AP psych test: Intro to psychology, research methods, developmental psych
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
The mental processes like thinking, perception, memory, language, problem-solving skills (this theory is opposite to behaviorism)
Cognitive psychology
Studies human and animal characteristics and their adaptive values to survive, how ancient humans ad natural selection influence biology (Darwin)
evolutionary psychology
divides the population into groups according to some characteristic that is important to study, then sampling from each group
stratified samples
Refers to your heredity and biological makeup
Nature
Refers to your environmental experiences, upbringing and culture
Nurture
The scientific study of only observable behavior
behaviorism
Studies how our thoughts and behaviors are influenced by our culture, race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomic status etc. (Most 20th century studies focus on upper-middle class white men in Western Culture)
Sociocultural psychology
Employed by businesses and government to deal with workplace issues; develop methods to boost production while avoiding burnout, improve working conditions, staff morale, train employees, and resolve colleague disputes
Industrial/organizational psychology
Neither the researcher nor the participant knows who took the drug or placebo. 3rd party may be present
double-blind study
An infant's understanding of objects depends on their present sensations (when a toy is hidden, it ceases to exist)
object permanence
A given quantity doesn't change when appearance does (Nickles in a row vs spread out)
Conservation
Difficulty perceiving things from another's pov. _________ ___ ______ is the opposite!
Egocentrism, Theory of mind
Children can now solve abstract problems, understand and enjoy hypothetical situations, use deductive reasoning, and inferential thinking (11 y/o and on)
Piaget's formal operational stage of development
What are primary sex characteristics
reproductive organs
Teens have explored identity issues and have freely made their own choices about them
Identity achievement
gender roles are learned through reinforcement, punishment, and modeling.
social learning theory of gender
Destroys memory and mental functioning due to brain deterioration
Alzheimers
A researcher uses debriefing when he
a-uses deception in a study.
b-explains the purpose of a study beforehand.
c-has a study approved by the APA.
d-explains the purpose of a study after the study is complete.
d
Which of the following research approaches would be best for testing the hypothesis that the presence of certain odors causes people to gamble more?*
experimental
3 multiple choice options
median is the most ________ of the data
representative
Only ________ research shows causation
experimental
What do samples need to be in order to be able to generalize results
Representative of the population, stratified samples with no sampling bias
Observing subjects in a natural setting without interfering
Naturalistic observation
Intensive study of a specific person or small group. Usually from unusual cases and can't prove anything about the general population but may lead to hypothesis that will later be tested on larger groups.
Case study
Data is collected from the same subjects over many years to see how a factor changes due to age or time. Same group is studied at regular intervals to measure behavioral consistency.
longitudinal study
Data from people of different ages are compared to determine differences due to age. Can be done at the same time, are less time consuming/expensive, but not testing the same people
cross-sectional study
Data obtained from asking people fixed sets of questions. (can be anonymous or as an interview)
surveys
Specifically define how variables are measured, which makes it easier to replicate a study.
operational definition
What experiments change to observe its effects vs what changes in relation to that
independent vs dependent variable
Participants are exposed to the experimental treatment (independent variable)
Experimental group
Same as experimental group except no manipulation or experimental treatment is applied
Control group
How are Control and Experimental groups assigned
randomly and then random assignment to avoid bias and representative of population
Measures the relationship between 2 variables
Correlation
direct relationships=
positive correlation
inverse relationships=
negative correlation
Correlation does not mean
causation
A number showing the degree of relationship between 2 variables. It indicates the direction the correlation (pos or neg) and indicates its strength (scatterplot)
correlation coefficient
if the correlation coefficient is close to zero that means there is a
weak correlation
If the correlation coefficient is 1 to 1, that means the correlation is
perfect
Confidentiality, informed consent, participants being allowed to withdrawal, and a debrief after the study to explain purpose are all factors required in an
ethical study on humans
Variability measure that describes the average distance of every score from the mean
standard deviation
Most frequent score (peak of frequency distribution graph) , average, middle
mode, mean, median
What is the effect of positively skewed data
Positively=higher outlier drags the mean higher
Negatively= lower outlier drags the mean lower
In order to draw conclusions about your hypothesis, these interpret whether data results are statistically significant or due to chance
inferential statistics
Associated by excessive alcohol usage during pregnancy- causing heart defects and more to the baby
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Infant turning toward the source of touching on their cheek when hungry
rooting reflex
What do infants prefer looking at most
Faces
Fitting objects and experiences into one's schema (calling cat doggy if schema is 4-legged animals)
assimilation
Adusting existing schemas to explain new experiences (child can differentiate between cat and dog)
Accommodation
Babies understand the world through their senses and motor actions- looking, hearing touching, etc (ages birth-2years) object permanence will develop throughout this stage. Struggles with object permanence
Piaget's sensorimotor stage of cognitive development
Child uses words, images, and symbols to understand the world and engage in pretend play (2-7 y/o) Has object permanence and egocentric thinking but not conservation, Intuition instead of logic.
