histology- digestive system
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
tubular, MSMS structure
except for glands, all digestive organs are _______(parenchymal or tubular), so all have____
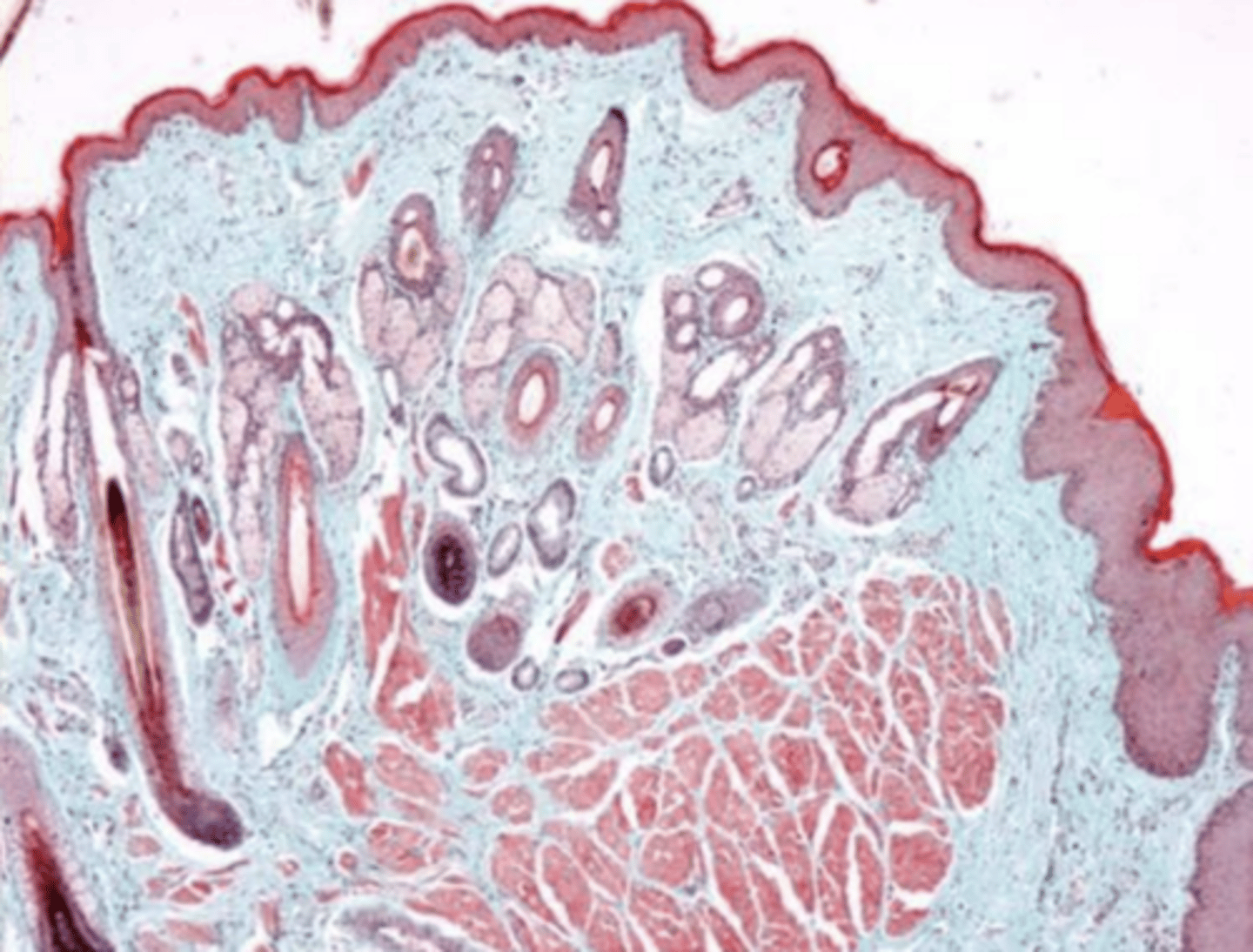
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, hair follicles, sebacious glands, sweat glands
describe the composition of the external region of the lips
cutaneous region,
red region,
oral mucosa region
what are the 3 regions of the lips/gums?
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, tall papillae with blood vessels
what composes the red region of the oral cavity?
cutaneous region
which region of the mouth is keratinized- cutaneous region, red region, or oral mucosa region?
lip
what is this?
left side, because there are hair follicles
the right is internal because there are salivary glands
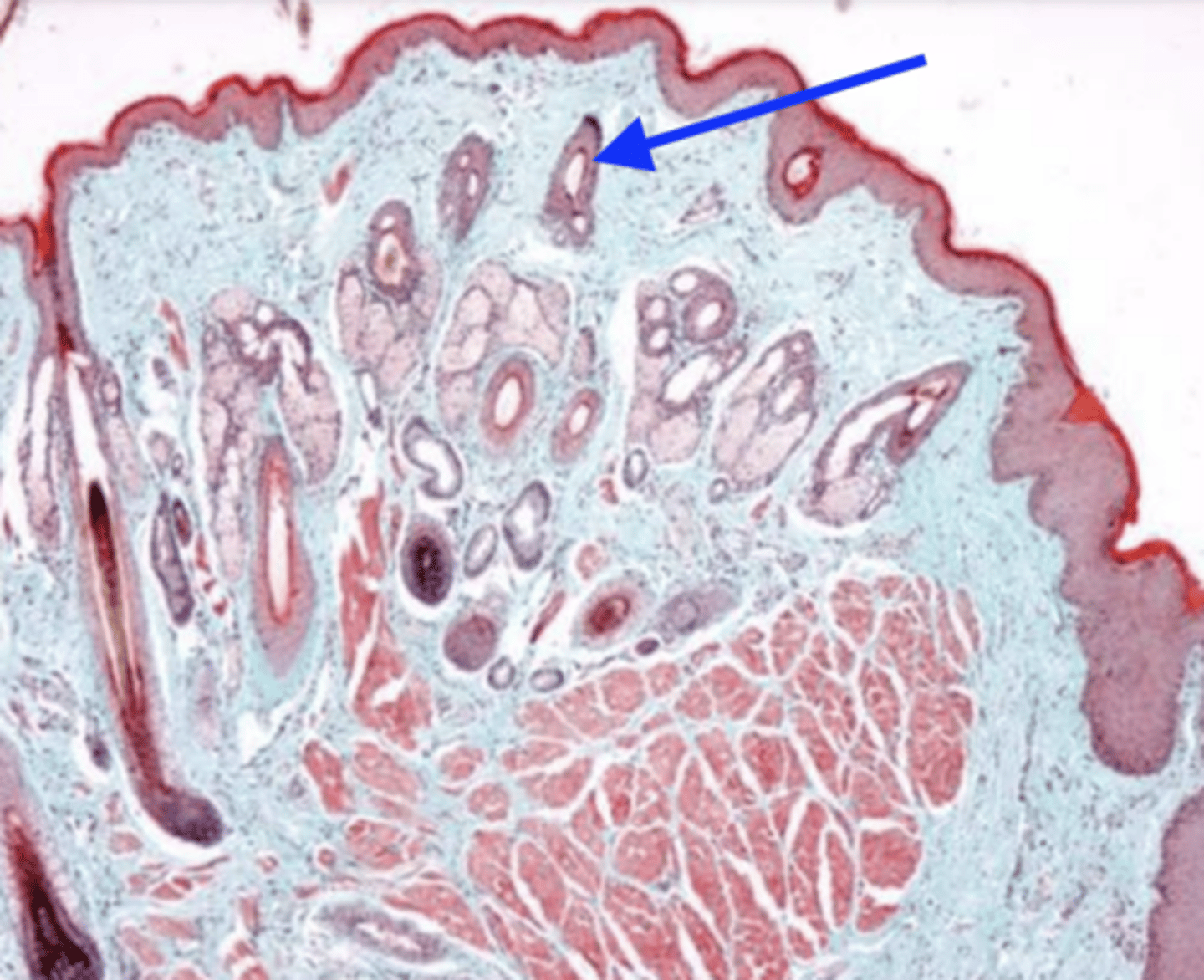
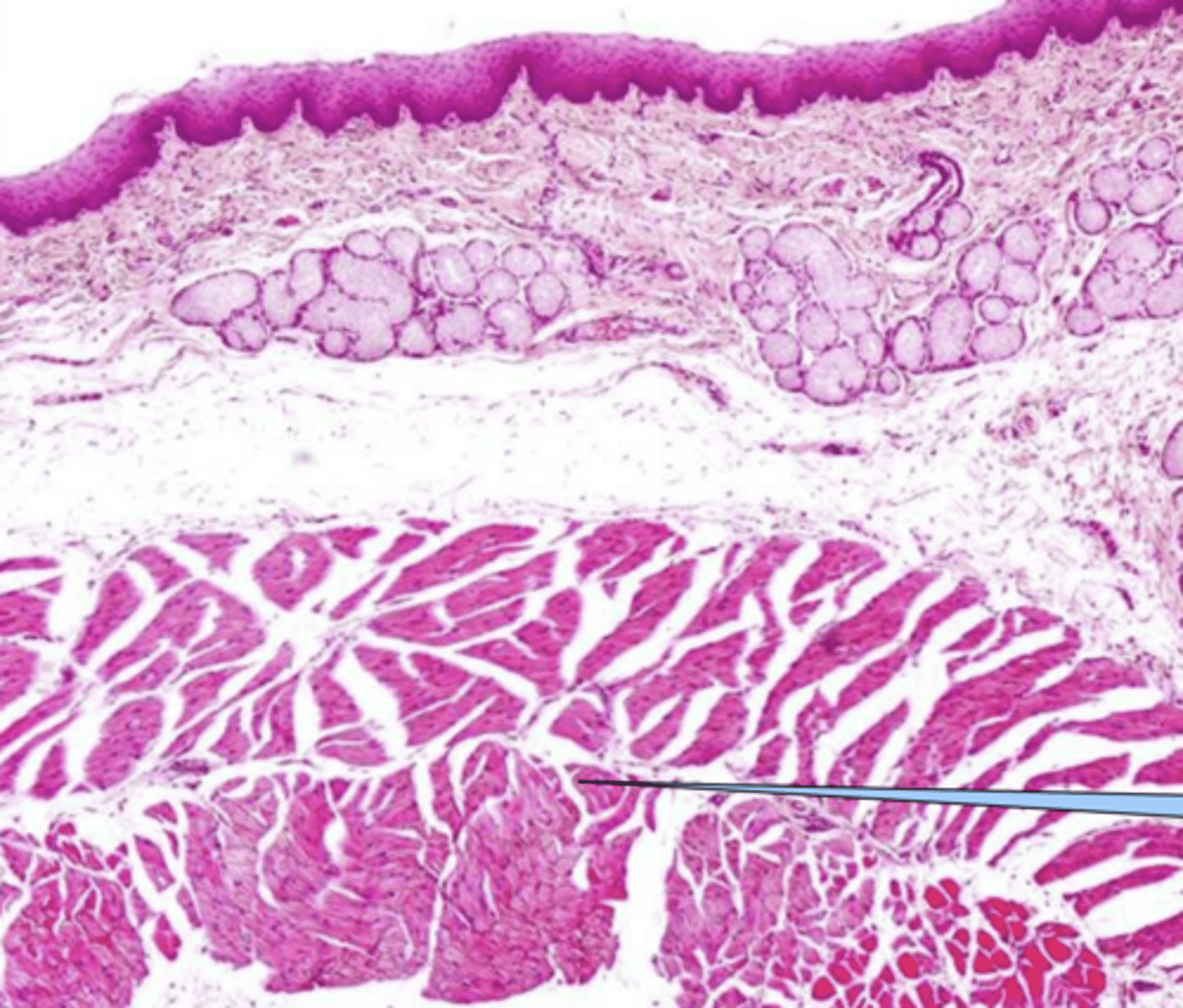
sample of a lip- which side is exterior, and why?
hair follicles (this is a sample of the lip)
what are these structures?
salivary glands of the lip
what are these structures?
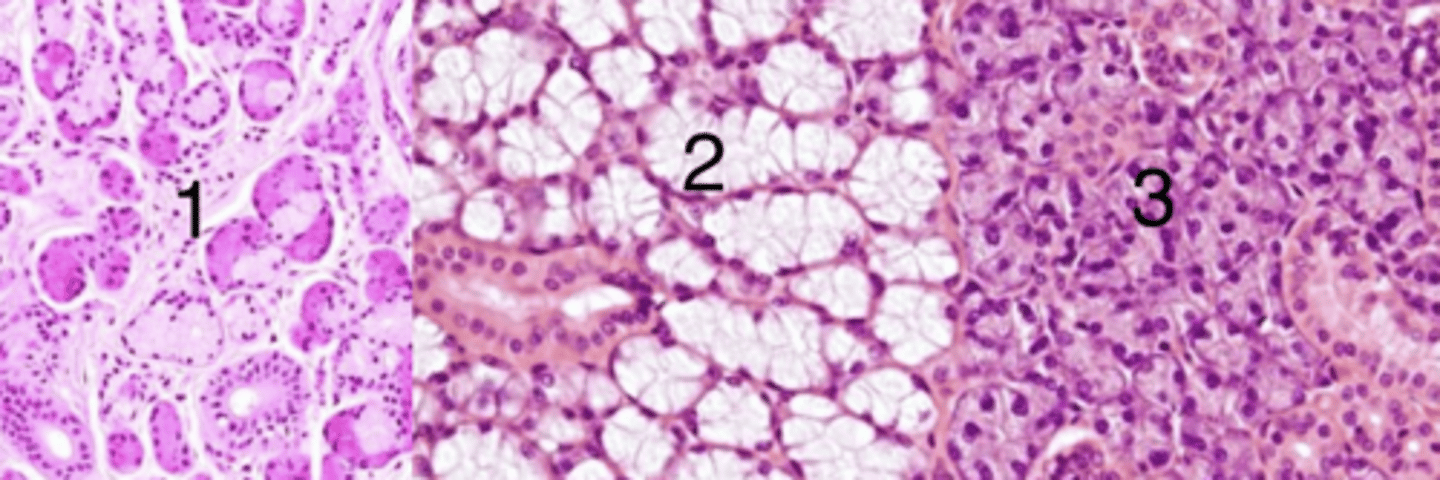
2, because it has mucus glands
which is a sample of the sublingual gland? why?
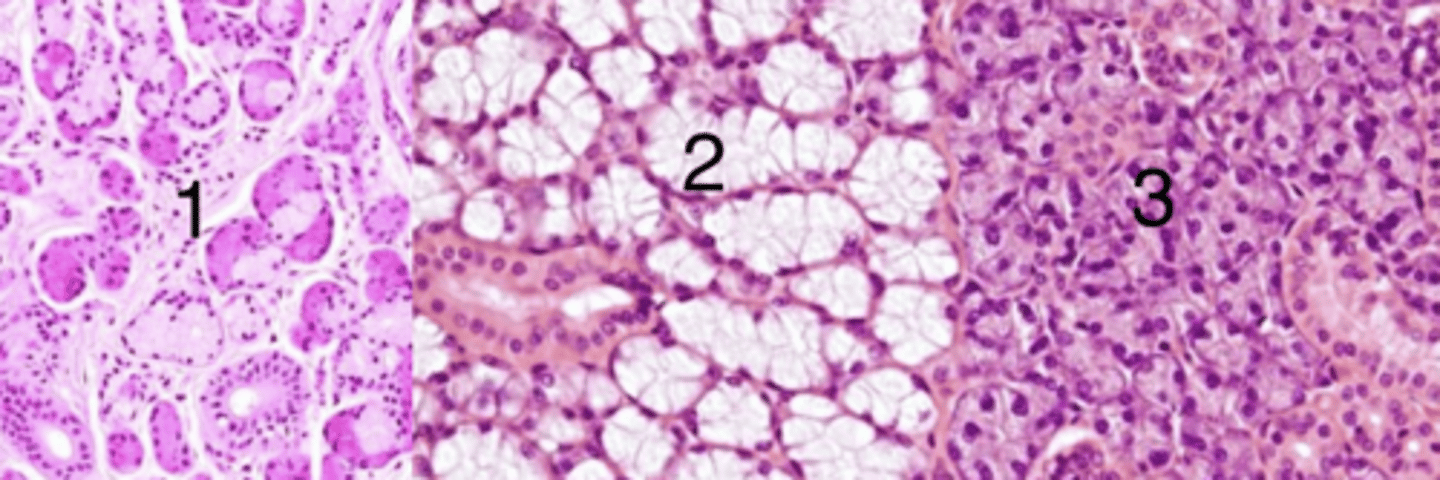
1
which has mixed glands (both serous and mucus)?
