NURS 330 Module 3 O2 Adaptations
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Dyspnea
difficulty breathing
hypoxia
Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the blood
Perfusion
The supply of oxygen to and removal of wastes from the cells and tissues of the body as a result of the flow of blood through the capillaries.
- depends on activity level
- depends on adequate blood supply and CV function
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
diffusion
exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli of lungs and circulating blood
hypoxemia
deficient amount of oxygen in the blood
atelectasis
collapsed lung
parenchyma
Fundamental tissue composed of thin-walled living cells that function in photosynthesis and storage.
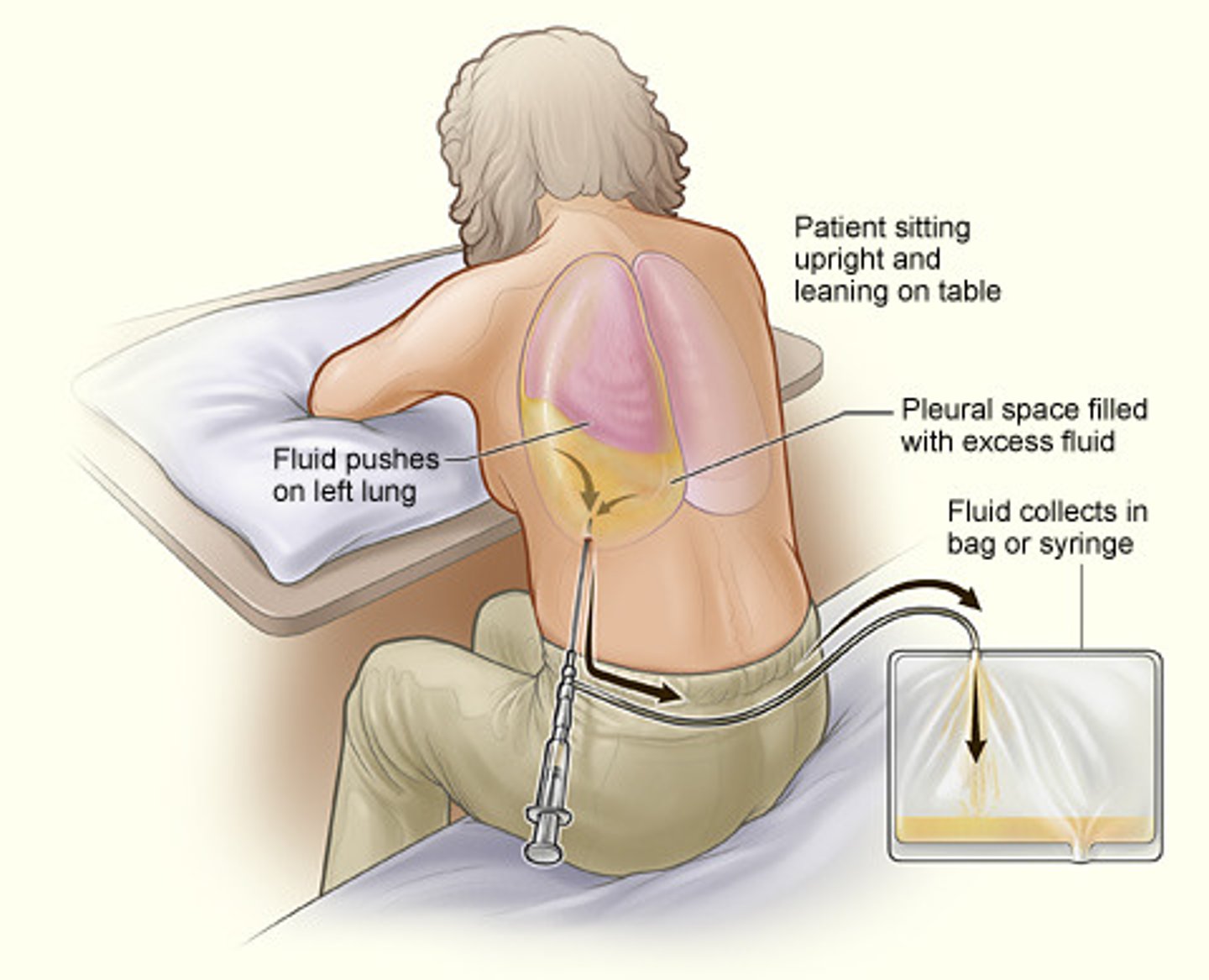
thoracentesis
surgical puncture to remove fluid from the pleural space
Tachypnea
rapid breathing
pleural effusion
abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space
cachexia
a condition of physical wasting away due to the loss of weight and muscle mass that occurs in patients with diseases such as advanced cancer or AIDS
cor pulmonale
right ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure due to pulmonary hypertension
Physical Obstructions & Resistance
Pregnancy
Posture
What would affect airflow?
Change in surface area
Thickening of the alveolar capillary membrane
partial pressure changes
What would affect diffusion?
Factors affecting cardiopulmonary function
Level of health
Developmental considerations
Medication considerations
Lifestyle considerations
Environmental considerations
Psychological health considerations
developmental considerations for cardiopulmonary function
Infants:
• Higher RR
• Surfactant (34 weeks)
• Small chest and short airways
School age:
• Elongated and less angular bronchi and bronchioles
