AP Exam 1
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Sensory Receptor
structures specialized to detect a stimulus. Includes bare nerve endings and sense organs.
Ex. Touch Receptors
Sense Organs
Receptors that combine nervous tissues w other tissues, such as epithelial, muscular, connective, to enhance a response to a stimulus
Ex. The Eye
Special and general senses differ in two significant ways
Many special senses rely on receptors that are not neurons; general sensory receptors are receptive ends of sensory neurons.
Special sensory organs are confined to head, so all information travels on axons of various cranial nerves; general sensory information travels on the axons of both cranial and spinal nerves.
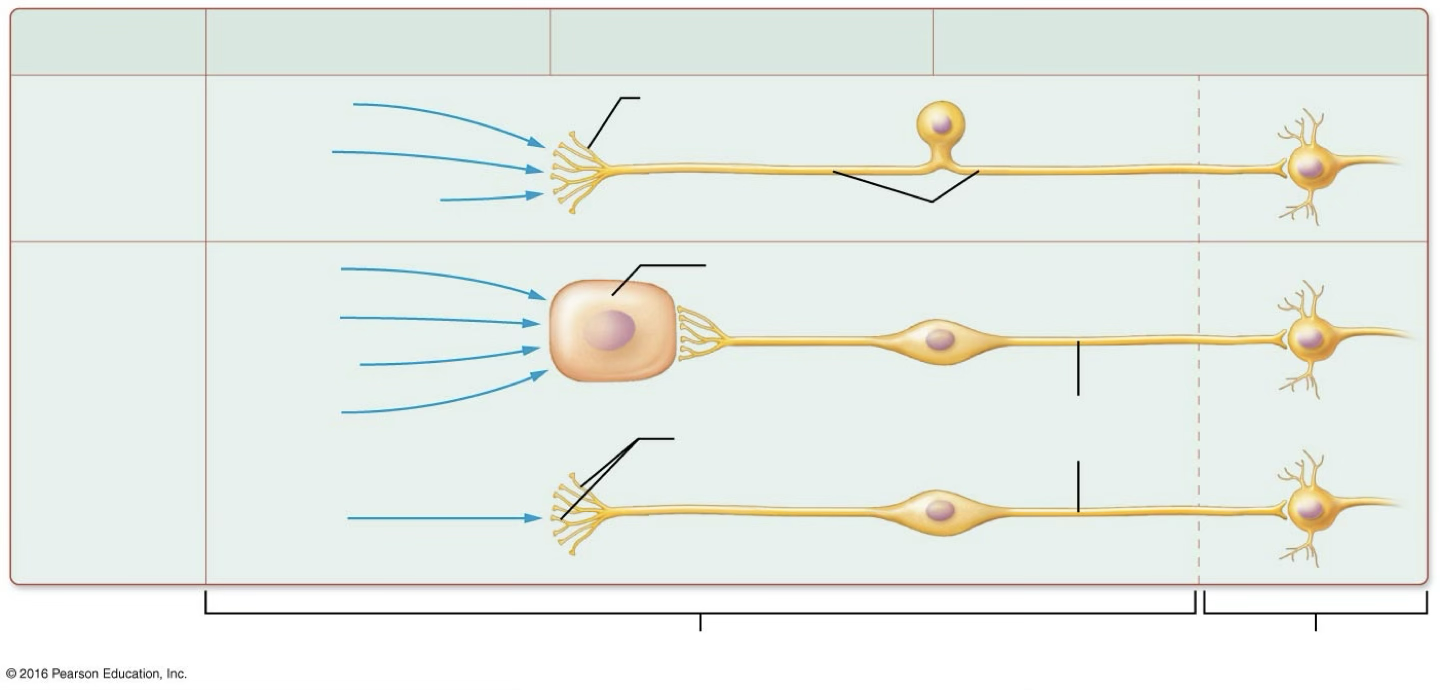
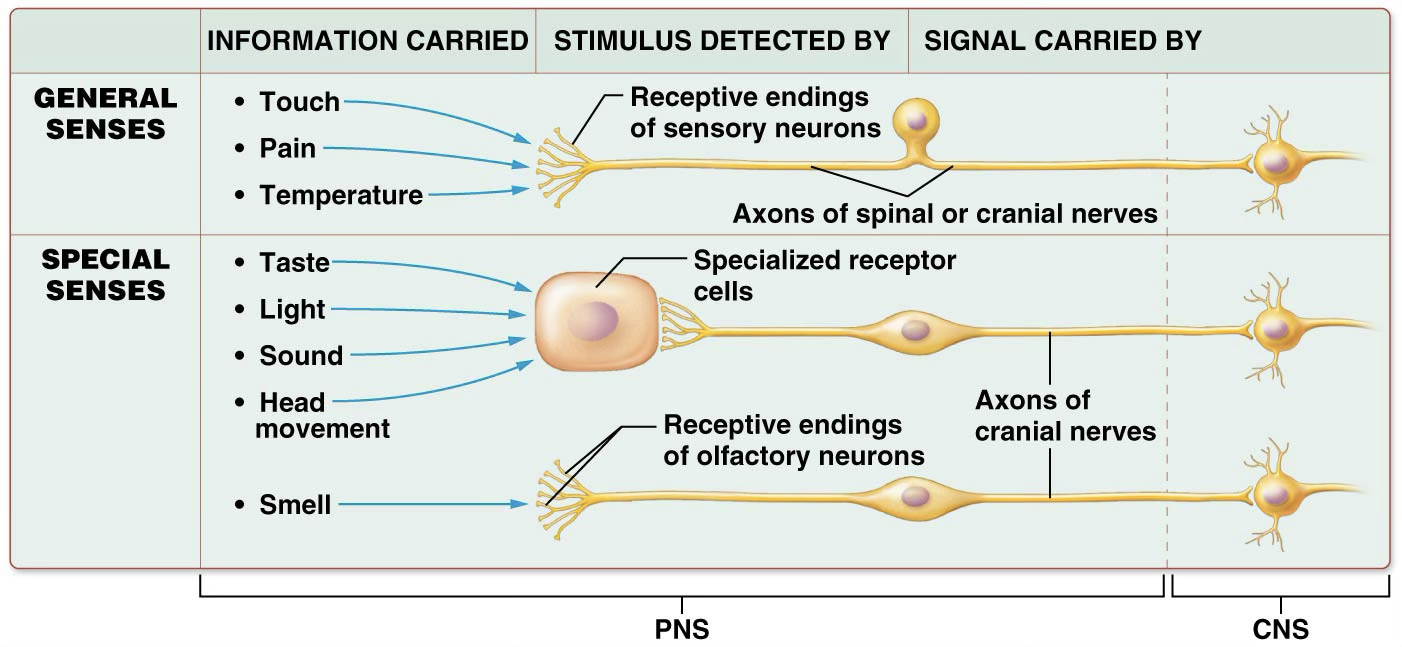
Sensation
Subjective awareness of a stimulus
Transduction
conversion of sensory stimuli into electrical signals that can be interpreted by CNS
Sensory receptors provide ___________ characteristics regarding a stimulus OR transmit four kinds of information:
1) Modality – form of a stimulus; type of sensation produced. Think of the brain as a “switchboard”. Whether we consciously perceive a stimulus is dependent upon which specific region of the CNS receives that sensory information.