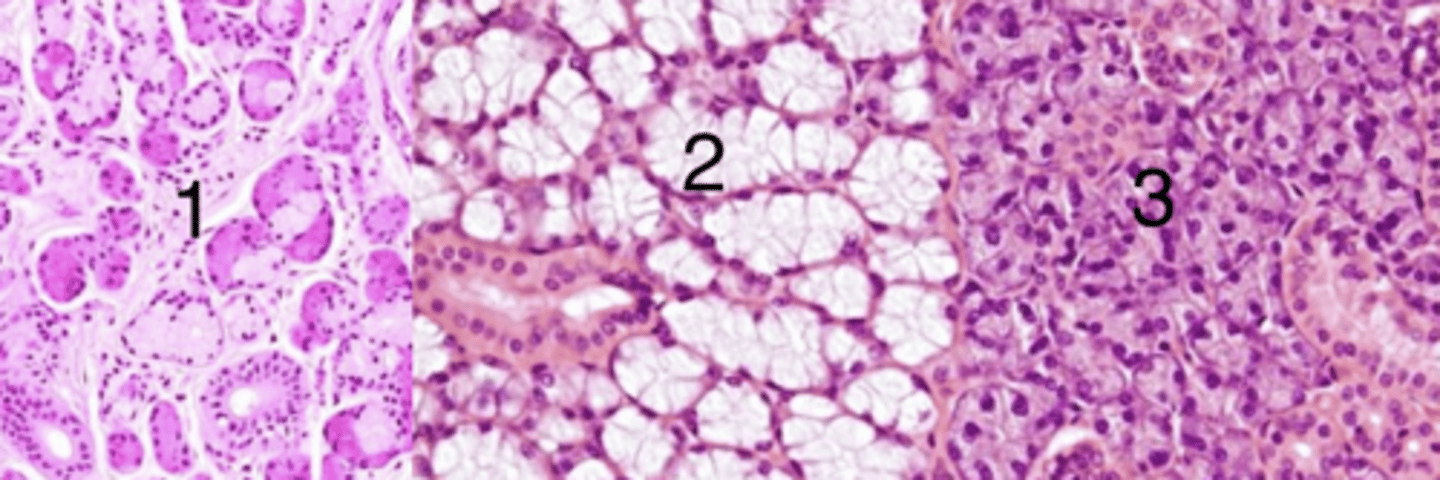
1, because it is mixed (has both mucus and serous glands)
which belongs to the mandibular gland? why?
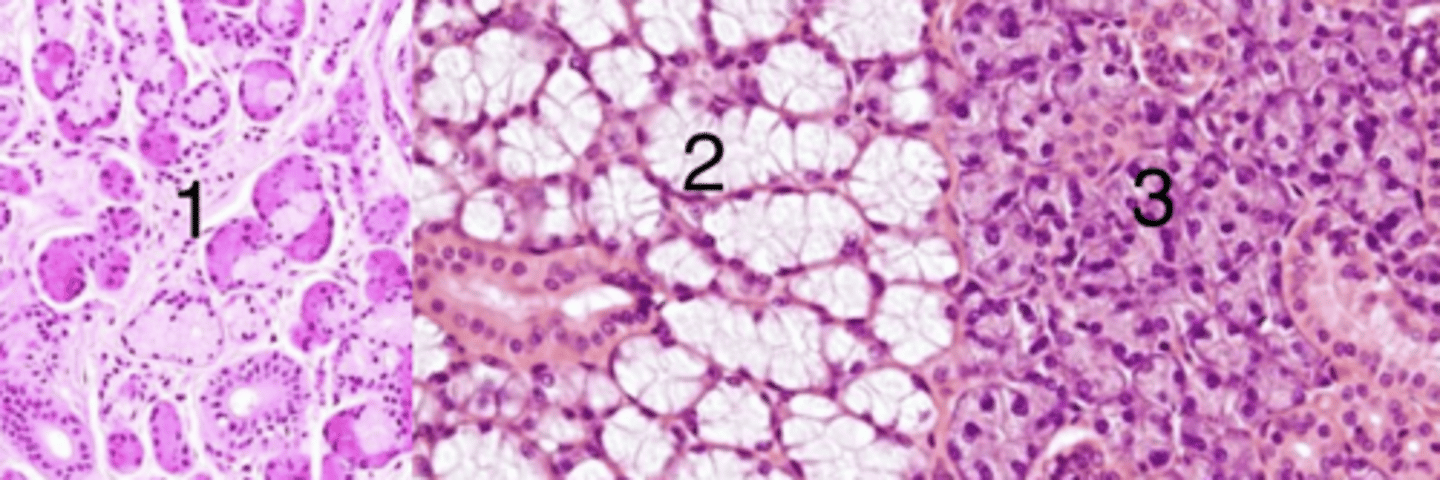
2
which is mucus glands?
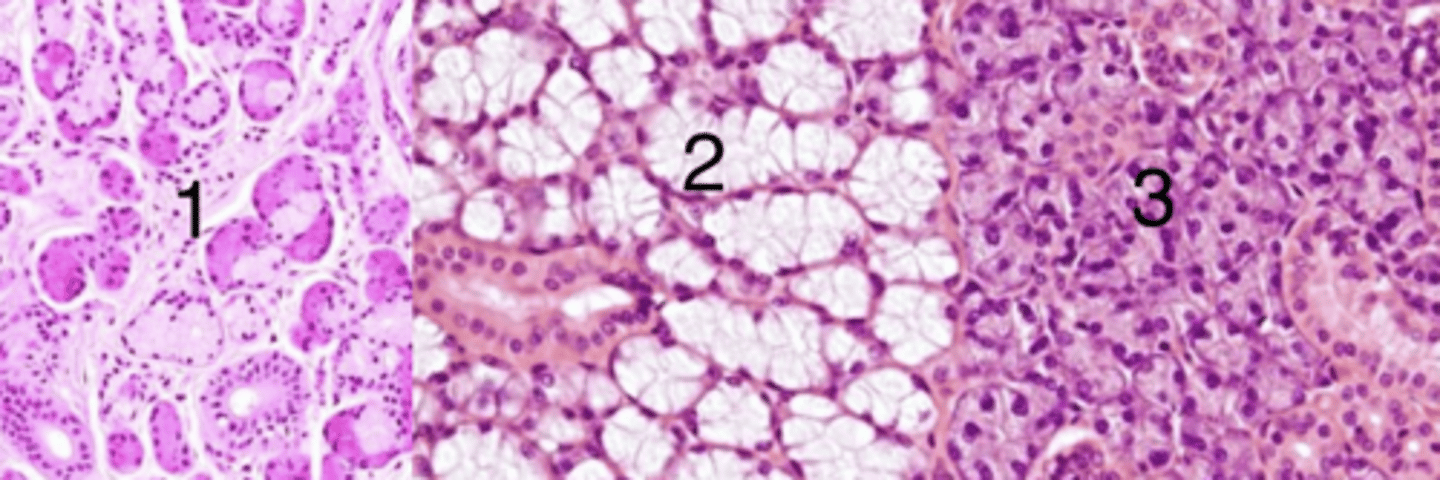
3, because it has serous glands
which is a sample of the parotid gland? why?
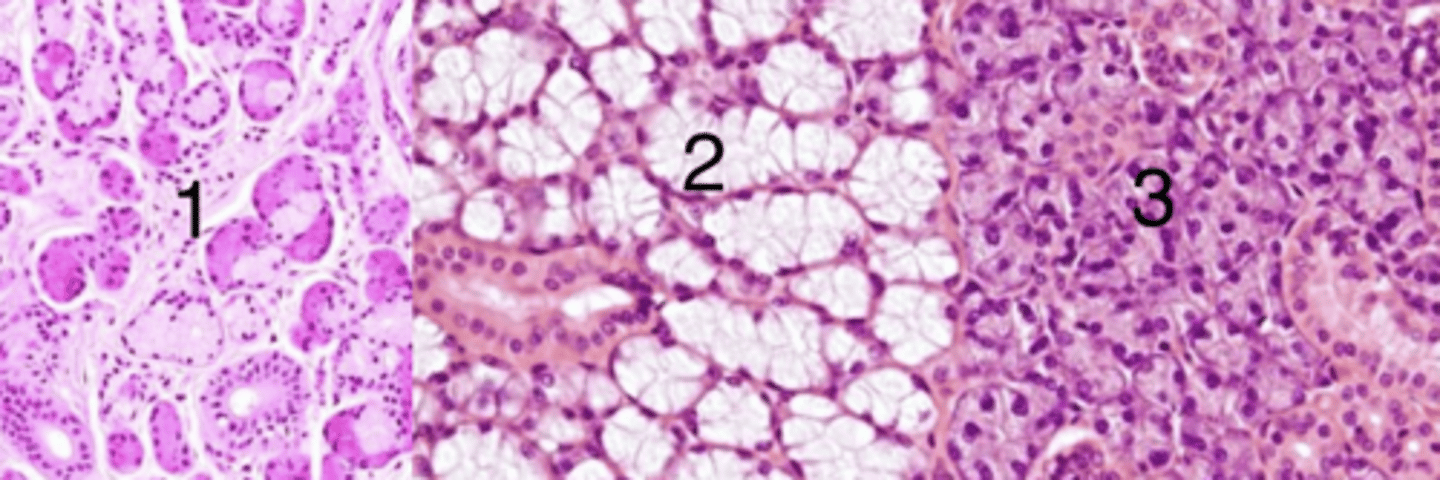
3
which has serous glands?
hair follicle
what is this?
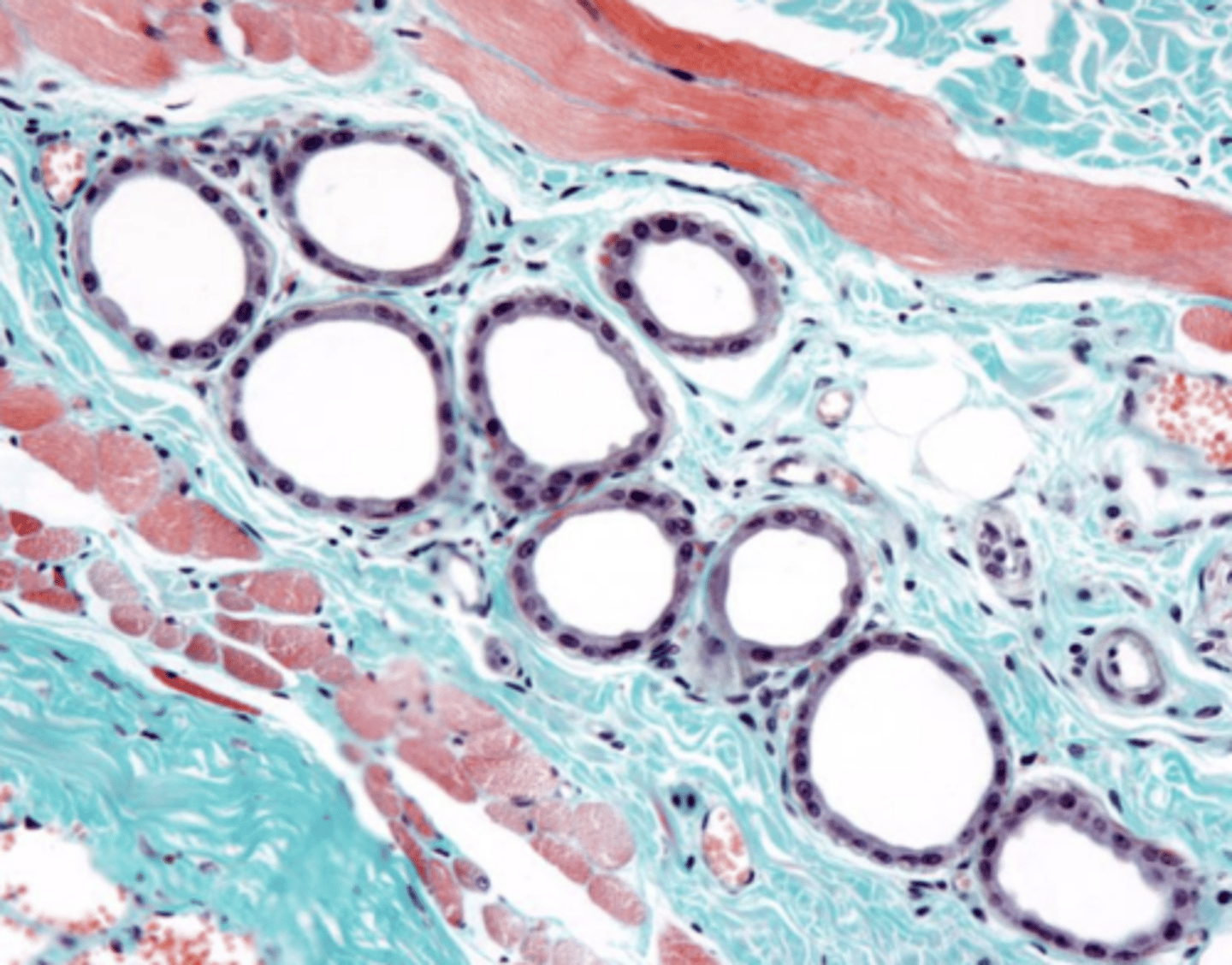
sweat glands
what are these?
