L01 - Cell Structure and Function Quiz
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
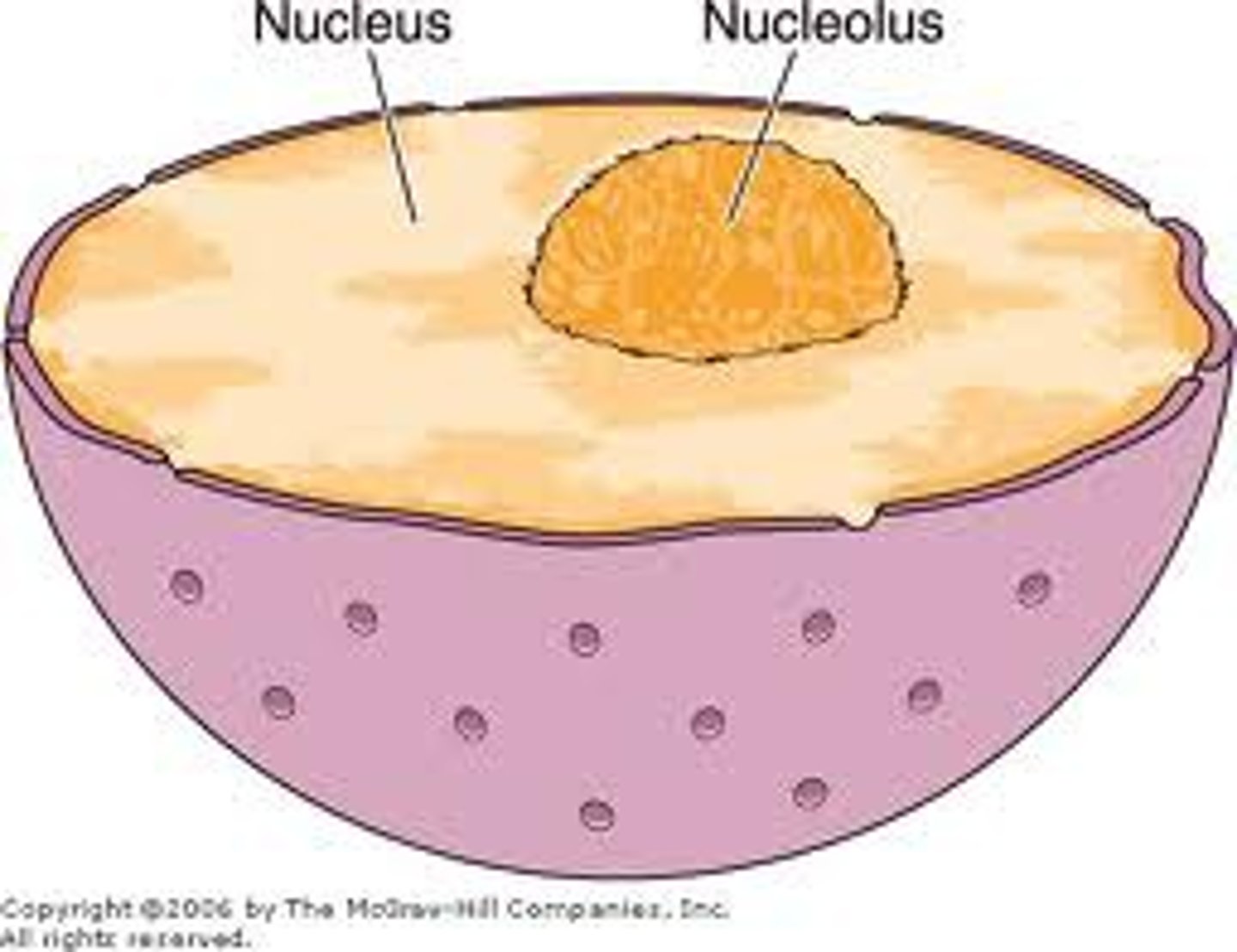
Structure associated with storing the cell's hereditary material, or DNA; coordinates cell growth, metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction (cell division)
a. nucleus
b. mitochondrion
c. chromatin
d. rough endoplasmic reticulum
e. nucleolus
a. nucleus
________________________
a. nucleus
b. mitochondrion = cellular respiration and generates ATP
