2.07 Visual Fields
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Why do we do perimetry
To assess the health of the visual pathway
Check for glaucoma, tumors, strokes, brain injury
What are the 2 types of perimetry
Kinetic and static
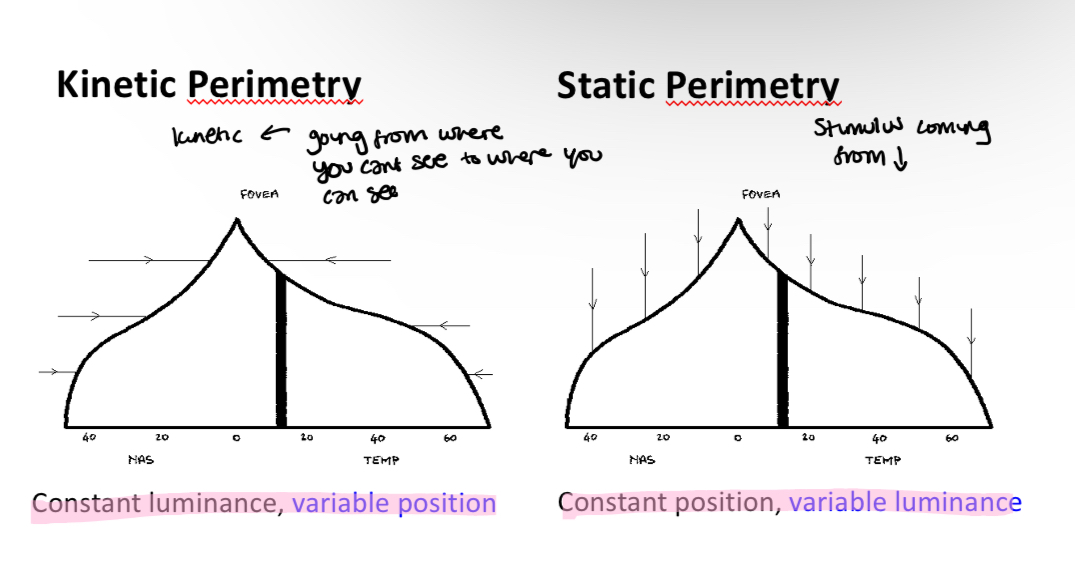
What are the 3 types of kinetic perimetry
Gross (arc) perimetry
Goldmann manual
Octopus semi automated
Classification of stimulus size and intensity
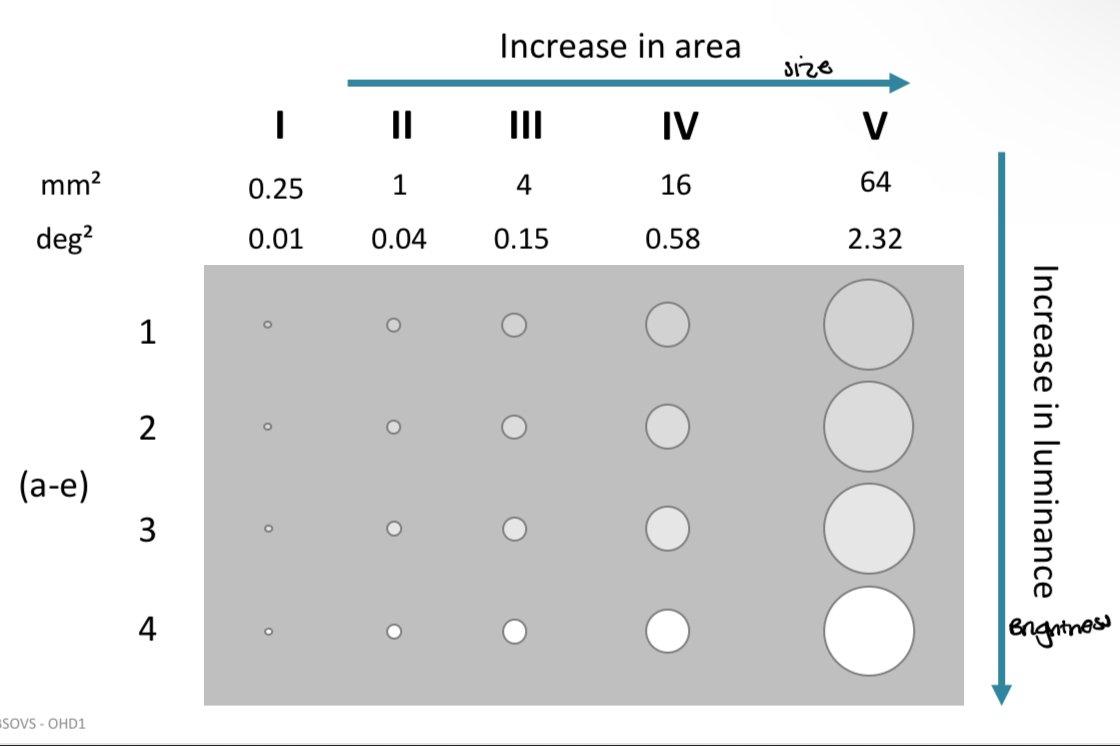
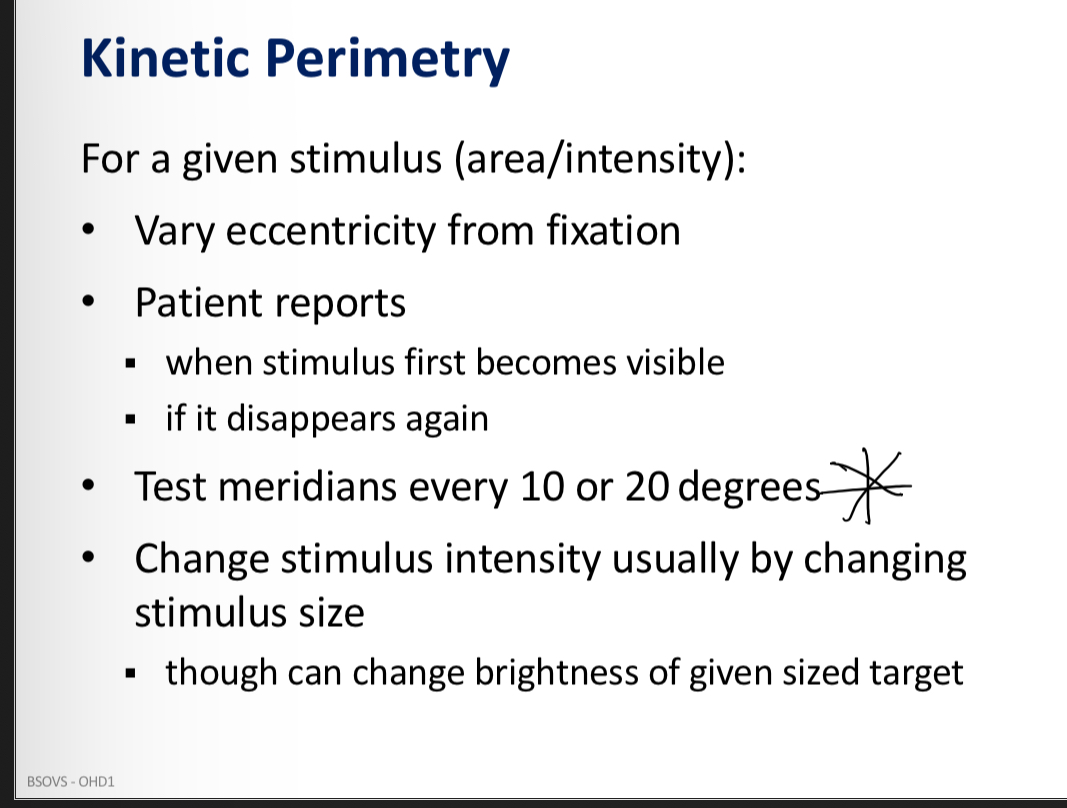
Kinetic perimetry general principles
Involves a moving target
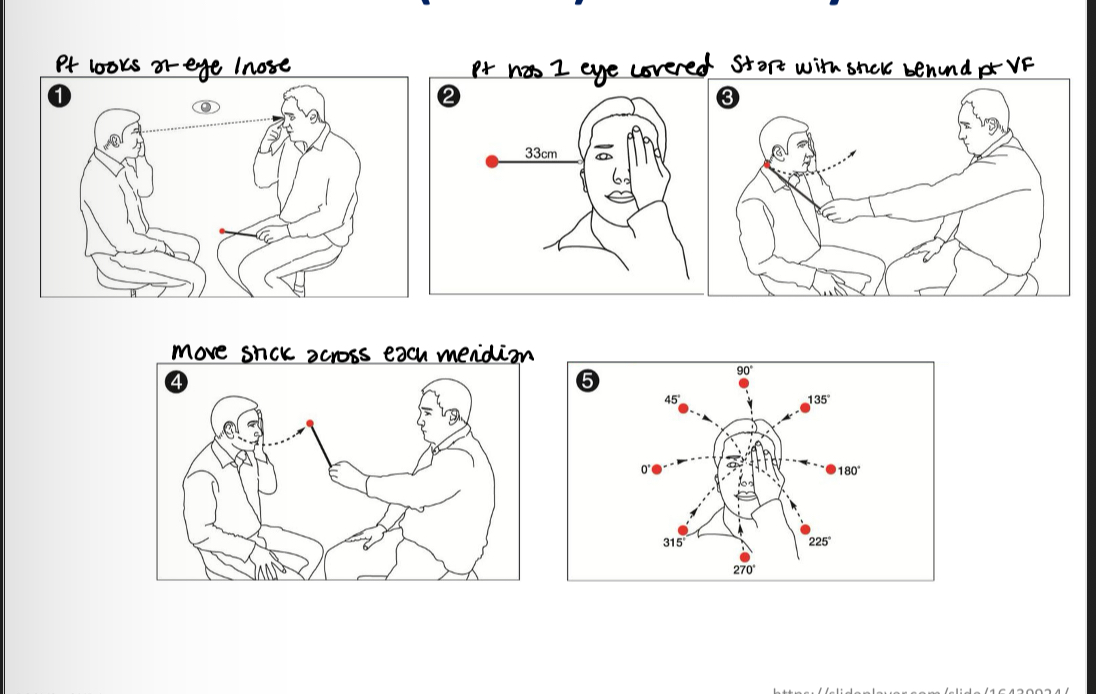
Gross perimetry procedure
A target is moved from an area of non seen to seen - patient reports when the targett first becomes visible and if the target diappears again
Goldmann manual perimetry
Patients eye is centered in the middle and praticitoner moves stimulus from the other side and marks where pt says they can see - maps the extent of the VF (isopter)
Can also be semi automated
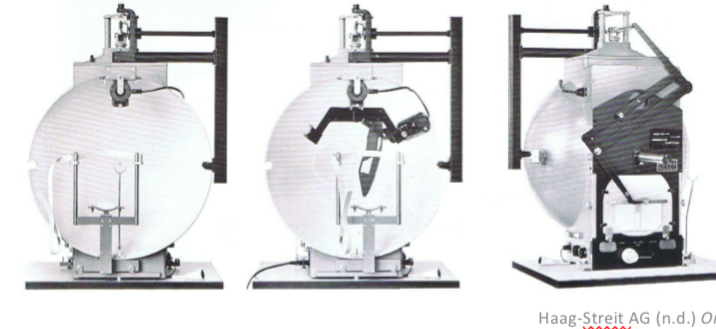
Octopus semi automated perimeter
Patient focuses on a central target and presses a button when they see the light move from non seeing to seeing areas of the visual field - maps the isopter
Light varies in size, brightness and location
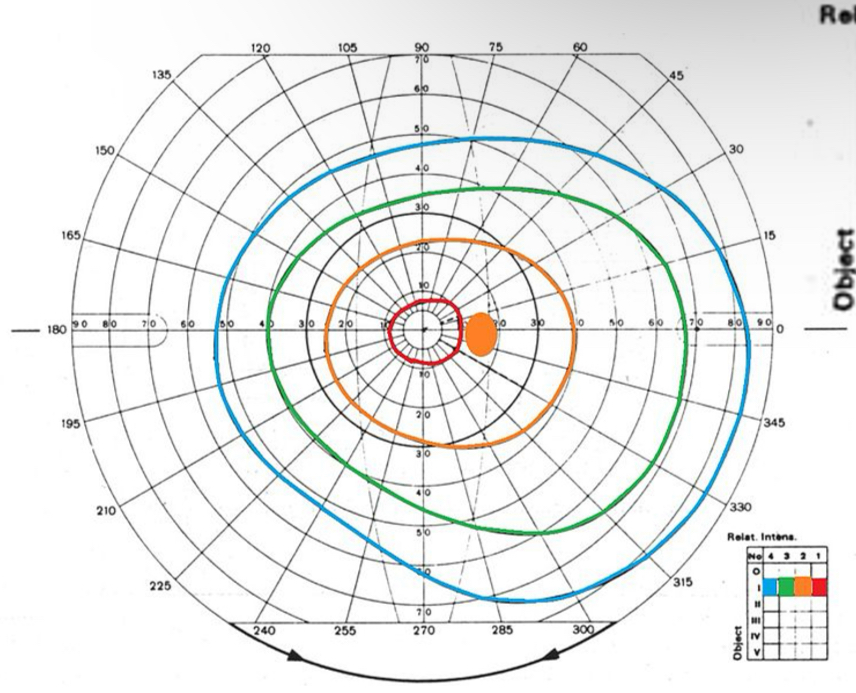
What is this VF plot called
Isopter
Used in kinetic perimetry - goldmann and octopus
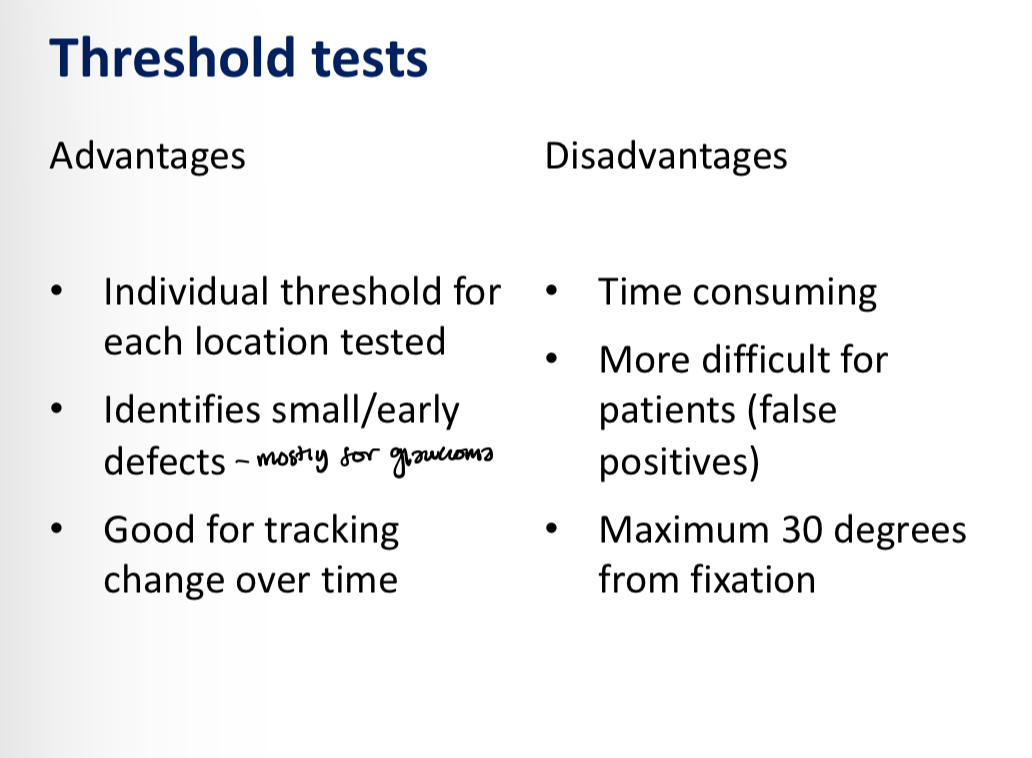
Kinetic perimetry advantages and disadvantages
Types of static perimetry
Amsler grid
Suprathreshold
Threshold
Amsler grid
Grid of lines
Pt looks at centre of grid from 30cms away
near correction worn (not bifocals or varifocals)
Pt reports if they see any distortion, fading of lines
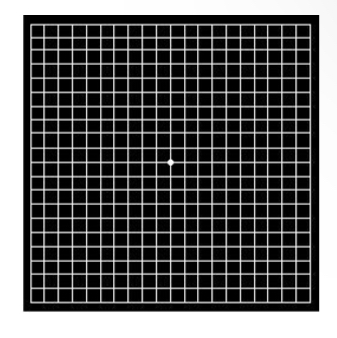
What disease can this amsler chart detect
Wet AMD
VF loss
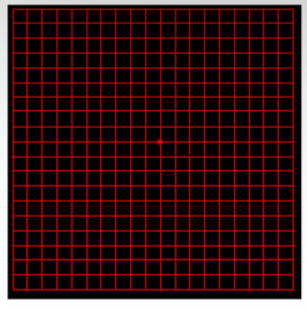
What disease can this amsler chart detect
Defects associated with toxicity (drugs)

