Function Mastery - AP Precalclus (2024)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Formula/Equation - Linear Function
f(x) = mx + b
m: slope
b: y-intercept
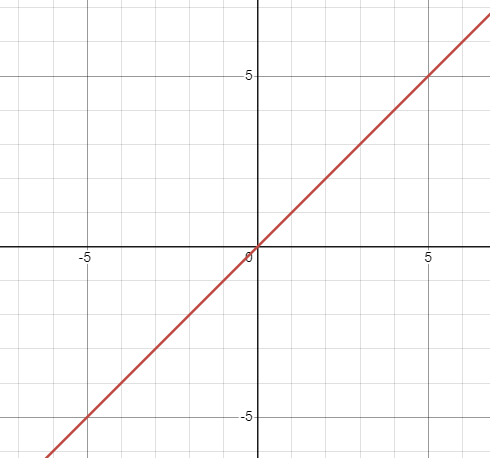
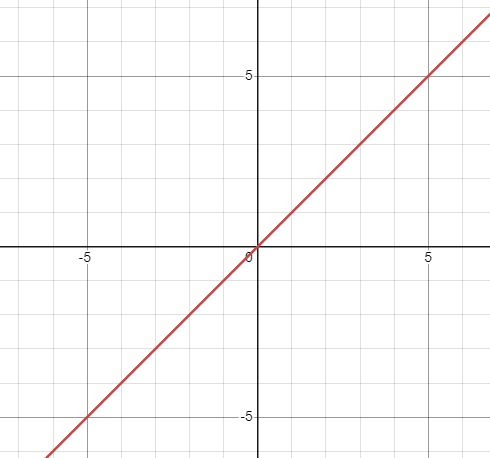
Domain & Range - Linear Function
Domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: (-∞, ∞)
Formula/Equation - Quadratic Function
f(x) = a × (b(x + c))² + d
a: vertical stretch/compress
b: horizontal compress/stretch (b > 0, compress horizontally)
c: horizontal phase shift (-c = right c)
d: vertical phase shift
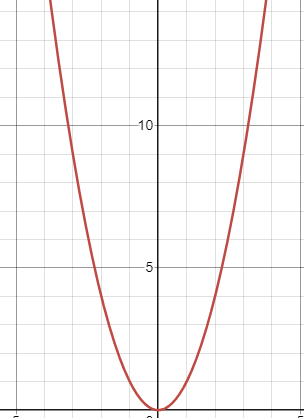
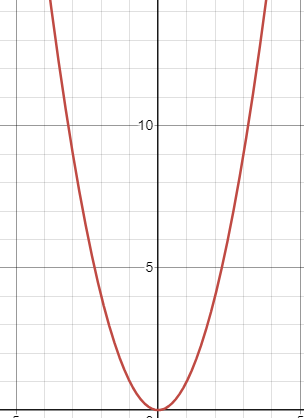
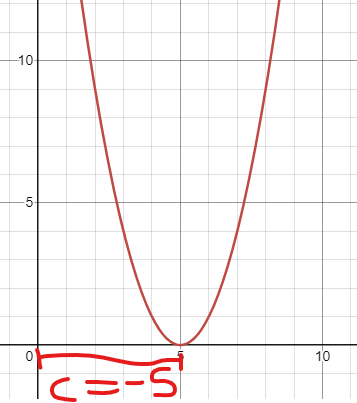
Domain & Range - Quadratic Function
Domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: [d, ∞)
Horizontal Stretch/Compress - All Rectangular Functions
Stretch: 0 < a < 1
Compress: a > 1
Stretch: 0 < b < 1
Compress: b > 1
Vertical Stretch/Compress - All Rectangular Functions
Stretch: a > 1
Compress: 0 < a < 1
Stretch: b > 1
Compress: 0 < b < 1
Phase Shift - All Rectangular Functions
Shift Left: +c
Shift Right: -c
Formula/Equation - Cubic Function
f(x) = a × (b(x + c))³ + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift (-c = right c)
d: Vertical Phase Shift
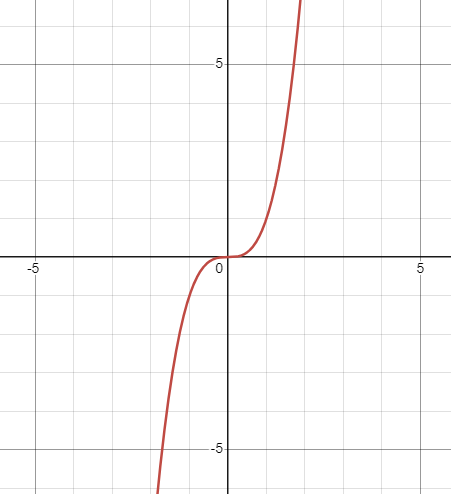
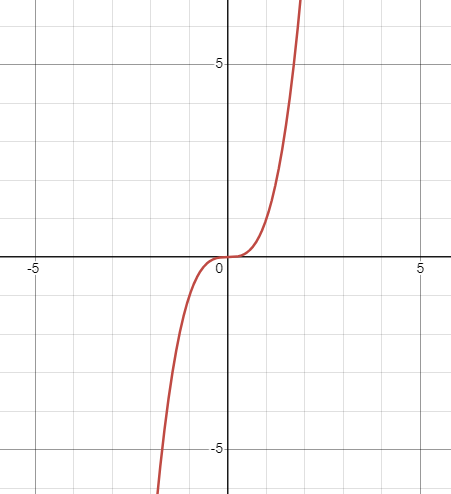
Domain & Range - Cubic Function
Domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: (-∞, ∞)
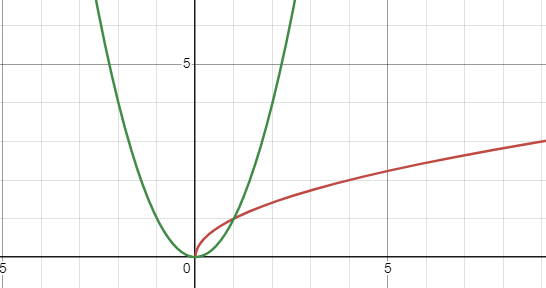
Formula/Equation - Square Root Function
f(x) =a × √(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
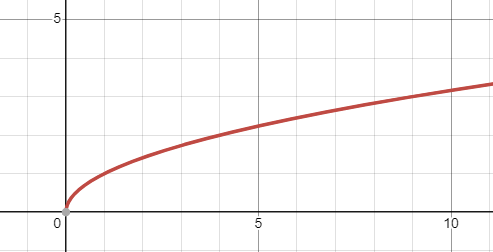
Domain & Range - Square Root Function
Domain: [-c, ∞)
Range: [d, ∞)
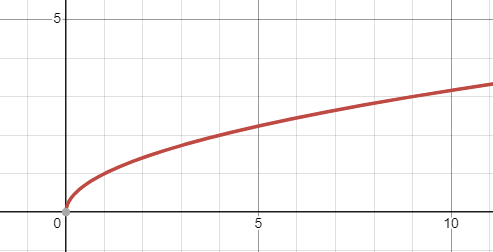
Inverse of what? - Square Root Function
Inverse of Quadratic function.
