
Stem functions
provide strength and structure, contains vascular system for roots to reach leaves
45
New cards
Leaf functions
specialized for photosynthesis, gas exchange, and moisture loss
46
New cards
Root functions
have root apex, which is the site of primary growth, absorb water and nutrients from soil
47
New cards
Monocot root
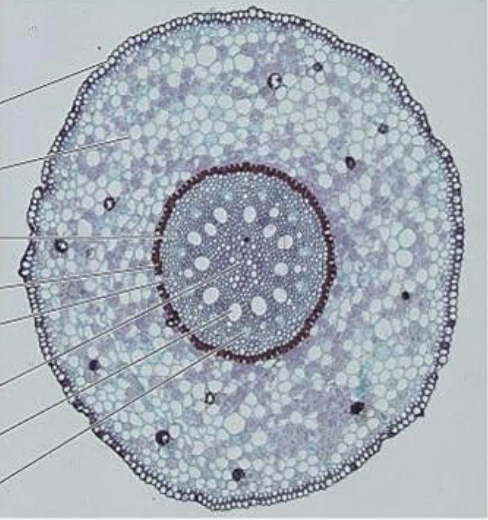
48
New cards
Dicot root
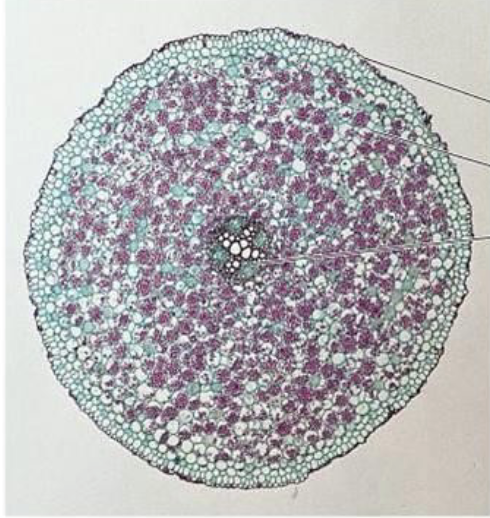
49
New cards
Monocot stem
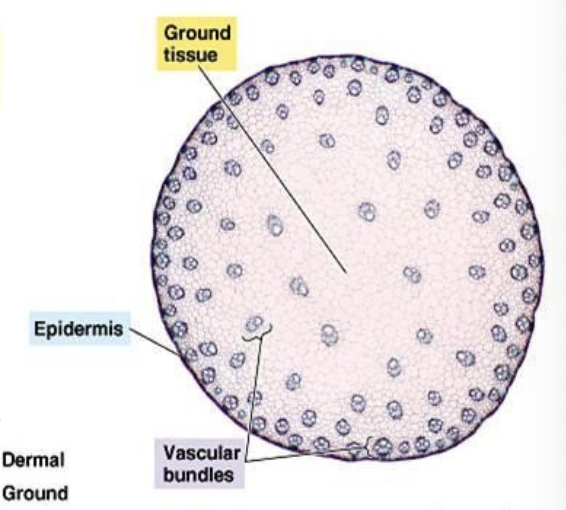
50
New cards
Dicot stem
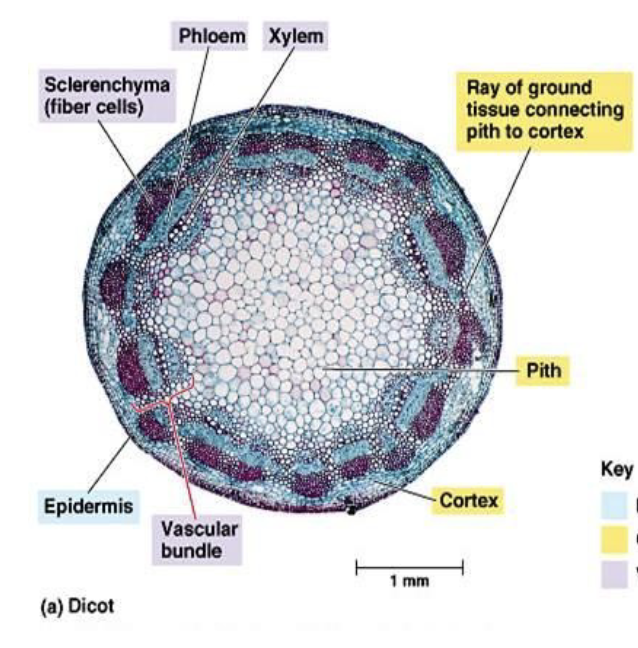
51
New cards
Monocot leaf
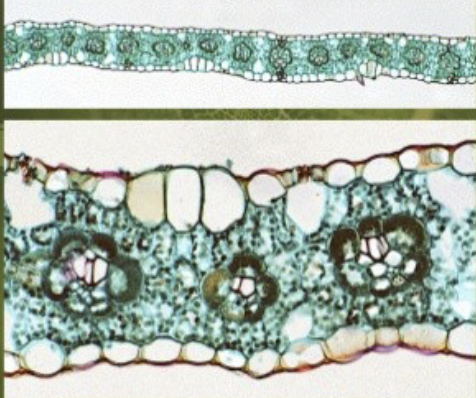
52
New cards
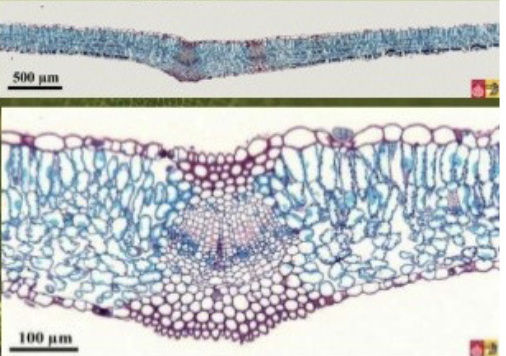
Dicot leaf
\
53
New cards
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