What disease can this amsler chart detect
Detection of scotomas
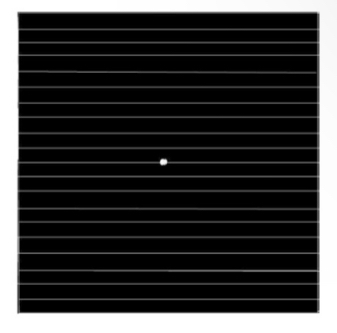
What disease can this amsler chart detect
Detection of metamorphopsia (distortion)
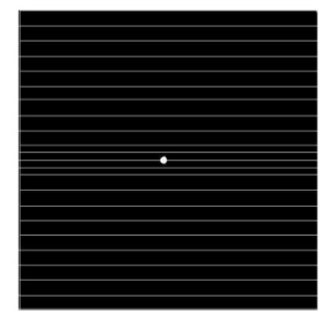
What disease can this amsler chart detect
Detection of more subtle distortion
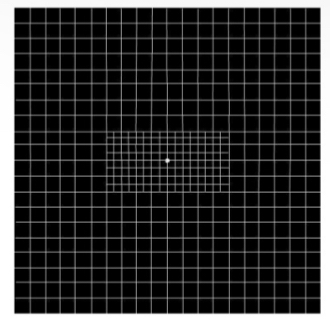
What disease can this amsler chart detect
More sensitive to subtle disturbances
Static perimetry general principles