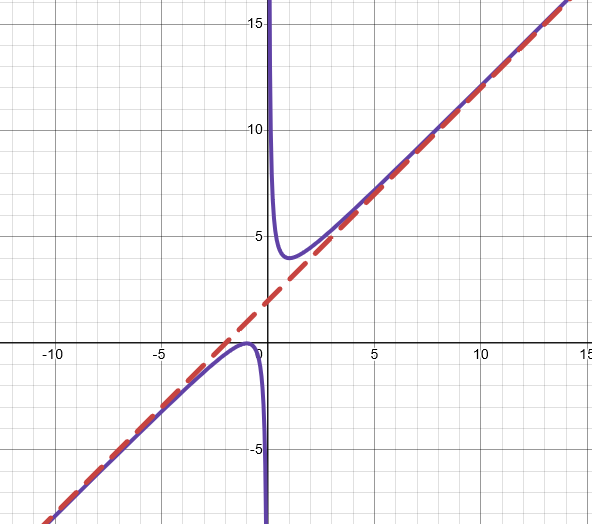
Formula/Equation - Rational Function
f(x) = (Zeroes) / (Vertical Asymptotes)
Horizontal Asymptotes - Rational Function
(n = degree)
Nn < Dn —> y = 1
Nn = Dn —> (N Ceofficent) / (D Ceofficient)
Nn > Dn —> (No Horizontal Asymptote)
Slant Asymptotes - Rational Function
Exists if Nn -1 = Dn e(If N degree is exactly one greater than of D)
To find slant asymptote:
Use long division or synthetic division.
Divide the numerator with the denominator
Ignore remainder
Formula/Equation - Exponential Function
f(x) = a × b(x + c)
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
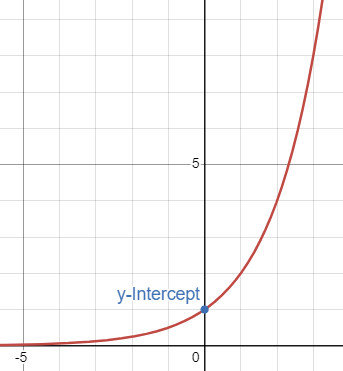
Domain & Range - Exponential Function
Domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: (0, ∞)
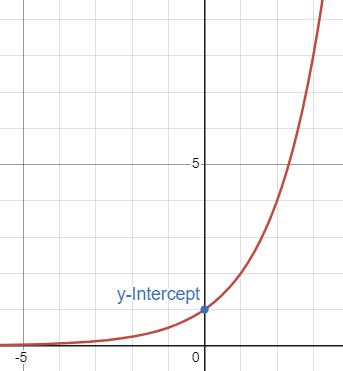
Horizontal Asymptote - Exponential Function
HA at value a.
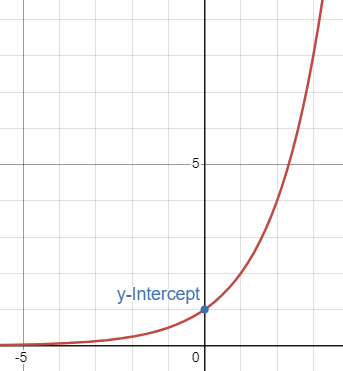
Growth - Exponential Function
When b > 1
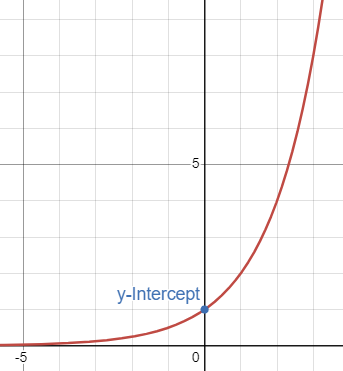
Decay - Exponential Function
When 0 < b < 1
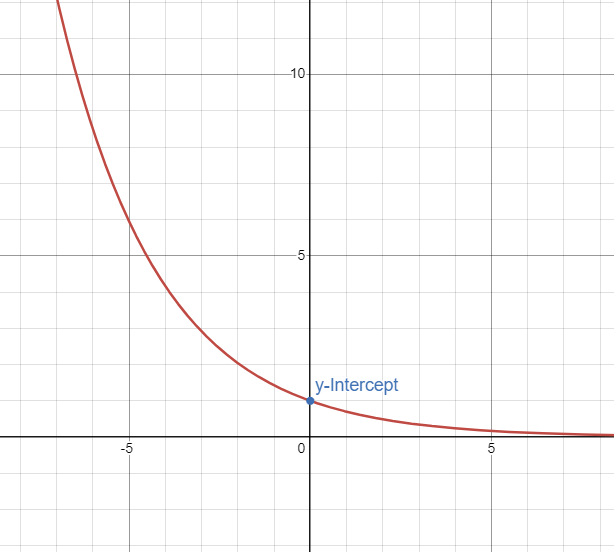
Formula/Equation - Logarithmic Function
f(x) =a × logb(x + c) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch (Note: reciprocated)
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
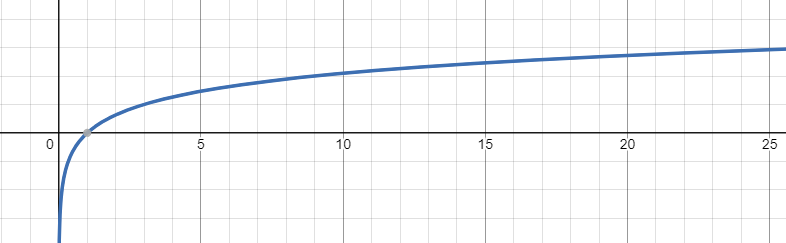
b Limitation - Logarithmic Function
MUST: B > 0
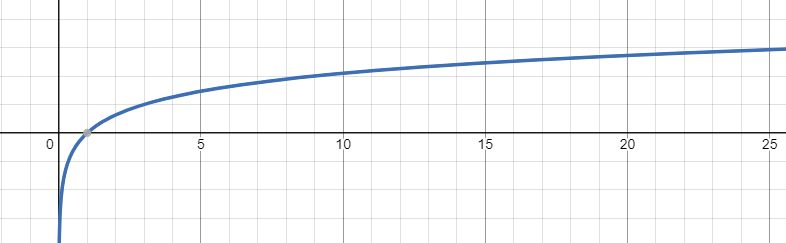
Vertical Asymptote - Logarithmic Function
VA at -c. (Horizontal Phase Shift)
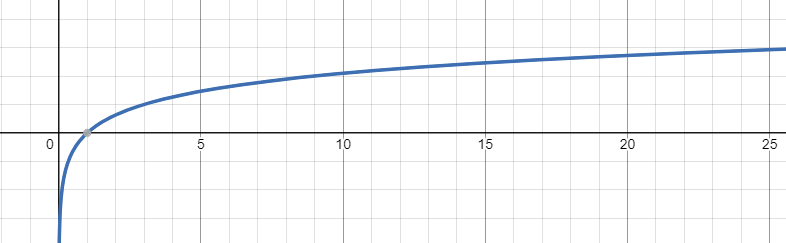
Domain & Range - Logarithmic Function