2) Location – of stimulus (which nerve fibers issues signals to the brain); incorporates where processed, e.g., to designated postcentral gyrus regions (recall, the primary somatosensory cortex and sensory homunculus – go back to Figure 14.21)? Plus, concept of receptive field – you had that in A&P I; see next slide.
3) Intensity – frequency and number of nerve signals received. Saladin has a good discussion on this; which neurons fire (are stimulated), how many, and how fast they fire!
4) Duration – how long a stimulus lasts.
Sensory adaptation
decrease in sensitivity to a continuous stimulus
Phasic receptors
exhibit rapid adaptation to a constant stimulus. Generate nerve signals only in a response to a new (or changing) stimulus and quickly decrease the # of nerve signals relayed to the CNS. Ex. Deep pressure receptors in the skin, such as lamellar (Pacinian) corpuscles and hair follicle receptors.
Tonic receptor
display limited adaptation. Continuously generate nerve signals and only slowly decrease the # of signals relayed to the CNS. Ex. Head position receptors in the inner ear, proprioceptors in joints, pain receptors, Merkel’s (tactile) discs, bulbous corpuscles.
rapidly adapting receptors
important for detecting the initiation of stimuli, but ignore ongoing stimuli. Ex. Rapidly adapting receptors are the reason why you can walk around your home in search of your sunglasses only to find out they were on top of your head the whole time.