Types of static perimeters
Humphrey field analyser (HFA 2)
Humphrey field analyser 3
Henson 7000
Henson 9000
Easyfield
Dicon TKS5000
Frequency doubling technology (FDT)
Octopus 900
What is a threshold
The intensity of a stimulus that is JUST visible
Stimuli brightee than the threshold are seen
Stimlus dimmer than the threshold is not seen
The threshold varies with position within the visual field (centre most sensitive)
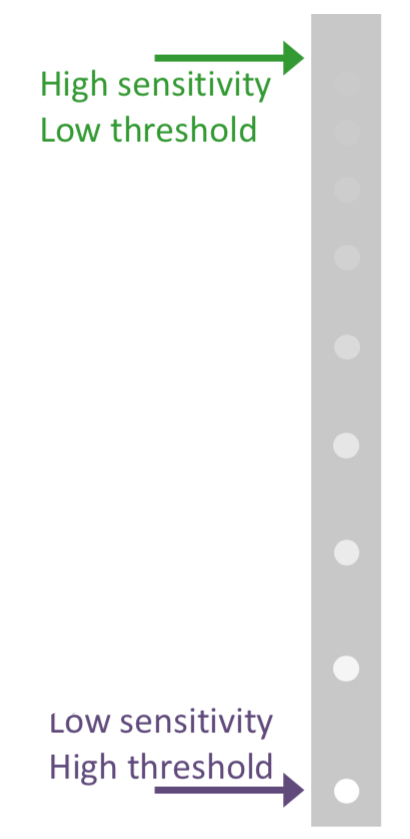
How to calculate sensitivity from threshold
1/threshold = sensitivity
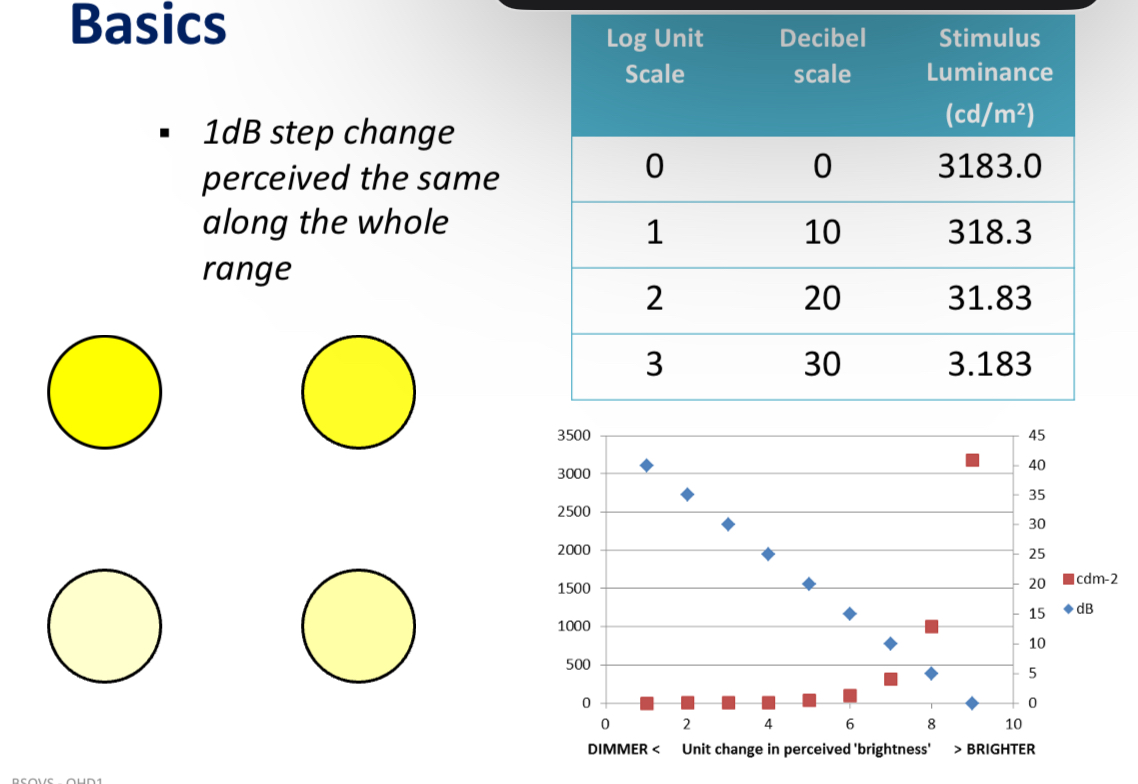
Static perimetry used a logarithmic scale because…
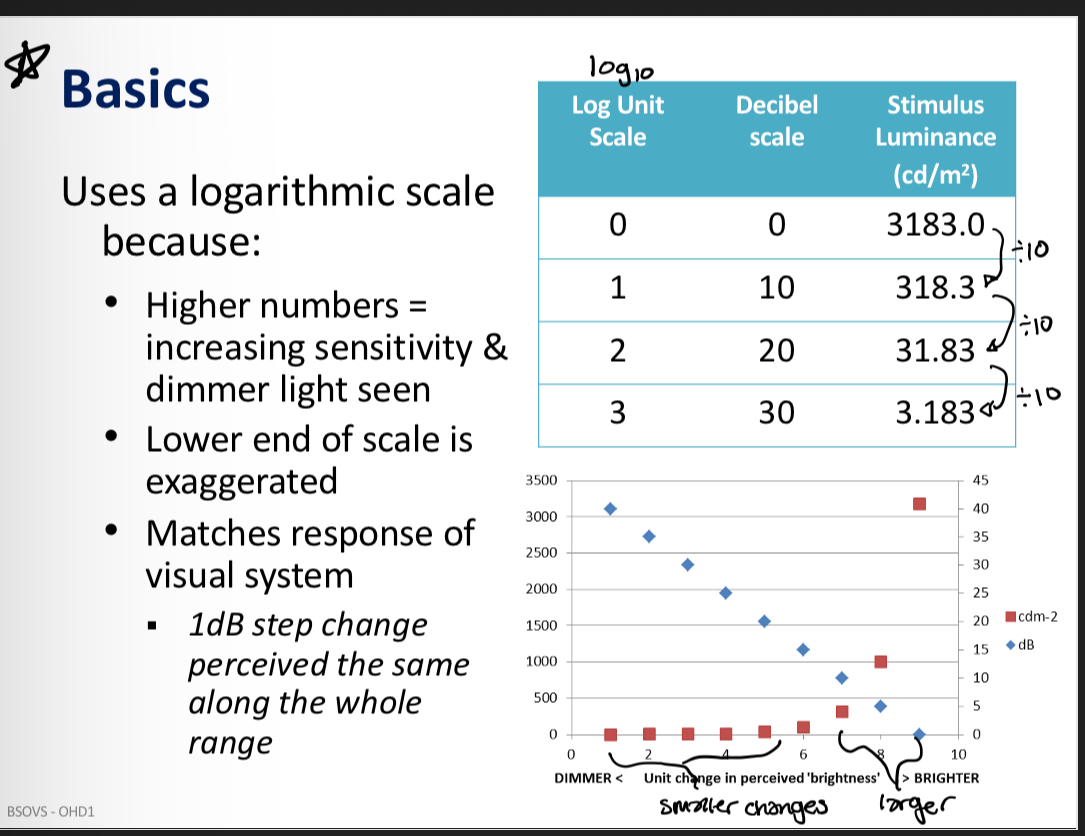
Static perimetry - decibel scale
1 dB step change is perceived the same along the whole range
dB scle is a relative scale - based on maximum luminance the instrument can generate
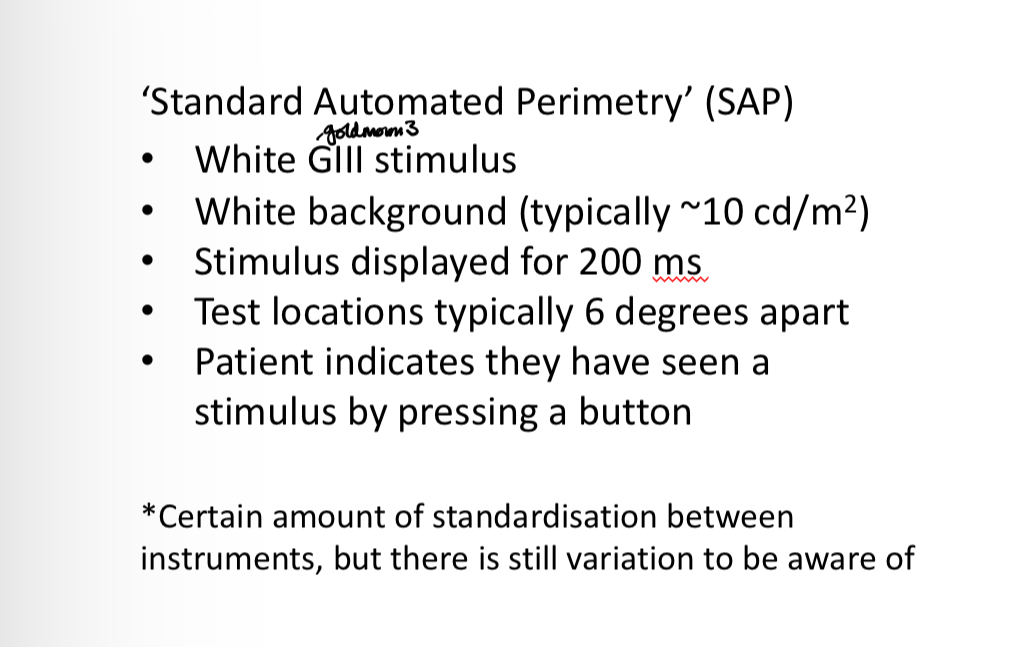
What size stimulus does static perimetry use and how long is it displayed for
Goldmann size 3
200ms
Size is fixed, brightness varies
Static perimetry procedure
Which diseases give tunnel vision/macular sparing
Glaucoma
Retinal detachment
Retinitis pigmentosa
Tumours
Diabetic retinopathy
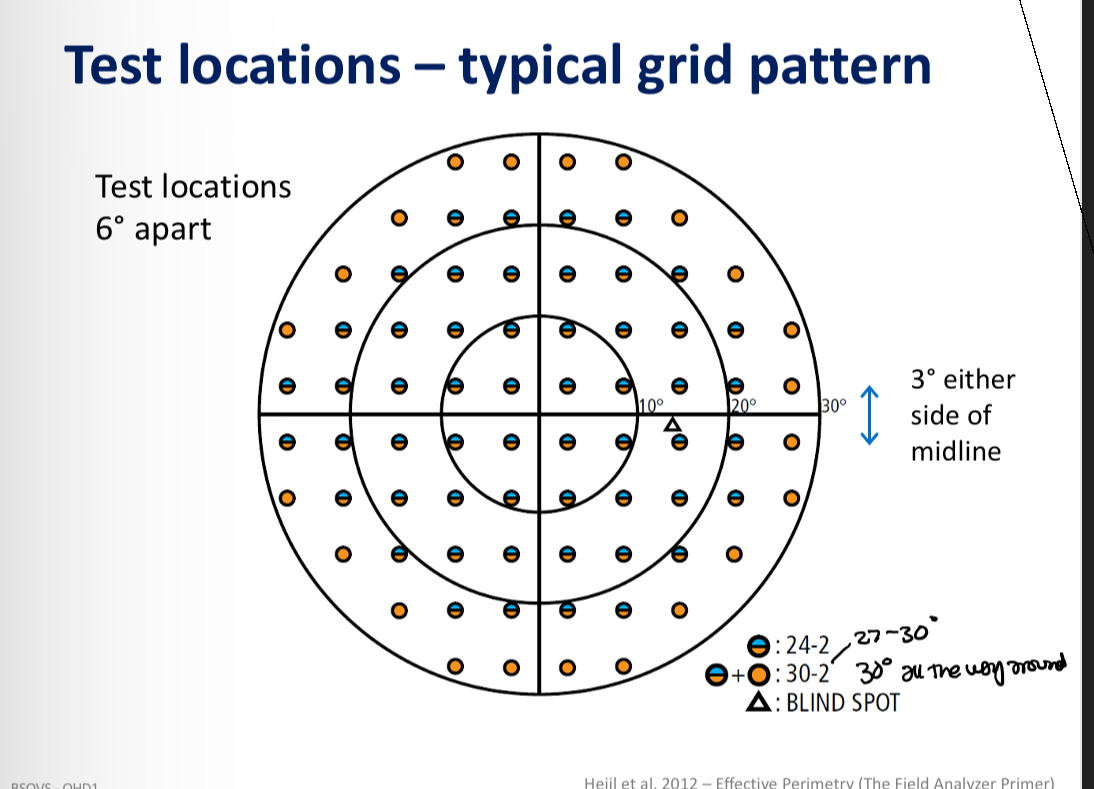
Central visual field testing
Test a maximum eccentricity of 25-30 degrees from fixation
Useful for testing VF of people with tunnel vision
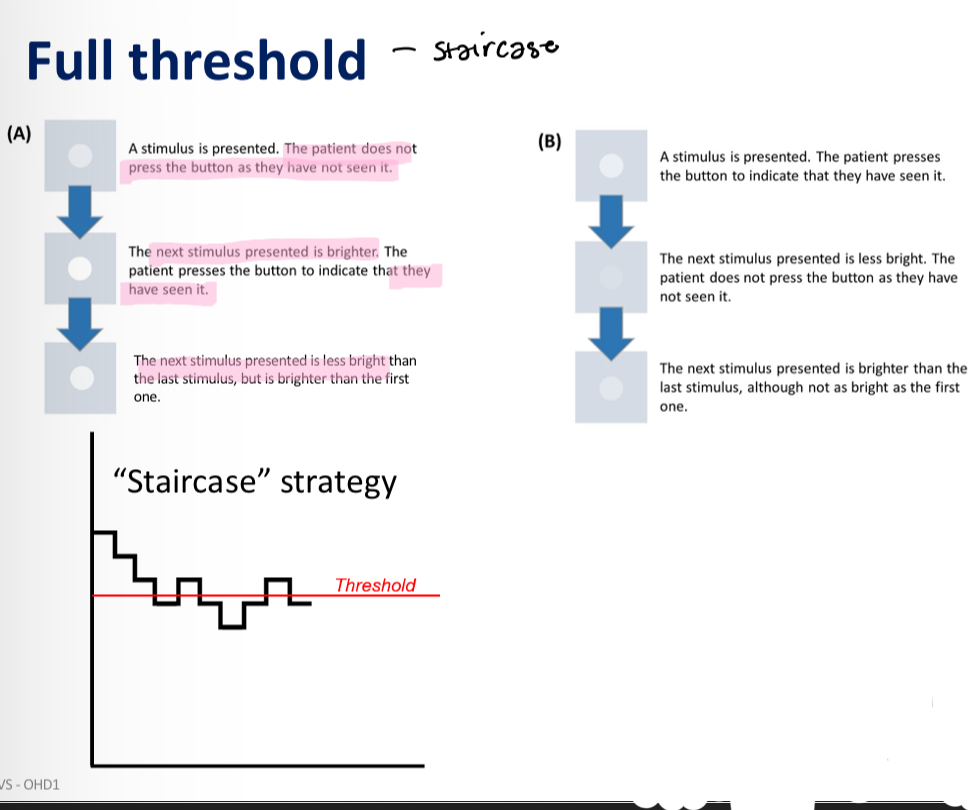
Full threshold staircase method
Which algorithms are threshold
SITA, ZEST, ZATA
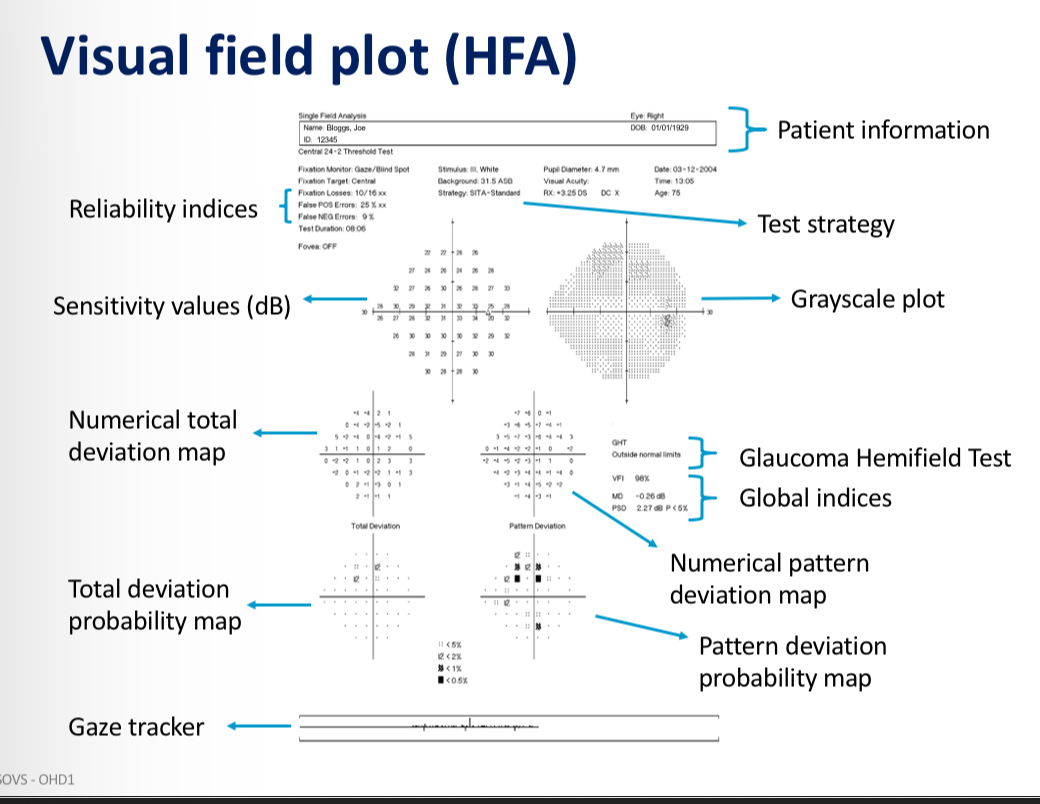
HFA visual field plot
Threshold tests advantages and disadvantages
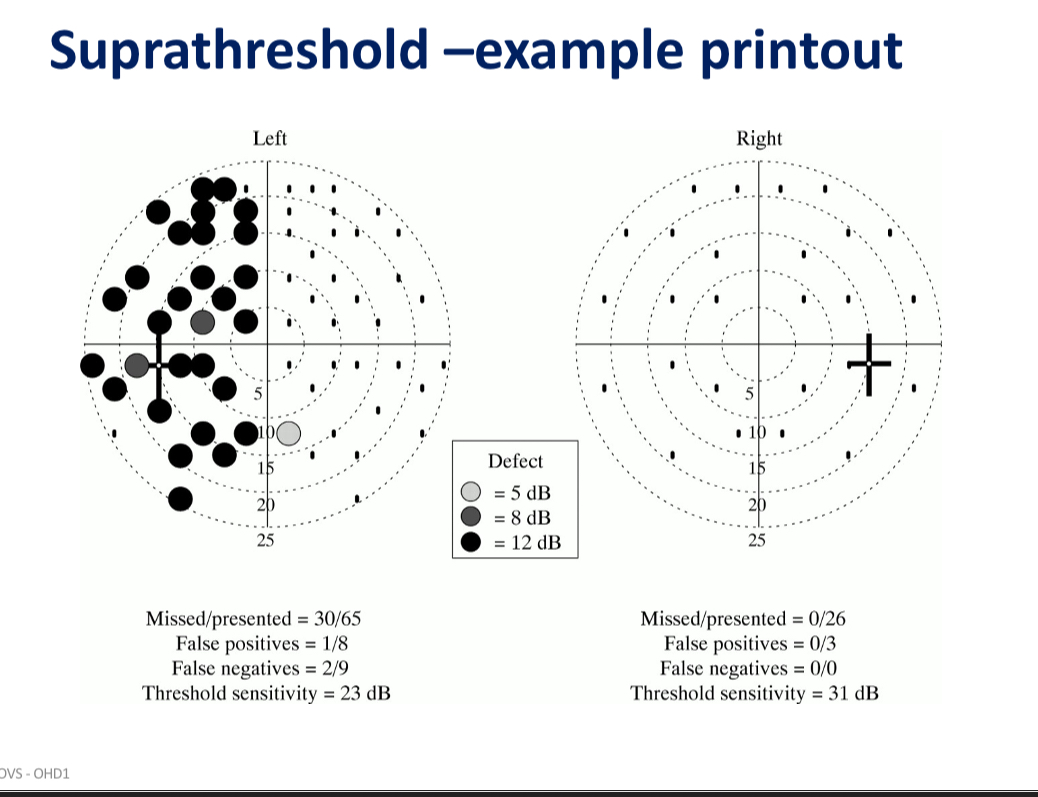
Difference between threshold and suprathreshold screening
Threshold VF determines the dimmest light stimulus a person can detect at various points in their VF - measuring sensitivity
Suprathreshold VF uses stimuli that are brighter than the expected threshold to identify significant vision loss but doesnt measure exact sensitivity
Suprathreshold screening
Stimuli brighter than expected threshold so patient is expected to see all the stimuli presented
If pt misses a stimulus it can be presented again and if they still miss it a brighter stimulus can be presented in the same location
How does suprathreshold determine how bright the test stimulus is
Age matched
Dan be wide variation within a group (eg refractive eroro)
More variability in older pts
Threshold test at a small number of central locations
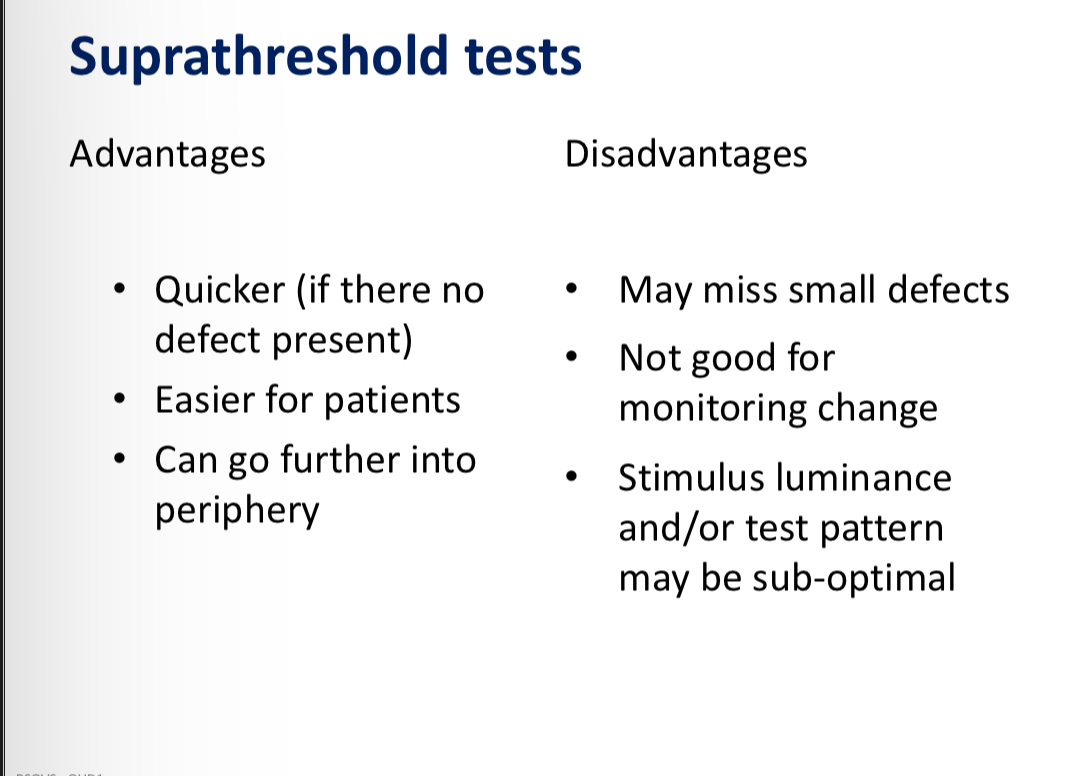
Suprathreshold test advantages and disadvantages
Multiple stimulus tests principles