Domain: (0, ∞)
Range: (-∞, ∞)
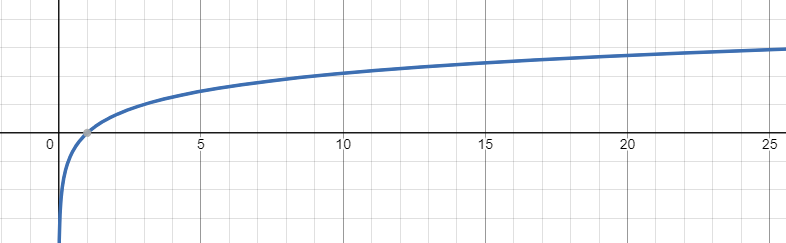
Inverse Function of what? - Logarithmic Function
Inverse of Exponential Function
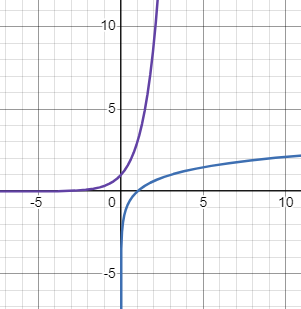
Growth - Logarithmic Function
When b > 1
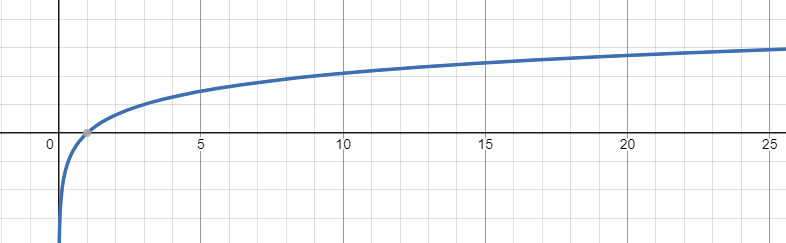
Decay - Logarithmic Function
When 0 < b < 1
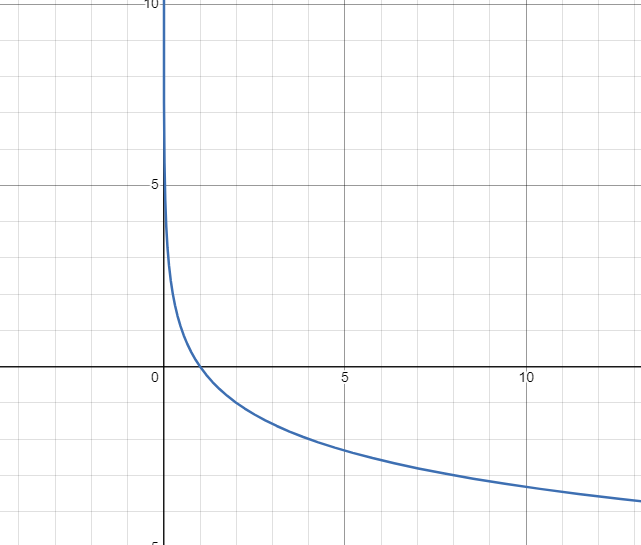
What is a period? (Def & Equation)
A single cycle of a periodic function.
Period = 2π / b
Exception for tangent: Period = π / b
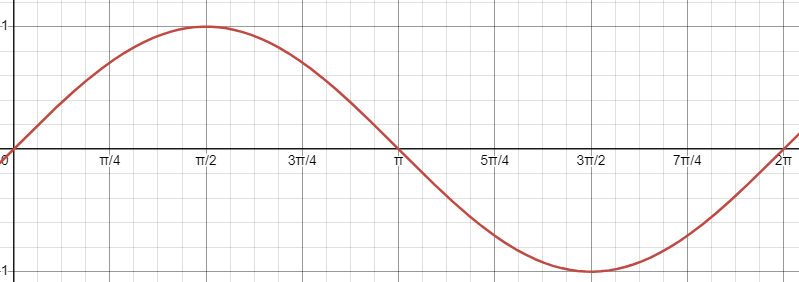
Formula/Equation - Sine Function
f(x) = a × sin(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
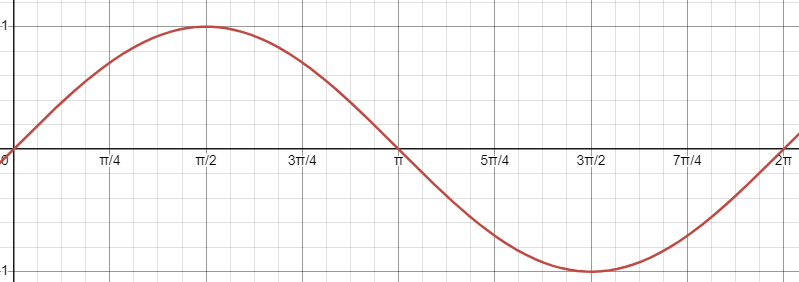
Domain, Range, & Period - Sine Function
Mid - Max - Mid - Min - Mid
Domain: [0, 2π]
Range |a|: [-1, 1]
Period: 2π / b
Midline: y = d
Starts at Mid
![<p><strong>Mid</strong> - Max - Mid - Min - Mid</p><p>Domain: [0, 2π]</p><p>Range |a|: [-1, 1]</p><p>Period: 2π / b</p><p>Midline: y = d</p><p>Starts at Mid</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2f10d51d-61dc-43b9-8165-b45e3b535cd4.png)
Formula/Equation - Cosine Function
f(x) =a × cos(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
Translating Sine Function ←→ Cosine Function
sin(x) = cos(x - π/2) [Shifts right]
cos(x) = sin(x + π/2) [Shifts left]
![<p>sin(x) = cos(x - π/2) [Shifts right]</p><p>cos(x) = sin(x + π/2) [Shifts left]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/91efacf0-baa4-4503-80cb-61f92f9d2715.png)
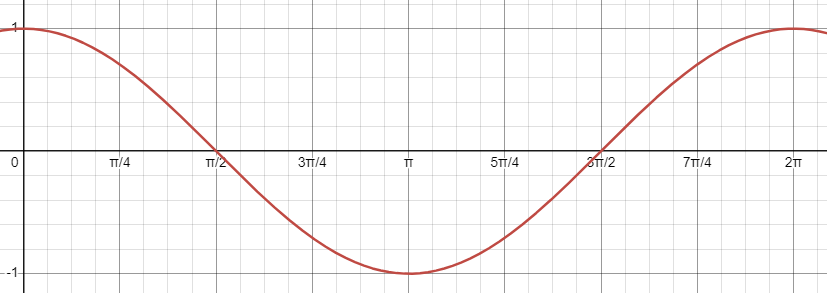