• Average number of colds/infections decrease until school
Older adults:
• Decreased elasticity in respiratory tract
• Weakened muscles and diaphragm move less effectively
• Airways collapse more easily
• Kyphosis
• Decreased physical activity
Medications that affect cardiopulmonary function
• Opioids depress medullary respiratory center
• Some medications increase/decrease HR
• Antihypertensives
Lifestyle considerations that affect cardiopulmonary function
• Activity levels
• Smoking
• Cultural influence
environmental considerations that affect cardiopulmonary function
• Correlation between pollution and lung cancer
• Occupational hazards; farmers, cleaners, asbestos, radon, coal
psychological considerations that affect cardiopulmonary function
• Stress - hyperventilation
• Depression - sedentary activity
postoperative considerations that affect cardiopulmonary function
• Anesthesia causes mismatch in alveolar ventilation and perfusion
• Loss of muscle tone and decrease in ventilation
• Relaxation of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
• Supine position chest wall expansion reduced from 30% to 10%
• Loss of cough reflex and increased secretions
measuring cardiopulmonary function
• Pulmonary Function Studies
• Spirometry
• Incentive Spirometry
• Peak Expiratory Flow Rate
• Capnography
• Pulse Oximetry
obstructive lung disease
is a class of respiratory diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems
restrictive lung disease
a decrease in the total volume of air that the lungs can hold; often due to a decrease in lung elasticity or by a problem related to chest wall expansion
spirometry
evaluates lung function and airway obstruction

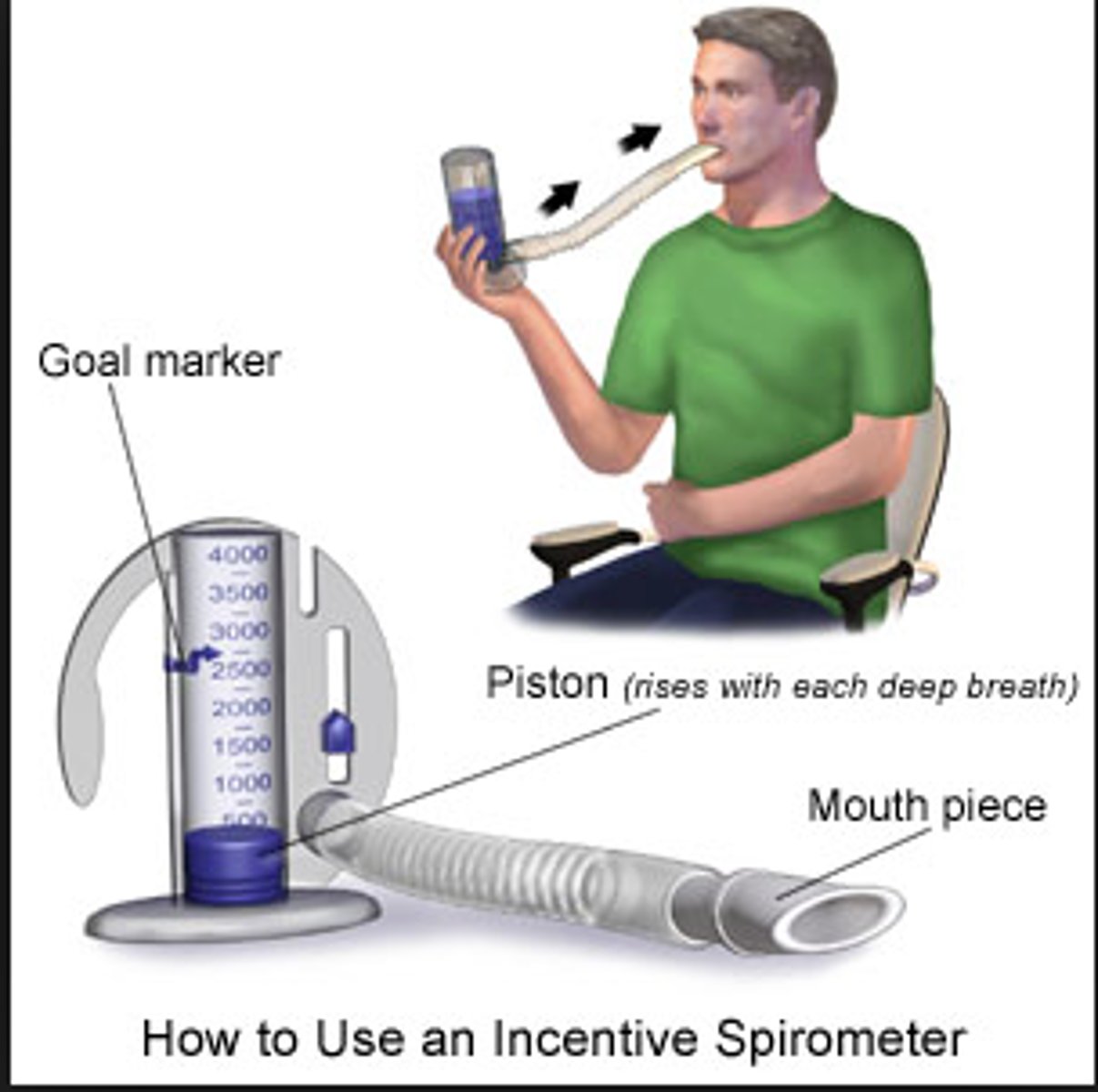
incentive spirometry
promotes increased lung expansion and gas exchange
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