Piaget's Preoperational stage of cognitive development
Children use logical reasoning about concrete events but not abstract or hypothetical ideas (7-11 y/o) . Child now has conservation but no egocentric/animism.
Piaget's Concrete operational stage of cognitive development
Parent and teacher can teach a child by interacting with them at any age. Progresses cognitive development
Scaffolding
A bond between an infant and their caregivers
Temperament
What did Mary Ainsworth find in her strange situation study about secure attachment
Secure attachment children have a better temperament and tend to become more resilient and competent with higher self-esteem
Time frame after birth where certain abilities are most easily learned and make a deep impression. Tendency of certain newborn animals to form attachments during the above question
Critical period, imprinting
What did Harry Harlow find in his monkey studies
the "contact comfort" mattered more than the feeding
strict parents who expect obedience, do not explain decisions, and discipline a lot
authoritarian
Kids have the final say in this type of parenting style. Parents give in
Permissive
Children in this parenting style end up with better self esteem and they typically take part in the decisions that are made. Also, parents are warm but have boundaries and limits
Authoritative
Erikson's four stages of psychosocial development for children
1. trust vs mistrust- infants, can I trust other people to meet my needs
2. Autonomy vs shame and doubt- toddlers, can I do things by myself
3. initiative vs guilt- preschoolers, pushing boundaries
4. Industry vs inferiority- elementary, successful socially and academically
Stages of pre conventional morality
Concerned with avoiding punishment and mutual benefit
Stages of Conventional morality
Focus on interpersonal expectations and concerned with law and order
Stages of Postconventional morality
Concerned if a law is fair or just, and Concerned with personal ethical principles and the good of society as a whole
What is Erikson's 5th stage of psychosocial development (experienced during adolescence)
Identity vs Role Confusion- identity crisis
Teens have no clear sense of identity, do not give identity issues serious thought and do not make any decisions about them. Tends to be early adolescence
Identity diffusion
Teens make identity decisions based on the ideas of others, not from thinking about them personally
Identity foreclosure
Teens actively think about and explore identity issues but make no choices or commitments
Identity moratorium
Characterized by the refusal to eat and maintain weight, Characterized by binge eating followed by purging
anorexia nervosa, bulimia
The gender roles of men seem to be more dominant, competitive, and emotionally reserved while women tend to be...
submissive, cooperative, emotionally responsive
Production of sex hormones sharply reduces and women stop ovulation and menstruating
menopause
Accumulated knowledge, increases with age
crystallized intelligence
Ability to solve new or abstract problems and adapt to new situations. decreases with age
fluid intelligence
What are Erikson's last three stages of psychosocial development (during adulthood)
6. Intimacy vs. Isolation- young adult, married? stable job?
7. Generativity vs Stagnation- Middle adulthood, guide future generations
8. Integrity vs Despair-old age, look back on life
A graduate student studying cognitive psychology would be most interested in...
a-understanding mental processes such as memory and learning.
b-the ways in which physical or genetic factors influence and determine behavior.
c-the effects of the environment on behavior.
d-how people relate to each other and influence each other.
a
Which of the following illustrates how a researcher might examine the influence of nature on behavior?
