BIOL 2120 Midterm Review
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All tested content (With pictures!)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Weekly lab quizzes
Open on Fridays and need to be completed by the end of Monday.
Handouts
Should be submitted as a PDF and consist of 1-4 questions.
Group handouts
Although handouts are done as a group, answers should not be the same for each group member.
BSL-2 lab
A lab that requires specific safety protocols due to the potential risk of moderate hazards.
Dress code
Should be covered from shoulder to knee in the lab.
Guesting policy
Only 2 times per semester.
Making up exams and quizzes
Quiz deadlines can be extended with a verifiable excuse within 24 hours of the original deadline.
Missed quizzes
Must be made up by the day after the deadline.
Exams make-up policy
Can be made up only with a verifiable excuse provided within 24 hours of the exam date.
Penalty for exam make-up without valid excuse
50% penalty.
Proper disposal of material
Plates, gloves, and pipettes go in the biohazard container; slides go into cans at the ends of tables; test tubes go upright in racks into test tube disposal; broken glass goes in the glass waste disposal unless hazardous; paper waste goes into regular trash; contaminated materials must go into the biohazard bin.
Handwashing
Hands should be washed before and after lab.
Parfocal
Stays in focus when focal lengths are changed; objective lenses are parfocal.
Resolution
Clarity/sharpness of the image, enabling observation of fine detail.
Numerical aperture
The light gathering ability of the objective lens and condenser; lenses with high N.A. are better at gathering refracted light.
Light wavelength
The distance between crests and troughs of light, measured in nanometers.
Staining
Dyeing samples in order to make their features more visible.
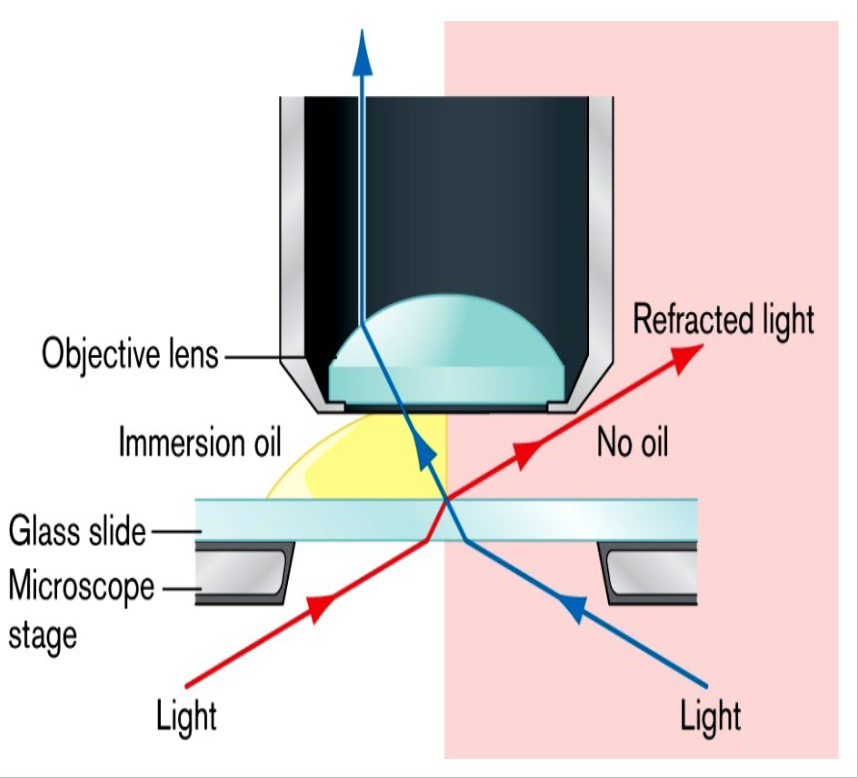
Oil immersion
Oil has the same refractive index as glass, reducing the refraction of light and allowing more light to enter the lens; used on bacteria with an objective magnification of 100x.
Limit of resolution
The minimum distance a microscope can distinguish between two points, calculated by the wavelength of light (usually 500 nm) divided by the sum of the numerical aperture of the objective lens and the condenser.