• Point of highest flow during forced expiration
• Asthma - measure severity of disease
• Repeat forced expiration 3x
• Asymptomatic personal best as benchmark
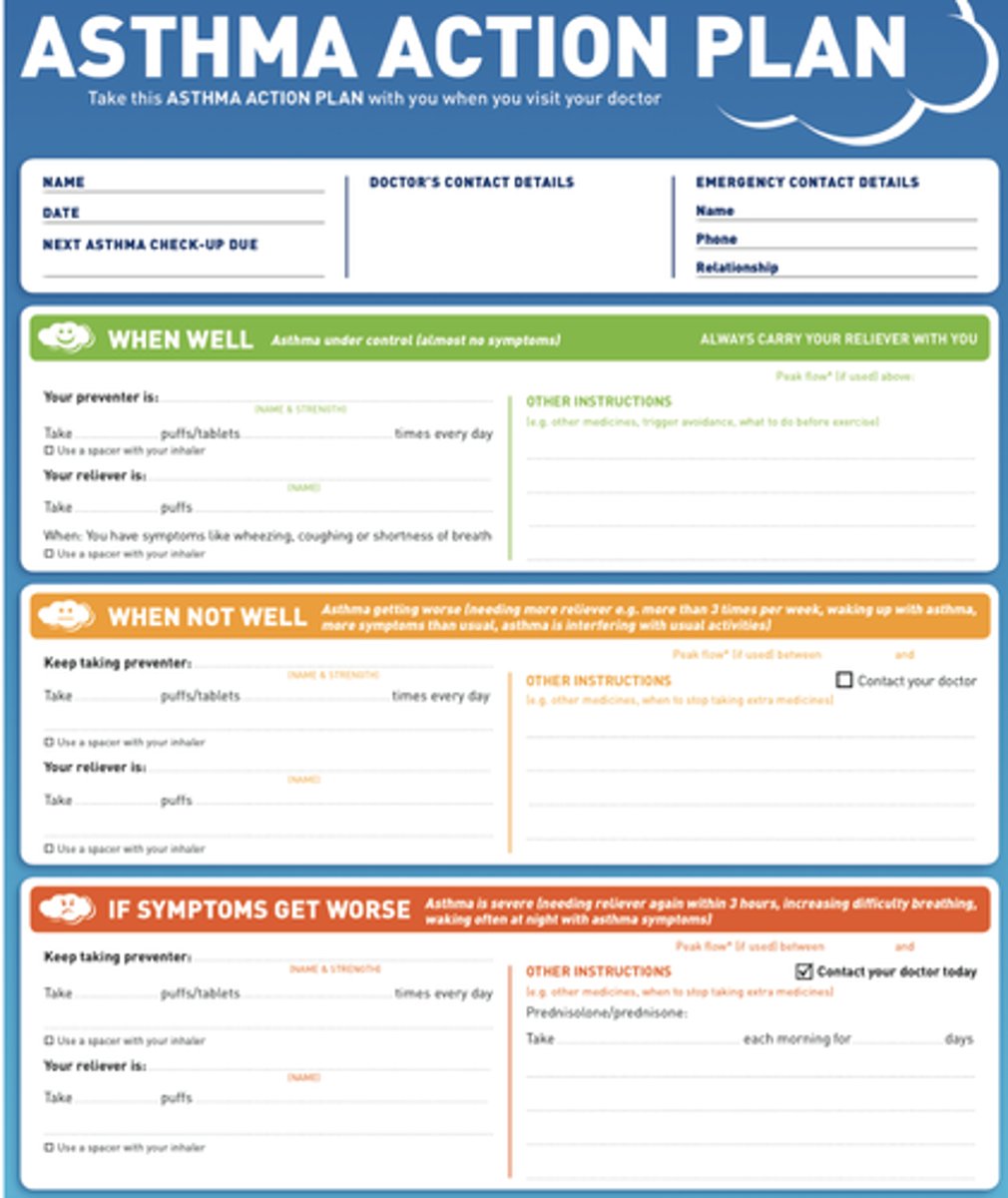
• Asthma action plan

asthma self management action plan
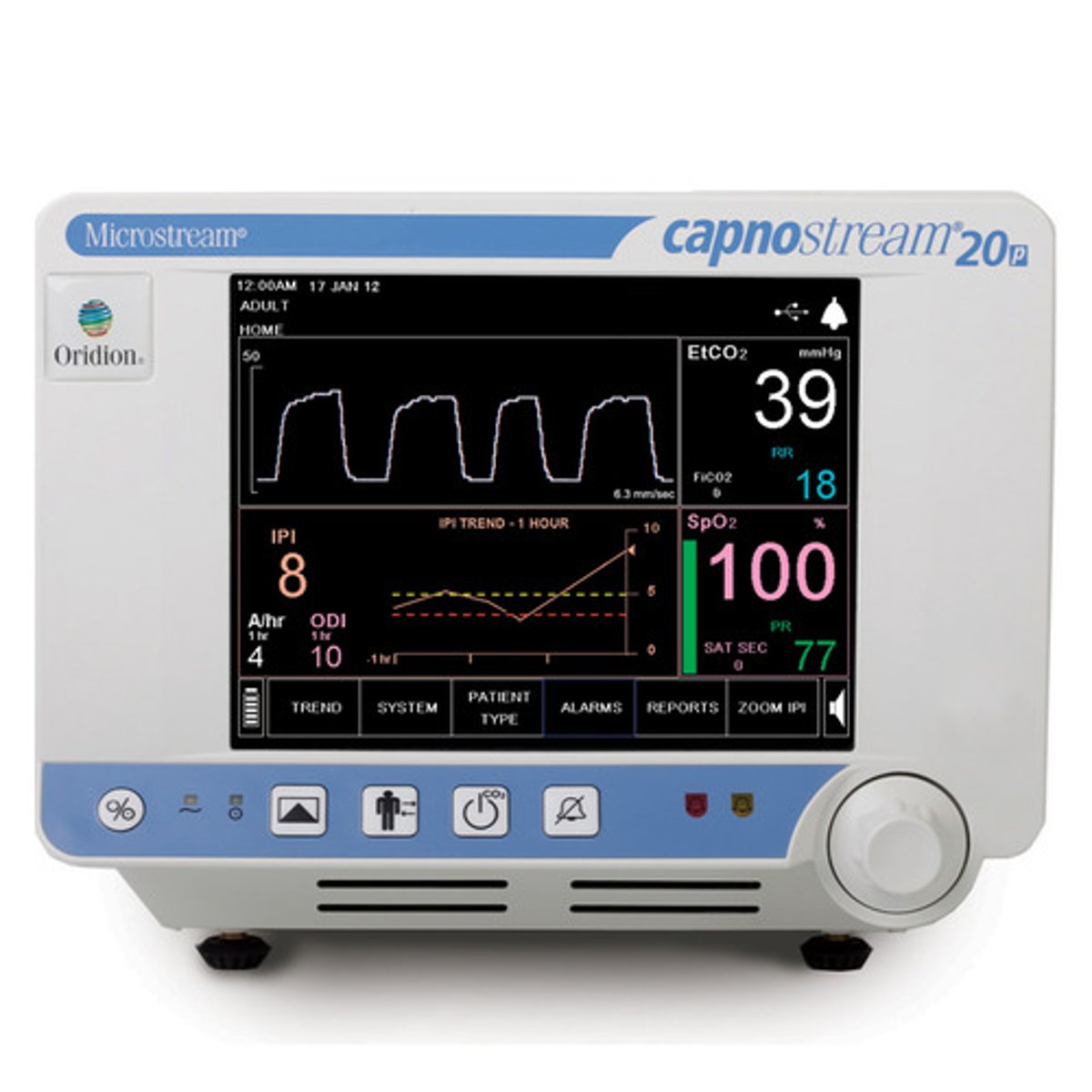
Capnography
• Measure CO2 levels (35-45 mmHg)
• COPD and obstructive sleep apnea most common causes
• Used to confirm ET or trach tube placement in mechanical ventilation
• Detects abnormal ventilation earlier than pulse oximetry
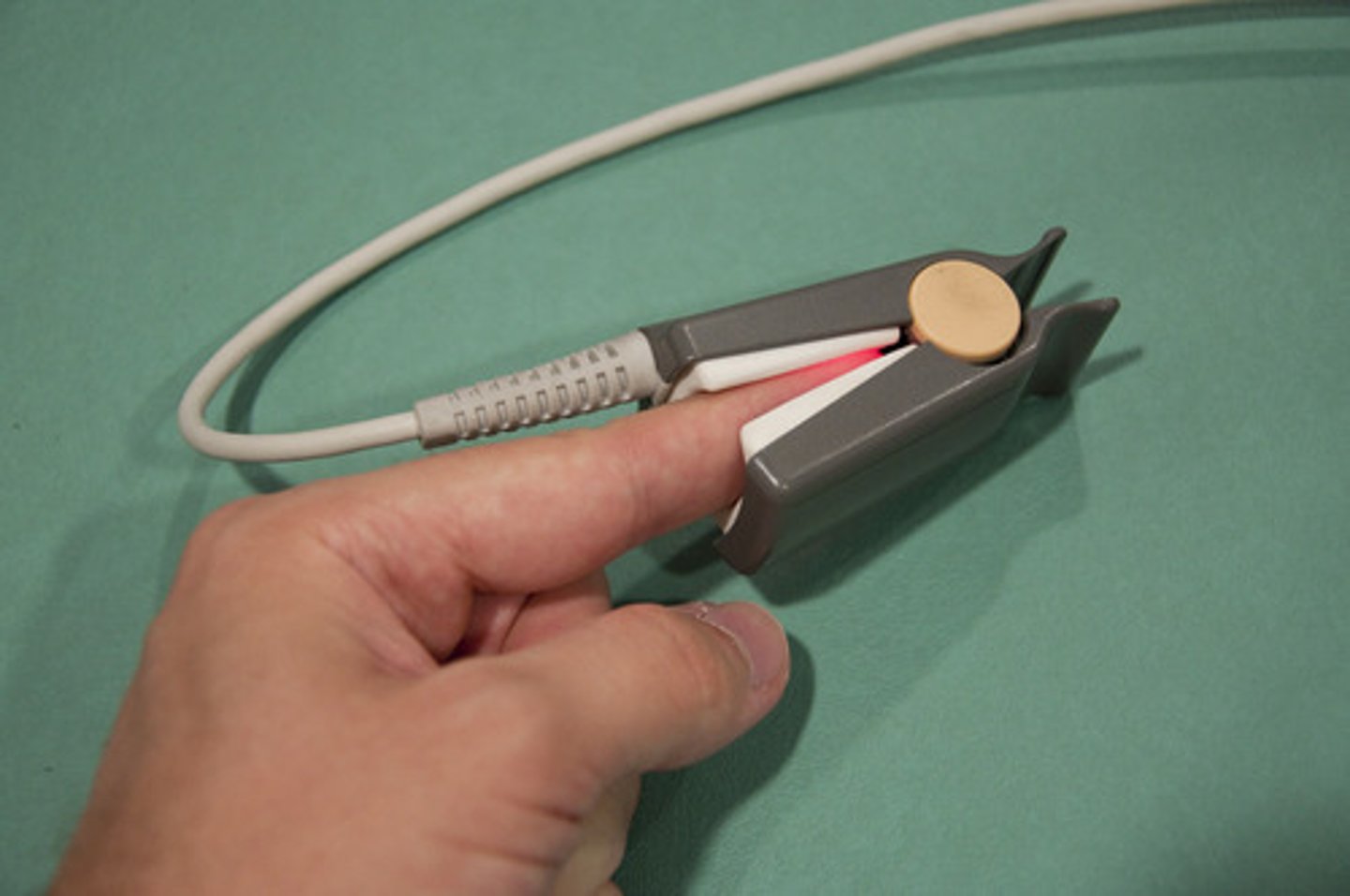
pulse oximetry
• Non-invasive measure peripheral arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation
• Ratio (as %) between actual oxygen content of hemoglobin and the potential maximum oxygen-carrying
capacity of the hemoglobin
• Helps in oxygen use, titration, monitoring those at risk, postoperative care
• Normal > 90%
• Presence of lung conditions = 88-92%
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
• Common and treatable disease
• Progressive airflow limitations
• Inflammatory response involving the airways, parenchyma, or both
• Structural lung changes due to chronic inflammation from prolonged exposure to noxious particles
• Chronic inflammation causes airway narrowing and
decreased lung recoil
• Primary symptoms = chronic cough, sputum production,
and dyspnea
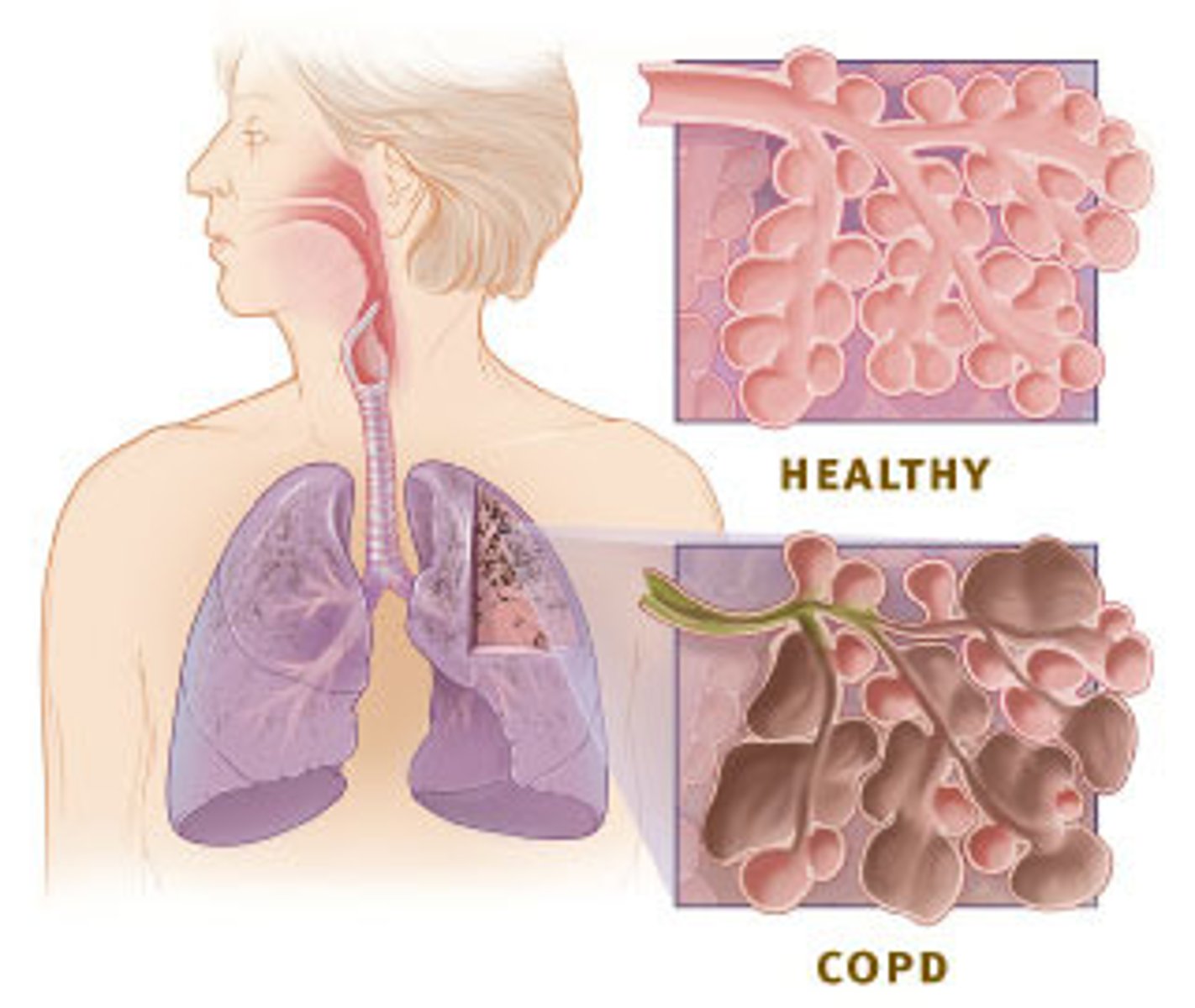
Pathophysiology of COPD
Proximal airways:
• Increased # of goblet cells + enlarged submucosal glands
= hypersecretion of mucous
Peripheral airways:
• Inflammation causes thickening of airway wall, fibrosis, exudate in airway
= overall airway narrowing
Over time, chronic injury and repair process
= scar tissue formation
= decrease in elastic recoil
= thickening of vessel lining
chronic bronchitis