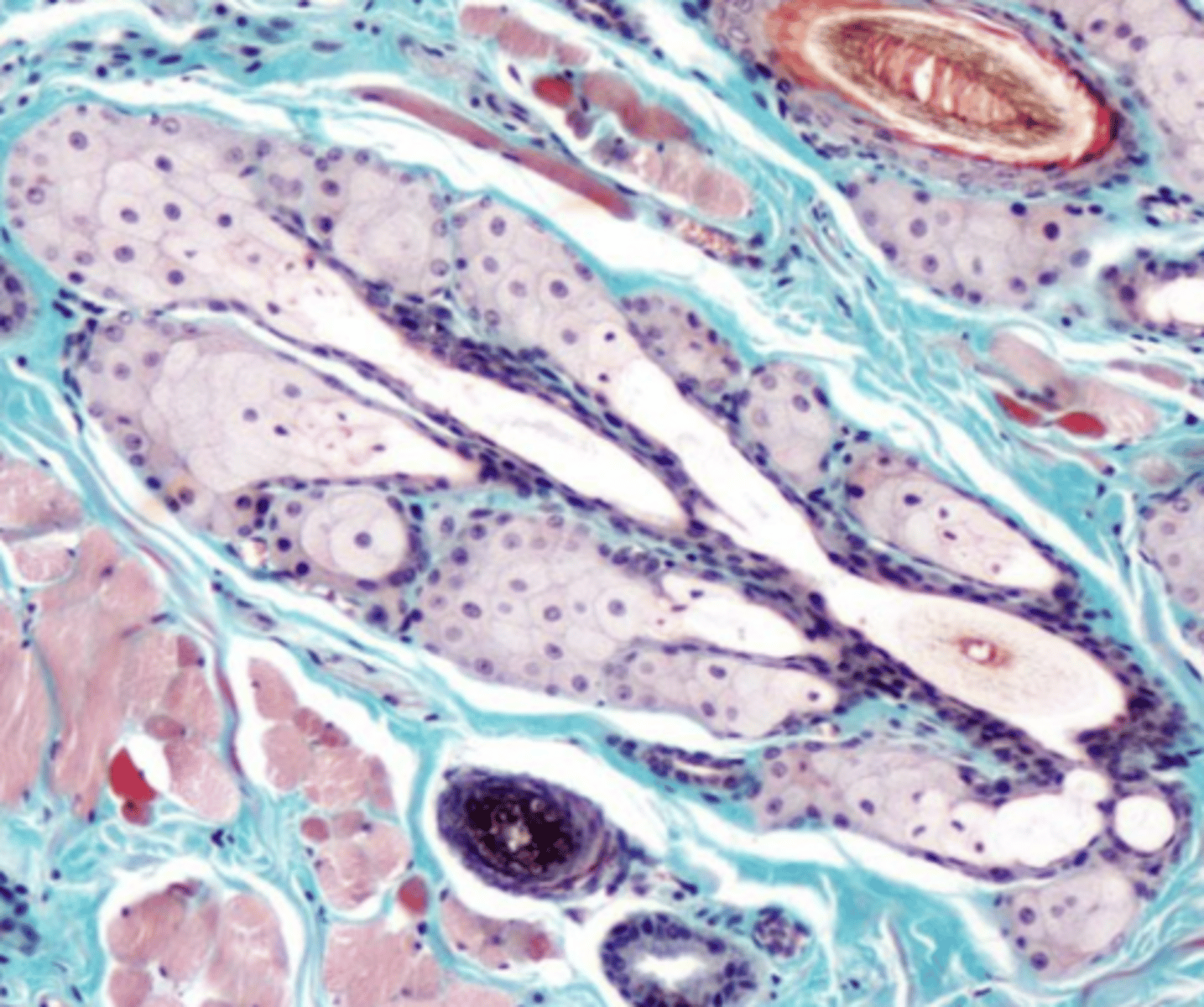
sebacious glands
what are these?
large hair follicle (whisker)
what is this?

lip/oral cavity because of the presence of sebacious and sweat glands and hair follicles and keratin on exterior
what is this? why?
the dorsal side is, the ventral side is not
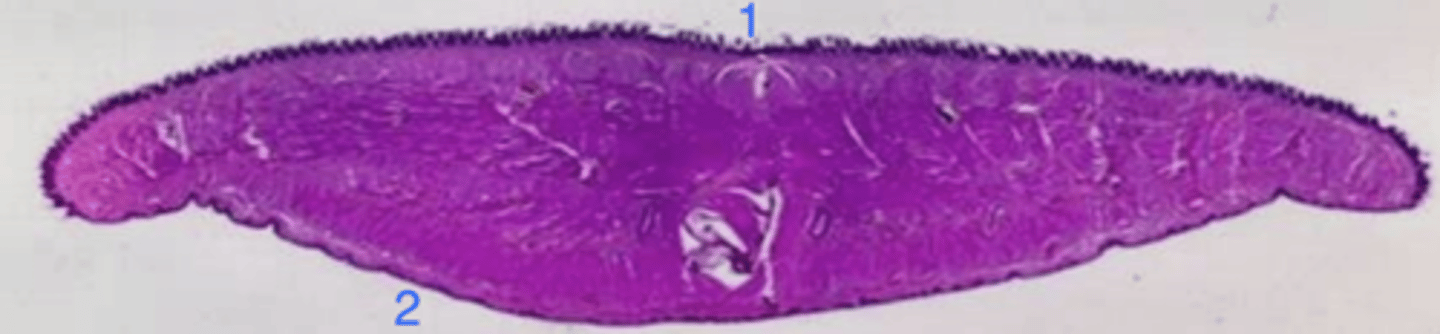
is the tongue keratinized?
muscle
what is the tongue mostly composed of ?
dorsal
which side of the tongue has lingual papillae?
no
does the ventral surface of the the tongue have papillae?
the tongue
what is this?

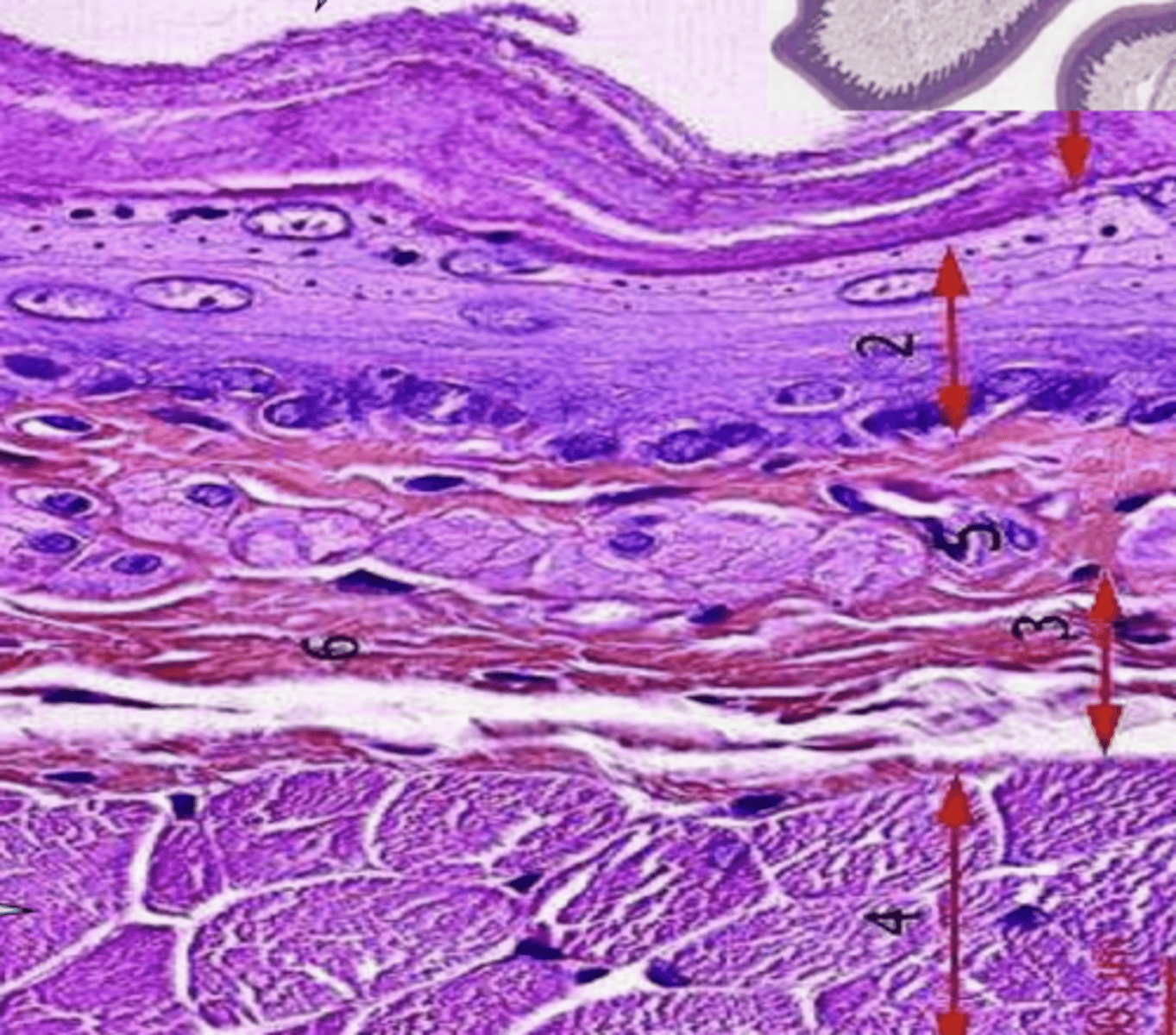
1- dorsal: papillae, keratin
2- ventral: no papillae, nonkeratinized
how can you distinguish between the ventral and dorsal surfaces of the tongue? which is which in this picture?
dense CT
the submucosa of the tongue is made of...
3 layers of skeletal muscle in 3 different directions
describe the muscularis of the tongue
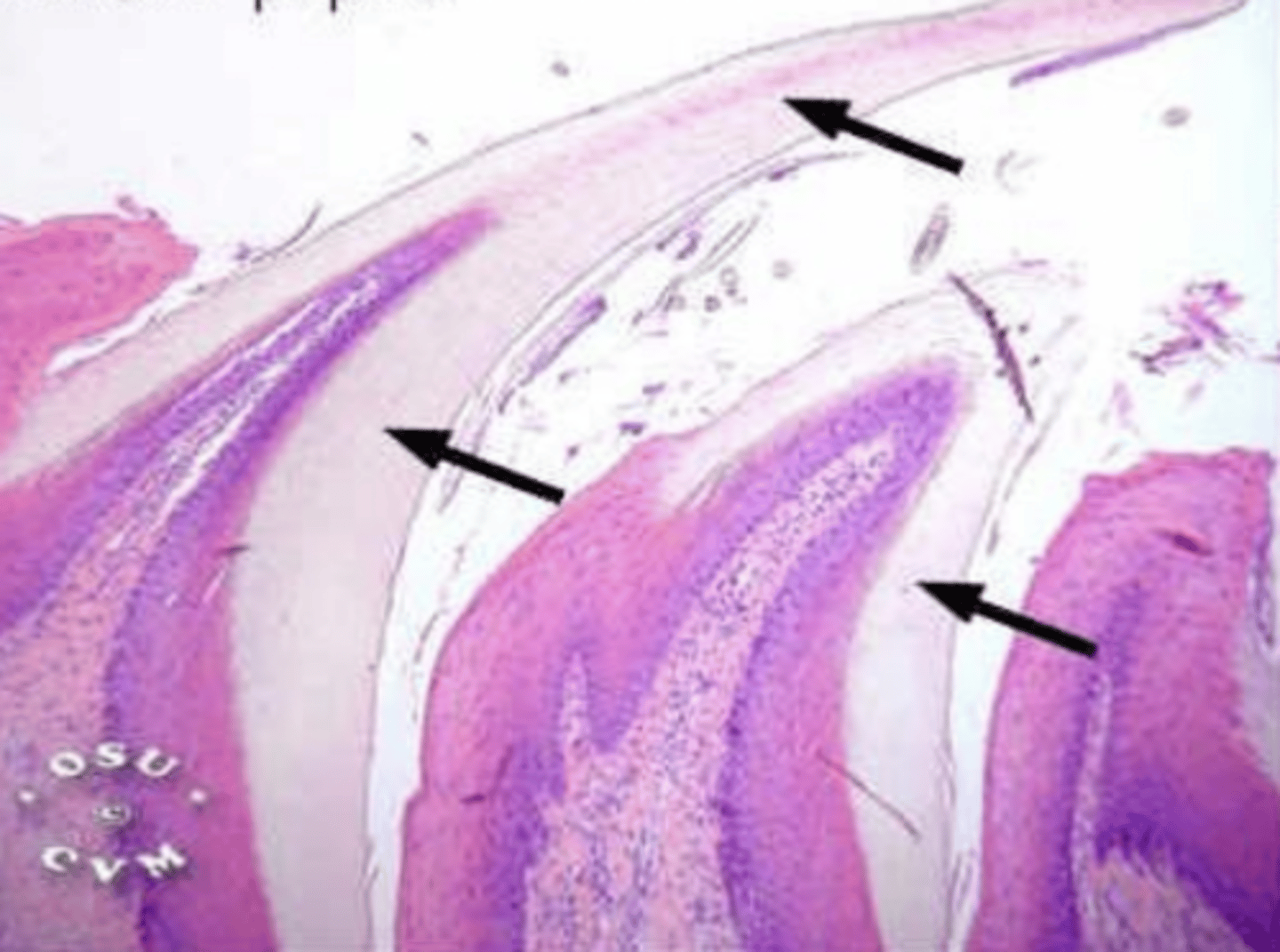
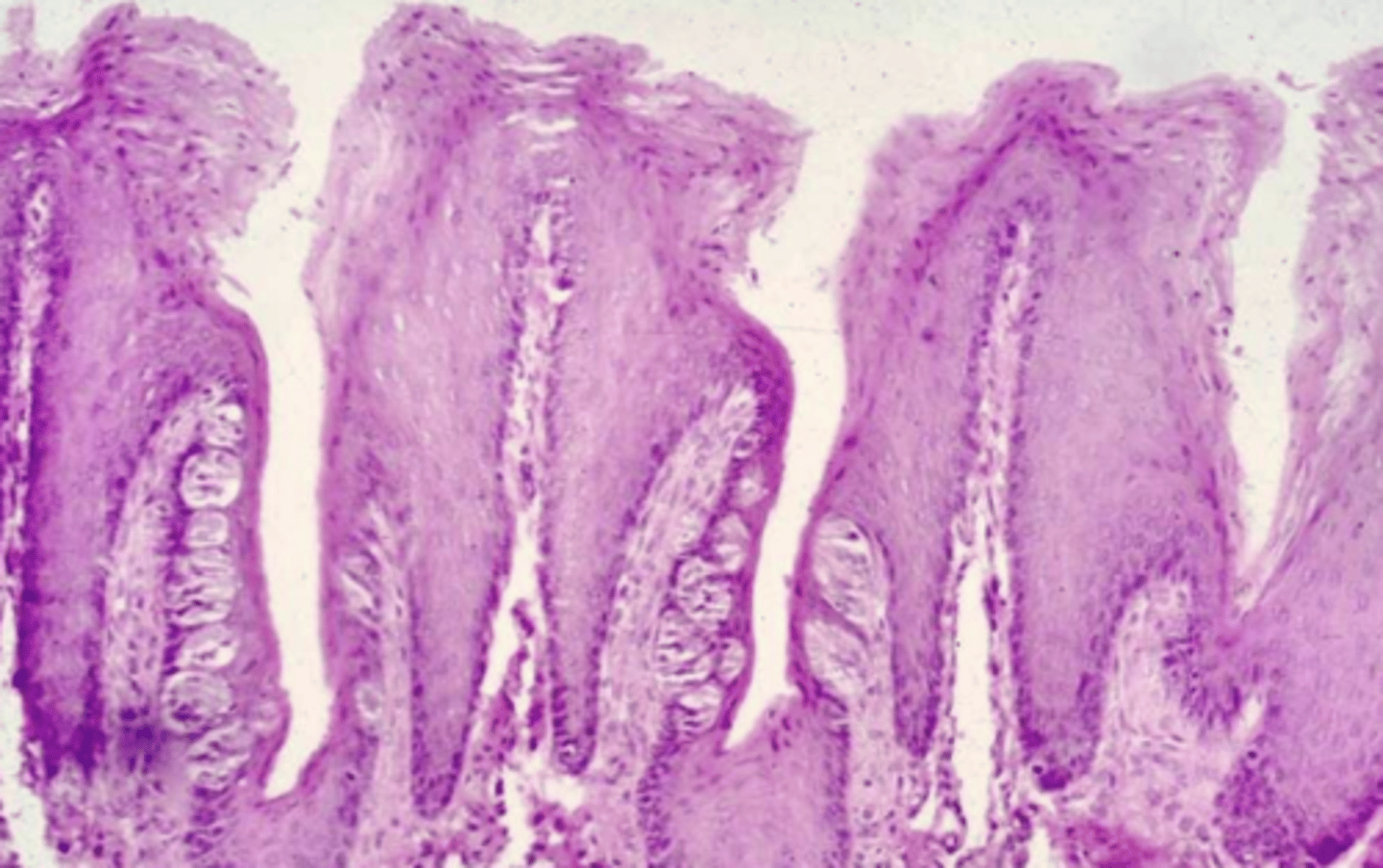
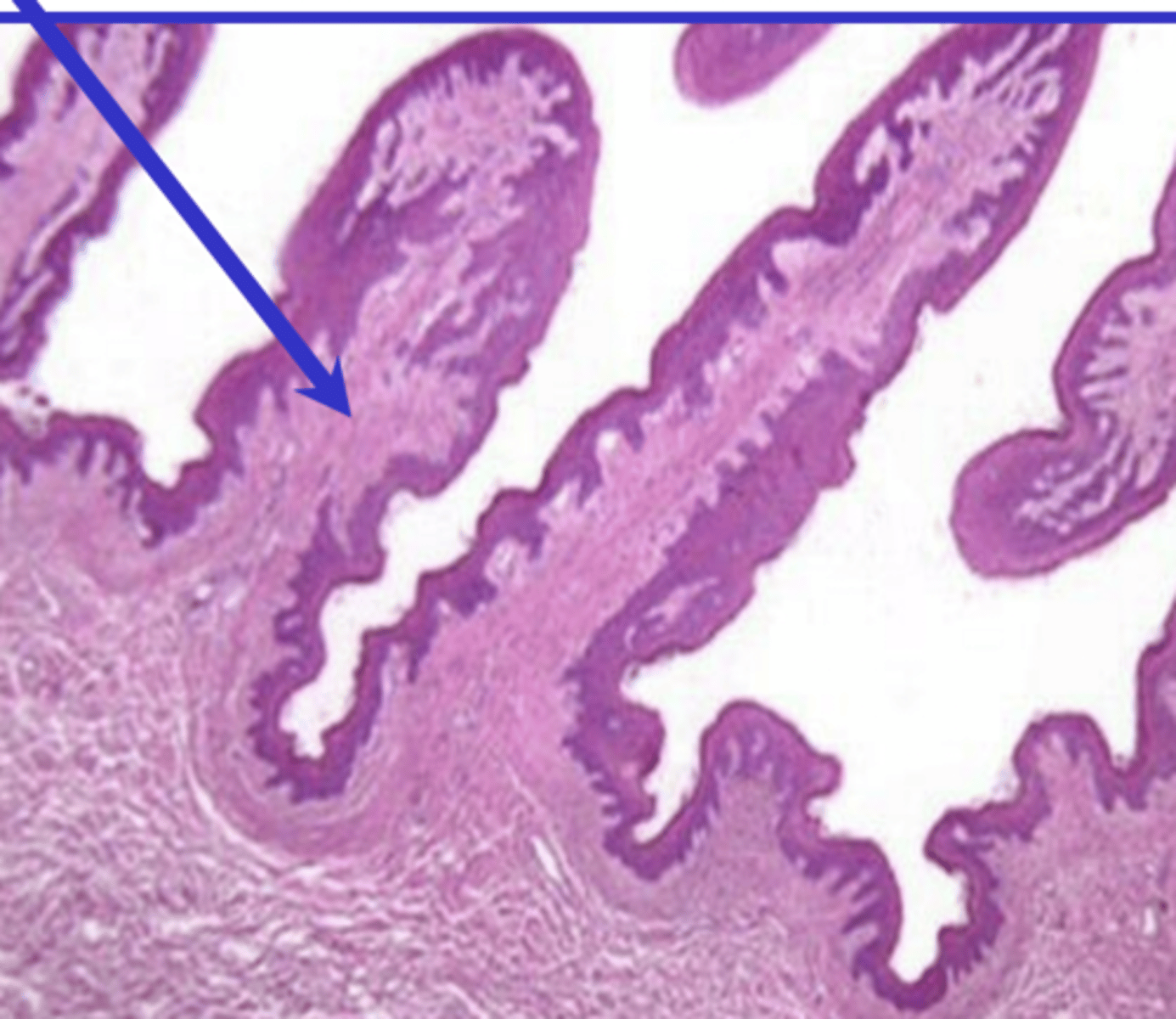
filiform- conical, long
what type of lingual papillae? why?
