Physiology Exam 2 - reflexes and Sensory Systems
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Monosynaptic reflex
has a single synapse between the afferent and efferent neurons
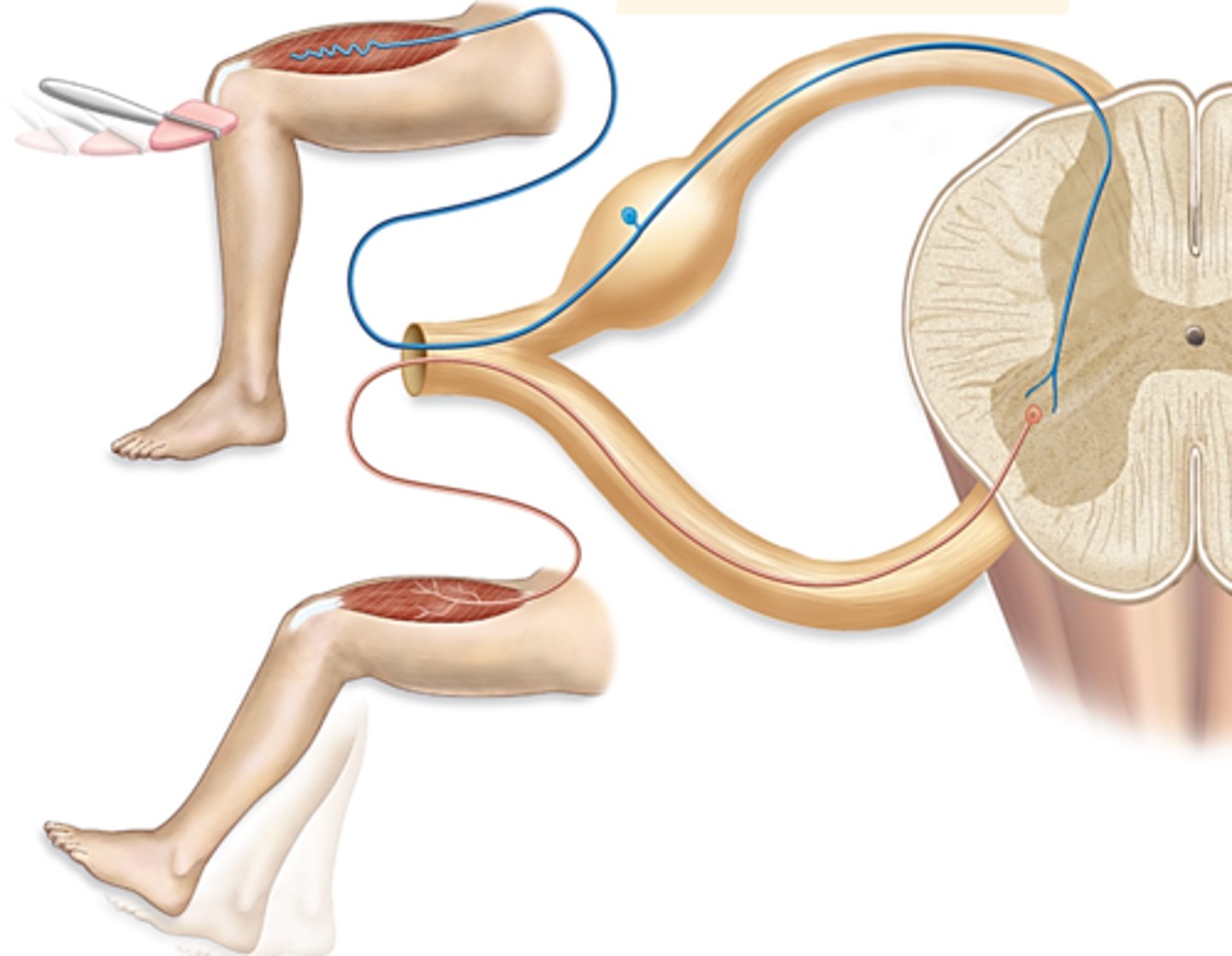
polysynaptic reflex