Multiple stimulus tests Advantages and disadvantages
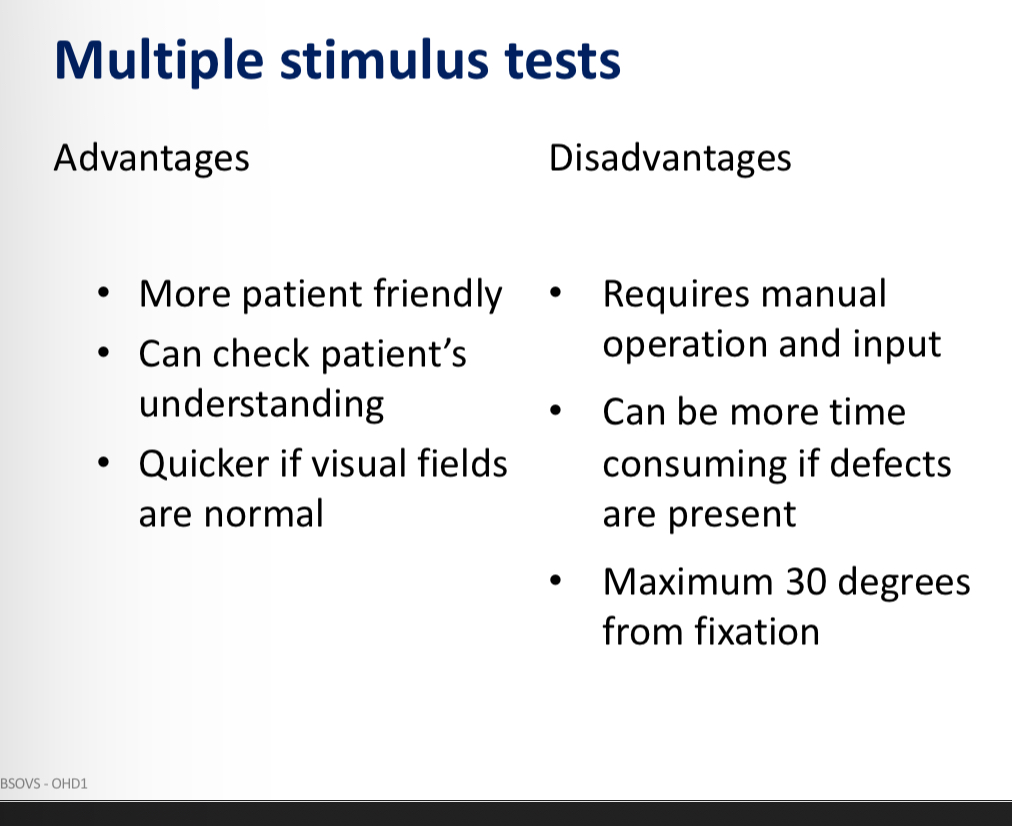
Testing closer to fixation test pattern
Good for advanced glaucoma
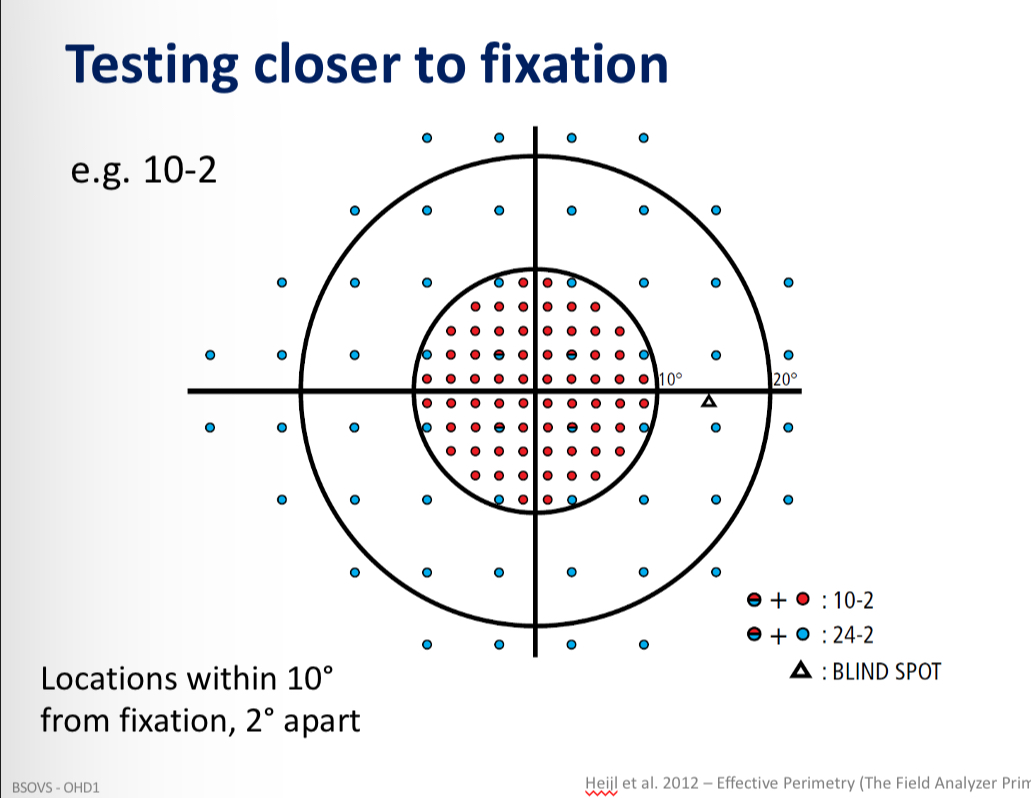
Testing further into the perimetry test pattern
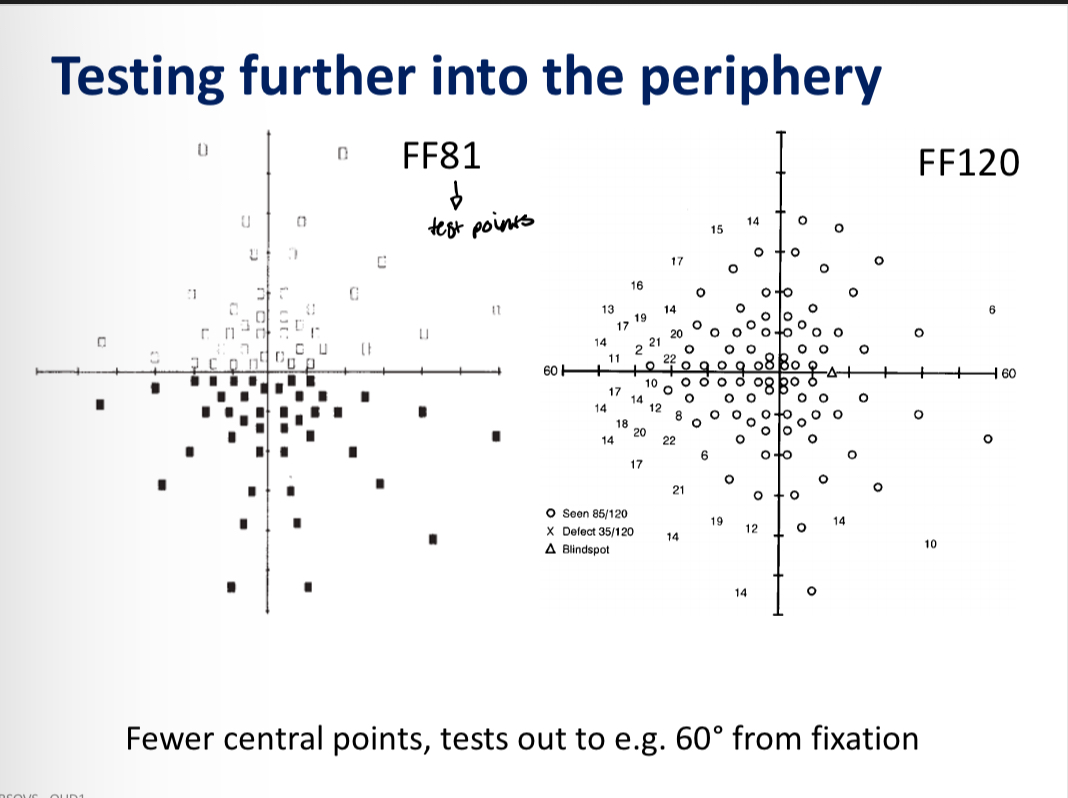
Esterman binocular test pattern
Need to have 120º binocular VF to legally drive
Short wavelength automated perimetry (SWAP)
•A blue, Goldmann V stimulus displayed on a bright (100 cd/m2) yellow background.
•Preferentially stimulates the short-wavelength (koniocellular) pathway.