fungiform- fungi shaped, protrusion (sticks out)
what type of lingual papillae? why?

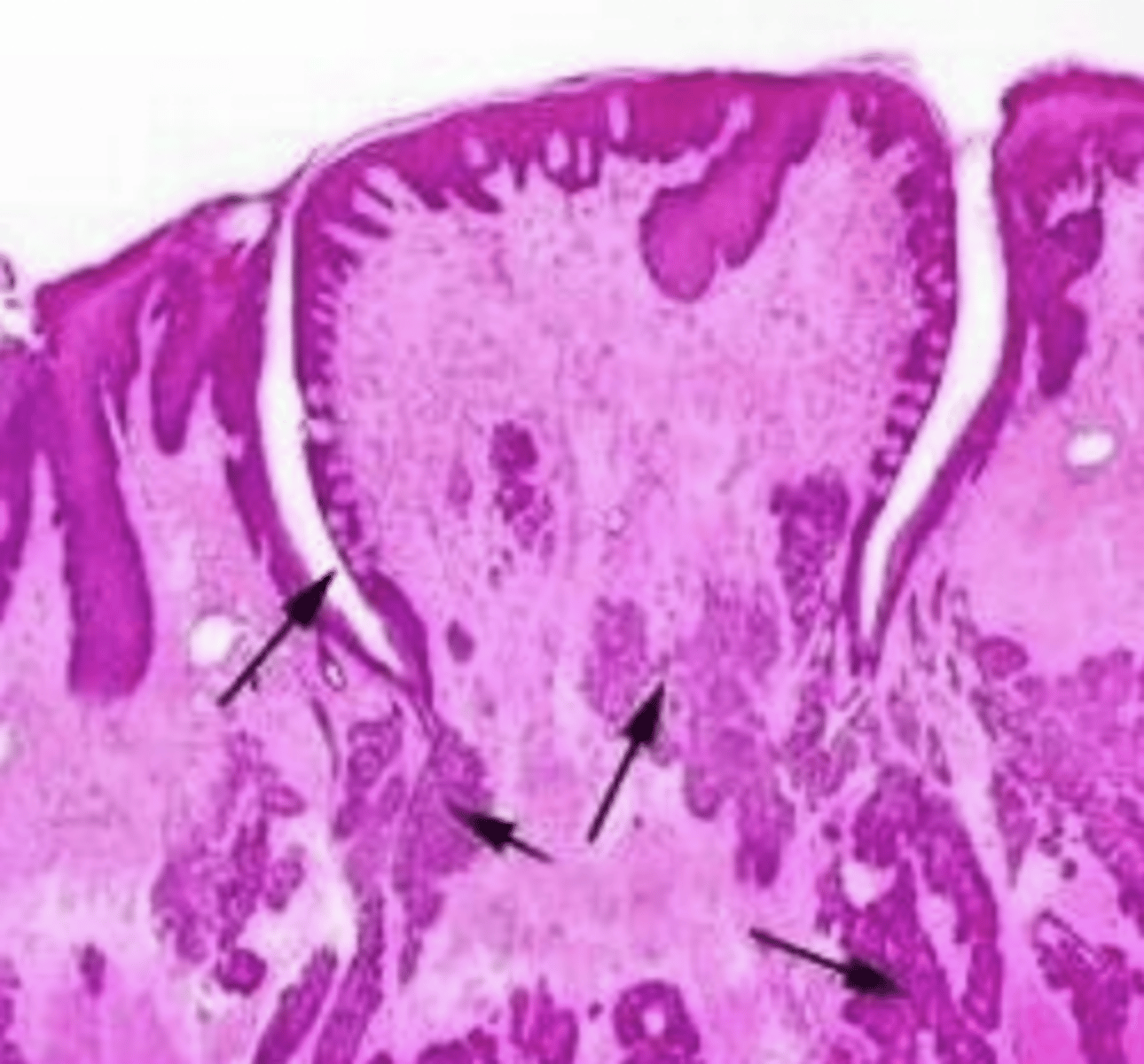
circumvallate- flat (not a protrusion of the mucosa), serosa glands at bottom, taste buds on lateral surface
what type of lingual papillae? why?
foliate- short, vertical, taste buds in surface
what type of lingual papillae? why?
1- fungiform (protrudes from mucosa)
2- circumvallate (flat against mucosa)
which is fungiform and which is circumvallate?
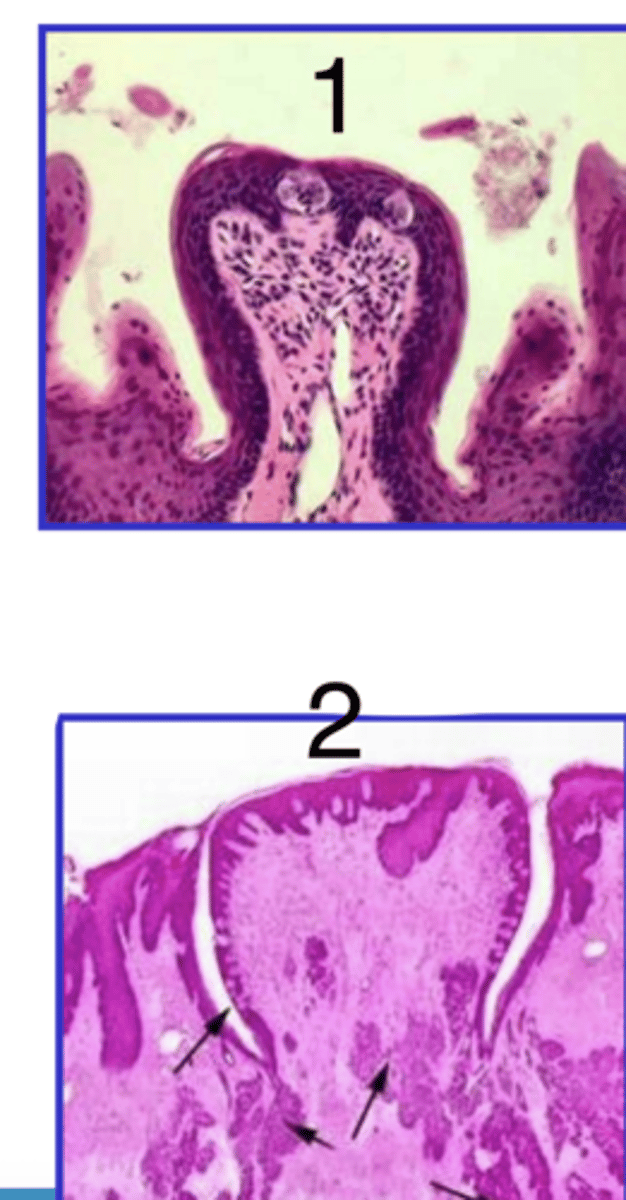
A- conical, protrusions
which is filiform?
foliate
what type of lingual papillae is B?
C
which is fungiform papillae?
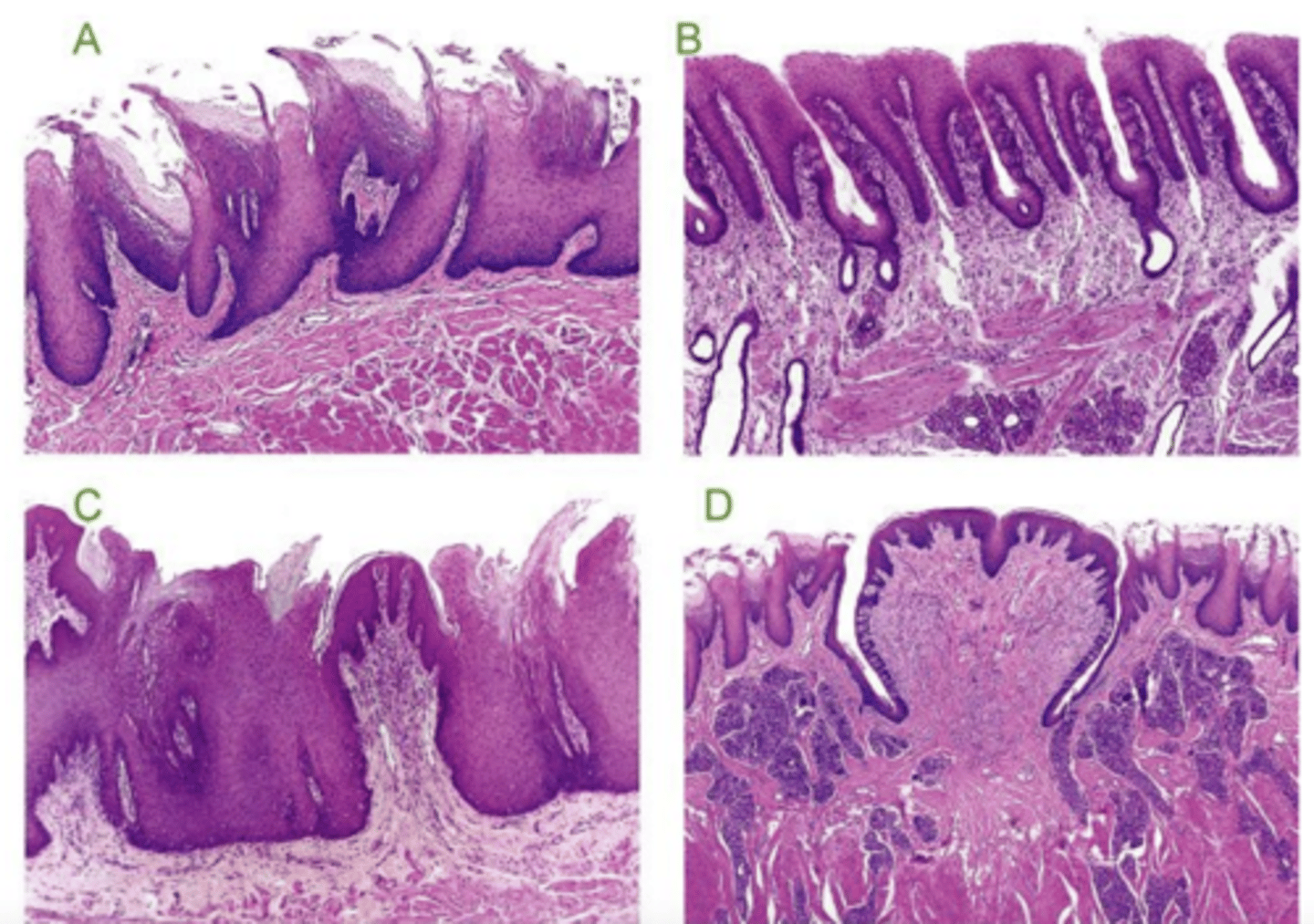
circumvallate
what type of papillae is D?