slowly adapting receptors
respond to stimuli with constant action potentials that do not diminish with time, Ex. The dull throbbing pain for a week after spraining your ankle is the work of slowly adapting receptors, i.e., in this case, nociceptors
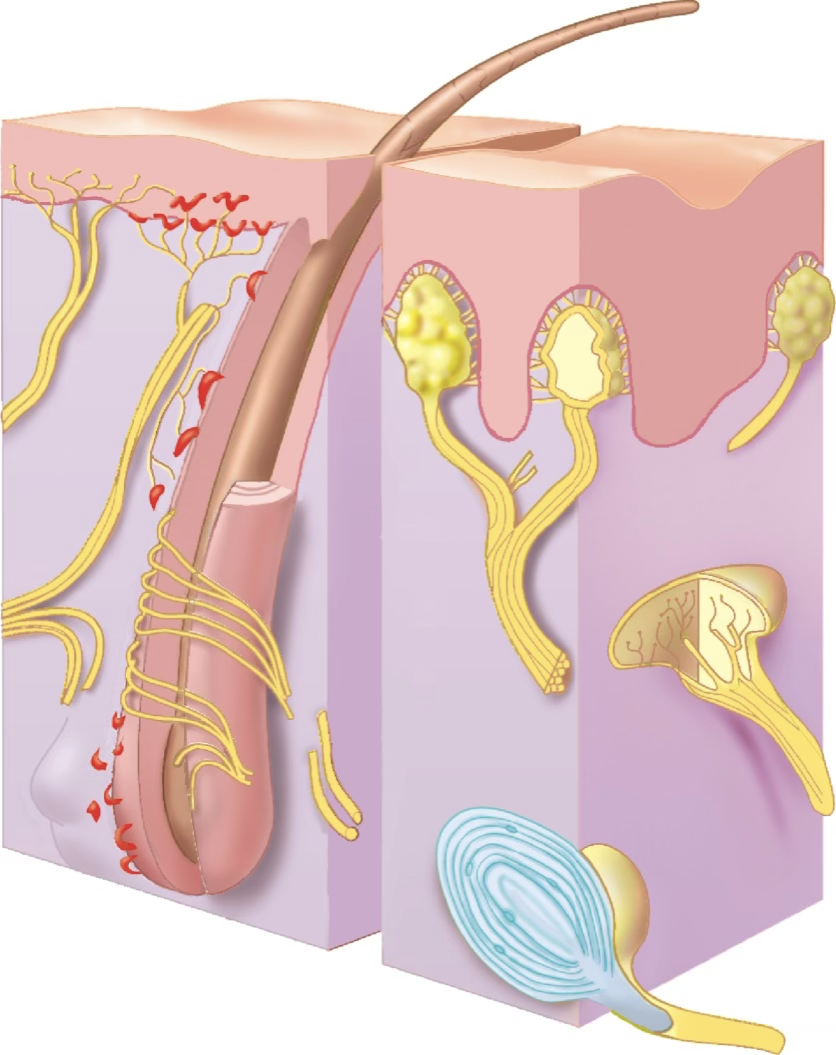
Tactile (Meissner) corpuscles
involved in two-point discrimination
Ruffini End Organ (Bulbous Corpuscle)
detects continuous touch or pressure and depression or stretch of the skin
Lamellar (Pacinian) Corpuscle
detects deep cutaneous pressure, vibration and proprioception
Hair Follicule Receptor
detects light touch and slight bending of hair
Merkel Disks
detects light touch and pressure
free nerve endings
respond to painful stimuli, temperature, itch, joint movement, proprioception
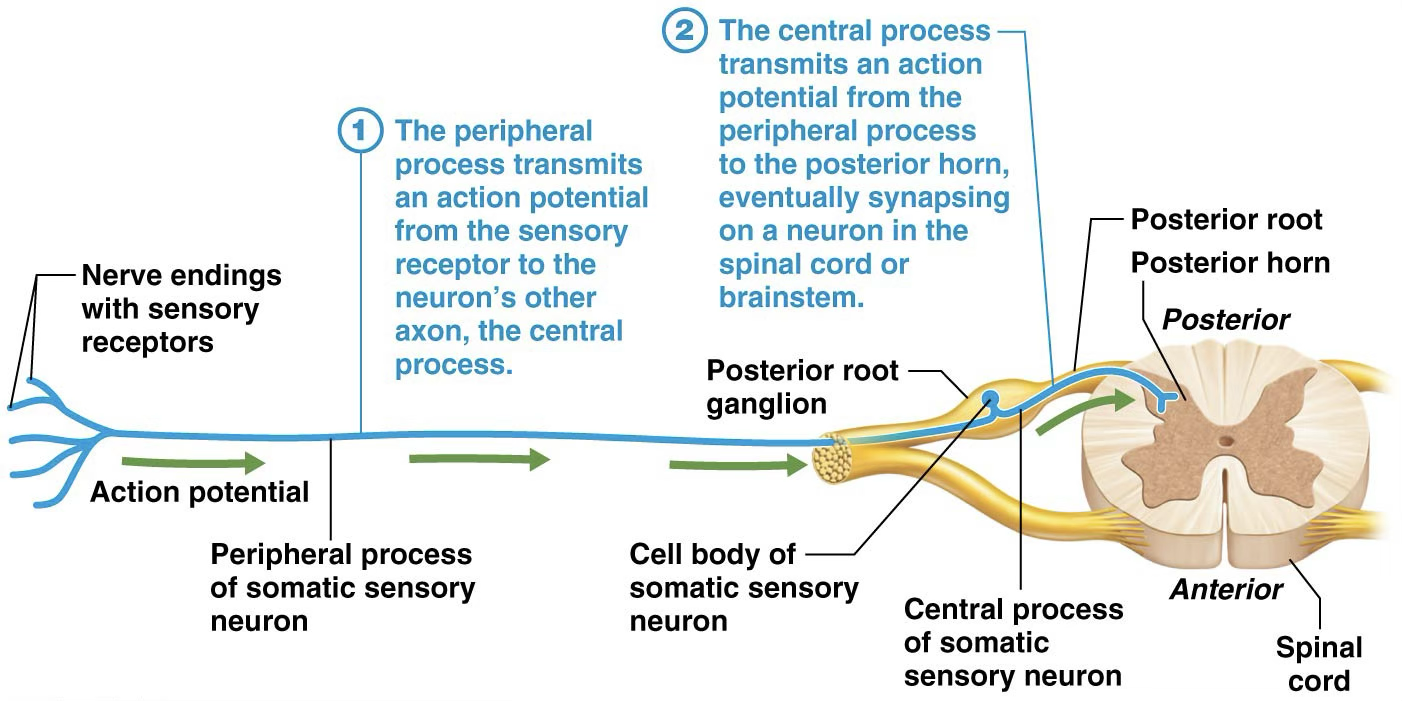
First-order
synapse of second-order neuron is posterior horn; then decussate
second-order neurons
neurons pass through the spinothalamic tracts of spinal cord and brainstem to thalmus
third-order neurons
in thalmus then transmit impulse to primary somatosensory cerebral cortex where it is processed
Enkephalins
two human analgesics are oligopeptides with 200x potency of morphine
endogenous opioids
endorphines and dynorphins
Spinal gating
block pain signals at posterior horns 1. descending analgesic fibers/postsynaptic inhibition 2. stimulating pain-inhibiting interneurons to secrete enkephalins
Type A fibers
fastest conduction speeds; largest diameter and heavily myelinated; found in sensory and motor axons associated with skeletal muscle and joints
Type B fibers
intermediate conduction speeds; mostly myelinated with intermediate diameter axons ; found in efferent (preganglionic) fibers of autonomic nervous system (ANS) and some sensory axons.