• Epithelial cells lining airways respond to irritant releasing cytokines
• Bronchial mucous membrane becomes edematous
• Reducing body's ability to clear mucus from airway
• Airways clogged by ↑ mucus, increasing irritation
• Characteristic cough caused by mucous secretions (over
3mos/2 years)
Emphysema
• Impaired O2 & CO2 exchange from destruction of the walls of the distended alveoli
• Abnormal distention and destruction of walls of alveoli =
↓ alveolar surface area in contact with capillaries decreases
• ↑ dead space where no gas exchange occurs and impaired oxygen diffusion
• Destruction of elastin leads to decreased lung recoil
• Results in airway collapse with exhalation (CO2 trapped)
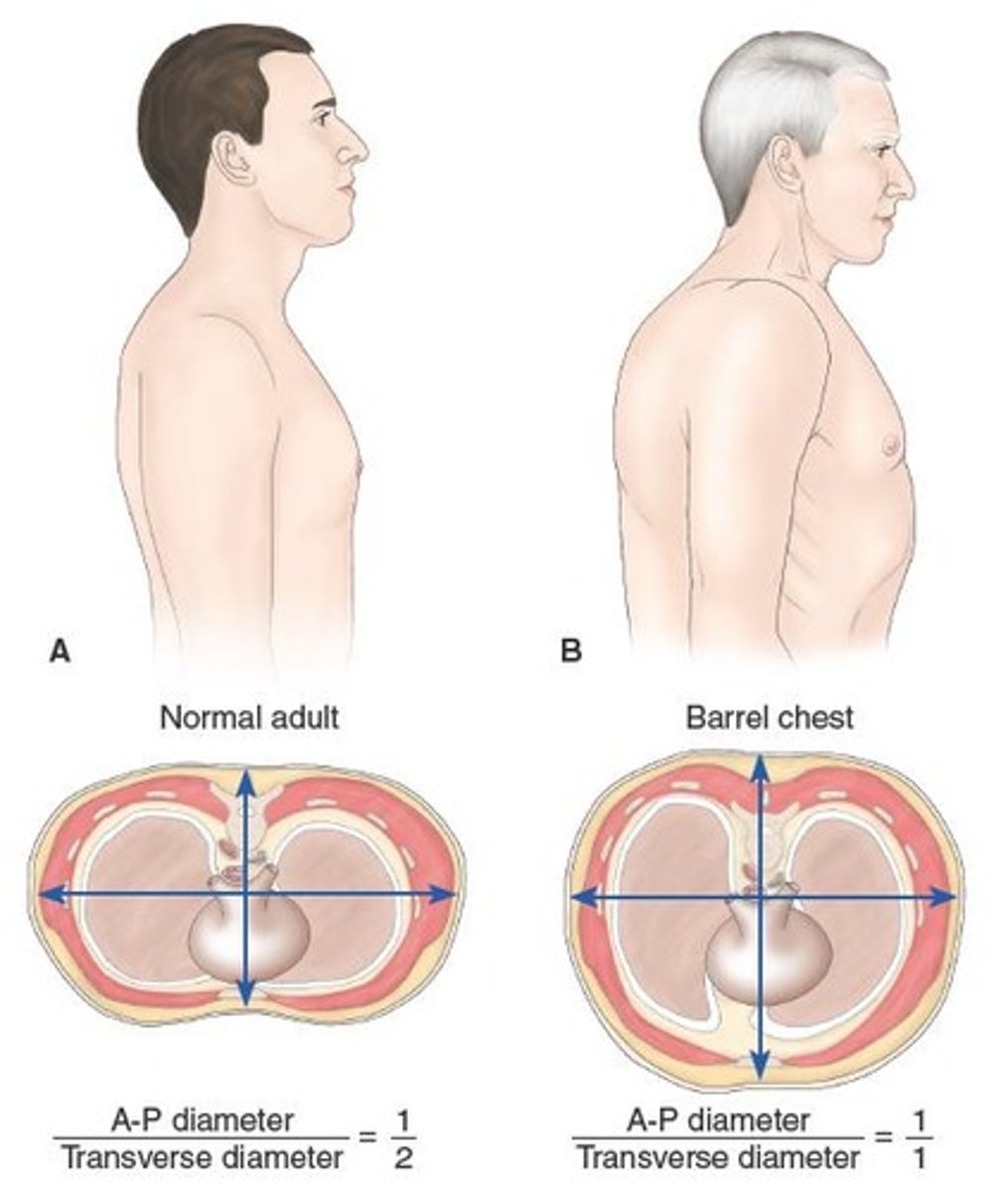
Clinical Manifestations of COPD
✓ Chronic cough
✓ Sputum production
✓ Dyspnea
✓ Weight loss
✓ Use of accessory muscles
✓ Barrel chest
✓ Musculoskeletal wasting
✓ Depression
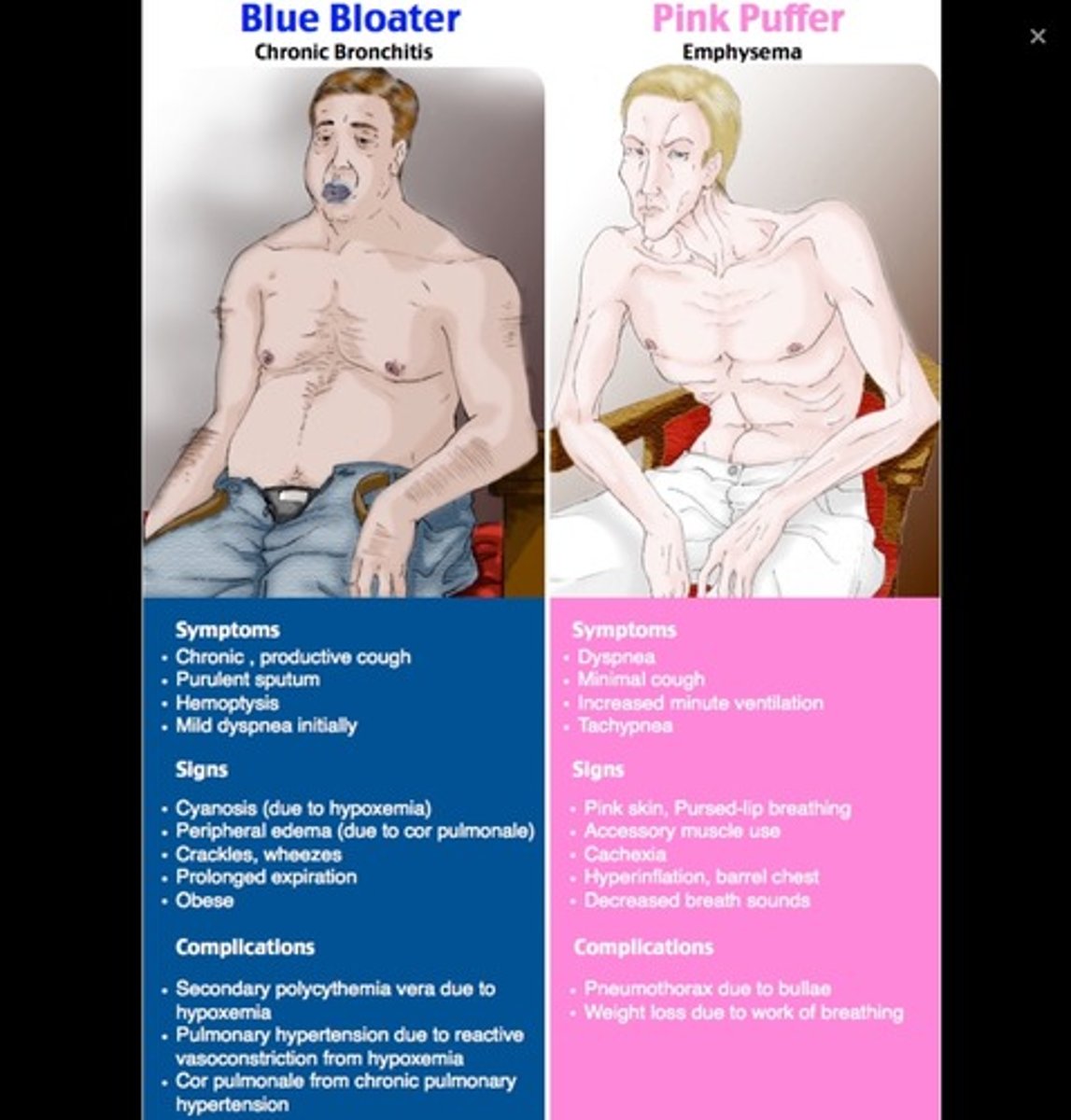
Blue bloater
Chronic bronchitis- hypoxemia, hypercapnia
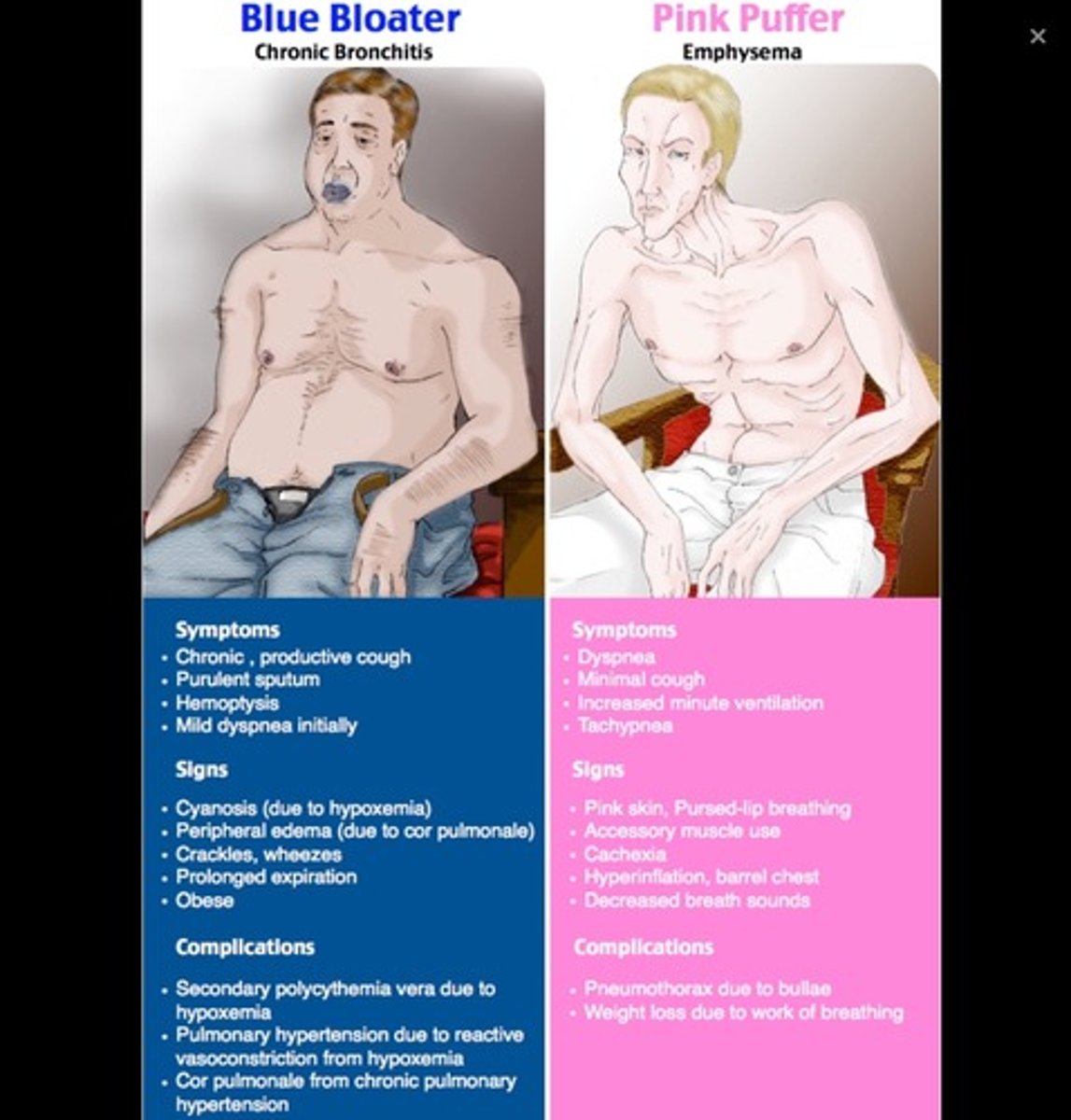
pink puffer
Dyspnea, hyperventilation (emphysema)
hypoxia (chronic)
• Altered thought processes
• Headaches
• Chest pain
• Enlarged heart
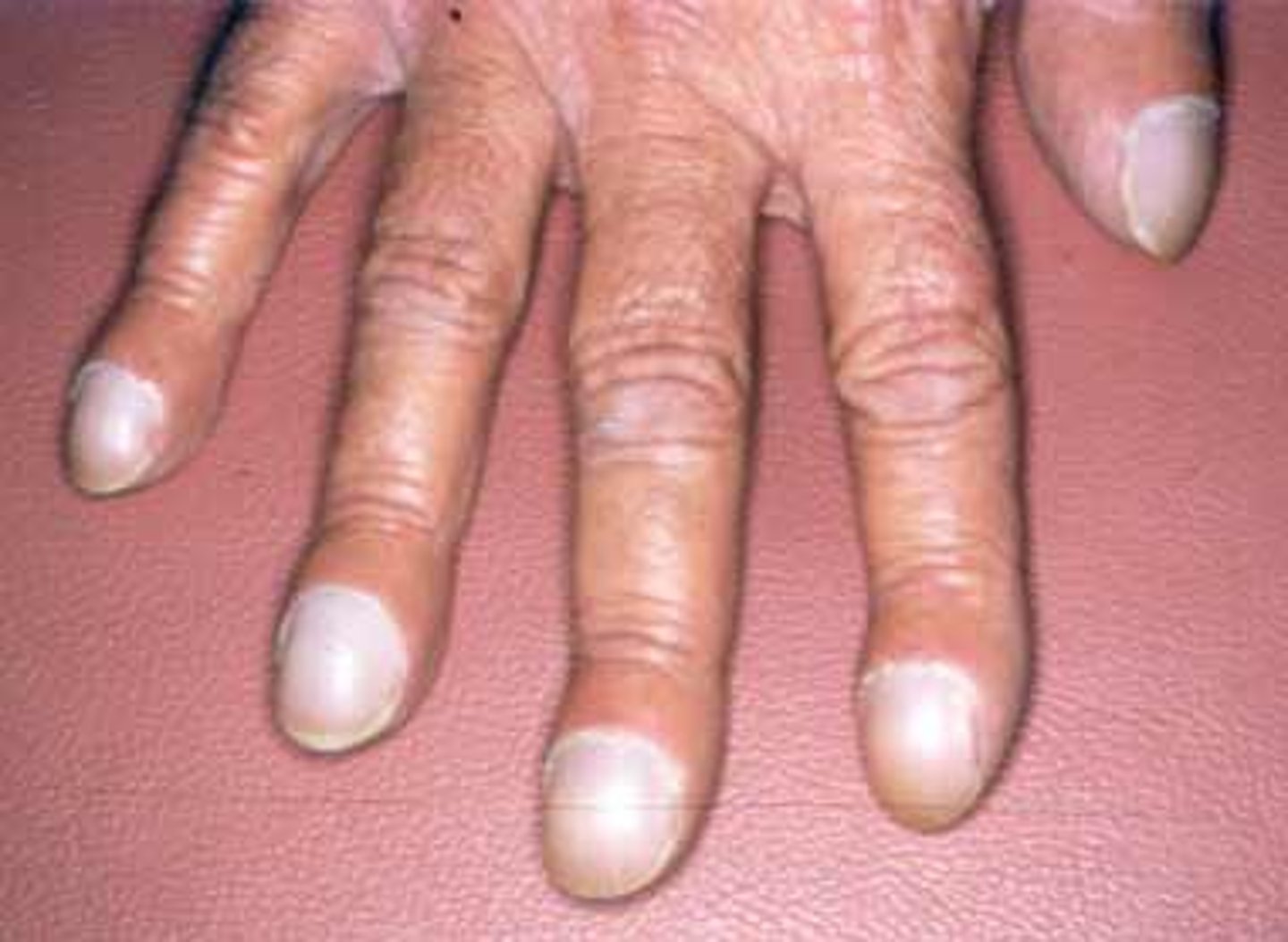
• Clubbing of fingers/toes
• Anorexia = cachexia
• Constipation
• Decreased urinary output
• Weakness of extremity muscles
• Muscle pain
Hypoxia acute early manifestations
• Dyspnea
• Elevated BP - narrow pulse pressure
• Increased respiratory rate
• Increased pulse rate
• Pallor skin/mucous membranes
• Anxiety
• Restlessness
• Confusion
• Drowsiness
• Use of accessory muscles
• Nasal flaring
• Adventitious lung sounds
Hypoxia - Acute
Late manifestations
• Cyanotic skin/mucous membranes
• Stupor
• Bradypnea
• Bradycardia
• Hypotension
• Cardiac dysrhythmias
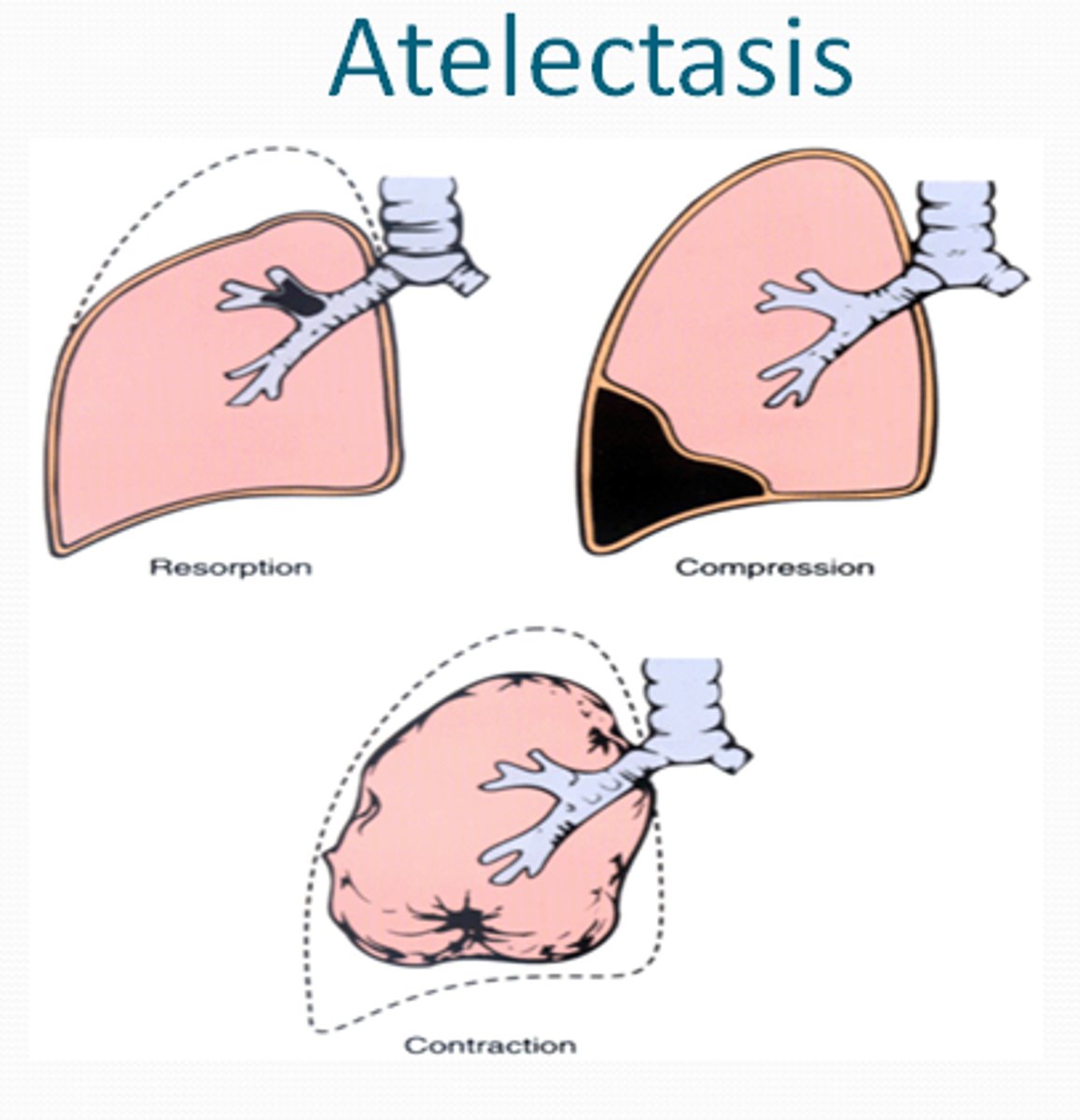
atelectasis