have 2 or more synapses (interneurons). This somatic motor reflect has both synapses in the CNS
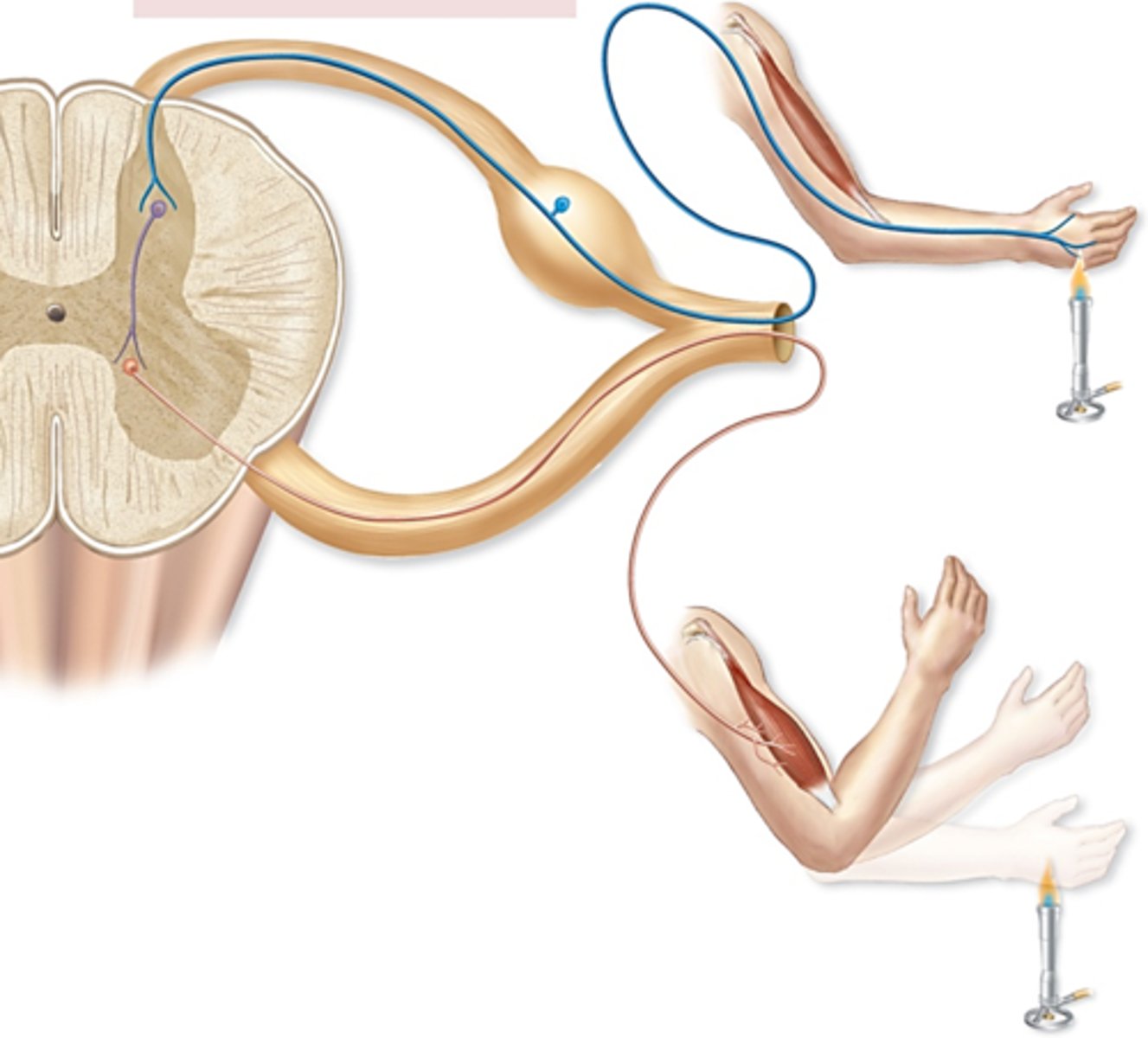
autonomic reflexes
- are polysynaptic
ex. cranial reflexes: regulation of heart rate, BP, breathing, eating, water balance, body temp, salivating, sneezing, vomiting, coughing etc.