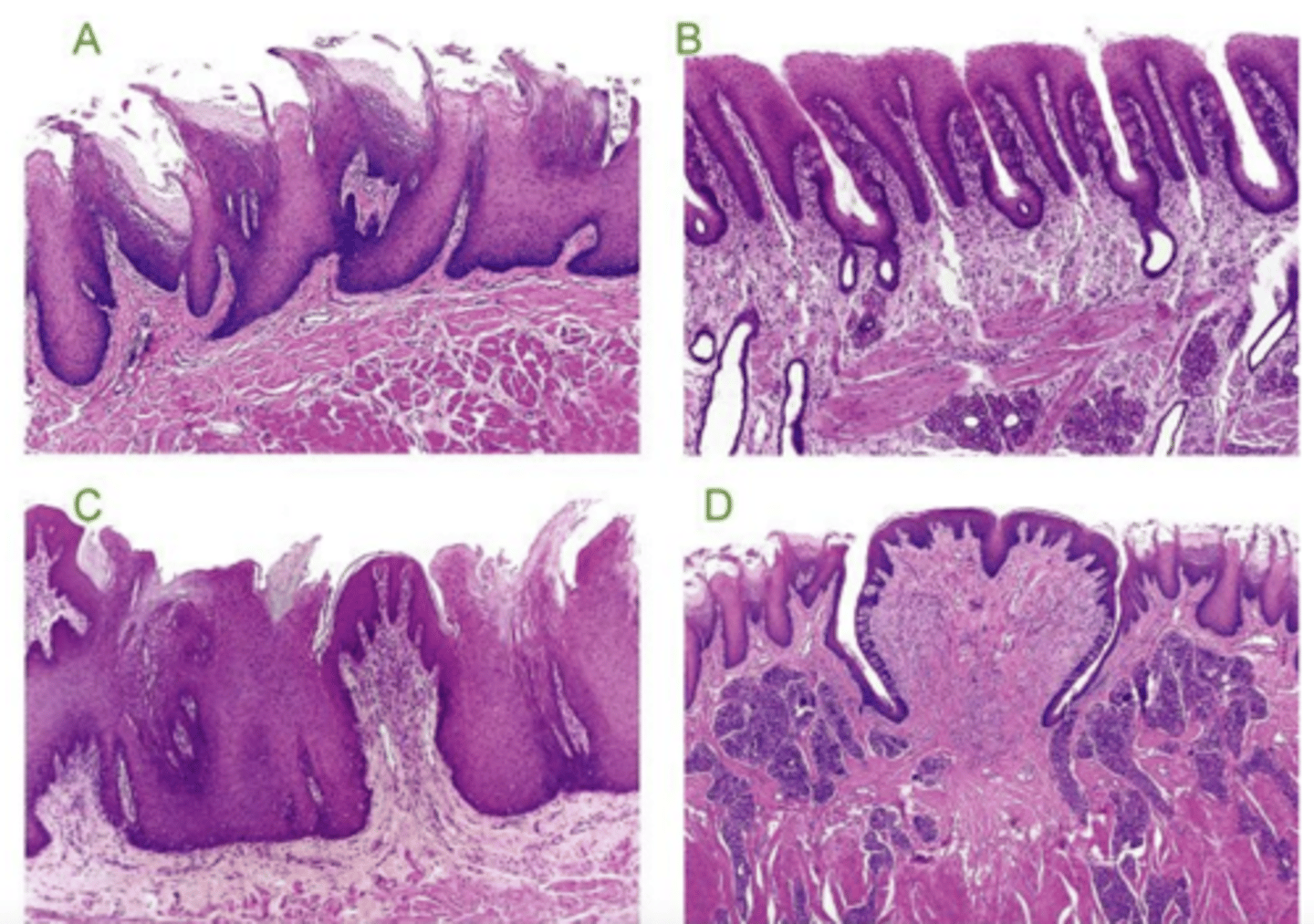
circumvallate
which lingual papillae has serosa glands at the base?
it is cornificated (keratinized)
what is different in the filiform papillae of cows and cats?
filiform and fungiform
which lingual papillae protrude from the mucosa?
bone with mucosa covering
what is the composition of hard palate?
oropharyx- stratified squamous
nasopharynx- pseudostratified columnar with cilia
what are the 2 types of epithelium of the pharynx?
stratified squamous
what type of epithelium is in the oropharynx?
pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia
what epithelium is in the nasopharynx?
no
are the tonsils keratinized?
only the nasopharynx
does the pharynx have cilia?
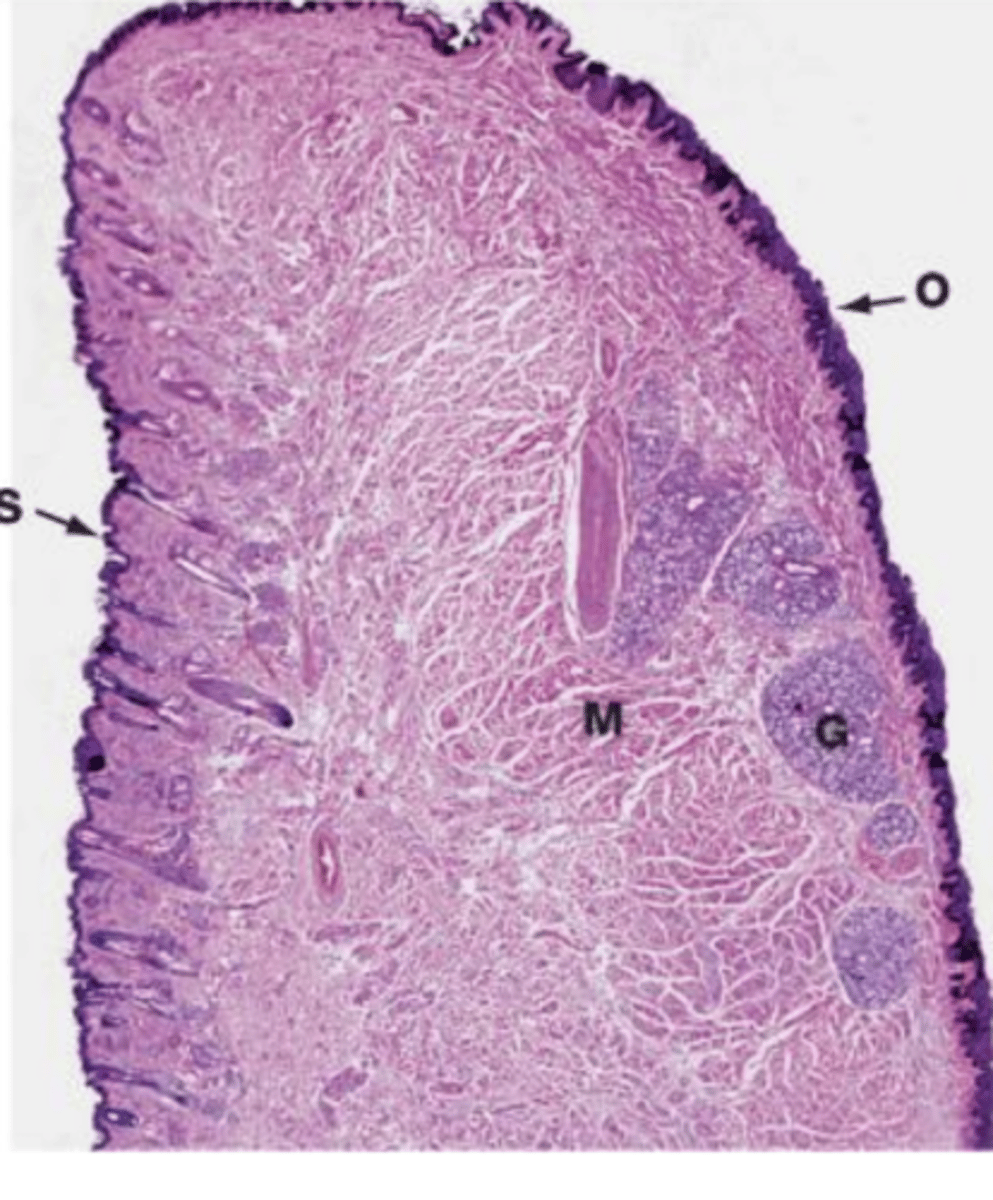
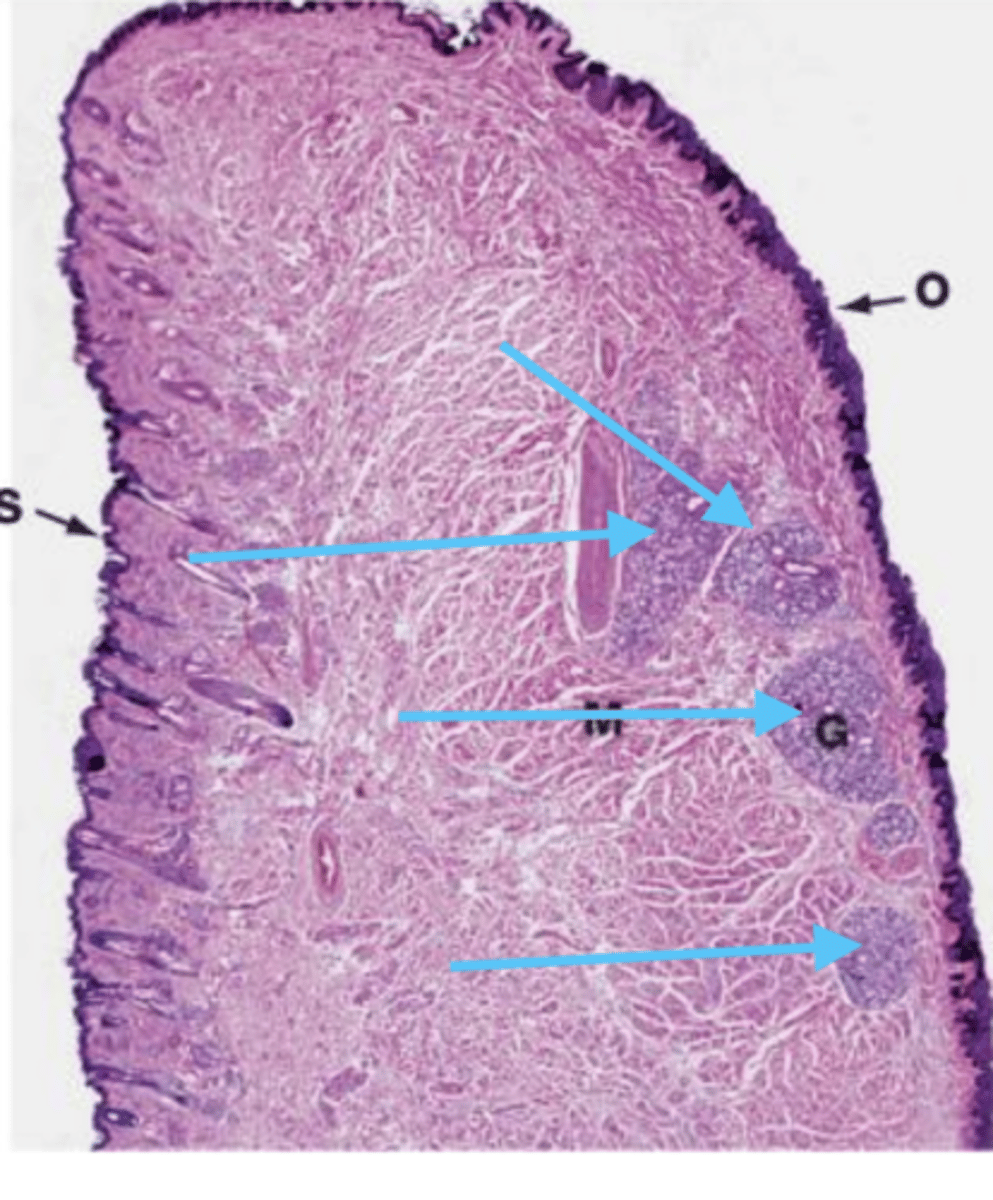
lymphoid follicles with B cells
interfollicular tissue with T cells
what important structures do you find in the tonsils?
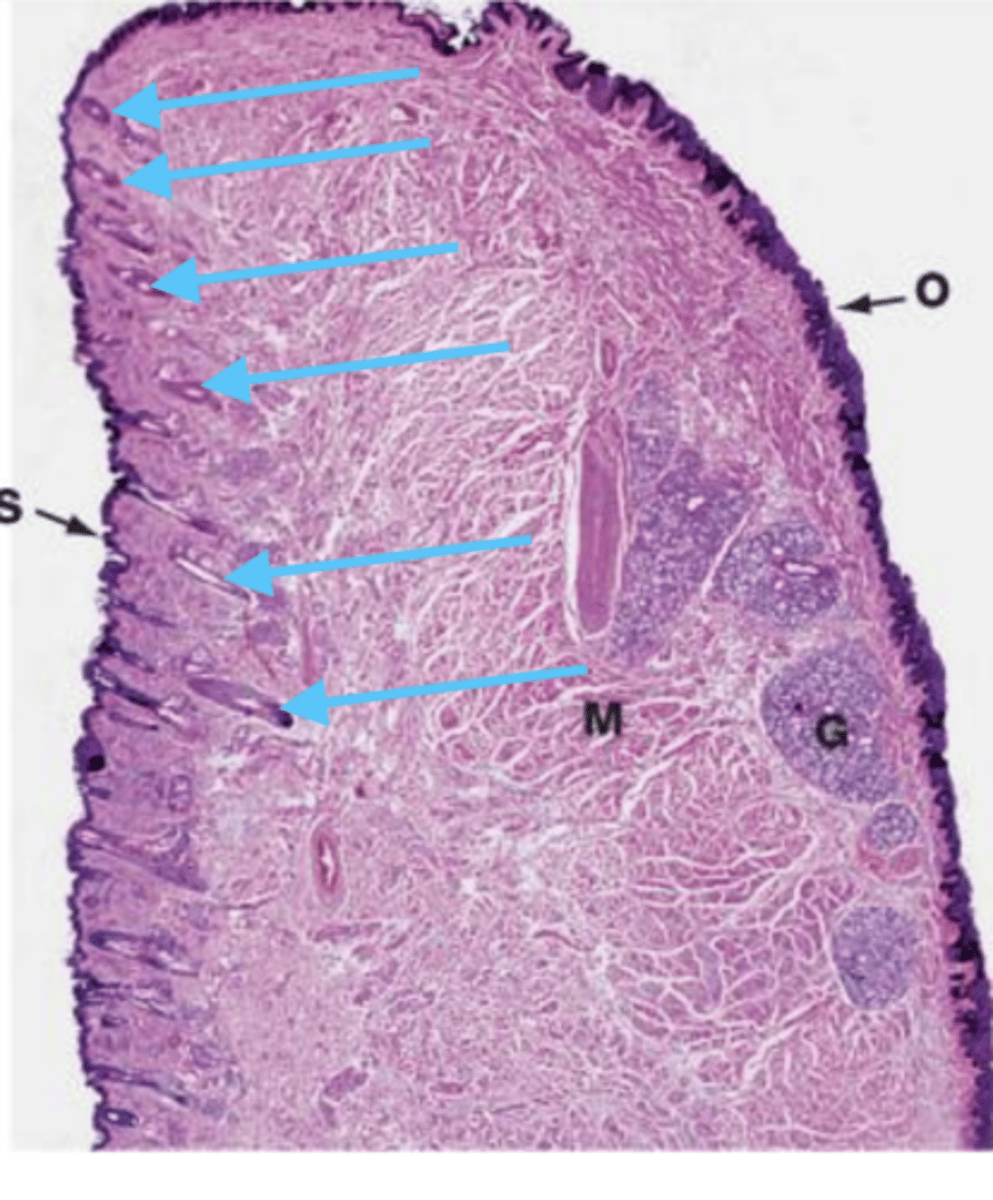
a tonsil
what is this?