a-Dr. Hayakawa examined the influence of parenting on eating choices in children.
b-Dr. Rojas examined the influence of genes on academic performance in teenagers.
c-Dr. Williams examined the influence of media exposure on occupational choice in college students.
d- Dr. Olofsson examined the influence of exercise on attention in middle schoolers.
b
Dr. Vaughn studies how population characteristics change over time based on how surviving members of a species pass their genes to future generations. Dr. Vaughn studies...
a-developmental psychology.
b-evolutionary psychology.
c-social psychology.
d-humanistic psychology.
b
Experimental research differs from correlational research in that experimental research
a-allows for prediction.
b-may reveal a causal relation.
c-defines the strength of the relation.
d-shows a direct or inverse relationship between variables.
b
A researcher wants to see whether a protein-enriched diet will enhance the maze-running performance of rats. One group of rats is fed the high-protein diet for the duration of the study; the other group continues to receive ordinary rat chow. In this experiment, the diet fed to the two groups of rats is what variable?
independent
Which correlation coefficients would indicate the strongest relationship between two variables?*
a- +0.58
b- +0.19
c- -0.97
d0 -0.05
c
June’s friends were at the mall, and someone suggested they do a little shoplifting just to see if they could get away with it. June wouldn’t participate and said stealing is wrong and against the law. What category of morality is June in, and why
Conventional Morality because June is concerned with law and order so she won't shoplift.
Scott thought about leaving school early and going to a baseball game. He stayed in school because he was afraid of getting caught. What category of morality is Scott in, and why?
preconventional Morality because Scott is concerned with avoiding punishment and won't skip school.
Mark lives with his mother in a poor section of the city. His mother is quite ill and needs outpatient services daily at a hospital home some miles away from their home. Mark steals a car to take his mother to the hospital. What category of morality is Mark in, and why?
Postconventional Morality because Mark is concerned with whether a law is fair or just and he believes in this situation, saving his mother is more important than breaking a law.
When asked what the saying “You can lead a horse to water but you can’t make it drink” means, Patrice said that it meant that you can provide someone with an opportunity, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that they will take advantage of it. What category of cognitive development is Patrice in, and why?
Formal operational because Patrice can not only solve abstract problems, but she can understand this hypothetical situation.
Twin brothers go “trick or treating” on Halloween. They went to the same houses and got exactly the same candy at each house. Yet, by the time the evening was over, Reggie was very upset. Because his bag was bigger than his brother’s, it didn’t seem to him that he had as much candy. What category of cognitive development is Reggie in, and why?
Preoperational because although Reggie has object permanence, remembering the amount of candy, but he is yet to understand that logically although the bags may be different sizes, they can have the same amount of candy in them.
While watching television with his dad, Bryce kept trying to grab the remote control. Finally, his dad hid the remote control behind his back. That didn’t seem to bother Bryce a bit, he just started reaching for the family cat. What category of cognitive development is Bryce in, and why?
Sensorimotor stage because Bryce doesn't have object permanence yet (when a toy is hidden, they will act like it doesn't exist).
When Duane headed out on his “big expedition,” he wasn’t that worried about getting lost. He knew that he would just have to go back the same way he had come. What category of cognitive development is Duane in, and why?
Concrete Operational because Duane is using logical reasoning but isn't thinking about the hypothetical idea that he could forget the way he came or something could change when he is seeing new places.
Alcohol is a teratogen that can slip through the ___________ and damage the fetus or embryo.
placenta
Your friend's baby brother, Matt, loves to play with his cat. When he sees a puppy, he points and calls it "Mi Mi", which is what he calls his cat. Matt is demonstrating Piaget's process of
assimilation
Which of the following would be considered a sign of secure attachment in a 1 year-old?
a- Showing no sign of stranger anxiety, whether the parent is present or not.
b- Not reacting to a parent leaving or returning after a brief separation.
c- Showing anger at the parent after a brief separation.
d- Becoming distressed when the parent leaves and seeking contact on return.
d
According to Erikson, what is the primary developmental task for adolescents?