Domain, Range, & Period - Cosine Function
Max - Mid - Min - Mid - Max
Domain: [0, 2π]
Range |a|: [-1, 1]
Period: 2π / b
Midline: y = d
Starts at Max
![<p><strong>Max</strong> - Mid - Min - Mid - Max</p><p>Domain: [0, 2π]</p><p>Range |a|: [-1, 1]</p><p>Period: 2π / b</p><p>Midline: y = d </p><p>Starts at Max</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f6edf04-82f9-482d-a909-54d60a62bdcd.png)
Formula/Equation - Tangent Function
f(x) = a × tan(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
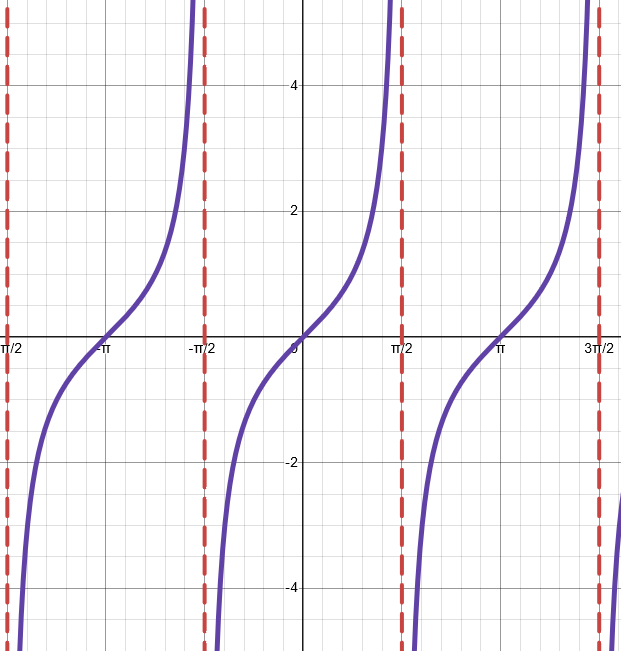
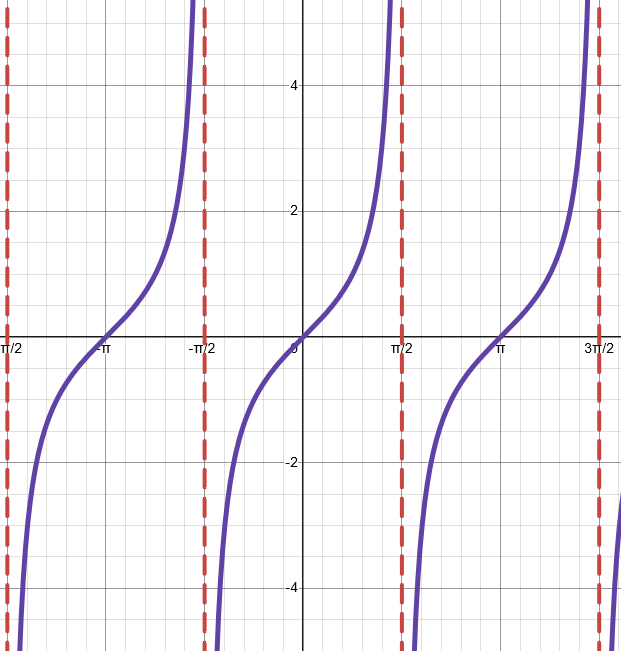
Domain, Range, & Period - Tangent Function
Domain: (-π/2, π/2)
Range |a|: (-∞, ∞)
Period: π / b (Parent Period: π)
Midline: y = d
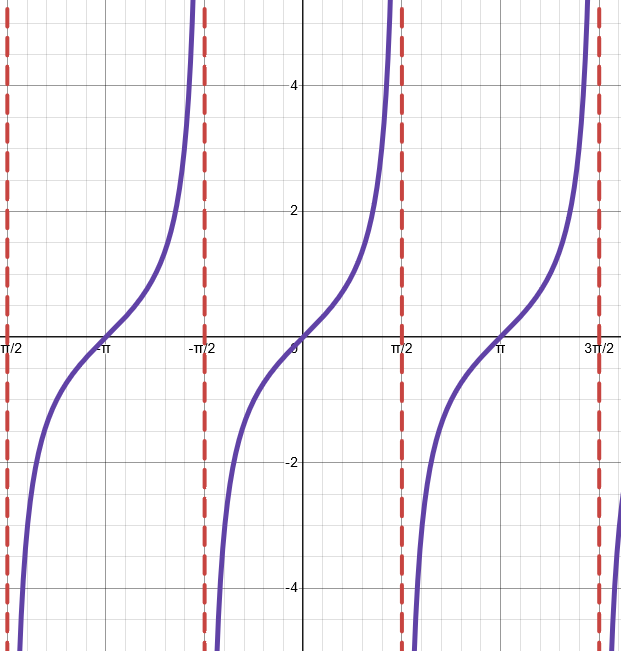
Asymptotes - Tangent Function
Each asymptote occurs at: π/2 ± πn where n ∈ ℤ
Define the notation: a ∈ ℤ
variable a is a set of all integers.
Formula/Equation - Cosecant Function (csc)
f(x) = a × csc(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
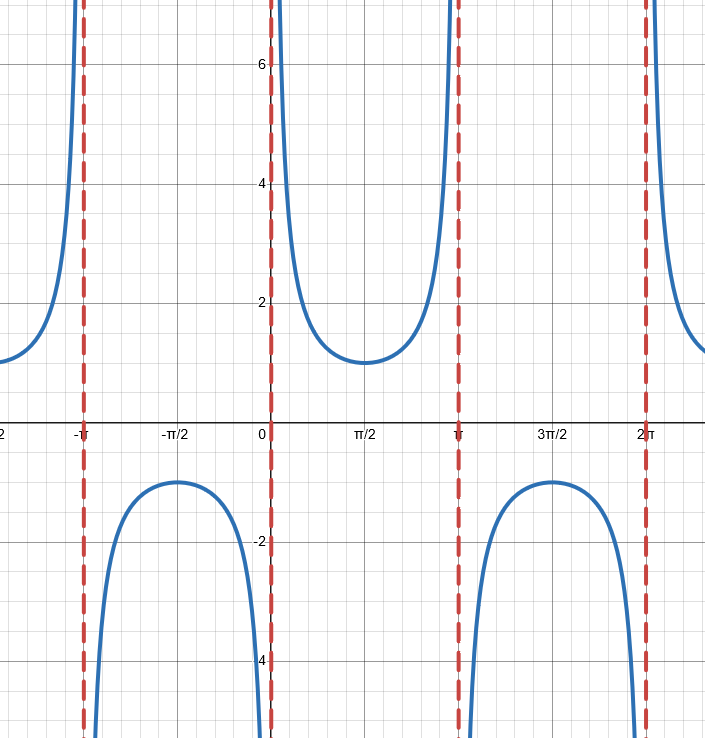
Domain, Range, & Period - Cosecant Function (csc)
Domain: (0, π) (of course changes with shifts)
Range: [a, ∞) & (-∞, -a]
Period: π / b (Parent Period: π)
Midline: y = d
![<p>Domain: (0, π) (of course changes with shifts)</p><p>Range: [a, ∞) & (-∞, -a]</p><p>Period: π / b (Parent Period: π)</p><p>Midline: y = d</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c481ae0f-1166-4f36-919c-cf09c52e30ba.png)
Reciprocal of what? - Cosecant Function (csc)
Reciprocal of sin.