Type C fibers
slowest conduction speeds; smallest diameter fibers; unmyelinated axons include efferent (postganglionic) fibers of the ANS and sensory axons; transmit pain, temperature, and certain pressure sensations.
Special senses
smell (olfaction), taste (gustation), vision, hearing (auditory), and vestibular (balance and equilibrium) sensation.
Special sensory neurons
detect light, chemicals, and vibration present in environment and convert or transduce these to electrical signals.
olfaction
Chemoreceptor;G-protein with signal transduction
Depolarization
Gustation
Chemoreceptor; Salty-Na+ Channel Sour-H+ channels, Sweet,bitter,umami:G-protein with signal transduction
Depolarization
Vision
Photoreceptors: Rods-noncolor and dark vision; Rhodopsin with G-protein; Cones-color and sharp vision; iodopsin with G-protein with red, green, blue wavelengths
Hyperpolarization Na+ channels
Hearing
Mechanoreceptor-inner hair cells
Depolarization K+ and Ca2+
Equilibrium
Mechanoreceptor-vestibule w/otoliths on stereocilia; Crista ampullaris-cupula on stereocilia of hair cell
Depolarization with K+
Gustatory Sense
involves chemoreceptors that are stimulated by various chemicals and also involves olfactory chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and nociceptors, in addition to gustatory chemoreceptors.
Taste buds
specialized receptor; small clusters of receptor and supporting cells scattered about tongue and other surfaces of oral cavity
which is covered with rounded projections called papillae; can be further classified into:
Vallate
largest
Fungiform
only a few taste buds
Foliate
Side of tongue;childhood
Filliform
long, thin cylinders scattered across tongue; devoid of taste buds; contain sensory nerve endings that detect food texture and temperature.
