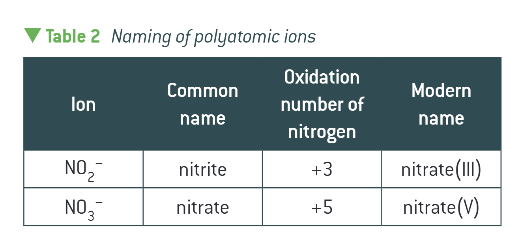Chapter 4: Acids, bases, titrations
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
acids are…
proton donors
What is a strong acid?
completely dissociates in aqueous solution.
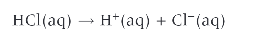
what is a weak acid?
partially dissociates in aqueous solution
(the equilibrium sign shows that the reaction is incomplete)
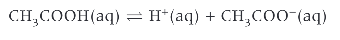
is ethanoic acid strong?
no!!
what is an alkali?
a bas that is dissolved in water, released OH- ions.
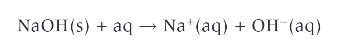
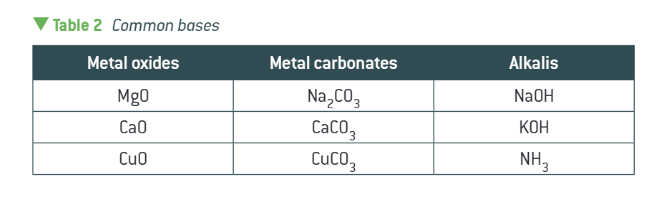
what are all these?
common bases
in neutralisation, what happens to the H+ ions from the acid?
they are replaced by metal / ammonium ions
acid + metal oxide/hydroxide → (aren’t my old hats somewhere west???) 🤠
salt + water
acid + alkali →
salt + water
ionic equation of HCl + NaOH → H2O + NaCl
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O (l)
acid + metal carbonate →
salt + water + carbon dioxide (gas)
what is a standard solution?
a solution of known concentration
what is the tolerance of a 100cm3 volumetric flask?
± 0.20cm3
what is the tolerance of a 250cm3 volumetric flask?
± 0.30cm3
how to prepare a standard solution:
the solid is weighed accurately on a mass balance
dissolve solid in beaker, using distilled water
solution is transferred to volumetric flask → last traces of solution are rinsed into flask with distilled water
flask carefully filled to graduation line with distilled water → until bottom of meniscus lines up exactly with graduation line
view at eye level for accuracy!
volumetric flask is inverted several times to mix solution thoroughly (with bung in!)
a burette recording is measured to the nearest…
half division → 2dp with the last number being a 0 or 5.
how to carry out an acid-base titration?
add measured volume of one solution → conical flask using a pipette.
other solution to burette, and take initial reading to the nearest 0.05cm3
add a few drops of indicator to conical and swirl
run solution from the burette into the conical flask, swirling conical flask → indicator changing colour indicates exact point at which reaction occurs.
record final burette volume
repeat accurately, adding solution dropwise until endpoint
keep doing titrations until 2 accurate titres are concordant.
what are concordant results?
within 0.10cm3
the oxidation number of an element is always…
zero
what is the oxidation number of H in metal hydrides?
-1
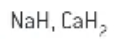
what is the oxidation number of Oxygen in peroxides?
-1 → H2O2
what is the oxidation number of Oxygen when bonded to Fluorine?
+2 → F2O
do oxidation numbers have the sign before or after the number?
before → +2, -1
sum of oxidation numbers =
total charge
what do Roman numerals represent?
the oxidation state of an element → iron (III) is Fe3+ with an oxidation number of +3
nitrite vs. nitrate?