Total magnification
The ocular lens magnification multiplied by the objective lens magnification.
Objective lenses
Common magnifications include 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x.
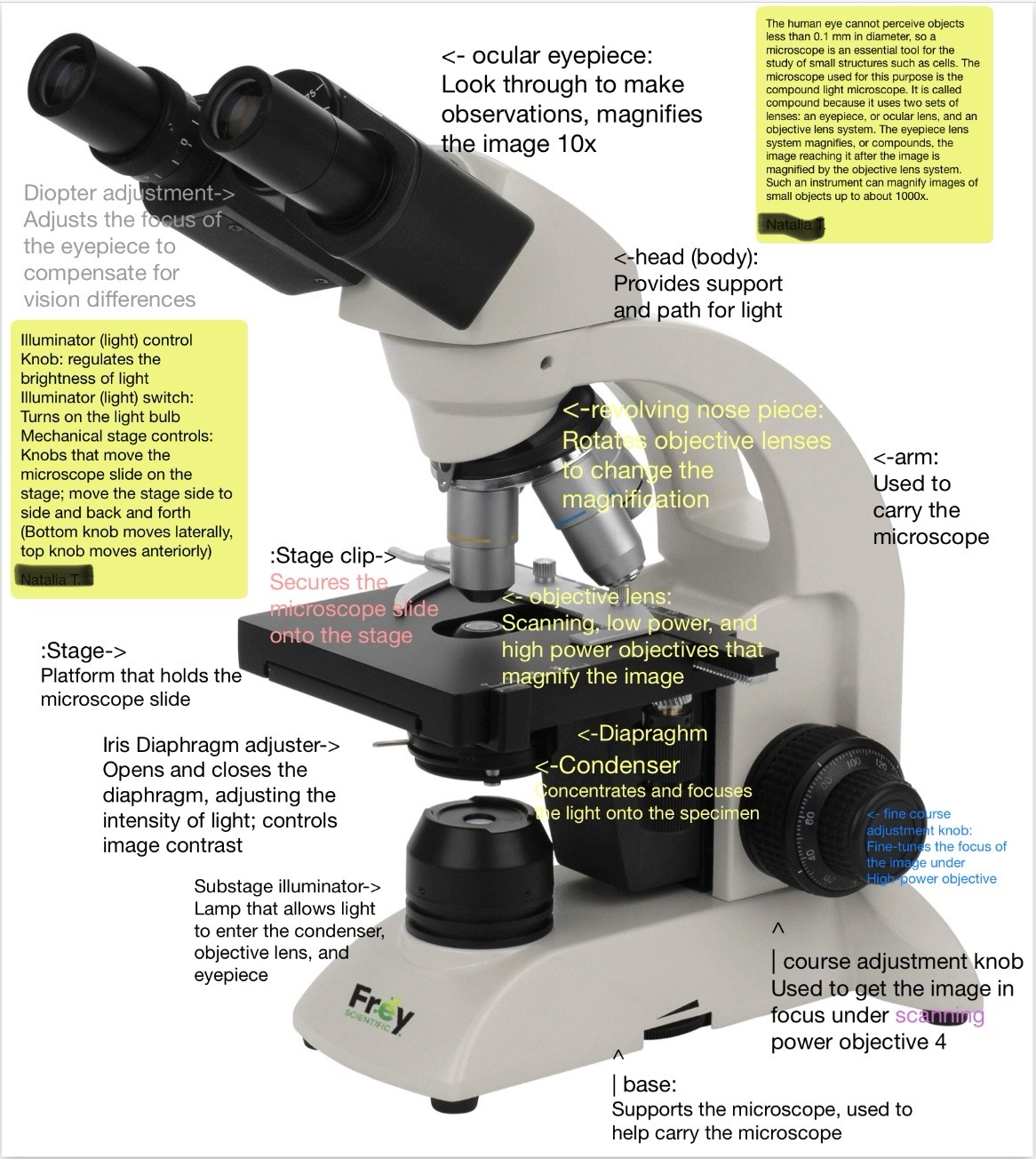
Proper microscope procedure
A series of steps including picking up the microscope by the arm and base, cleaning lenses, adjusting the diaphragm, and properly disposing of slides.