c. chromatin = what chromosomes are composed of; consists of protein, RNA, and DNA
d. rough endoplasmic reticulum = network of sacs
e. nucleolus = small, dense, in the nucleus of a cell during interphase, produces ribosomes
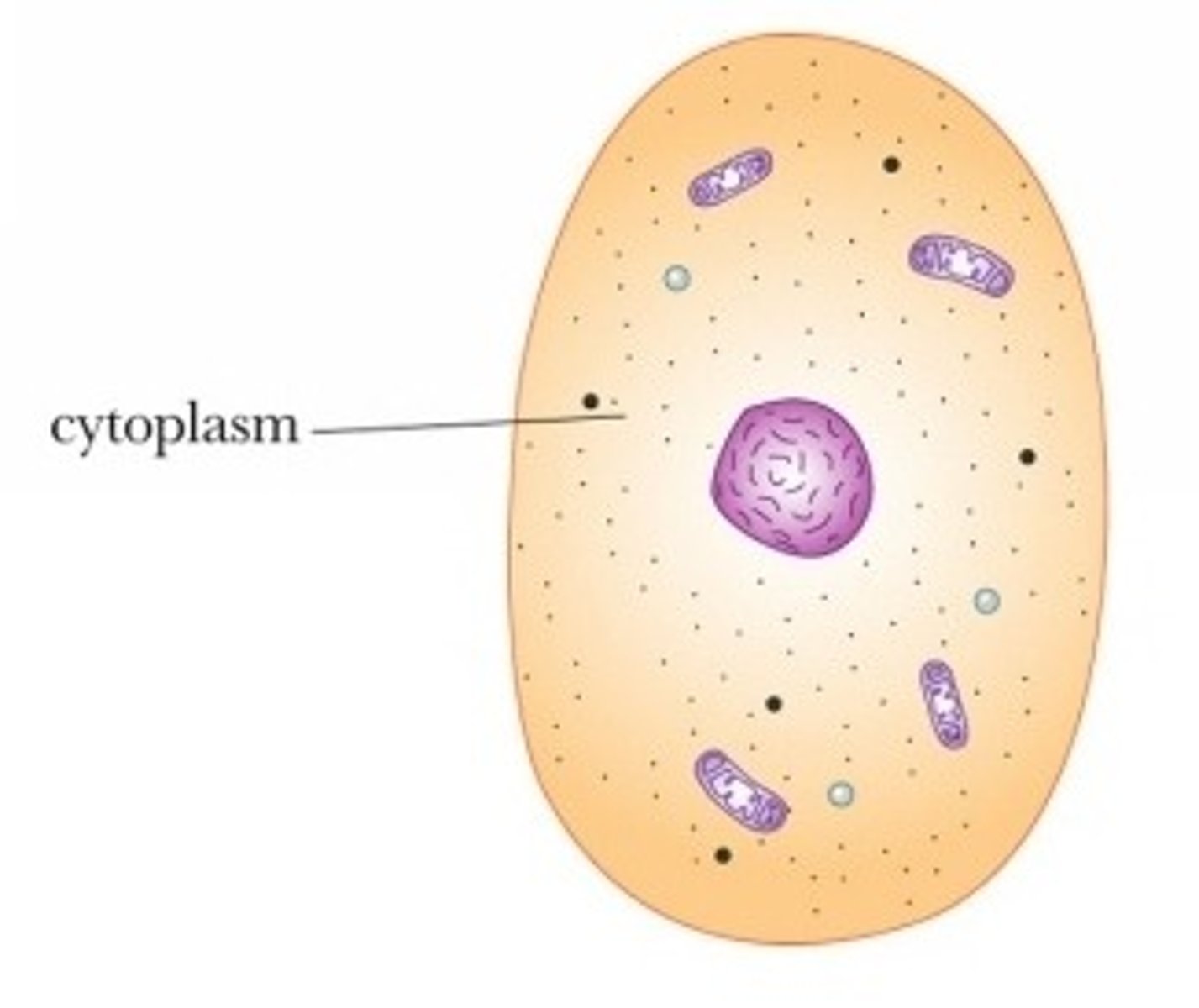
All cellular contents bounded by the plasma membrane.
a. endosome
b. lysosome
c. cytoplasm
d. cytosol
e. desmosome
c. cytoplasm
____________________________
a. endosome = Membrane-bound, formed via endocytosis
b. lysosome = gets rid of cell waste
c. cytoplasm
d. cytosol = Jelly-like fluid