It covers, lines, and protects organs, organ systems, and organism
54
New cards
3 major layer patterns of epithelial tissue
Squamous, stratified, psuedostratified
55
New cards
3 major cell shapes of epithelial cells
Simple, cuboidal, columnar
56
New cards
Stratified squamous
epidermis of skin
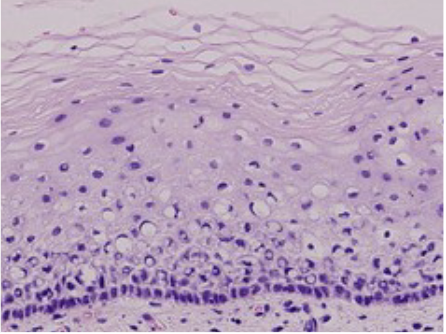
57
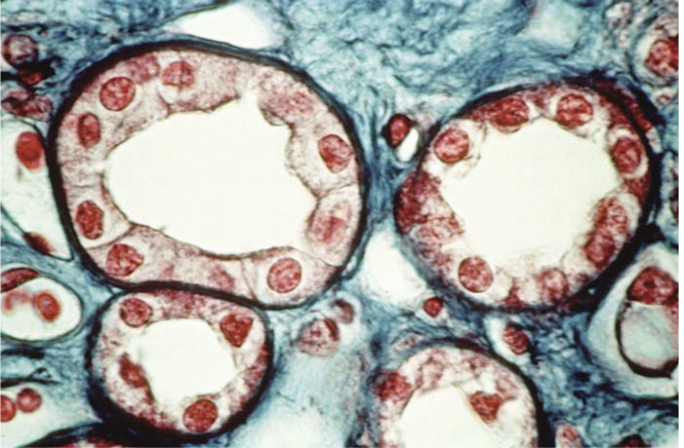
New cards
Simple cuboidal
lining of kidney tubule
58
New cards
Simple columnar
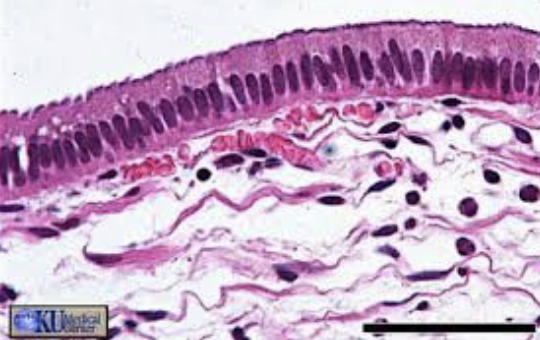
59
New cards
Stratified columnar
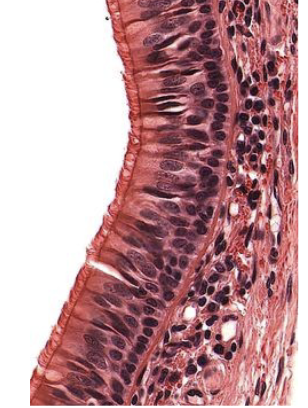
60
New cards
What two features are used to name epithelial cells
Layer and cell shape
61
New cards
Define connective tissue
consists of a few living cells in a non-living cellular matrix
62
New cards
What are the different types of connective tissue?