ex. spinal reflexes: urination and defecation
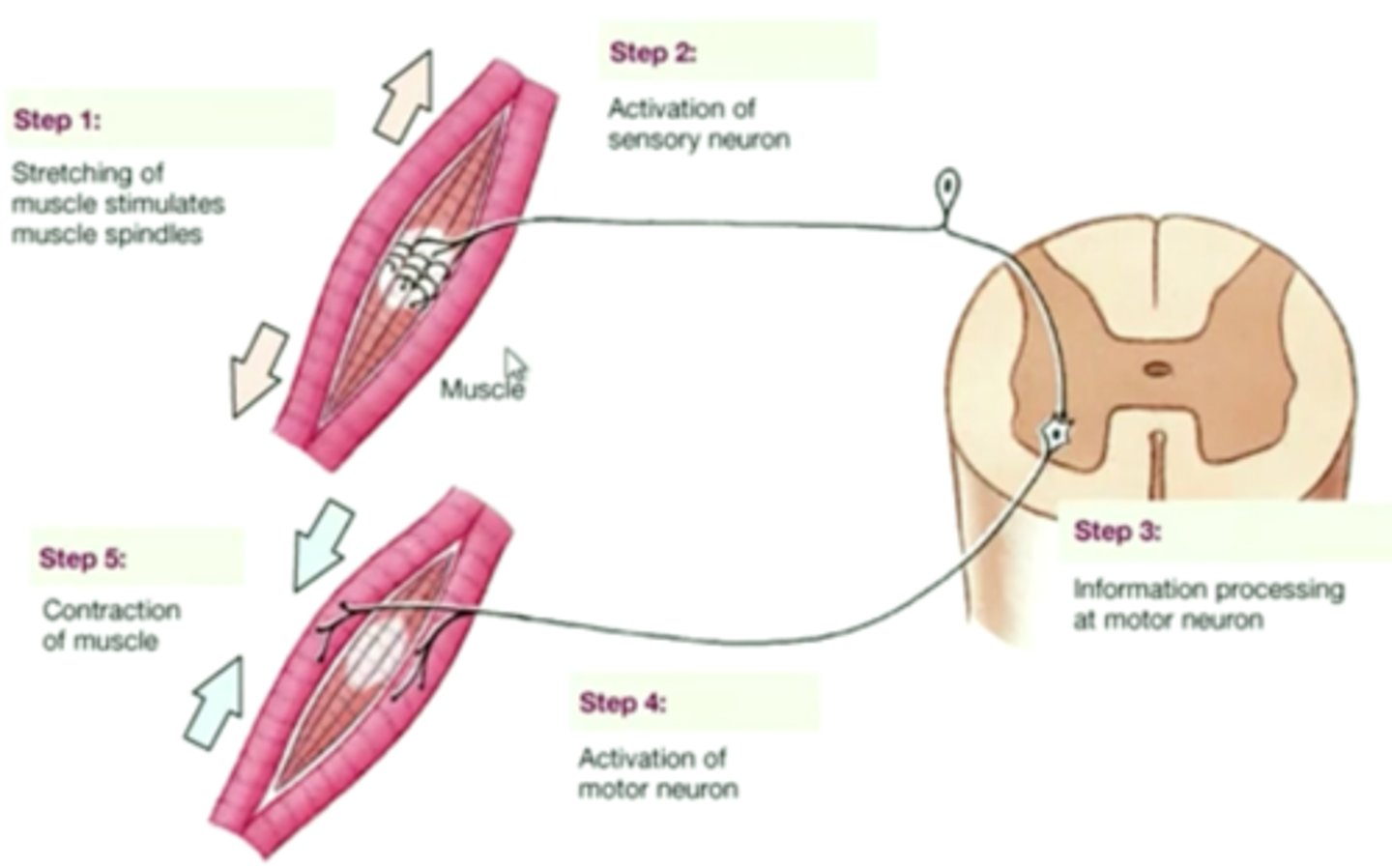
stretch reflex
the contraction of a muscle in response to stretch of that muscle
Muscle stretch and there is an increase in afferent signal to spinal cord ->increased efferent output through alpha motor neurons and the muscle contracts
ex. close your eyes and your mother hands you a super heavy bag of groceries your muscle will immediately adjust to hold the weight = stretch reflex
intrafusal muscle fibers
the ends contract and are innervated by gamma motor neurons
central region has no myofibrils and is surrounded by sensory nerve endings that stimulate by stretch.