e. desmosome = two adjacent cells are attached
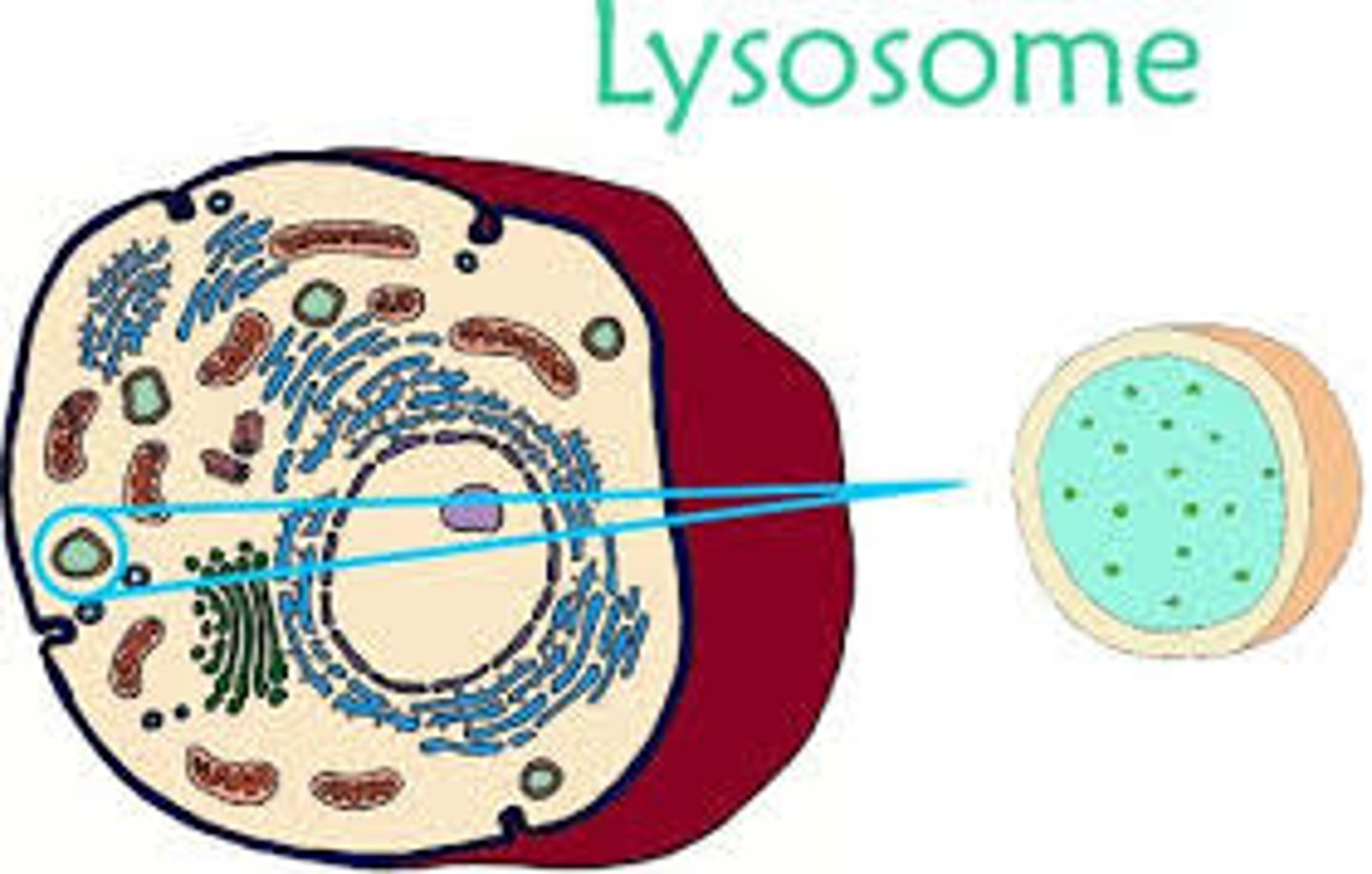
Degradation of cellular waste products and debris from outside the cell into simple compounds, that can be transferred to the cytoplasm as new cell-building materials.
a. peroxisome
b. lysosome
c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
d. endosome
e. desmosome
b. lysosome
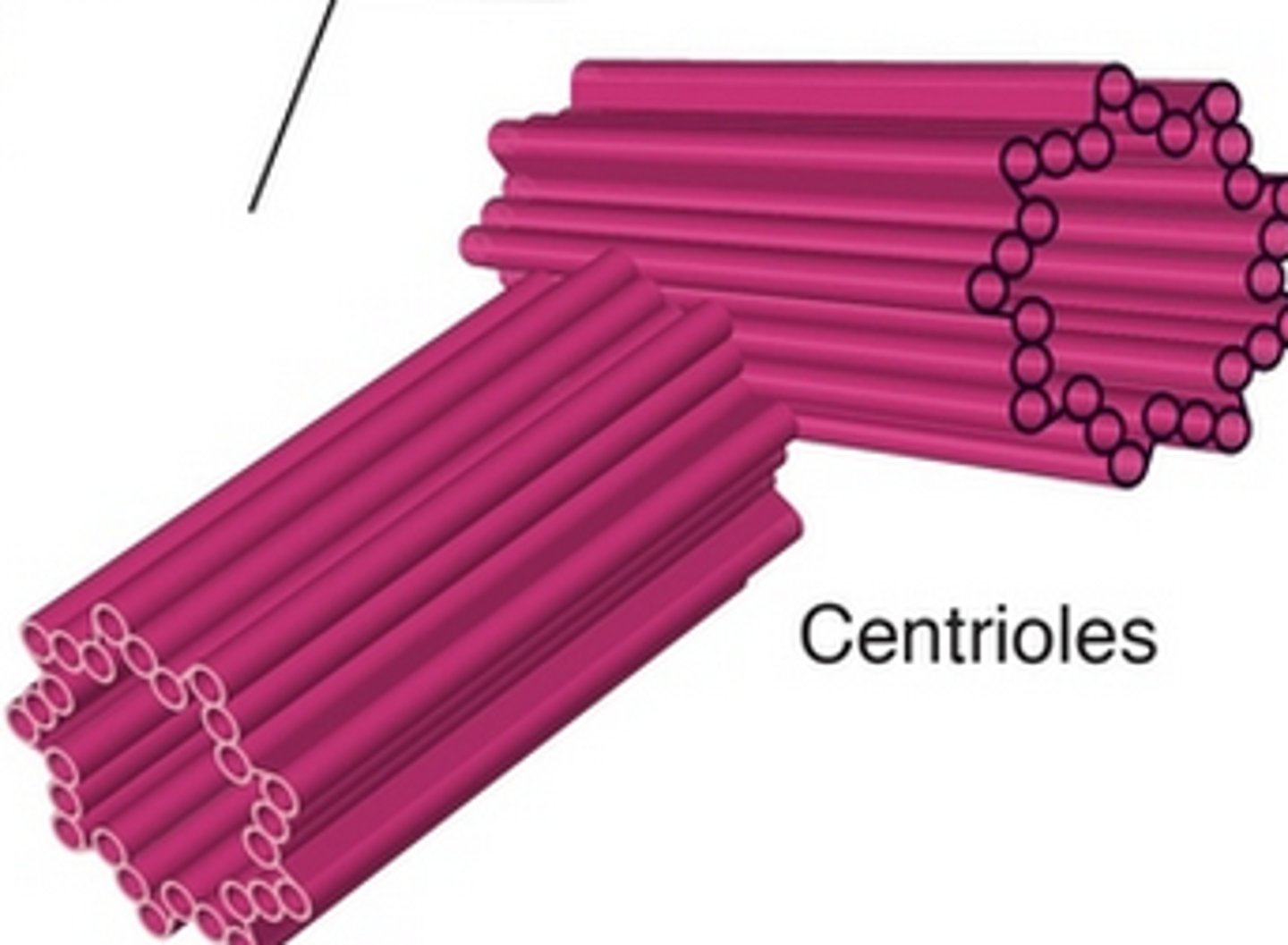
Self-replicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules; found only in animal cells; appear to help in organizing cell division.