Alveolar volume loss resulting in collapse of a portion of the lung
Causes:
• Airway obstruction - mucous plugging, tumor, foreign body, bronchial intubation
• Airway compression -hemothorax, lymphadenopathy, tumor
• Lung compression - pleural effusion, pneumothorax
• Hypoventilation - general anesthesia, opioids, obesity
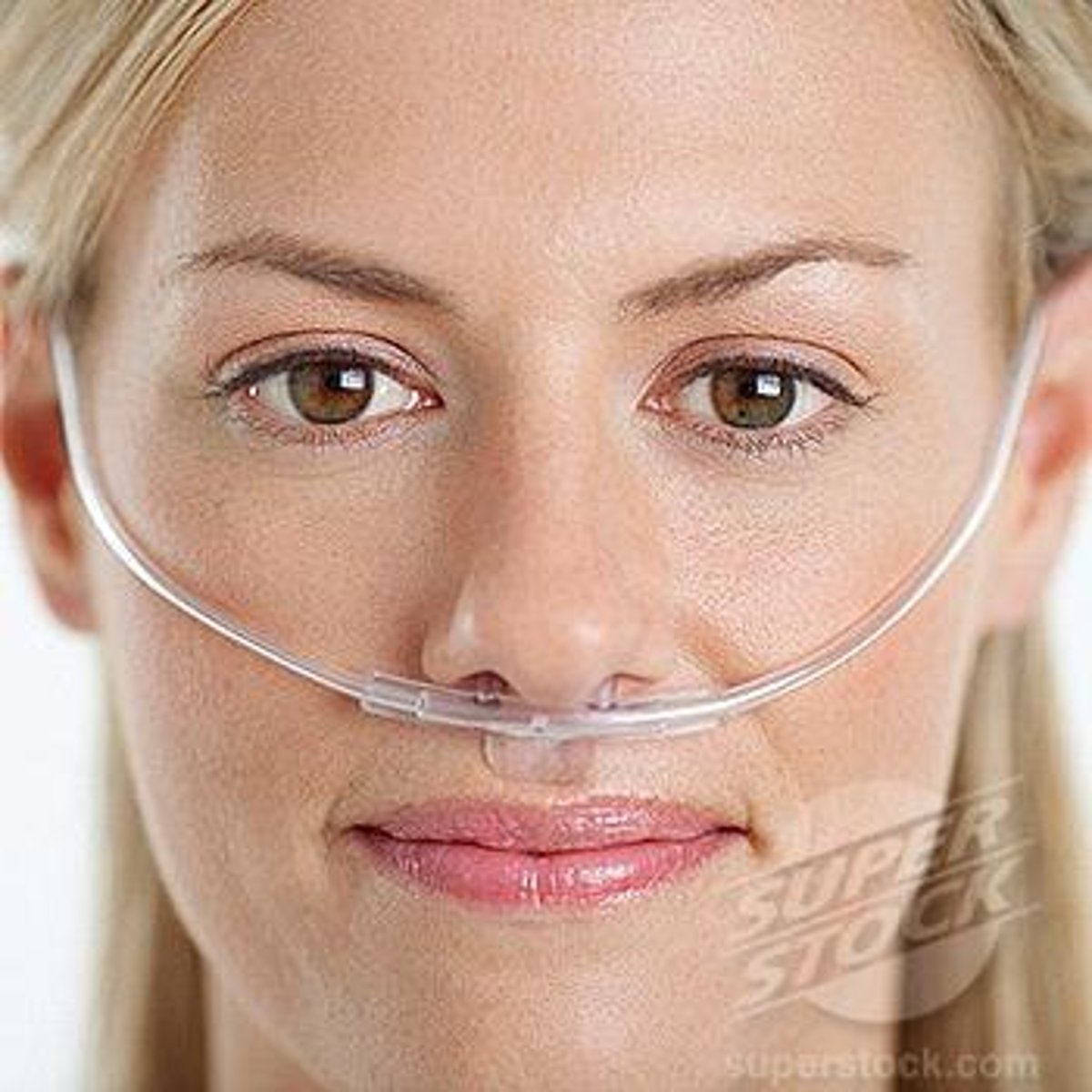
nasal cannula
• Mix oxygen with room air
• Low flow 1-6L/min only
• Room air = 21% FiO2
• 1L = 24% FiO2
• 2L = 28% FiO2
• 3L = 32% FiO2
• 4L = 36% FiO2
• 5L = 40% FiO2
• 6L = 44% FiO2

High flow nasal cannula
Continuous delivery of air/oxygen through a heater/humidifier
• 10L/minute = 65% oxygen
• 15L/minute = 90% oxygen
Wide bore nasal canula
Maintains a small amount of continuous positive pressure during the breathing cycle
Patients with mild to moderate respiratory failure (avoiding invasive mechanical ventilation)
Close monitoring to avoid delay if airway intervention needed
simple face mask
• Delivers low to moderate amount of oxygen
• Contains holes to allow exhaled air out and prevent
suffocation
• 35-50% FiO2 at 6-10L/min
• Do not set below 5L to prevent rebreathing of CO2
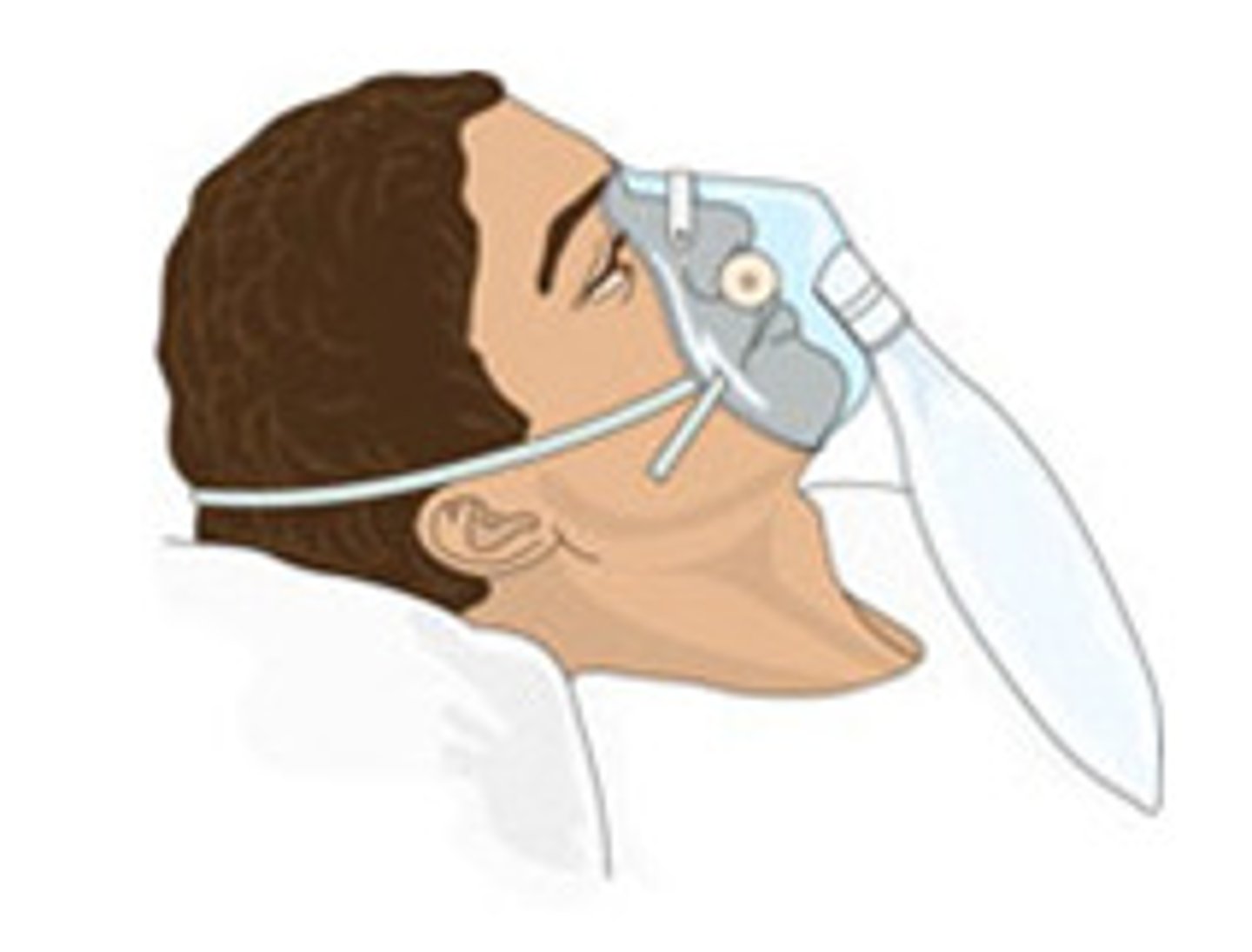
Non-rebreather mask
• 60-80% FiO2
• Emergency situations
• One-way inspiration valve opens during inhalation directing oxygen from a reservoir bag into mask
• On exhalation, gas exits mask through one-way expiration valve into room air
• Minimum of 10L/min only to avoid rebreathing CO2
• Must inflate bag with O2 prior to applying
Venturi mask
• 24-50% FiO2 - high-flow, fixed
• Different colors correspond to % FiO2
• Delivers highly accurate O2 concentration
• Often used for transporting trach patients

humidified air
Dry air removes normal moisture in respiratory passages
• Compromises ciliary function and mucous production