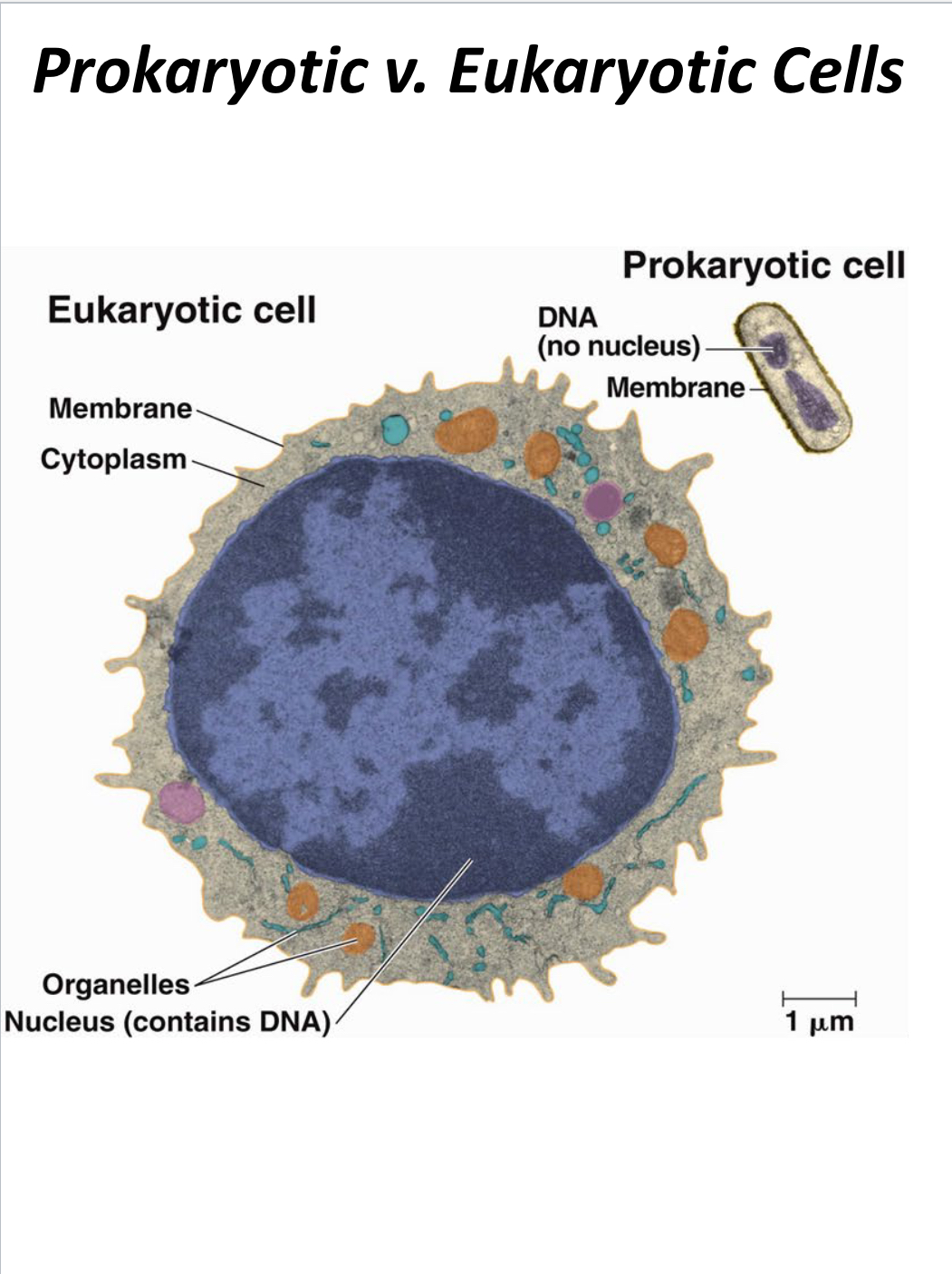
Prokaryotic cells
Cells that do not have membrane-bound organelles and typically have a single chromosome.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that are larger, have membrane-bound organelles, and multiple chromosomes.
