BSC 2086: Lesson 7 (Circulatory System)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Cardiology is the __________
study of the heart and its disorders
What is the cardiovasulcar system made up of?
The heart and blood vessels
The function of the hear is to _______/
Pump blood through the vessels
Where do blood vessels deliver blood to?
Body tissues & return it to the heart
Arteries are vessels that carry blood __________
Away from the heart
veins are vessels that carry blood
Towards the heart
Capillaries are microscopic vessels that connect _________.
The smallest arteries & to the smallest veins
The circulatory system refers to __________>
Heart, vessels, and blood.
The two major divisions that make up the cardiovascular.
Pulmonary circuit
Systemic circuit
The pulmonary circuit is responsible for carrying _____________.
Blood to the lungs for gas exchange (CO2) & back to the heart
Which side of the heart is responsible for the pulmonary circuit?
The right side
The systemic circuit is responsible for supplying __________.
Supplies O2 blood to all tissues of the body and return it to the heart
Which side of the heart is responsible for the systemic circuit?
the left side
The major arteries & veins _____ & ______ the heart are called the __________ ________
Entering & leaving; great vessels
Where is the heart located?
Mediastinum (Base+Apex)
The base is the __________.
Wide
Superior portion of the heart
What attaches to the base of the heart?
Large vessels
The apex is the __________.
Inferior ends, tilts to the left
What are the characteristics that make up the heart
Weighs about 10 ounces
3.5 in. wide at base
5 in from base to apex
AT ANY AGE = the size of a fist
The heart is enclosed by the ________.
Pericardium (a double-walled sac)
What function does the pericardium have?
Allows heart to beat w/o friction = room to expand resists expansion
The pericardium anchored to ______ _______ & ________ _____
Diaphragm inferiorly; sternum & anteriorly
The structures of the pericardium consist of:
Fibrous pericardium
Serous Pericardium’
Pericardial cavity
Fibrous pericardium is the _______.
Outermost layer
Fibrous sac
Serous Pericardium ___________
Parietal layer (line fibrous pericardium)
Visceral layer (adheres to heart surface)
The pericardial cavity is the space _______
Between the visceral & parietal of serous pericardium (filled w/ pericardial)
Pericarditis is the _________.
Inflammation of the pericardium = friction rub
What are the 3 layers of the heart wall?
Epicardium
Endocardium
Myocardium
Visceral layer of serous pericardium is the ____________.
Epicardium
What are some characteristics that make up the endocardium?
Smooth inner lining of heart & blood vessels
Covers the valve surface & is continuous w/ endothelium blood vessels
What are the characteristics that make up the myocardium?
Layer of cardiac muscle, thickness is proportional to the workload
Vortex of the heart arrangement produces a wringing motion during contraction.
The vortex of the heart are ____________
Muscle spirals around the heart; arrangement produces wringing motion contraction
Fibrous skeleton are _______
Framework of collagenous & elastic fibers
Provides structural support & attachment for cardiac muscle
Electrical insulation between atria & ventricles (Important in timing & coordination of contractile activity)
The heart chambers are made up of __________.
Two atria (Right and Left atria)
Two ventricles
What are the characteristics that define the chambers of the heart
R&L Atria
Interatrial septum
Auricle
Thin flaccid walls
Two superior chambers that receive blood returning to the heart separate each other by __________.
Interatrial septum
An earlike flap that increases the chamber volume
Auricle (found in both right & left atria)
The walls of the ventricles are ____________
Thin, flaccid
Two inferior chambers eject blood into the arteries; separated by the ________
Interventricular septum
The left Ventricle is _____________ than the right ventricle
2-4x thicker
Explain why the left ventricle is thicker than the right ventricle
Due to the greater workload of pumping blood to the entire body
List the external features for the chambers of the heart
Boundaries marked by sulci (grooves)
Coronary sulcus
Anterior & posterior interventricular sulci
Separate atria above from ventricles below; encircles heart near base _________.
Coronary sulcus
Separates left and right ventricles; overlie interventricular septum and extend obliquely down the heart from the base to apex _________.
Anterior & posterior inverventricular sulci
Why are the valves essential for blood flow distribution?
They ensure one-way flow of blood through the heart
The fibrous flaps that cover the valves are called _________.
Cusps & leaflets
Control blood flow between atria & ventricles are the _________.
Atrioventricular valves
The __________ valve has 3 cusps
Tricuspid (Right AV Valve)
The ____________ valve has two cusps
(Mitral) Left AV
Strings of connective tissue that attach valve cusps to papillary muscles on the floor of ventricle.
Chordae tendinae (tendinous cords)
What functions do the chordae tendinae have?
Prevent AV valves from flipping or bulbing into the atria when the ventricles contract.
Control flow form the ventricles into great arteries are ____________
Semilunar valves
Controls the opening between the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk are ______________.
Pulmonary valve
Controls the opening between the left ventricle and aorta
Aortic valve
List the process of how the valves work
During ventricular contraction & blood ejection, cusps pressed up against arterial walls
When ventricles relax, blood flows back toward the ventricles & fills cusps causing valves to close.
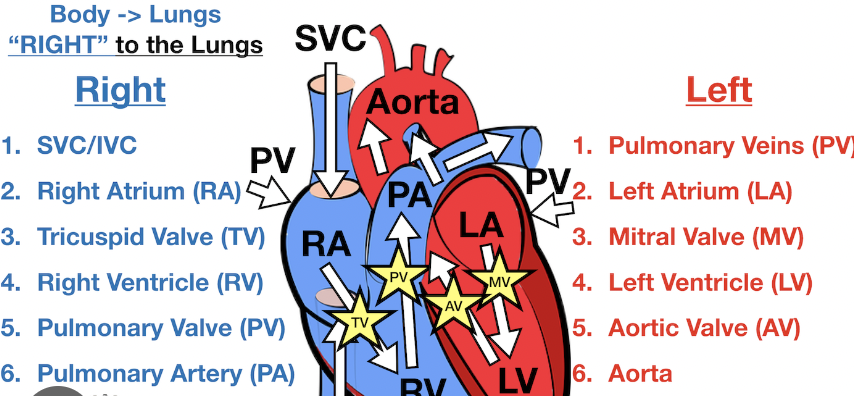
Blood flow though the chambers (1)
Blood enters R Atrium from Superior & Inferior Venae cavae
Blood flow through the chambers (2)
Blood in right atrium flows through right AV valve
Blood through the chambers (3)
Contraction of right ventricles forces pulmonary valve OPEN
Blood flow through the chambers (4)
Blood flows through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary trunk
Blood flow through the chambers (5)
Blood is distributed by R&L arteries → lungs = unloading CO2 + Load O2
(6) Blood flow through the chambers
Blood returns from lungs via Pulmonary vein → Left atrium
(7) Blood flow through the chambers
Blood in left artrium → through left AV Valve → left ventricle
(8) Blood flows through the chambers
Contraction of left ventricle + right ventricles (w/ pulmonary valve) = forces aortic valve to open.
(9) Blood flow through the chambers
BLOOD flows → Aortic valve → ascending aorta
(10) Blood flow through the chambers
(10) Blood in the aorta is distributed to EVERY ORGAN IN BODY (unloads O2 &CO2)
(11) Blood flow through the chambers
BLOOD RETURNS TO RIGHT ATRIUM = Venae Cavae
Describe out loud what’s going on in the picture as if you’re explaining it to a elementary schooler.