• Patients c/o itchiness, dryness, sore throat
Vaporizer - add water vapor/moisture to the air
Humidifier - releases cool mist into the air
• Use distilled water to prevent mineral buildup
Monitoring patients with supplemental O2
• Initiation, administration, and titration based on patient's target saturation range
Monitor:
✓ Flow rate
✓ Patient color
✓ Respiratory rate
✓ Respiratory depth
✓ Work of breathing
✓ Pulse oximetry levels
✓ ABG results
✓ Comfort
✓ Oral and nasal mucous membranes
✓ Pressure points
✓ Fluid status
✓ Routine oral hygiene
Positive Airway Pressure
• Mild air pressure to keep airways open
• Maintains better CO2 and O2 levels in blood
• For sleep apnea, obstructive sleep apnea, heart failure, COPD, acute respiratory failure
CPAP
continuous positive airway pressure
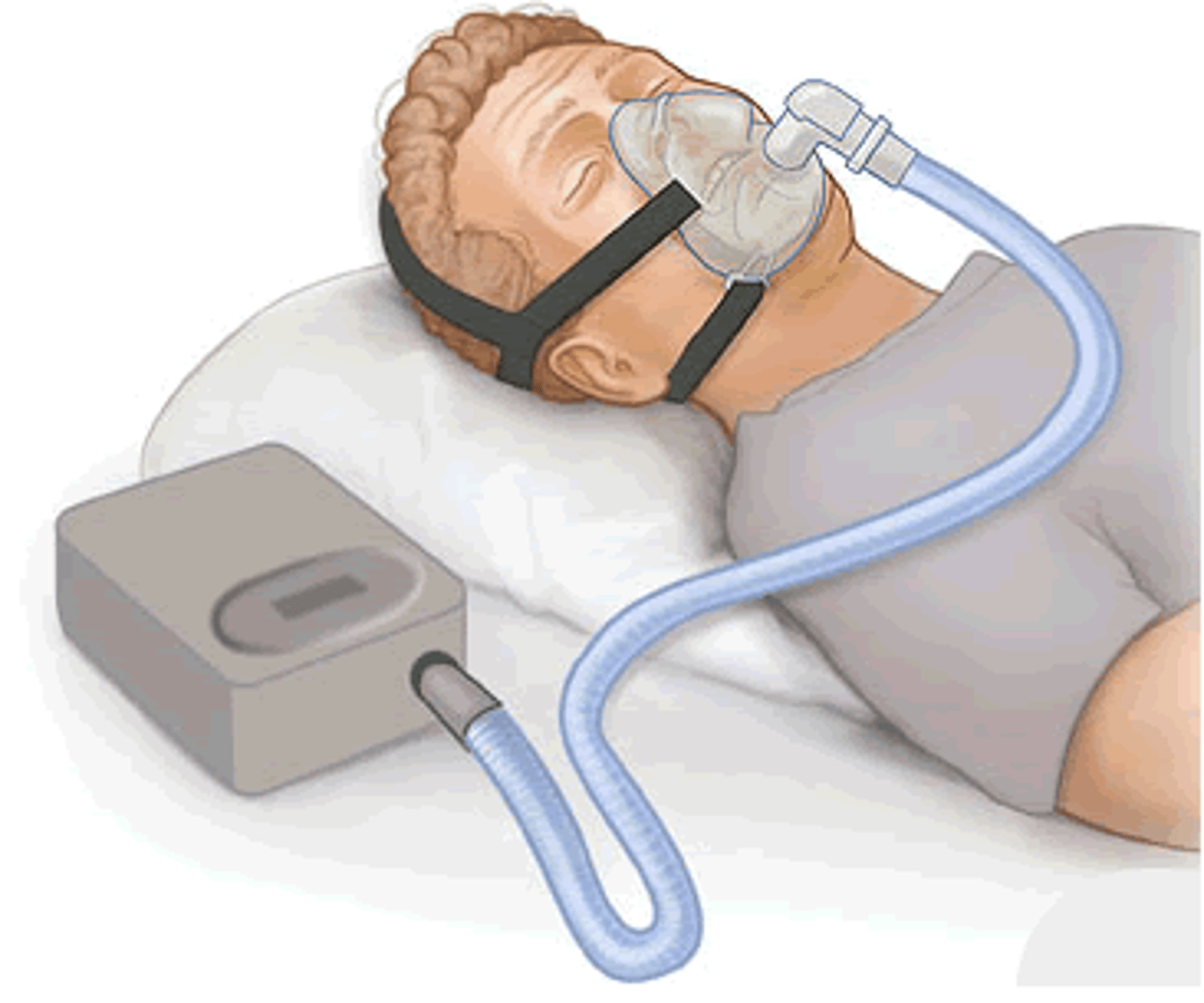
BiPAP
bilevel positive airway pressure
Changes air pressure while breathing in and out
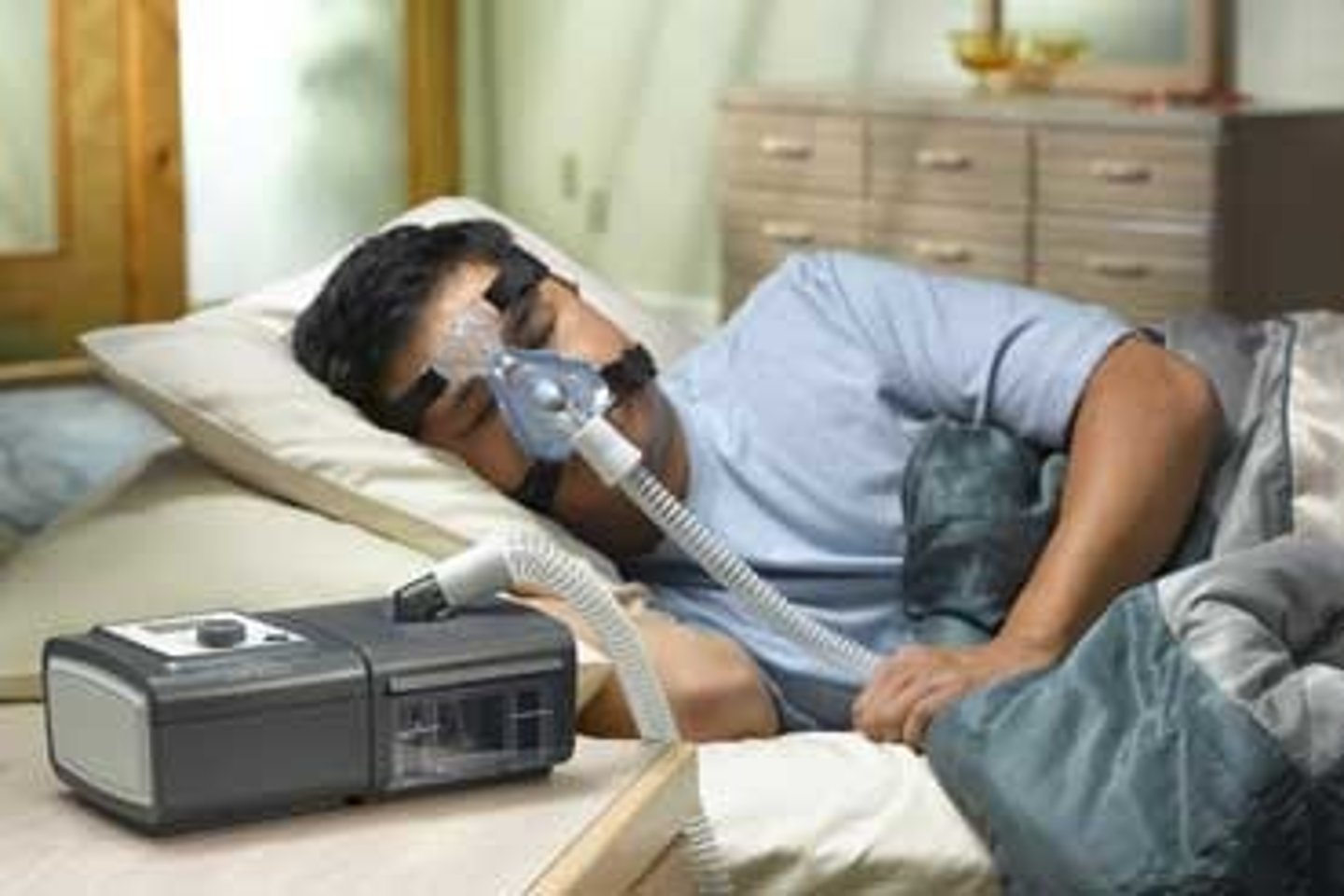

APAP
auto-titrating positive airway pressure
• Adjustable changes in pressure based on breathing
patterns
High Fowler's Position
Dyspnea or orthopnea
• Accessory muscles can easily be used to promote respiration
• Allows free movement of diaphragm and expansion of chest wall
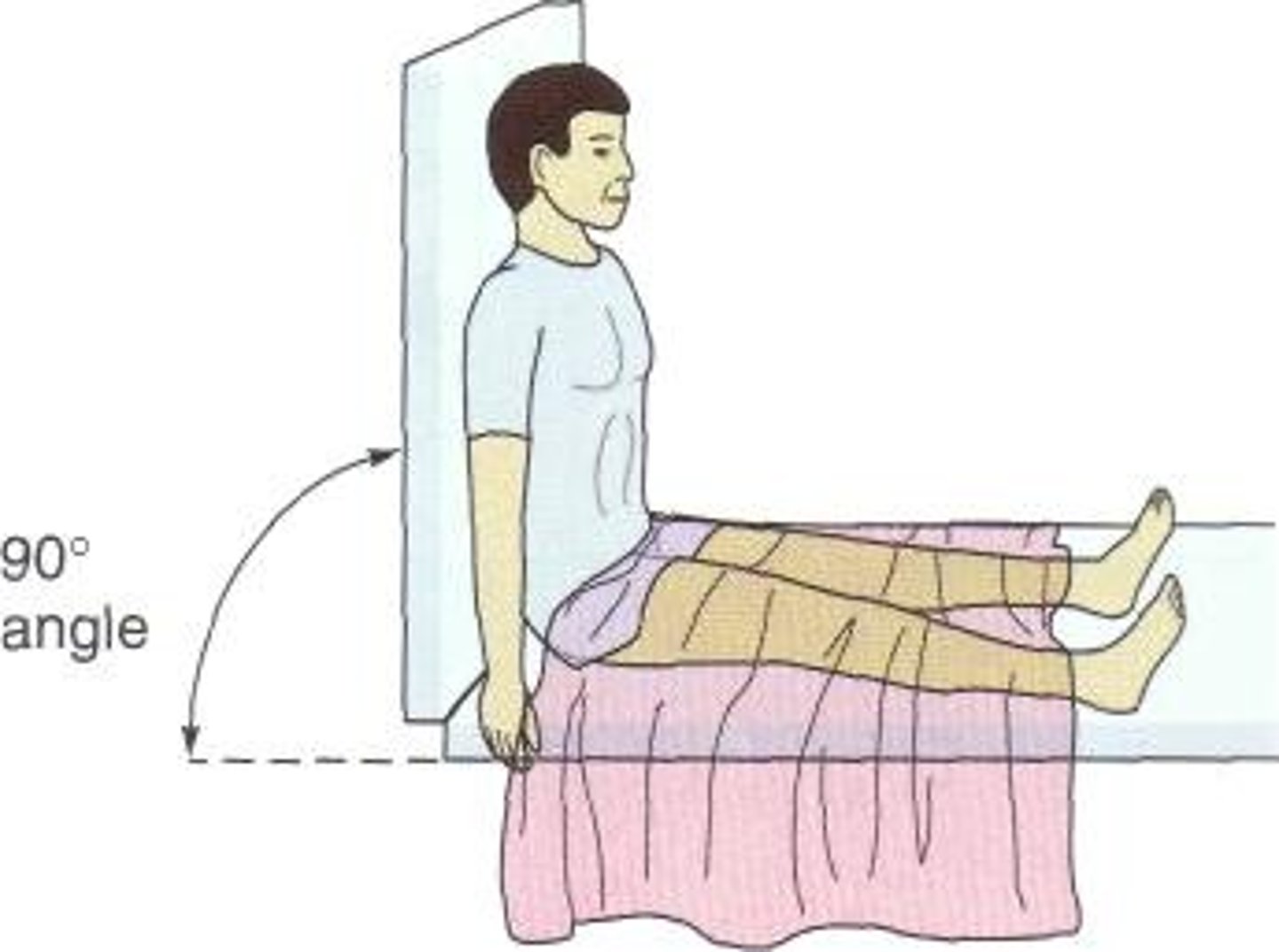
prone position
• Acute illness (ARDS, RF)
• Benefits:
• Posterior dependent secretions of lungs better ventilated and perfused
• Gravitational pressure on lung structures is decreased
• Compression of lungs from abdominal contents decreased
• Enhances chest wall compliance
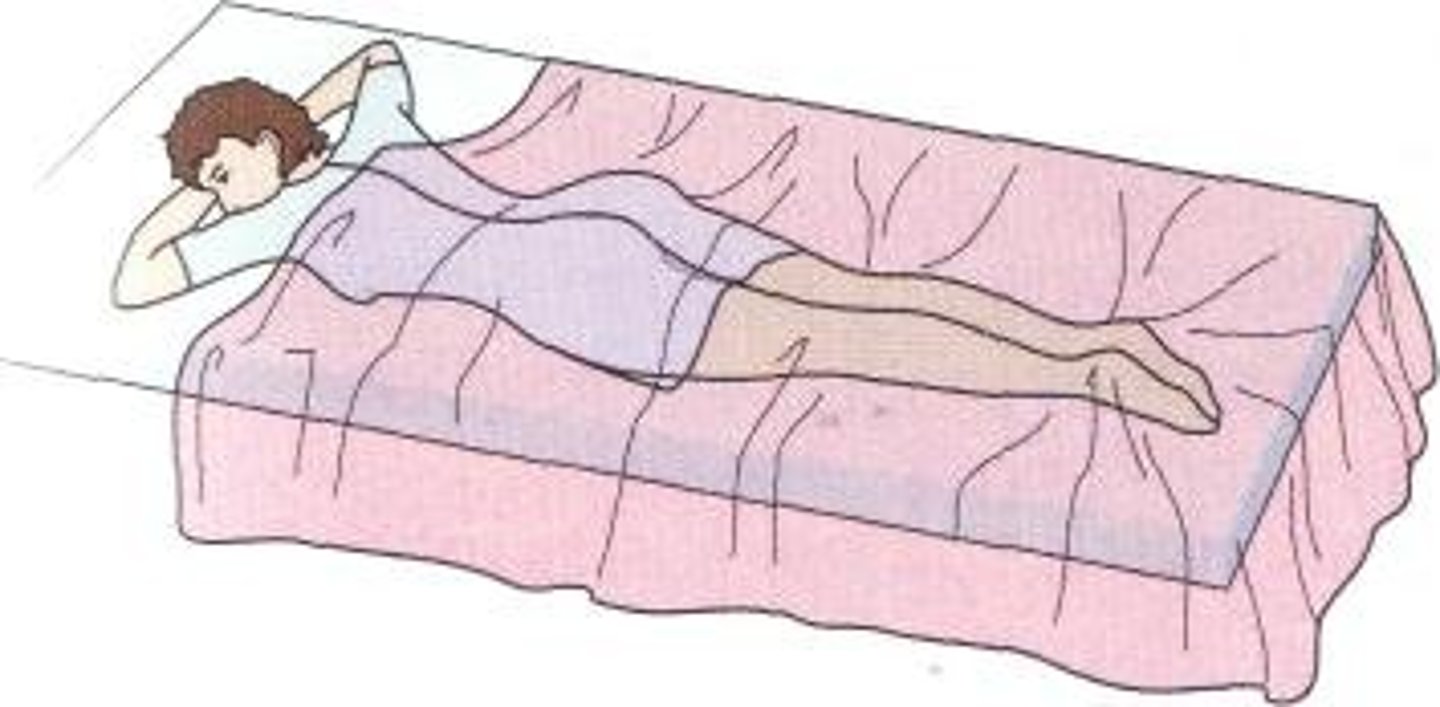
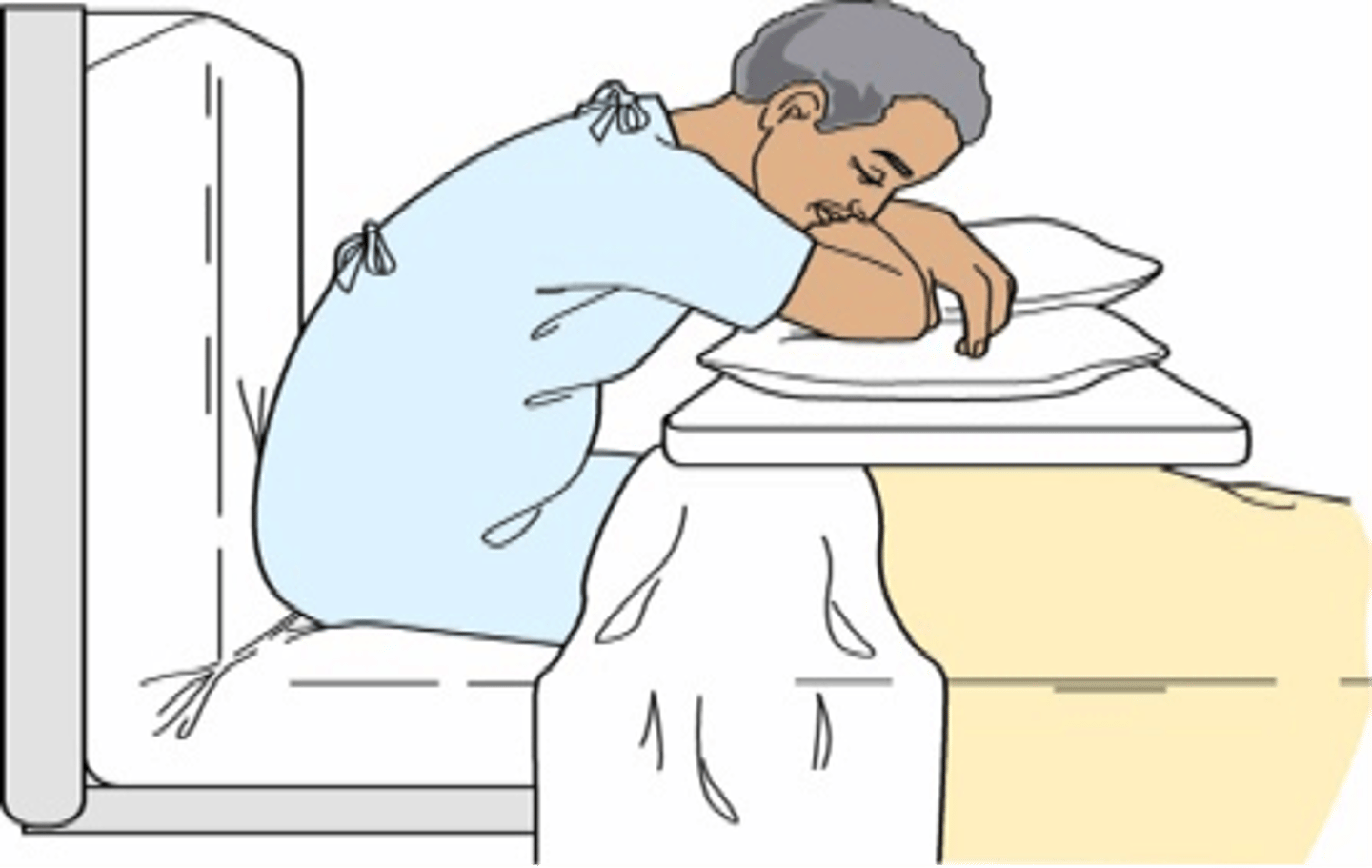
orthopneic position (tripod)
• Maximizes chest and lung expansion
• Helps in exhaling by pressing the lower part of the chest against the edge of the overbed table
• Decreases breathing effort
reducing anxiety