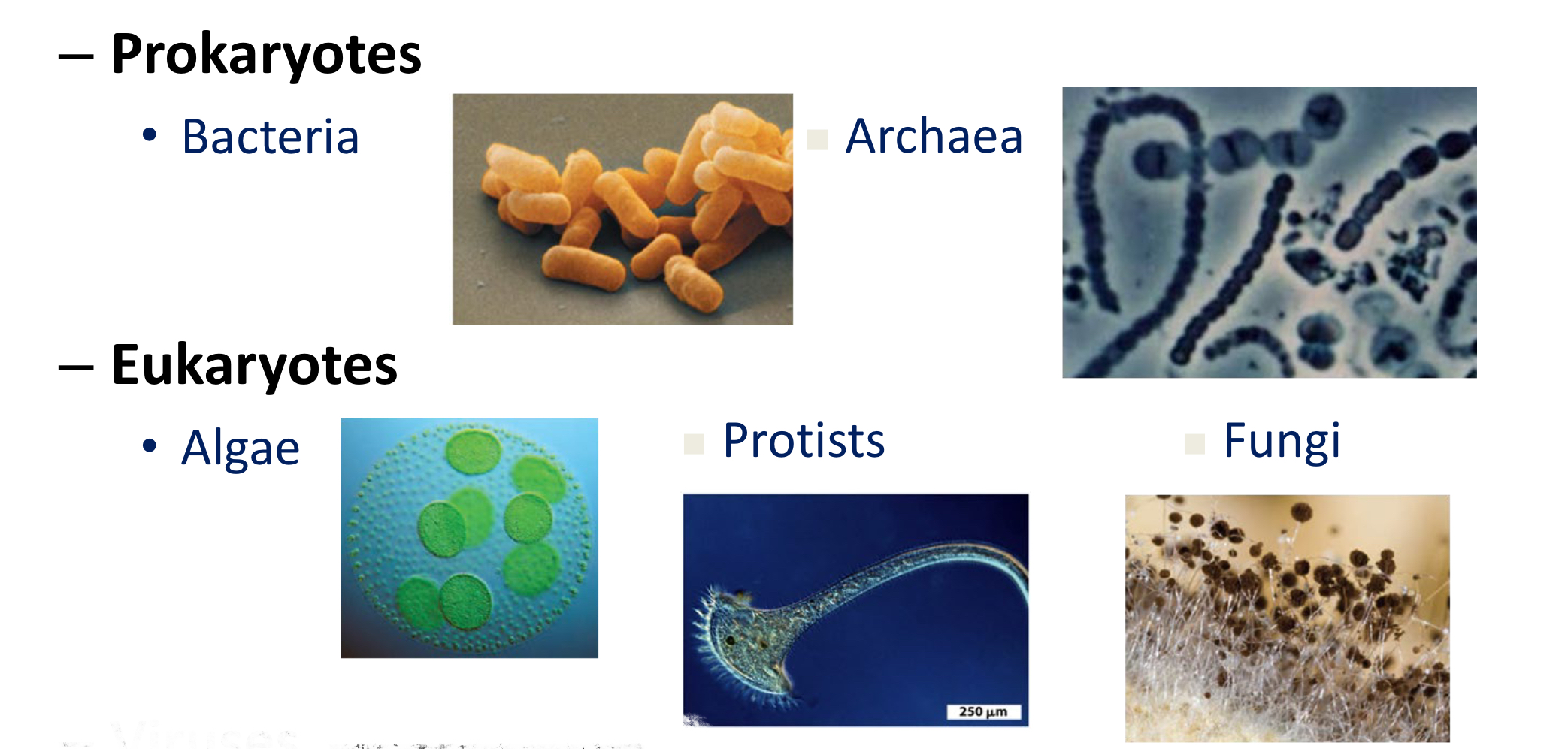
Domain classification
Eukaryotes include protozoans, algae, molds, and yeast; Prokaryotes include Archaea and Bacteria, which have separate respective domains.