SWAP disadvantages

Frequency doubling technology (FDT)
Sine grating like stimulus thought to stimulate the magnocellular pathway but now known this isnt the case

FDT avantages and disadvantages

What to think about when deciding which test to choose

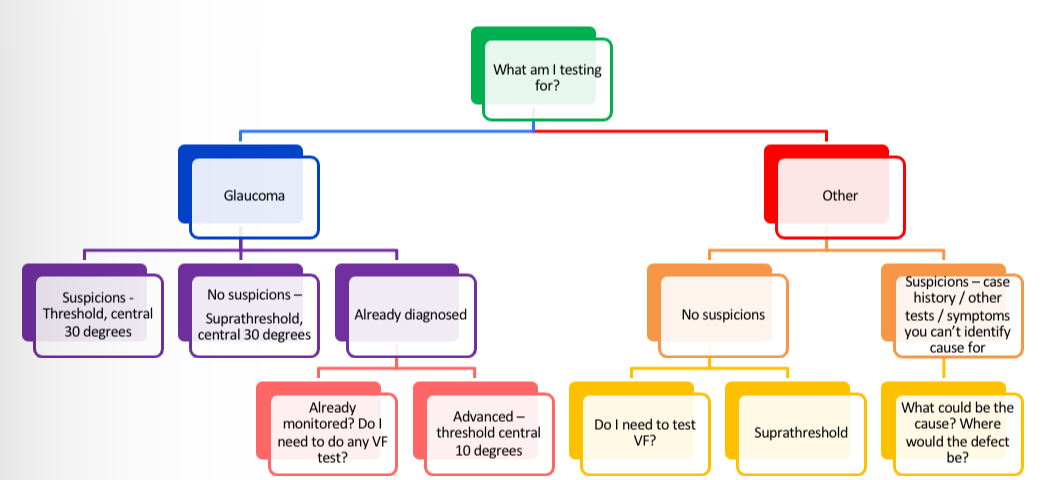
Which test do you choose - What are you testing for?

Which test do oyu choose - what am i testing for flowchart
How to record the results of the VF test
State the instrument used, program/algorithm, moderate/fast/faster, test pattern
If no defects - all seen R&L
If defects - be specific where they missed points

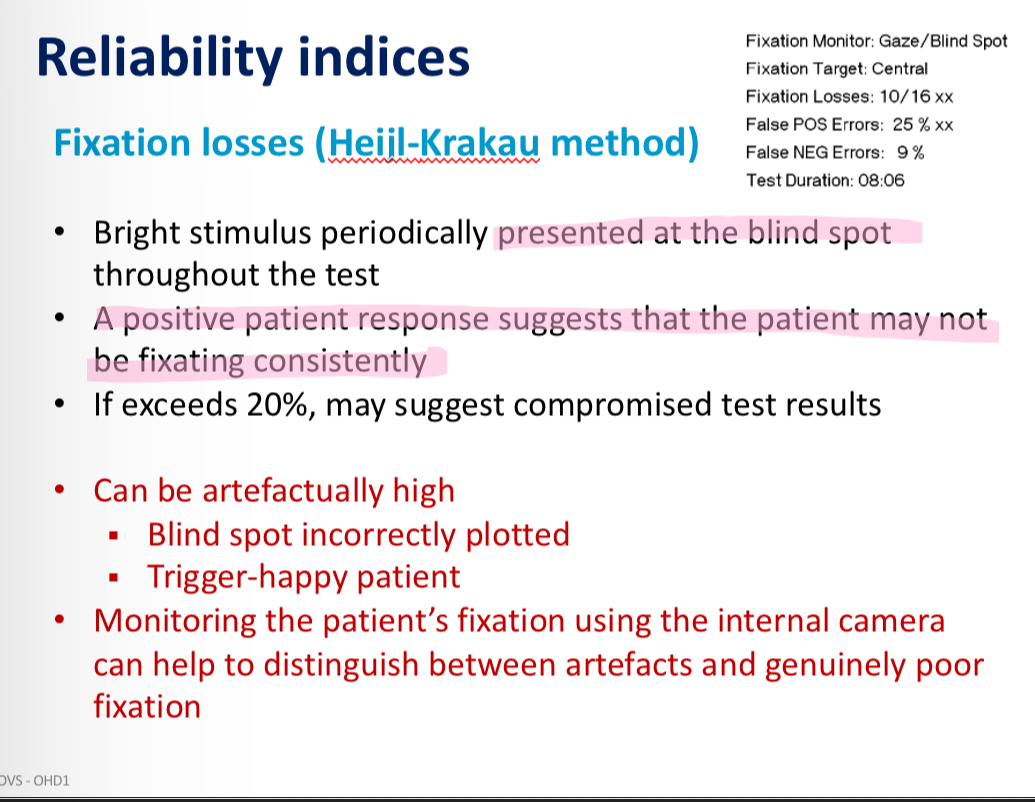
What are the HFA reliability indicies

Reliability indicies - fixation losses
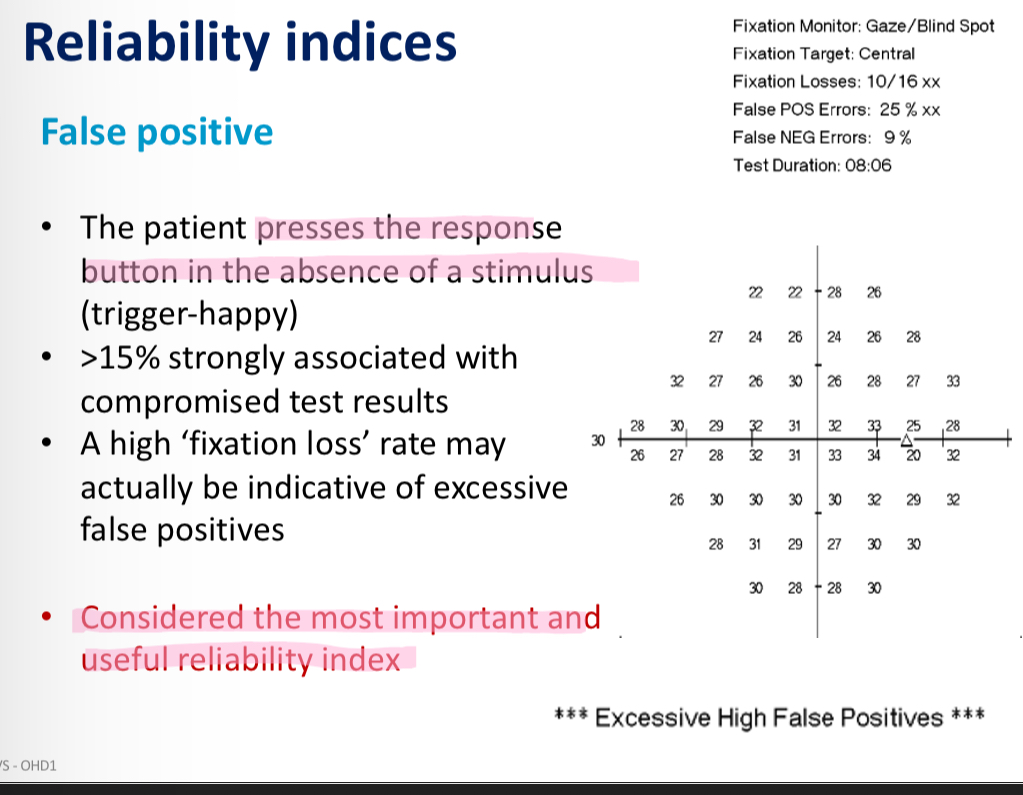
Reliability Indices - false positives
Reliability indicies- false negatives