a-trust vs. mistrust
b-initiative vs. guilt
c-identity vs. role confusion
d- intimacy vs. isolation
c
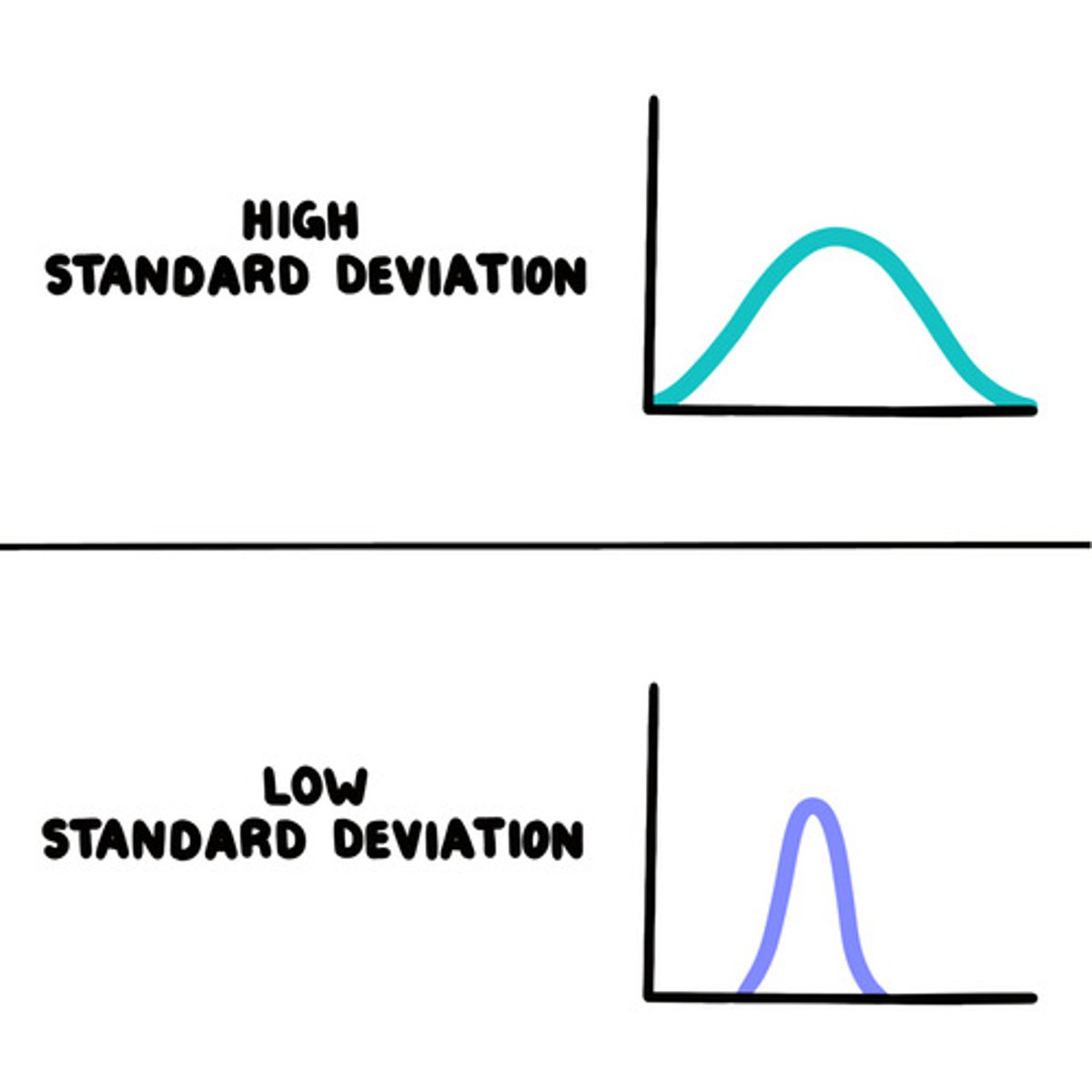
If your data is very spread out
large standard deviation
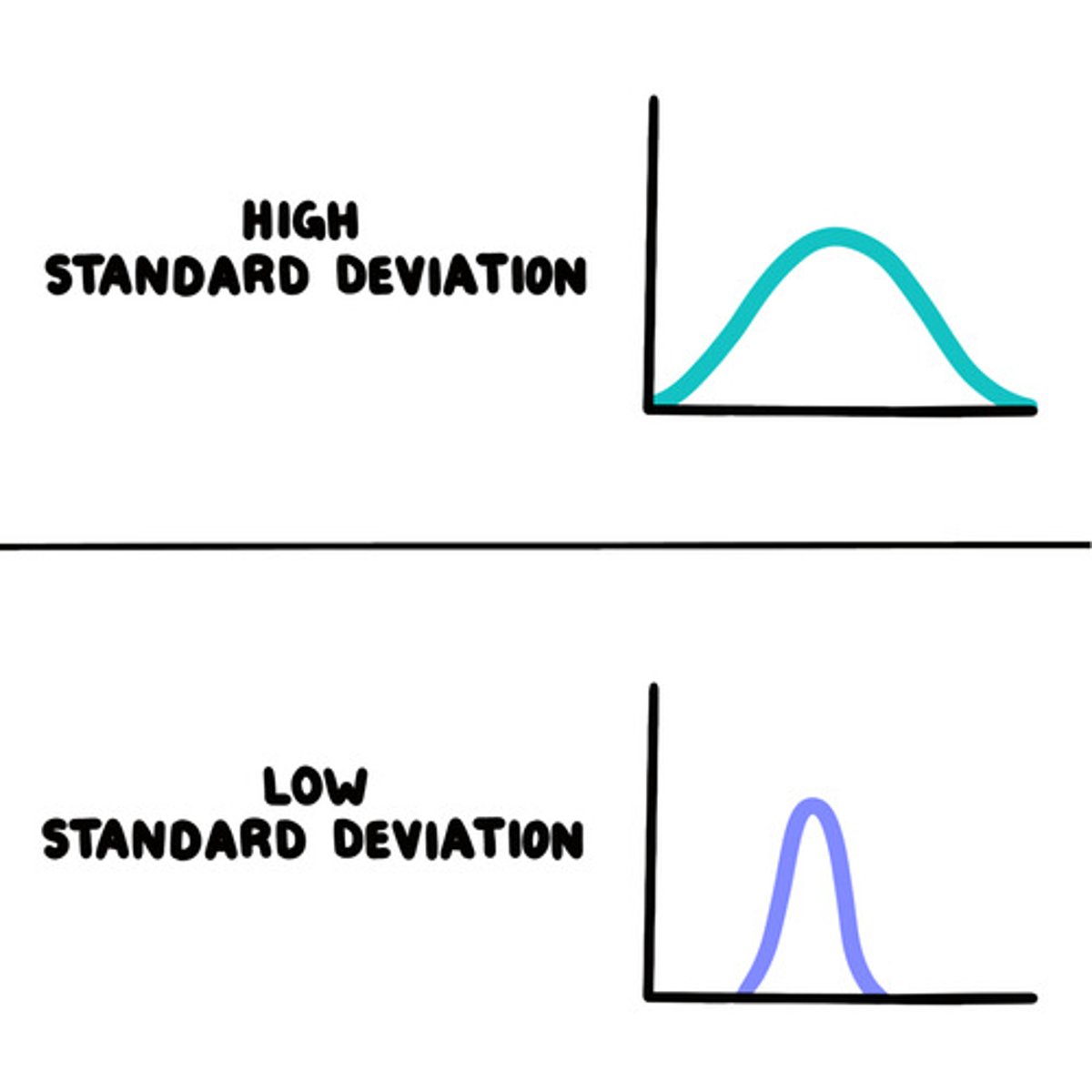
Data bunched together
small standard deviation
the typical age kids crawl and walk is referred to their
developmental norms
What gender theory says we learn gender roles from modeling, reinforcement, and punishment
social learning theory
3 multiple choice options
What is referred to when a high outlier drags the mean above the median
a positive skew
What determines variability in a set of data
standard deviation
What does an experimenter need to specify how the variables are measured
operational definition
Still learning (21)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!