a. intermediate filament
b. microfilament
c. centriole
d. microtubule
c. centriole
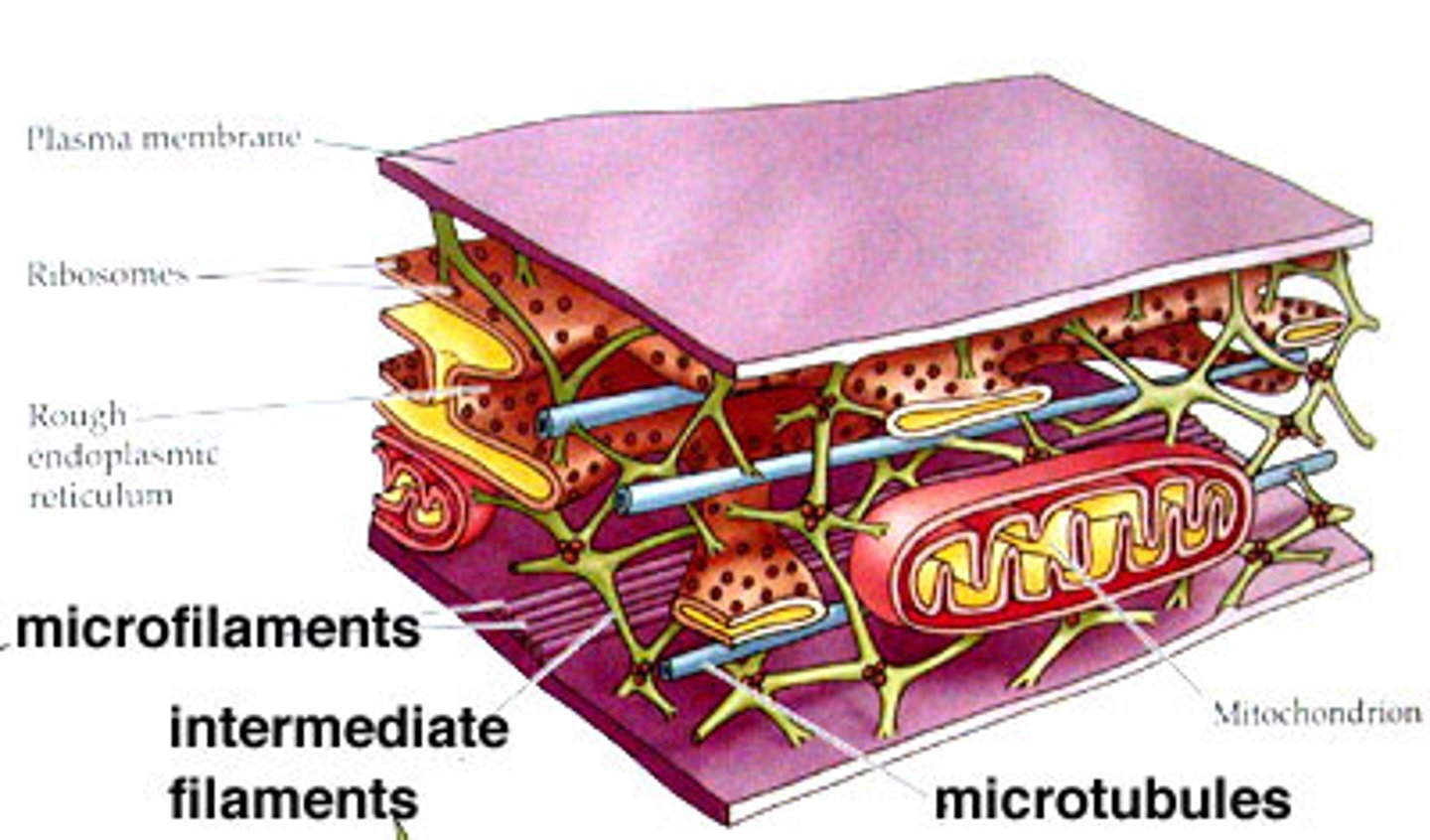
A class of fibrous proteins playing an important role as both structural and functional elements of the cytoskeleton; function as tension-bearing elements to help maintain cell shape and rigidity.