Incubation at 25 degrees Celsius
Tests for microbial growth at around room temperature.
Incubation at 37 degrees Celsius
Tests for microbial growth in or on humans.
Ubiquity of microorganisms
Microbes are found everywhere except uninhabitable areas and can be swabbed from any surface.
Sterile mediums
Will not develop microbes as they have not been exposed to the environment.
Microbial presence
Objects that are clean will have less microbial presence, while dirty objects will have a high microbial presence.
Growth of bacteria on solid medium
Microbes grow in distinct colonies with apparent physical characteristics enabling pure culturing.
Incubation time and temperature
Greatly affect microbial growth; some microbes grow slowly while others grow quickly with varying optimal temperatures.
Colony shapes on solid medium
Can be round, irregular, filamentous, or rhizoid.
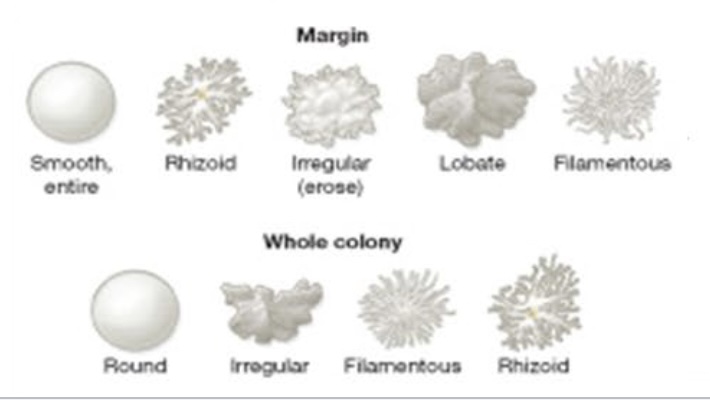
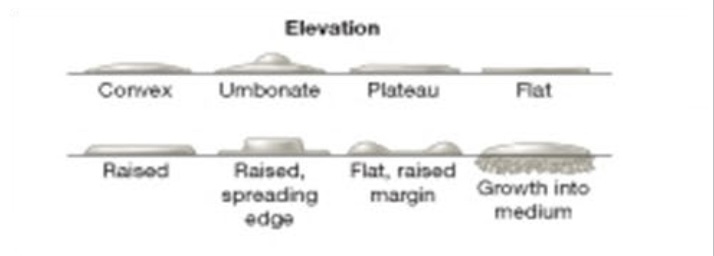
Elevations of colonies
Can be flat, raised, convex, umbonate, plateau, or grow into the medium.
Agar slants
Used for stock cultures to keep microbes viable and usually show pure cultures.
Microbes in liquid medium
Grow suspended and have easier access to nutrients; Yields high growth.
Types of growth in liquid medium
Can include uniform fine turbidity, pellicle growth, sediment growth, ring growth, and flocculent growth.
Mycobacterium smegmatis
Has a fried egg appearance due to a waxy cell membrane and is non-motile with pellicle formation in liquid medium.
Streptomyces griseus
Has a dry texture with a mold-like appearance.
Proteus mirabilis
Colony spreads and is highly motile.
Serratia marscens
Produces a red colored pigment below 30 degrees Celsius.
Bacillus subtilis
Has a soil odor and forms endospores.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Produces blue/green (pyocyanin) and yellow/green (pyoverdine) pigments.
Staphylococcus aureus
Characterized by yellow pigmentation.
Chromobacter violaceum
Produces violet pigmentation.
Micrococcus roseus
Produces pink to red pigment (carotenoids).
Enterobacter aerogenes
Motile and produces uniform turbidity.
Staphylococcus epidermis
Non-motile, produces sediment, and is white.
Streak plating
A technique where an inoculating loop is flamed, cooled, and used to inoculate agar plates with specific streaking patterns.
Nutrient broth
A medium used for cultivating bacteria that must be free of interfering microbes and contamination.
Simple staining
A procedure used to view the overall size and shape of a smear's cells by applying a basic dye.
Heat fixing
The process of passing a smear through a flame 2-3 times to adhere the cells to the slide.