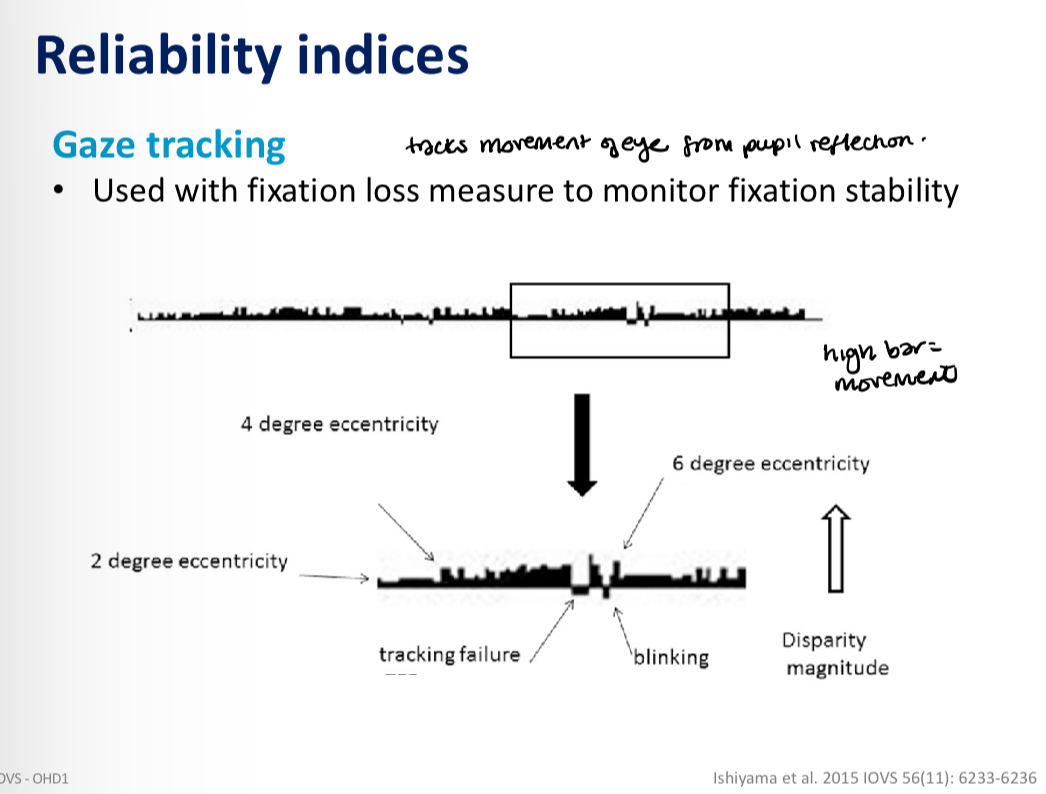
Reliability indicies- gaze tracking
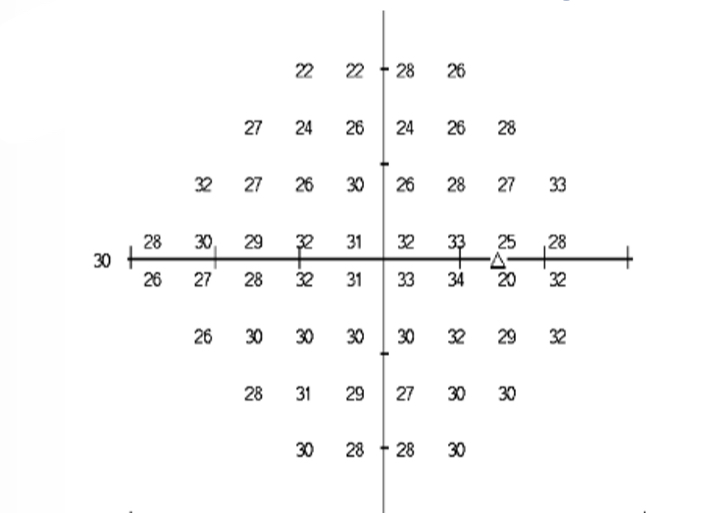
What does this visual field plot show us
‘Raw’ sensitivity of the eye
The higher the value = the more sensitive the eye is - can detect dimmer lights
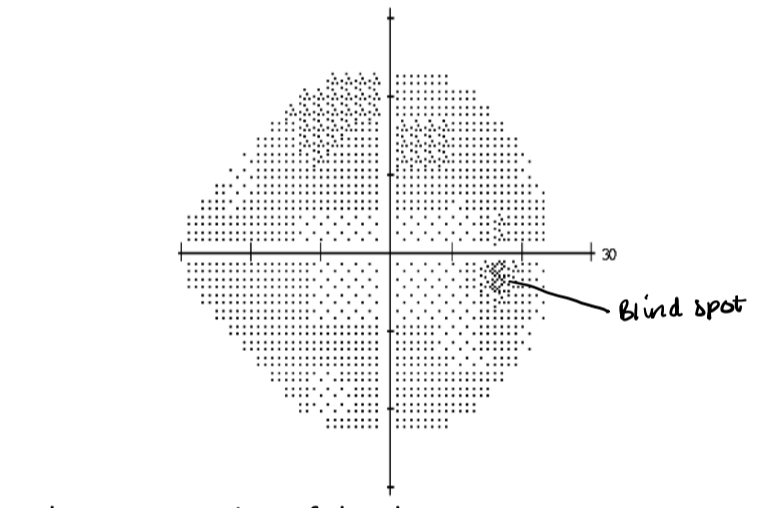
What is this VF plot called
Greyscale
What are the global indicies
mathematical summaries of all sensitivity values
VFI (visual field index)
MD (mean deviation)
PSD (pattern standard deviation)
Global indicies - VFI

global indicies - MD

global indicies - PSD

What is a total deviation map
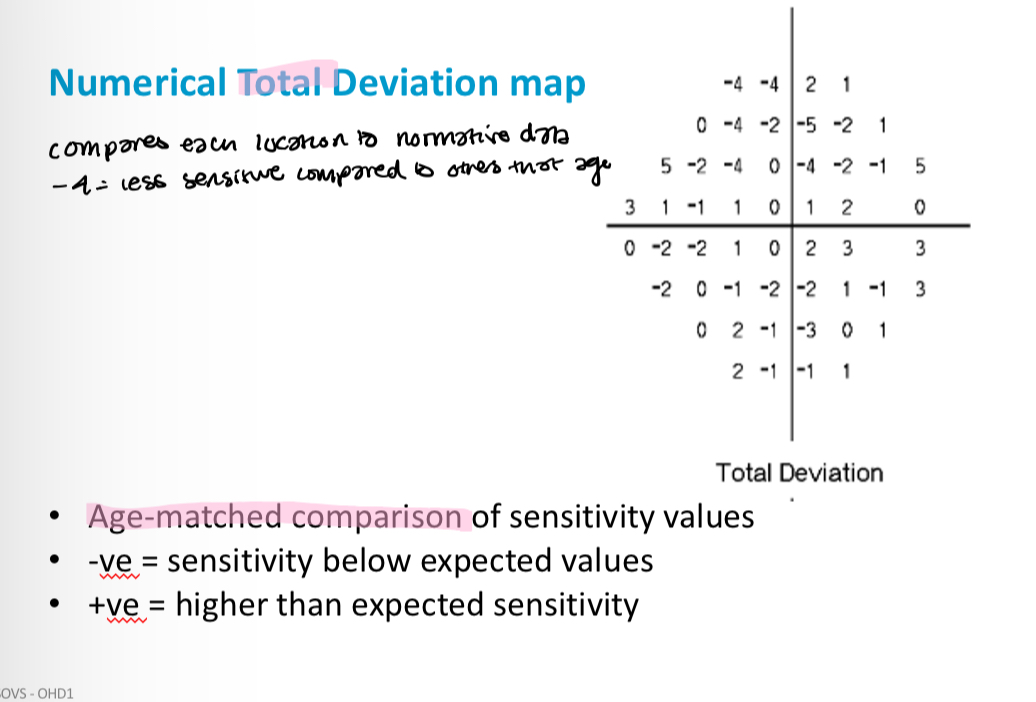
What people are included in the normative database