a. endosome
b. intermediate filament
c. centriole
d. microfilament
e. microtubule
b. intermediate filament
------------------------------
- intermediate filament = fibrous protein, tension bearing, structural
Think:
intermediate filament = I F
fibrous = F I
- microfilament = globular proteins, actin, structural
- microtubule = Straight, hollow cylinders, all eukaryotic cells
Think: tube = hallow cylinder
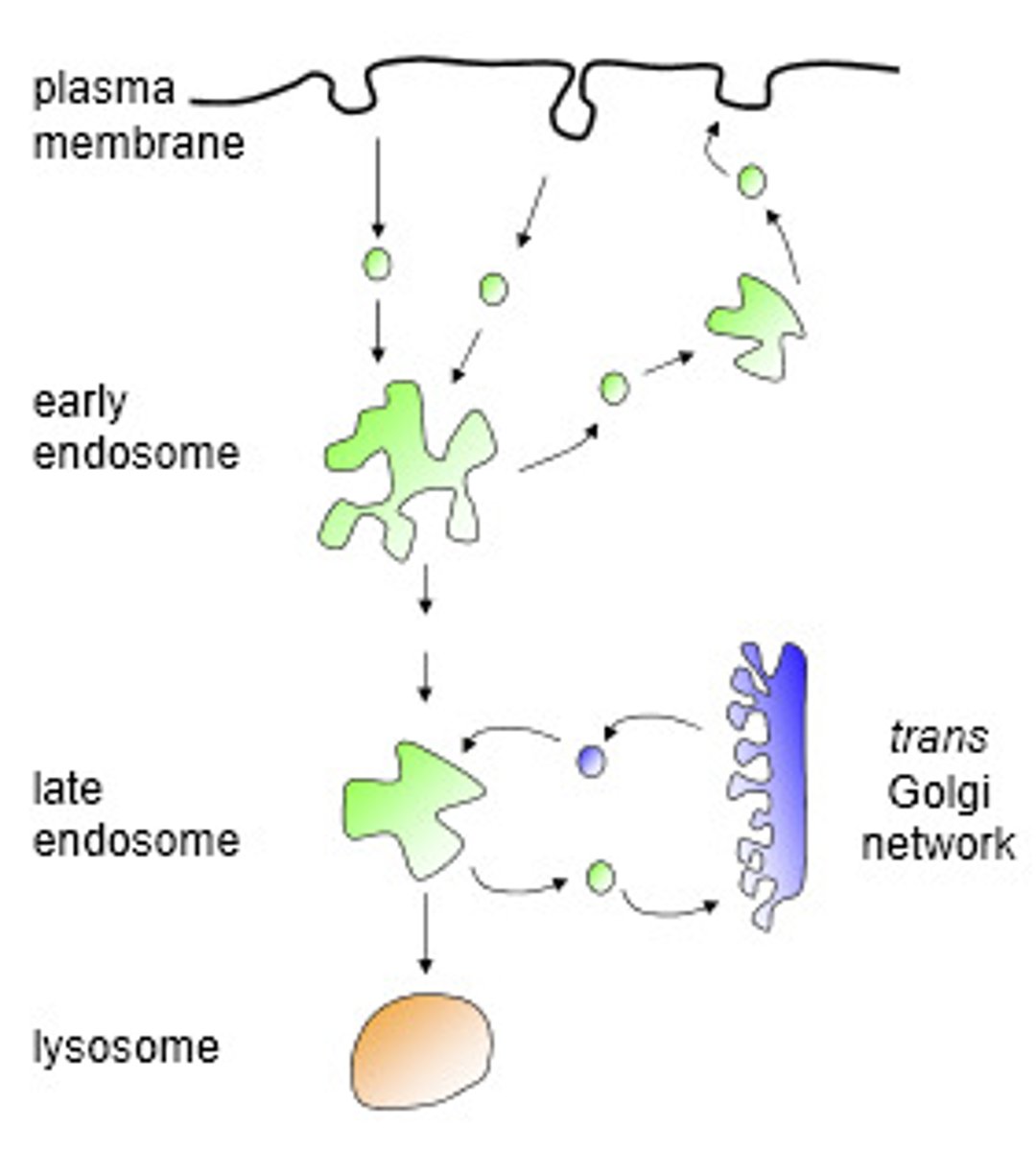
Membrane-bound vesicles, formed via a complex family of processes collectively known as endocytosis
a. endosome
b. peroxisome
c. desmosome
d. ribosome
e. lysosome
a. endosome
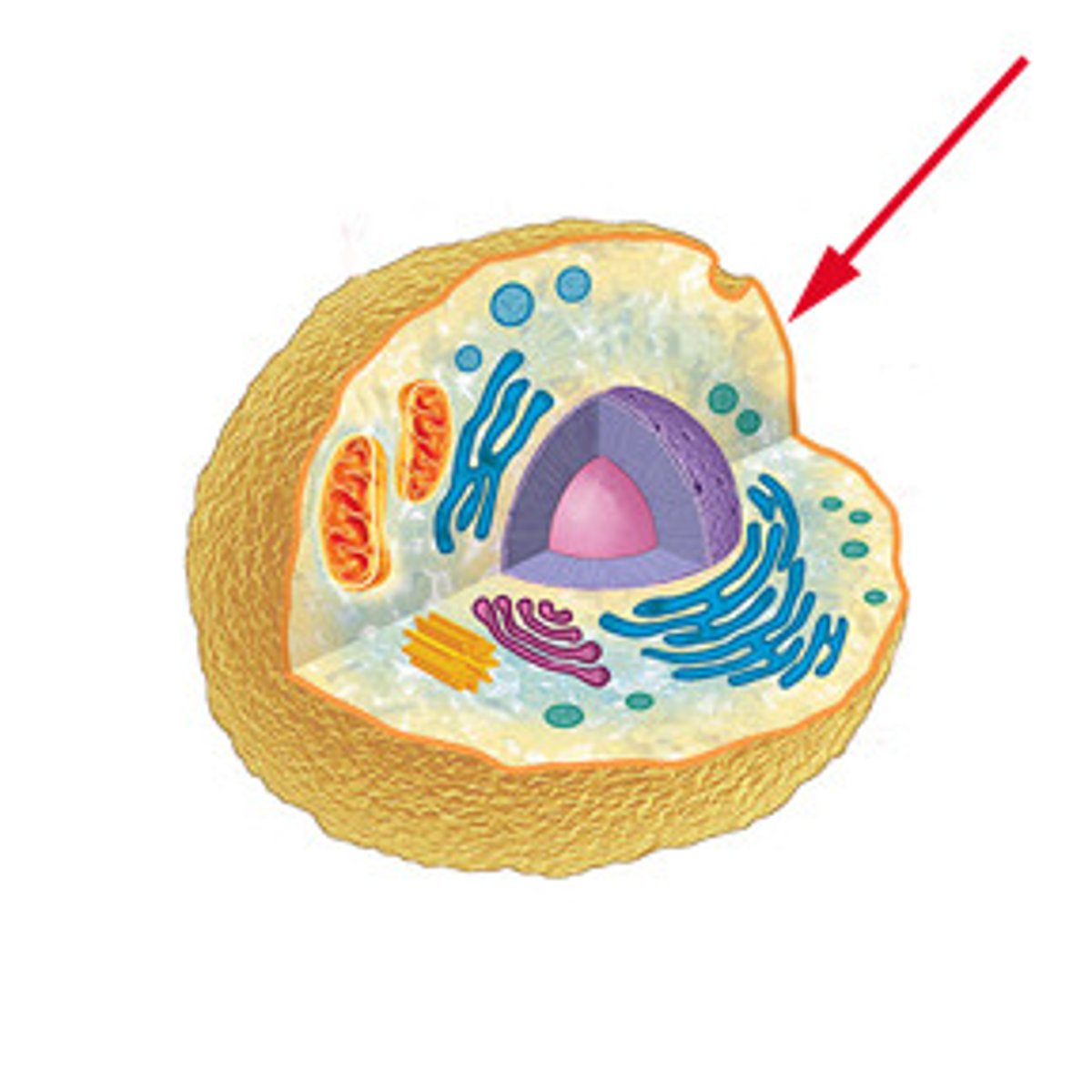
Encloses cellular contents; regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cell
a. cytoplasm
b. cytosol
c. Golgi apparatus
d. peroxisome
e. plasma membrane
e. plasma membrane
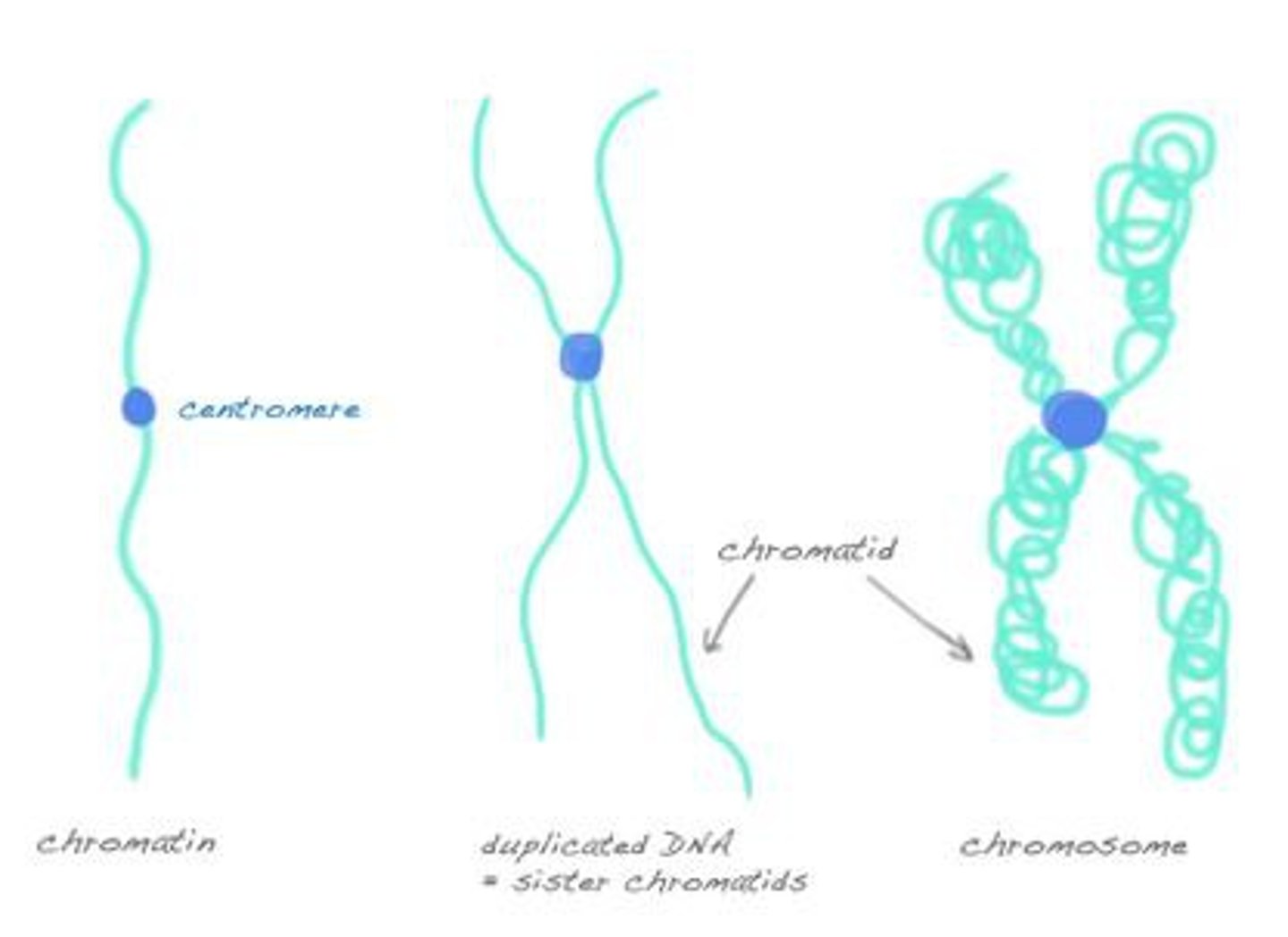
The material of which the chromosomes are composed; consists of protein, RNA, and DNA
a. mitochondrion
b. cytosol
c. microtubule
d. chromatin