Loose CT and Dense CT
63
New cards
Adipose LCT
Adipocytes - filled with lipids
64
New cards
Areolar LCT
fibroblast in a protein matrix \[collagen, elastin\], connects & binds structures
65
New cards
What are the thick bands in Areolar LCT?
Collagen
66
New cards
What are the thin bands in Areolar LCT?
Elastin
67
New cards
Dense Connective Tissue functions, cells, and matrix componets
fibroblasts in a protein matrix \[collagen, elastin, reticulum\], binds and connects, more structural
68
New cards
Areolar LCT
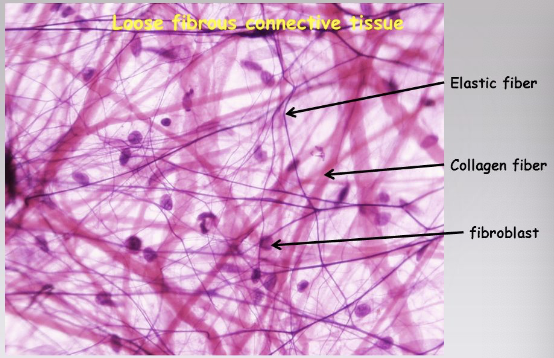
69
New cards
Adipose LCT
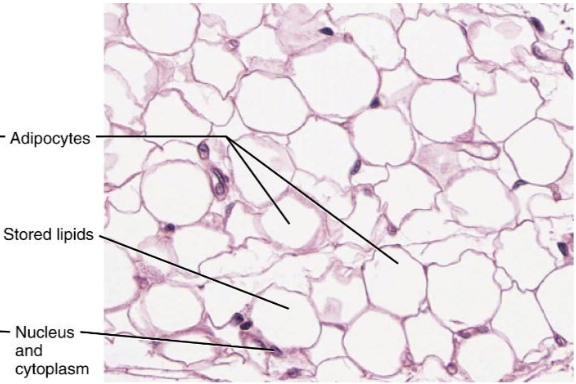
70
New cards
Skeletal muscle tissue
parallel striated
multi nuclei per cell
voluntary
multi nuclei per cell
voluntary
71
New cards
Skeletal muscle tissue
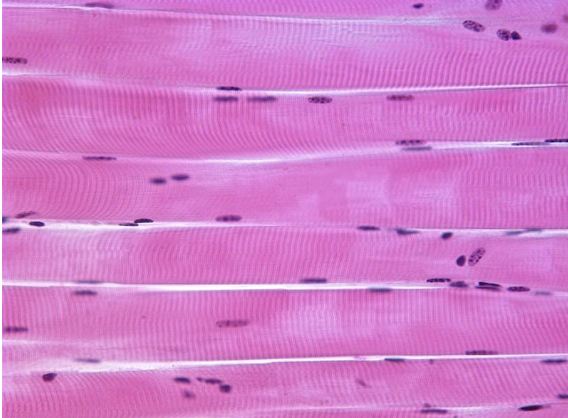
72
New cards
Cardiac muscle tissue
Branched striated
1 nuclei per cell
involuntary