Colony Forming Unit (CFU)
The microbe(s) that produced a colony, which may not always descend from a single cell.
Aseptic technique
Methods used to obtain a pure culture by properly sterilizing and using uncontaminated tools and mediums.
Dilution streak plate method
A technique that allows different microbes to grow without encroaching on each other by progressively reducing the number of microbes inoculated into each quadrant.
Contamination
The presence of unwanted microorganisms in a culture, which can occur from airborne particles or improper handling.
Growth requirements for microbes
Microbes require nutrients, oxygen or other gases, moisture, optimal pH, and temperature for growth.
Complex medium
A type of growth medium that contains some unknown ingredients or components.
Defined medium
A type of growth medium with a precise chemical composition.
Negative staining
A technique used to see the inner structures and capsule of a smear's cells without heat fixation.

Basic dye
A positively charged dye that is attracted to negatively charged cell walls, used in simple staining.
Basic dyes
crystal violet, methylene blue, malachite green, safranin red.
Acidic dye
A negatively charged dye that stains the background of negatively charged cells, used in negative staining.
Acidic dyes
Nigrosin, eosin
Heat-sensitive cells
Cells that are better viewed using negative staining due to less distortion of cell structure.
Streak lines
Lines along which bacterial growth should occur in a solid plate; growth outside of these lines indicates contamination.
Inoculating loop
A tool used to transfer bacteria to a nutrient broth or slide during microbiological procedures.
Moisture in media
An essential requirement for microbial growth, ensuring that the medium supports life.
Optimal pH and temperature
Conditions that must be maintained for the effective growth of microbes.
Sterilizing tools
The process of cleaning and preparing tools to prevent contamination in microbiological work; performed with a Bunsen burner in lab.
Incubator
A device used to maintain optimal growth conditions for microbes, including temperature and humidity.
Chromophore
The color-producing component of a stain, and its ionic charge determines whether or not it binds to a specimen.
Errors in Simple Staining
Include under/overheating, and over-staining.
Errors in Negative Staining
Include over-inoculation, and not spreading the smear enough.
Cocci
Bacterial cells that are round/circular.
Vibrio
Bacterial cells that are bent.
Bacilli
Bacterial cells that are pill shaped.
Spirillum
Bacterial cells that are spiral and only have one flagellum at the end.
Spirochete
Bacterial cells that are elongated and spiral/bent.
Diplo
Cells that are arranged in pairs.
Strepto
Cells that are multiple in chains.
Sarcinae
Cells that are arranged in cubes of eight.
Staph
Cells that are multiple in clusters.
Coccobacillus
Cells that are both circular and pill-shaped.
Pleomorphic
Cells that are irregular/adaptable.
Differential Staining
Includes gram staining, acid fast staining, capsule staining, and endospore staining, used to differentiate between types of bacteria and identify pathogens.
Gram Staining
Reveals whether a cell is gram positive or gram negative.
Acid Fast Staining
Used on mycobacterium due to their thick, waxy texture.
Endospore Staining
Reveals whether a cell is in a vegetative state or the endospore stage.