e. centriole
d. chromatin
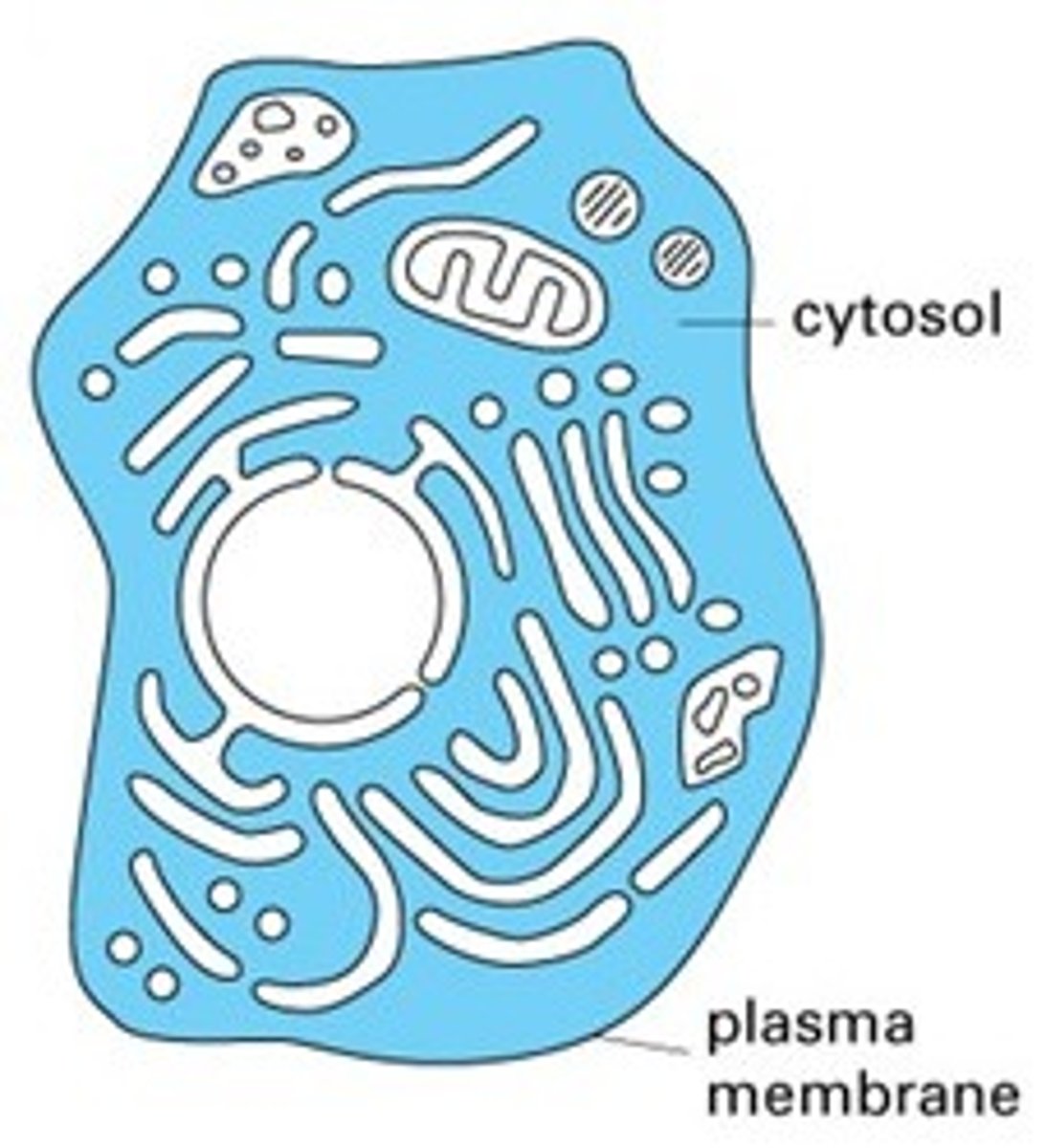
Jelly-like fluid that surrounds the organelles
a. cytosol
b. lysosome
c. desmosome
d. peroxisome
e. cytoplasm
a. cytosol
A small dense structure in the nucleus of a cell during interphase; produces and assembles ribosomes
a. chromatin
b. nucleolus
c. nucleus
d. mitochondrion
e. centriole
b. nucleolus
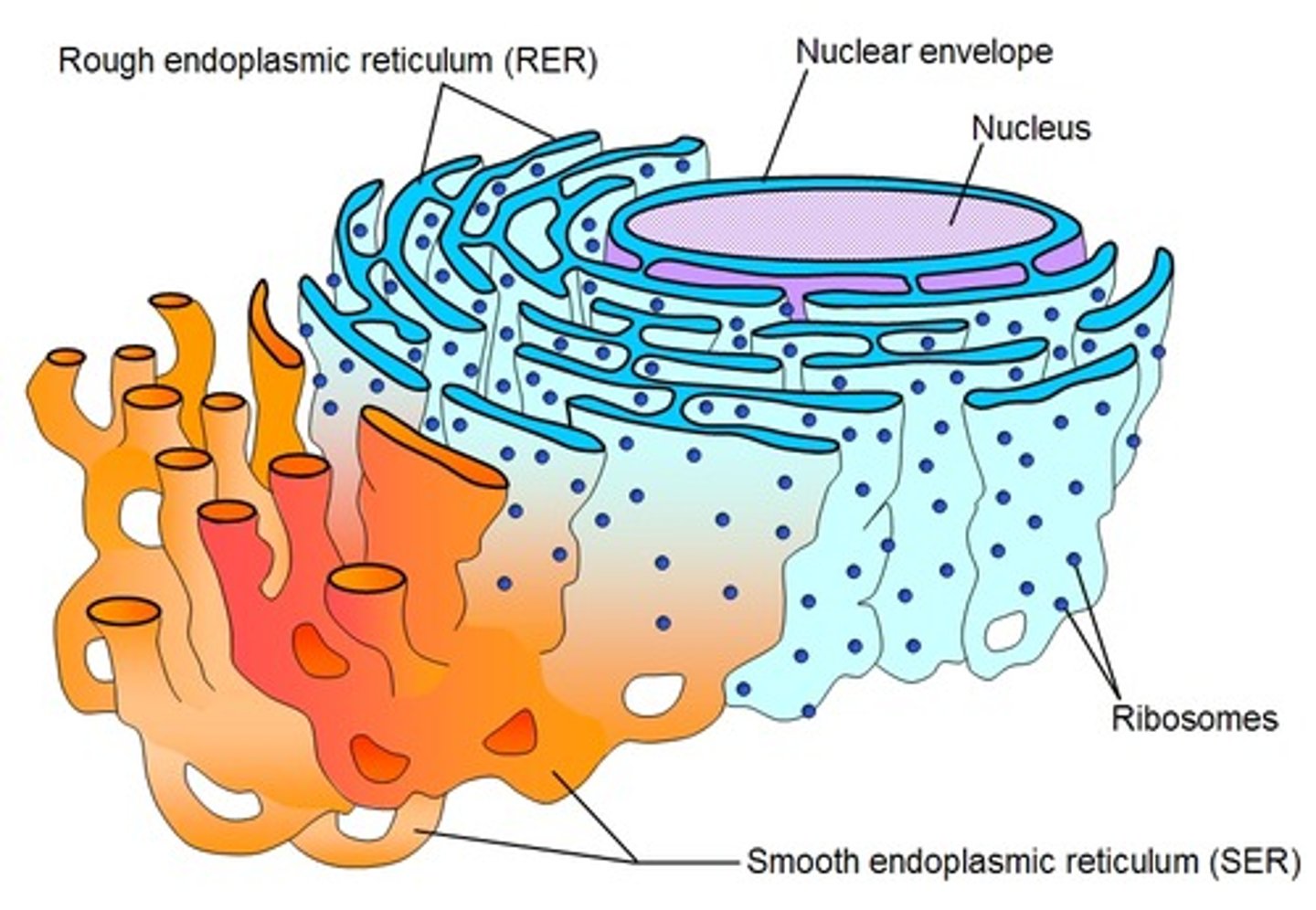
Tubular structure associated with lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, regulation of calcium concentration, and drug detoxification
a. ribosome
b. peroxisome
c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
d. endosome
e. lysosome
c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum
A network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell; connected to the nuclear envelope, providing a pipeline between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
a. lysosome
b. desmosome
c. mitochondrion
d. rough endoplasmic reticulum
e. Golgi apparatus
d. rough endoplasmic reticulum