Gustatory (taste) cells
specialized epithelial cells with microvilli that project into a small opening on papilla surface called taste pore; display receptors that detect different tastes
associated sensory neurons carry taste stimuli to CNS via CN VII, CN IX, or CN X;
Texture – filiform and fungiform innervated by lingual branch of C.N. V, the trigeminal.
Basal cells
stem cells that continuously differentiate into new gustatory cells.
Supporting Cells
surround and physically support gustatory cells, but have no role in taste sensation.
Sweet
elicited by simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose; lead paint and ethylene glycol also have sweet taste- can cause accidental poisoning; G-protein.
Sour
produced by hydrogen ions, such as citric acid found in lemon juice; H+ leak channel.
Salty
elicited by presence of metal ions, such as sodium and potassium ions; Na+/K+ leak channel.
Bitter
produced by nitrogen-containing compounds; commonly found in poisonous substances; G-protein.
Umami
taste associated with meat or broth; produced by glutamate or other amino acids; G-protein.
1. Messenger such as epinephrine bings to receptor
The receptor releases a G protein, which travels freely in the cytoplasm
The g-protein binds to an enzyme adelynate cyclase, in plasma membrane converts to cAMP the second messenger
cAMP activates the enzyme kinase
Kinase adds phosphate groups to other cytoplasmic enzymes
Taste receptor
classified by substance they detect, with only one type of receptor associated with an individual gustatory cell.
Activation of taste receptor
substance must first dissolve in saliva before it can reach a taste bud, where it may be detected as a gustatory stimulus.
Activation of taste receptor
1. Chemical dissolves in saliva and changes in ion movements depolarize the gustatory cell’s plasma membrane.
2. Depolarization of membrane opens voltage-gated calcium ion channels, and calcium ions enter cell.
3. Calcium ions trigger release of neurotransmitters; produce an action potential in axon of sensory neuron.
1. Axons of the ______________, __________________,
and _______ cranial nerves carry taste stimuli from the tongue into the CNS. The _______________ nerve carries sensations of texture and temperature of food.
2. Axons of these nerves terminate in the ____________ ______________________.
3. These axons terminate in the ______________, the relay center for all sensory information, except smell.
4. Primary gustatory cortex in the lobe and ___________ perceive taste. Then to the ____________ lobe for integration with visual and olfactory information or to the ____ system, which provides emotional reactions to taste.
Facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus,
sollitary nucleus
Olfactory epithelium
located in superior nasal cavity
penetrates ethmoid bone at cribiform plate
The olfactory mucosa is 5 cm2 of the superior nasal concha, cribiform plate, and nasal septum of each nasal cavity.
Olfactory neurons
bipolar neurons; chemoreceptors that detect chemical substances perceived as odors.
Humans
5 to 20 million olfactory receptor cells; 400 different types of odor receptors.
Dogs
220 million; up to 1 billion; 100x
Bears
1 billion or more
1. Binding of an _ to its receptor activates _
2. Activated G-protein triggers enzyme _ _ to convert _ into _
3. cAMP opens ion channels that allow __ _ __ __to enter cell; causes depolarization and action potential generation if threshold is reached.
Odorant, G-protein
Adenylate cyclase, atp, cyclic AMP
Sodium and calcium ions
1. Axons of _ _ (olfactory nerve) carry olfactory stimuli to olfactory bulb in CNS and synapse with dendrites of — —in olfactory bulb.
2. — — travels from the olfactory bulb to the — — — in temporal lobe for awareness and identification of odor (no synapse with thalamus!)
3. Hypothalamus and components of the — —(amygdala and hippocampus) receive information from the primary olfactory cortex, which evokes emotional and visceral responses to odors.
4. Integration within frontal lobe.
Olfactory neurons, mitral cells
Olfactory tract, primary olfactory cortex,
limbic system
Anosmia and Hyposmia
anything that blocks air from reaching olfactory epithelium will interfere with olfaction—olfaction contributes significantly to sense of taste, so food loses much of its appeal.
Bony labyrinth
open passageways that make up inner ear chamber of temporal bone; includes the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals.
Membranous labyrinth
membranes that line bony labyrinth [A collection of ducts and sacs, includes the utricle and saccule and the cochlear duct] and contain:
Endolymph
fluid in which K+ concentration is greater than Na+ concentration; transduces sound waves and head movements into electrical signals.
Perilymph
fluid found between bony and membranous labyrinths in which Na+ concentration is greater than K+ concentration.