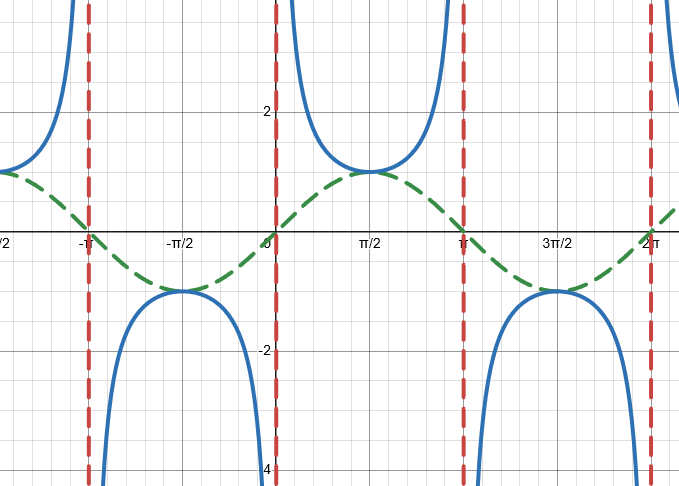
Formula/Equation - Secant Function (sec)
f(x) = a × sec(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
Domain, Range, & Period - Secant Function (sec)
Domain: (-π/2, π/2)
Range: [a, ∞) & (-∞, -a]
Period: π / b (Parent Period: π)
Midline: y = d
![<p>Domain: (-π/2, π/2)</p><p>Range: [a, ∞) & (-∞, -a]</p><p>Period: π / b (Parent Period: π)</p><p>Midline: y = d</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d3620e3e-6e9f-4b4a-9c7a-b089d25351dc.png)
Reciprocal of what? - Secant Function (sec)
Reciprocal of cos.
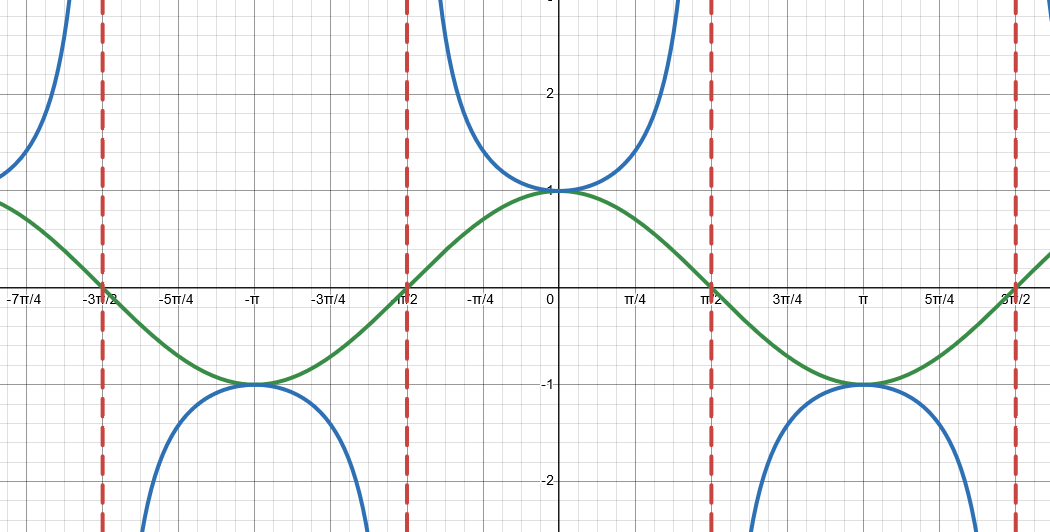
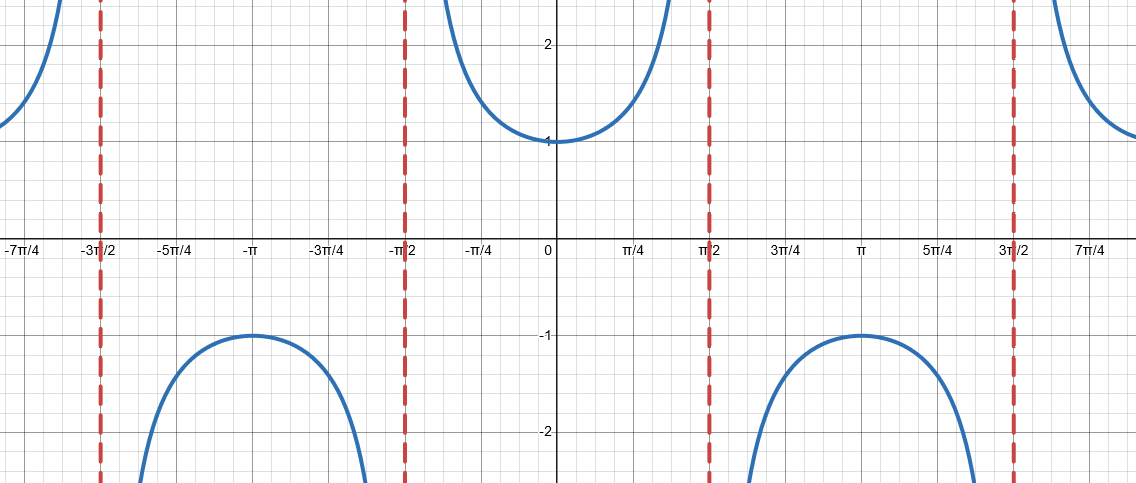
Formula/Equation - Cotangent Function (cot)
f(x) = a × cot(b(x + c)) + d
a: Vertical Stretch
b: Horizontal Stretch
c: Horizontal Phase Shift
d: Vertical Phase Shift
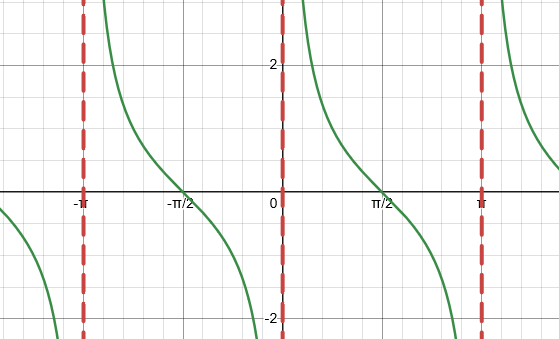
Domain, Range, & Period - Cotangent Function (cot)
Domain: (0, π)
Range: (-∞, ∞)
Period: π / b (Parent Period: π)
Midline: y = d
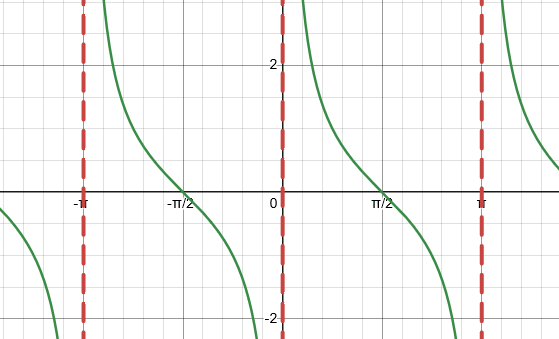
Reciprocal of what? - Cotangent Function (cot)
Reciprocal of tan.