1 nuclei per cell
involuntary
73
New cards
Cardiac muscle tissue
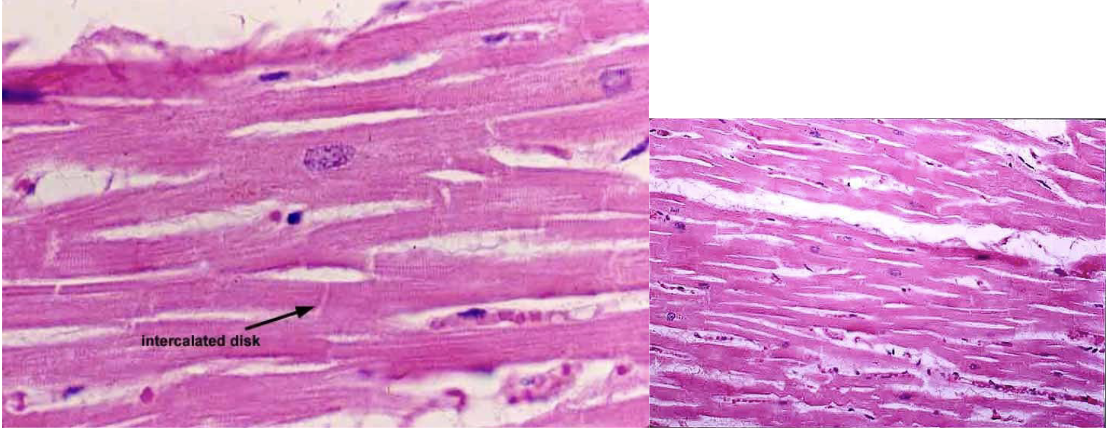
74
New cards
Smooth muscle tissue
Spindle shape, non striated
1 nuclei per cell
involuntary
1 nuclei per cell
involuntary
75
New cards
Smooth muscle tissue
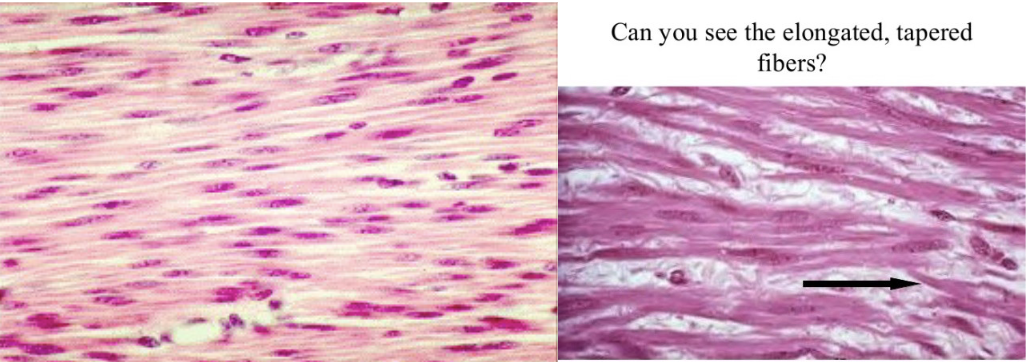
76
New cards
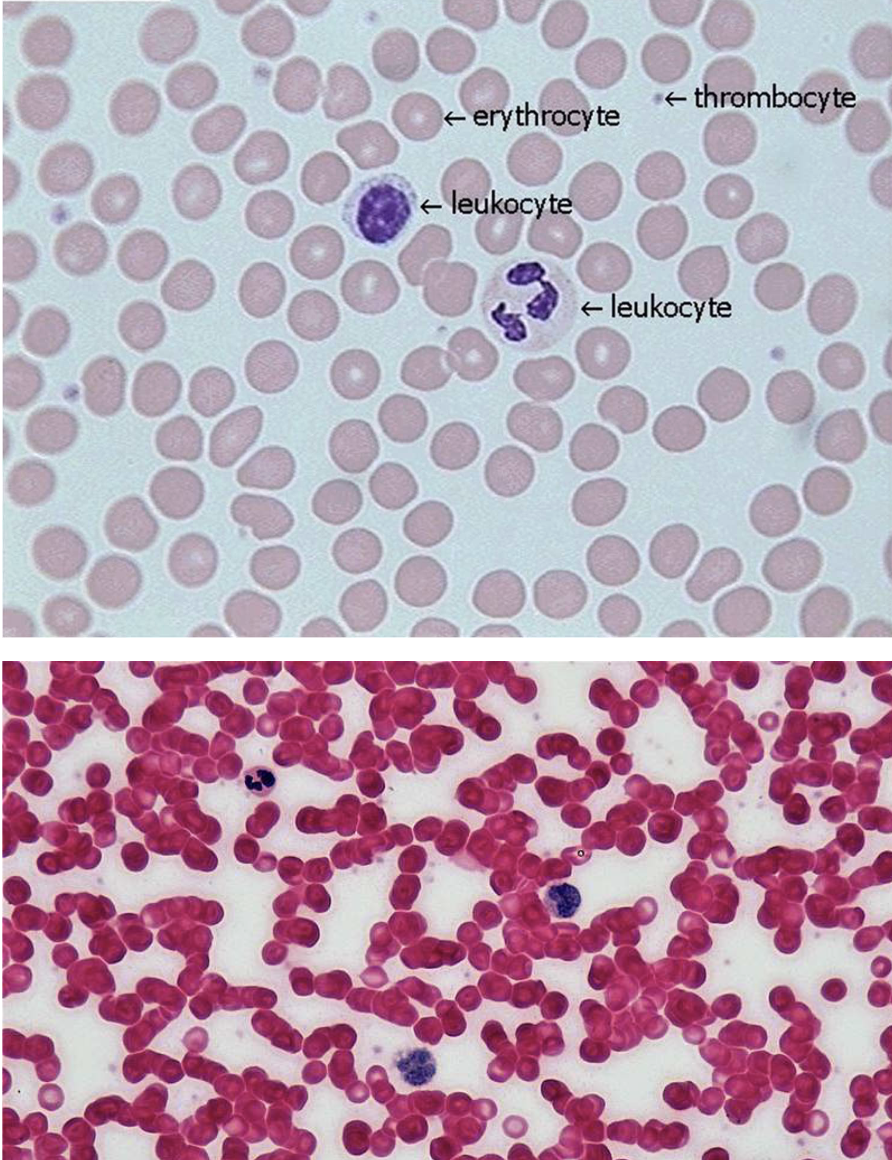
Blood connective tissue functions, cells, and matrix components
cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes
in a liquid matrix - plasma
in a liquid matrix - plasma
77
New cards
Blood connective tissue
78
New cards
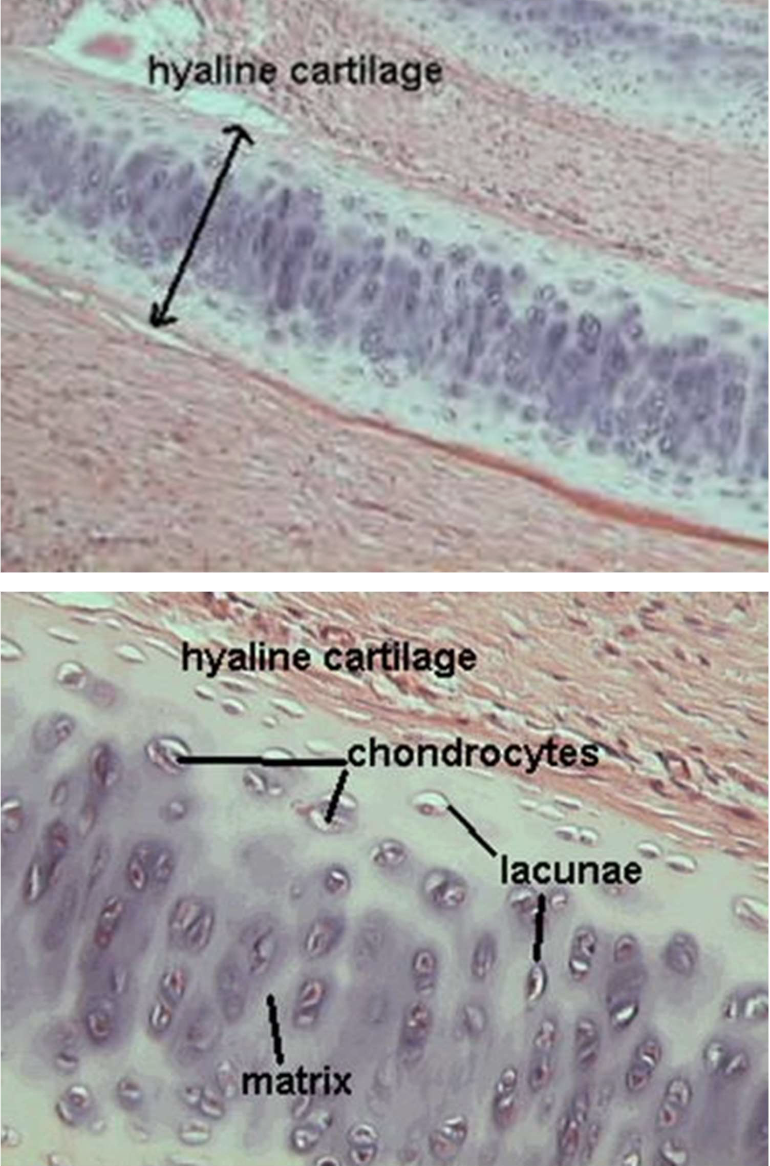
Cartilage connective tissue functions, cells, and matrix components
cells: chondrocytes inside lacunae
in a protein matrix - collagen
in a protein matrix - collagen
79
New cards
Cartilage connective tissue
80
New cards
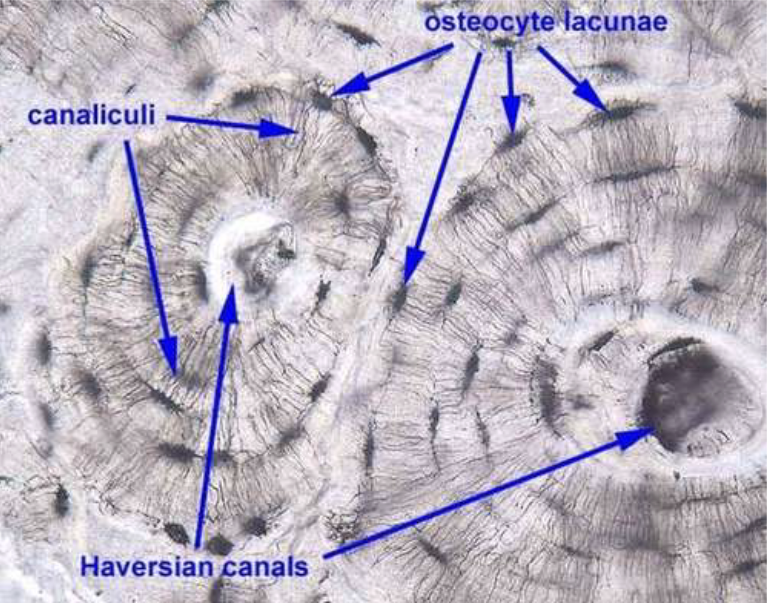