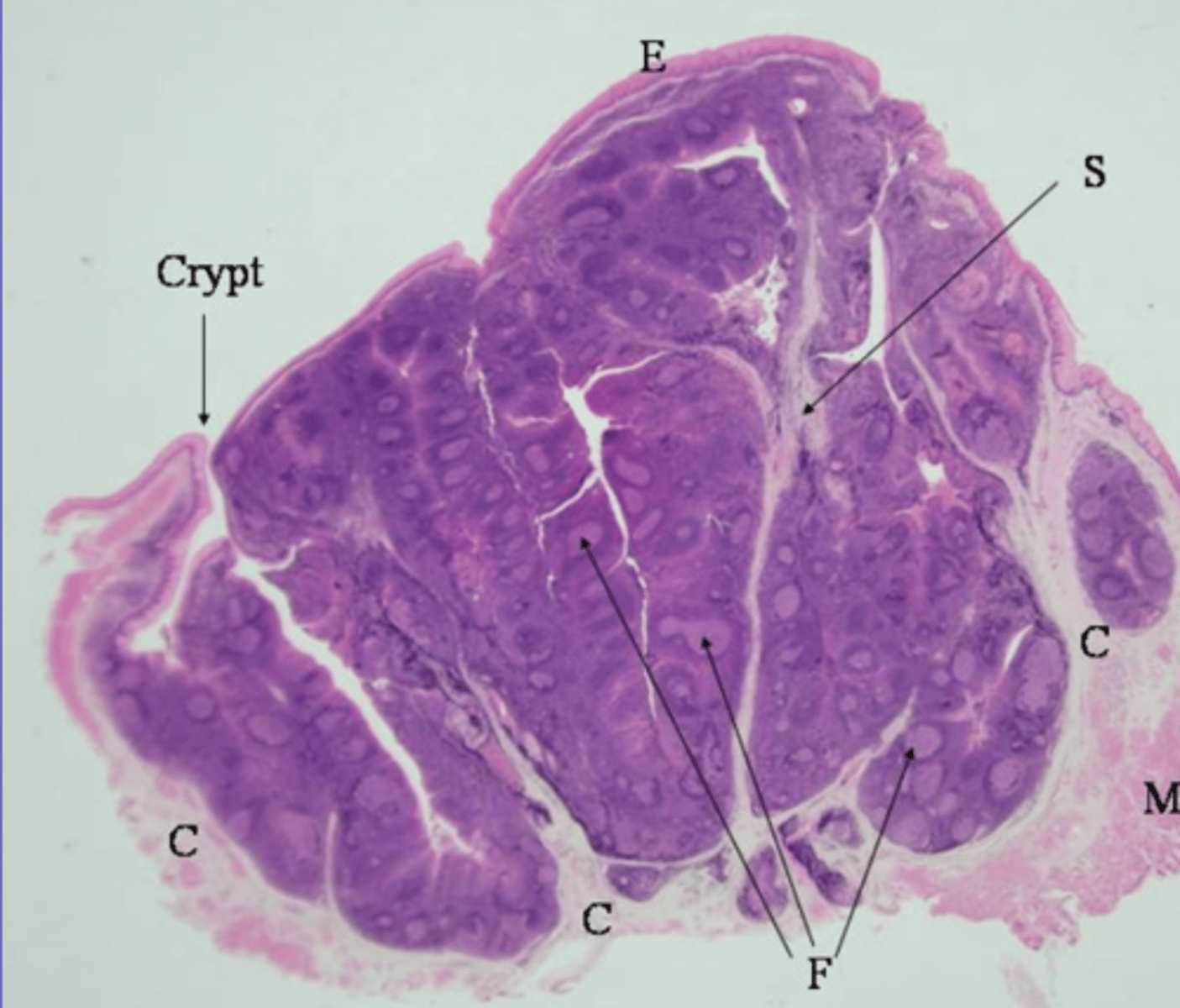
it is deeply folded
what is the appearance of the mucosa of the esophagus when it is relaxed?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (carnivores don't have keratin)
what is the epithelium of the esophagus?
yes, except for carnivores
is the esophagus keratinized?
pig
what species has lymphoid accumulation in the lamina propria of the esophagus?
close to the stomach
where is the muscularis layer of the esophagus the thickest?
usually 2
how many layers of muscle is in the muscularis of the esophagus?
ruminant and dog
which species have all striated muscle in the esophagus?
horses, cats
which species have mostly striated and a little smooth muscle in esophagus?
pig
which species have equal amount of stratified and smooth muscle in the esophagus?
the mediastinal pleura
the serosa of the thoracic esophagus is continuous with...
the peritoneum
the serosa of the abdominal esophagus is continuous with...
carnivores
which species do not have keratin in the esophagus?
pig, dog
which species have a discontinuous muscularis mucosa in the esophagus?
horse, cat, ruminant
which species have a continuous muscularis mucosa in the esophagus?
discontinuous
do dogs have a complete or discontinuous muscularis mucosa in the esophagus?
horse, cat, or ruminant, because the muscularis mucosa is complete
esophagus- which species? why?
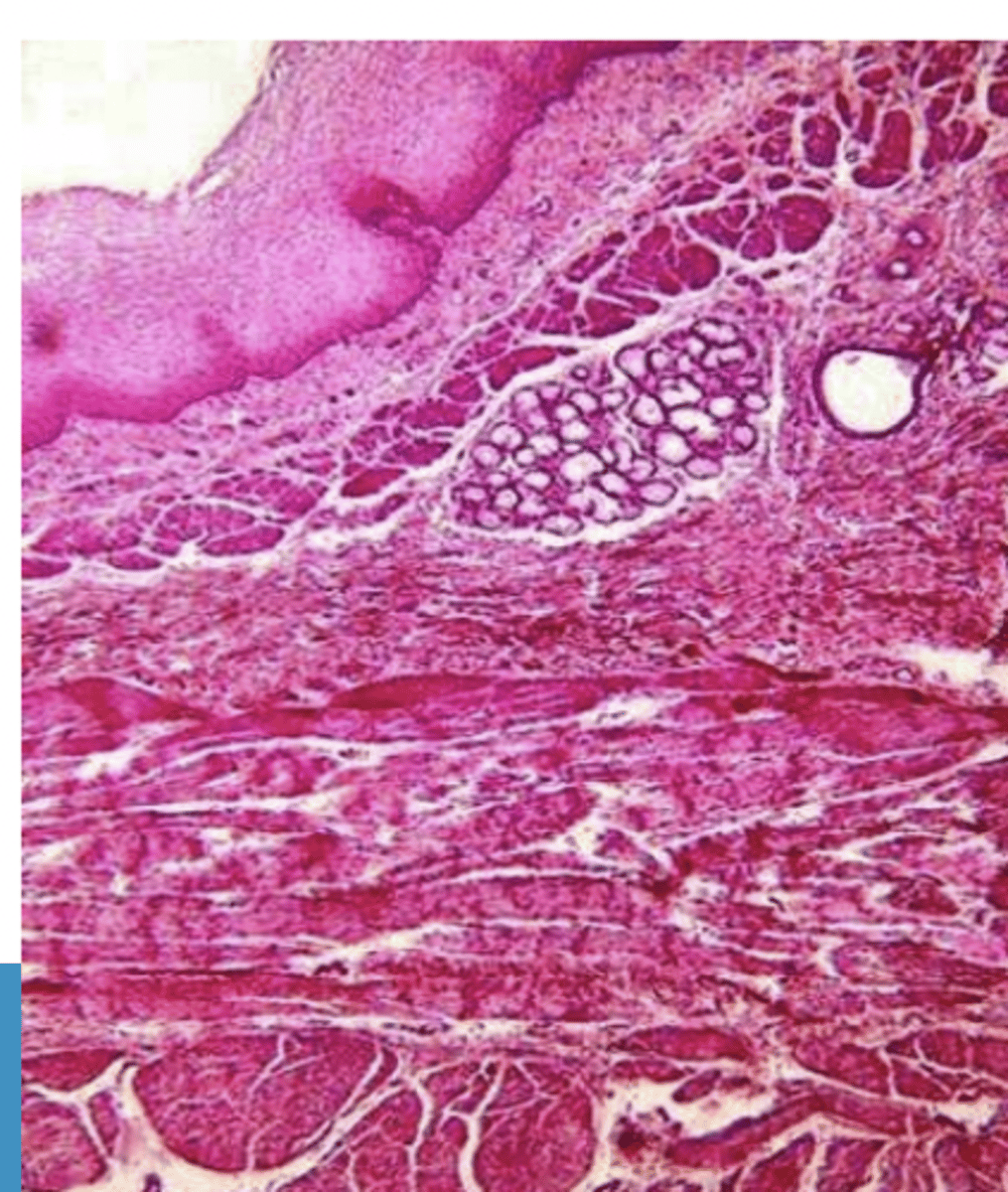
dog- discontinuous muscularis mucosa, non keratinized
esophagus- what species? why?
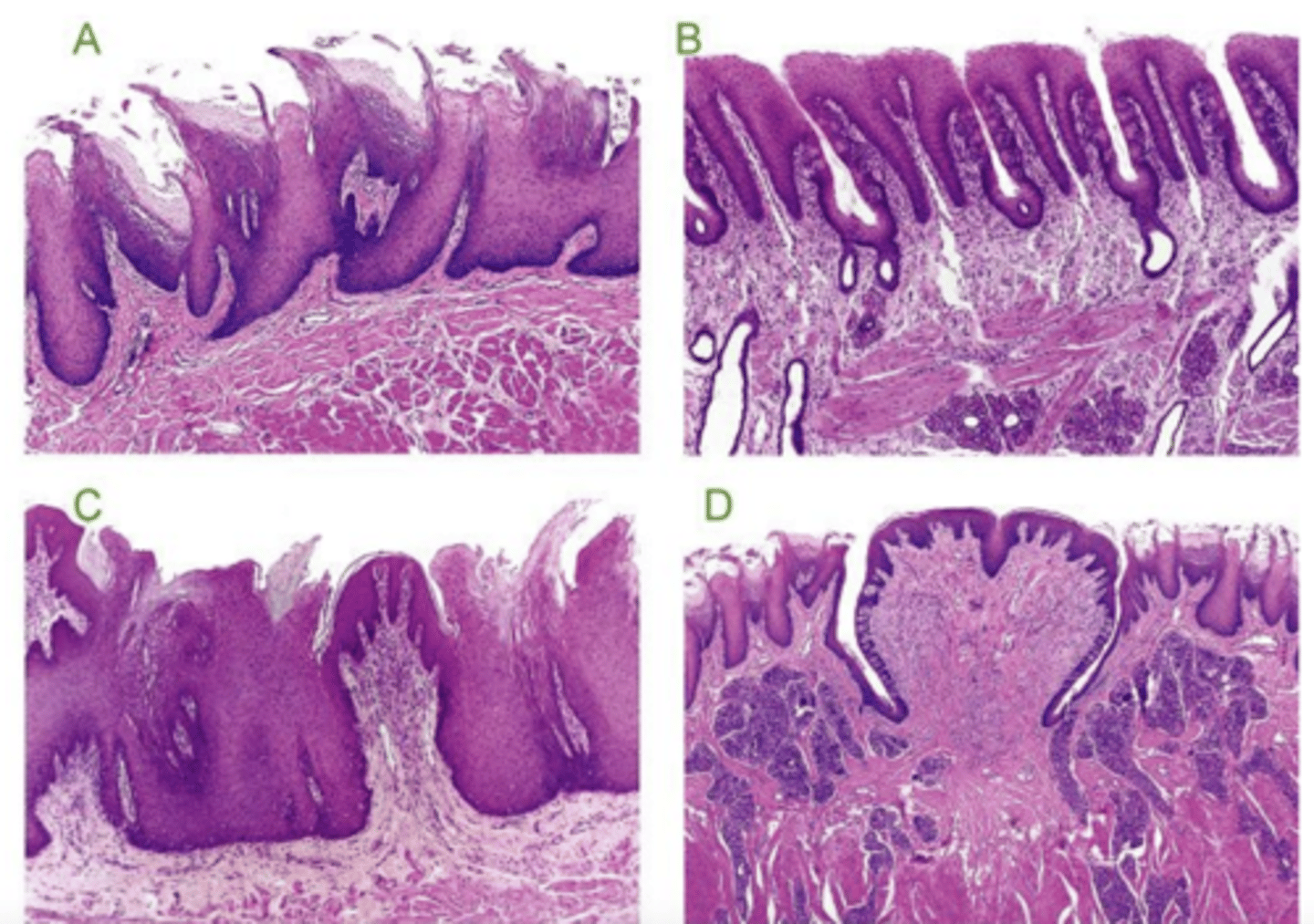
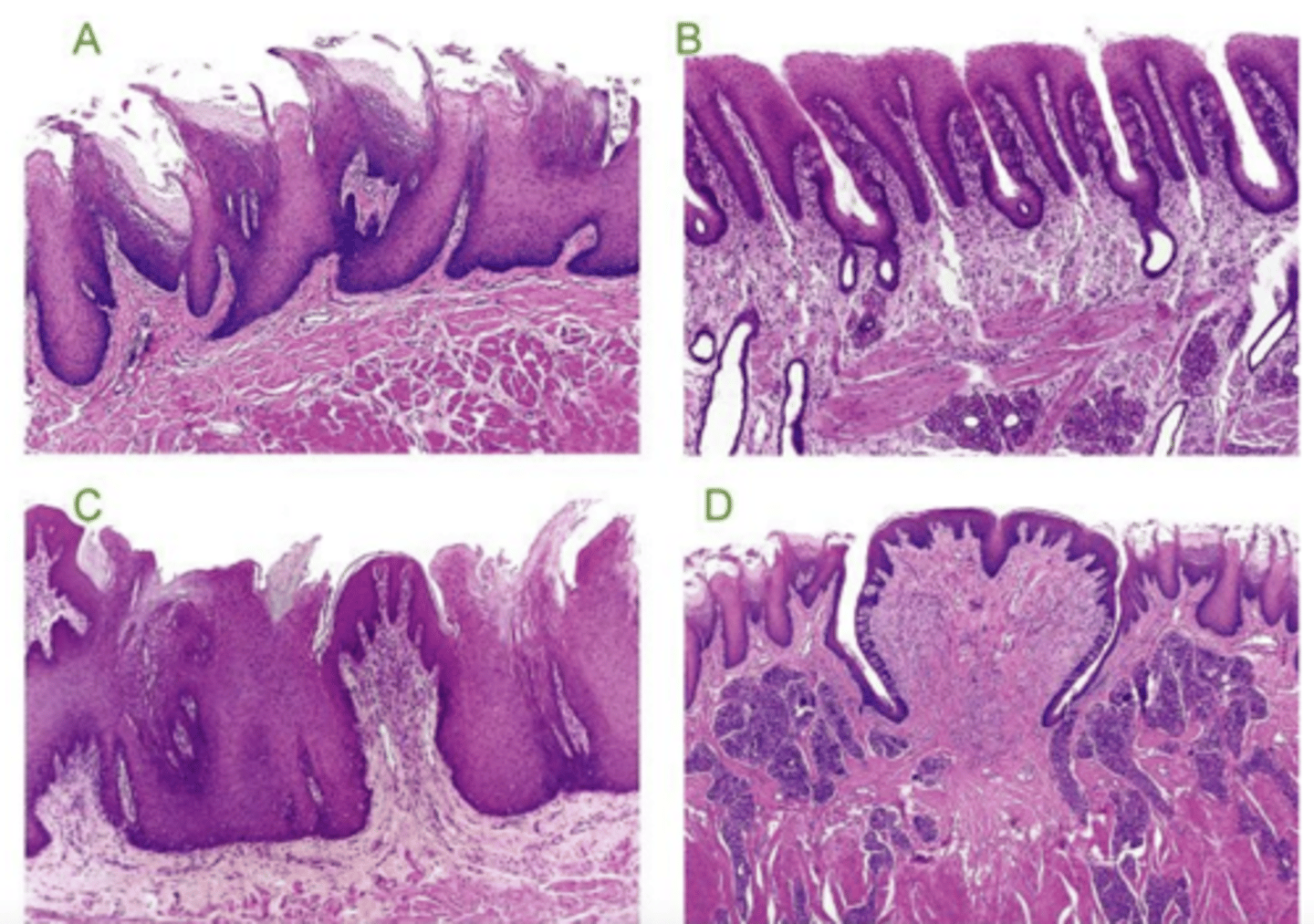
keratin:
yes- ruminant, horse, pig
no- dog, cat
muscularis mucosa:
continuous- horse, ruminant, cat
discontinuous- pig, dog
how can you distinguish species when looking at a sample of an esophagus?