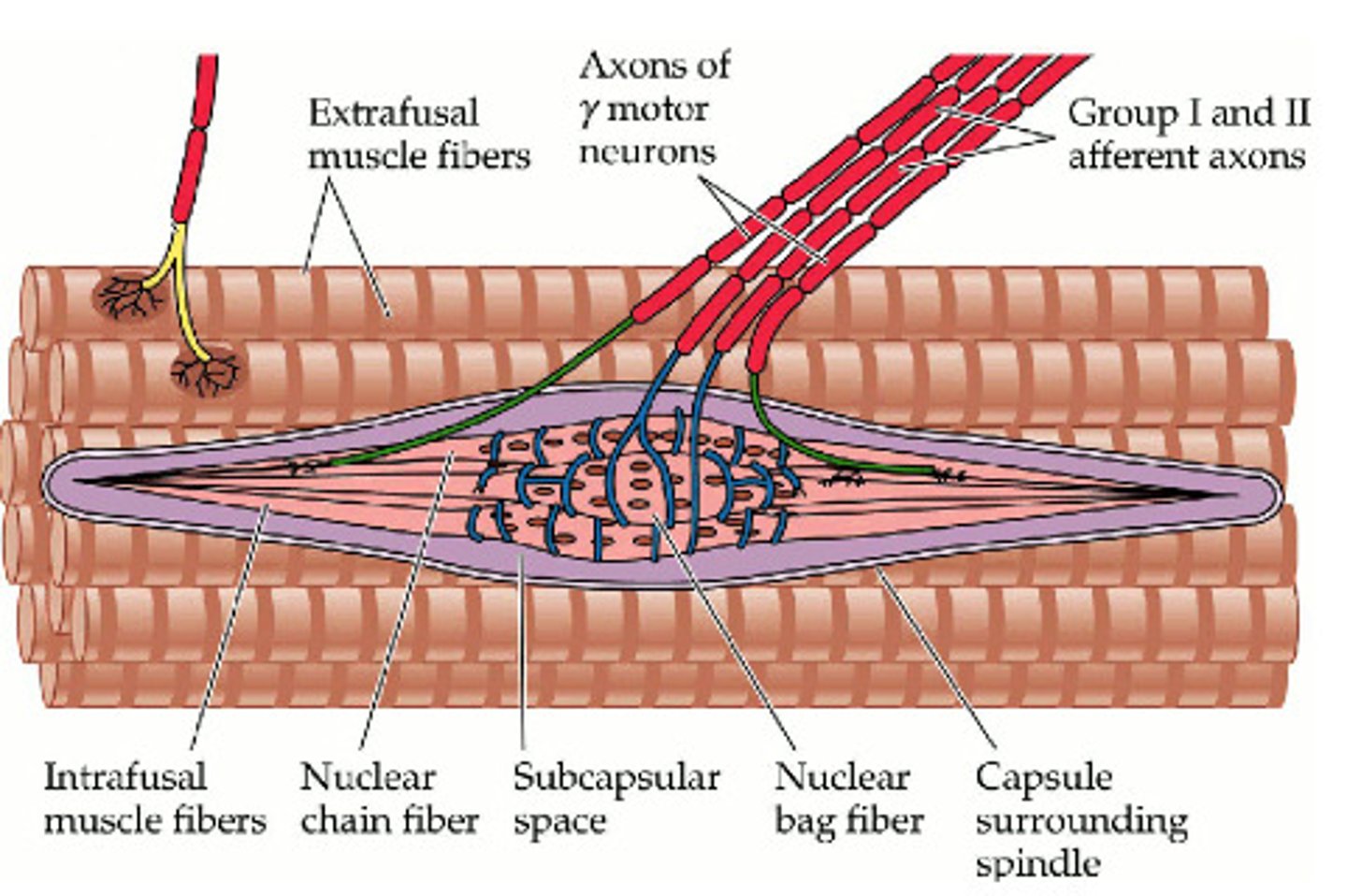
Proprioceptors
Types: muscle spindles, Golgi Tendon organs, joint receptors
these monitor limb position, movements, and exertion to give awareness of your body in space
alpha motor neurons
fancy word for the typical somatic neurons that carry APs to cause skeletal muscle to contract
extrafusal muscle fibers