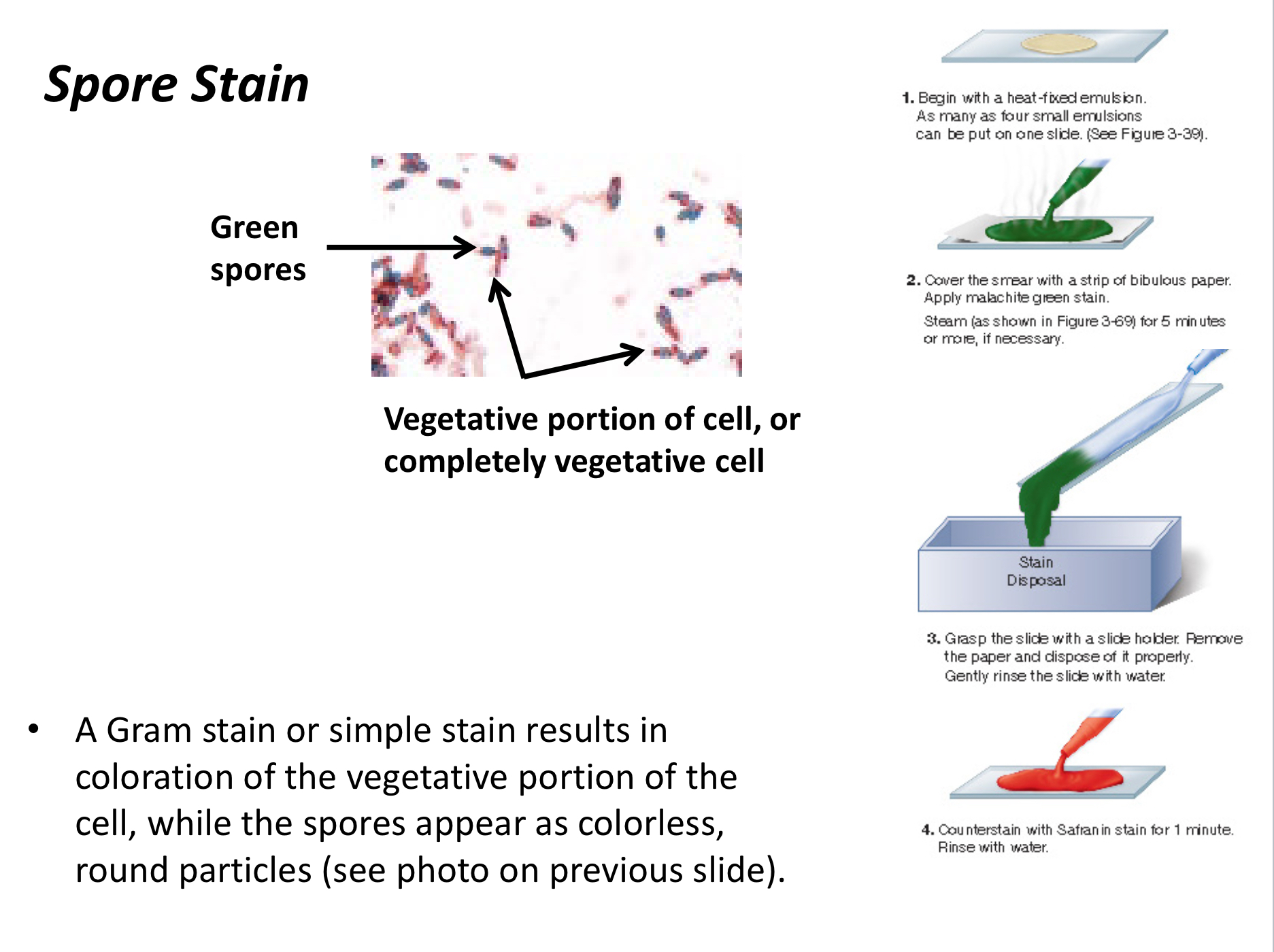
Primary Stain
The initial stain applied in differential staining that binds to specific cell types.
Counterstain
A stain applied after the primary stain that binds to cells/structures that don't bind to the primary stain.
Mycolic Acids
Cause the thick, waxy cell envelope of mycobacteria.
Glycocalyx
The thick structure that makes up the capsule, often found on pathogenic bacteria.
Capsule Staining
A combination of a simple stain and a negative stain used to identify disease-causing pathogens.
Common mistakes with gram staining
Making the smear too thick, overheating the slide, overstaining or under-staining the smear, over rinsing the smear, leaving the decolorizer on for too long, under-decolorizing the smear.
Gram positive cell walls
Have one membrane with thick layers of peptidoglycan reinforced by teichoic acids.
Gram negative cell walls
Have one outer membrane, one inner membrane, and a thin cell wall (periplasm) with very little peptidoglycan.
Lipoproteins in Gram negative bacteria
Present in the outer membrane along with lipopolysaccharides.
Peptidoglycan content in Gram positive bacteria
Higher content and cross-linkage allow them to resist decolorization, retaining the primary stain.
Lipid content in Gram negative bacteria
Higher lipid content makes them susceptible to decolorization, as alcohol extracts the lipids.