ruminant- continuous muscularis mucosa, keratin
esophagus- what species? why?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
how is the epithelium of the forestomachs of a ruminant?
no muscularis mucosa
thickened folds that form grooves, called pillars of the rumen
describe the main attributes of the rumen
long and short folds
muscularis mucosa in apical parts of long folds only
describe the main attributes of the reticulum
long folds with cornified papillae
muscularis mucosa in all folds
describe the main attributes of the omasum
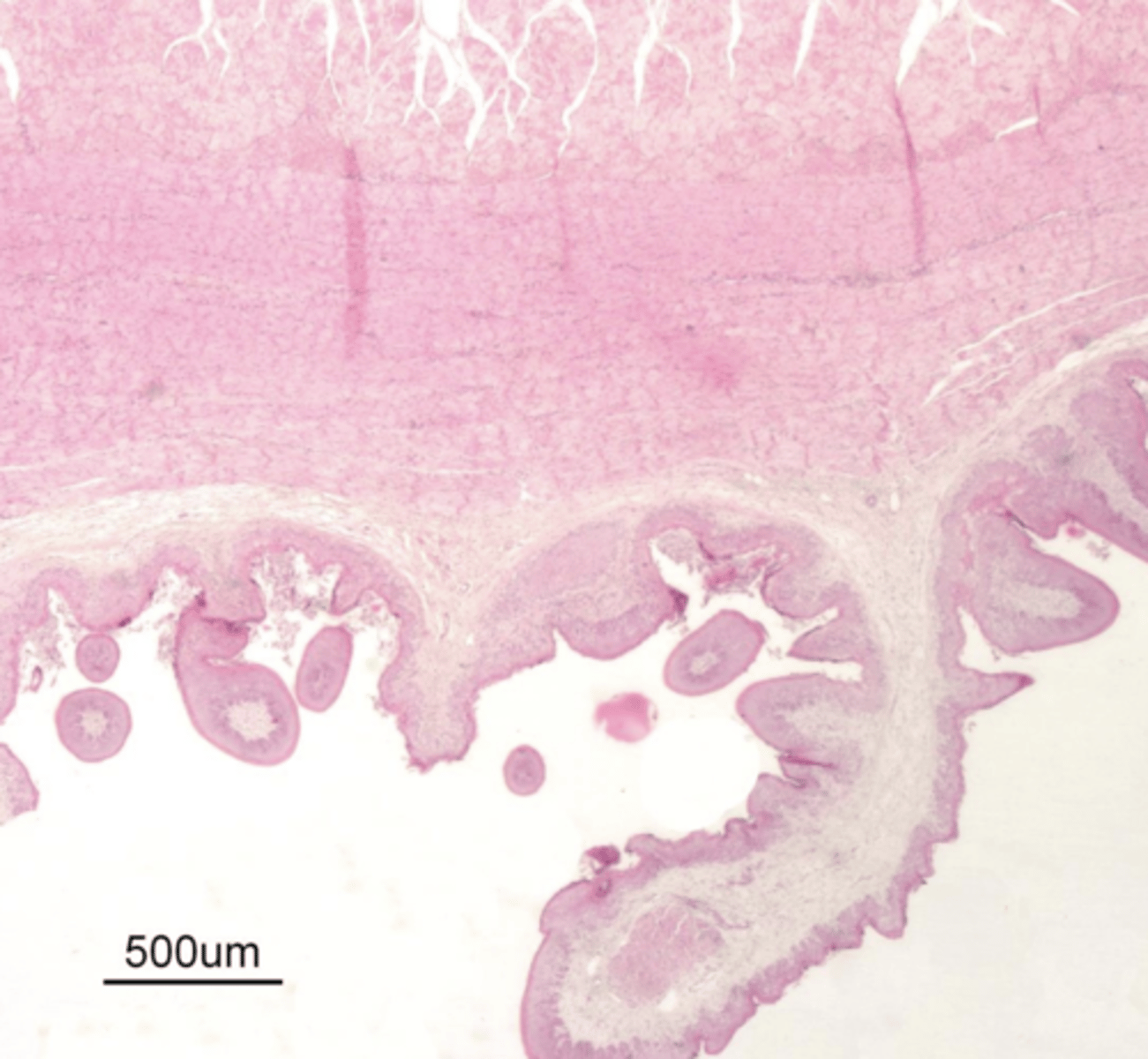
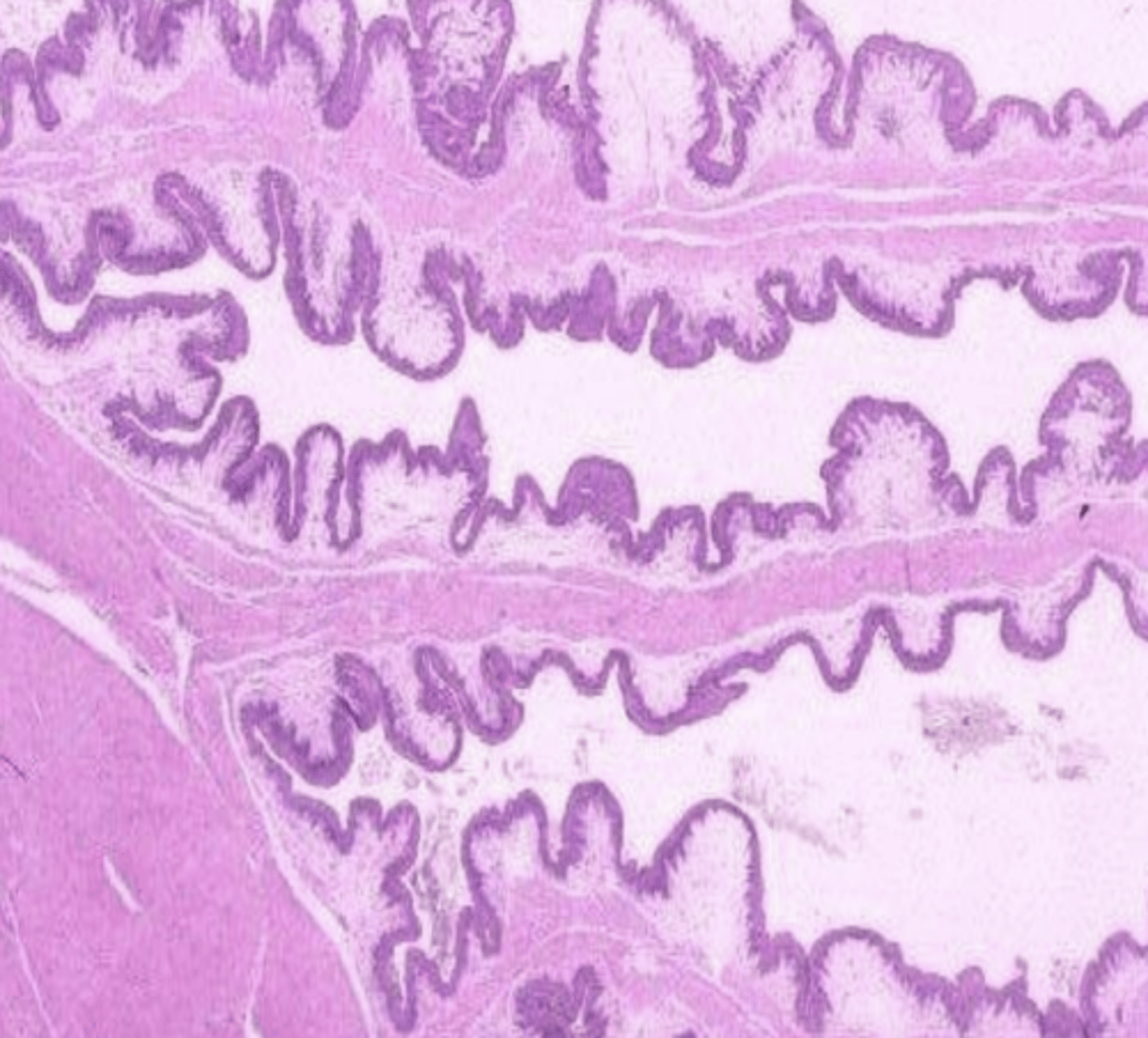
rumen- no muscularis mucosa
which forestomach? why?
reticulum- short and long folds, long folds with muscularis mucosa at apical part
which forestomach? why?
omasum- only long folds, all with muscularis mucosa
which forestomach? why?
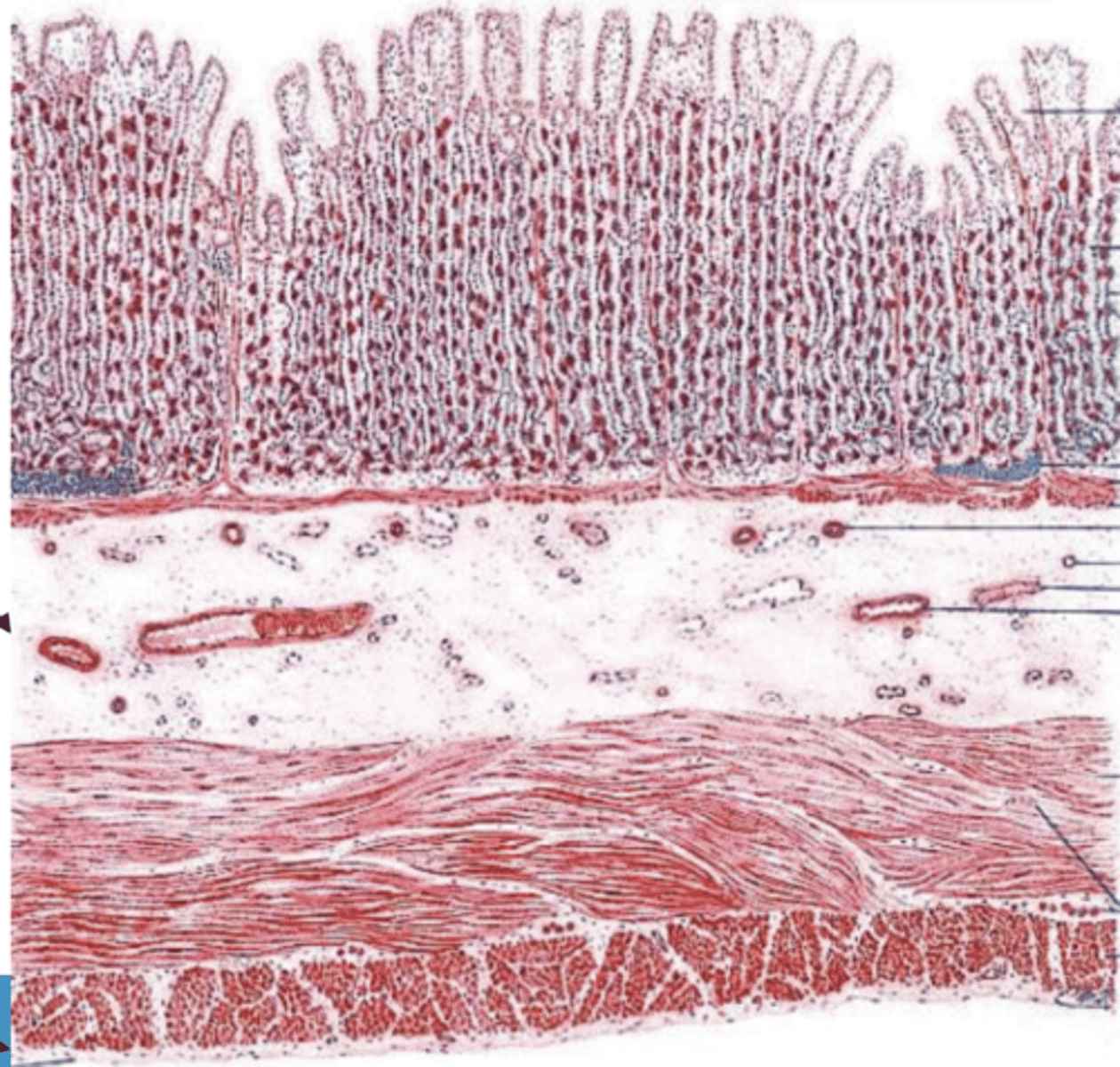
lamina propria of mucosa
in which layer of the glandular stomach are there gastric glands?
3
how many layers of muscle in the muscularis of the glandular stomach?
3 layers:
inner- oblique
middle- circular
outer- longitudinal
describe the muscularis of the glandular stomach
columnar with mucous cells
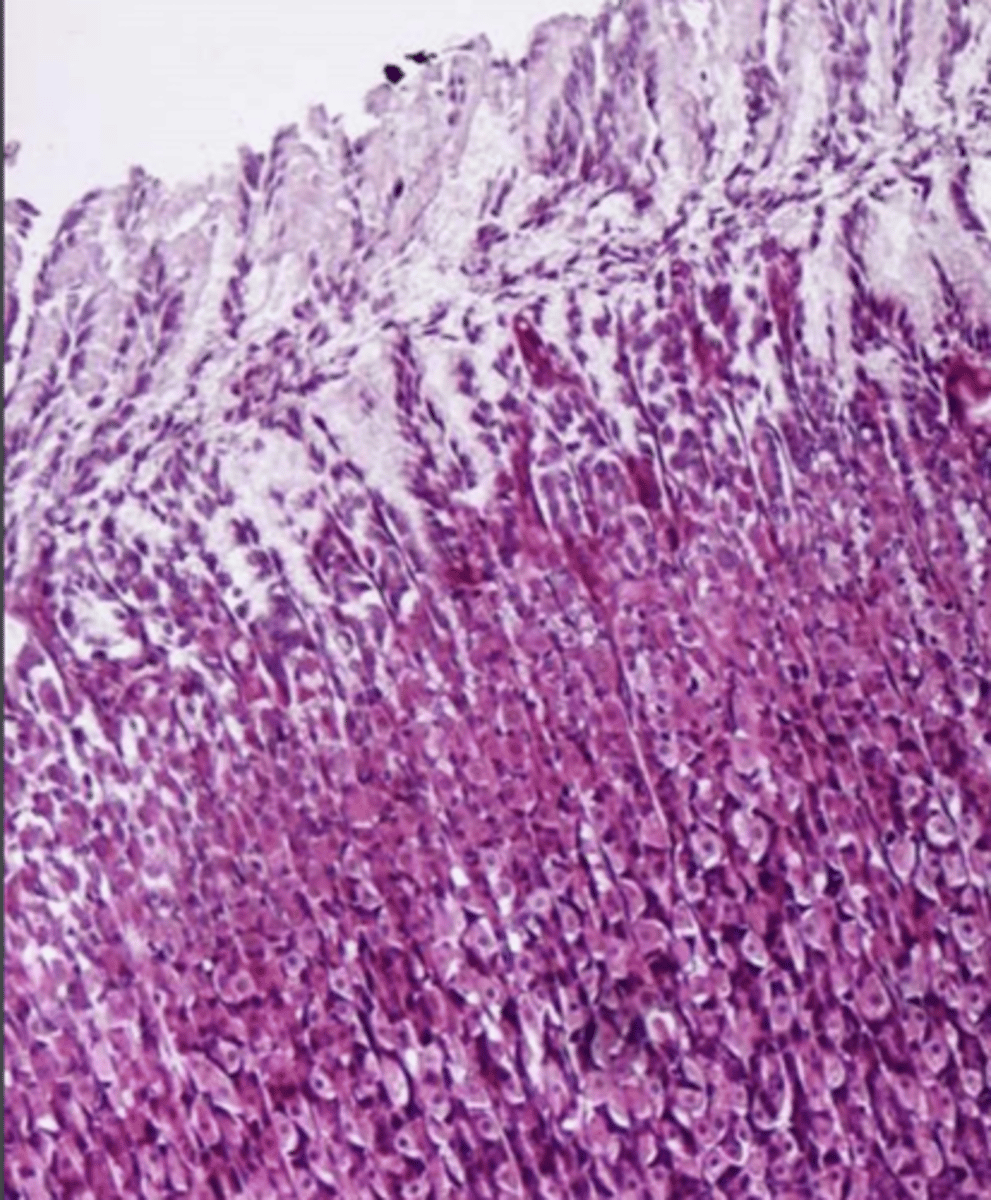
what is the epithelium of the mucosa of the glandular stomach?
glandular stomach
what is this?