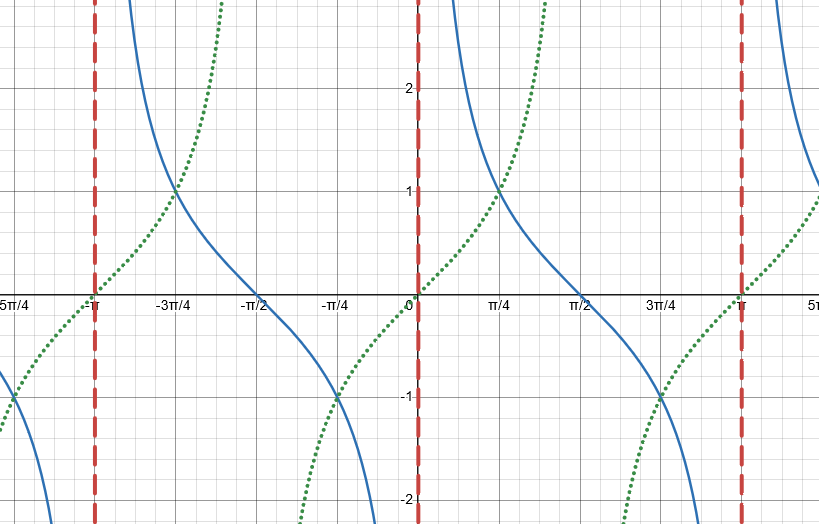
Domain & Range - Inverse Sine Function (Arcsin)
Domain: [-1, 1]
Range: [π/2, -π/2]
![<p>Domain: [-1, 1]</p><p>Range: [π/2, -π/2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/82ff8f39-e954-4595-aac3-0bff929e47b4.png)
Domain & Range - Inverse Cosine Function (Arccos)
Domain: [-1, 1]
Range: [0, π]
![<p>Domain: [-1, 1]</p><p>Range: [0, π]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3f5a59a9-c1ee-4256-b3f2-4b87c1f478c1.png)
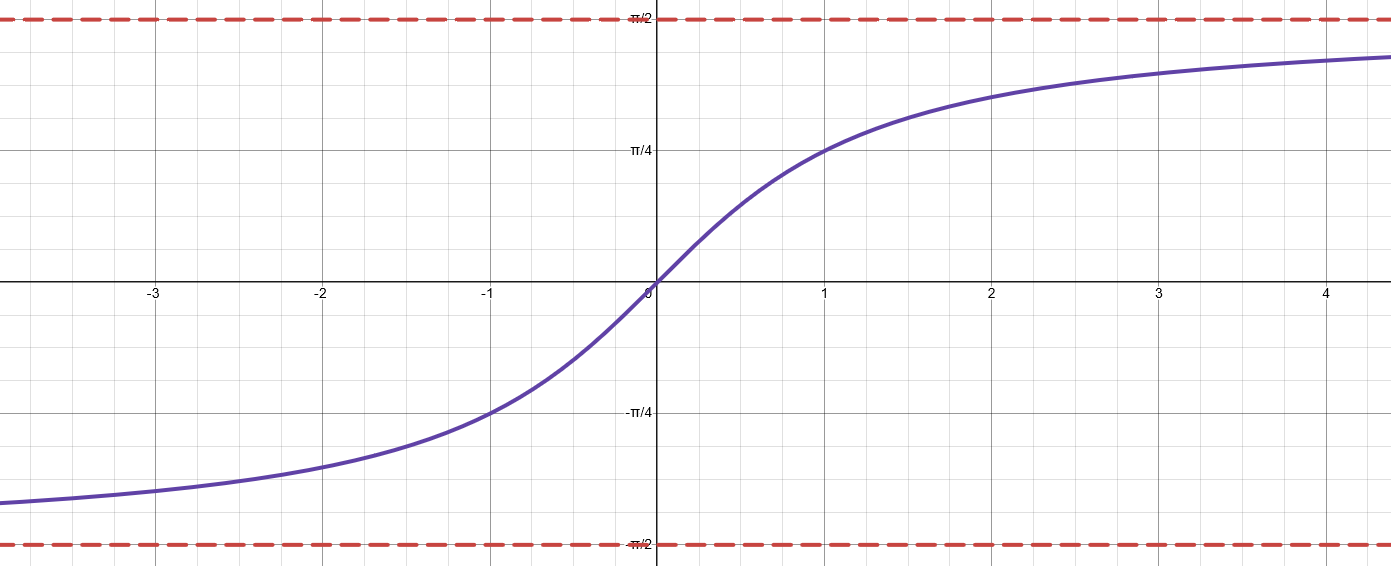
Domain & Range - Inverse Tangent Function (Arctan)
Domain: (-∞, ∞)
Range: (π/2, -π/2)
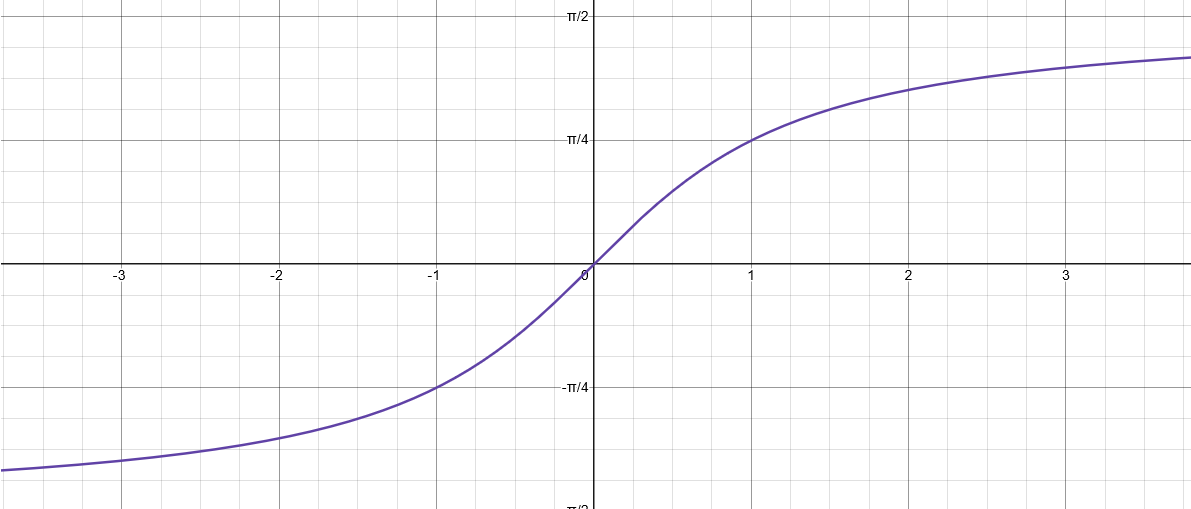
Asymptotes - Inverse Tangent Function (Arctan)
Two Vertical Asymptotes:
y = (π × a)/2
y = -(π × a)/2
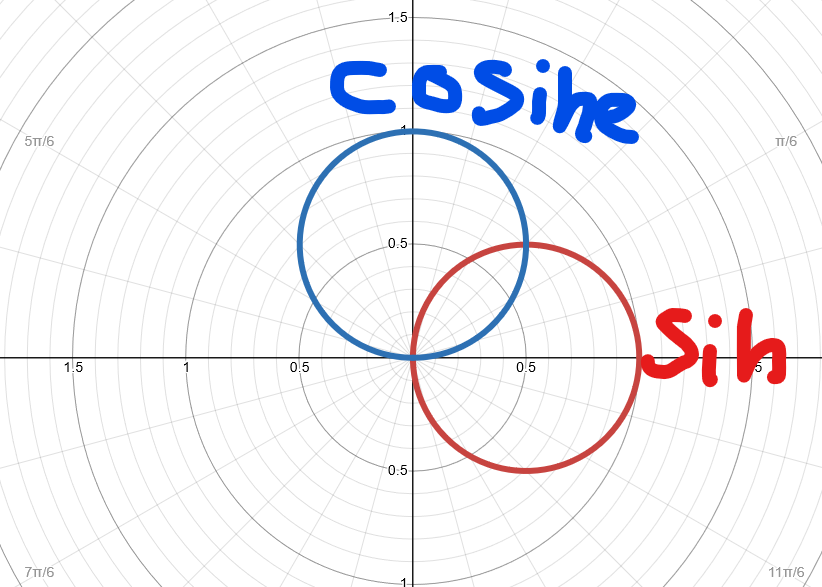
Cosine vs. Sin Polar Function