Labeling, sorting, and packaging proteins and fats synthesized in the er preparing them for export to the outside of the cell.
a. cytosol
b. golgi apparatus
c. endosome
d. peroxisome
e. rough endoplasmic reticulum
b. golgi apparatus
Solid rods made of globular proteins called actin having primarily structural in function and are an important component of the cytoskeleton.
a. centriole
b. microtubule
c. desmosome
d. intermediate filament
e. microfilament
e. microfilament
--------------------
- intermediate filament = fibrous protein, tension bearing, structural
- microfilament = globular proteins, actin, structural
- microtubule = Straight, hollow cylinders, all eukaryotic cells
Carries out oxidative reactions using molecular oxygen; generate hydrogen peroxide, and destroy excess peroxide by means of the catalase; have an important role in the synthesis of specialized phospholipids.
a. centriole
b. peroxisome
c. lysosome
d. desmosome
e. mitochondrion
b. peroxisome
Comprised of small and large subunits, these organelles function in protein synthesis, translating mRNA
a. Endosome
b. Peroxisome
c. Ribosome
d. Desmosome
e. Lysosome
c. Ribosome
Straight, hollow cylinders found throughout the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells and function as structural support and in movement of organelles.
a. centrioles
b. desmosomes
c. intermediate filaments
d. microtubules
e. microfilaments
d. microtubules
------------------------
- intermediate filament = fibrous protein, tension bearing, structural
- microfilament = globular proteins, actin, structural
- microtubule = Straight, hollow cylinders, all eukaryotic cells
A structure by which two adjacent cells are attached, formed from protein plaques in the cell membranes linked by filaments.
a. Intermediate Filament
b. Microfilament
c. Desmosome
d. Centriole
e. Microtubule
c. Desmosome
Oblong shaped organelles found in the cytoplasm functioning in cellular respiration and in generating ATP.
a. Chromatin
b. Peroxisome
c. Centriole
d. Ribosome
e. Mitochondrion
e. Mitochondrion