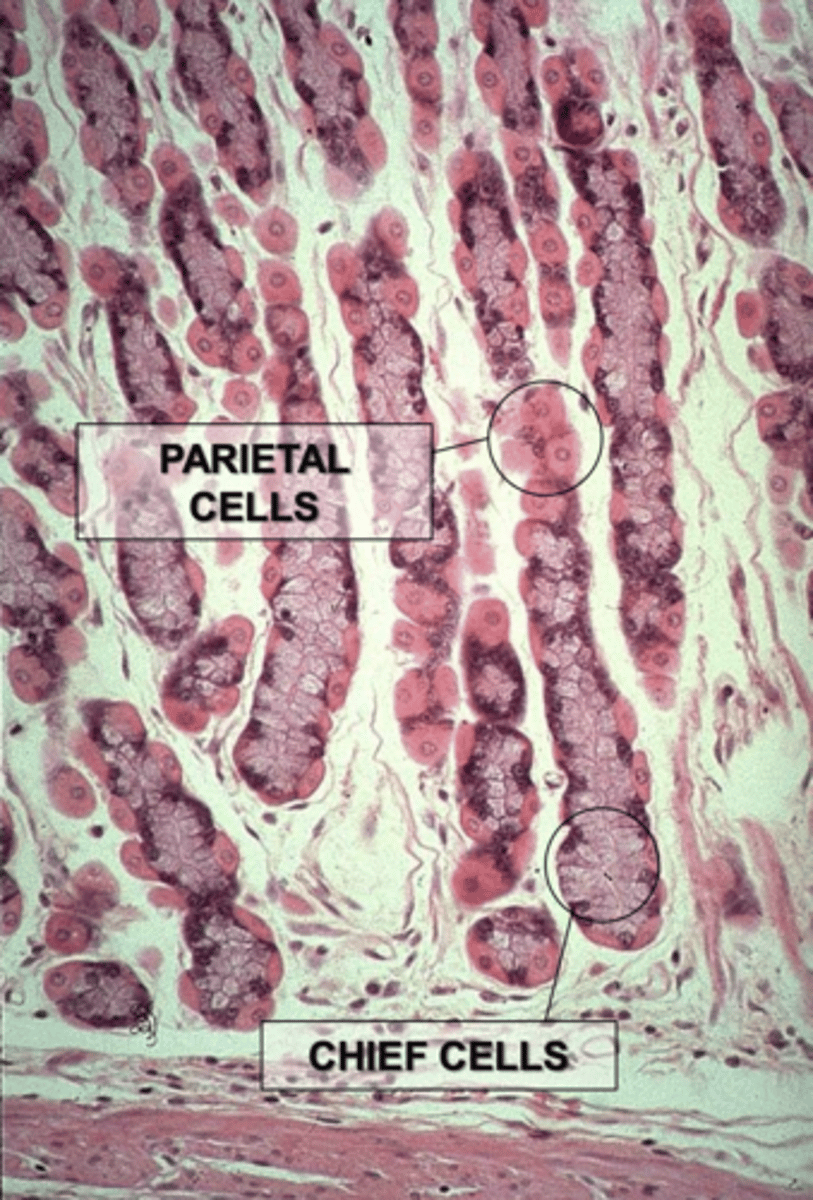
parietal cells and chief cells
what are the 2 types of gastric glands in the lamina propria of the glandular stomach?
looks like fried egg
lots of cytoplasm
individually distributed cells
central nucleus
eosinophilic cytoplasm
basophilic nucleus
secrete gastric acid
describe parietal cells (appearance and function)
secrete gastric acid
what do parietal cells do?
clustered together
nucleus at base
basophilic cytoplasm
what do chief cells look like?
secrete pepsin
what do chief cells do?
the mucosa of the glandular stomach
what is this?
parietal cells
what are the cells at 1?
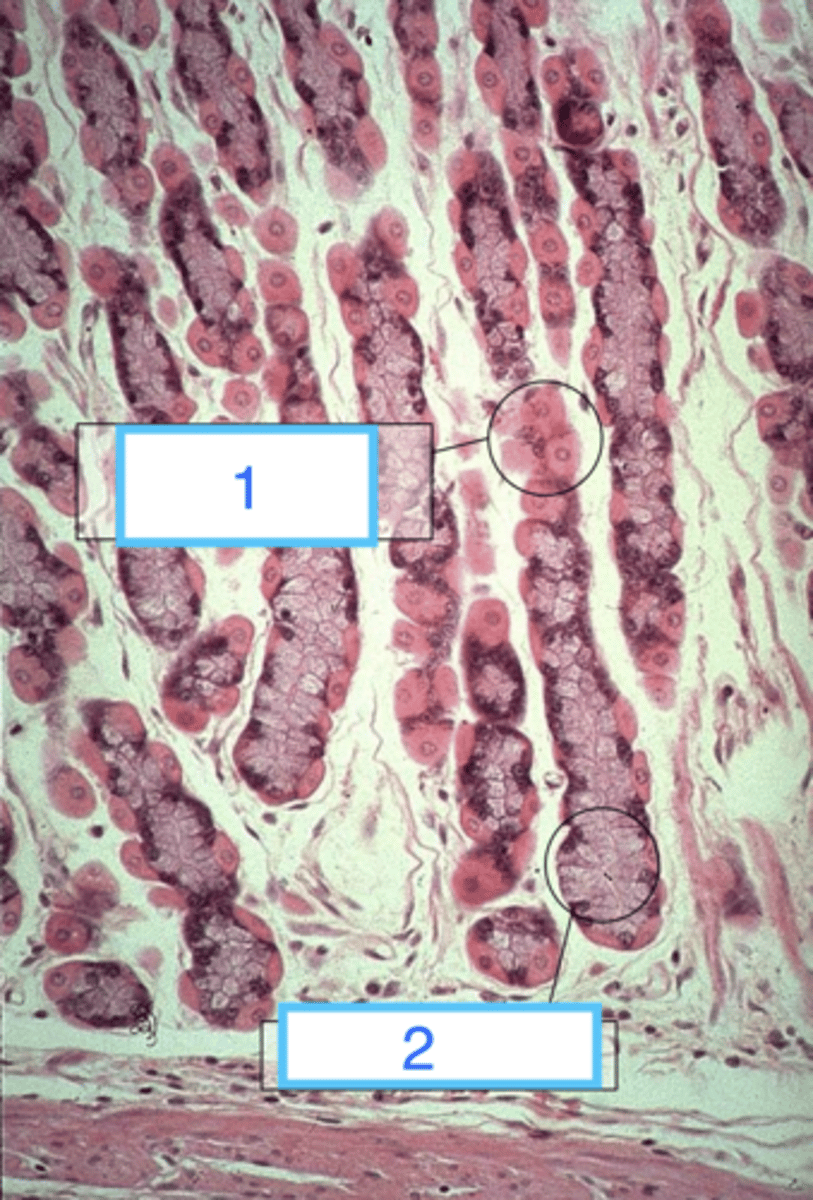
chief cells
what are 2?
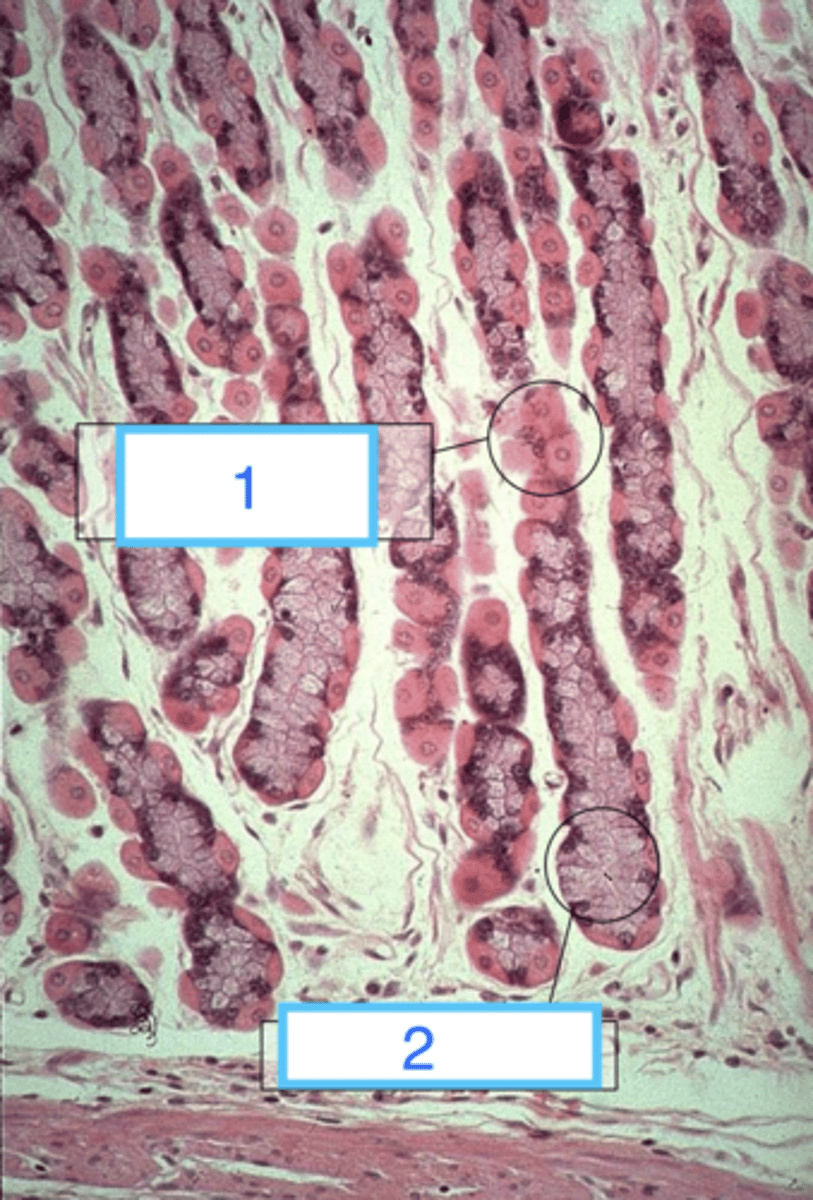
the mucosa of the glandular stomach
what is this?
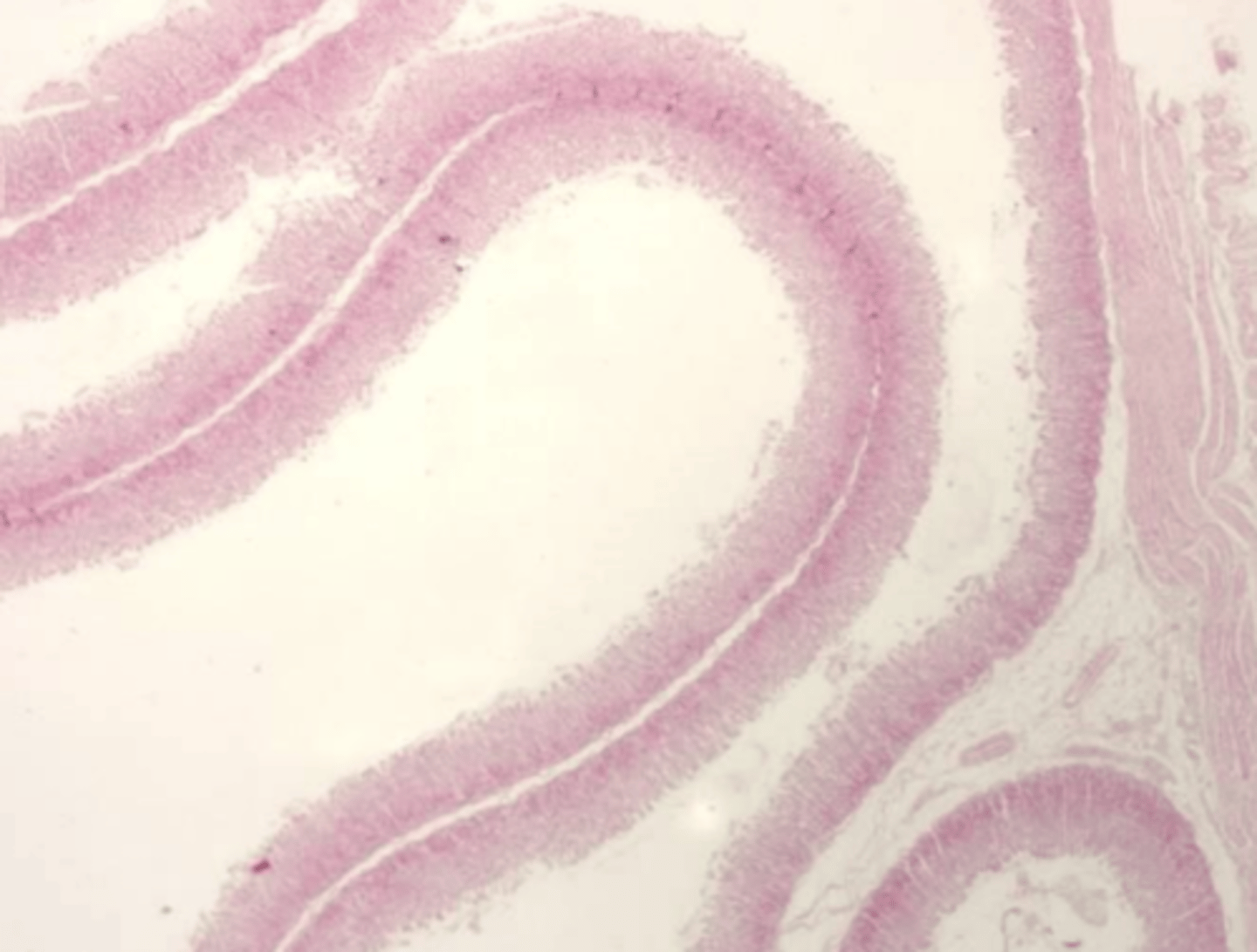
the abomasum
what is this?
1. very long organ
2. mucosa and submucosa are folded in circular arrangements called plicae circulares
3. villi on mucosa surface
4. microvilli on enterocytes
what factors allow the small intestine to have large surface area?
it is only at the apical part of the enterocytes, so it allows the cells to open and close to allow molecules past into the bloodstream (for absorption)
what is the function of the gap junctions of the mucosa of the small intestine?
at the apical part of the enterocytes
where are gap junctions located in the small intestine?
columnar
what is the epithelium of the small intestine?
enterocytes, goblet cells, neuroendocrine cells, lymphocytes
what types of cells do we see in the mucosa of the small intestine?
yes
are there goblet cells in the small intestine?
enterocytes
what are the most abundant cells of the mucosa of the small intestine?
tall and columnar with a basal nucleus and microvilli on the surface
describe the appearance of enterocytes
stomach- no goblet cells, parietal and chief cells
small intestine- goblet cells, intestinal glands
what is the difference between the mucosa of the glandular stomach and the mucosa of the small intestine?
brunner's glands
what structures are unique to the duodenum?
in the submucosa of the duodenum
where are brunners glands located in the digestive system?