Cosine functions are ALWAYS on the x-axis
Sine functions are ALWAYS on the y-axis
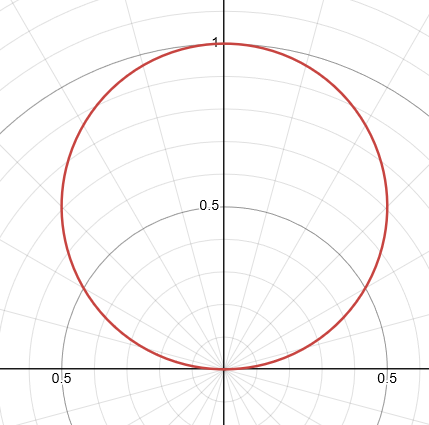
Formula/Equation - Polar Circle Function
r = a × sin(θ)
a: amplitude/scale
Domain - All Limacone Functions
Domain: [0, 2π]
(Except for even rose curves)
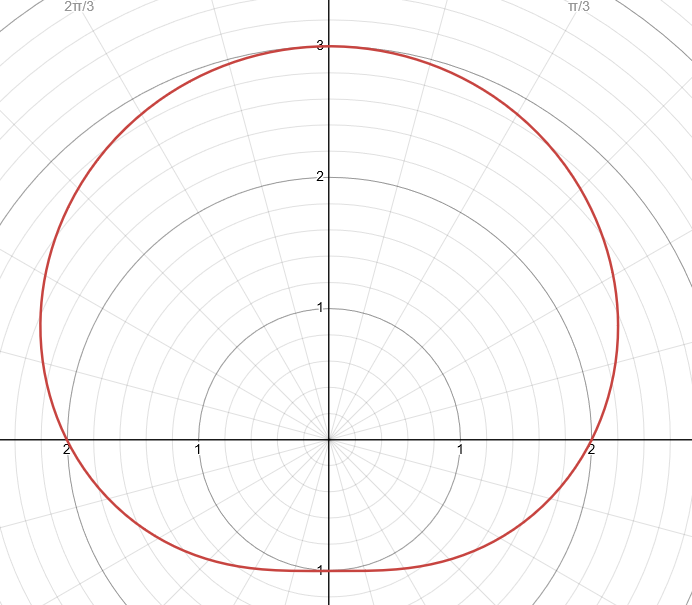
Formula/Equation - Polar Cardioid Limacone Function
r = a ± b × sin(θ)
MUST: (a / b) = 1
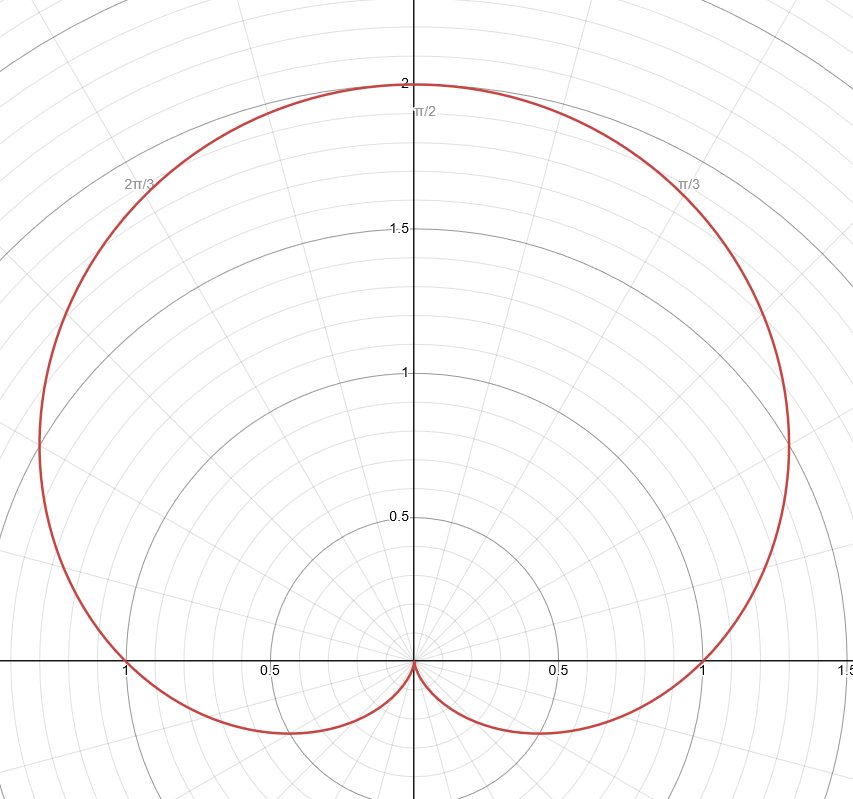
Formula/Equation - Polar Dimpled Limacone Function
r = a ± b × sin(θ)
MUST: 1 < (a / b) < 2
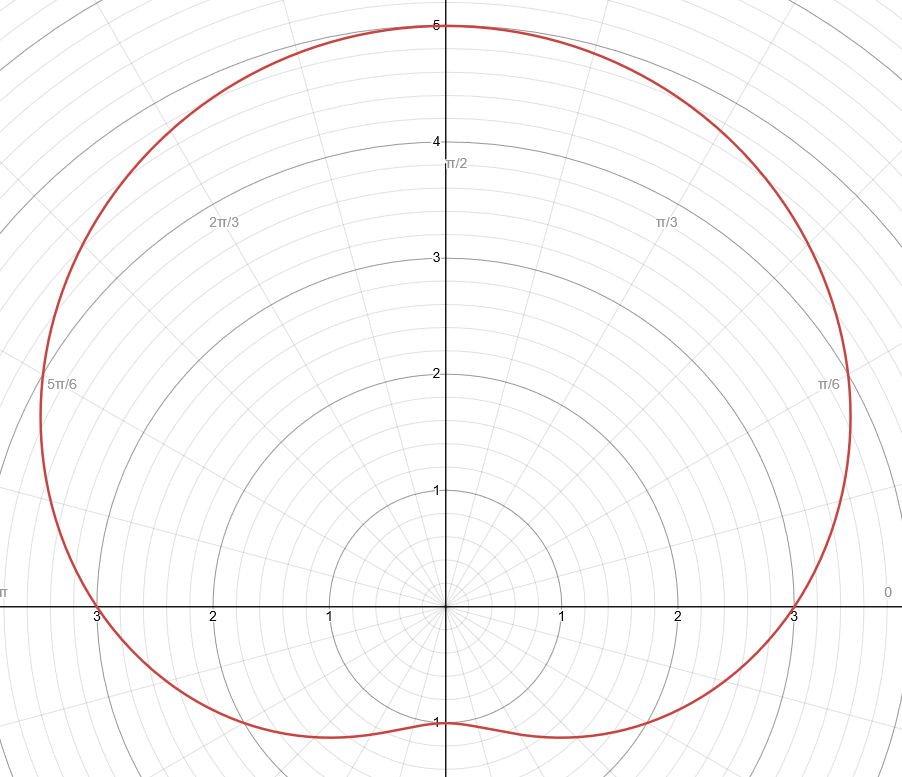
Formula/Equation - Polar Convex Limacone Function
r = a ± b × sin(θ)
MUST: (a / b) > 2
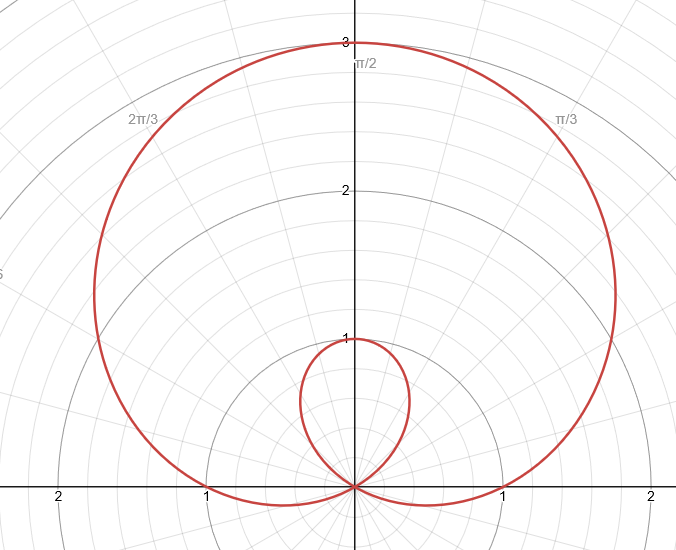
Formula/Equation - Polar Inner-loop Limacone Function
r = a ± b × sin(θ)
MUST: (a / b) < 1