typical muscle fiber
muscle spindle
a muscle receptor that lies parallel to extrafusal fibers (normal muscle fiber) and sends impulses to the central nervous system when the muscle is stretched
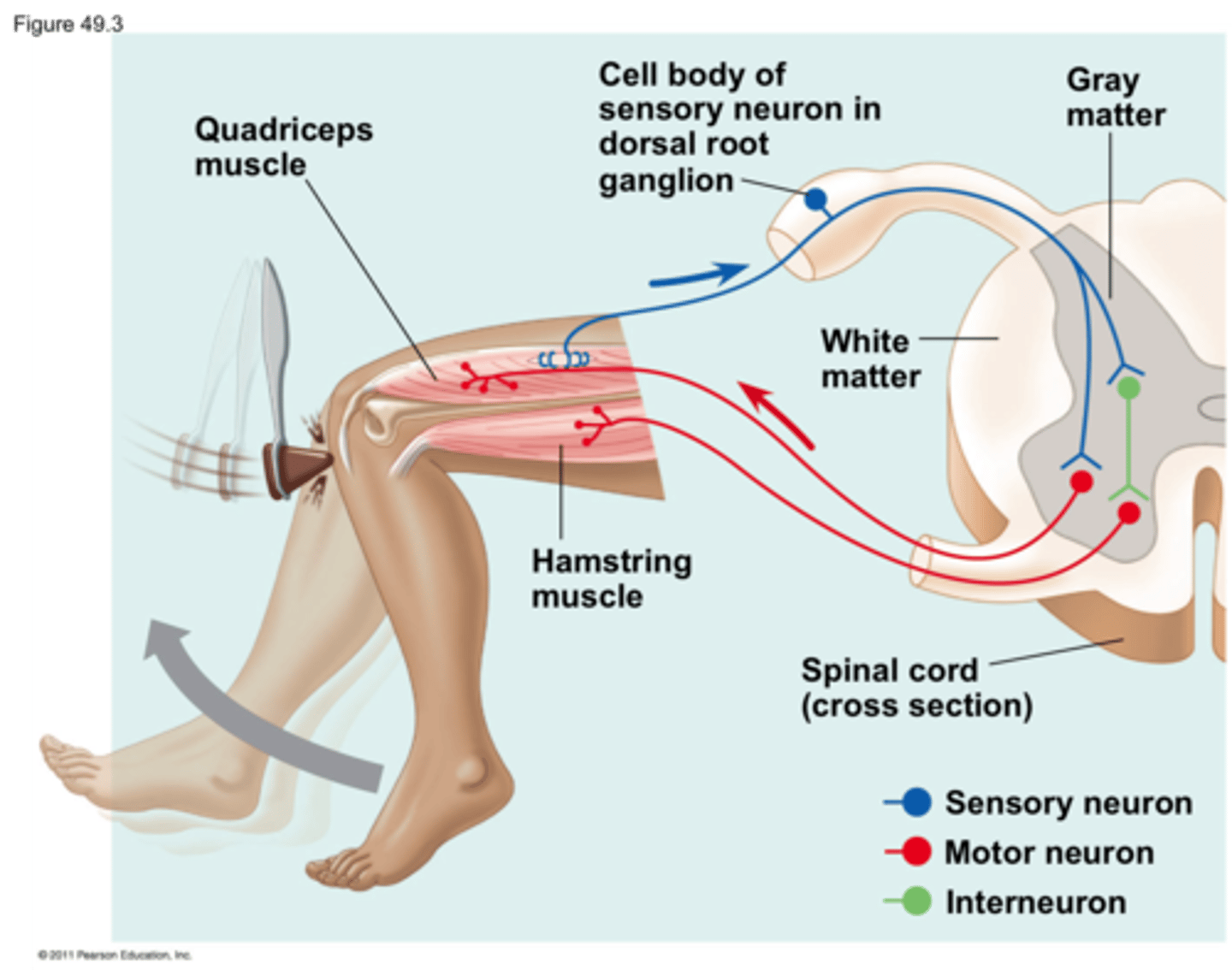
knee jerk reflex
utilizes a 2 neuron (sensory and motor neurons) - "monosynaptic" reflex arc.