Bone connective tissue functions, cells, and matrix components
cells: osteocytes inside lacunae
in a mineral matrix - CaPO4
in a mineral matrix - CaPO4
81
New cards
Bone connective tissue
82
New cards
What are the 2 main divisions of the skeletal system?
Axial and appendicular
83
New cards
What are the 2 girdles in the appendicular division?
Pectoral and pelvis
84
New cards
What bones belong to the axial division?
Frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital, maxilla, mandible, ribs, sternum, cervical, thoracic, lumbar
85
New cards
What bones belong to the appendicular division, pectoral girdle?
Scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpels, clavicles, metacarpels, phalanges
86
New cards
What bones belong to the appendicular division, pelvis girdle?
pelvis, femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
87
New cards
frontal bone - axial
88
New cards
temporal bone - axial
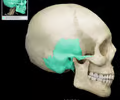
89
New cards
occipital bone - axial
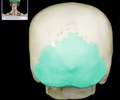
90
New cards
mandible bone - axial
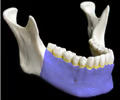
91
New cards
maxilla bone - axial
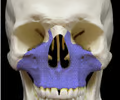
92
New cards
cervical bone - axial
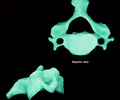
93
New cards
thoracic bone - axial
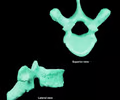
94
New cards
lumbar bone - axial

95
New cards
ribs - axial
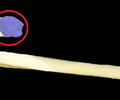
96
New cards
sternum bone - axial
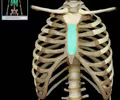
97
New cards
scapula - appendicular, pectoral girdle
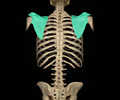
98
New cards
humerus bone - appendicular, pectoral girdle
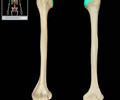
99
New cards
radius bone - appendicular, pectoral girdle

100
New cards
ulna bone - appendicular, pectoral girdle