Formula/Equation - Polar Rose Curves Function
r = a × sin(n × θ)
a: Amplitude
n: number of petals
Double petals when n is even
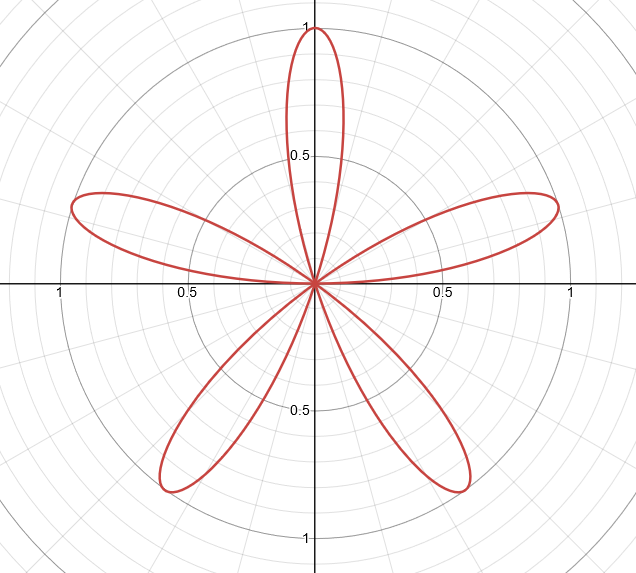
When n is odd - Polar Rose Curves Function
graph has n petals.
Domain: [0, π]
![<p>graph has n petals.</p><p>Domain: [0, π]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0c6619d9-cc7d-41c2-9c1b-fca1c24fd19a.png)
When n is even - Polar Rose Curves Function
graph has 2n petals. (Double)
Domain: [0, 2π]
Note: Even Sin Rose Curves Function’s petals do not intercept x or y axis.
![<p>graph has 2n petals. (Double)</p><p>Domain: [0, 2π]</p><p>Note: <strong>Even Sin Rose Curves Function’s petals </strong>do not intercept x or y axis.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/77e46357-9645-4942-b6eb-ac056633b4c7.png)