stimulus: tap to tendon stretches muscle
Receptor: muscle spindle stretches and fires
Afferent path: AP travels through sensory neuron
Intergration center: Sensory neuron synapses in spinal cord
Efferent path 1: somatic motor neuron
effector 1: quadriceps muscle
response: quadriceps contracts
*reciprocal inhibition: efferent path 2: interneuron inhibiting somatic motor neuron to hamstring muscle, response= hamstring stays relaxed (allowing extension of leg)
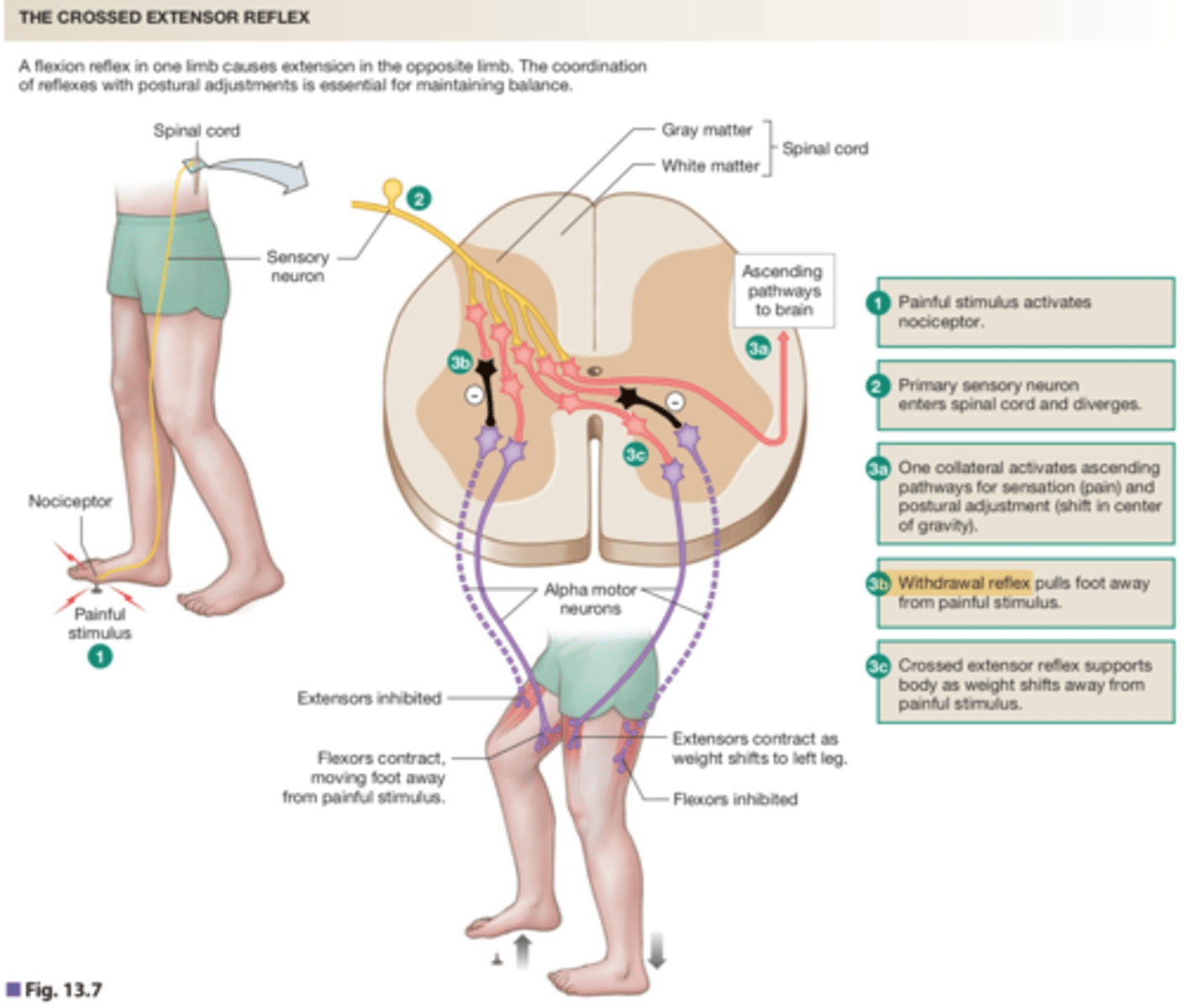
flexion/ crossed extensor reflex
stimulus: pain
receptor: activate nociceptor
Afferent path: AP travels to spinal cord and diverges
a. collateral activates ascending pathway for sensation, pain, and postural adjustments to the brain
b. withdrawal reflex pulls foot away from painful stimulus
c. crossed extensor reflex supports body as weight shifts away from painful stimulus (activate extensors, inhibit flexors)