Illness - asthma, COPD, CHF exacerbation, trauma, respiratory illness
• Calming environment (reduce sensory)
• Effective listening skills
• Non-judgmental
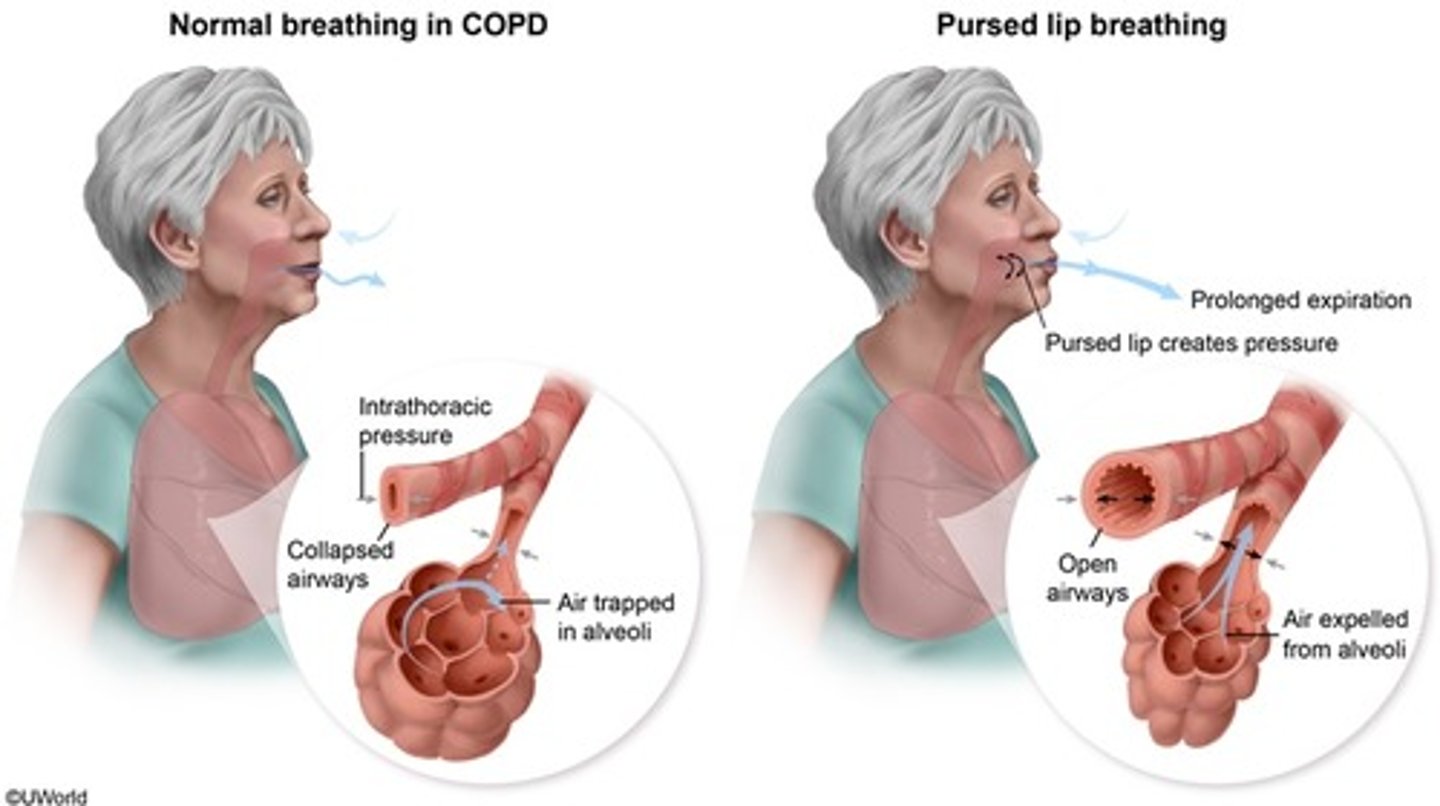
pursed lip breathing
• Slowing and prolonging expiration
• Decreased airway narrowing during expiration
• Prevent the collapse of small airways
• Improved gas exchange
• Control rate and rhythm of respirations
diaphragmatic breathing
Consciously use diaphragm to take deep breaths; allows you to use lungs at 100% capacity to increase lung efficiency
• Strengthens the diaphragm
• Decreases the work of breathing by slowing breathing rate
• Decreases oxygen demand
• Uses less effort and energy to breathe

maintain adequate food and fluid intake
Estimated that approximately one fourth of the daily water requirements are used up by water loss during respiration
• 1.5 - 2L fluids daily (maximum that patient's health state can tolerate)
• Keeps secretions thin
• Monitor sodium intake
promoting and controlling coughing
Cleaning mechanism of the body
• Keeps airways clear of secretions/debris
• Effective cough produces enough of a muscle contraction to force air/liquid/solid to be expelled
Non-productive = dry
Productive cough = secretions
Sputum = secretions expelled by coughing or clearing throat
Phlegm = thick secretions
Congestion = excessive fluids or secretions in an organ or body tissue
non productive
dry cough
productive cough
secretions are expectorated
sputum
secretions expelled by coughing or clearing throat
phlegm
thick mucus
congestion
excessive fluids or secretions in an organ or body tissue
chest physiotherapy
• Percussion, vibration, and postural drainage
• Loosens and mobilizes secretions
• Increases mucous clearance
• Contraindications - head injuries, aspiration risk, children
with PNA, adults with COPD, postoperative adults