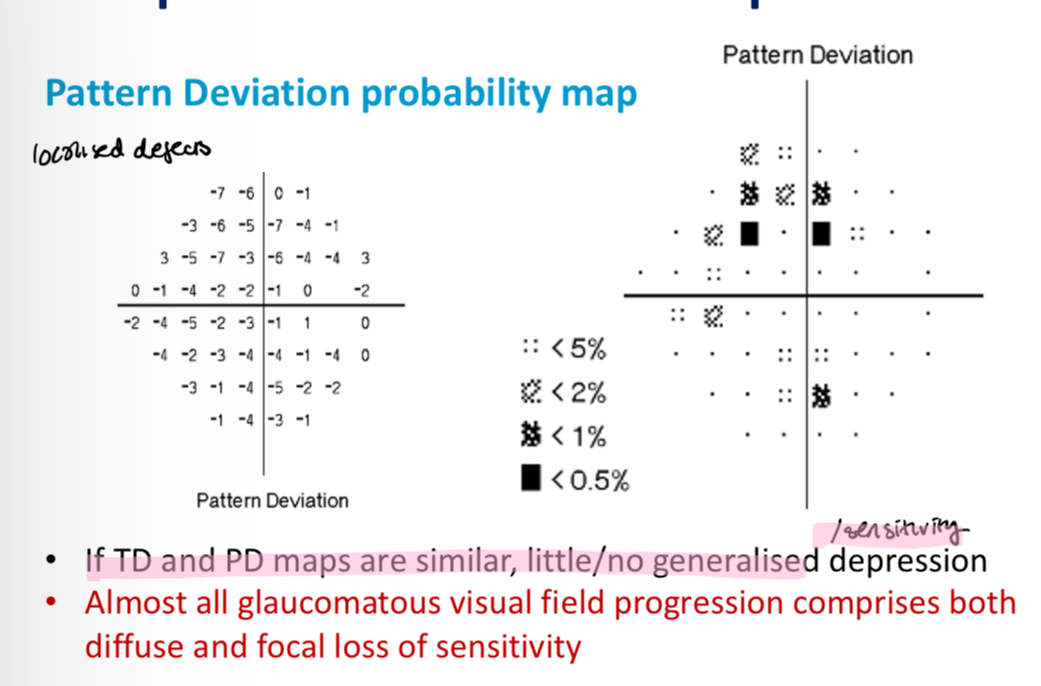
What is a pattern deviation map
Highlights localised VF loss (compares pt with themselves)
What is glaucoma hemifield test
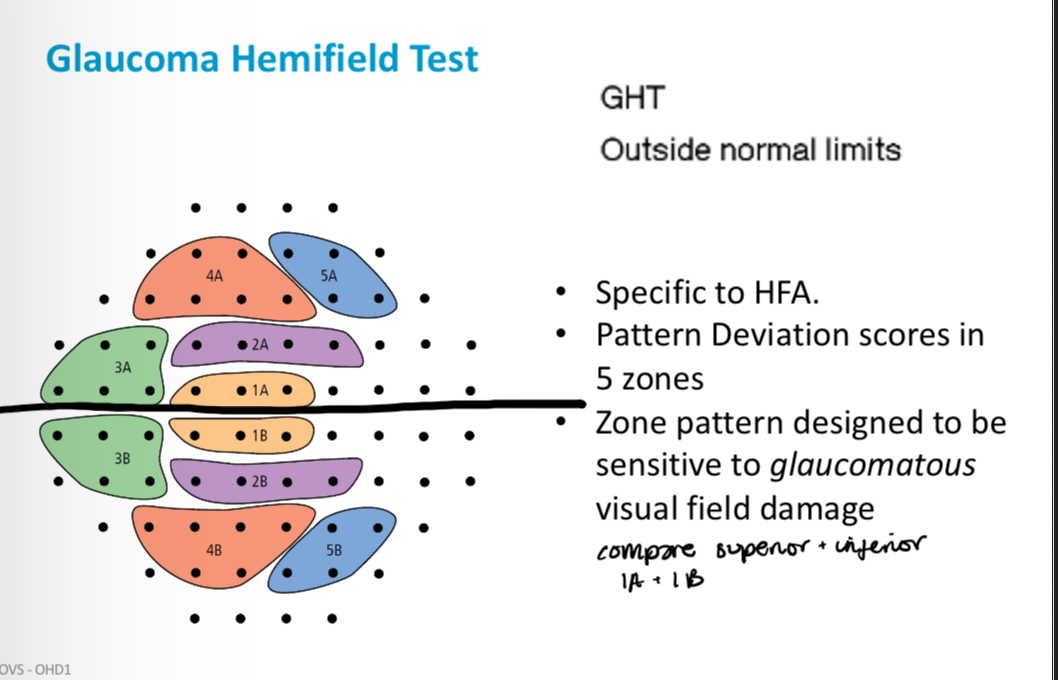
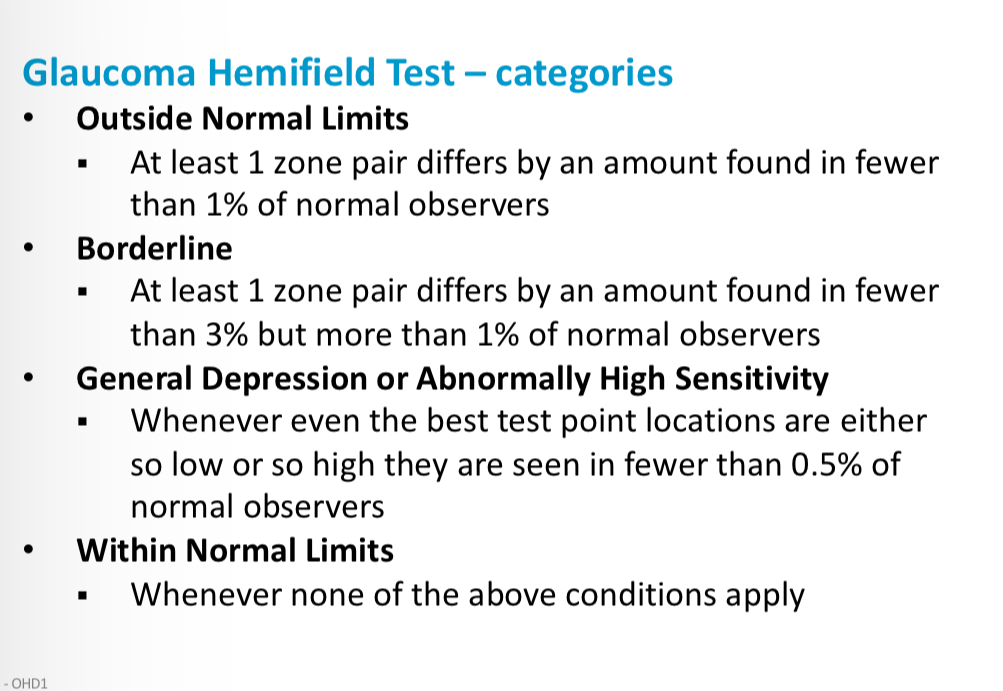
Glaucoma hemifield test categories
If VF defect respects the horizontal midline its caused by..
A retinal defect
If VF defect respects the vertical midline its caused by..
Defect after the optic chiasm
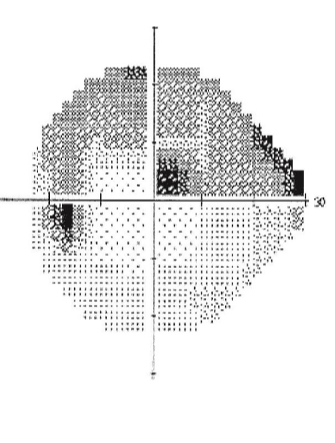
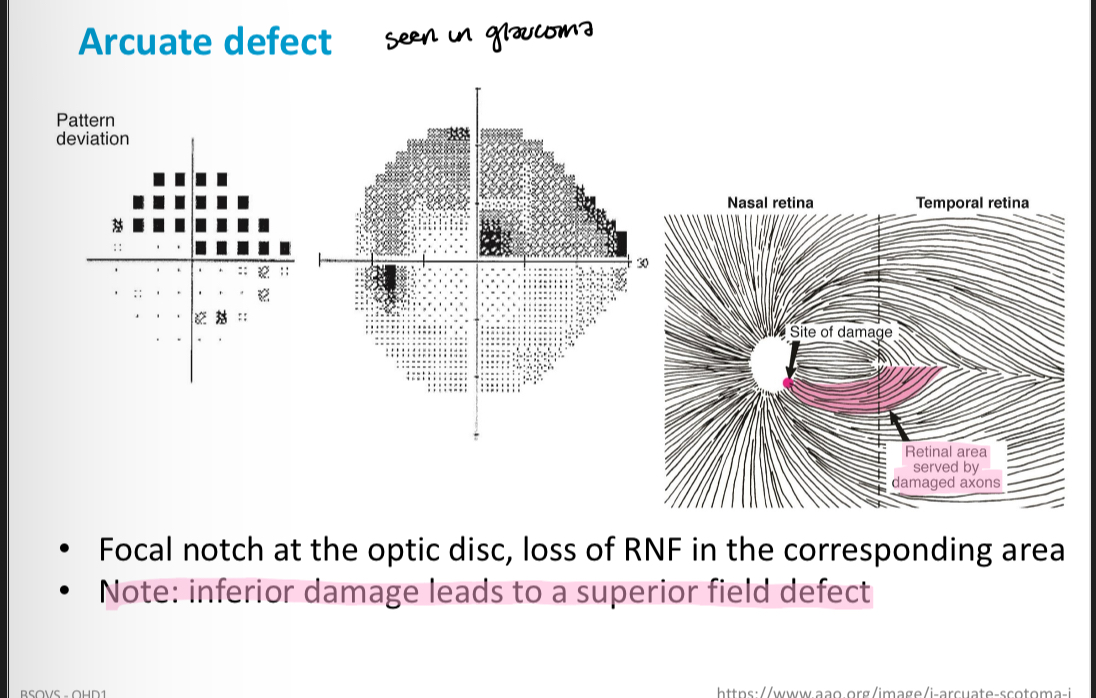
What kind of defect is this
Arcuate
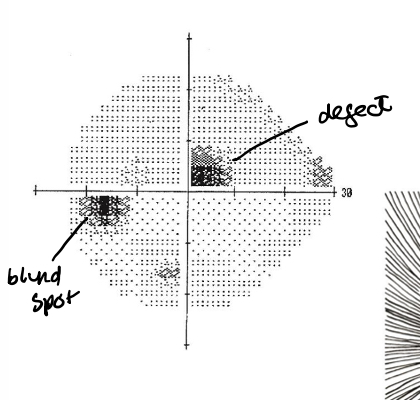
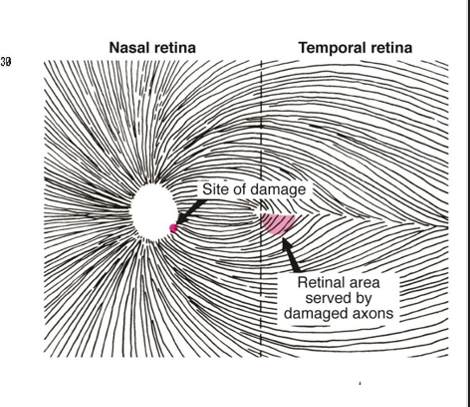
What kind of defect is this
Paracentral
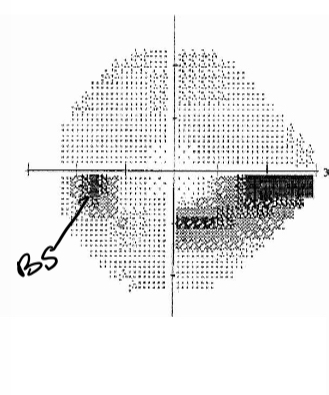
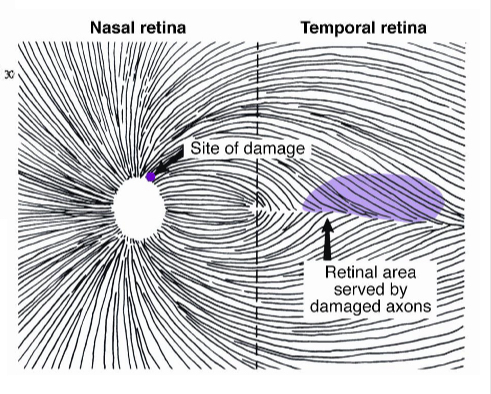
What kind of defect is this
Nasal step
Assymetric involvement of superior and imferior field

What kind of defect is this
Temporal wedge defect
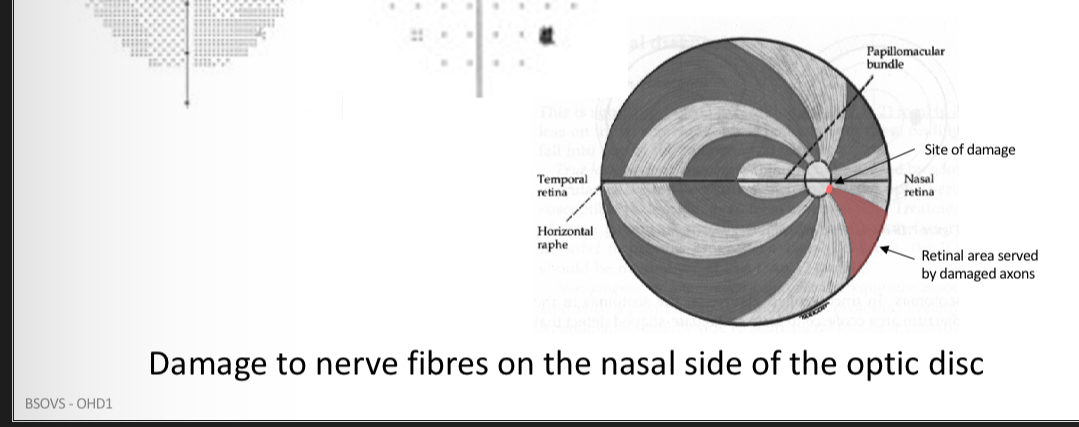
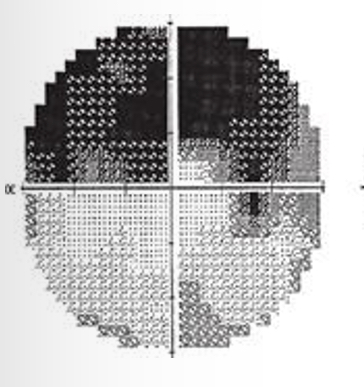
What kind of defect is this
Altitudinal
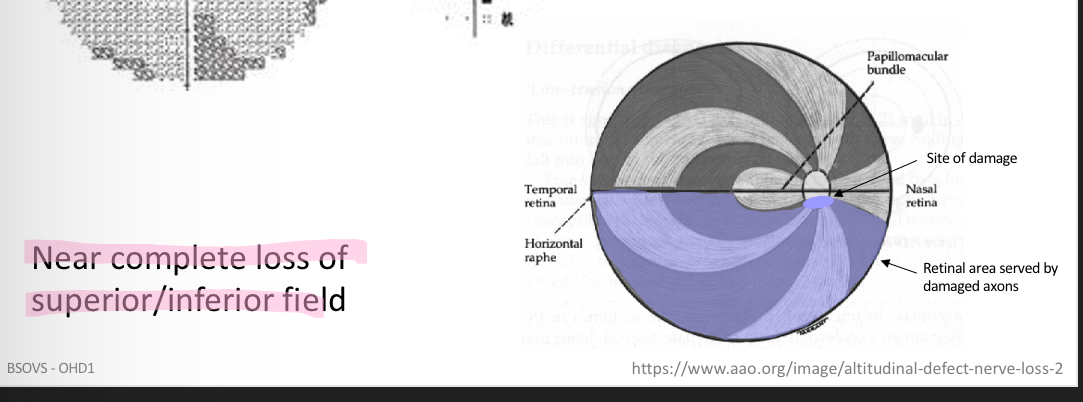
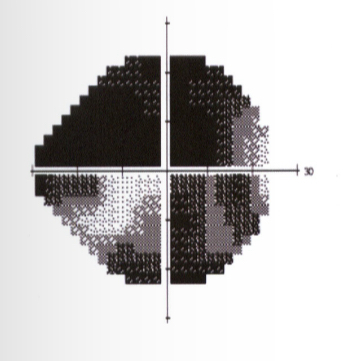
What kind of defect is this
Advanced glaucoma
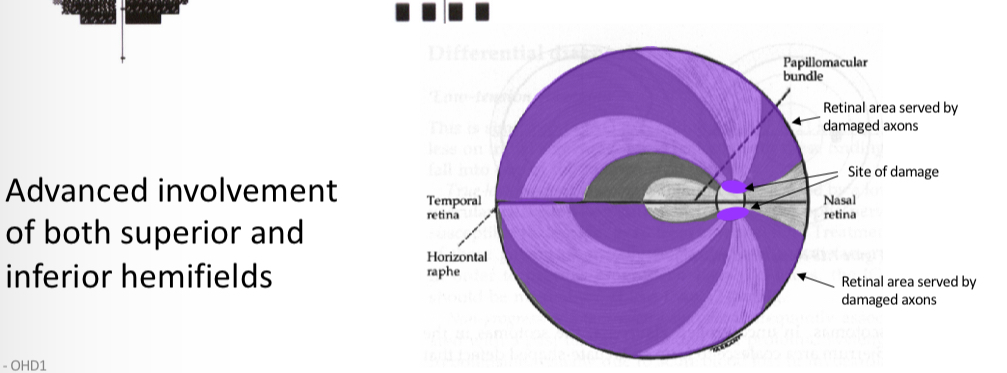
Notes to remember