• Limited evidence for effectiveness
oral and naso-oral suctioning
• Indicated to maintain patent airway
• Removes saliva, pulmonary secretions, blood, vomitus, or foreign material
• Able to raise secretions from airway but not expectorate
Method:
✓ Preoxygenate prior to suctioning
✓ Proper PPE
✓ Assess respiratory rate, work of breathing
✓ Color, amount, odor, consistency
✓ Blood may indicate damage to mucosa
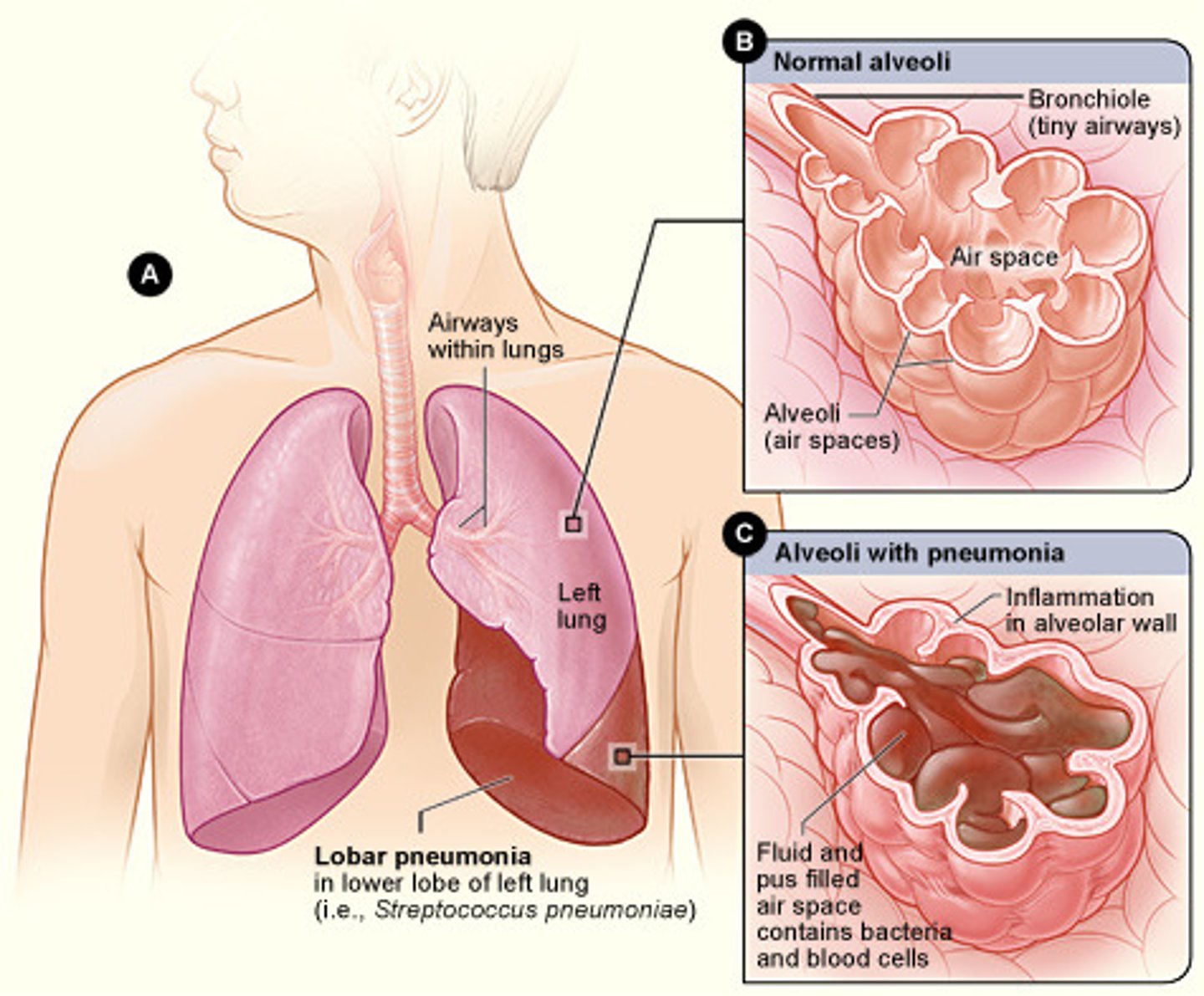
pneumonia
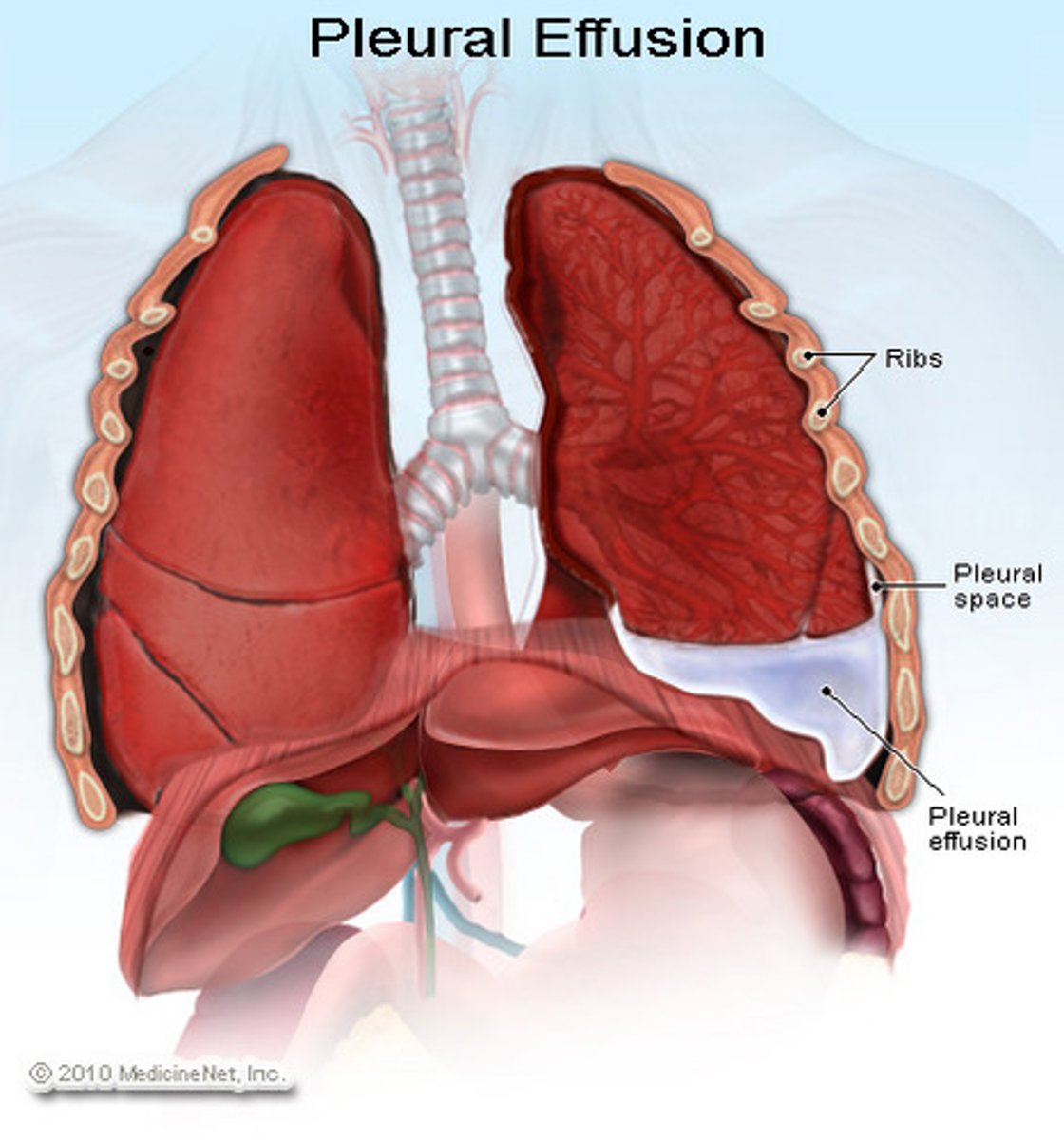
pleural effusion
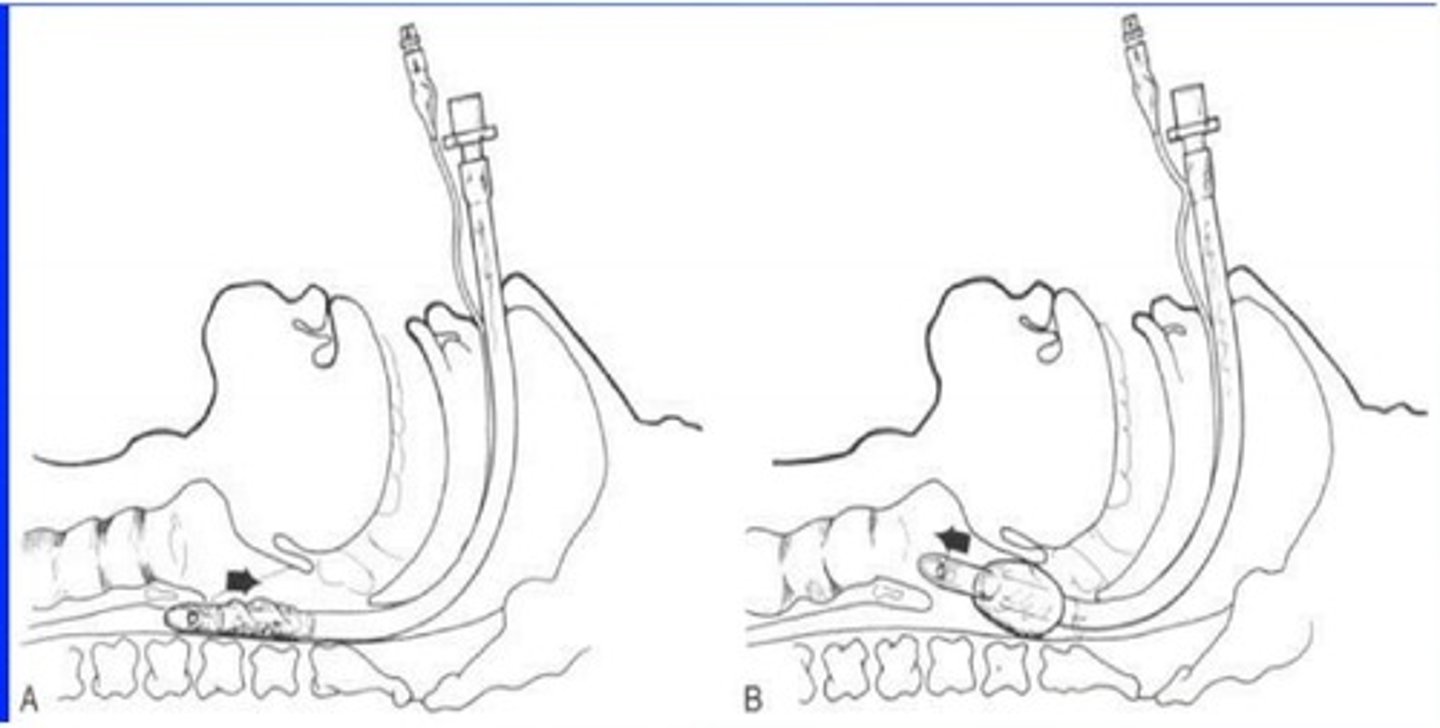
thoracentesis
• Aspirate air, fluid, or both from pleural space
• Performed at bedside or interventional radiology
• Other purposes:
• Obtain specimen (diagnostic)
• Decrease respiratory effort
• Instill medications
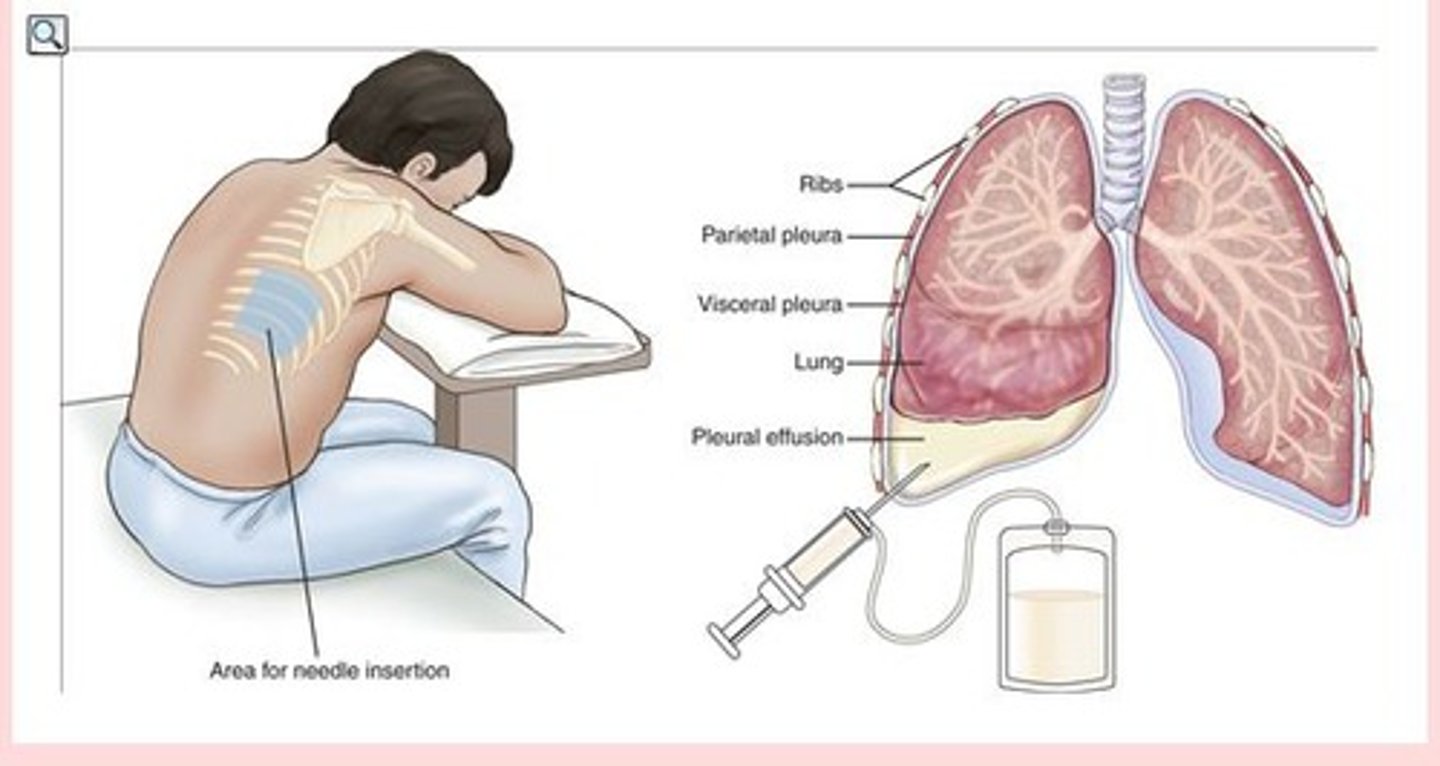
Thoracentesis - post procedure
CXR performed post procedure
Monitor for complications:
• Vital signs
• Puncture site
• Lung sounds
• Dyspnea or cough
• Respiratory distress
• Coughing
• Blood in sputum
B. Assist the client to a Fowler's position
The nurse is caring for a client who is having difficulty breathing. The client is lying in bed and already receiving oxygen therapy via nasal cannula. Which of the following interventions is the nurse's priority?
A. Increase the oxygen flow
B. Assist the client to a Fowler's position
C. Promote the removal of pulmonary secretions
D. Obtain a specimen for arterial blood gases
A. Restlessness
B. Tachypnea
D. Confusion
E. Hypertension
A nurse is assessing a client who has an acute respiratory infection, increasing the risk for hypoxemia. Which of the following findings are early indications that should alert the nurse that the client is developing hypoxia? Select all that apply.
A. Restlessness
B. Tachypnea
C. Bradycardia
D. Confusion
E. Hypertension