which VF machine is the reference standard according to NICE
The Humphrey field analayzer (HFA)

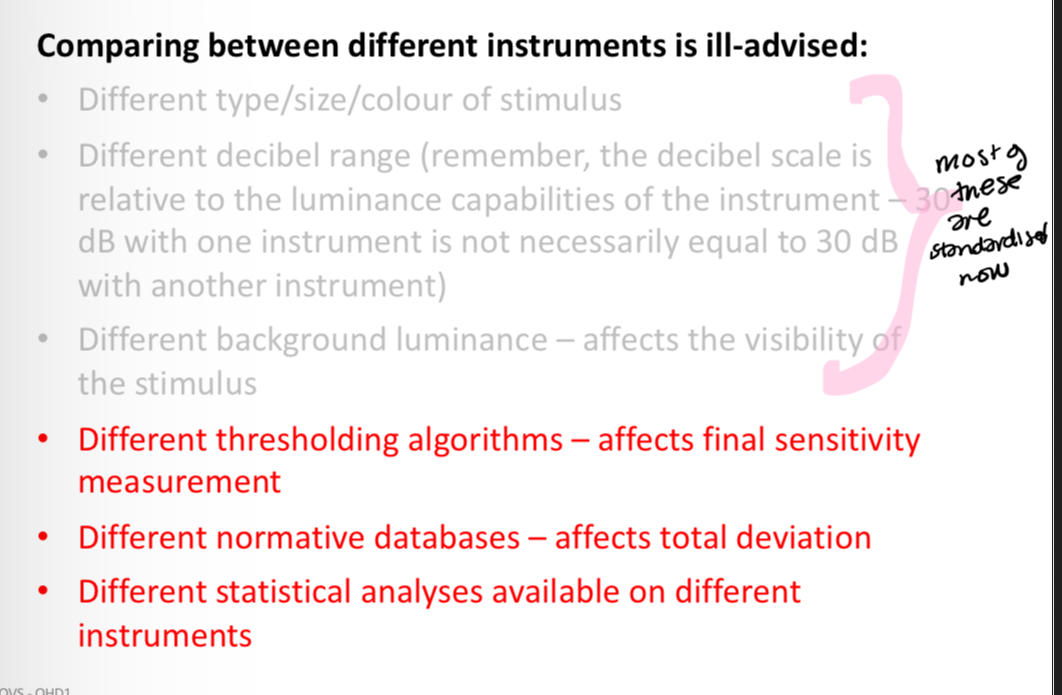
Identifying change - why shouldnt you compare between different instruments

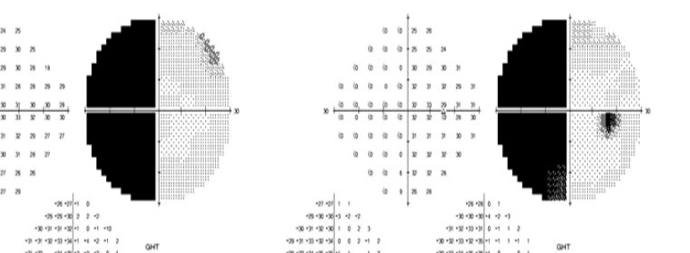
What is this VF plot showing
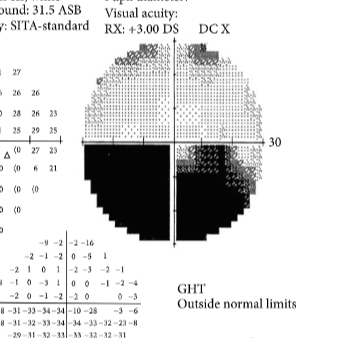
Bitemporal hemonopia -reduced VF temporally in both eyes
Optic chasm defect
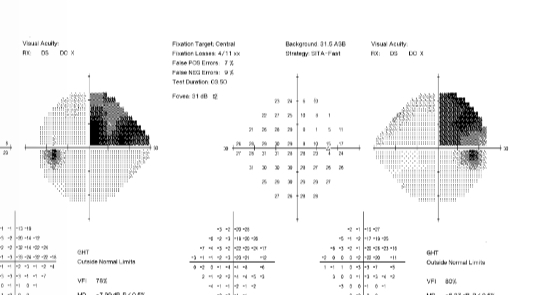
What is this VF plot showing
Homonymous hemionopia - defect after optic chiasm
What is this VF plot showing
Homonymous superior quadrontopia

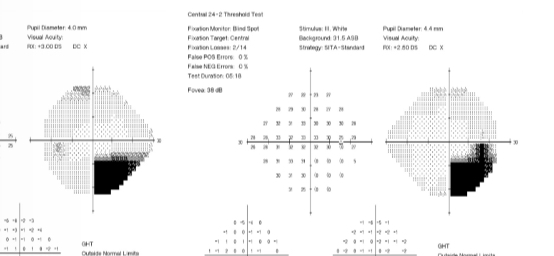
What is this VF plot showing
Homonymous inferior quadrontopia

What is this VF plot showing
Homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing
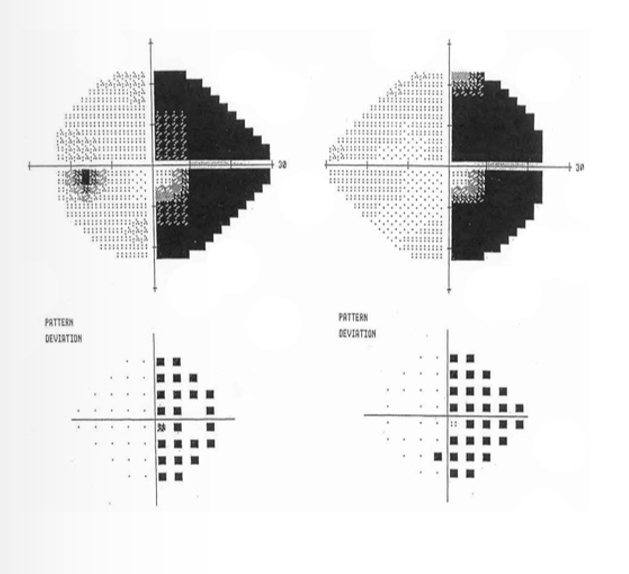
What is this VF plot showing
Anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy

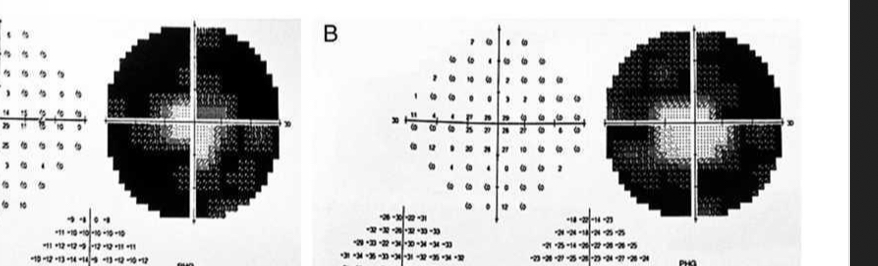
What is this VF plot showing
Retinitis pigmentosa
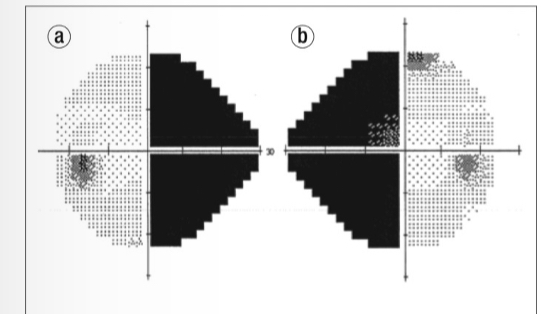
What is this VF plot showing
Binasal defect

What is this VF plot showing
VF artefacts
Lid ptosis - lid covers pupil
(Trial) Lens atefact - fault in machine set up
Attentional artefact - press too much or lose attention and domt press
Advantages and disadvantages of pre screening the patient

Advantages and disadvantages of post screening the patient

Henson multiple stimulus
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Multiple lights shown quickly in different locations.
Suprathreshold.
Central 30°.
Screening for glaucoma. Fast, good for busy clinics.
Humphrey C-76
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Static test using a fixed suprathreshold intensity.
Suprathreshold.
Central 76 points (wide area).
Screening for large defects.
Octopus 30-2
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Static perimetry with threshold strategy.
Threshold.
Central 30°.
Monitoring and routine exams in glaucoma or neuro cases.
Henson ZATA 24-2
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Static perimetry with adaptive thresholding (ZATA algorithm)
Threshold.
Central 24°.
Monitoring glaucoma. Faster than standard threshold tests.
Humphrey FF 120
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Tests 120 locations with fixed intensity.
Suprathreshold.
Wide field, central and peripheral.
Screening for field loss, especially neurological.
FDT C-20
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Frequency Doubling Technology, tests magnocellular cells -(damaged in glaucoma)
Suprathreshold (screening) or threshold versions exist.
Central 20°.
Early glaucoma detection, quick screening.
Humphrey SITA faster 24-2C
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Static perimetry with improved speed and accuracy.
Threshold.
Central 24° + extra central points.
Routine monitoring of glaucoma, faster than SITA Standard.
Humphrey SITA standard 10-2
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Fine grid of test points near fixation.
Threshold.
Central 10°.
Monitoring macular damage, advanced glaucoma, retinal disease.
Octopus kinetic perimetry
how it works
Threshold or suprathreshold
VF measured
Use for
Moving targets (kinetic), manually plotted.
Threshold/Suprathreshold: Variable (can be both).
Full field, including far periphery.
Neurological cases, driving assessments, peripheral loss.
Which test would be best for a routine person with no symtoms but have a family history of glaucoma and why
Humphrey SITA faster 24-2C
Threshold test – detects subtle early changes.
Faster than SITA Standard – saves time with similar accuracy.
24-2 grid – covers central 24°, ideal for glaucoma.
Extra central points (“C”) – improves detection near fixation.
Low patient fatigue – short test helps maintain attention.
Good for early glaucoma – suitable for high-risk, asymptomatic patients.